Dissipative Particle Dynamics Modeling of Polyelectrolyte Membrane–Water Interfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dissipative Particle Dynamics
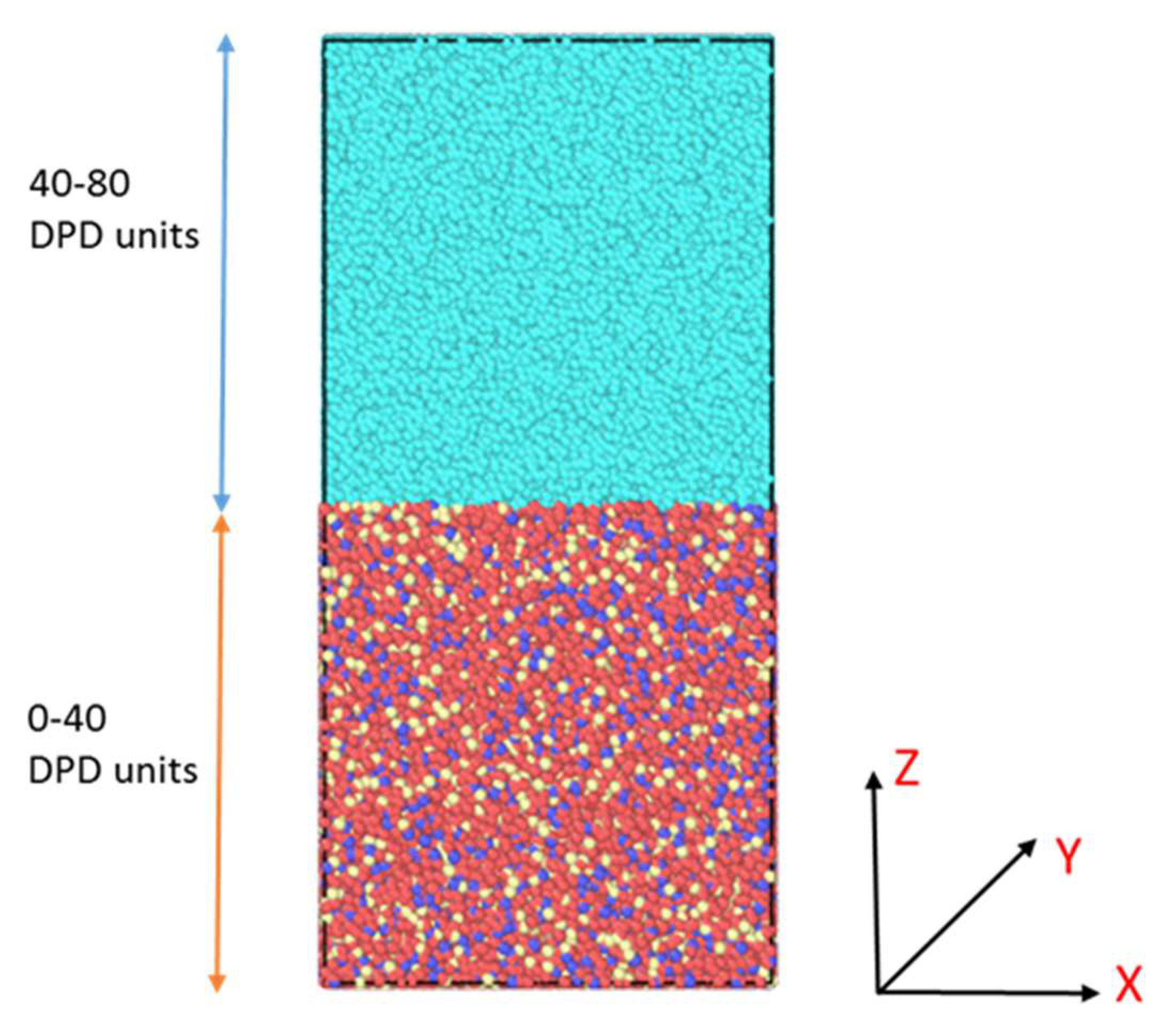
2.2. Simulation Model
2.3. Analysis Methods
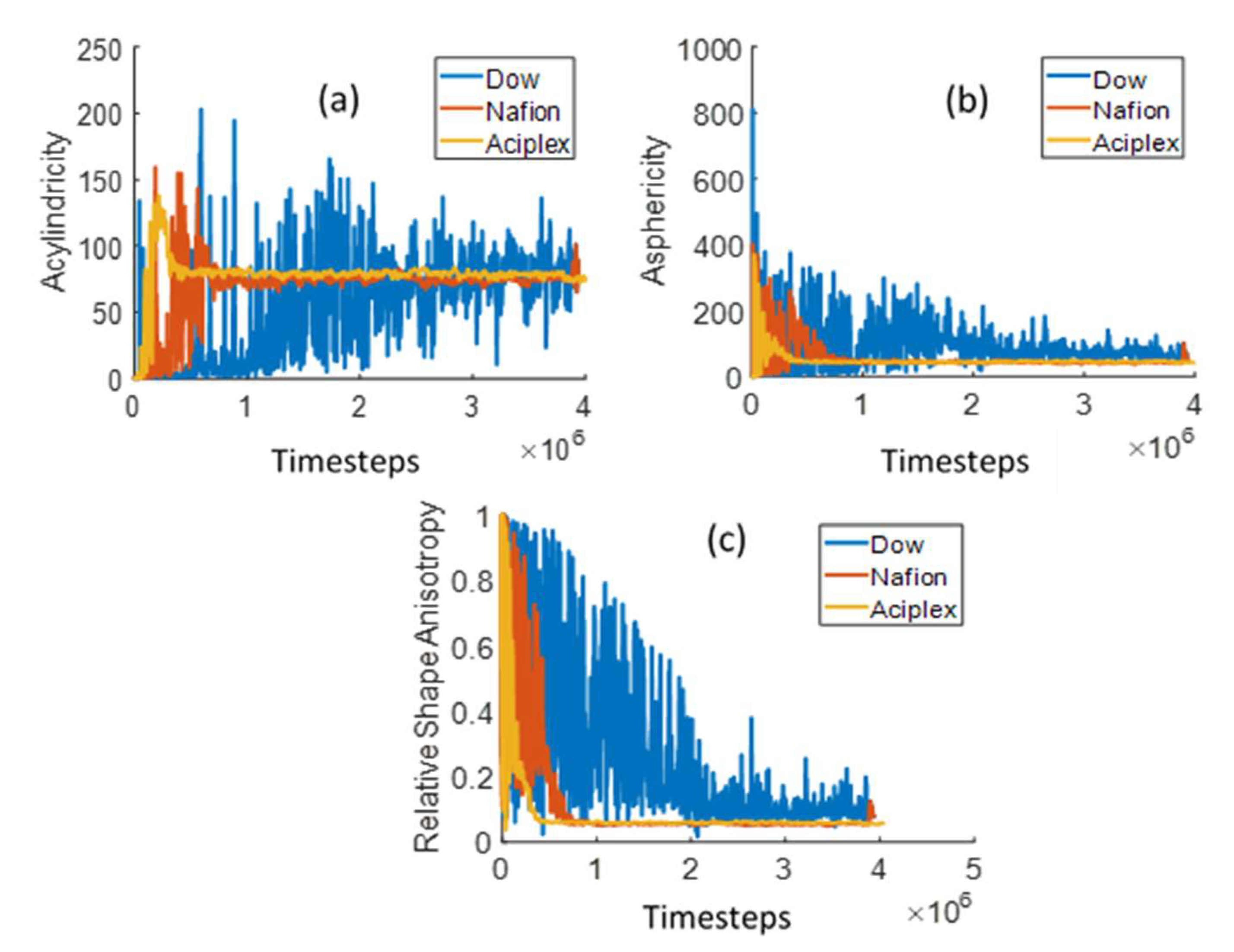
3. Results
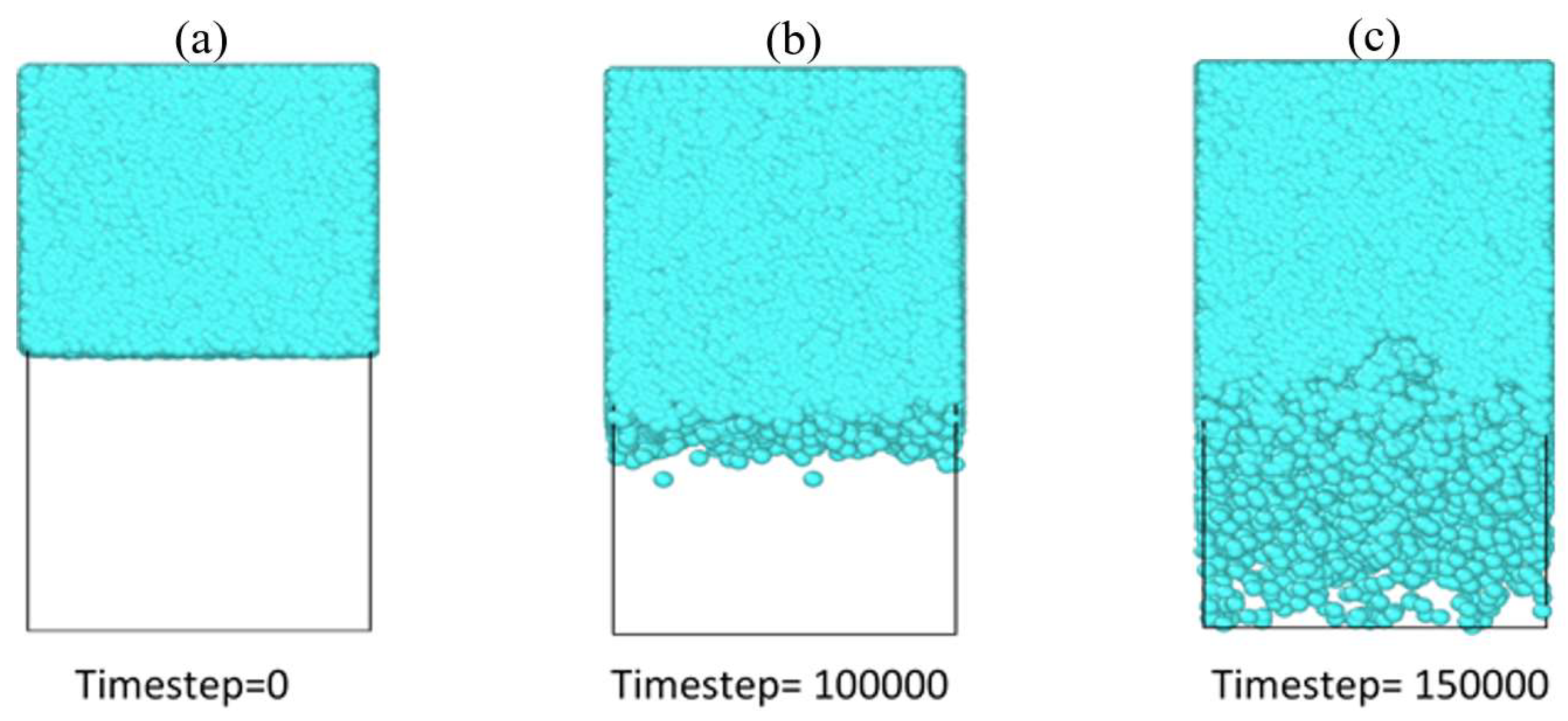
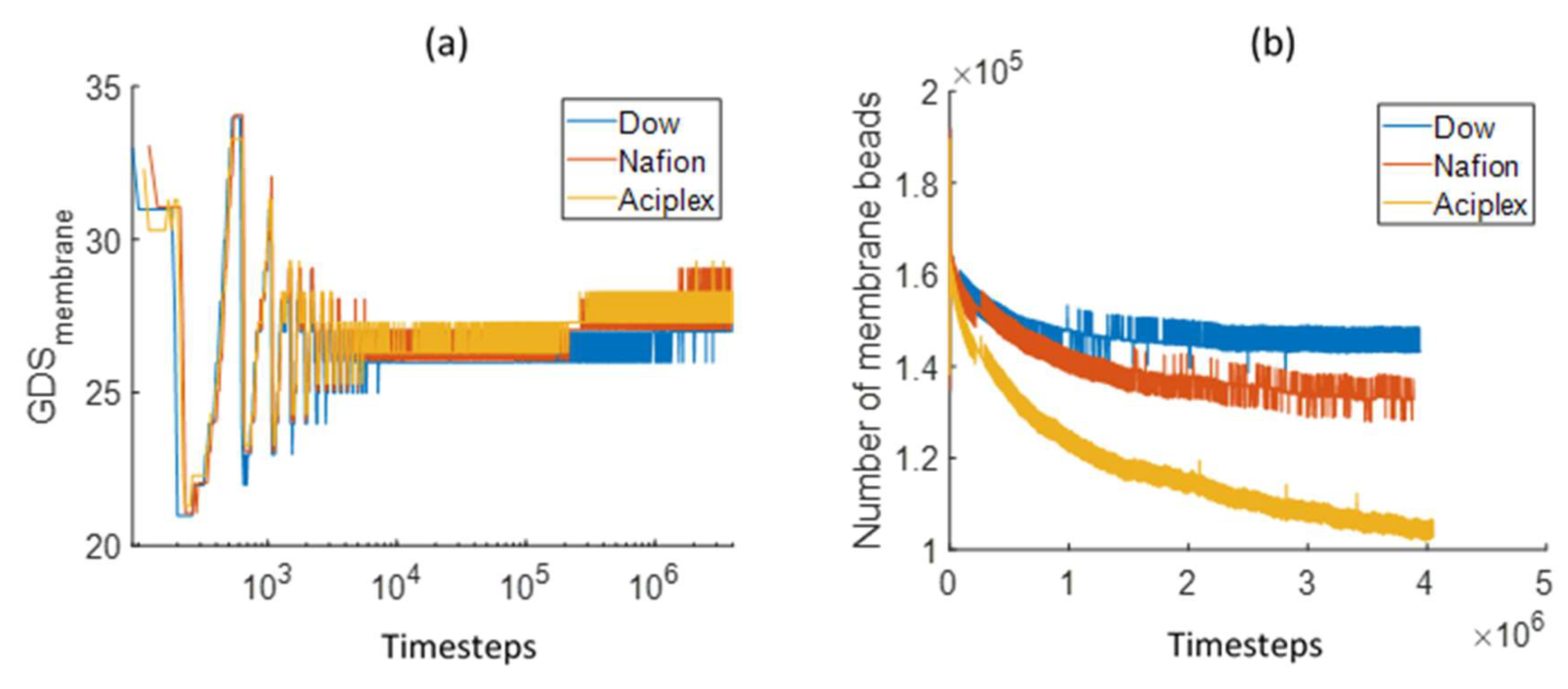
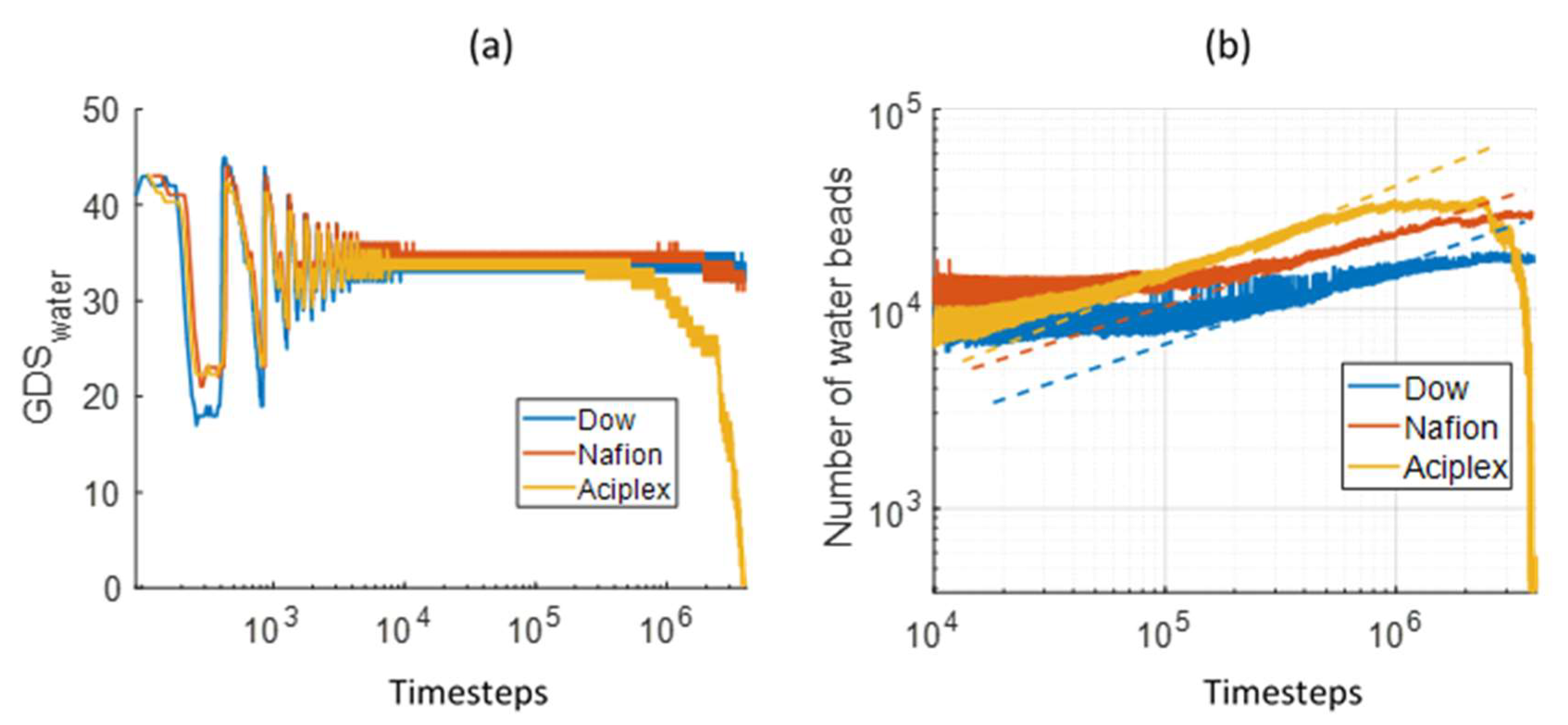
3.1. Interface Evolution
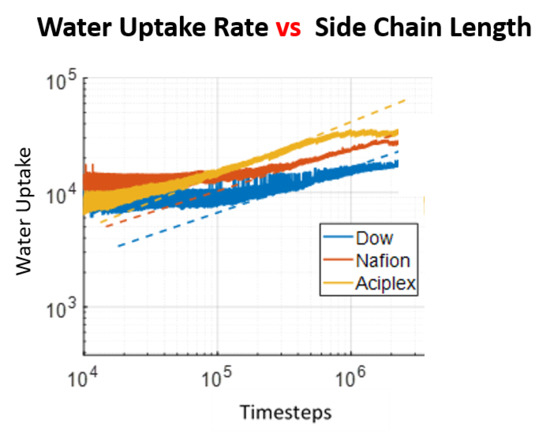
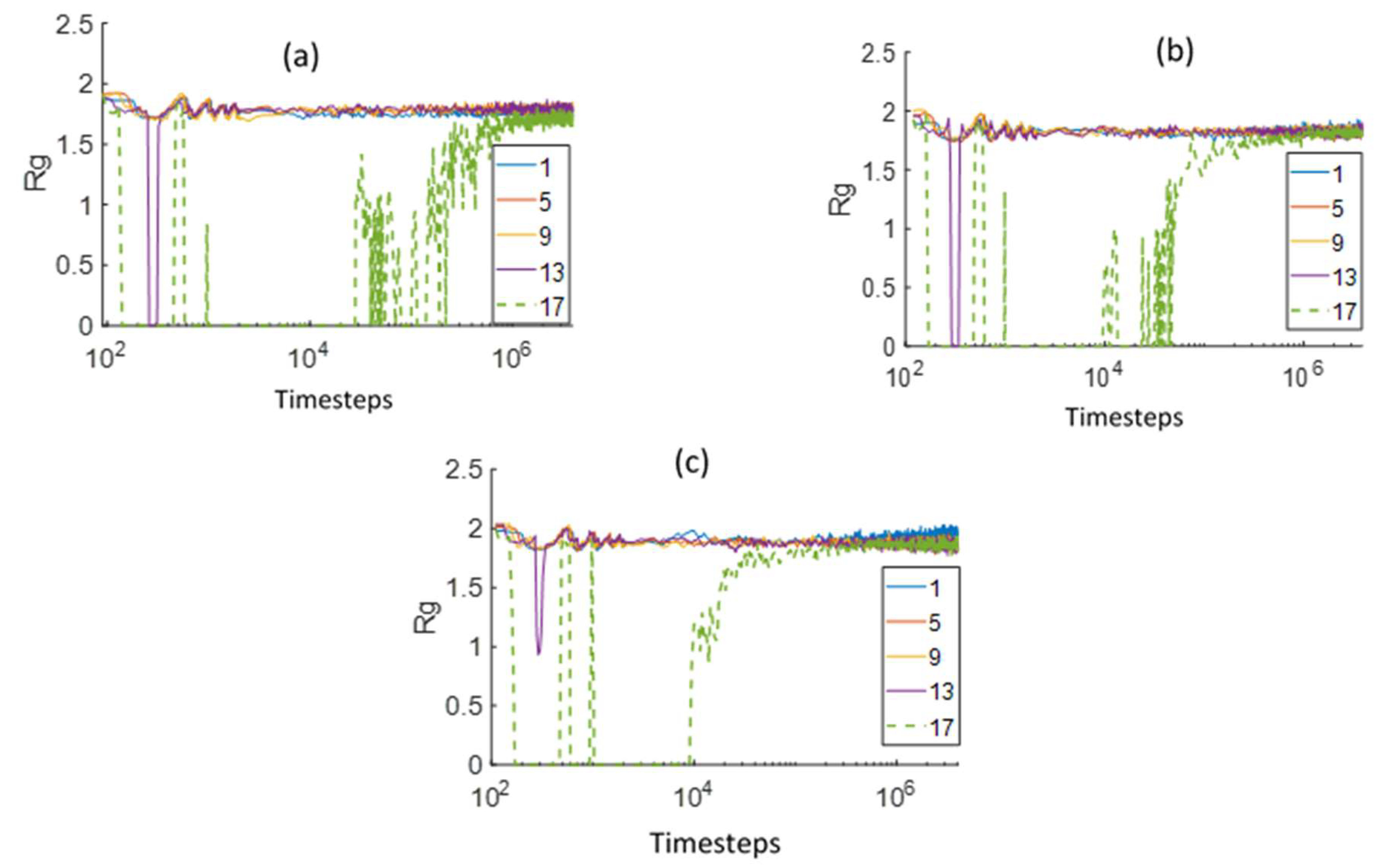
3.2. Chain Statistical Properties
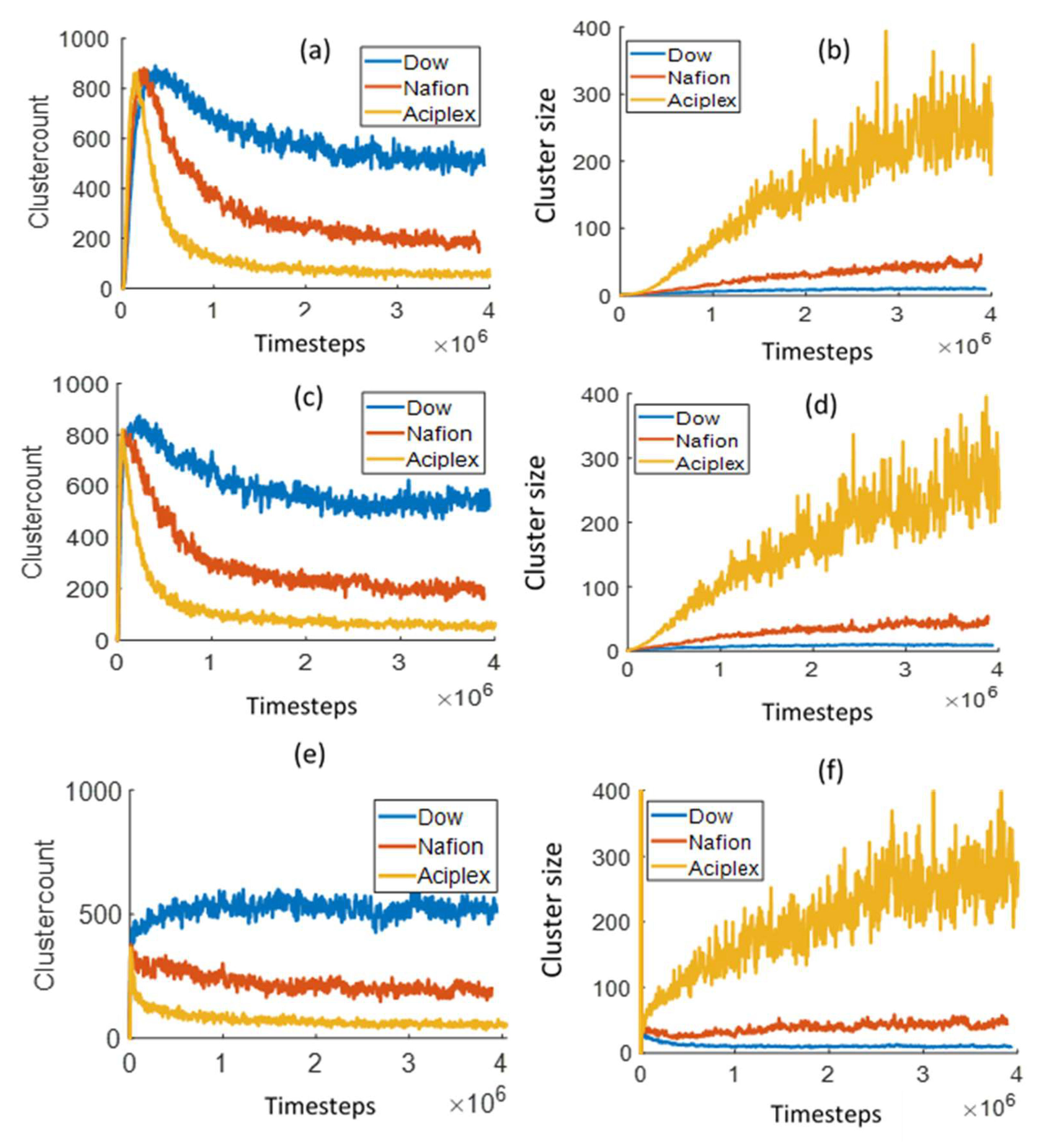
3.3. Water Cluster Formation Dynamics and Morphology
3.4. Water Diffusion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsu, W.Y.; Gierke, T.D. Ion transport and clustering in nafion perfluorinated membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 1983, 13, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierke, T.D.; Munn, G.E.; Wilson, F.C. Morphology in Nafion Perfluorinated Membrane Products, as Determined by Wide- and Small-Angle X-Ray Studies. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-2 Polym. Phys. 1981, 19, 1687–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceynowa, J. Electron microscopy investigation of ion exchange membranes. Polymer 1978, 19, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorenbos, G. Competition between side chain length and side chain distribution: Searching for optimal polymeric architectures for application in fuel cell membranes. J. Power Sources 2015, 276, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigma-Aldrich; Casciola, M. Perfluorosulfonic Acid Membranes for Fuel Cell and Electrolyser Applications; Sigma-Aldrich: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kusoglu, A.; Weber, A.Z. New Insights into Perfluorinated Sulfonic-Acid Ionomers. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 987–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allahyarov, E.; Taylor, P.L. Simulation study of the equilibrium morphology in ionomers with different architectures. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandell, D.; Karo, J.; Liivat, A.; Thomas, J.O. Molecular dynamics studies of the Nafion®, Dow® and Aciplex® fuel-cell polymer membrane systems. J. Mol. Model. 2007, 13, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunda, A.P.; Venkatnathan, A. Atomistic simulations of structure and dynamics of hydrated Aciplex polymer electrolyte membrane. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 10827–10836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko-Jereb, L.V.; Kelterer, A.M.; Berezina, N.P.; Pimenov, A.V. Conductometric and computational study of cationic polymer membranes in H+ and Na+-forms at various hydration levels. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 444, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko-Jereb, L.; Rynkowska, E.; Kujawski, W.; Lunghammer, S.; Kujawa, J.; Marais, S.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Chappey, C.; Kelterer, A.-M. Ab initio study of cationic polymeric membranes in water and methanol. Ionics (Kiel) 2016, 22, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Hyodo, S.A. A computer simulation study of the mesoscopic structure of the polyelectrolyte membrane Nafion. Polym. J. 2003, 35, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Paddison, S.J.; Elliott, J.A.; Hamrock, S.J. Mesoscale Modeling of Hydrated Morphologies of 3M Perfluorosulfonic Acid-Based Fuel Cell Electrolytes. Langmuir 2010, 26, 14308–14315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorenbos, G.; Morohoshi, K. Pore morphologies and diffusion within hydrated polyelectrolyte membranes: Homogeneous vs heterogeneous and random side chain attachment. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 064902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorenbos, G. Water diffusion within hydrated model grafted polymeric membranes with bimodal side chain length distributions. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 2794–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehr, F.; Liu, H.; Luo, X.; Bae, C.; Tuckerman, M.E.; Hickner, M.A.; Paddison, S.J. Mesoscale Simulations of Anion Exchange Membranes Based on Quaternary Ammonium Tethered Triblock Copolymers. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 4397–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhou, G.; Khalid, S.; Sun, X.; Sun, W.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, G. Dissipative particle dynamics and molecular dynamics simulations on mesoscale structure and proton conduction in a SPEEK/PVDF-g-PSSA membrane. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39676–39684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarov, P.V.; Veselov, I.N.; Chu, P.P.; Khalatur, P.G. Mesoscale simulation of polymer electrolyte membranes based on sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) and Nafion. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorenbos, G.; Suga, Y. Simulation of equivalent weight dependence of Nafion morphologies and predicted trends regarding water diffusion. J. Memb. Sci. 2009, 330, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawodzinski, T.A.; Gottesfeld, S.; Shoichet, S.; McCarthy, T.J. The contact angle between water and the surface of perfluorosulphonic acid membranes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1993, 23, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinan, D.T.; De Angelis, M.G.; Giacinti Baschetti, M.; Sarti, G.C.; Elabd, Y.A. Non-Fickian Diffusion of Water in Nafion. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 4667–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Smith, H.L.; Majewski, J.; Fujimoto, C.H.; Cornelius, C.J.; Perahia, D. Interfacial Effects on Water Penetration into Ultrathin Ionomer Films: An in Situ Study Using Neutron Reflectometry. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 5745–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, D.; Agrawal, A.; Perahia, D.; Grest, G.S. Structured Ionomer Thin Films at Water Interface: Molecular Dynamics Simulation Insight. Langmuir 2017, 33, 11070–11076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogerbrugge, P.J.; Koelman, J.M.V.A. Simulating Microscopic Hydrodynamic Phenomena with Dissipative Particle Dynamics. Europhys. Lett. 1992, 19, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelman, J.M.V.A.; Hoogerbrugge, P.J. Dynamic Simulations of Hard-Sphere Suspensions Under Steady Shear. Europhys. Lett. 1993, 21, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, R.D.; Warren, P.B. Dissipative particle dynamics: Bridging the gap between atomistic and mesoscopic simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 4423–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, R.D.; Rabone, K.L. Mesoscopic simulation of cell membrane damage, morphology change and rupture by nonionic surfactants. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Español, P.; Warren, P.B. Perspective: Dissipative particle dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.S.; Molinero, V.; Tahir, C.; Goddard, W.A., III. Nanophase-Segregation and Transport in Nafion 117 from Molecular Dynamics Simulations: Effect of Monomeric Sequence. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 3149–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanathan, R.; Venkatnathan, A.; Rousseau, R.; Dupuis, M.; Frigato, T.; Gu, W.; Helms, V. Atomistic simulation of water percolation and proton hopping in Nafion fuel cell membrane. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 13681–13690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Lyulin, A.V. Molecular Modeling of Structure and Dynamics of Nafion Protonation States. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 6882–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumma, S.; Talu, O. Gibbs Dividing Surface and Helium Adsorption. Adsorption 2003, 9, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukowski, A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO-the Open Visualization Tool. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 18, 015012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
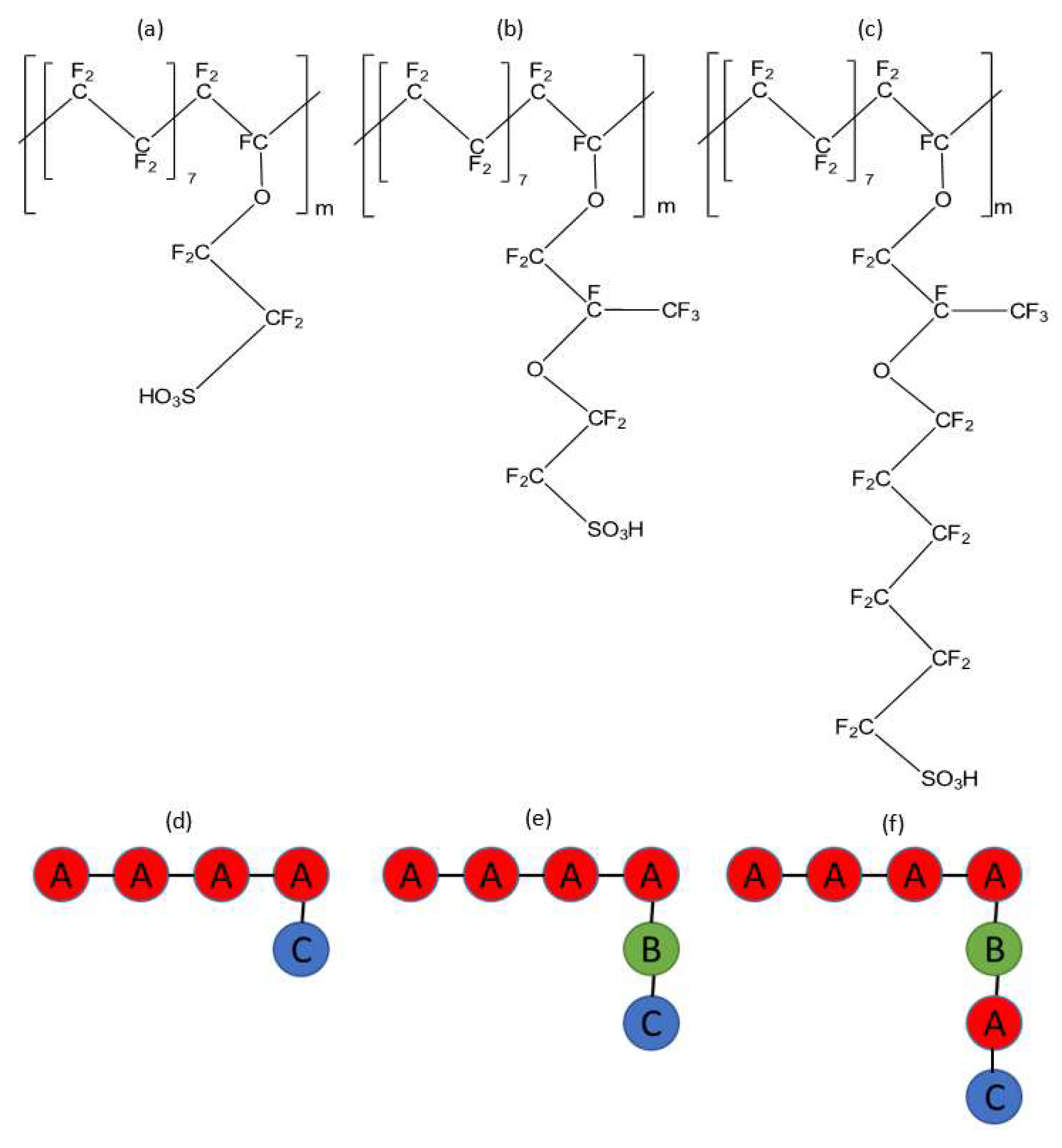



| Bead Pair | (Flory–Huggins Parameter) | (DPD Repulsion Parameter) |
|---|---|---|
| A–B | 0.022 | 104.1 |
| A–C | 3.11 | 114.2 |
| A–W | 5.79 | 122.9 |
| B–C | 1.37 | 108.5 |
| B–W | 4.90 | 120.0 |
| C–W | −2.79 | 94.9 |
| Analysis | Number and Location of Layers |
|---|---|
| Number density | 80 layers of 1 DPD unit thickness in the Z-direction |
| Chain radius of gyration (Rg) and side-chain order parameter (OP) | 20 layers of 2.25 DPD unit thickness starting from the bottom Z boundary |
| Cluster analysis | 3 layers of thickness of 10 DPD units starting at 5, 15, and 25 DPD units distance from the bottom Z boundary |
| Mean square displacement (MSD) | 4 layers of 8 DPD unit thickness starting from the bottom Z boundary |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sengupta, S.; Lyulin, A. Dissipative Particle Dynamics Modeling of Polyelectrolyte Membrane–Water Interfaces. Polymers 2020, 12, 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040907
Sengupta S, Lyulin A. Dissipative Particle Dynamics Modeling of Polyelectrolyte Membrane–Water Interfaces. Polymers. 2020; 12(4):907. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040907
Chicago/Turabian StyleSengupta, Soumyadipta, and Alexey Lyulin. 2020. "Dissipative Particle Dynamics Modeling of Polyelectrolyte Membrane–Water Interfaces" Polymers 12, no. 4: 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040907
APA StyleSengupta, S., & Lyulin, A. (2020). Dissipative Particle Dynamics Modeling of Polyelectrolyte Membrane–Water Interfaces. Polymers, 12(4), 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040907