Synthesis and Characterization of a Fe3O4@PNIPAM-Chitosan Nanocomposite and Its Potential Application in Vincristine Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of NpFe3O4
2.3. NIPAM Polymerization on NpFe3O4 in Presence CS (Fe3O4@PNIPAM-CS)
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Vincristine Sulfate Loading
2.6. Vincristine Sulfate Release Study Mathematical Release Model
3. Results
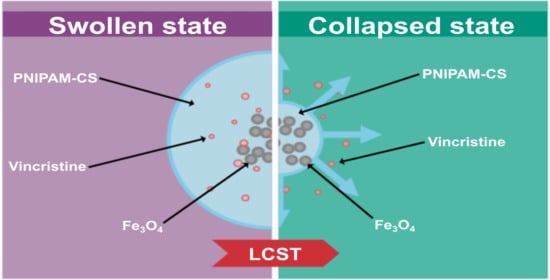
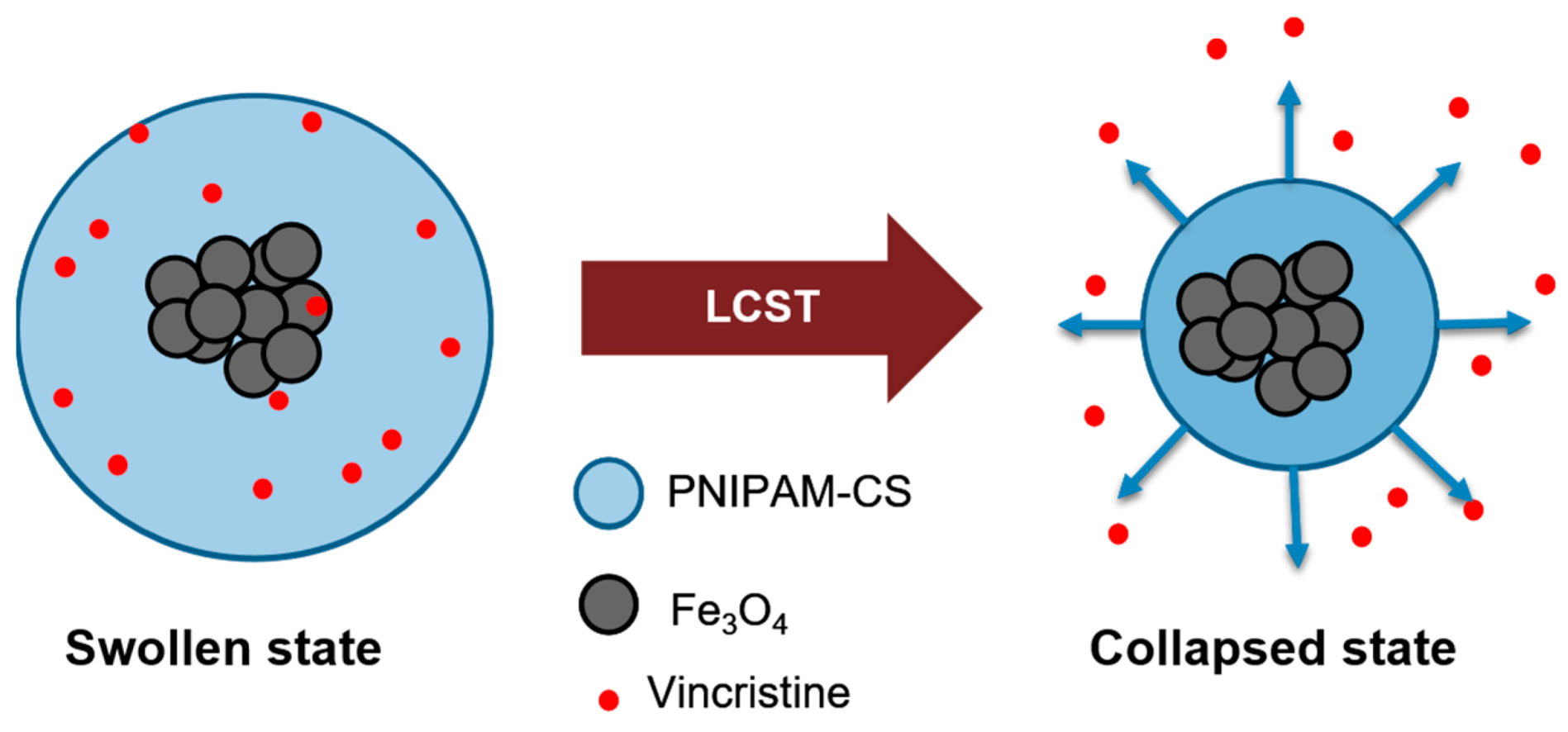
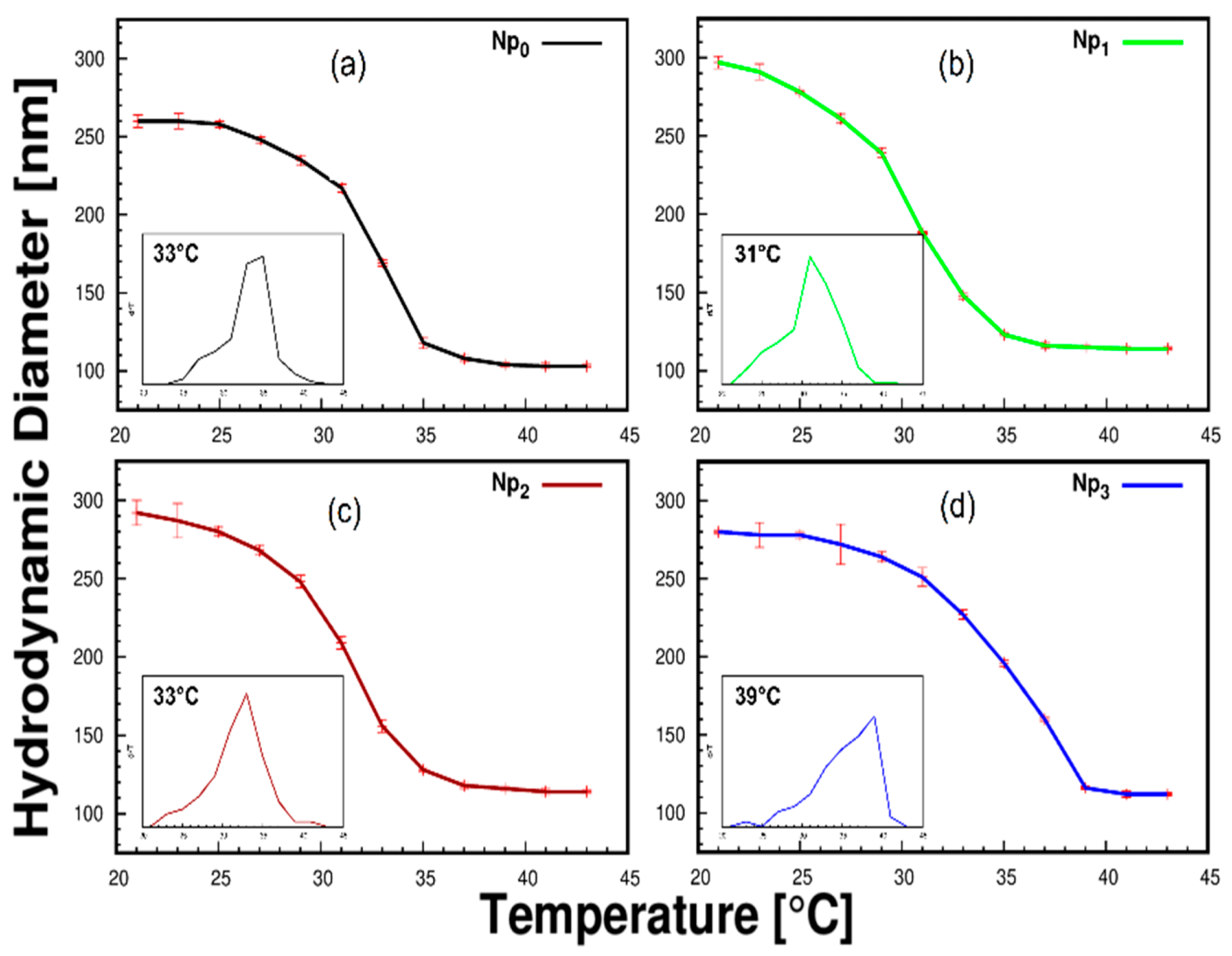
3.1. Swelling Kinetics and LCST
3.2. Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
3.3. Magnetic Properties
3.4. ζ-Potential
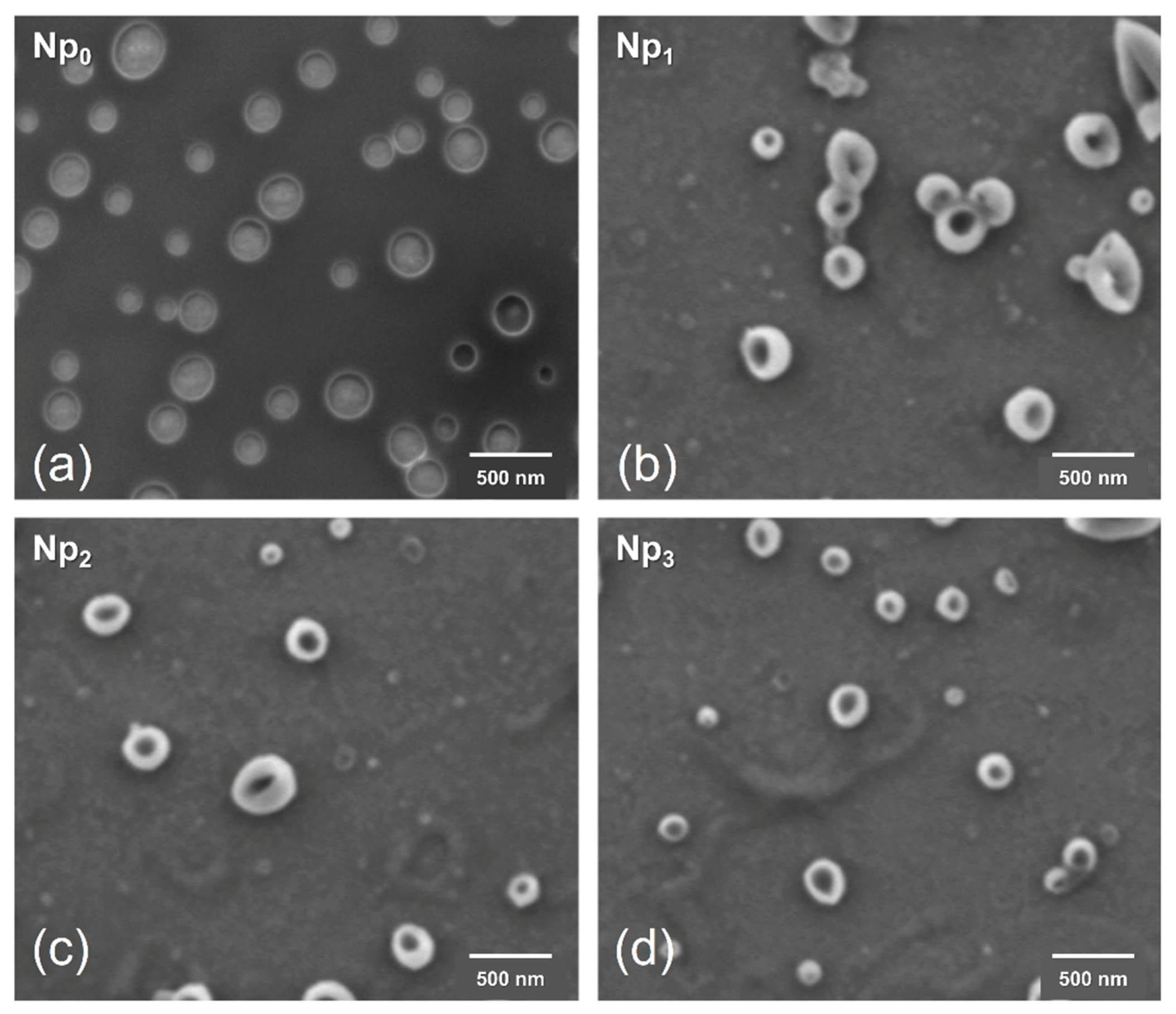
3.5. Morphology Analysis
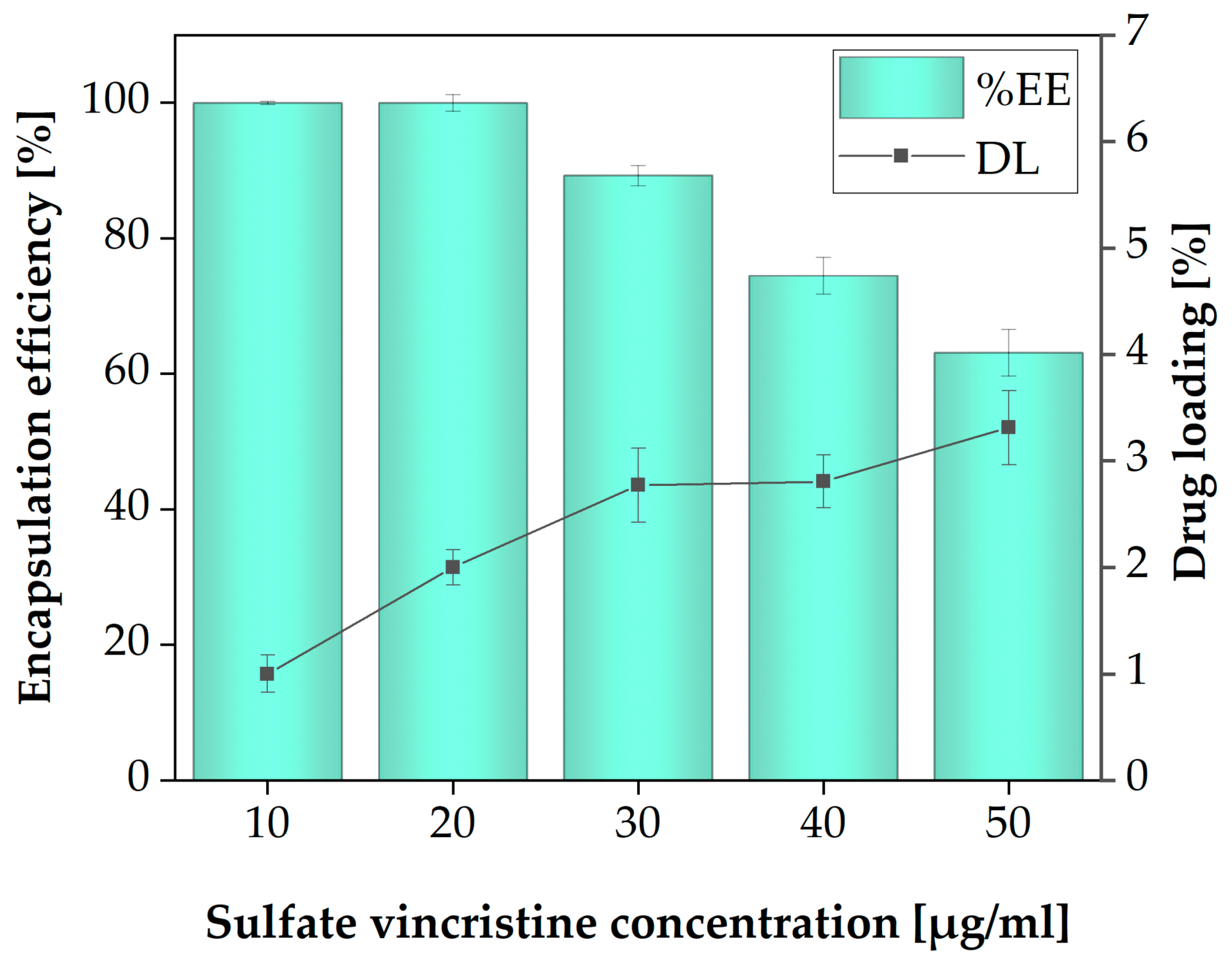
3.6. Drug Loading (DL) and Encapsulation Efficiency (%EE)
3.7. Effect of Temperature on Drug Delivery
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grande, A.H. Nanotecnología y nanopartículas magnéticas: La física actual en lucha contra la enfermedad. Rev. R. Acad. Cienc. Exact. Fís. Nat. 2007, 101, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, N.; Peng, Q.; Cheng, X.; Li, W. Temperature/pH dual-responsive and luminescent drug carrier based on PNIPAM-MAA/lanthanide-polyoxometalates for controlled drug delivery and imaging in HeLa cells. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coral, D.F.; Jenny, A.; Mera, J.A.M. Una guía para el estudio de nanopartículas magnéticas de óxidos de hierro con aplicaciones biomédicas. Parte II. Ing. Cienc. 2017, 13, 207–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Long, S.; Yang, J. Novel PNIPAm-based electrospun nanofibres used directly as a drug carrier for “on-off” switchable drug release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umapathi, R.; Reddy, P.M.; Kumar, A.; Venkatesu, P.; Chang, C.J. The biological stimuli for governing the phase transition temperature of the ‘smart’ polymer PNIPAM in water. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, I. Nanoparticles for electronic device applications: A brief review. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2005, 38, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Payán, D.A.; Koyani, R.D.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R. Chitosan-based biocatalytic nanoparticles for pollutant removal from wastewater. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2017, 100, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokardekar, R.R.; Shah, V.K.; Mody, H.R. PNIPAM Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide): A thermoresponsive “smart” polymer in novel drug delivery system. Med. Update 2012, 7, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bahl, S.; Nagar, H.; Singh, I.; Sehgal, S. Smart materials types, properties and applications: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseri, R.; Deutschman, C.P.; Han, L.; Pope, M.A.; Tam, K.C. Cellulose nanocrystals in smart and stimuli-responsive materials: A review. Mater. Today Adv. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakula, M.; Naveen, N.R. Prospection of recent chitosan biomedical trends: Evidence from patent analysis (2009–2020). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanoj Rejinold, N.; Sreerekha, P.R.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Biocompatible, biodegradable and thermo-sensitive chitosan-g-poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) nanocarrier for curcumin drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, N.; Ghandehari, H. Polymeric conjugates for drug delivery. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häfeli, U.O.; Sweeney, S.M.; Beresford, B.A.; Humm, J.L.; Macklis, R.M. Effective targeting of magnetic radioactive90Y-microspheres to tumor cells by an externally applied magnetic field. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo results. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1995, 22, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighian, S.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Hosseini-Monfared, H.; Hamidi, M. Doxorubicin-conjugated core-shell magnetite nanoparticles as dual-targeting carriers for anticancer drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Venkatasubramanian, R.; Hein, S.; Misra, R.D.K. A stimulus-responsive magnetic nanoparticle drug carrier: Magnetite encapsulated by chitosan-grafted-copolymer. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1024–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicia, J.D.; Javier, C.H. Nanopartículas magnéticas de zinc y calcio para aplicaciones en hipertermia magnética. Rev. Fac. Ing. 2016, 25, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Honey Priya, J.; Rijo, J.; Anju, A.; Anoop, K.R. Smart polymers for the controlled delivery of drugs—A concise overview. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebadi, M.; Buskaran, K.; Bullo, S.; Hussein, M.Z.; Fakurazi, S.; Pastorin, G. Synthesis and cytotoxicity study of magnetite nanoparticles coated with polyethylene glycol and sorafenib–zinc/aluminium layered double hydroxide. Polymers 2020, 12, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petters, C.; Irrsack, E.; Koch, M.; Dringen, R. Uptake and metabolism of iron oxide nanoparticles in brain cells. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 1648–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, P.; Lucero-Acuña, A.; Moreno-Cortez, I.E.; Esquivel, R.; Álvarez-Ramos, E. Thermo-magnetic properties of Fe 3 O 4 @poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) core–shell nanoparticles and their cytotoxic effects on HeLa and MDA-MB-231 cell lines. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 20, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.F.; Jia, J.F.; Guo, X.K.; Zhao, Y.P.; Chen, D.S.; Guo, Y.Y.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, X.L. Biocompatibility of chitosan-coated iron oxide nanoparticles with osteoblast cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5593–5602. [Google Scholar]
- Kean, T.; Thanou, M. Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Dmour, I.; Taha, M.O. Degradability of chitosan micro/nanoparticles for pulmonary drug delivery. Heliyon 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briceño, S.; Hernandez, A.C.; Sojo, J.; Lascano, L.; Gonzalez, G. Degradation of magnetite nanoparticles in biomimetic media. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Jalodia, K.; Kumar, P.; Gautam, H.K. Recent advances in nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 41, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Shim, K.H.; An, S.S.A.; Yi, D.K. Review on gold nanoparticles and their applications. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2011, 3, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalil, A.; Strand, S.; Mucker, E.; Huggins, J.W.; Jahrling, P.B.; Ibrahim, S.M. Inhibition of Monkeypox virus replication by RNA interference. Virol. J. 2009, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández Paredes, H.G. Efecto Antiproliferativo de la Betanina y Coadyuvante con Vincristina en Células de Leucemia Lingoblástica Aguda Tipo T. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Querétaro, Santiago de Querétaro, Mexico, October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett, S.L.; Grant, I.; Hall, P.N.; Kelsall, A.W.R.; Nicholson, J.C. Vincristine as a treatment for a large haemangioma threatening vital functions. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 2004, 57, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.A.; Deitcher, S.R. Marqibo® (vincristine sulfate liposome injection) improves the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vincristine. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquivel, R.; Canale, I.; Ramirez, M.; Hernández, P.; Zavala-Rivera, P.; Álvarez-Ramos, E.; Lucero-Acuña, A. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-coated gold nanorods mediated by thiolated chitosan layer: Thermo-pH responsiveness and optical properties. E-Polymers 2018, 18, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammel, T.; Thit, A.; Cui, X.; Mouneyrac, C.; Baun, A.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Sturve, J.; Selck, H. Trophic transfer of CuO NPs from sediment to worms (Tubifex tubifex) to fish (Gasterosteus aculeatus): A comparative study of dissolved Cu and NPs enriched with a stable isotope tracer (65Cu). Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerli, S.; Alver, U.; Göğebakan, M. Investigation of the electrical properties of Al85Y9Ni6 metallic glass and formulation of the results. Glass Phys. Chem. 2020, 46, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Gong, X.; Han, H.; Gao, Y.; Lu, W.; Liu, Y.; Xian, M.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C. Facile synthesis of orange fluorescence carbon dots with excitation independent emission for pH sensing and cellular imaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1042, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hoffman, A.S. Graft copolymers that exhibit temperature-induced phase transitions over a wide range of pH. Nature 1995, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Chuang, T.J.; Ke, C.J.; Yao, C.H. Doxorubicin-gelatin/Fe3O4-Alginate dual-layer magnetic nanoparticles as targeted anticancer drug delivery vehicles. Polymers 2020, 12, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Quinto, C.A.; Zhang, L.; Mohindra, P.; Bao, G. Size-dependent heating of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6808–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertmann, U.; Cornell, R.M. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrence, and Uses; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Atabaev, T.S.; Kim, H.K.; Hwang, Y.H. Fabrication of bifunctional core-shell Fe3O4 particles coated with ultrathin phosphor layer. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shagholani, H.; Ghoreishi, S.M.; Mousazadeh, M. Improvement of interaction between PVA and chitosan via magnetite nanoparticles for drug delivery application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 78, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruniaux, J.; Ben Djemaa, S.; Aubert, K.H.; Marchais, H.; Chourpa, I.; David, S. Stealth magnetic nanocarriers of siRNA as platform for breast cancer theranostics. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.M.M.; Elashkar, A.A.; El-Kassas, H.Y.; Salim, E.I. Methotrexate loaded on magnetite iron nanoparticles coated with chitosan: Biosynthesis, characterization, and impact on human breast cancer MCF-7 cell line. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.K.; Kim, J.C. FITC-dextran releases from chitosan microgel coated with poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid). Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhu, A.M.; Zhang, Q.G. One-pot synthesis of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/chitosan composite microspheres via microemulsion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawes, G.J.S.; Fratila-Apachitei, L.E.; Mulia, K.; Apachitei, I.; Witkamp, G.J.; Duszczyk, J. Size effect of PLGA spheres on drug loading efficiency and release profiles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, K.; He, X.; Song, Z.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Uckun, F.M.; Jiang, C.; Cheng, J. Dimeric drug polymeric nanoparticles with exceptionally high drug loading and quantitative loading efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3458–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, Y.; Khodadust, R.; Akkoc, Y.; Utkur, M.; Saritas, E.U.; Gozuacik, D.; Acar, H.Y. Development of tailored SPION-PNIPAM nanoparticles by ATRP for dually responsive doxorubicin delivery and MR imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Ahmad, I.; Umar, S.; Iqbal, Z.; Samim, M.; Ahmad, F.J. PNIPAM nanoparticles for targeted and enhanced nose-to-brain delivery of curcuminoids: UPLC/ESI-Q-ToF-MS/MS-based pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic evaluation in cerebral ischemia model. Drug Deliv. 2014, 7544, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



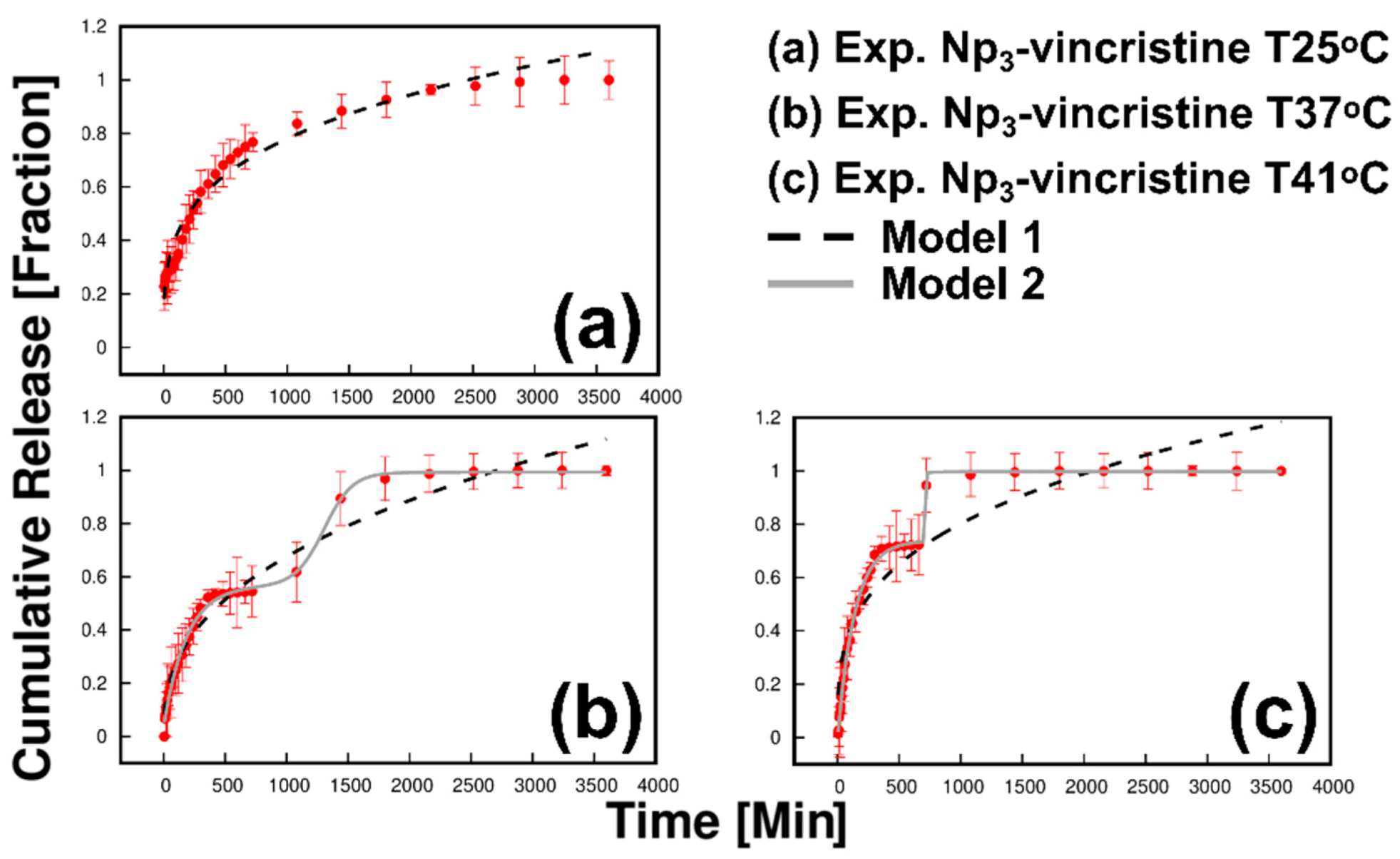
| Temperature (°C) | K1 | N | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.1168 | 0.2749 | 0.9754 |
| 37 | 0.0447 | 0.3929 | 0.9781 |
| 41 | 0.0985 | 0.3035 | 0.8911 |
| Temperature (°C) | A1 | A2 | Logx01 | Logx02 | h1 | h2 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 37 | −9.7686 | 0.9931 | −526.4825 | 1304.0414 | 0.0037 | 0.0037 | 0.99639 |
| 41 | −66.5933 | 0.9977 | −619.7001 | 715.7139 | 0.1503 | 0.1503 | 0.99853 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Téllez, C.N.; Luque-Alcaraz, A.G.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Higuera-Valenzuela, H.J.; Burgos-Hernández, M.; García-Flores, N.; Álvarez-Ramos, M.E.; Iriqui-Razcon, J.L.; Gonzalez, R.E.; Hernández-Abril, P.A. Synthesis and Characterization of a Fe3O4@PNIPAM-Chitosan Nanocomposite and Its Potential Application in Vincristine Delivery. Polymers 2021, 13, 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111704
Hernández-Téllez CN, Luque-Alcaraz AG, Plascencia-Jatomea M, Higuera-Valenzuela HJ, Burgos-Hernández M, García-Flores N, Álvarez-Ramos ME, Iriqui-Razcon JL, Gonzalez RE, Hernández-Abril PA. Synthesis and Characterization of a Fe3O4@PNIPAM-Chitosan Nanocomposite and Its Potential Application in Vincristine Delivery. Polymers. 2021; 13(11):1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111704
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Téllez, Cynthia N., Ana G. Luque-Alcaraz, Maribel Plascencia-Jatomea, Hiram J. Higuera-Valenzuela, Mabeth Burgos-Hernández, Nadia García-Flores, Mario E. Álvarez-Ramos, Jorge L. Iriqui-Razcon, Reynaldo Esquivel Gonzalez, and Pedro A. Hernández-Abril. 2021. "Synthesis and Characterization of a Fe3O4@PNIPAM-Chitosan Nanocomposite and Its Potential Application in Vincristine Delivery" Polymers 13, no. 11: 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111704
APA StyleHernández-Téllez, C. N., Luque-Alcaraz, A. G., Plascencia-Jatomea, M., Higuera-Valenzuela, H. J., Burgos-Hernández, M., García-Flores, N., Álvarez-Ramos, M. E., Iriqui-Razcon, J. L., Gonzalez, R. E., & Hernández-Abril, P. A. (2021). Synthesis and Characterization of a Fe3O4@PNIPAM-Chitosan Nanocomposite and Its Potential Application in Vincristine Delivery. Polymers, 13(11), 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111704