Functional Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Spatially Programmable Adhesion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
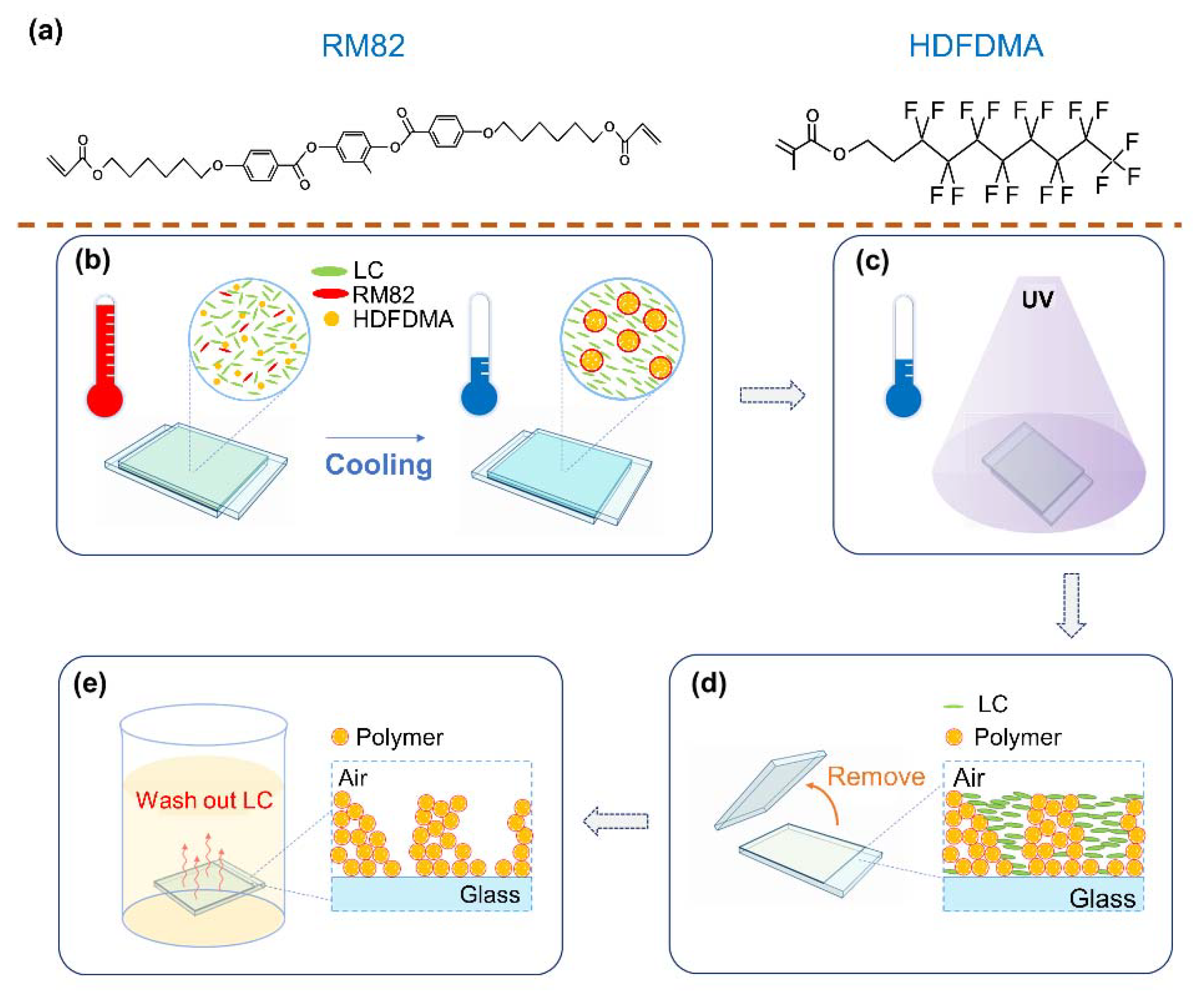
2.1. Sample Fabrication
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
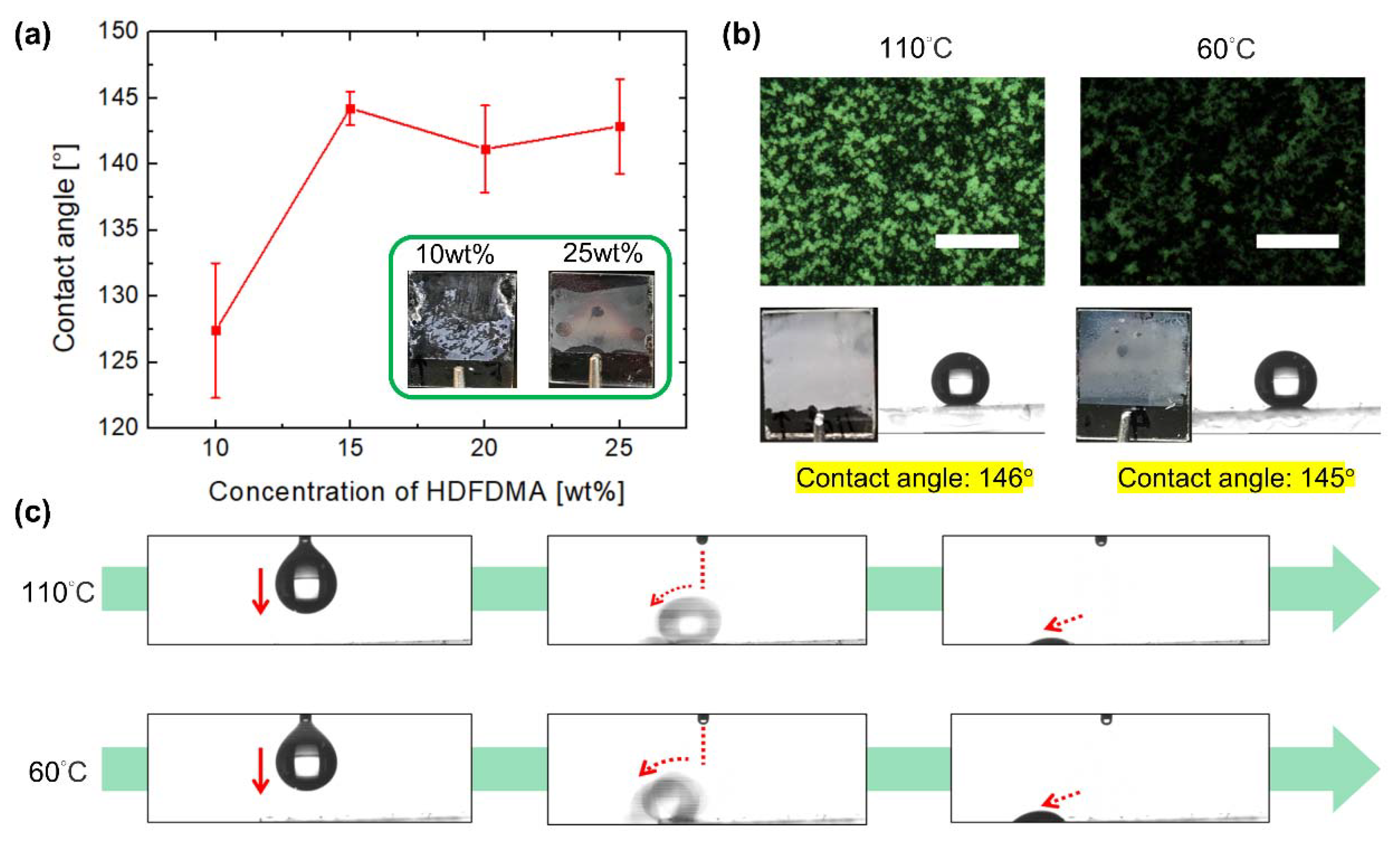
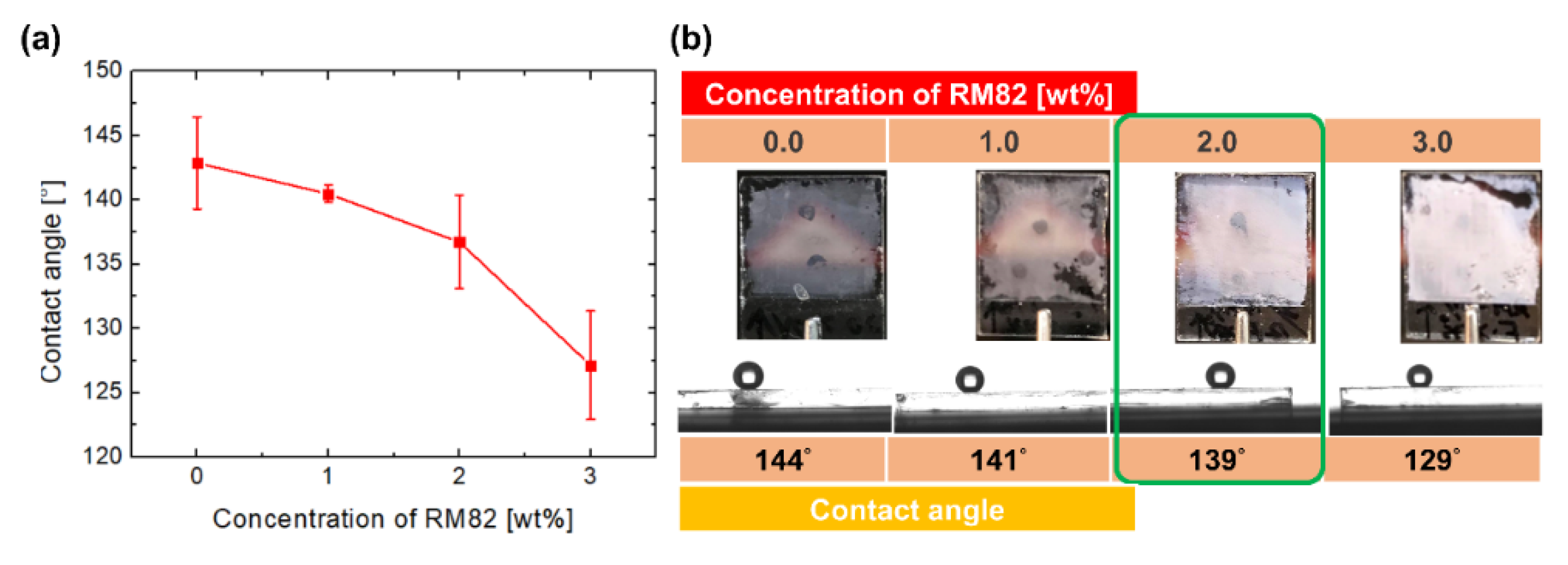
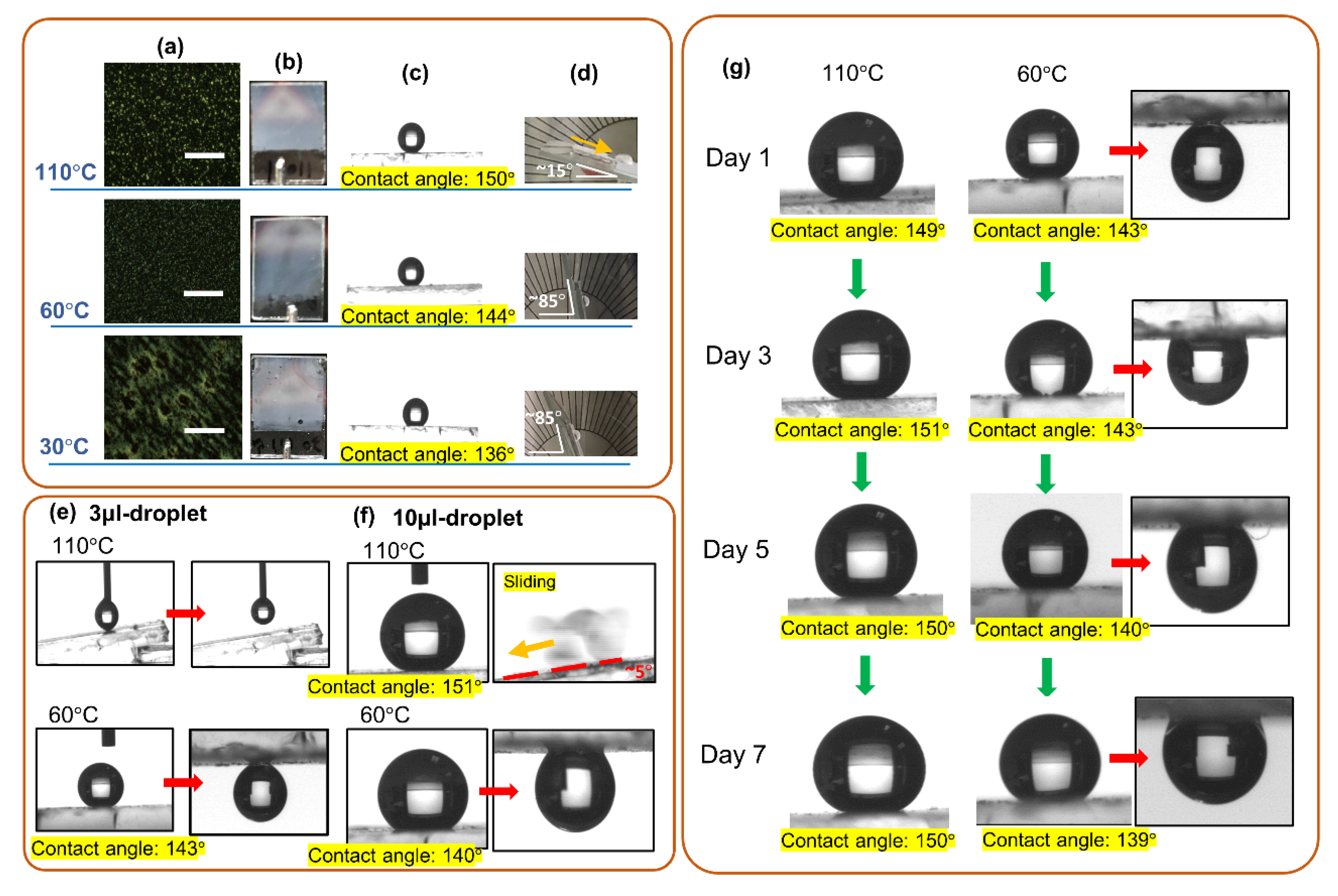
3.1. Investigation of Polymer Constituents
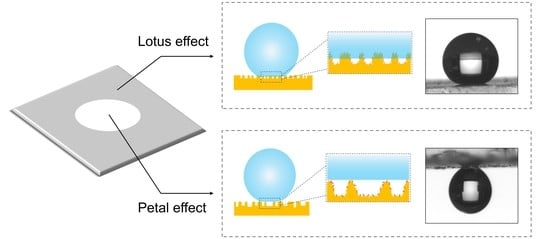
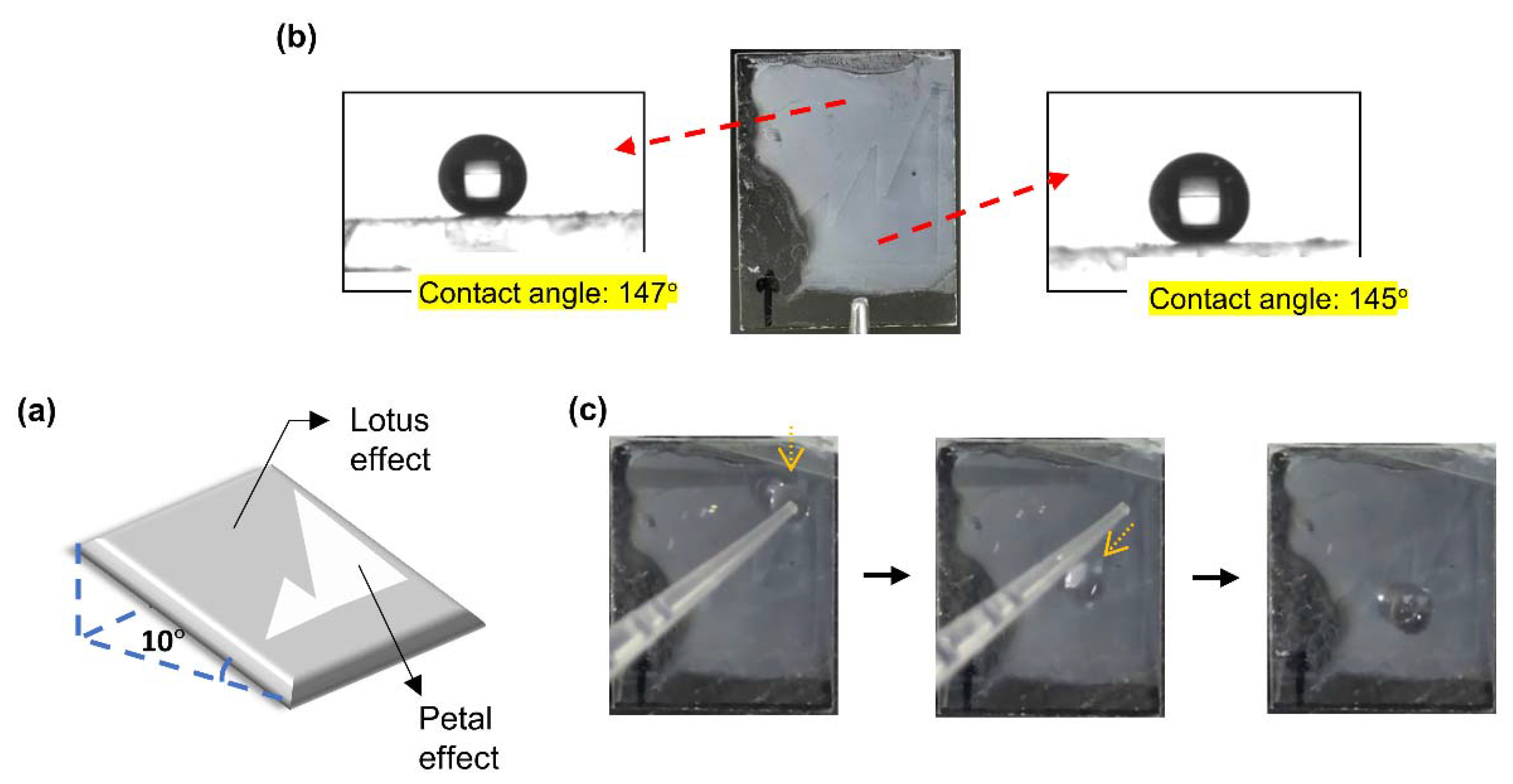
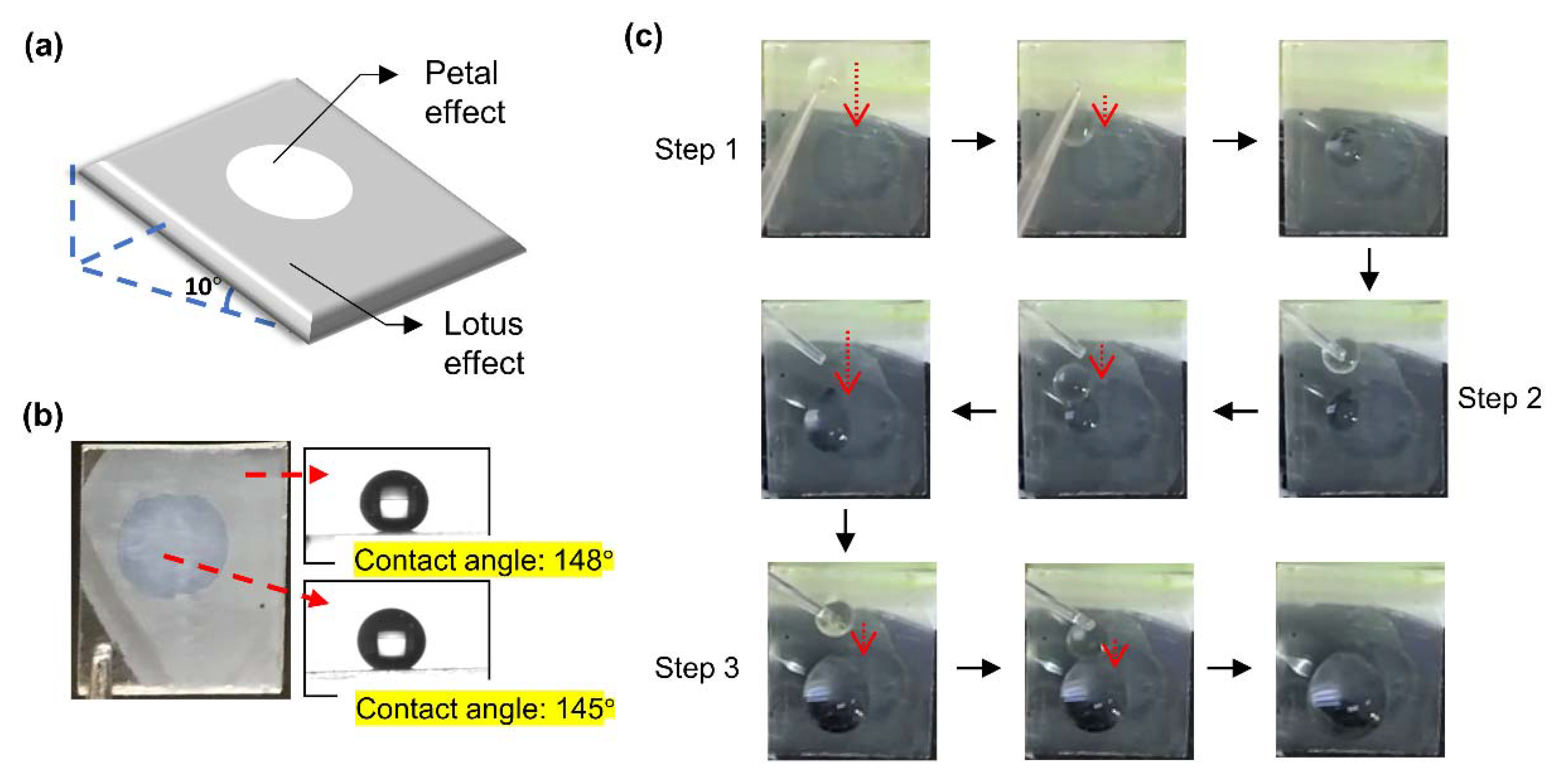
3.2. Lotus or Petal Effect of the Surface
3.3. Demonstration
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, S.-P.; Ma, Y.; Lou, Q.; Zhu, H.; Yang, B.; Fang, Q. Three-Dimensional Cell Culture and Drug Testing in a Microfluidic Sidewall-Attached Droplet Array. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10153–10157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iino, R.; Matsumoto, Y.; Nishino, K.; Yamaguchi, A.; Noji, H. Design of a Large-Scale Femtoliter Droplet Array for Single-Cell Analysis of Drug-Tolerant and Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, D.H.; Jung, H.-S.; Kim, K.; Kim, J. Mussel-Inspired Universal Bioconjugation of Polydiacetylene Liposome for Droplet-Array Biosensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 42210–42216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.-W.; Xu, B.-Y.; Ye, W.-k.; Xia, X.-H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Xu, J.-J. Versatile Microfluidic Droplets Array for Bioanalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Huang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Qu, L.; Lu, Y. Hybrid Superhydrophilic—Superhydrophobic Micro/Nanostructures Fabricated by Femtosecond Laser-Induced Forward Transfer for Sub-Femtomolar Raman Detection. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Xie, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Du, K.; Lu, Y. Low-Adhesive Superhydrophobic Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Substrate Fabricated by Femtosecond Laser Ablation for Ultratrace Molecular Detection. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Tiwari, M.K.; Doan, N.V.; Poulikakos, D. Mechanism of Supercooled Droplet Freezing on Surfaces. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreder, M.J.; Alvarenga, J.; Kim, P.; Aizenberg, J. Design of Anti-Icing Surfaces: Smooth, Textured or Slippery? Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Super-Antiwetting Interfaces with Special Liquid—Solid Adhesion. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jiang, L. Switchable Adhesion on Liquid/Solid Interfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 3753–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, N.; Xia, F.; Jiang, L. Petal Effect: A Superhydrophobic State with High Adhesive force. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4114–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, B.; Nosonovsky, M. The Rose Petal Effect and the Modes of Superhydrophobicity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 4713–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, B.; Nosonovsky, M.; Jung, Y.C. Lotus Effect: Roughness-Induced Superhydrophobic Surfaces. In Nanotribology and Nanomechanics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 19, pp. 995–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto, S.; Bhushan, B. Bioinspired Self-Cleaning Surfaces with Superhydrophobicity, Superoleophobicity, and Superhydrophilicity. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Feng, S.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y. Lotus Effect in Wetting and Self-Cleaning. Biotribology 2016, 5, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nun, E.; Oles, M. Self-Cleaning Lotus Effect Surfaces Having Antimicrobial Properties. U.S. Patent Application No.US 2003/0147932 A1, 7 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.J.; Zhao, D.; Chen, Y.; Chang, J.; Chung, T.-S. Rheologically Controlled Design of Nature-Inspired Superhydrophobic and Self-Cleaning Membranes for Clean Water Production. NPJ Clean Water 2020, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latthe, S.S.; Sutar, R.S.; Kodag, V.S.; Bhosale, A.; Kumar, A.M.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Xing, R.; Liu, S. Self–Cleaning Superhydrophobic Coatings: Potential Industrial Applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 128, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truesdell, R.; Mammoli, A.; Vorobieff, P.; van Swol, F.; Brinker, C.J. Drag Reduction on a Patterned Superhydrophobic Surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 044504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniello, R.J.; Waterhouse, N.E.; Rothstein, J.P. Drag reduction in turbulent flows over superhydrophobic surfaces. Physics of Fluids 2009, 21, 085103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z. Superhydrophobic Surfaces Created by a One-Step Solution-Immersion Process and Their Drag-Reduction Effect on Water. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 18909–18914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Xiang, B.; Fan, Y.; Guo, C.F.; Ruan, S. Laser Direct Writing of Tree-Shaped Hierarchical Cones on a Superhydrophobic Film for High-Efficiency Water Collection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 29248–29254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Tang, X.; Qiu, Z.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, H.; Liang, D.; Li, J. Cellulose-Based Superhydrophobic Surface Decorated with Functional Groups Showing Distinct Wetting Abilities to Manipulate Water Harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 40968–40978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkleman, A.; Gotesman, G.; Yoffe, A.; Naaman, R. Immobilizing a Drop of Water: Fabricating Highly Hydrophobic Surfaces That Pin Water Droplets. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned Paper as a Platform for Inexpensive, Low-Volume, Portable Bioassays. Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 1340–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, B.; Berry, A.D.; Hess, D.W.; Breedveld, V. Patterning of Superhydrophobic Paper to Control the Mobility of Micro-Liter Drops for Two-Dimensional Lab-on-Paper Applications. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3066–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Adhesion Behaviors on Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3900–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Wang, Y.; Lv, T.; Li, L.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, Y. Bio-Inspired Design of Hierarchical PDMS Microstructures with Tunable Adhesive Superhydrophobicity. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6151–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Mao, M.; Qiu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, B. Biomimetic Superhydrophobic Engineering Metal Surface with Hierarchical Structure and Tunable Adhesion: Design of Microscale Pattern. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Hou, Y.; Yu, M.; Fu, S. Mimicking from Rose Petal to Lotus Leaf: Biomimetic Multiscale Hierarchical Particles with Tunable Water Adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 7431–7440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teisala, H.; Tuominen, M.; Aromaa, M.; Stepien, M.; Mäkelä, J.M.; Saarinen, J.J.; Toivakka, M.; Kuusipalo, J. Nanostructures Increase Water Droplet Adhesion on Hierarchically Rough Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Langmuir 2012, 28, 3138–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosonovsky, M. Model for Solid-Liquid and Solid-Solid Friction of Rough Surfaces with Adhesion Hysteresis. The J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 224701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Hess, D.W.; Wong, C. Relationship between Work of Adhesion and Contact Angle Hysteresis on Superhydrophobic Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 11403–11407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuma, A.; Quéré, D. Superhydrophobic States. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Wang, H.; He, J. Superhydrophobic Titania Membranes of Different Adhesive Forces Fabricated by Electrospinning. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 14220–14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Qing, X.; Wang, F.; Deng, D.; Wei, J.; Yu, Y. Directed Pinning of Moving Water Droplets on Photoresponsive Liquid Crystal Mats. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qin, L.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Yu, Y. Manipulating Small Water Droplets on a Photo-Switchable Mat of Fluorinated Linear Liquid Crystal Polymers. Giant 2020, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, B.; Breedveld, V.; Hess, D.W. Fabrication of “Roll-Off” and “Sticky” Superhydrophobic Cellulose Surfaces via Plasma Processing. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4785–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, T.-J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, M.-S.; Yoon, S.M.; Kim, S.J.; Oh, K.H.; Nahm, S.; Moon, M.-W. Single-Step Plasma-Induced Hierarchical Structures for Tunable Water Adhesion. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Du, M.; Lai, H.; Zhang, N.; Sun, K. From Petal Effect to Lotus Effect: A Facile Solution Immersion Process for the Fabrication of Super-Hydrophobic Surfaces with Controlled Adhesion. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2776–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic CuO Surfaces with Tunable Water Adhesion. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 4726–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Du, G.; Si, J.; Yun, F.; Hou, X. Femtosecond Laser Weaving Superhydrophobic Patterned PDMS Surfaces with Tunable Adhesion. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 24907–24912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Fan, P.; Gong, D.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Zhong, M. Superhydrophobic Surfaces Fabricated by Femtosecond Laser with Tunable Water Adhesion: From Lotus Leaf to Rose Petal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9858–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Ngo, C.-V.; Singh, S.C.; Yang, J.; Xin, W.; Yu, Z.; Guo, C. Bioinspired Hierarchical Surfaces Fabricated by Femtosecond Laser and Hydrothermal Method for Water Harvesting. Langmuir 2019, 35, 3562–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Han, Z.; Ren, L. Fabrication of Biomimetic Superhydrophobic Surface with Controlled ADHESION by electrodeposition. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 248, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Zha, F.; Lei, Z. Facile Fabrication of Superhydrophobic ZnO Surfaces from High to Low Water Adhesion. Mater. Lett. 2012, 75, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Hou, R.; Du, Y.; Lai, H.; Fu, K.; Zhang, N.; Sun, K. Designing Heterogeneous Chemical Composition on Hierarchical Structured Copper Substrates for the Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Controlled Adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8753–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Kang, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, J. A Facile Approach to Fabricate a Stable Superhydrophobic Film with Switchable Water Adhesion on Titanium Surface. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 239, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Chen, Z.; Tiwari, M.K. All-Organic Superhydrophobic Coatings with Mechanochemical Robustness and Liquid Impalement Resistance. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wei, W.; Li, Z.; Duan, W.; Han, H.; Xie, Q. A Superhydrophobic Fluorinated PDMS Composite as a Wearable Strain Sensor with Excellent Mechanical Robustness and Liquid Impalement Resistance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 3509–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cheng, F.; Lv, J.-A.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Jiang, L.; Yu, Y. Light-Controlled Quick Switch of ADHESION on a micro-Arrayed Liquid Crystal Polymer Superhydrophobic Film. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 3730–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, J.; Cheng, F.; Liu, M.; Jiang, L.; Yu, Y. In Situ Fully Light-Driven Switching of Superhydrophobic Adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Lu, Y.; Sun, J.; Yu, Y. Dynamic Interfacial Regulation by Photodeformable Azobenzene-Containing Liquid Crystal Polymer MICRO/nanostructures. Langmuir 2020, 36, 6611–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Gao, M.; Song, J.; Xu, W. Controlling the Adhesion of Superhydrophobic Surfaces Using Electrolyte Jet Machining Techniques. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
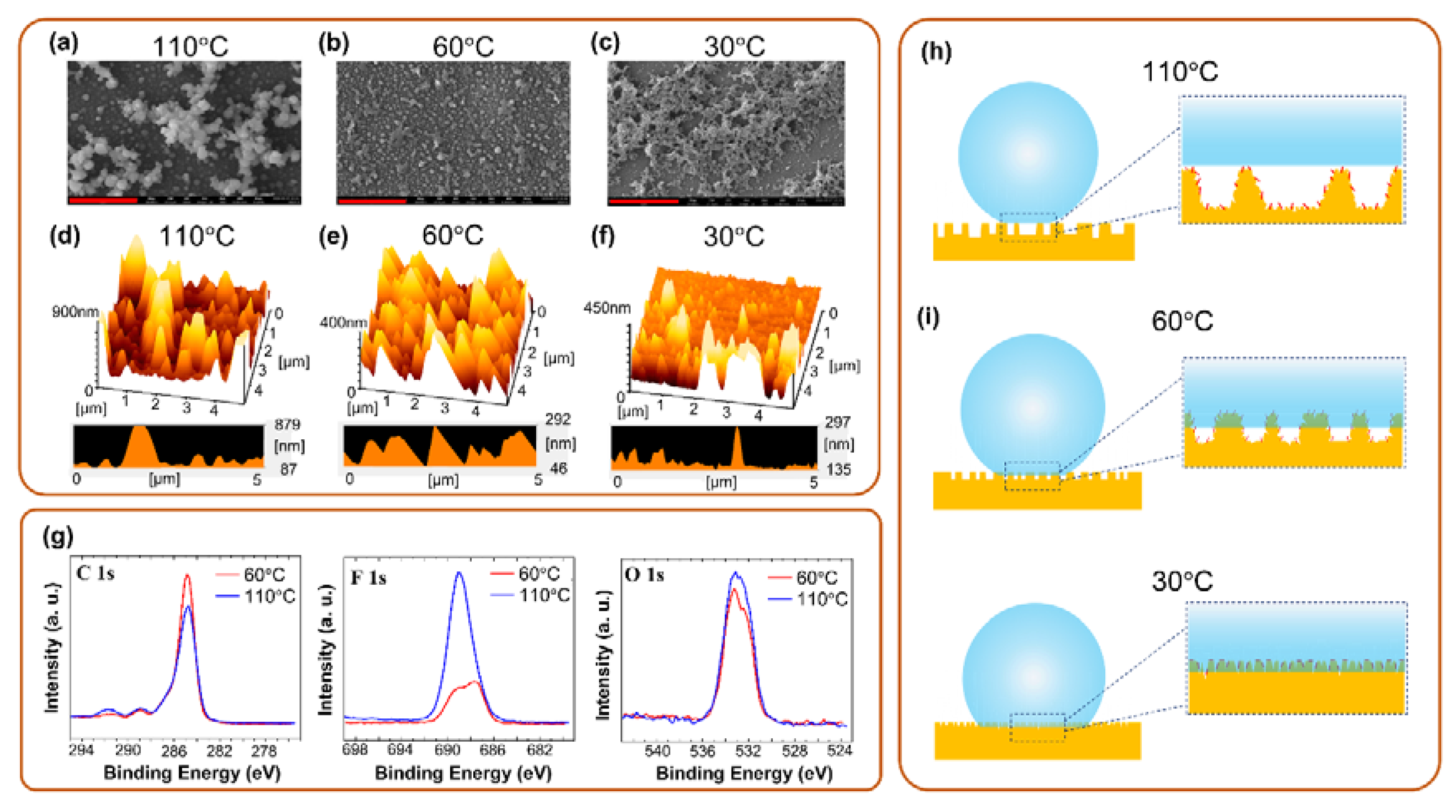
| Fabricated Temperature/Element | C 1s | O 1s | F 1s | In 3d5 | Sn 3d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 110 °C | 84.11% | 10.39% | 5.49% | <0.1% | <0.1% |
| 60 °C | 73.69% | 11.72% | 14.54% | <0.1% | <0.1% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, D.-Y.; Li, C.-H.; Chang, L.-M.; Jau, H.-C.; Lo, W.-C.; Lin, W.-C.; Wang, C.-T.; Lin, T.-H. Functional Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Spatially Programmable Adhesion. Polymers 2020, 12, 2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122968
Guo D-Y, Li C-H, Chang L-M, Jau H-C, Lo W-C, Lin W-C, Wang C-T, Lin T-H. Functional Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Spatially Programmable Adhesion. Polymers. 2020; 12(12):2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122968
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Duan-Yi, Cheng-Huan Li, Li-Min Chang, Hung-Chang Jau, Wei-Chun Lo, Wei-Chun Lin, Chun-Ta Wang, and Tsung-Hsien Lin. 2020. "Functional Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Spatially Programmable Adhesion" Polymers 12, no. 12: 2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122968
APA StyleGuo, D.-Y., Li, C.-H., Chang, L.-M., Jau, H.-C., Lo, W.-C., Lin, W.-C., Wang, C.-T., & Lin, T.-H. (2020). Functional Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Spatially Programmable Adhesion. Polymers, 12(12), 2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122968