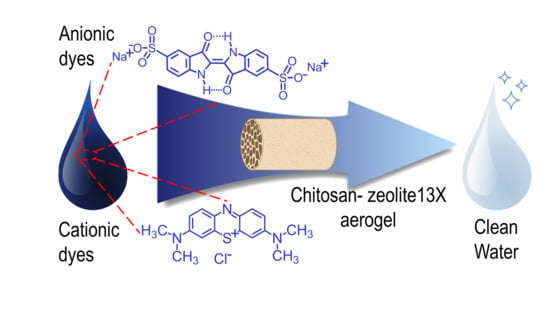
Chitosan/Zeolite Composite Aerogels for a Fast and Effective Removal of Both Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Aerogels Preparation
2.3. Characterization
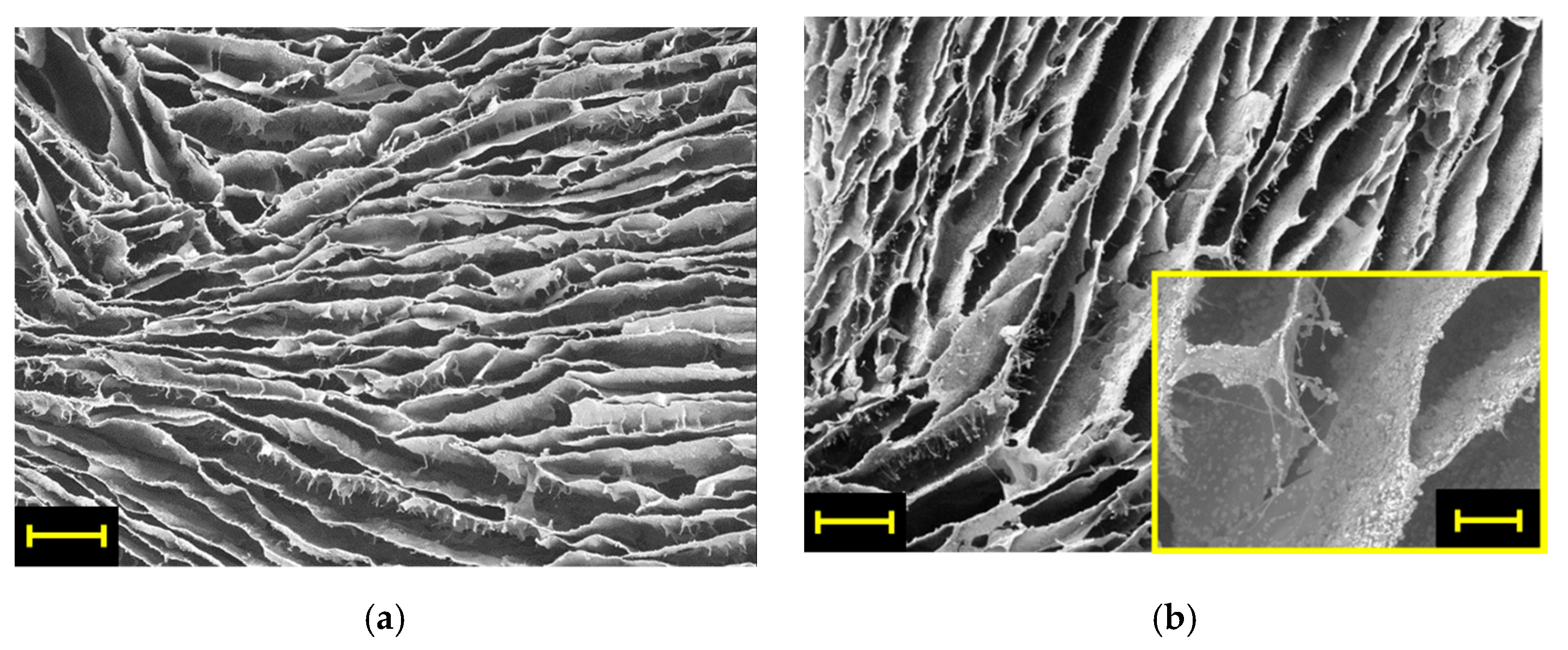
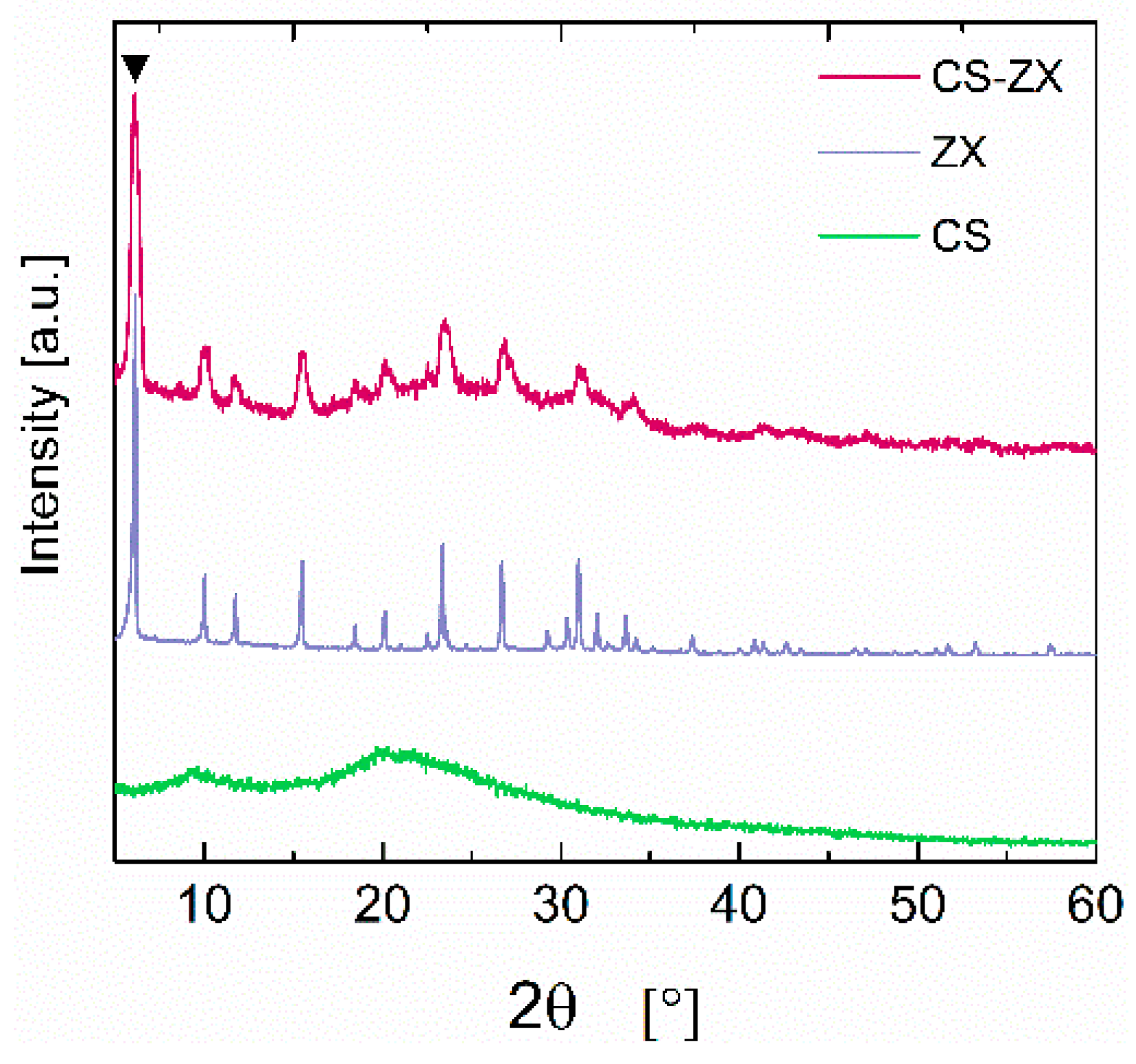
3. Results and Discussion
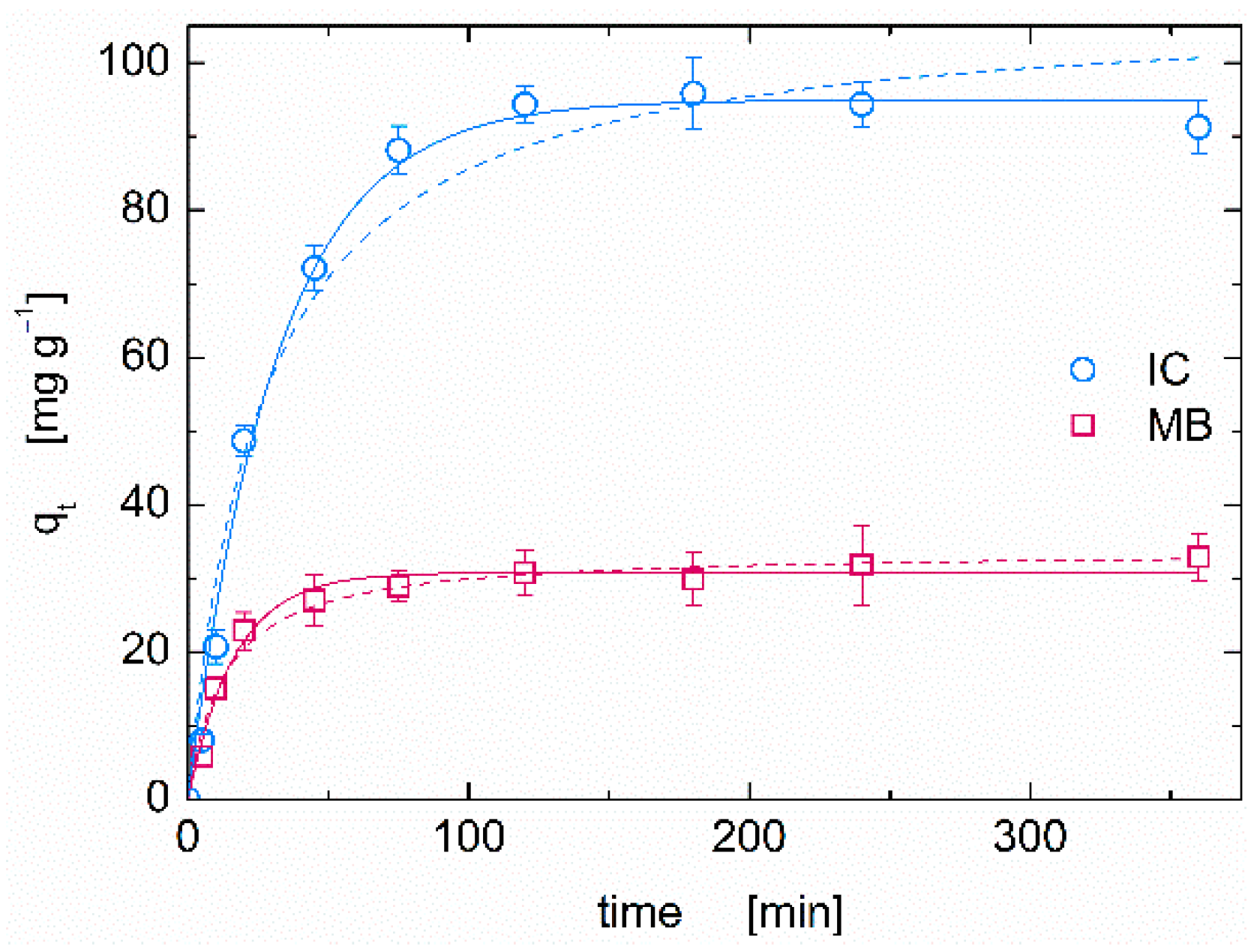
3.1. Dye Ddsorption
3.2. Mechanical Properties
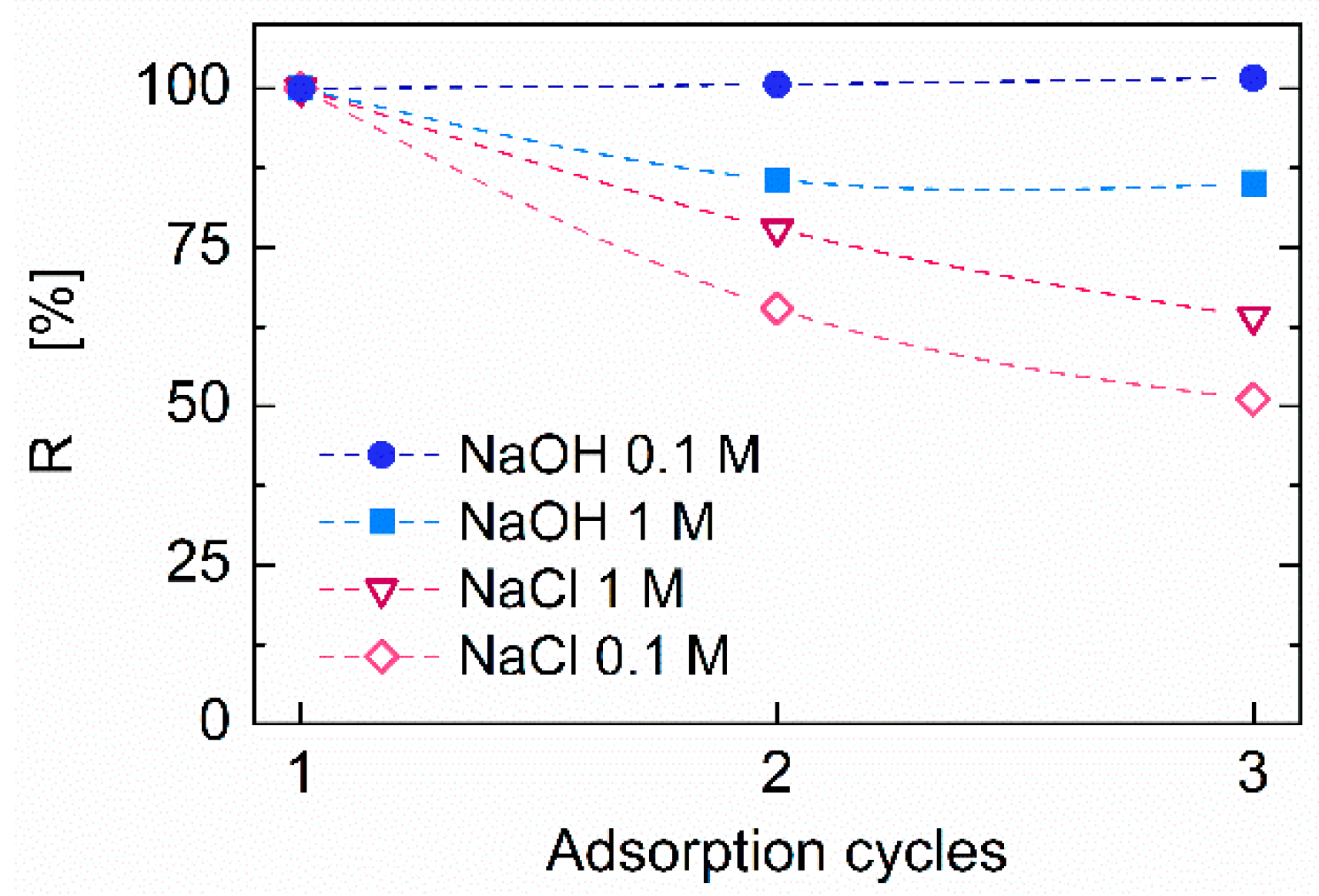
3.3. Aerogels Reusability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katheresan, V.; Kansedo, J.; Lau, S.Y. Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4676–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, K.G.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Jaikumar, V.; Sundar Rajan, P. Removal of colorants from wastewater: A review on sources and treatment strategies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 75, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjaneyulu, Y.; Sreedhara Chary, N.; Samuel Suman Raj, D. Decolourization of industrial effluents-Available methods and emerging technologies-A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 245–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, F.I.; Yamamoto, K.; Fukushi, K. Hybrid treatment systems for dye wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 37, 315–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Holtzl, T.; Szekely, G. Scavenging organic micropollutants from water with nanofibrous hypercrosslinked cyclodextrin membranes derived from green resources. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cseri, L.; Topuz, F.; Abdulhamid, M.A.; Alammar, A.; Budd, P.M.; Szekely, G. Electrospun Adsorptive Nanofibrous Membranes from Ion Exchange Polymers to Snare Textile Dyes from Wastewater. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 2000955, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaleshtari, Z.A.; Foudazi, R. Polypyrrole@polyHIPE Composites for Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Water. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 3196–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alammar, A.; Park, S.H.; Ibrahim, I.; Deepak, A.; Holtzl, T.; Dumée, L.F.; Lim, H.N.; Szekely, G. Architecting neonicotinoid-scavenging nanocomposite hydrogels for environmental remediation. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 21, 100878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Andrews, M.P. Carboxylated Cellulose Nanocrystal Microbeads for Removal of Organic Dyes from Wastewater: Effects of Kinetics and Diffusion on Binding and Release. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 11217–11228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M. Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics of dye removal using alginate in binary systems. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 2802–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. Applications of chitin- and chitosan-derivatives for the detoxification of water and wastewater-A short review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 152, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquerdo, V.M.; Cadaval, T.R.S.; Dotto, G.L.; Pinto, L.A.A. Chitosan scaffold as an alternative adsorbent for the removal of hazardous food dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 424, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Ngah, W.S.; Teong, L.C.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chatterjee, T.; Lim, S.R.; Woo, S.H. Adsorption of a cationic dye, methylene blue, on to chitosan hydrogel beads generated by anionic surfactant gelation. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Molla, A.; Chowdhury, A.; Kumari, S.; Hussain, S. Surface-Charge-Controlled Synthesis of ZnIn 2 S 4 Nanosheet-Based Materials for Selective Adsorption of Organic Dyes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reghioua, A.; Barkat, D.; Jawad, A.H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Al-Kahtani, A.A.; Alothman, Z.A. Parametric optimization by Box-Behnken design for synthesis of magnetic chitosan-benzil/ZnO/Fe3O4nanocomposite and textile dye removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belachew, N.; Hinsene, H. Preparation of Zeolite 4A for Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue: Optimization, Kinetics, Isotherm, and Mechanism Study. Silicon 2021, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Xu, F.; Wei, W.; Gao, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P. Efficient and fast adsorption of methylene blue dye onto a nanosheet MFI zeolite. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 295, 121917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoor, S.; Karayil, J.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. Removal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous environment using polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate/ZSM-5 zeolite membrane. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, S.; Xiao, Z. Hierarchical mesoporous ZIF-67@LDH for efficient adsorption of aqueous Methyl Orange and Alizarine Red S. Powder Technol. 2021, 377, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Fu, K.; Yu, D.; Hristovski, K.D.; Westerhoff, P.; Crittenden, J.C. Review of Advances in Engineering Nanomaterial Adsorbents for Metal Removal and Recovery from Water: Synthesis and Microstructure Impacts. ACS ES&T Eng. 2021, 1, 623–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Bai, H.; Li, L. Graphene oxide-chitosan composite hydrogels as broad-spectrum adsorbents for water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1992–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luna, M.S.; Ascione, C.; Santillo, C.; Verdolotti, L.; Lavorgna, M.; Buonocore, G.G.; Castaldo, R.; Filippone, G.; Xia, H.; Ambrosio, L. Optimization of dye adsorption capacity and mechanical strength of chitosan aerogels through crosslinking strategy and graphene oxide addition. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Luna, M.S.; Sirignano, M. Upcycling soot particles into chitosan-based aerogels for water purification from organic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2021, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Lou, T. Preparation of fibrous chitosan/sodium alginate composite foams for the adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 124054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkli, Y.E.; Can, M.F.; Turan, M.; Çelik, M.S. Modification of organo-zeolite surface for the removal of reactive azo dyes in fixed-bed reactors. Water Res. 2005, 39, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armaǧan, B.; Özdemir, O.; Turan, M.; Çelik, M.S. The removal of reactive azo dyes by natural and modified zeolites. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2003, 78, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, J.; Vossoughi, M.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Alemzadeh, I. Synthesis of amine-modified zeolitic imidazolate framework-8, ultrasound-assisted dye removal and modeling. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 39, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzzi, E.; Aprea, P.; de Luna, M.S.; Caputo, D.; Filippone, G. Mechanically Coherent Zeolite 13X/Chitosan Aerogel Beads for E ff ective CO 2 Capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 20728–20734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Yu, D.; Hristovski, K.D.; Fu, K.; Shen, Y.; Westerhoff, P.; Crittenden, J.C. Critical Review of Advances in Engineering Nanomaterial Adsorbents for Metal Removal and Recovery from Water: Mechanism Identification and Engineering Design. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Badot, P.M. Application of chitosan, a natural aminopolysaccharide, for dye removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption processes using batch studies: A review of recent literature. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 399–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivalingam, S.; Sen, S. Swift sono-hydrothermal synthesis of pure NaX nanocrystals with improved sorption capacity from industrial resources. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 463, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoor, S.; Karayil, J.; Jayakumar, A.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. Efficient removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution using mesoporous ZSM-5 zeolite: Synthesis, kinetics and isotherm studies. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 611, 125852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarish, R.; Unnikrishnan, G. PVA/PDADMAC/ZSM-5 zeolite hybrid matrix membranes for dye adsorption: Fabrication, characterization, adsorption, kinetics and antimicrobial properties. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3860–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Ni, H. Surface functionalization of cellulose with hyperbranched polyamide for efficient adsorption of organic dyes and heavy metals. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Lv, W.; Xie, Z.; Tan, Y.; Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Environmentally friendly reduced graphene oxide as a broad-spectrum adsorbent for anionic and cationic dyes: Via π-π Interactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 12126–12135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, Y. International Journal of Adhesion & Adhesives Development of Nicolais–Narkis model for yield strength of polymer nanocomposites reinforced with spherical nanoparticles. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 70, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgül, M.; Karabakan, A. Promoted dye adsorption performance over desilicated natural zeolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 145, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | EC [kPa] | ρ [g cm−3] | EC/ρ [kPa·g−1 cm−3] | SD [%] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | dry | 2.25 ± 0.67 | 0.022 ± 0.001 | dry | 103.7 | 47.5 ± 1.9 |
| wet | 0.13 ± 0.07 | wet | 5.8 | |||
| CS–ZX | dry | 13.13 ± 8.63 | 0.043 ± 0.003 | dry | 305.6 | 23.0 ± 2.9 |
| wet | 0.23 ± 0.07 | wet | 5.3 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marotta, A.; Luzzi, E.; Salzano de Luna, M.; Aprea, P.; Ambrogi, V.; Filippone, G. Chitosan/Zeolite Composite Aerogels for a Fast and Effective Removal of Both Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Water. Polymers 2021, 13, 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111691
Marotta A, Luzzi E, Salzano de Luna M, Aprea P, Ambrogi V, Filippone G. Chitosan/Zeolite Composite Aerogels for a Fast and Effective Removal of Both Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Water. Polymers. 2021; 13(11):1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111691
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarotta, Angela, Enrica Luzzi, Martina Salzano de Luna, Paolo Aprea, Veronica Ambrogi, and Giovanni Filippone. 2021. "Chitosan/Zeolite Composite Aerogels for a Fast and Effective Removal of Both Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Water" Polymers 13, no. 11: 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111691
APA StyleMarotta, A., Luzzi, E., Salzano de Luna, M., Aprea, P., Ambrogi, V., & Filippone, G. (2021). Chitosan/Zeolite Composite Aerogels for a Fast and Effective Removal of Both Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Water. Polymers, 13(11), 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111691