Insights into Adsorption Characterization of Sulfated Xylans onto Poly(ethylene terephthalate)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Xylans
2.1.2. Poly(ethylene terephthalate)
2.2. Sulfation of Xylan Samples
2.3. FTIR Spectroscopy
2.4. Elemental Analysis
2.5. Polyelectrolyte Titrations
2.6. Determination of Activated Partial Thromboplastine Time (APTT)
2.7. Model PET Films Preparation by the Spin-Coating Technique
2.8. Adsorption Studies by Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM-D)
2.9. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.10. Wettability and Contact Angle Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Efficiency of the Sulfation Procedure
3.2. Adsorption Studies
3.2.1. Influence of pH
3.2.2. Influence of Ionic Strength
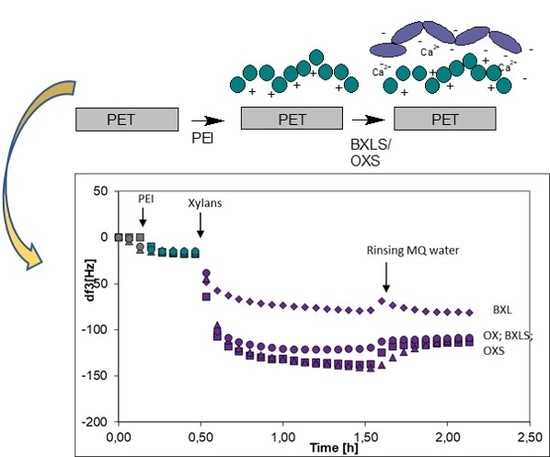
3.2.3. Influence of Anchoring Agents
3.3. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy XPS
3.4. Wettability and Contact Angle
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PET | Poly(ethylene terephthalate) |
| QCM-D | Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation |
| PEI | Polyethyleneimine |
| BXL | 4-O-methyl glucuronoxylan |
| OX | Arabinoxylan |
| BXLS | Sulfated glucuronoxylan |
| OXS | Sulfated arabinoxylan |
| SCA | Surface Contact Angles |
References
- Perez, H.A.; Allende, G.F.; Ajayi, E.I.O.; Porta, D.J.; García, N.H. Atherosclerosis plaque area reduction: Working hypothesis to prevent cardiovascular event. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 28, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashneh-Tala, S.; MacNeil, S.; Claeyssens, F. The Tissue-Engineered Vascular Graft-Past, Present, and Future. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2016, 22, 68–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshi, R.A.; Van Lith, R.; Jen, M.C.; Allen, J.B.; Lapidos, K.A.; Ameer, G. The blood and vascular cell compatibility of heparin-modified ePTFE vascular grafts. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bick, R.L.; Frenkel, E.P. Clinical aspects of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis and other side effects of heparin therapy. Clin. Appl. Thromb./Hemost. Off. J. Int. Acad. Clin. Appl. Thromb./Hemost. 1999, 5 (Suppl. 1), S7–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, S.K.; Shamloo, A. Bilayered heparinized vascular graft fabricated by combining electrospinning and freeze drying methods. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongchan, P.; Sajomsang, W.; Subyen, D.; Kongtawelert, P. Anticoagulant activity of a sulfated chitosan. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.C. Implantable Devices: An Overview. Med. Text. Biomater. Healthc. 2006, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gericke, M.; Doliška, A.; Stana, J.; Liebert, T.; Heinze, T.; Stana-Kleinschek, K. Semi-synthetic polysaccharide sulfates as anticoagulant coatings for PET, 1--cellulose sulfate. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasl, H.; Stana, J.; Stropnik, D.; Strnad, S.; Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Ribitsch, V. Improvement of the hemocompatibility of PET surfaces using different sulphated polysaccharides as coating materials. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tea, I.; Janne, L.; Leena-Sisko, J.; Karin, S.-K.; Simona, S.; Renate, D.; Volker, R. Adsorption of Fucoidan and Chitosan Sulfate on Chitosan Modified PET Films Monitored by QCM-D. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Du, Y.; Yang, J.; Fan, L. Influence of functional groups on the in vitro anticoagulant activity of chitosan sulfate. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.-H. Carbohydrate-based drug discovery in the battle against bacterial infections: New opportunities arising from programmable One-Pot Oligosaccharide synthesis. In Carbohydrate-Based Drug Discovery; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; Volume 2, p. 899. [Google Scholar]
- Kindness, G.; Long, W.F.; Williamson, F.B. Anticoagulant effects of sulphated polysaccharides in normal and antithrombin III-deficient plasmas. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1980, 69, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinichen-Herrero, J.C.; Carbonero, E.R.; Sassaki, G.L.; Gorin, P.A.J.; Iacomini, M. Anticoagulant and antithrombotic activities of a chemically sulfated galactoglucomannan obtained from the lichen Cladonia ibitipocae. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2005, 35, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daus, S.; Petzold-Welcke, K.; Kötteritzsch, M.; Baumgaertel, A.; Schubert, U.S.; Heinze, T. Homogeneous Sulfation of Xylan from Different Sources. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielii, I.; Gatenholm, P.; Glasser, W.G.; Jain, R.K.; Kenne, L. Separation, characterization and hydrogel-formation of hemicellulose from aspen wood. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 43, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.; Venditti, R.A.; Pawlak, J.J.; El-Tahlawy, K. Crosslinked hemicellulose citrate–chitosan aerogel foams. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, K.; Günther, W.; Kötteritzsch, M.; Heinze, T. Synthesis and characterization of methyl xylan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrin, P.; Katrin, S.; Wolfgang, G.; Thomas, H. Carboxymethyl Xylan—Control of Properties by Synthesis. Macromol. Symp. 2005, 232, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Ebringerová, A.; Hromádková, Z.; Heinze, T. Hemicellulose. In Polysaccharides; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, B.C. Hemicellulose bioconversion. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.K.; Jayapal, N.; Jayaram, C.; Roy, S.; Kolte, A.P.; Senani, S.; Sridhar, M. Xylooligosaccharides as prebiotics from agricultural by-products: Production and applications. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2015, 5, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, C.; Carmona, E.; Brienzo, M. Xylooligosaccharides production process from lignocellulosic biomass and bioactive effects. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2019, 18, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, Q.; Yan, Y.; Peng, F.; Sun, R.; Ren, J. Hemicellulose from Plant Biomass in Medical and Pharmaceutical Application: A Critical Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 2430–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chinga-Carrasco, G.; Cheng, F.; Xu, W.; Willför, S.; Syverud, K.; Xu, C. Hemicellulose-reinforced nanocellulose hydrogels for wound healing application. Cellulose 2016, 23, 3129–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold-Welcke, K.; Schwikal, K.; Daus, S.; Heinze, T. Xylan derivatives and their application potential—Mini-review of own results. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 100, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.E.; Silva, A.E.; Júnior, T.N.; Gomes, M.C.S.; Aguiar, L.M.; Marcelino, H.R.; Araújo, I.B.; Bayer, M.P.; Ricardo, N.M.P.S.; Oliveira, A.G.; et al. Xylan from corn cobs, a promising polymer for drug delivery: Production and characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5402–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimkovic, I.; Tracz, A.; Kelnar, I.; Uhliariková, I.; Mendichi, R. Quaternized and sulfated xylan derivative films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, A.; Heinze, T. Synthesis of pyridine-free xylan sulfates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebringerová, A.; Hromádková, Z. Xylans of industrial and biomedical importance. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 1999, 16, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, S.J.; Striker, L.J.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Jacot, T.A.; Striker, G.E. Pentosan polysulfate decreases proliferation and net extracellular matrix production in mouse mesangial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrušev, N.; Fras Zemljič, L.; Saake, B.; Strnad, S. Study of xylan adsorption onto poly(ethylene terephthalate) using QCM-D. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrichs, H.; Zschirnt, K. Untersuchungen über den enzymatischen Abbau von Holocellulosen in vitro. Investigations on the enzymatic degradation of holocelluloses in vitro. Holz als Roh und Werkstoff 1972, 30, 66. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saake, B.; Erasmy, N.; Kruse, T.; Schmekal, E.; Puls, J. Isolation and characterization of arabinoxylan from oat spelts. In Hemicelluloses: Science and Technology; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 864, pp. 52–65. [Google Scholar]
- Strnad, S.; Velkova, N.; Saake, B.; Doliška, A.; Bračič, M.; Zemljič, L.F. Influence of sulfated arabino- and glucuronoxylans charging-behavior regarding antithrombotic properties. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indest, T.; Laine, J.; Ribitsch, V.; Johansson, L.-S.; Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Strnad, S. Adsorption of chitosan on PET films monitored by quartz crystal microbalance. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doliška, A.; Strnad, S.; Stana, J.; Martinelli, E.; Ribitsch, V.; Stana-Kleinschek, K. In Vitro Haemocompatibility Evaluation of PET Surfaces Using the Quartz Crystal Microbalance Technique. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 697–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, T.; Spirk, S.; Kargl, R.; Doliška, A.; Ehmann, H.M.A.; Köstler, S.; Ribitsch, V.; Stana-Kleinschek, K. Watching cellulose grow—Kinetic investigations on cellulose thin film formation at the gas–solid interface using a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D). Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 400, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indest, T.; Jevšek, M.; Košir, G.; Stana, J.; Stropnik, D.; Strnad, S. Introducing and optimization of the in-vitro method for determining the hemocompatibility of modified poly(ethylene)terephthalate surfaces. Acta Med. Biotech. 2009, 2, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kačuráková, M.; Wellner, N.; Ebringerová, A.; Hromádková, Z.; Wilson, R.H.; Belton, P.S. Characterisation of xylan-type polysaccharides and associated cell wall components by FT-IR and FT-Raman spectroscopies. Food Hydrocoll. 1999, 13, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kačuráková, M.; Wilson, R.H. Developments in mid-infrared FT-IR spectroscopy of selected carbohydrates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 44, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Lin, K.; Zhao, Y.P. Kerogen Pyrolysis: The Constructions and Pyrolysis of 3D Kerogen Macromolecular Models: Experiments and Simulations (Global Challenges 5/2019). Glob. Chall. 2019, 3, 1970051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, P.; Marquis, M.; Barron, C.; Guillon, F.; Saulnier, L. FT-IR investigation of cell wall polysaccharides from cereal grains. Arabinoxylan infrared assignment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7014–7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doliška, A.; Willför, S.; Strnad, S.; Ribitsch, V.; Kleinschek, K.S.; Eklund, P.; Xu, C. Antithrombotic properties of sulfated wood-derived galactoglucomannans. Holzforschung Int. J. Biol. Chem. Phys. Technol. Wood 2012, 66, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidija, F.; Janne, L.; Per, S.; Karin, S.-K.; Volker, R.; Valter, D. Determination of dissociable groups in natural and regenerated cellulose fibers by different titration methods. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 3186. [Google Scholar]
- Fras Zemljič, L.; Dimitrušev, N.; Saake, B.; Strnad, S. Functionalisation of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) surfaces with two cationised xylans by means of two anchoring polymers. Holzforschung Int. J. Biol. Chem. Phys. Technol. Wood 2019, 73, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Cheng, C. Which is the most efficient candidate for the recovery of confined methane: Water, carbon dioxide or nitrogen? Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2016, 9, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowski, S.; Grządka, E.; Patkowski, J. Influence of a Type of Electrolyte and its Ionic Strength on the Adsorption and the Structure of Adsorbed Polymer Layer in the System: Polyacrylic Acid/SiO2. Croat. Chem. Acta 2009, 82, 623–631. [Google Scholar]
- Doliška, A.; Strnad, S.; Ribitsch, V. Improving the Biocompatibility of PET Surfaces by Adsorbing Mannans and Mannan Derivatives. Ph.D. Thesis, Naturwissenschaftlichen Fakultät der Karl-Franzens-Universität, Graz, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Doliška, A.; Strnad, S.; Stana-Kleinschek, K. Heparin adsorption onto model poly(ethylene terephtalate) (PET) surfaces monitored by QCM-D; Spremljanje adsorpcije heparina na modelne polietilentereftalatne (PET) površine s pomočjo kremenove mikrotehtnice. Mater. Tehnol. 2012, 46, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg, K.; Jönsson, B.; Kronberg, B.; Lindman, B. Surfactants and Polymers in Aqueous Solution; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ristić, T.; Lasič, S.; Kosalec, I.; Bračič, M.; Fras-Zemljič, L. The effect of chitosan nanoparticles onto Lactobacillus cells. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 97, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Román, J.; Buján, J.; Bellón, J.M.; Gallardo, A.; Escudero, M.C.; Jorge, E.; de Haro, J.; Alvarez, L.; Castillo-Olivares, J.L. Experimental study of the antithrombogenic behavior of Dacron vascular grafts coated with hydrophilic acrylic copolymers bearing salicylic acid residues. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 32, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipehia, R.; Liszkowski, M.; Lu, A. In Vivo evaluation of ammonia plasma modified ePTFE grafts for small diameter blood vessels replacement. A preliminary report. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2001, 42, 537–542. [Google Scholar]
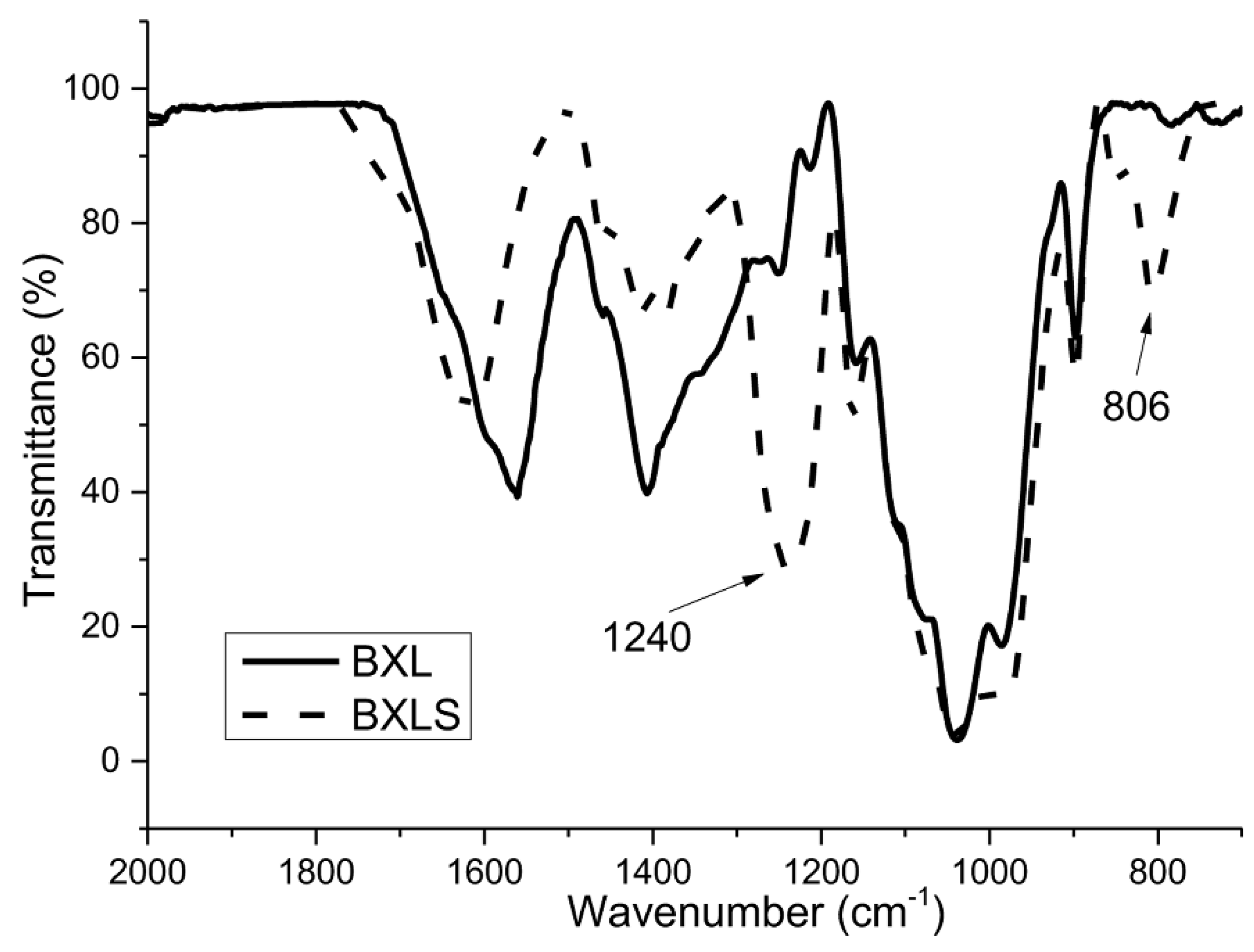

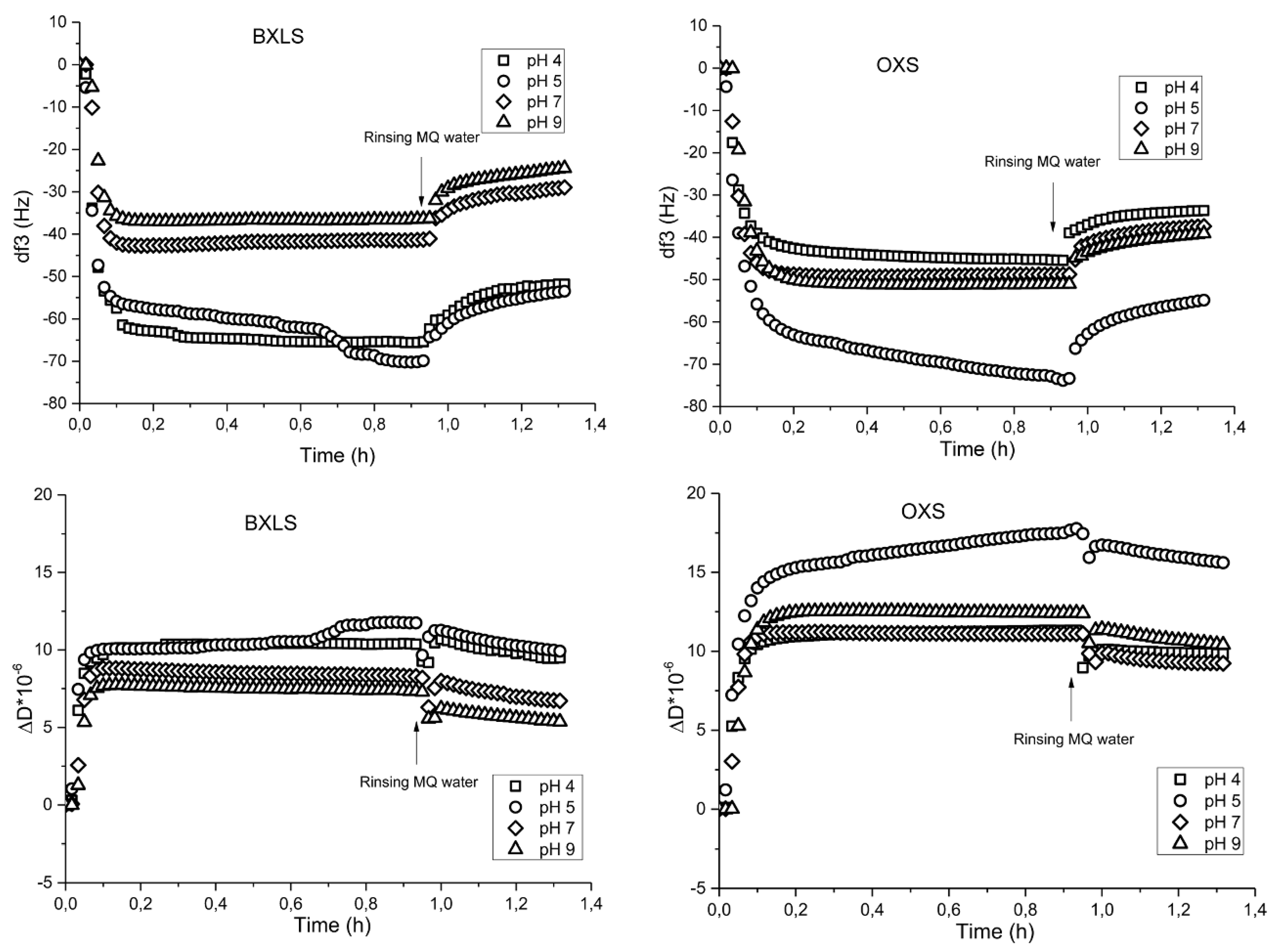
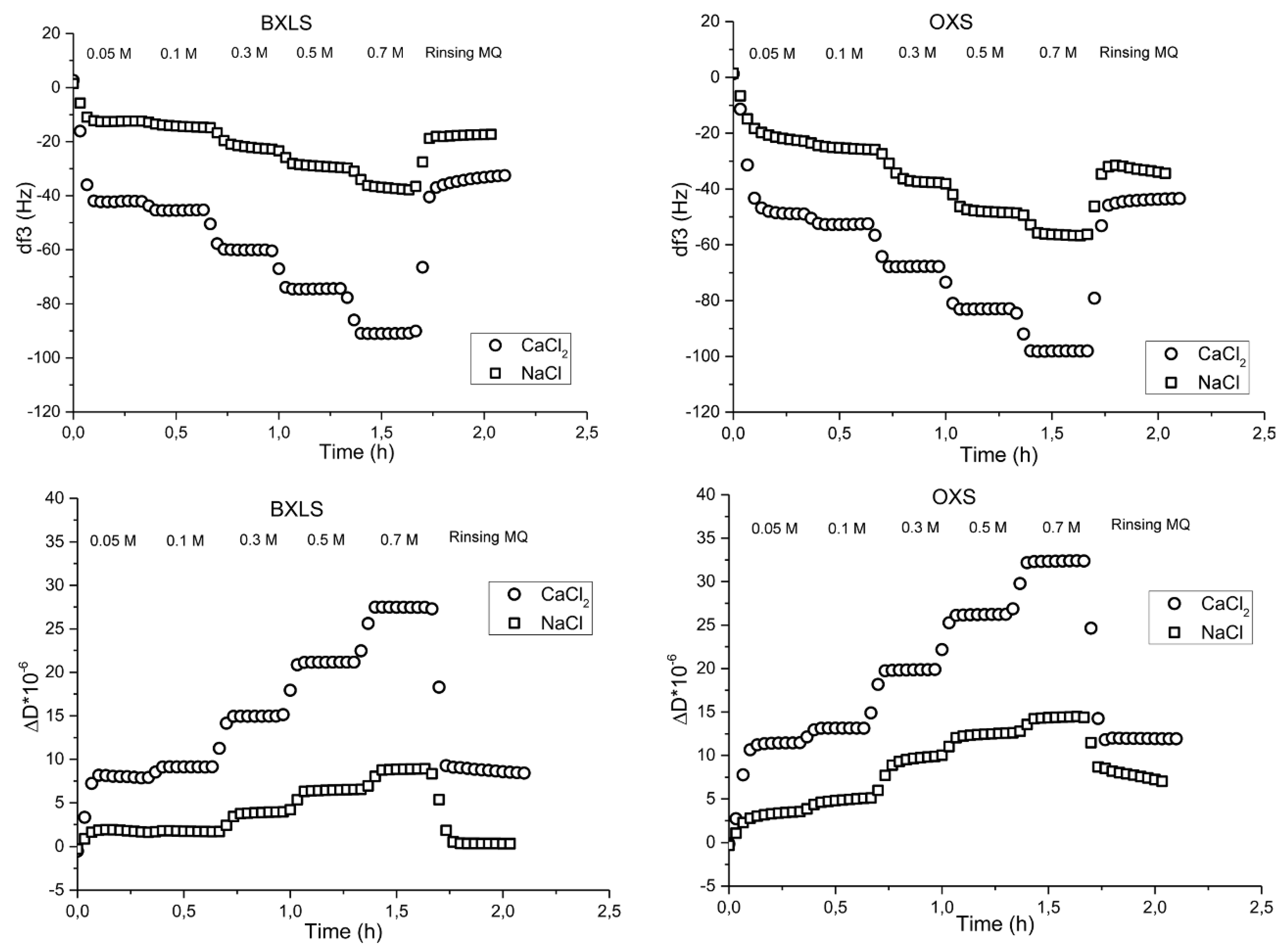
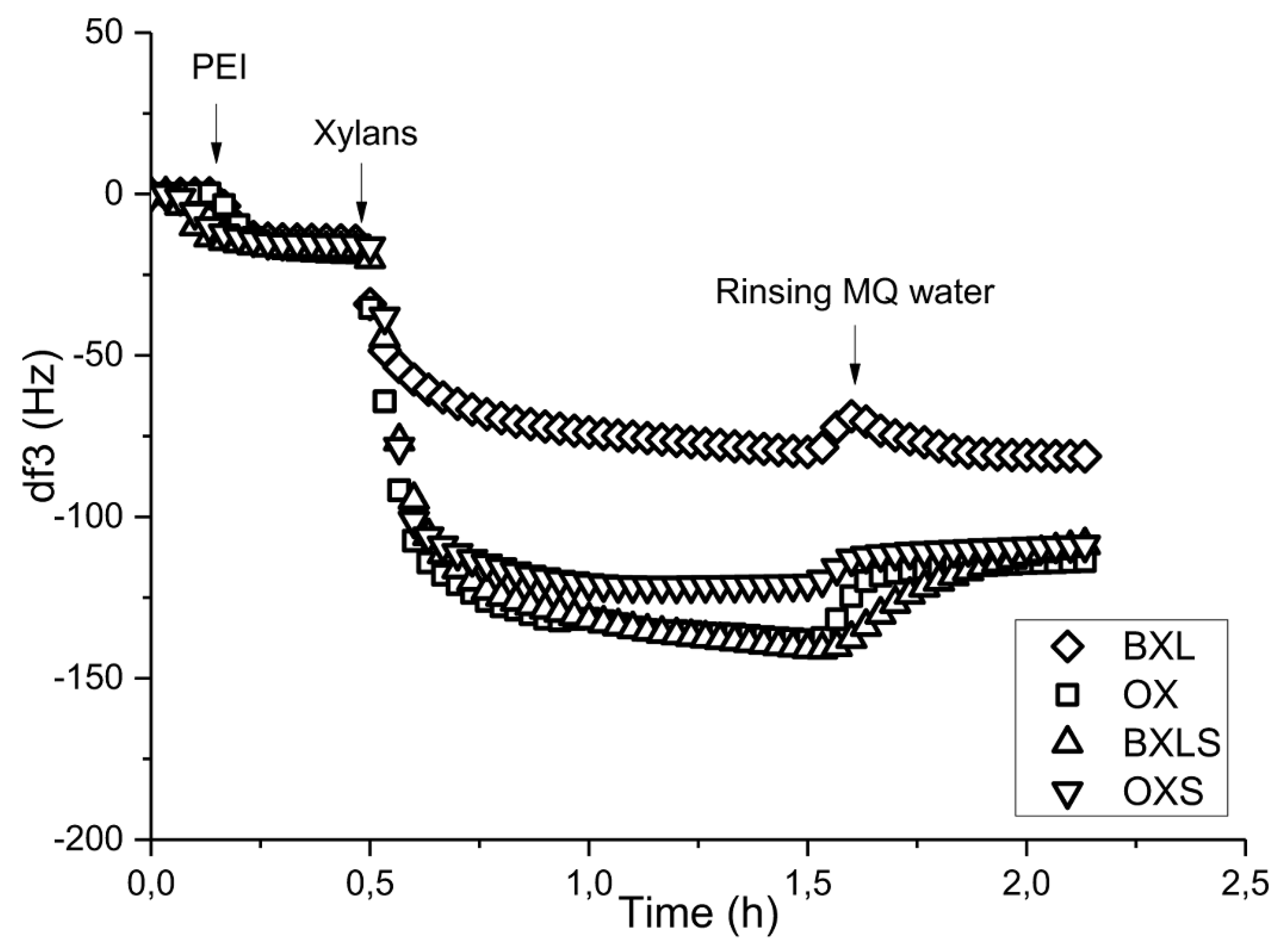

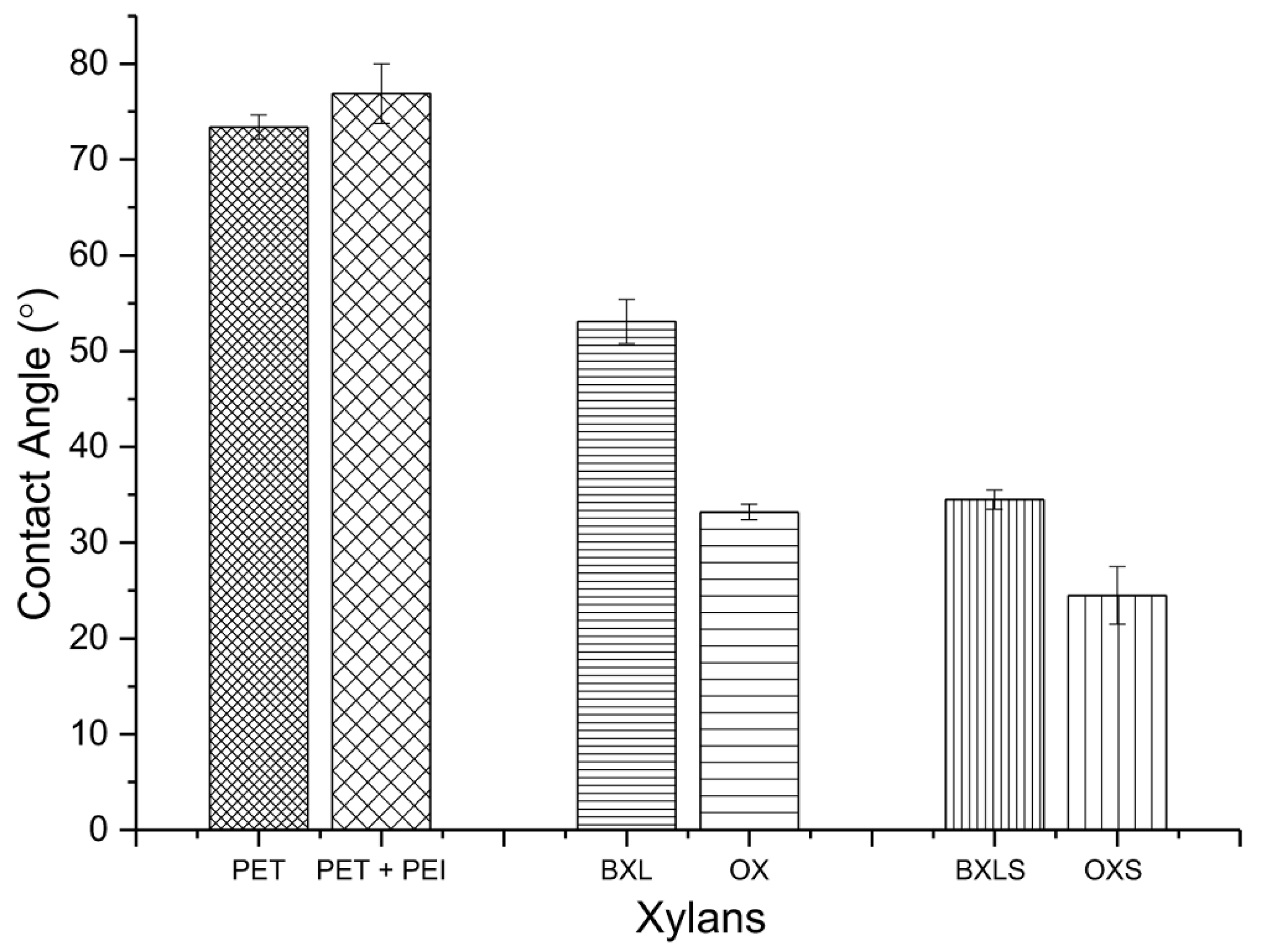
| Xylan Sample | Amounts of Deprotonated Functional Groups [mmol/g] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| pH8 | pH4 | pH2 | |
| BXLS | 3.11 ± 0.52 | 2.16 ± 0.00 | 1.65 ± 0.0 |
| OXS | 2.43 ± 0.07 | 2.11 ± 0.00 | 1.39 ± 0.0 |
| Xylan Sample conc. (mg/L) | APTT (s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BX | OX | BXLS | OXS | |
| 0 | 34.8 | 35.2 | 34.8 | 35.2 |
| 5 | 34.8 | 35.2 | 51.4 | 52.1 |
| 10 | 34.8 | 35.2 | 64.3 | 57.8 |
| 15 | 34.8 | 35.2 | 98.2 | 82 |
| 20 | 34.8 | 35.2 | 115.9 | 113.3 |
| Xylan Sample | C | N | O | S | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | 74.1 | 25.9 | |||
| PET-PEI | 71.7 | 6.6 | 19.7 | 0.6 | 0.9 |
| PET-PEI-BXL | 67.1 | 5.4 | 26.5 | ||
| PET-PEI-OX | 63.4 | 4.6 | 31.4 | 0.7 | |
| PET-PEI-BXLS | 58.1 | 8.3 | 30.4 | 2.5 | |
| PET-PEI-OXS | 56.2 | 8.8 | 30.6 | 3.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fras Zemljič, L.; Dimitrušev, N.; Zaplotnik, R.; Strnad, S. Insights into Adsorption Characterization of Sulfated Xylans onto Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polymers 2020, 12, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040825
Fras Zemljič L, Dimitrušev N, Zaplotnik R, Strnad S. Insights into Adsorption Characterization of Sulfated Xylans onto Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polymers. 2020; 12(4):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040825
Chicago/Turabian StyleFras Zemljič, Lidija, Nena Dimitrušev, Rok Zaplotnik, and Simona Strnad. 2020. "Insights into Adsorption Characterization of Sulfated Xylans onto Poly(ethylene terephthalate)" Polymers 12, no. 4: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040825
APA StyleFras Zemljič, L., Dimitrušev, N., Zaplotnik, R., & Strnad, S. (2020). Insights into Adsorption Characterization of Sulfated Xylans onto Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polymers, 12(4), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040825