Morphology and Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Wood Fiber/Polylactic Acid Composite Parts Using Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): The Effects of Printing Speed
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
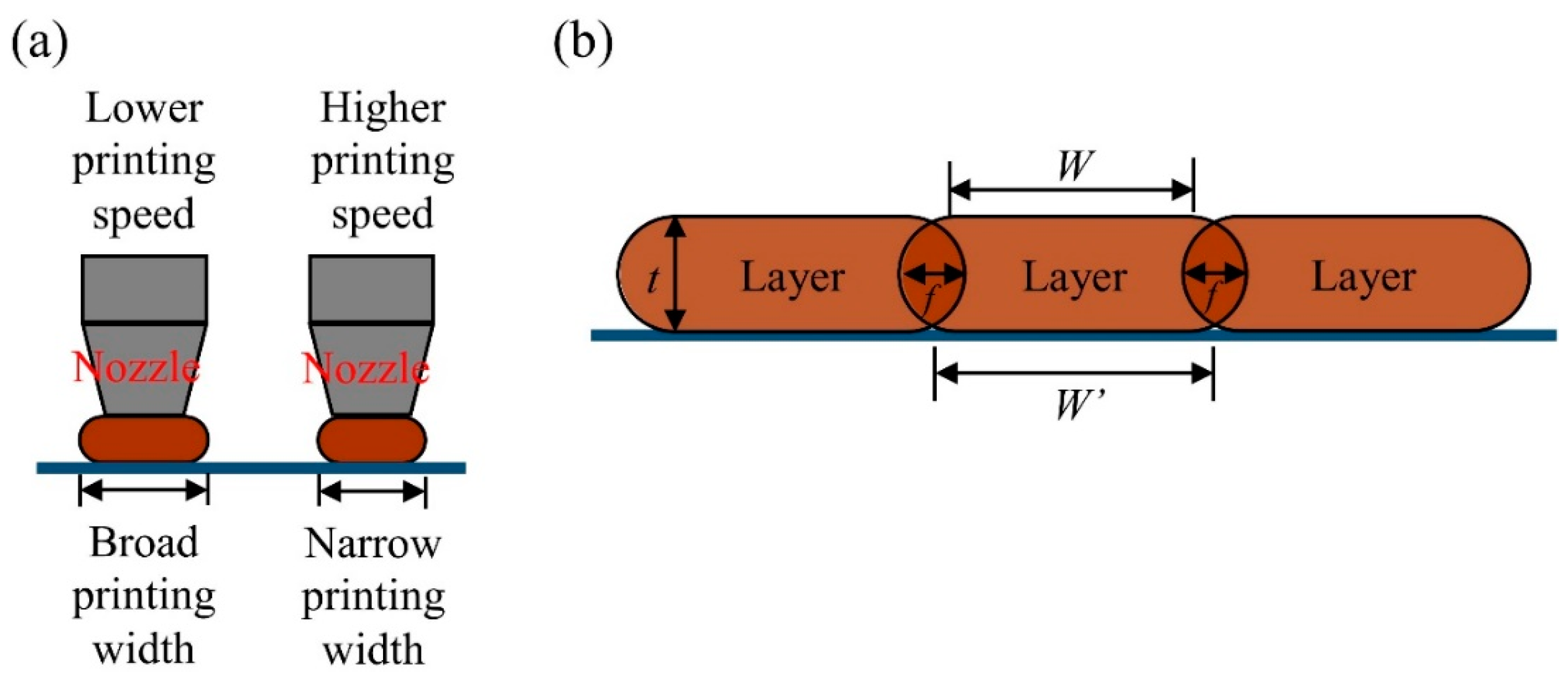
2.2. Preparation of FDM-Printed WPC Parts
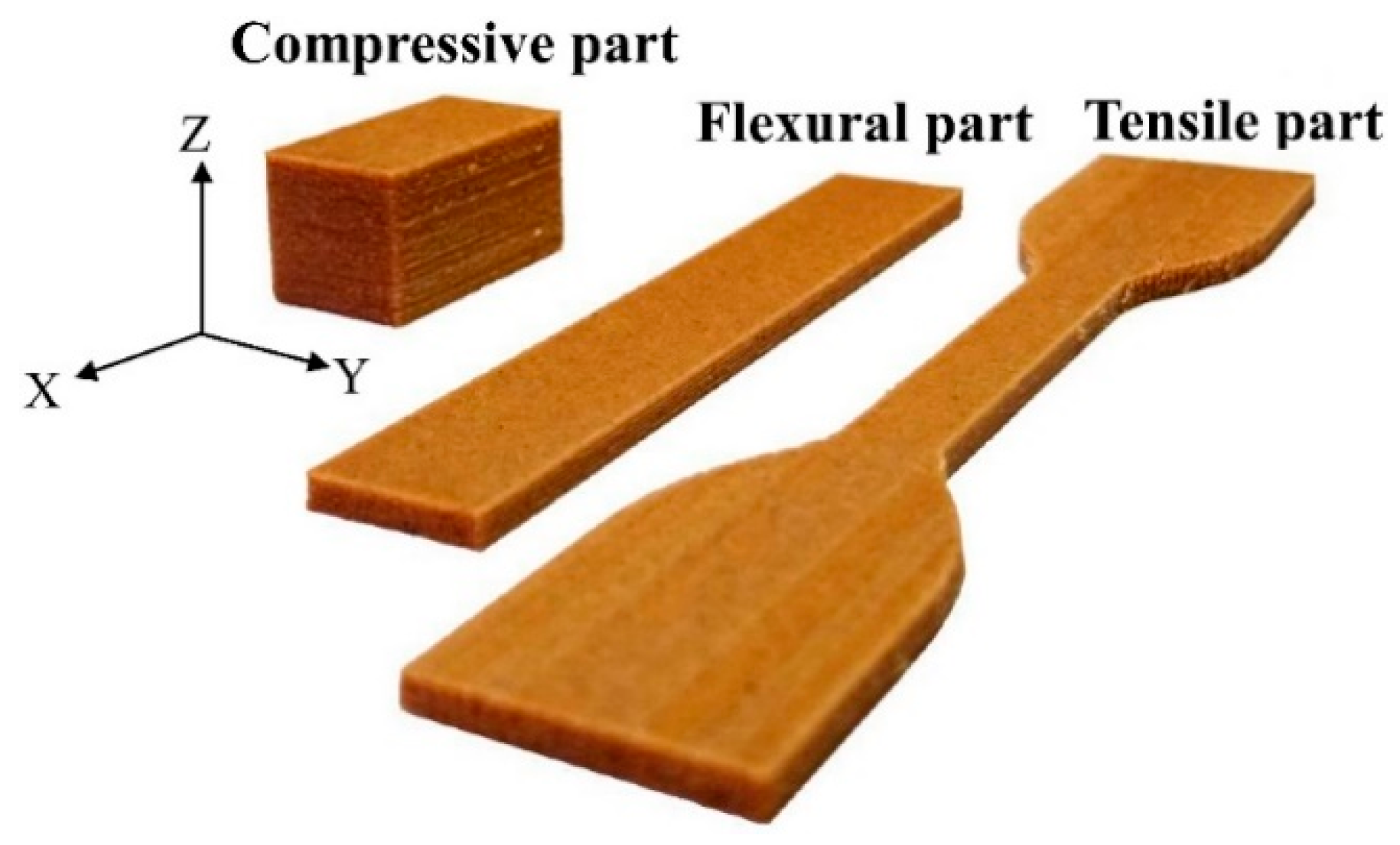
2.3. Determining Properties of the Printed Parts
2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5. Morphology of the Printed Parts
2.6. Surface Color
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. DSC Measurement
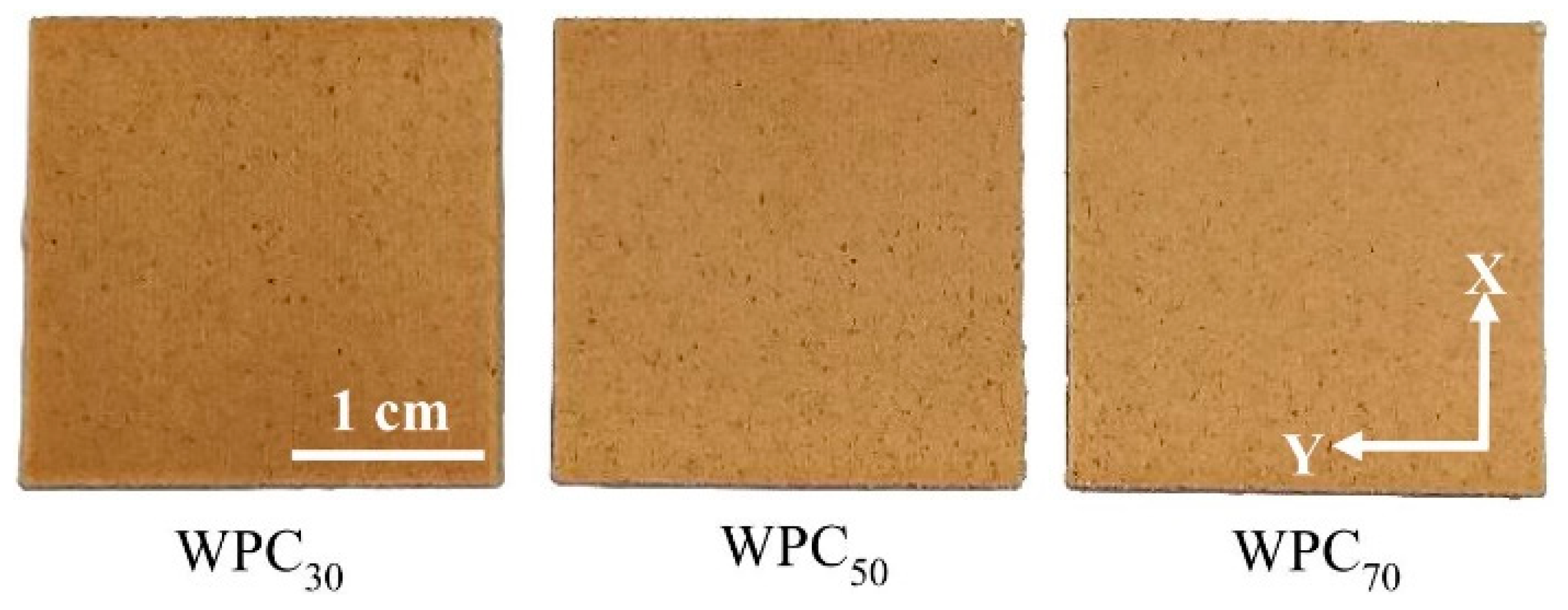
3.2. Surface Color
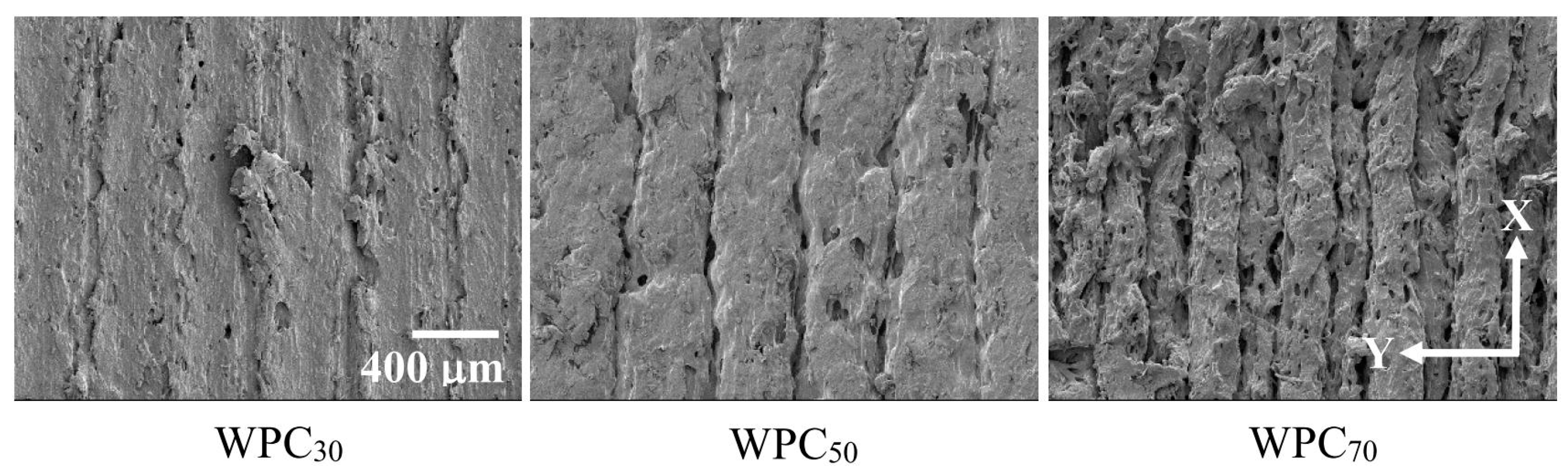
3.3. Density, Printing Time, and Surface Morphology
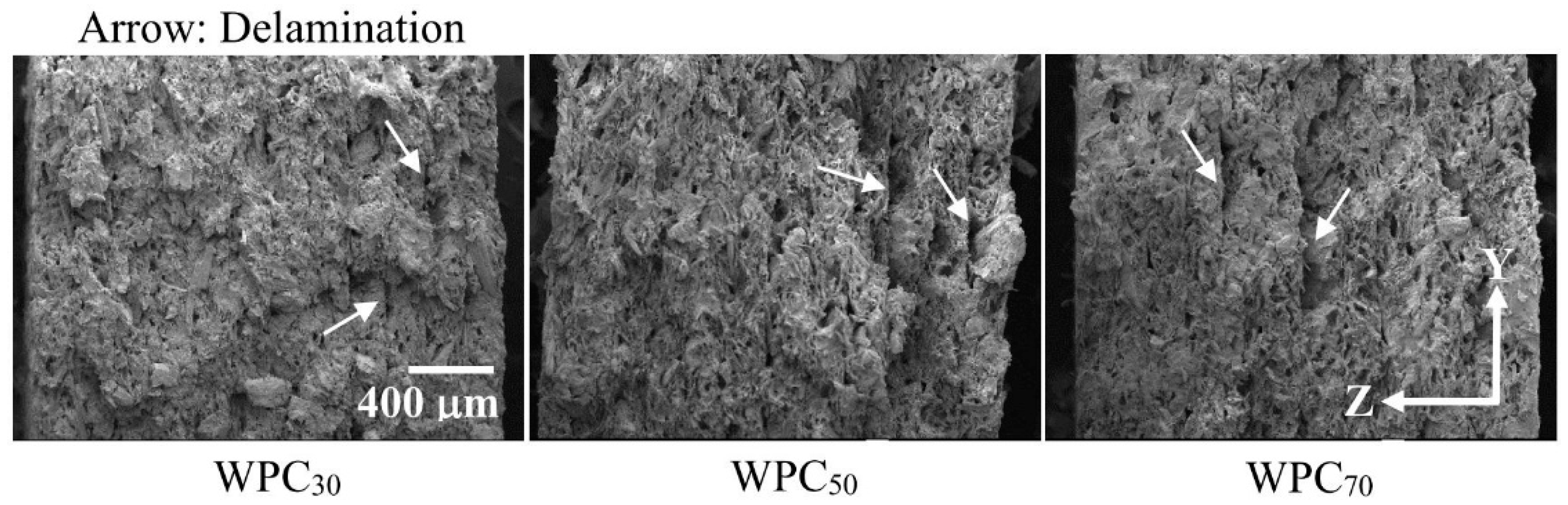
3.4. Fracture Morphology and Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Standard, A. F2792, Standard Terminology for Additive Manufacturing Technologies; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G.N.; Schindel, R.; Kruth, J.-P. Rapid manufacturing and rapid tooling with layer manufacturing (LM) technologies, state of the art and future perspectives. Cirp Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2003, 52, 589–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, O.; Williams, C.; Campbell, T. Additive manufacturing (AM) and nanotechnology: Promises and challenges. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2013, 19, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsoom, U.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Paull, B. Recent developments in 3D printable composite materials. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 60355–60371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, O.S.; Silva, A.F.; Gomes, R. Fused deposition modeling with polypropylene. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, V.E.; Solonin, A.N.; Urzhumtsev, O.D.; Schilling, R.; Tavitov, A.G. Strength of PLA components fabricated with fused deposition technology using a desktop 3D printer as a function of geometrical parameters of the process. Polymers 2018, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, J.M.; Caminero, M.A.; García-Plaza, E.; Núñez, P.J. Additive manufacturing of PLA structures using fused deposition modelling: Effect of process parameters on mechanical properties and their optimal selection. Mater. Des. 2017, 124, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymrak, B.M.; Kreiger, M.; Pearce, J.M. Mechanical properties of components fabricated with open-source 3-D printers under realistic environmental conditions. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullu, E.; Korkmaz, E.; Yay, K.; Ozdoganlar, O.B.; Kara, L.B. Enhancing the structural performance of additively manufactured objects through build orientation optimization. J. Mech. Des. 2015, 137, 111410–111419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, W.; Yee, K.; Lee, K.-Y.; Tagarielli, V.L. Measurement of the mechanical response of unidirectional 3D-printed PLA. Mater. Des. 2017, 123, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsouknidas, A.; Pantazopoulos, M.; Katsoulis, I.; Fasnakis, D.; Maropoulos, S.; Michailidis, N. Impact absorption capacity of 3D-printed components fabricated by fused deposition modelling. Mater. Des. 2016, 102, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, E.; Artzi, D. Enhancing aerospace engineering students’ learning with 3D printing wind-tunnel models. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2011, 17, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.V.; Hernandez, A. A review of additive manufacturing. Isrn Mech. Eng. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, D.B. Use of 3D printing by museums: Educational exhibits, artifact education, and artifact restoration. 3d Print. Addit. Manuf. 2015, 2, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.V.; Atala, A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksman, K.; Skrifvars, M.; Selin, J.-F. Natural fibers as reinforcement in polylactic acid (PLA) composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, T.; Nao, N. PLA based biopolymer reinforced with natural fibre: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, M.S.; Drzal, L.T.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Chopped glass and recycled newspaper as reinforcement fibers in injection molded poly(lactic acid) (PLA) composites: A comparative study. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 1813–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.-P.; Sain, M. Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1552–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, V.; Malagutti, L.; Mollica, F. FDM 3D printing of polymers containing natural fillers: A review of their mechanical properties. Polymers 2019, 11, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-C. Effect of extrusion temperature on the physico-mechanical properties of unidirectional wood fiber-reinforced polylactic acid composite (WFRPC) components using fused deposition modeling. Polymers 2018, 10, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Duigou, A.; Castro, M.; Bevan, R.; Martin, N. 3D printing of wood fibre biocomposites: From mechanical to actuation functionality. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 106–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.; Cong, W.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H. Additive manufacturing of carbon fiber-reinforced plastic composites using fused deposition modeling: Effects of process parameters on tensile properties. J. Compos. Mater. 2017, 51, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.B.; Strong, R.; Gold, S.A. A review of melt extrusion additive manufacturing processes: I. Process design and modeling. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2014, 20, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.G.; Zou, J.R.; Wu, H.H.; Xu, B.P. Balance between bonding and deposition during fused deposition modeling of polycarbonate and acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene composites. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozior, T.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Adhesion of three-dimensional printing on textile fabrics: Inspiration from and for other research areas. J. Eng. Fiber Fabr. 2020, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozior, T.; Mamun, A.; Trabelsi, M.; Sabantina, L.; Wortmann, M.; Ehrmann, A. Electrospinning on 3D printed polymers for mechanically stabilized filter composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaefe, D.; Poncsak, S.; Boluk, Y. Effect of heat treatment on the chemical composition and mechanical properties of birch and aspen. BioResources 2008, 3, 517–537. Available online: https://ojs.cnr.ncsu.edu/index.php/BioRes/article/view/7474 (accessed on 18 March 2020).
- Korkut, S.; Kök, M.S.; Korkut, D.S.; Gürleyen, T. The effects of heat treatment on technological properties in Red-bud maple (Acer trautvetteri Medw.) wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1538–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaez-Samaniego, M.R.; Yadama, V.; Lowell, E.; Espinoza-Herrera, R. A review of wood thermal pretreatments to improve composites properties. Wood Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1285–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboorani, A. Thermal properties of composites made of heat-treated wood and polypropylene. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 2599–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrilmis, N.; Jarusombuti, S.; Fueangvivat, V.; Bauchongkol, P. Effect of thermal-treatment of wood fibers on properties of flat-pressed wood plastic composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummer, D.; Cifuentes-Cuéllar, S.; Rietzel, D. Suitability of PLA/TCP for fused deposition modeling. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2012, 18, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. An investigation on distortion of PLA thin-plate part in the FDM process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 79, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.W.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.R.; Deng, Y.H. Incorporation of graphitic nano-filler and poly(lactic acid) in fused deposition modeling. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guessasma, S.; Belhabib, S.; Nouri, H. Understanding the microstructural role of bio-sourced 3D printed structures on the tensile performance. Polym. Test. 2019, 77, 105924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zou, B.; Wang, P.; Ding, H. Effects of nozzle temperature and building orientation on mechanical properties and microstructure of PEEK and PEI printed by 3D-FDM. Polym. Test. 2019, 78, 105948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuniwa, M.; Iura, K.; Dan, Y. Melting behavior of poly(L-lactic acid): Effects of crystallization temperature and time. Polymer 2007, 48, 5398–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granda, L.A.; Méndez, J.A.; Espinach, F.X.; Puig, J.; Delgado-Aguilar, M.; Mutjé, P. Polypropylene reinforced with semi-chemical fibres of Leucaena collinsii: Thermal properties. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2016, 94, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.P.; Gironès, J.; Méndez, J.A.; El Mansouri, N.E.; Llop, M.; Mutjé, P.; Vilaseca, F. Stone-ground wood pulp-reinforced polypropylene composites: Water uptake and thermal properties. BioResources 2012, 7, 5478–5487. Available online: https://ojs.cnr.ncsu.edu/index.php/BioRes/article/view/3182 (accessed on 18 March 2020). [CrossRef]
- Suryanegara, L.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Yano, H. The effect of crystallization of PLA on the thermal and mechanical properties of microfibrillated cellulose-reinforced PLA composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-C.; Wu, T.-L.; Hung, K.-C.; Wu, T.-M.; Wu, J.-H. A comparison of annealing process and nucleating agent (zinc phenylphosphonate) on the crystallization, viscoelasticity, and creep behavior of compression-molded poly(lactic acid) blends. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2015, 121, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masirek, R.; Kulinski, Z.; Chionna, D.; Piorkowska, E.; Pracella, M. Composites of poly(L-lactide) with hemp fibers: Morphology and thermal and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Yang, T.-C.; Wu, T.-L.; Hung, K.-C.; Wu, J.-H. The influence of bamboo fiber content on the non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of bamboo fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites (BPCs). Holzforschung 2018, 72, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-W.; Yang, T.-C.; Hung, K.-C.; Xu, J.-W.; Wu, J.-H. The effect of maleated polypropylene on the non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of wood fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhu, Y.-S.; Yang, T.-C.; Hung, K.-C.; Xu, J.-W.; Wu, T.-L.; Wu, J.-H. Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of acetylated bamboo fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites. Polymers 2018, 11, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, Y.; Gao, J.; Stark, N.M. The effect of heat treatment on the chemical and color change of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) wood flour. BioResources 2012, 7, 1157–1170. Available online: https://ojs.cnr.ncsu.edu/index.php/BioRes/article/view/BioRes_07_1_1157_Chen_FGS_Heat_Treat_Chem_Color_Wood (accessed on 18 March 2020). [CrossRef]
- Bekhta, P.; Niemz, P. Effect of high temperature on the change in color, dimensional stability and mechanical properties of spruce wood. Holzforschung 2003, 57, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgois, P.J.; Janin, G.; Guyonnet, R. The color measurement: A fast method to study and to optimize the chemical transformations undergone in the thermically treated wood. Holzforschung 1991, 45, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kačíková, D.; Kačík, F.; Čabalová, I.; Ďurkovč, J. Effects of thermal treatment on colour traits in Norway spruce wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Jafari, M.A.; Danforth, S.C.; Safari, A. Tool path-based deposition planning in fused deposition process. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME 2002, 124, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Jafari, M.A.; Seyed, K. Process speeding up via deposition planning in fused deposition-based layered manufacturing processes. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2003, 9, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niska, K.O.; Sain, M. Wood-Polymers Composites; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.-C.; Chien, Y.-C.; Wu, T.-L.; Hung, K.-C.; Wu, J.-H. Effects of heat-treated wood particles on the physico-mechanical properties and extended creep behavior of wood/recycled-HDPE composites using the time–temperature superposition principle. Materials 2017, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaPlante, G.; Lee-Sullivan, P. Moisture effects on FM300 structural film adhesive: Stress relaxation, fracture toughness, and dynamic mechanical analysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 95, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, D.; Wolcott, M. Interaction between coupling agent and lubricants in wood-polypropylene composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrote, G.; Dominiguez, H.; Parajó, J.C. Study on the deactylation of hemicelluloses during the hydrothermal processing of Eucalyptus wood. Holz. Roh. Werkst. 2001, 59, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, S.; Çolakoğlu, G.; Aydin, I.; Kalaycioğlu, H. Effects of steaming process on some properties of eucalyptus particleboard bonded with UF and MUF adhesives. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Code | Printing Speed (mm/s) | L* | a* | b* | ΔE* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPC30 | 30 | 54.2 ± 0.7 c | 15.8 ± 0.5 a | 22.2 ± 0.2 a | - |
| WPC50 | 50 | 55.7 ± 0.6 b | 15.7 ± 0.5 a | 22.1 ± 0.1 a | 1.6 ± 0.5 b |
| WPC70 | 70 | 57.1 ± 0.7 a | 15.4 ± 0.2 a | 22.4 ± 0.3 a | 3.0 ± 0.7 a |
| Code | Printing Speed (mm/s) | w (g) | V (cm3) | Density (g/cm3) | Printing Time (min) | TSP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPCf30 | 30 | 2.55 ± 0.02 a | 2.41 ± 0.05 a | 1.06 ± 0.02 a | 39.4 ± 0.5 a | - |
| WPCf50 | 50 | 2.47 ± 0.01 b | 2.41 ± 0.02 a | 1.02 ± 0.01 b | 26.6 ± 0.5 b | 32.5 |
| WPCf70 | 70 | 2.40 ± 0.02 c | 2.39 ± 0.01 a | 1.00 ± 0.01 b | 22.6 ± 0.5 c | 42.6 |
| Code | Printing Speed (mm/s) | w (g) | V (cm3) | Density (g/cm3) | Printing Time (min) | TSP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPCc30 | 30 | 3.90 ± 0.03 a | 3.65 ± 0.01 a | 1.07 ± 0.01 a | 61.0 ± 0.7 a | - |
| WPCc50 | 50 | 3.74 ± 0.03 b | 3.63 ± 0.03 a | 1.03 ± 0.01 b | 42.4 ± 0.5 b | 30.5 |
| WPCc70 | 70 | 3.44 ± 0.02 c | 3.58 ± 0.02 a | 0.96 ± 0.02 c | 36.4 ± 0.5 c | 40.3 |
| Code | Tensile Properties | Flexural Properties | Compressive Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS (MPa) | TM (MPa) | MOR (MPa) | MOE (MPa) | CS (MPa) | CM (MPa) | |
| WPC30 | 19.8 ± 0.8 a | 1731 ± 60 a | 34.0 ± 1.5 a | 1680 ± 78 a | 31.8 ± 0.6 a | 852 ± 8 a |
| WPC50 | 19.2 ± 0.7 a | 1650 ± 60 a | 33.1 ± 0.5 a | 1620 ± 70 a | 27.7 ± 0.9 b | 825 ± 11 a |
| WPC70 | 19.8 ± 0.3 a | 1682 ± 27 a | 32.3 ± 0.4 a | 1575 ± 34 a | 20.9 ± 1.8 c | 728 ± 28 b |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, T.-C.; Yeh, C.-H. Morphology and Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Wood Fiber/Polylactic Acid Composite Parts Using Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): The Effects of Printing Speed. Polymers 2020, 12, 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061334
Yang T-C, Yeh C-H. Morphology and Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Wood Fiber/Polylactic Acid Composite Parts Using Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): The Effects of Printing Speed. Polymers. 2020; 12(6):1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061334
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Teng-Chun, and Chin-Hao Yeh. 2020. "Morphology and Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Wood Fiber/Polylactic Acid Composite Parts Using Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): The Effects of Printing Speed" Polymers 12, no. 6: 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061334
APA StyleYang, T.-C., & Yeh, C.-H. (2020). Morphology and Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Wood Fiber/Polylactic Acid Composite Parts Using Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): The Effects of Printing Speed. Polymers, 12(6), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061334







