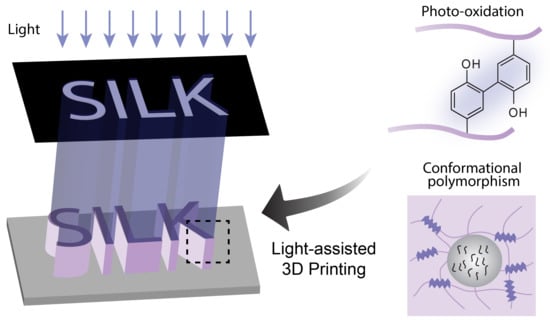
Photo-Crosslinked Silk Fibroin for 3D Printing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
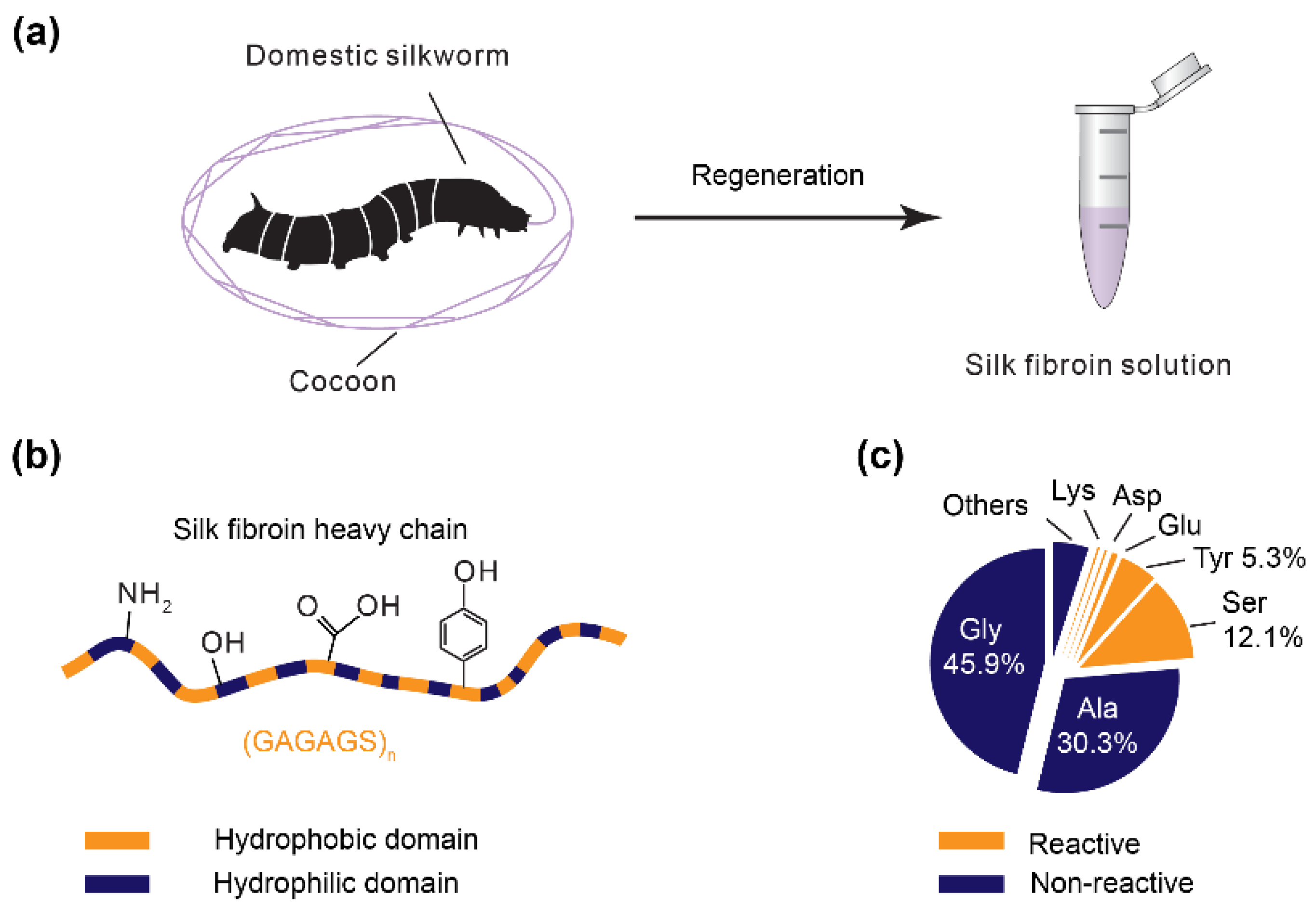
2. Photo-Oxidization
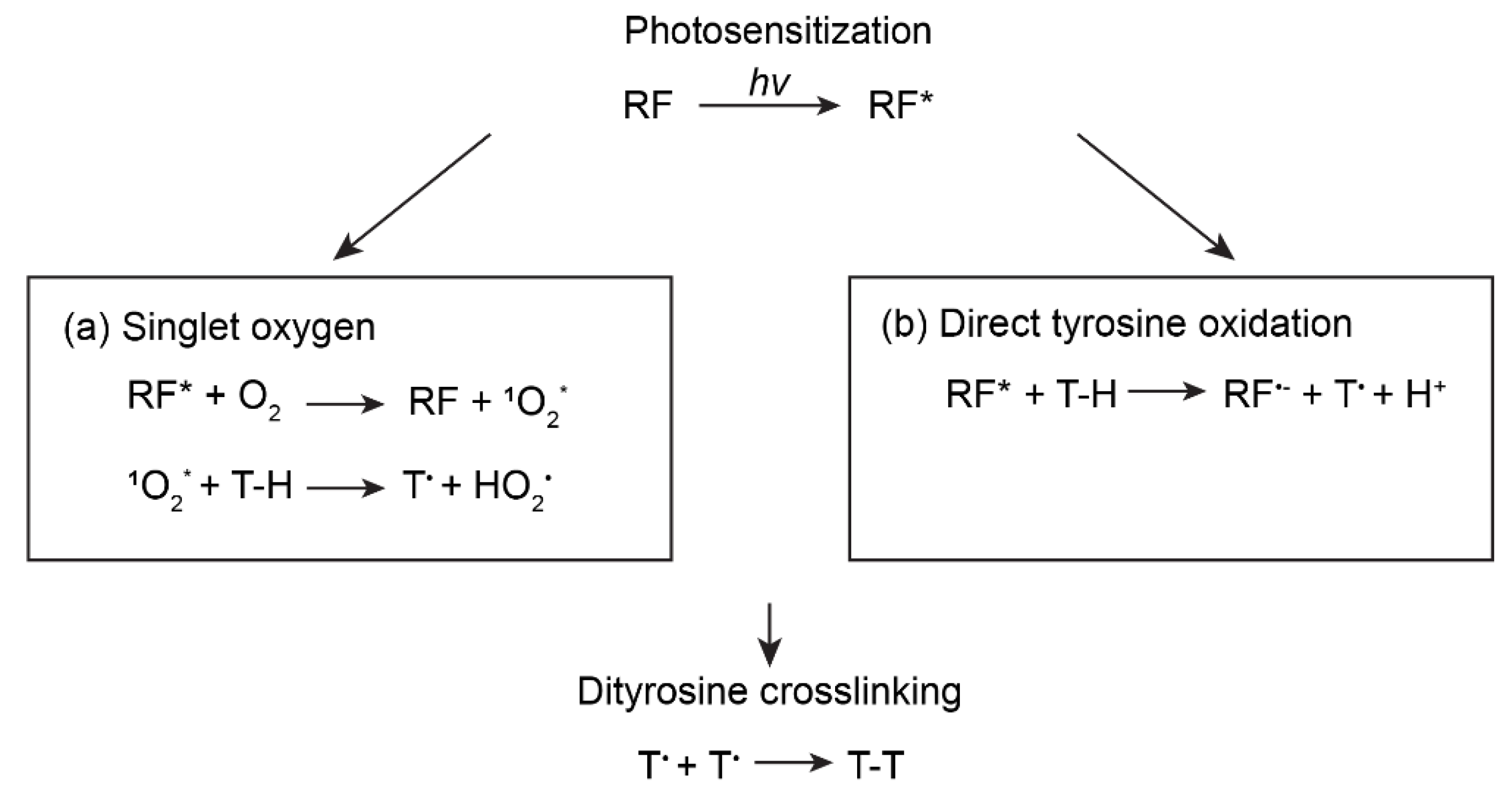
2.1. Ru(II)/Persulfate
2.2. Riboflavin
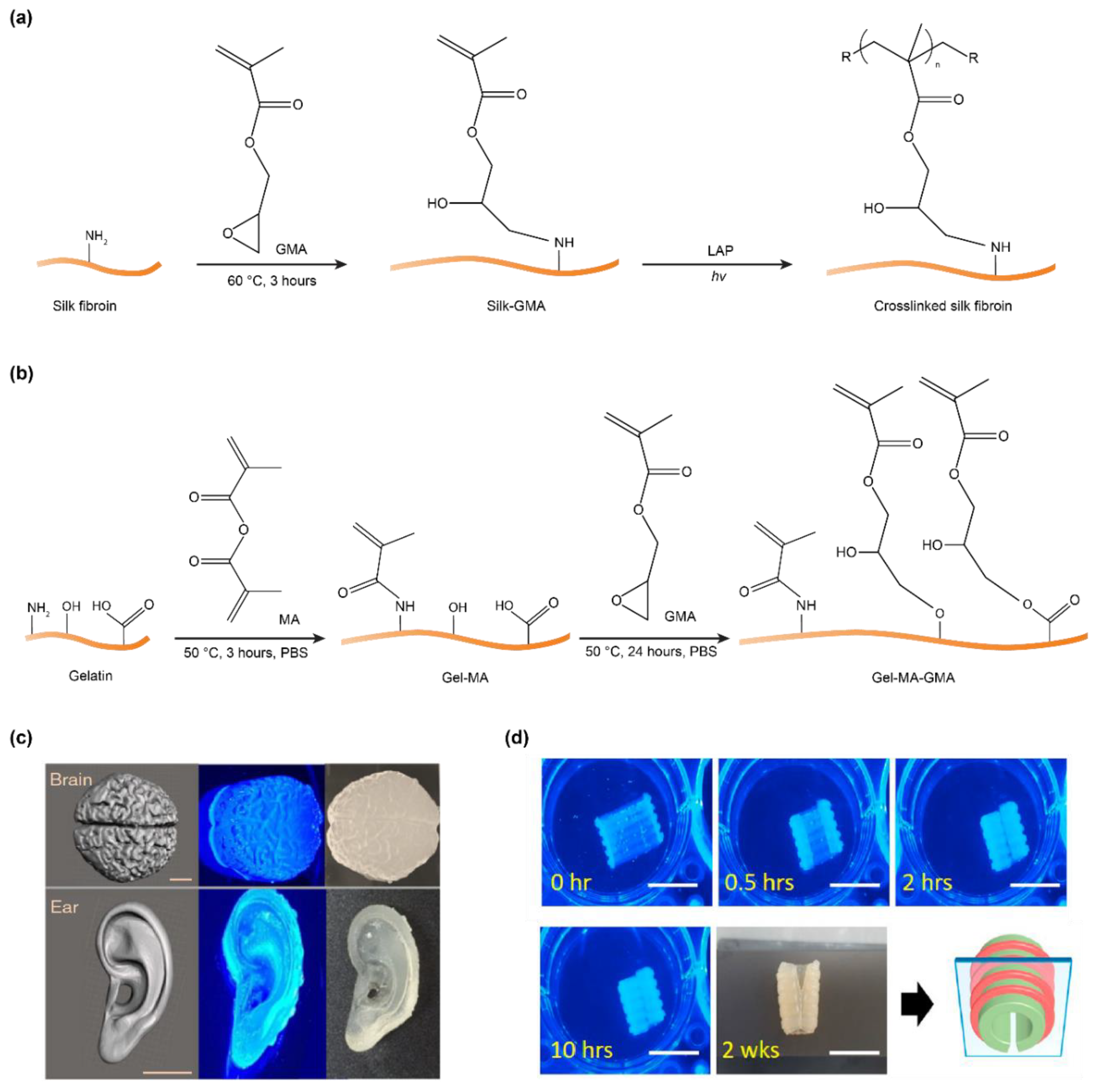
3. Methacryloyl-Modification
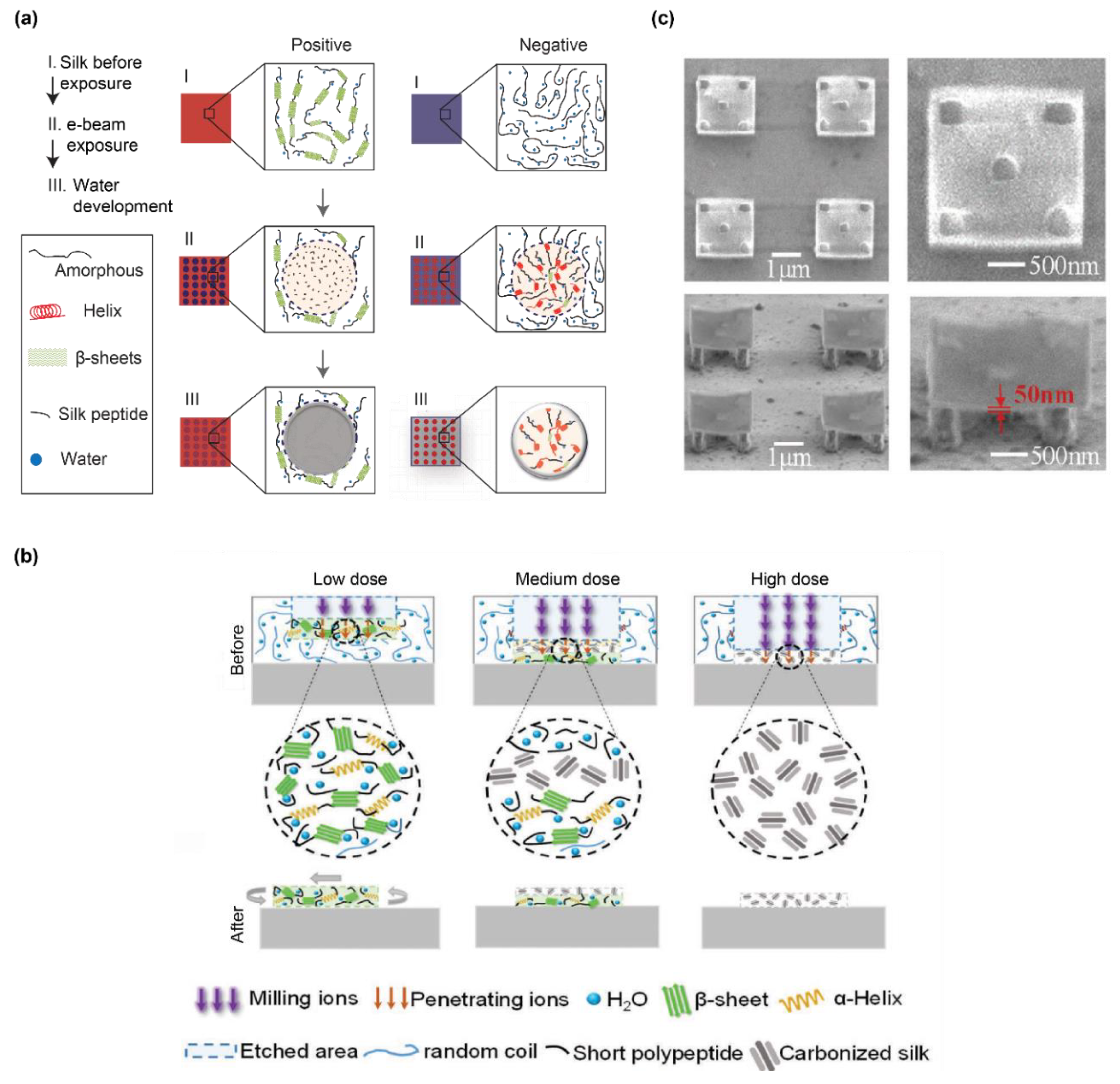
4. Conformational Polymorphism
5. Double Crosslinking
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, C.; Li, C.; Mu, X.; Kaplan, D.L. Engineering silk materials: From natural spinning to artificial processing. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 011313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Fitzpatrick, V.; Kaplan, D.L. From Silk Spinning to 3D Printing: Polymer Manufacturing using Directed Hierarchical Molecular Assembly. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 1901552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockwood, D.N.; Preda, R.C.; Yücel, T.; Wang, X.; Lovett, M.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1612–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozzi, L.; Laurent, P.-A.; Di Buduo, C.A.; Mu, X.; Massaro, A.; Bretherton, R.; Stoppel, W.; Kaplan, D.L.; Balduini, A. Multi-channel silk sponge mimicking bone marrow vascular niche for platelet production. Biomaterials 2018, 178, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Viventi, J.; Amsden, J.J.; Xiao, J.; Vigeland, L.; Kim, Y.-S.; Blanco, J.A.; Panilaitis, B.; Frechette, E.S.; Contreras, D. Dissolvable films of silk fibroin for ultrathin conformal bio-integrated electronics. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torculas, M.; Medina, J.; Xue, W.; Hu, X. Protein-based bioelectronics. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, H.; Leow, W.R.; Cai, Y.; Loh, X.J.; Han, M.Y.; Chen, X. Silk fibroin for flexible electronic devices. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4250–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Mitropoulos, A.N.; Spitzberg, J.D.; Tao, H.; Kaplan, D.L.; Omenetto, F.G. Silk inverse opals. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, L.S.; Hu, X.; Gallego, J.; Georgakoudi, I.; Omenetto, F.G.; Schmidt, D.; Kaplan, D.L. Effect of processing on silk-based biomaterials: Reproducibility and biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2011, 99, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Z. Effect of various dissolution systems on the molecular weight of regenerated silk fibroin. Biomacromolecules 2012, 14, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, J.K.; Choi, J.; Hasturk, O.; Laubach, I.; Descoteaux, M.L.; Mosurkal, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, N.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk degumming time controls horseradish peroxidase-catalyzed hydrogel properties. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 4176–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, A.R.; Kaplan, D.L. Biomedical applications of chemically-modified silk fibroin. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6443–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Numata, K.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Mechanism of enzymatic degradation of beta-sheet crystals. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2926–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Rudym, D.D.; Walsh, A.; Abrahamsen, L.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, H.S.; Kirker-Head, C.; Kaplan, D.L. In vivo degradation of three-dimensional silk fibroin scaffolds. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3415–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horan, R.L.; Antle, K.; Collette, A.L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Moreau, J.E.; Volloch, V.; Kaplan, D.L.; Altman, G.H. In vitro degradation of silk fibroin. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3385–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. New opportunities for an ancient material. Science 2010, 329, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Z.; Vollrath, F. Surprising strength of silkworm silk. Nature 2002, 418, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebe, P.; Hu, X.; Kaplan, D.L.; Zhuravlev, E.; Wurm, A.; Arbeiter, D.; Schick, C. Beating the Heat-Fast Scanning Melts Silk Beta Sheet Crystals. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Kaplan, D.; Cebe, P. Determining beta-sheet crystallinity in fibrous proteins by thermal analysis and infrared spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6161–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorishetty, P.; Dutta, N.K.; Choudhury, N.R. Silk fibroins in multiscale dimensions for diverse applications. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 33227–33247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Li, C.; Vu, H.V.; Hanna, P.; Lechtig, A.; Qiu, Y.; Mu, X.; Ling, S.; Nazarian, A.; Lin, S.J. Thermoplastic moulding of regenerated silk. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Han, G.; Yan, S.; Zhang, Q. 3D printing of silk fibroin for biomedical applications. Materials 2019, 12, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeBari, M.K.; Keyser, M.N.; Bai, M.A.; Abbott, R.D. 3D printing with silk: Considerations and applications. Connect. Tissue Res. 2018, 61, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Midha, S.; Sharma, A.; Ghosh, S. Silk-based bioinks for 3D bioprinting. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2018, 7, 1701204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorishetty, P.; Dutta, N.K.; Choudhury, N.R. Bioprintable tough hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Adv. Colloid Int. Sci. 2020, 281, 102163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.A.; Liu, W.; Jimenez, A.; Yang, J.; Akpek, A.; Liu, X.; Pi, Q.; Mu, X.; Hu, N.; Schiffelers, R.M. Bioprinting: 3D Bioprinting: From Benches to Translational Applications. Small 2019, 15, 1970126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, J.; Ghosh, S. Cellular Proliferation, Self-Assembly, and Modulation of Signaling Pathways in Silk Fibroin Gelatin-Based 3D Bioprinted Constructs. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, C.; Zhang, J.; Øvrebø, Ø.; Huang, B.; Roberts, I.; Setty, M.; Allardyce, B.; Haugen, H.; Rajkhowa, R.; Bartolo, P. 3D printing of silk microparticle reinforced polycaprolactone scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 118, 111433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Li, Y.; Ling, S.; Huang, W.; Cebe, P.; Hsu, H.H.; De Ferrari, F.; Jiang, X.; et al. 3D Printing of Silk Protein Structures by Aqueous Solvent-Directed Molecular Assembly. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, 1900191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagn, F.; Eisoldt, L.; Hardy, J.G.; Vendrely, C.; Coles, M.; Scheibel, T.; Kessler, H. A conserved spider silk domain acts as a molecular switch that controls fibre assembly. Nature 2010, 465, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, U.-J.; Park, J.; Kim, H.J.; Wada, M.; Kaplan, D.L. Three-dimensional aqueous-derived biomaterial scaffolds from silk fibroin. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2775–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Hou, J.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Kaplan, D.L.; Lu, S. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-induced rapid gelation of silk fibroin. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2185–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazawa, K.; Ishida, K.; Masunaga, H.; Hikima, T.; Numata, K. Influence of water content on the β-sheet formation, thermal stability, water removal, and mechanical properties of silk materials. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guziewicz, N.; Best, A.; Perez-Ramirez, B.; Kaplan, D.L. Lyophilized silk fibroin hydrogels for the sustained local delivery of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2642–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Q.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Kluge, J.A.; Lu, S.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Water-insoluble silk films with silk I structure. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Parker, S.T.; Wang, X.; Kaplan, D.L.; Lewis, J.A. Direct-Write Assembly of Microperiodic Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, M.R.; Schaffner, M.; Carnelli, D.; Studart, A.R. 3D printing of hierarchical silk fibroin structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34677–34685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wu, S.; Kuss, M.; Jiang, X.; Sun, R.; Reid, P.; Qin, X.; Duan, B. 3D printing of silk fibroin-based hybrid scaffold treated with platelet rich plasma for bone tissue engineering. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partlow, B.P.; Hanna, C.W.; Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Moreau, J.E.; Applegate, M.B.; Burke, K.A.; Marelli, B.; Mitropoulos, A.N.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Highly tunable elastomeric silk biomaterials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4615–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, D.; Wu, F.; Yin, Z.; Zhu, T.; Xing, T.; Kundu, S.C.; Lu, S. Silk fibroin/polyvinyl pyrrolidone interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels. Polymers 2018, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Pati, F.; Choi, Y.-J.; Rijal, G.; Shim, J.-H.; Kim, S.W.; Ray, A.R.; Cho, D.-W.; Ghosh, S. Bioprintable, cell-laden silk fibroin–gelatin hydrogel supporting multilineage differentiation of stem cells for fabrication of three-dimensional tissue constructs. Acta Biomater. 2015, 11, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.B.; Silva-Correia, J.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reis, R.L. Fast setting silk fibroin bioink for bioprinting of patient-specific memory-shape implants. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2017, 6, 1701021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Guo, C.; Kumarasena, A.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. 3D Printing of Functional Microalgal Silk Structures for Environmental Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 4808–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, M.; Coburn, J.M.; Partlow, B.P.; Mu, X.; Kaplan, D.L. Molecular and macro-scale analysis of enzyme-crosslinked silk hydrogels for rational biomaterial design. Acta Biomater. 2017, 63, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.; Bae, K.H.; Kurisawa, M. Injectable hydrogel systems crosslinked by horseradish peroxidase. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 11, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Liu, W.; Wang, W. Fenton reaction-initiated formation of biocompatible injectable hydrogels for cell encapsulation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3932–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; McGill, M.; Raia, N.R.; Hasturk, O.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk Hydrogels Crosslinked by the Fenton Reaction. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2019, 8, 1900644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbanks, B.D.; Schwartz, M.P.; Bowman, C.N.; Anseth, K.S. Photoinitiated polymerization of PEG-diacrylate with lithium phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate: Polymerization rate and cytocompatibility. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6702–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Yeon, Y.K.; Lee, J.M.; Chao, J.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, Y.B.; Sultan, M.T.; Lee, O.J.; Lee, J.S.; Yoon, S.-I. Precisely printable and biocompatible silk fibroin bioink for digital light processing 3D printing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fancy, D.A.; Kodadek, T. Chemistry for the analysis of protein–protein interactions: Rapid and efficient cross-linking triggered by long wavelength light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6020–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, X.; Soliman, B.G.; Alcala-Orozco, C.R.; Li, J.; Vis, M.A.M.; Santos, M.; Wise, S.G.; Levato, R.; Malda, J.; Woodfield, T.B.F.; et al. Rapid Photocrosslinking of Silk Hydrogels with High Cell Density and Enhanced Shape Fidelity. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 1901667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, H.; Lin, C.C. Visible-light-mediated thiol-Ene hydrogelation using eosin-Y as the only photoinitiator. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Hoz, A.; Kochevar, I.E.; Omenetto, F.; Marcos, S. Photobonded silk-fibroin films for corneal dressing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 2019, 60, 3218. [Google Scholar]
- Applegate, M.B.; Partlow, B.P.; Coburn, J.; Marelli, B.; Pirie, C.; Pineda, R.; Kaplan, D.L.; Omenetto, F.G. Photocrosslinking of Silk Fibroin Using Riboflavin for Ocular Prostheses. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2417–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moné, M.J.; Volker, M.; Nikaido, O.; Mullenders, L.H.; Van Zeeland, A.A.; Verschure, P.J.; Manders, E.M.; Van Driel, R. Local UV-induced DNA damage in cell nuclei results in local transcription inhibition. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulivi, C.; Traaseth, N.J.; Davies, K.J. Tyrosine oxidation products: Analysis and biological relevance. Amino Acids 2003, 25, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.C.; Yu, Z.; Burlingame, A.L.; Craik, C.S. Determining Protein−Protein Interactions by Oxidative Cross-Linking of a Glycine-Glycine-Histidine Fusion Protein. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 4397–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whittaker, J.L.; Choudhury, N.R.; Dutta, N.K.; Zannettino, A. Facile and rapid ruthenium mediated photo-crosslinking of Bombyx mori silk fibroin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 6259–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, J.; Dutta, N.; Elvin, C.; Choudhury, N. Fabrication of highly elastic resilin/silk fibroin based hydrogel by rapid photo-crosslinking reaction. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6576–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Yang, Y.J.; Bahn, S.Y.; Cha, H.J. A bioinspired dual-crosslinked tough silk protein hydrogel as a protective biocatalytic matrix for carbon sequestration. NPG Asia Mat. 2017, 9, e391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, G.; Lapidot, S.; Numata, K.; Hu, X.; Meirovitch, S.; Dekel, M.; Podoler, I.; Shoseyov, O.; Kaplan, D.L. Expression, cross-linking, and characterization of recombinant chitin binding resilin. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvin, C.M.; Carr, A.G.; Huson, M.G.; Maxwell, J.M.; Pearson, R.D.; Vuocolo, T.; Liyou, N.E.; Wong, D.C.; Merritt, D.J.; Dixon, N.E. Synthesis and properties of crosslinked recombinant pro-resilin. Nature 2005, 437, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, R.E.; Lesieur, E.; Kim, M.; Wong, D.C.; Huson, M.G.; Nairn, K.M.; Brownlee, A.G.; Pearson, R.D.; Elvin, C.M. Design and facile production of recombinant resilin-like polypeptides: Gene construction and a rapid protein purification method. Protein Eng. Des. Select. 2007, 20, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Dudek, D.M.; Cao, Y.; Balamurali, M.; Gosline, J.; Li, H. Designed biomaterials to mimic the mechanical properties of muscles. Nature 2010, 465, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvin, C.M.; Vuocolo, T.; Brownlee, A.G.; Sando, L.; Huson, M.G.; Liyou, N.E.; Stockwell, P.R.; Lyons, R.E.; Kim, M.; Edwards, G.A. A highly elastic tissue sealant based on photopolymerised gelatin. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8323–8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, S.; Ohi, H.; Hotta, T.; Kamei, H.; Taya, M. Differentiation potential of human adipose stem cells bioprinted with hyaluronic acid/gelatin-based bioink through microextrusion and visible light-initiated crosslinking. Biopolymers 2018, 109, e23080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjork, J.W.; Johnson, S.L.; Tranquillo, R.T. Ruthenium-catalyzed photo cross-linking of fibrin-based engineered tissue. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piluso, S.; Gomez, D.F.; Dokter, I.; Texeira, L.M.; Li, Y.; Leijten, J.; Van Weeren, R.; Vermonden, T.; Karperien, M.; Malda, J. Rapid and cytocompatible cell-laden silk hydrogel formation via riboflavin-mediated crosslinking. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 9566–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvin, C.M.; Brownlee, A.G.; Huson, M.G.; Tebb, T.A.; Kim, M.; Lyons, R.E.; Vuocolo, T.; Liyou, N.E.; Hughes, T.C.; Ramshaw, J.A. The development of photochemically crosslinked native fibrinogen as a rapidly formed and mechanically strong surgical tissue sealant. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorishetty, P.; Balu, R.; Athukoralalage, S.S.; Greaves, T.L.; Mata, J.; De Campo, L.; Saha, N.; Zannettino, A.C.; Dutta, N.K.; Choudhury, N.R. Tunable biomimetic hydrogels from silk fibroin and nanocellulose. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2375–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, M.Y.; Dutta, N.K.; Choudhury, N.R.; Kim, M.; Elvin, C.M.; Nairn, K.M.; Hill, A.J. The effect of hydration on molecular chain mobility and the viscoelastic behavior of resilin-mimetic protein-based hydrogels. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8462–8473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balu, R.; Reeder, S.; Knott, R.; Mata, J.; De Campo, L.; Dutta, N.K.; Choudhury, N.R. Tough photocrosslinked silk fibroin/graphene oxide nanocomposite hydrogels. Langmuir 2018, 34, 9238–9251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkoc, P.; Uvak, I.; Nazeer, M.A.; Batool, S.R.; Odeh, Y.N.; Akdogan, O.; Kizilel, S. 3D Printing of Cytocompatible Gelatin-Cellulose-Alginate Blend Hydrogels. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, 2000106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.S.-C.; Kim, Y.; Liu, J.C. Resilin: Protein-based elastomeric biomaterials. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, X.; Kaplan, D.L.; Buehler, M.J. Integration of Stiff Graphene and Tough Silk for the Design and Fabrication of Versatile Electronic Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiew, S.F.; Kiew, L.V.; Lee, H.B.; Imae, T.; Chung, L.Y. Assessing biocompatibility of graphene oxide-based nanocarriers: A review. J. Control. Release 2016, 226, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ruan, J.; Song, H.; Zhang, J.; Wo, Y.; Guo, S.; Cui, D. Biocompatibility of Graphene Oxide. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, J.; Peng, C.; Hu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Li, W.; Fan, C.; Huang, Q. Distribution and biocompatibility studies of graphene oxide in mice after intravenous administration. Carbon 2011, 49, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, D.; Jiang, F.; Wu, F.; Kaur, K.; Ghosh, S.; Kundu, S.C.; Lu, S. Highly elastomeric photocurable silk hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Seo, Y.B.; Yeon, Y.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, H.S.; Sultan, M.T.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, O.J.; Hong, H. 4D-bioprinted silk hydrogels for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2020, 260, 120281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Seo, Y.B.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.; Ajiteru, O.; Sultan, M.T.; Lee, O.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, C.H. Digital light processing 3D printed silk fibroin hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2020, 232, 119679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.S.; Schon, B.S.; Mekhileri, N.V.; Brown, G.C.; Chia, C.M.; Prabakar, S.; Hooper, G.J.; Woodfield, T.B. New visible-light photoinitiating system for improved print fidelity in gelatin-based bioinks. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1752–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.Y.; Hwang, B.H.; Yang, Y.J.; Kim, B.J.; Choi, B.-H.; Jung, G.Y.; Cha, H.J. Rapidly light-activated surgical protein glue inspired by mussel adhesion and insect structural crosslinking. Biomaterials 2015, 67, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athukoralalage, S.S.; Balu, R.; Dutta, N.K.; Roy Choudhury, N. 3D bioprinted nanocellulose-based hydrogels for tissue engineering applications: A brief review. Polymers 2019, 11, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolesky, D.B.; Homan, K.A.; Skylar-Scott, M.A.; Lewis, J.A. Three-dimensional bioprinting of thick vascularized tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3179–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batchelor, R.; Kwandou, G.; Spicer, P.; Stenzel, M. (−)-Riboflavin (vitamin B2) and flavin mononucleotide as visible light photo initiators in the thiol–ene polymerisation of PEG-based hydrogels. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, A.J.; Benson, J.M.; Donnelly, P.E.; Torzilli, P.A. Light Absorptive Properties of Articular Cartilage, ECM Molecules, Synovial Fluid, and Photoinitiators as Potential Barriers to Light-Initiated Polymer Scaffolding Procedures. Cartilage 2019, 10, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.S.; Galarraga, J.H.; Cui, X.; Lindberg, G.C.; Burdick, J.A.; Woodfield, T.B. Fundamentals and Applications of Photo-Cross-Linking in Bioprinting. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10662–10694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, A.S.; Kraft, S.; Edelhauser, H.F.; Kidder, G.W.; Lundquist, R.R.; Bradshaw, H.E.; Dedeic, Z.; Dionne, M.J.; Clement, E.M.; Conrad, G.W. Mechanisms of corneal tissue cross-linking in response to treatment with topical riboflavin and long-wavelength ultraviolet radiation (UVA). Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spikes, J.D.; Shen, H.R.; Kopečková, P.; Kopeček, J. Photodynamic crosslinking of proteins. III. Kinetics of the FMN-and rose bengal-sensitized photooxidation and intermolecular crosslinking of model tyrosine-containing N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide copolymers. Photochem. Photobiol. 1999, 70, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.-R.; Spikes, J.D.; Smith, C.J.; Kopeček, J. Photodynamic cross-linking of proteins: IV. Nature of the His–His bond (s) formed in the rose bengal-photosensitized cross-linking of N-benzoyl-L-histidine. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2000, 130, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hua, J.; Ng, P.F.; Fei, B. Photochemistry of Bioinspired Dityrosine Crosslinking. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placone, J.K.; Navarro, J.; Laslo, G.W.; Lerman, M.J.; Gabard, A.R.; Herendeen, G.J.; Falco, E.E.; Tomblyn, S.; Burnett, L.; Fisher, J.P. Development and characterization of a 3D printed, keratin-based hydrogel. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.Y.; Roper, T.M.; Jonsson, E.S.; Kudyakov, I.; Viswanathan, K.; Nason, C.; Guymon, C.A.; Hoyle, C.E. The kinetics of vinyl acrylate photopolymerization. Polymer 2003, 44, 2859–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Alvarez, M.M.; Tamayol, A.; Annabi, N.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, K.; Chen, N.; Liu, X.; Mu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.S. A General Strategy for Extrusion Bioprinting of Bio-Macromolecular Bioinks through Alginate-Templated Dual-Stage Crosslinking. Macromol. Biosci. 2018, 18, 1800127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noshadi, I.; Hong, S.; Sullivan, K.E.; Sani, E.S.; Portillo-Lara, R.; Tamayol, A.; Shin, S.R.; Gao, A.E.; Stoppel, W.L.; Black III, L.D. In vitro and in vivo analysis of visible light crosslinkable gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 2093–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billiet, T.; Gevaert, E.; De Schryver, T.; Cornelissen, M.; Dubruel, P. The 3D printing of gelatin methacrylamide cell-laden tissue-engineered constructs with high cell viability. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudshoorn, M.H.; Rissmann, R.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Hennink, W.E. Synthesis of methacrylated hyaluronic acid with tailored degree of substitution. Polymer 2007, 48, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valmikinathan, C.M.; Mukhatyar, V.J.; Jain, A.; Karumbaiah, L.; Dasari, M.; Bellamkonda, R.V. Photocrosslinkable chitosan based hydrogels for neural tissue engineering. Soft Mater. 2012, 8, 1964–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, K.; Li, X.; Schrobback, K.; Sheikhi, A.; Annabi, N.; Leijten, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.S.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Klein, T.J.; et al. Structural analysis of photocrosslinkable methacryloyl-modified protein derivatives. Biomaterials 2017, 139, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reis, A.V.; Fajardo, A.R.; Schuquel, I.T.; Guilherme, M.R.; Vidotti, G.J.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Reaction of glycidyl methacrylate at the hydroxyl and carboxylic groups of poly (vinyl alcohol) and poly (acrylic acid): Is this reaction mechanism still unclear? J. Organ. Chem. 2009, 74, 3750–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucciarelli, A.; Muthukumar, T.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, W.K.; Quaranta, A.; Maniglio, D.; Khang, G.; Motta, A. Preparation and Statistical Characterization of Tunable Porous Sponge Scaffolds using UV Cross-linking of Methacrylate-Modified Silk Fibroin. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 6374–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. Fabrication of highly crosslinked gelatin hydrogel and its influence on chondrocyte proliferation and phenotype. Polymers 2017, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Hu, N.; Cairns, D.M.; Liu, H.; Timko, B.P. Photo–cross-linkable, insulating silk fibroin for bioelectronics with enhanced cell affinity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurland, N.E.; Dey, T.; Kundu, S.C.; Yadavalli, V.K. Precise Patterning of Silk Microstructures Using Photolithography. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6207–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R.K.; Kurland, N.E.; Jiang, C.; Kundu, S.C.; Zhang, N.; Yadavalli, V.K. Fabrication of precise shape-defined particles of silk proteins using photolithography. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 85, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Davoudi, Z.; Xing, X.; Yu, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, Z.; Deng, H.; Wang, Q. Advanced Silk Fibroin Biomaterials for Cartilage Regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 2704–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, R.J.; Hollister, S.J.; Niedner, M.F.; Mahani, M.G.; Park, A.H.; Mehta, D.K.; Ohye, R.G.; Green, G.E. Mitigation of tracheobronchomalacia with 3D-printed personalized medical devices in pediatric patients. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 285ra264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoury, L.R.; Slawinski, M.; Collison, D.R.; Popa, I. Cation-induced shape programming and morphing in protein-based hydrogels. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaehr, B.; Shear, J.B. Multiphoton fabrication of chemically responsive protein hydrogels for microactuation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8850–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ehrick, J.D.; Deo, S.K.; Browning, T.W.; Bachas, L.G.; Madou, M.J.; Daunert, S. Genetically engineered protein in hydrogels tailors stimuli-responsive characteristics. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Mu, X.; Ling, S.; Yu, H.; Chen, W.; Guo, C.; Watson, M.C.; Yu, Y. Stimuli-responsive composite biopolymer actuators with selective spatial deformation behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14602–14608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shao, J.; Zheng, J. Radiation grafting/crosslinking of silk using electron-beam irradiation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 2028–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Marelli, B.; Brenckle, M.A.; Mitropoulos, A.N.; Gil, E.-S.; Tsioris, K.; Tao, H.; Kaplan, D.L.; Omenetto, F.G. All-water-based electron-beam lithography using silk as a resist. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, S.; Shi, Z.; Tabarini, J.; Lee, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gilbert Corder, S.; Li, X.; Dong, F. Precise protein photolithography (P3): High performance biopatterning using silk fibroin light chain as the resist. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1700191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, S.; Qian, Z.; Qin, N.; Song, W.; Sun, L.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, X. Protein Bricks: 2D and 3D Bio-Nanostructures with Shape and Function on Demand. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Yao, M.; Liu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, X.; Shao, Z. Enhancing mechanical properties of silk fibroin hydrogel through restricting the growth of β-sheet domains. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2017, 9, 17489–17498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Illeperuma, W.R.; Suo, Z.; Vlassak, J.J. Hybrid hydrogels with extremely high stiffness and toughness. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Shin, D.; Shin, S.; Hyun, J. Effect of gelatin on dimensional stability of silk fibroin hydrogel structures fabricated by digital light processing 3D printing. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 89, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, M.B.; Dennis, P.B.; Tondiglia, V.P.; Nadeau, L.J.; Singh, K.M.; Drummy, L.F.; Partlow, B.P.; Brown, D.P.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. 3D Printing of Regenerated Silk Fibroin and Antibody-Containing Microstructures via Multiphoton Lithography. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 2064–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-L.; Li, Q.; Sun, S.-M.; Huang, J.-C.; Zheng, B.-Y.; Chen, Q.-D.; Shao, Z.-Z.; Sun, H.-B. Aqueous multiphoton lithography with multifunctional silk-centred bio-resists. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Fourkas, J.T. Multiphoton polymerization. Mater. Today 2007, 10, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkatzidis, K.; Chatzinikolaidou, M.; Kaliva, M.; Bakopoulou, A.; Farsari, M.; Vamvakaki, M. Multiphoton 3D Printing of Biopolymer-Based Hydrogels. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 6161–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, I.; Jung, G.S.; Narayanan, N.; Buehler, M.J. Perspectives on 3D printing of self-assembling materials and structures. Cur. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 15, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, E.L.; Su, I.; Buehler, M.J. WebNet: A biomateriomic three-dimensional spider web neural net. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2020, 42, 101034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
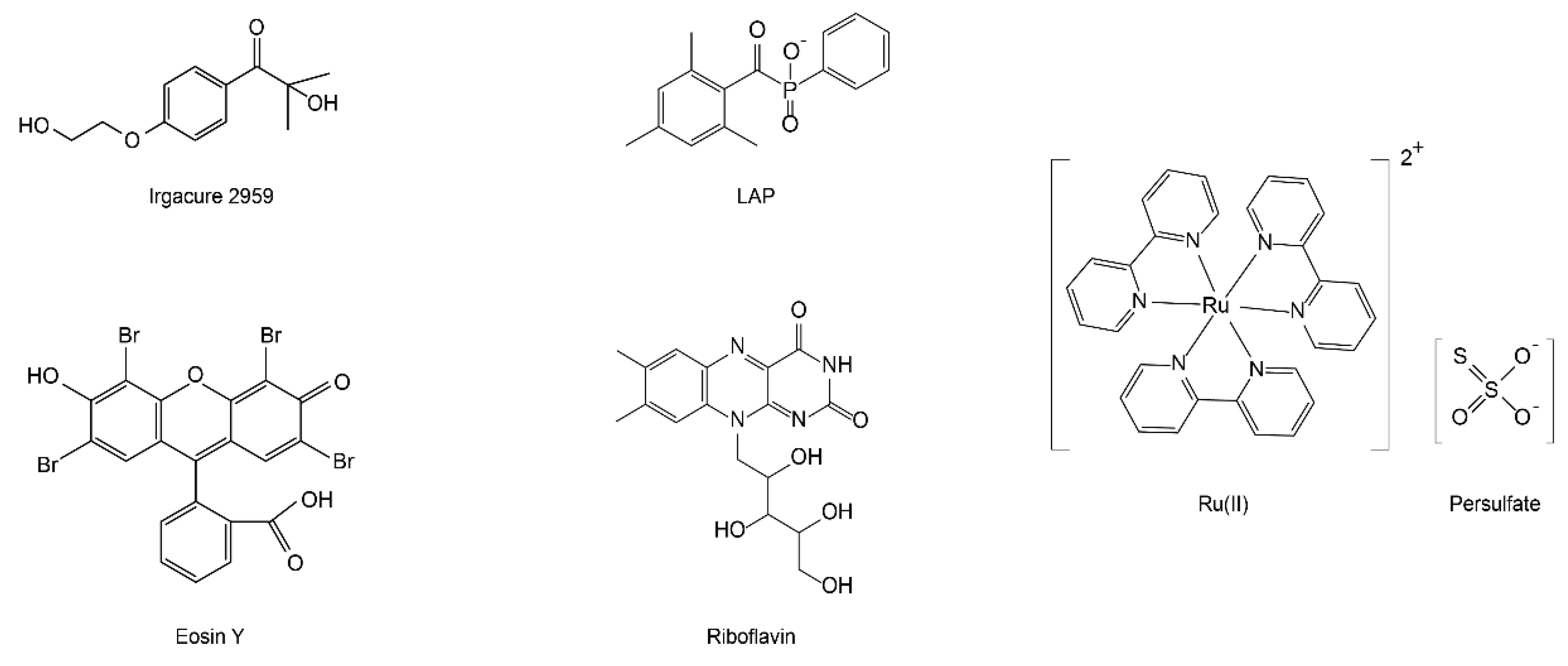
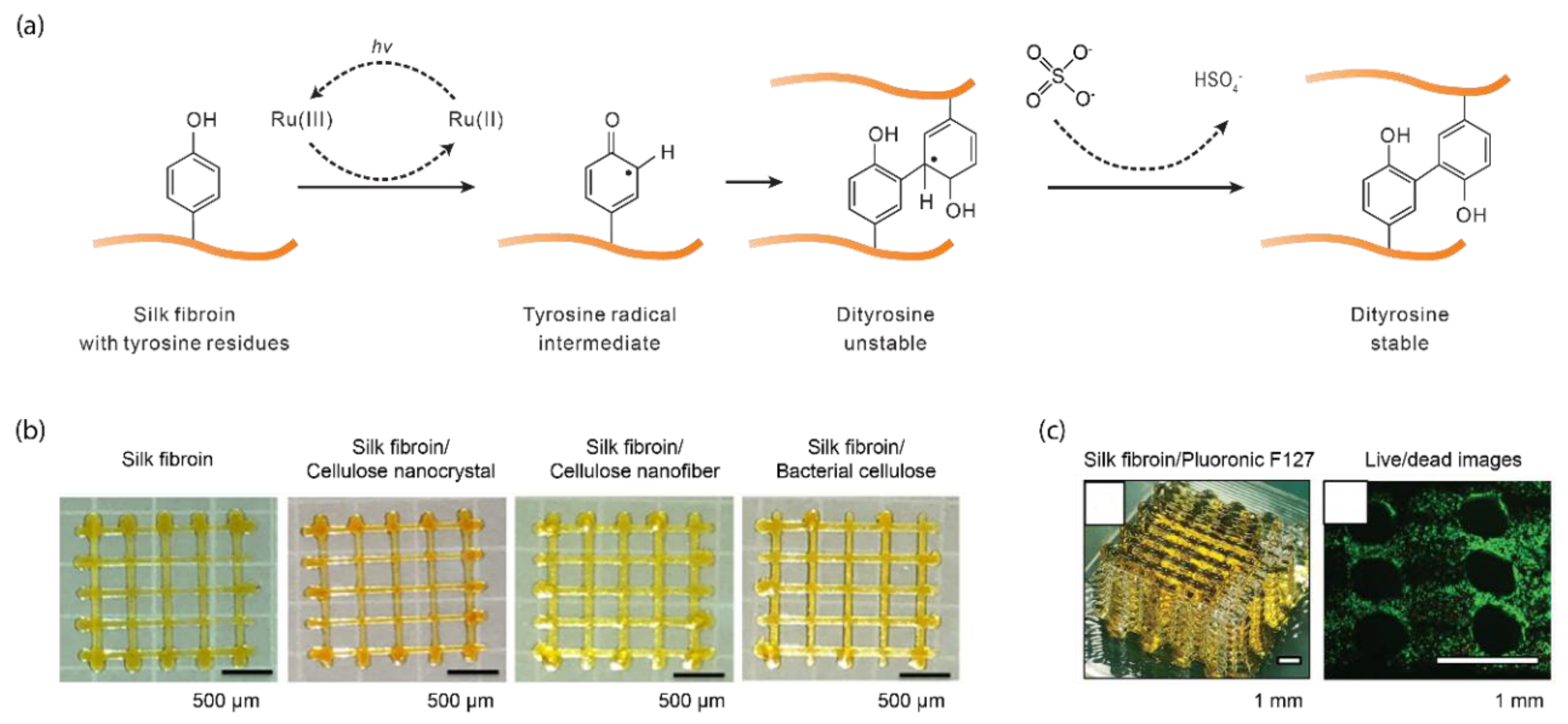
| Proteins | Crosslinking Sites | Solution/Ink (mg/mL) | Photoinitiators | Light Source | Exposure Distance | Exposure Time | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silk fibroin | Tyrosine (~5.3 mol%) a | 75 (+100 Resilin) | Ru(II), 5 mM APS, 28 mM | 250 W white | N/A | 120 + 60 s (Two sides) | [59] |
| ~300 | Ru (II), 0.16–10 mM APS, 20, 28, 100 mM | 250 W white | N/A | 120 + 60 s (Two sides) | [58] | ||
| ~20 | Ru(II), 0.5 mM APS, 5 mM | 400–450 nm 30 mW/cm2 | N/A | 3 min | [51] | ||
| 10–50 | Riboflavin (0.1 mM) HRP (10 U/mL) | 365 nm 300 W/m2 | N/A | 30 min | [79] | ||
| 50 | Riboflavin 5′-monophosphate, 2 mM | 450 nm (×3 leds) 18.7 mW/cm2 | N/A | ~60 min | [54] | ||
| Methacryloyl | 100–300 | LAP, 0.2% | 365 nm 30 mW/cm2 | N/A | N/A | [49] | |
| 100–300 | LAP, 0.2% | 365 nm 3.5 mW/cm2 | N/A | ~5 s (each layer) | [80] | ||
| 100–300 | LAP, 0.6% | 365 nm | N/A | ~5 s (each layer) | [81] | ||
| Gelatin/Collage | Tyrosine (~0.9%) a | 10, Gel-MA/ 0.6, Collagen | Ru(II), 0.2–2 mM APS, 2–20 mM | 400–450 nm 3–100 mW/cm2 | N/A | 15 min | [82] |
| 100–175, gelatin | Ru(II), 1 mM SPS, 20 mM | 600 W white | 150 mm | 30 s | [65] | ||
| Fibrin | Tyrosine (4.9%, β-chain; 5.6%, γ-chain; 0.65%, α-chain) | 3 | Ru(II), 2 mM SPS, 43 mM | 458 nm 28 mW/cm2 | 30 mm | 10 s | [67] |
| 100, 150 | Ru(II), 2 mM SPS, 20 mM | 600 W white | 150 mm | 20 s | [69] | ||
| GB1-resilin polyprotein | Tyrosine (~6%) a | 200 | Ru(II), 0.2 mM APS, 50 mM | 200 W white | N/A | 30 s | [64] |
| Rec1-resilin | Tyrosine (~6%) a | 200 | Ru(II), 0.2–2 mM APS, 10 mM | 600 W white | 150 mm | 20 s | [62] |
| Mussel adhesive proteins | Tyrosine (~20%) a | 100–300 | Ru(II), 2 mM SPS, 10–30 mM | 460 nm 1200 mW/cm2 | 20 mm | 60 s | [83] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, X.; Sahoo, J.K.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Photo-Crosslinked Silk Fibroin for 3D Printing. Polymers 2020, 12, 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122936
Mu X, Sahoo JK, Cebe P, Kaplan DL. Photo-Crosslinked Silk Fibroin for 3D Printing. Polymers. 2020; 12(12):2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122936
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Xuan, Jugal Kishore Sahoo, Peggy Cebe, and David L. Kaplan. 2020. "Photo-Crosslinked Silk Fibroin for 3D Printing" Polymers 12, no. 12: 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122936
APA StyleMu, X., Sahoo, J. K., Cebe, P., & Kaplan, D. L. (2020). Photo-Crosslinked Silk Fibroin for 3D Printing. Polymers, 12(12), 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122936