Conductive Polymer (Graphene/PPy)–BiPO4 Composite Applications in Humidity Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design
2.1. Materials
2.2. Method of Synthesis
2.3. Characteristic Methods
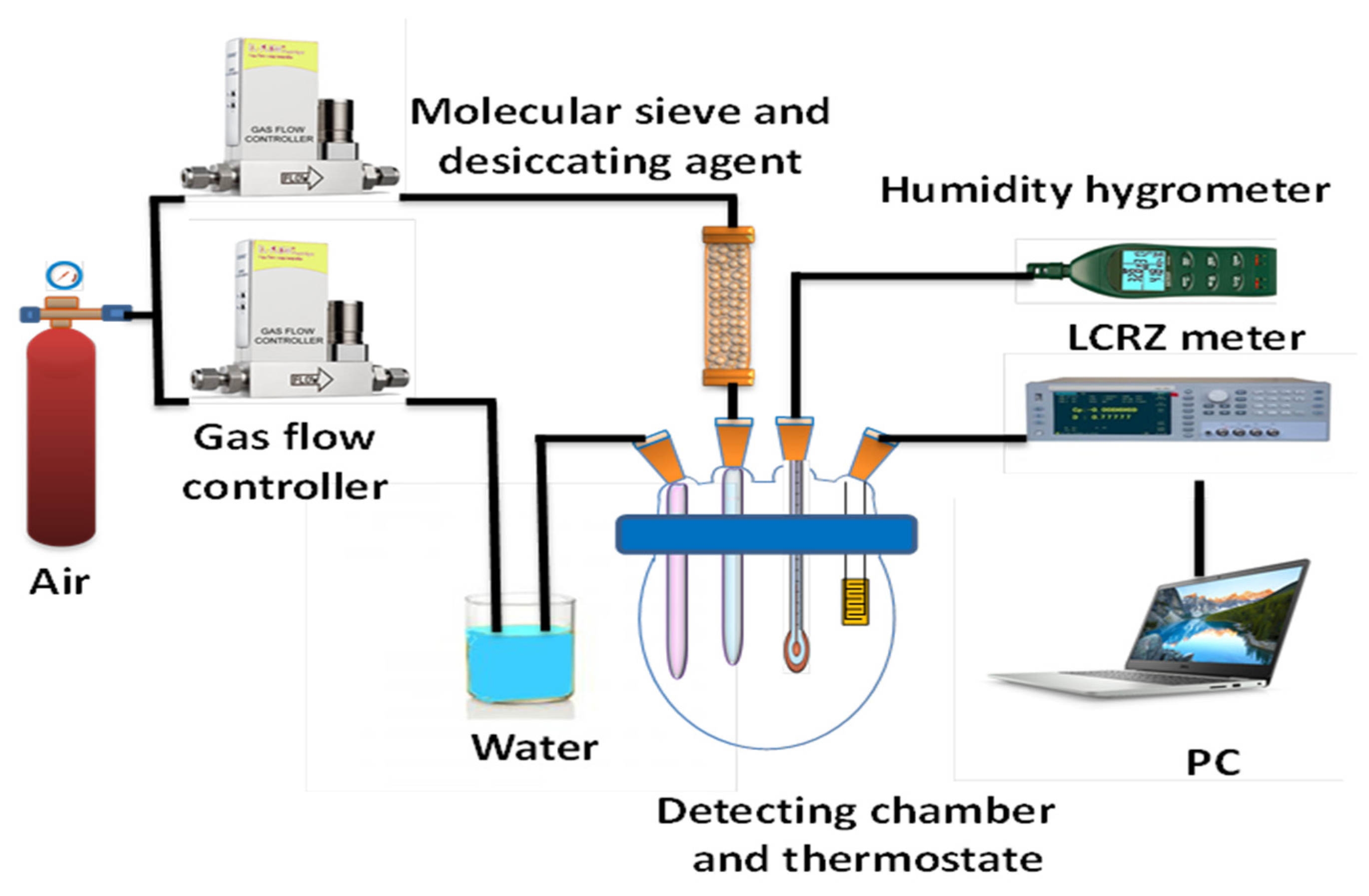
2.4. Sensor Fabrication and Humidity Testing
3. Results and Discussion
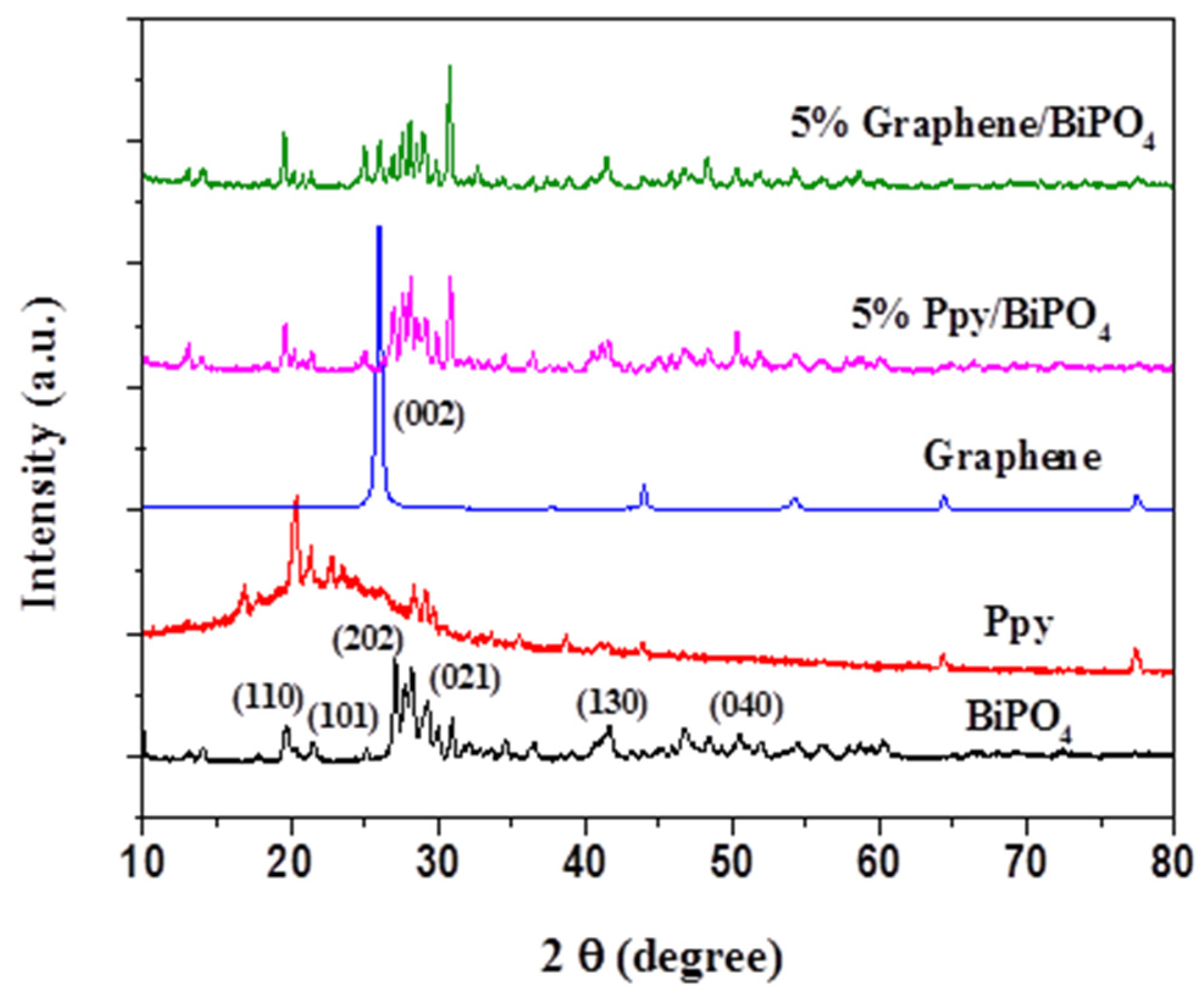
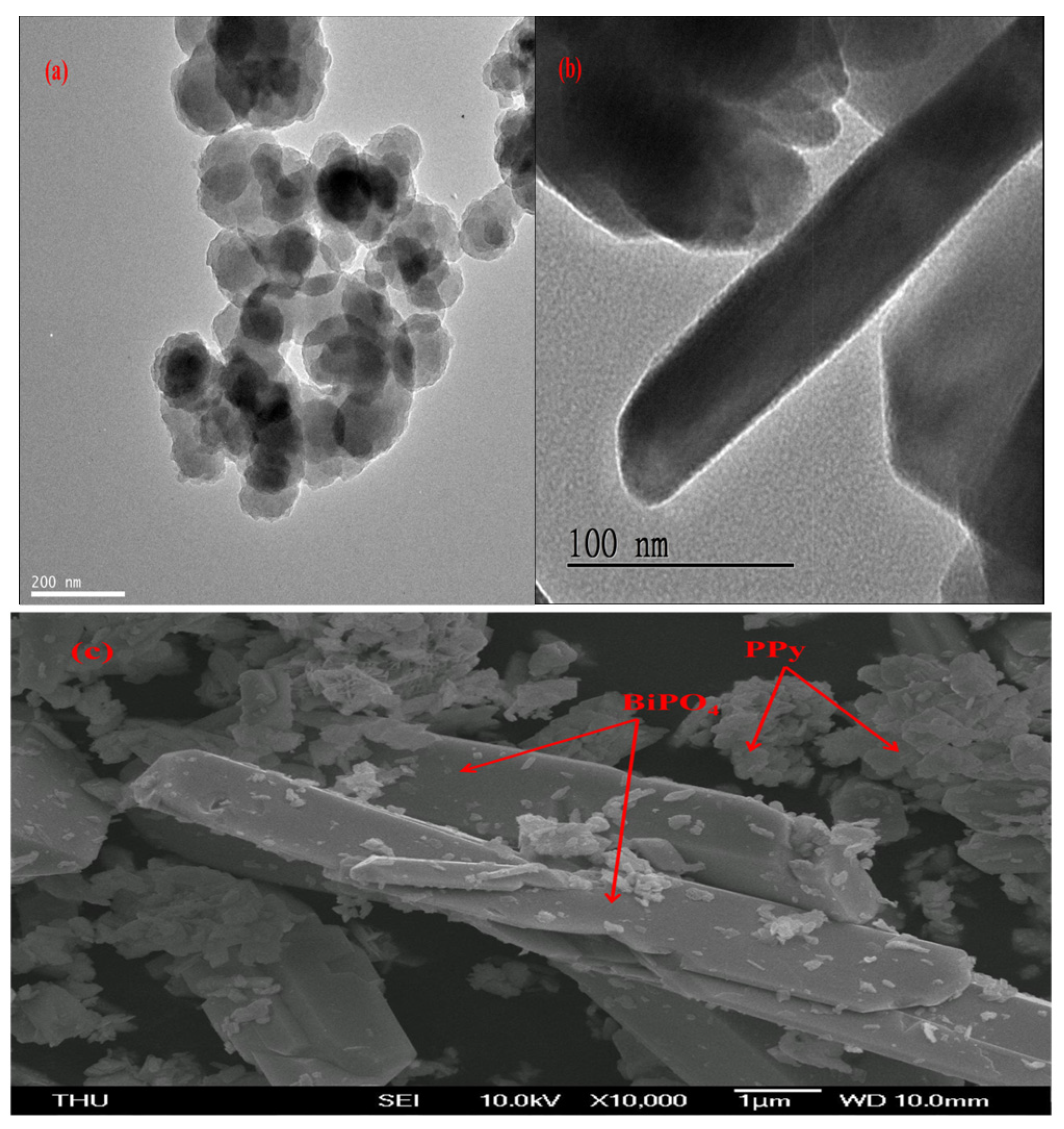
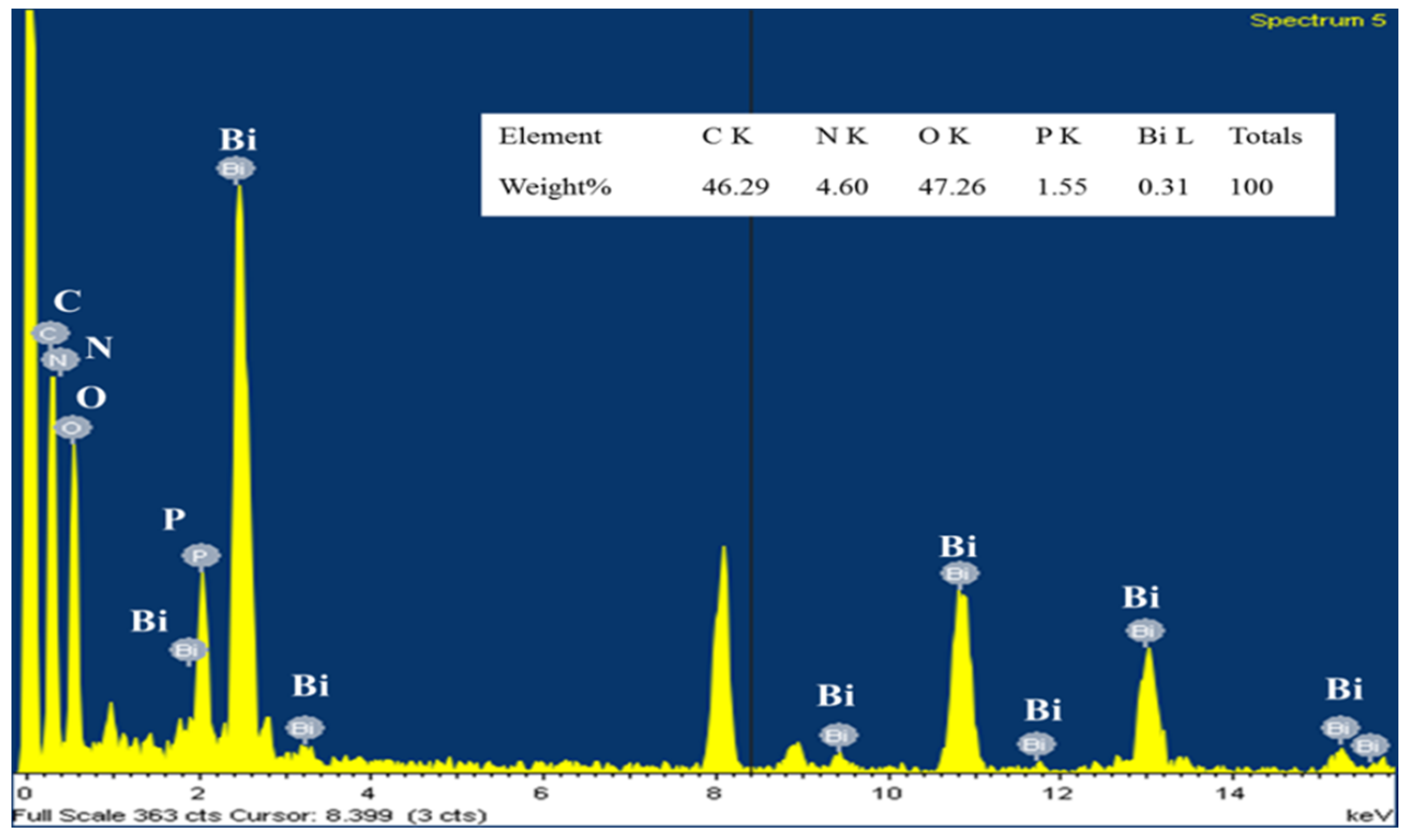
3.1. Material Characterizations
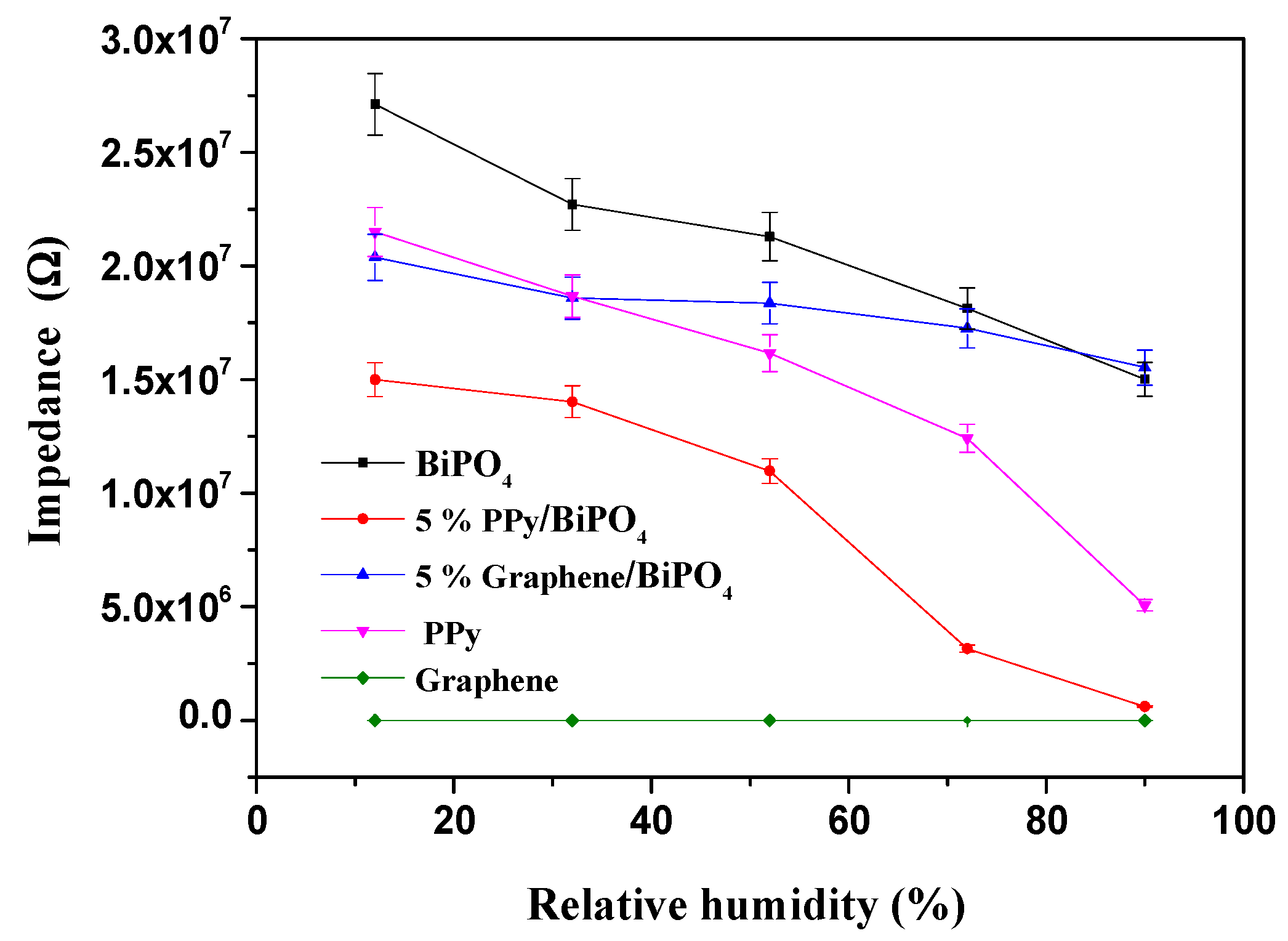
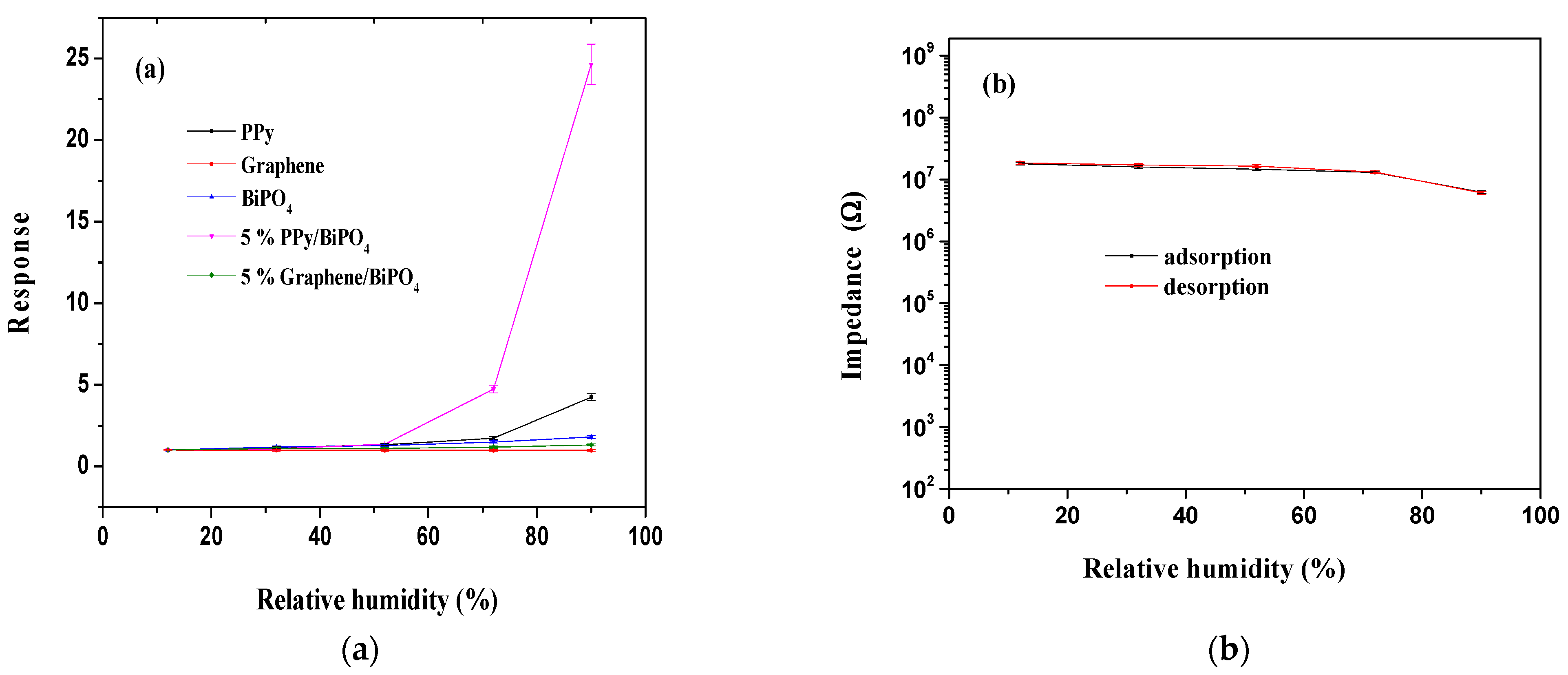
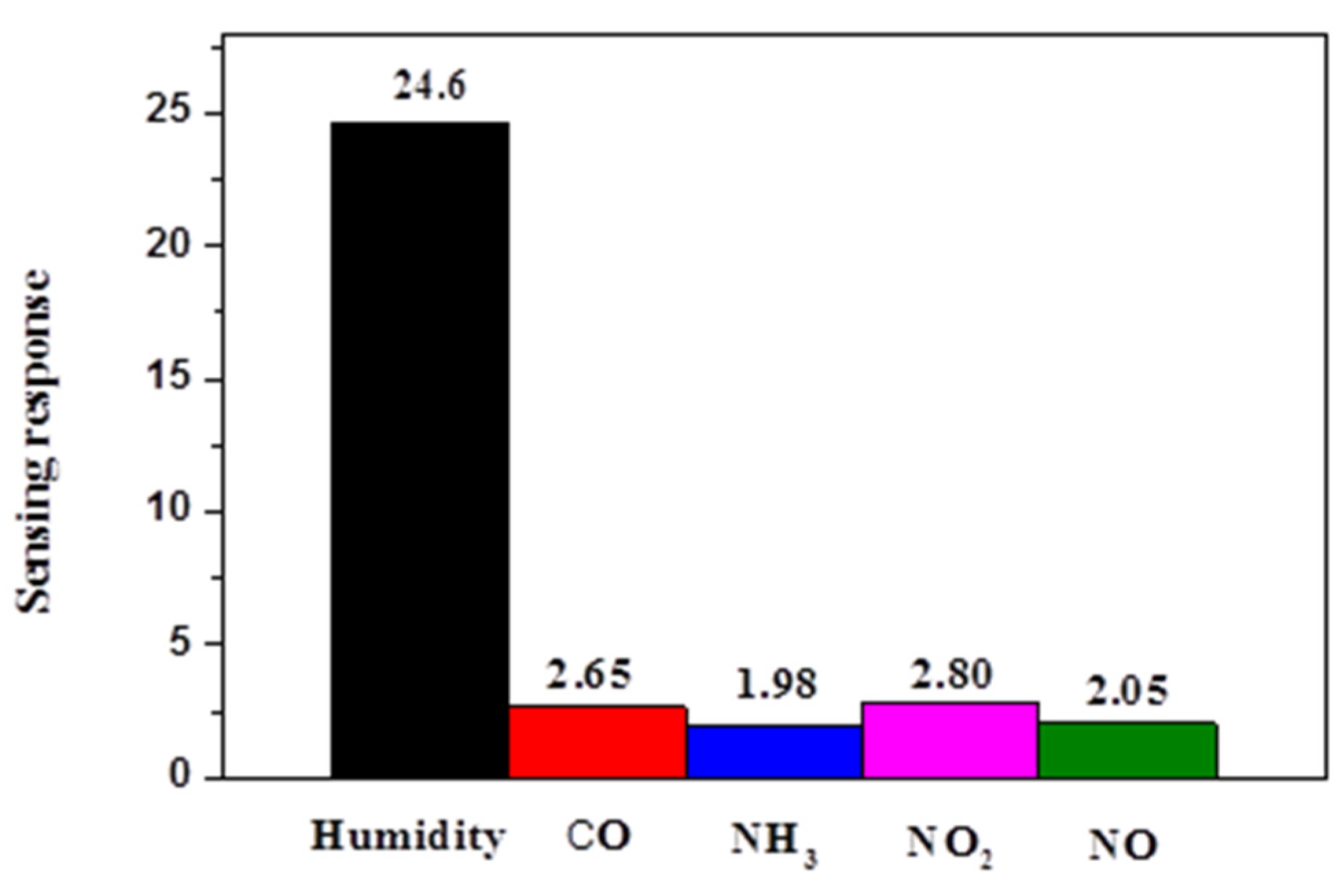
3.2. Sensing Humidity
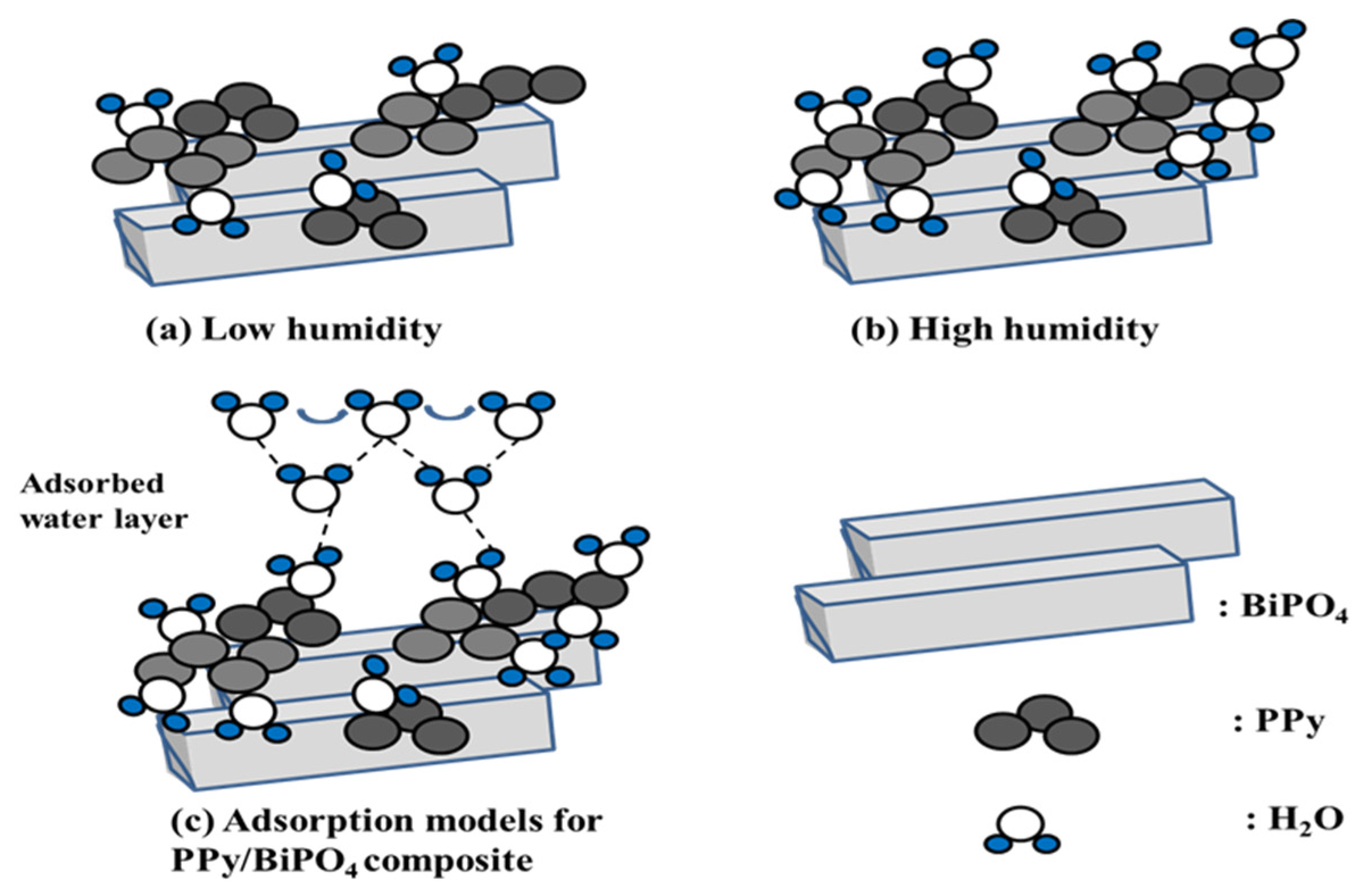
3.3. Humidity-Sensing Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, M.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, P.; Xie, G.; Du, X.; Tai, H. Facile, Flexible, Cost-Saving, and Environment-Friendly Paper-Based Humidity Sensor for Multifunctional Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 21840–21849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.-X.; Zhang, B.; Ramakrishna, S.; Yu, M.; Ma, J.-W.; Long, Y.-Z. In Situ Assembly of Well-Dispersed Ag Nanoparticles throughout Electrospun Alginate Nanofibers for Monitoring Human Breath—Smart Fabrics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 19863–19870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Jameel, M.A.; Gupta, A.; Langford, S.J.; Shafiei, M. Capacitive humidity sensing performance of naphthalene diimide derivatives at ambient temperature. Synth. Met. 2021, 275, 116739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Zhang, T.; Guan, X.; Dai, J.; Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Fei, T. Capacitive humidity sensors based on mesoporous silica and poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene) composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 565, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, V.; Fernández, I.; Carrasco, P.; Cabañero, G.; Grande, H.J.; Herrán, J. Graphene quantum dots as a novel sensing material for low-cost resistive and fast-response humidity sensors. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2015, 218, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.-Y.; Chan, Y.C.; Zhang, K. Fast response resistive humidity sensitivity of polyimide/multiwall carbon nanotube composite films. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2011, 152, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harith, Z.; Batumalay, M.; Irawati, N.; Harun, S.W.; Arof, H.; Ahmad, H. Relative humidity sensor employing tapered plastic optical fiber coated with seeded Al-doped ZnO. Optik 2017, 144, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Gan, W.; Yang, M. Optical fiber Fabry–Perot humidity sensor based on polyimide membrane: Sensitivity and adsorption kinetics. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2018, 281, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Tang, R.; Zhu, J.; Oiler, J.; Yu, C.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H. The effects of temperature, relative humidity and reducing gases on the ultraviolet response of ZnO based film bulk acoustic wave resonator. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2011, 151, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xue, Y. Influence of the oxygen content on the humidity sensing properties of functionalized graphene films based on bulk acoustic wave humidity sensors. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2016, 222, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Zhang, T.; Shao, J.; Yang, B.; Fei, T.; Wang, R. A QCM humidity sensor constructed by graphene quantum dots and chitosan composites. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2019, 287, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, D.; Li, P.; Zhou, X.; Zong, X.; Dong, G. Facile fabrication of high-performance QCM humidity sensor based on layer-by-layer self-assembled polyaniline/graphene oxide nanocomposite film. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 255, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, J. Effect of interdigital electrode gap on the performance of SnO2-modified MoS2 capacitive humidity sensor. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 271, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Touati, F.; Shakoor, R.A. Improvement of humidity sensing properties of PVDF-TiO2 nanocomposite films using acetone etching. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 288, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, V.T.; Nguyen, C.T.; Luong, H.B.; Nguyen, D.C.; Nguyen, H.L. Ultralow-detection limit ammonia gas sensors at room temperature based on MWCNT/WO3 nanocomposite and effect of humidity. Solid State Sci. 2021, 113, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arularasu, M.V.; Harb, M.; Vignesh, R.; Rajendran, T.V.; Sundaram, R. PVDF/ZnO hybrid nanocomposite applied as a resistive humidity sensor. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 21, 100780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebian, H.Y.; Taher, H.J. Relative humidity sensor based on no-core multimode interferometer coated with Al2O3-PVA composite films. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2020, 54, 102110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.Z.; Ariya, P.A. Co-adsorption of gaseous benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, m-xylene (BTEX) and SO2 on recyclable Fe3O4 nanoparticles at 0–101% relative humidities. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 31, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Liu, B.; Xiao, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Cai, D.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; et al. High-performance humidity sensors based on CeO2 nanoparticles. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2015, 215, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, V.; Sikarwar, S.; Yadav, B.C.; Vigneselvan, S.; Mane, R.S.; Chandrasekaran, J.; Mirzaei, A. Rapid humidity sensing activities of lithium-substituted copper-ferrite (Li−CuFe2O4) thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 229, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, V.; Sikarwar, S.; Yadav, B.C.; Mane, R.S. Fabrication of tin substituted nickel ferrite (Sn-NiFe2O4) thin film and its application as opto-electronic humidity sensor. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2018, 272, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douani, R.; Lamrani, N.; Oughanem, M.H.; Saidi, M.; Guhel, Y.; Chaouchi, A.; Boudart, B. Improvement of humidity sensing performance of BiFeO3 nanoparticles-based sensor by the addition of carbon fibers. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2020, 307, 111981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrizabalaga, O.; Velasco, J.; Zubia, J.; Sáez de Ocáriz, I.; Villatoro, J. Miniature interferometric humidity sensor based on an off-center polymer cap onto optical fiber facet. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 297, 126700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chen, S.; Zhou, B.; Liu, L.; Ding, B.; Wang, H. Highly stable and sensitive humidity sensors based on quartz crystal microbalance coated with bacterial cellulose membrane. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2011, 159, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.S.; Shin, D.H.; Lee, W.J.; Jang, C.W.; Kim, S.; Choi, S.-H. All-two-dimensional semitransparent and flexible photodetectors employing graphene/MoS2/graphene vertical heterostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 864, 158118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hayali, S.K.; Salman, A.M.; Hadi Al-Janabi, A. Effect of hygroscopic polymer-coatings on the performance of relative humidity sensor based on macro-bend single-mode fiber. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2021, 62, 102460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-J.; Lee, S.; Kim, B.; Kim, J.-H.; So, J.-H.; Koo, H.-J. Impedance study on humidity dependent conductivity of polymer composites with conductive nanofillers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 202, 108412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Mu, S.; Wu, R.; Wang, Z. Cellulose nanocrystal/plant oil polymer composites with hydrophobicity, humidity-sensitivity, and high wet strength. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231, 115739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, M.; Wuzella, G.; Lammer, H.; Mahendran, A.R. Smart paper from graphene-coated cellulose for high-performance humidity and piezoresistive force sensor. Synth. Met. 2020, 266, 116420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Lin, E.S.; Zhu, J.; Ong, J.W.; Abid, H.A.; Uddin, M.H.; Liew, O.W.; Ng, T.W. Sustained graphene oxide coated superhydrophilicity and superwetting using humidity control. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 613, 126097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Tao, L.-Q.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y. Graphene oxide humidity sensor with laser-induced graphene porous electrodes. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2020, 325, 128790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Chen, J.; Ji, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, L.; Xia, J.; Li, H. Reactable ionic liquid induced homogeneous carbon superdoping of BiPO4 for superior photocatalytic removal of 4-chlorophenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Jiang, D.; Li, H.; Bao, J.; Xu, L.; Qian, J.; Chen, C.; Xia, J. BiPO4 nanocrystal/BiOCl nanosheet heterojunction as the basis for a photoelectrochemical 4-chlorophenol sensor. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 279, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Hong, W.-G.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wu, R.-J. Novel Nanoarchitechtonics Olive-Like Pd/BiVO4 for the Degradation of Gaseous Formaldehyde Under Visible Light Irradiation. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luk, H.N.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Han, Y.W.; Wu, R.J.; Chavali, M. A Novel Co3O4–BiPO4 Nanoarchitectonics Material Preparation for the Electrocatalytic Detection of Epinephrine. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 2705–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.-D.; Chang, H.-M.; Wu, R.-J. Applied novel sensing material graphene/polypyrrole for humidity sensor. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2013, 181, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-D.; Liao, C.-T.; Chang, T.-C.; Chen, S.-H.; Wu, R.-J. Humidity sensing properties of novel graphene/TiO2 composites by sol-gel process. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2015, 209, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, W.; Zhang, X.; Lin, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. Facile fabrication of laser-scribed graphene humidity sensors by a commercial DVD drive. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2020, 321, 128483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, G.; Feng, C.; Wu, H.; Mei, H. Highly sensitive detection of chromium (VI) by a photoelectrochemical sensor under visible light based on Bi SPR-promoted BiPO4/BiOI heterojunction. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2020, 305, 127449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Shokri, M. A new humidity sensor based upon graphene quantum dots prepared via carbonization of citric acid. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2016, 222, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Yadav, B.C.; Haldar, T.; Dixit, C.K.; Yadawa, P.K. Synthesis of MWCNT/PPY nanocomposite using oxidation polymerization method and its employment in sensing such as CO2 and humidity. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 113, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Lin, X.; Dai, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, S.; Fei, T.; Zhang, T. Humidity sensors based on MCM-41/polypyrrole hybrid film via in-situ polymerization. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 277, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chang, H.; Li, P.; Liu, R.; Xue, Q. Fabrication and characterization of an ultrasensitive humidity sensor based on metal oxide/graphene hybrid nanocomposite. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2016, 225, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappanda, K.N.; Chaix, A.; Surya, S.G.; Moosa, B.A.; Khashab, N.M.; Salama, K.N. Trianglamine hydrochloride crystals for a highly sensitive and selective humidity sensor. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 294, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Li, Z.; Wei, T.; Li, Y.; Cui, P. Highly sensitive humidity sensor at low humidity based on the quaternized polypyrrole composite film. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2009, 142, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.H.; Parks, G.A. Electrical conductivity of silica gel in the presence of adsorbed water. J. Phys. Chem. 1968, 72, 3662–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernsberger, F.M. The Nonconformist Ion. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1983, 66, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalbore-Miceli, G.; Yang, M.J.; Camaioni, N.; Mari, C.M.; Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Ling, M. Investigations on the ion transport mechanism in conducting polymer films. Solid State Ion 2000, 131, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sensing Material | Measurement Range (% RH) | Response/Recovery Time (s) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-41/PPy | 11–95 | −915/−100 | [42] |
| RGO/SnO2 | 11–97 | 102/6 | [43] |
| Trianglamine hydrochloride | 5–95 | 720/300 | [44] |
| MCM-41/PEDOT | 11–95 | 165/115 | [4] |
| PPy | 11–95 | 41/120 | [45] |
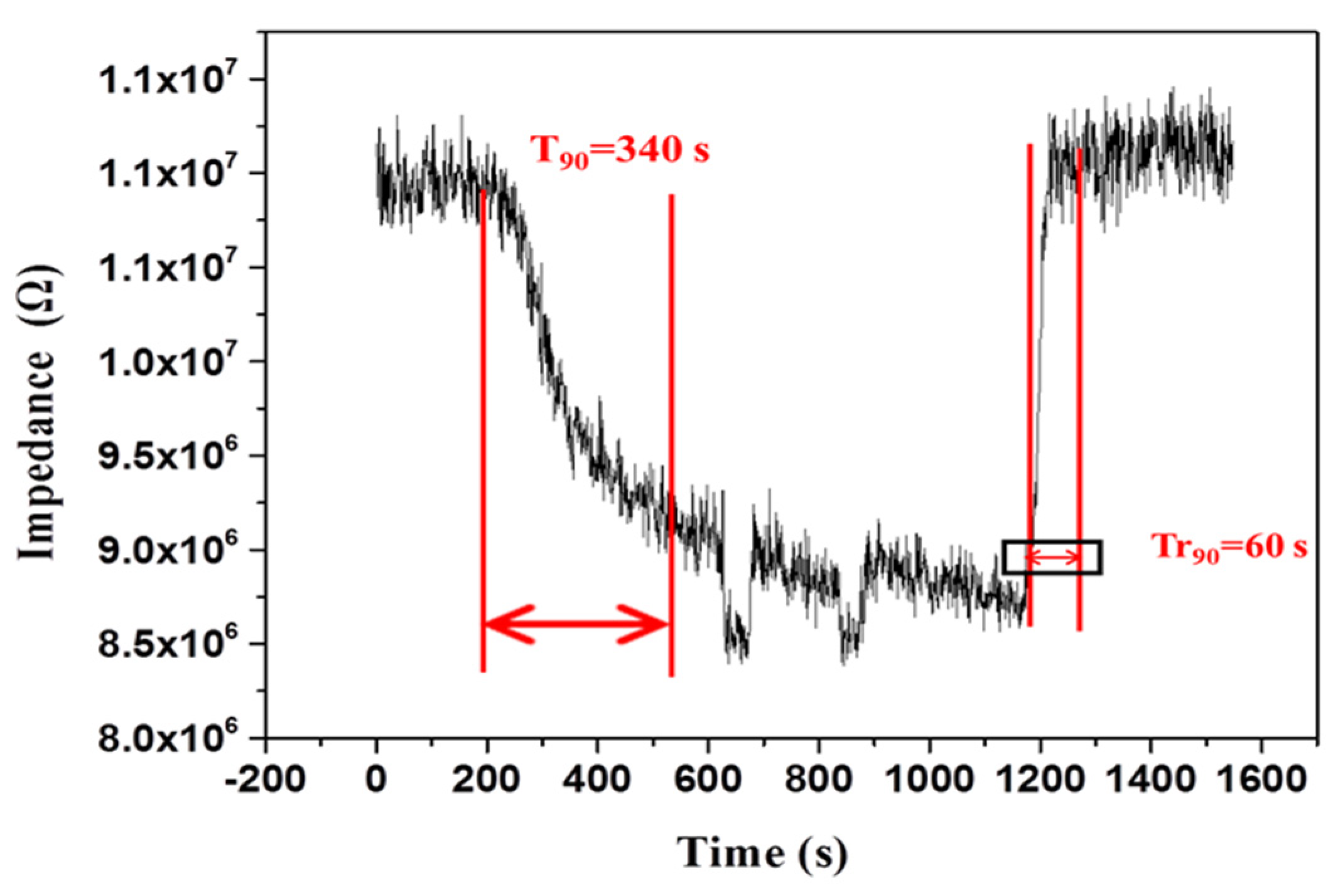
| PPy/BiPO4 | 12–90 | 340/60 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Lin, W.-D.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Chuang, M.-H.; Wu, R.-J.; Chavali, M. Conductive Polymer (Graphene/PPy)–BiPO4 Composite Applications in Humidity Sensors. Polymers 2021, 13, 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13122013
Zhu Z, Lin W-D, Lin Z-Y, Chuang M-H, Wu R-J, Chavali M. Conductive Polymer (Graphene/PPy)–BiPO4 Composite Applications in Humidity Sensors. Polymers. 2021; 13(12):2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13122013
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zhen, Wang-De Lin, Zhi-Yi Lin, Ming-Hong Chuang, Ren-Jang Wu, and Murthy Chavali. 2021. "Conductive Polymer (Graphene/PPy)–BiPO4 Composite Applications in Humidity Sensors" Polymers 13, no. 12: 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13122013
APA StyleZhu, Z., Lin, W.-D., Lin, Z.-Y., Chuang, M.-H., Wu, R.-J., & Chavali, M. (2021). Conductive Polymer (Graphene/PPy)–BiPO4 Composite Applications in Humidity Sensors. Polymers, 13(12), 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13122013








