Hollow Mesoporous Microspheres Coating for Super-Hydrophobicity Wood with High Thermostability and Abrasion Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
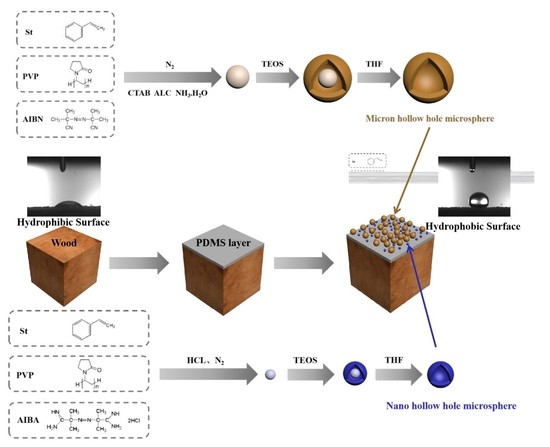
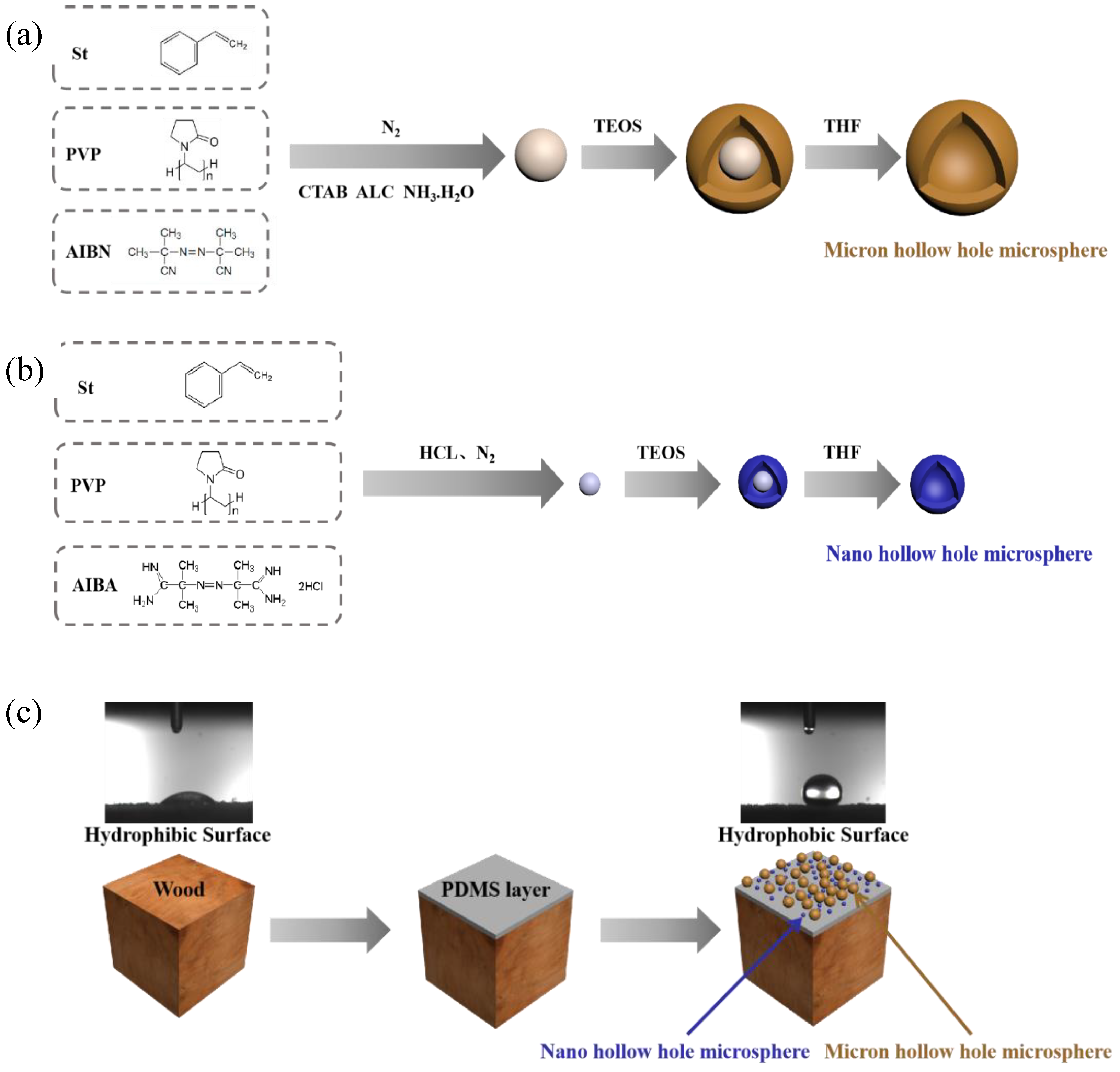
2.1. Preparation Micro/Nano Hollow Mesoporous Silica
2.1.1. Preparation of Nano Polystyrene
2.1.2. Preparation of Micron Polystyrene
2.1.3. Nano Core-Shell Structure Polystyrene/Silica Microspheres
2.1.4. Micron Core-Shell Structure Polystyrene/Silica Microspheres
2.1.5. Preparation of Nano Hollow Mesoporous Silica
2.1.6. Preparation of Micron Hollow Mesoporous Silica
2.2. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Surface
2.3. Superhydrophobicity Measurement
2.4. Surface Observation
2.4.1. Core-Shell Particle Surface
2.4.2. Wood Surface
2.5. FT-IR Analysis
2.6. XRD Analysis
2.7. TG Experiments
2.8. Mechanical Durability of the Hydrophobic Coatings
3. Results and Discussion
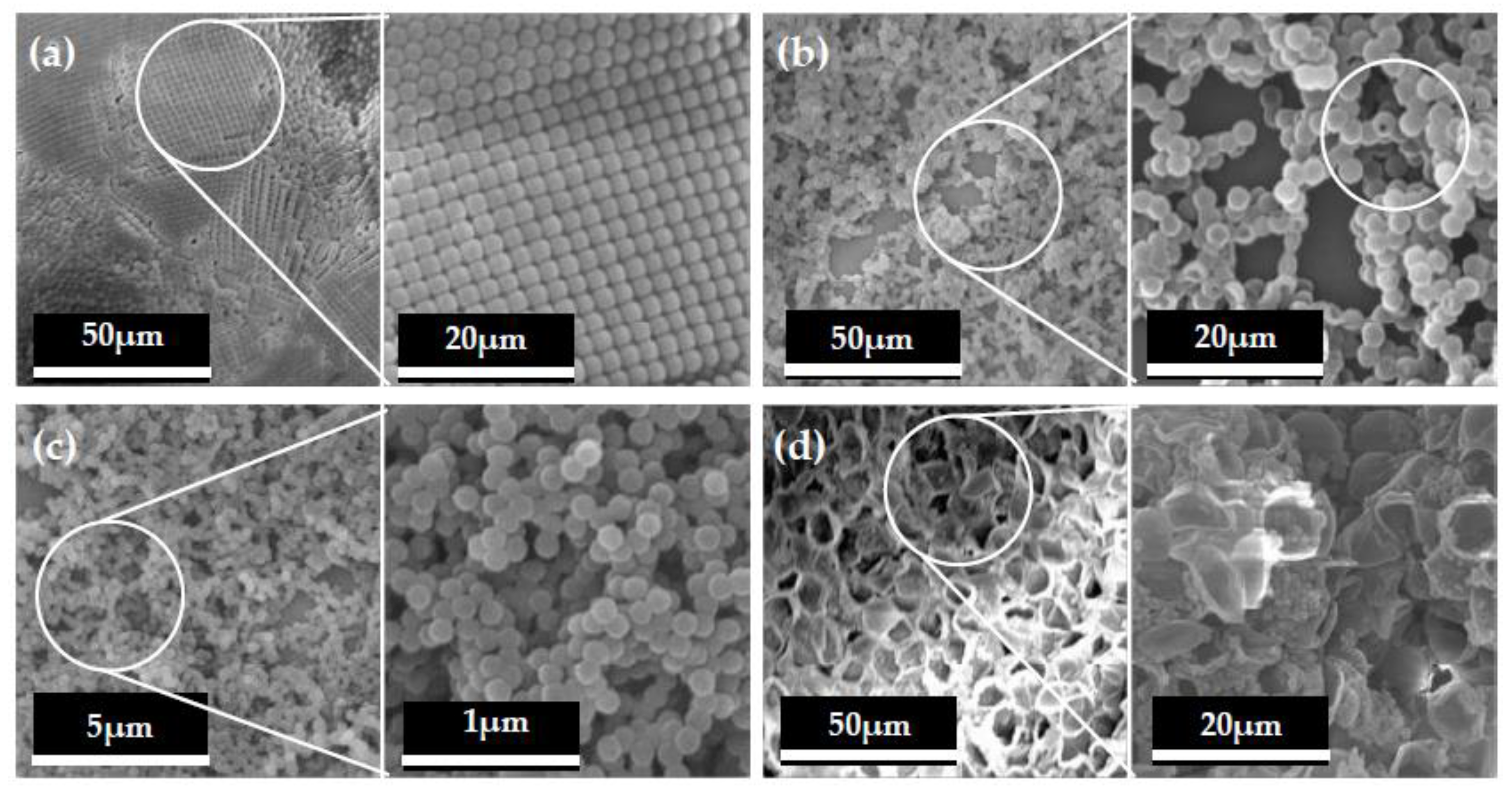
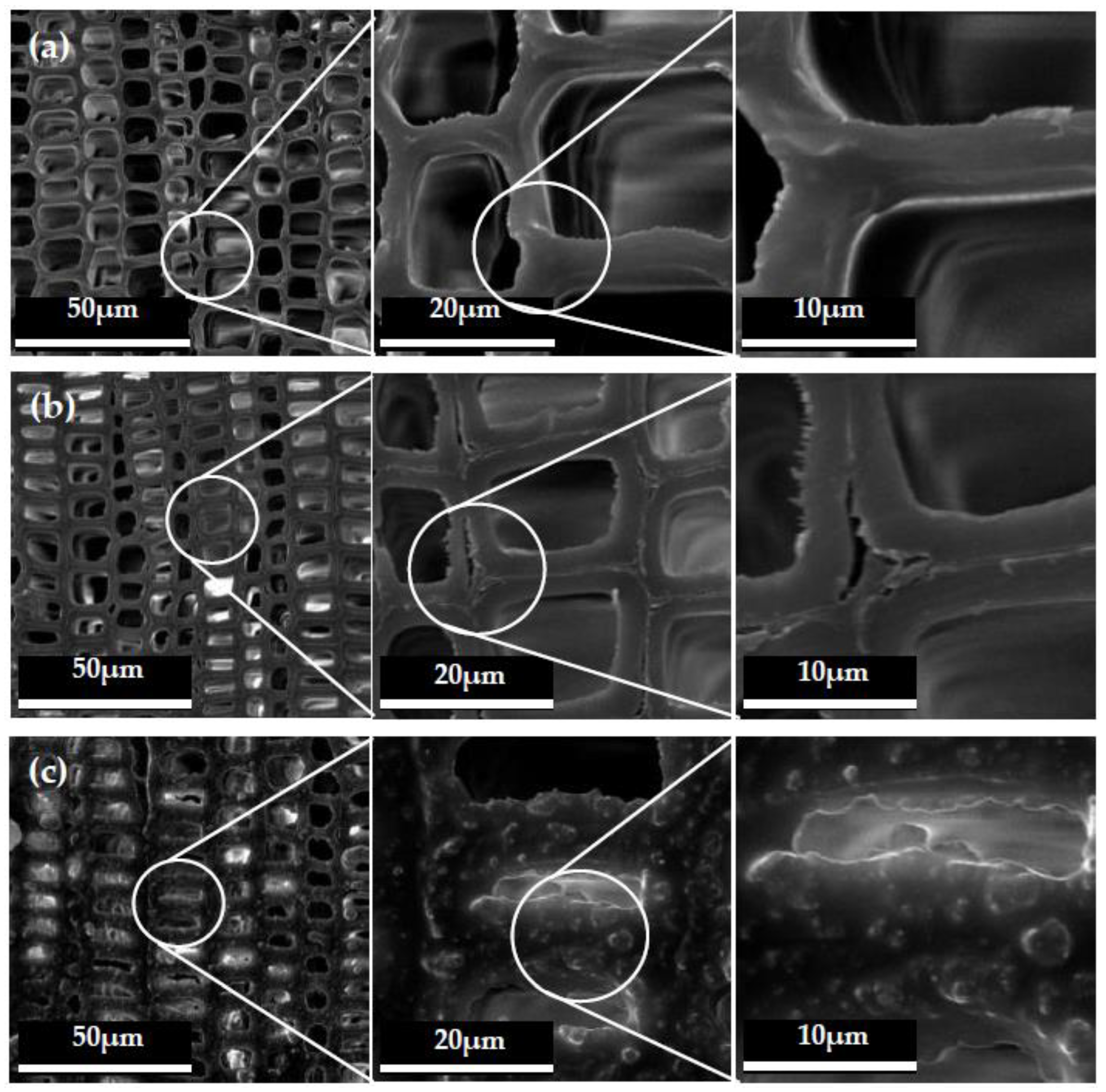
3.1. Microtopography of Hollow Mesoporous Microspheres and Wood Surface
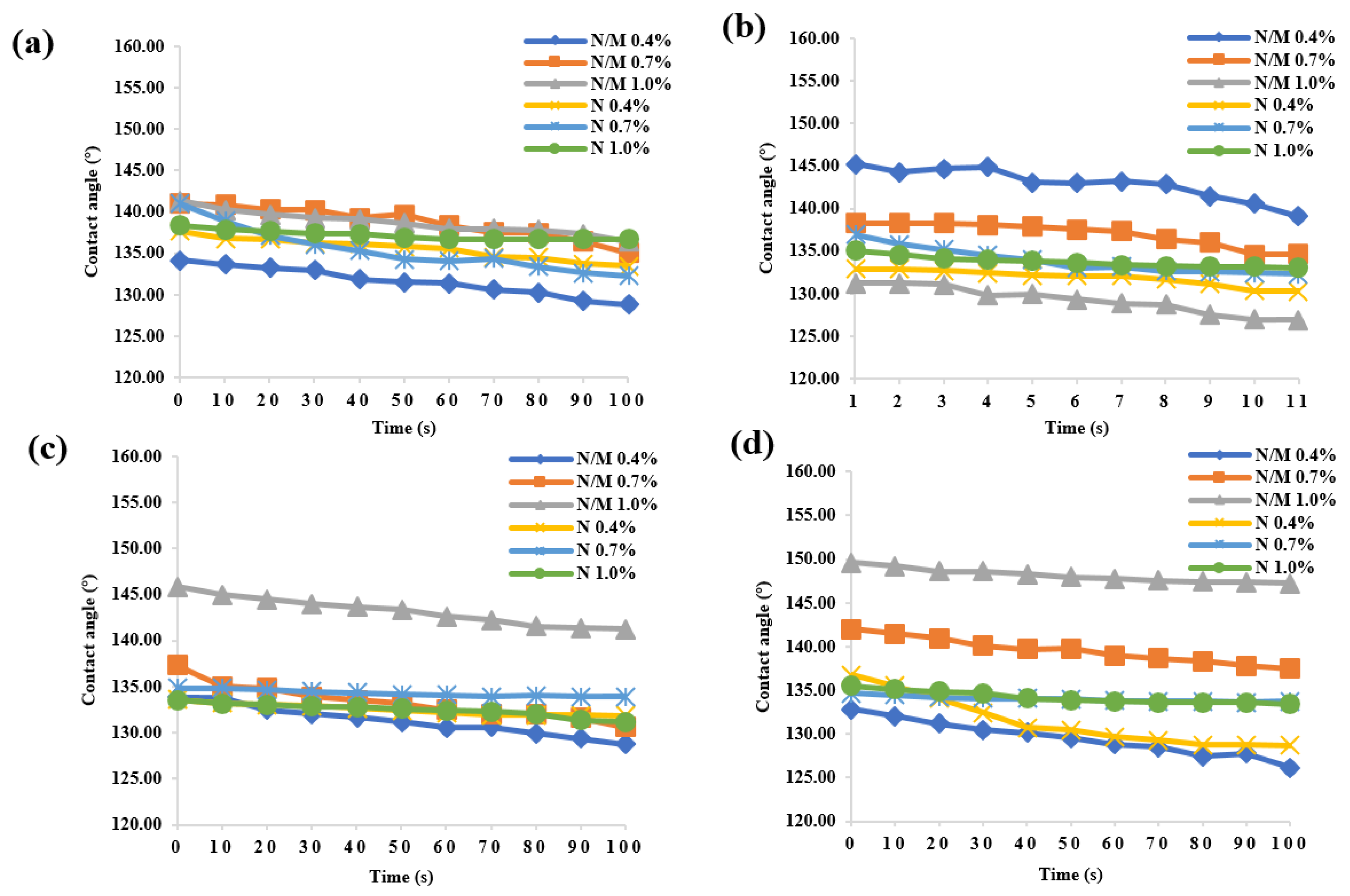
3.2. Superhydrophobicity of Wood Surface
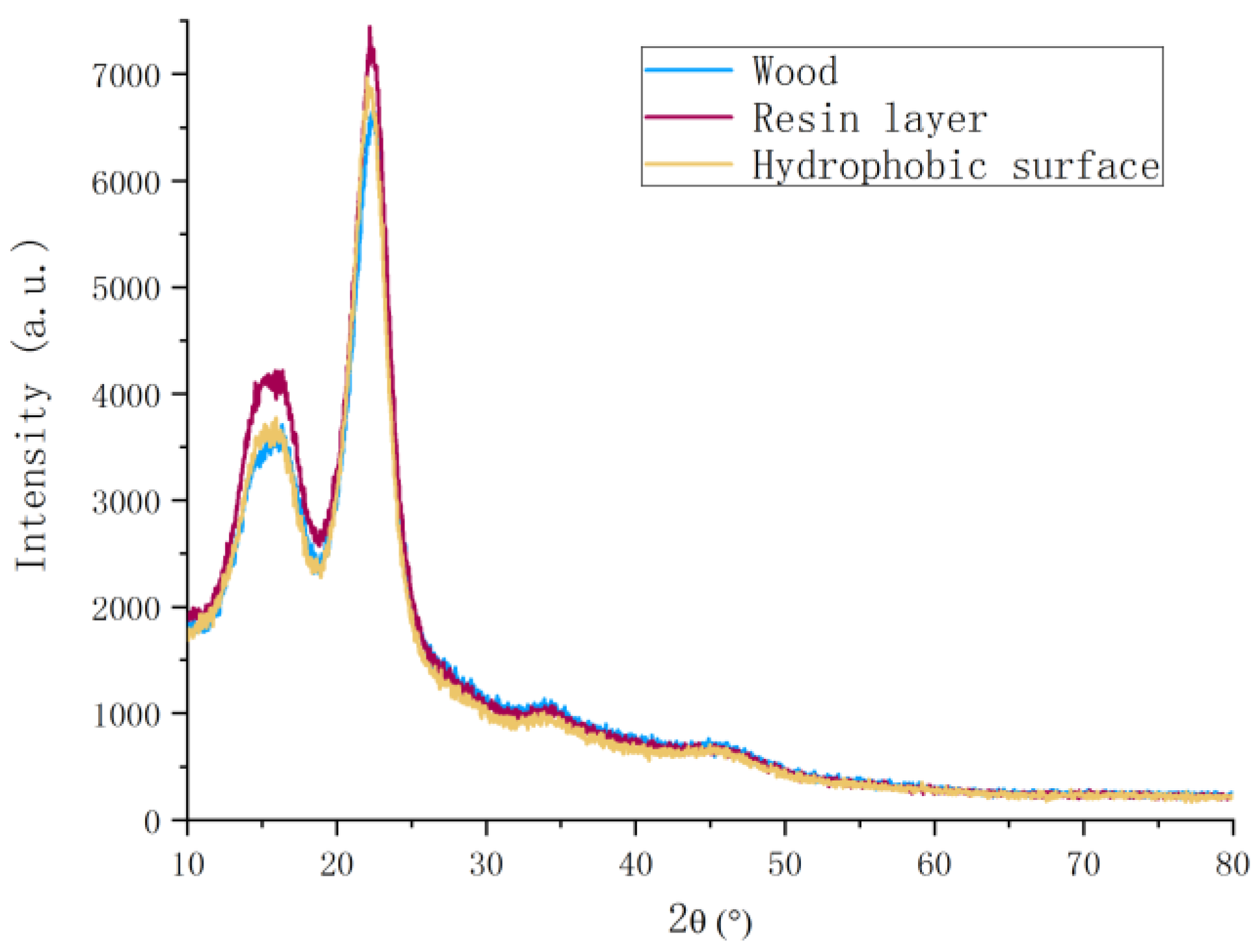
3.3. Chemical Structure Investigation of Wood
3.4. Thermostability of Wood
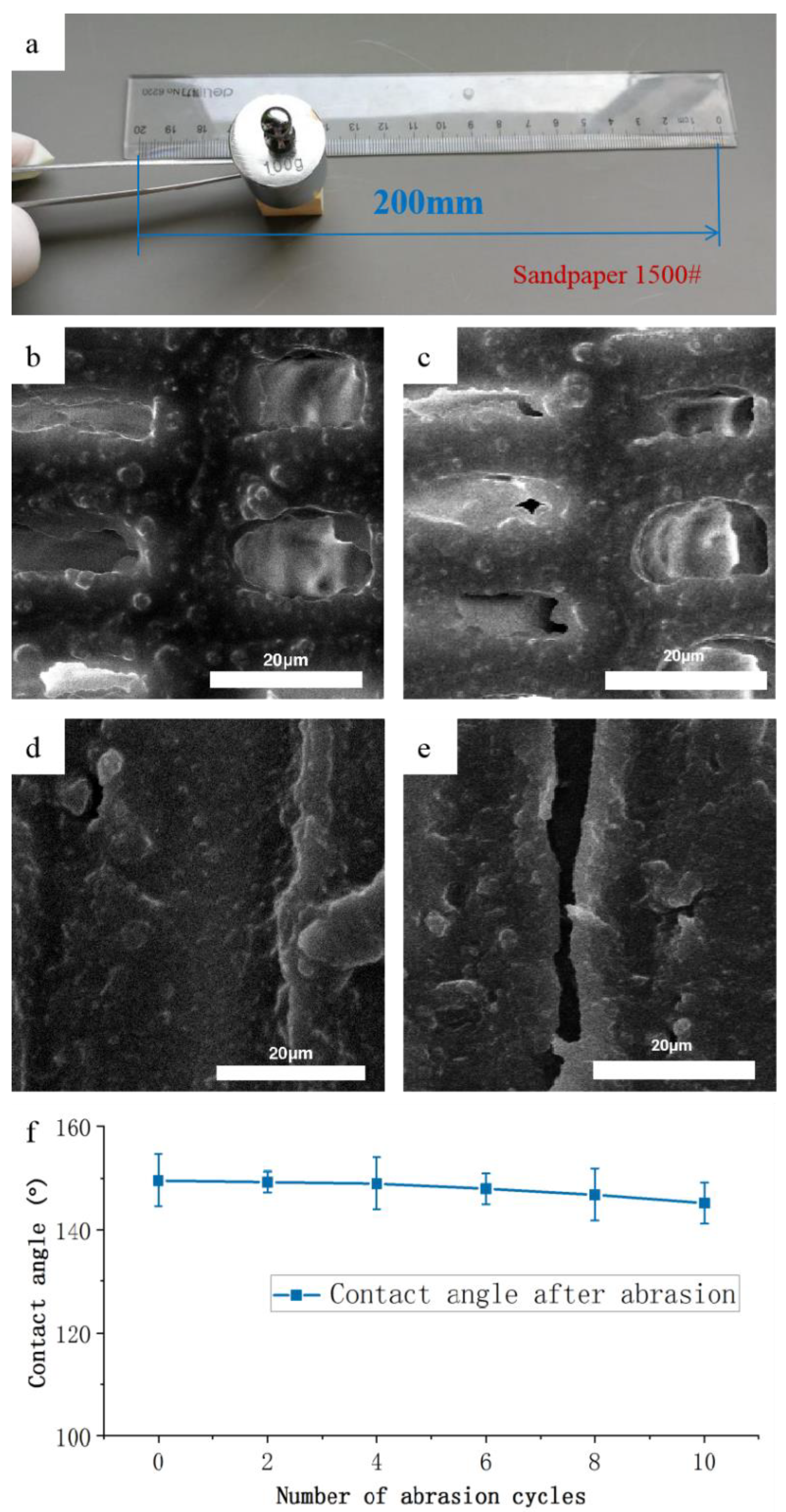
3.5. Mechanical Durability of the Hydrophobic Coatings
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mi, R.; Chen, C.; Keplinger, T.; Pei, Y.; He, S.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Dai, J.; Hitz, E.; Yang, B.; et al. Scalable aesthetic transparent wood for energy efficient buildings. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Latib, H.; Liat, L.C.; Ratnasingam, J.; Law, E.L.; Azim, A.A.A.; Mariapan, M.; Natkuncaran, J. Suitability of Paulownia Wood from Malaysia for Furniture Application. Bioresources 2020, 15, 4727–4737. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Luo, W.; Ciesielski, P.N.; Fang, Z.; Zhu, J.Y.; Henriksson, G.; Himmel, M.E.; Hu, L. Wood-Derived Materials for Green Electronics, Biological Devices, and Energy Applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 9305–9374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidon, T.E.; Wood, C.D.; Shupe, A.M.; Wang, Y.; Graves, M.; Liu, S. Biorefinery: Conversion of woody biomass to chemicals, energy and materials. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2008, 2, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laurichesse, S.; Averous, L. Chemical modification of lignins: Towards biobased polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1266–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, B.M.; Pereira, H.M. Wood Modification by Heat Treatment: A Review. Bioresources 2009, 4, 370–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Ma, E.; Cao, J. Dynamic moisture sorption and dimensional stability of furfurylated wood with low lignin content. Holzforschung 2020, 74, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.; Cao, J.; Mei, C. Improved Hydrophobicity and Dimensional Stability of Wood Treated with Paraffin/Acrylate Compound Emulsion through Response Surface Methodology Optimization. Polymers 2020, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, W. Improved Water Repellency and Dimensional Stability of Wood via Impregnation with an Epoxidized Linseed Oil and Carnauba Wax Complex Emulsion. Forests 2020, 11, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Chao, W.; Wang, N.; Ding, X.; Liu, F.; Yu, Q.; Yang, T.; Yang, Z.; et al. Wood-based composite phase change materials with self-cleaning superhydrophobic surface for thermal energy storage. Appl. Energy 2020, 261, 114481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Song, J.; Yang, C.; Kuang, Y.; Vellore, A.; Hitz, E.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, F.; Yao, Y.; et al. Strong and Superhydrophobic Wood with Aligned Cellulose Nanofibers as a Waterproof Structural Material. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Hu, P.; Li, X.; Hong, C.; Zhang, X.; Han, J. NiCo2S4 nanosheets on 3D wood-derived carbon for microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, N.; Zhao, T.; Li, B.; Ji, Y. Magnetic Properties of FeNi₃ Nanoparticle Modified Pinus radiata Wood Nanocomposites. Polymers 2019, 11, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mei, C.; Li, Y.; Duan, G.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Ma, C.; Jiang, S. Wood-Inspired Anisotropic Cellulose Nanofibril Composite Sponges for Multifunctional Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35513–35522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Xie, Y.; Ou, R.; Guo, C.; Hao, X.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Q. The influence of double-layered distribution of fire retardants on the fire retardancy and mechanical properties of wood fiber polypropylene composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 242, 118047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibier, M.; Lacoste, C.; Corn, S.; Pucci, M.F.; Quoc Khoi, T.; Haurie, L.; Sonnier, R. Flame retardancy of wood-plastic composites by radiation-curing phosphorus-containing resins. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 170, 108547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Hu, Y. Layer-by-layer Deposition of TiO2 Nanoparticles in the Wood Surface and its Superhydrophobic Performance. Bioresources 2016, 11, 4605–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Strawhecker, K.E.; Snyder, J.F.; Orlicki, J.A.; Reiner, R.S.; Rudie, A.W. Cellulose nanocrystals as a reinforcing material for electrospun poly(methyl methacrylate) fibers: Formation, properties and nanomechanical characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2488–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Eadula, S.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, K.; Grozdits, G.; Lvov, Y. Layer-by-layer nanoparticle coatings on lignocellulose wood microfibers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 292, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, S.; Militz, H.; Mai, C. Wood modification with alkoxysilanes. Wood Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Isobe, T.; Katsumata, K.-I.; Kameshima, Y.; Nakajima, A.; MacKenzie, K.J.D. Porous ceramics mimicking nature-preparation and properties of microstructures with unidirectionally oriented pores. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2011, 12, 064701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tshabalala, M.A.; Sung, L.-P. Wood surface modification by in-situ sol-gel deposition of hybrid inorganic-organic thin films. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2007, 4, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, A.; Evans, P.D. Etching of wood surfaces by glow discharge plasma. Wood Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janin, A.; Zaviska, F.; Drogui, P.; Blais, J.-F.; Mercier, G. Selective recovery of metals in leachate from chromated copper arsenate treated wastes using electrochemical technology and chemical precipitation. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 96, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chereddy, S.; Aguirre, J.; Dikin, D.; Wunder, S.L.; Chinnam, P.R. Gel Electrolyte Comprising Solvate Ionic Liquid and Methyl Cellulose. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Sakai, S.; Wu, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, N.; Huang, C.; Sun, S.; Zhang, M.; Umemura, K.; Yong, Q. Further Exploration of Sucrose-Citric Acid Adhesive: Investigation of Optimal Hot-Pressing Conditions for Plywood and Curing Behavior. Polymers 2019, 11, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, K.L.; Dong, Y.M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.F.; Li, J.Z. Bulk superhydrophobility of wood via in-situ deposition of ZnO rods in wood structure. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 383, 125240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.; Kong, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Semitransparent, durable superhydrophobic polydimethylsiloxane/SiO2 nanocomposite coatings on varnished wood. Holzforschung 2016, 70, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Sakai, S.; Wu, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, N.; Gui, C.; Zhang, M.; Umemura, K.; Yong, Q. Investigation of Synthesis Mechanism, Optimal Hot-Pressing Conditions, and Curing Behavior of Sucrose and Ammonium Dihydrogen Phosphate Adhesive. Polymers 2020, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.J.; Martin, A.E.; Conrad, C.M. An Empirical Method for Estimating the Degree of Crystallinity of Native Cellulose Using the X-ray Diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Liang, Y.; Hong, S.; Zuo, S.; Wu, Y.; Shi, J.; Cai, L.; Li, J.; Mao, H.; Ge, S.; et al. Novel Low-Temperature Chemical Vapor Deposition of Hydrothermal Delignified Wood for Hydrophobic Property. Polymers 2020, 12, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J.; Gan, L. The Antibacterial Properties and Safety of a Nanoparticle-Coated Parquet Floor. Coatings 2019, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, R.; Cao, Q.; Liang, Y.; Hong, S.; Xia, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Cai, L.; Sonne, C.; Le Quyet, V.; et al. High capacity oil absorbent wood prepared through eco-friendly deep eutectic solvent delignification. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Tham, N.; Thi Vinh Khanh, N.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, F.; Zheng, Z.; Che, W.; Xie, Y. Combustion behavior of poplar (Populus adenopoda Maxim.) and radiata pine (Pinus radiata Don.) treated with a combination of styrene-acrylic copolymer and sodium silicate. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2019, 77, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, N.; Lin, L.; Liu, F.; Pan, Q. Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

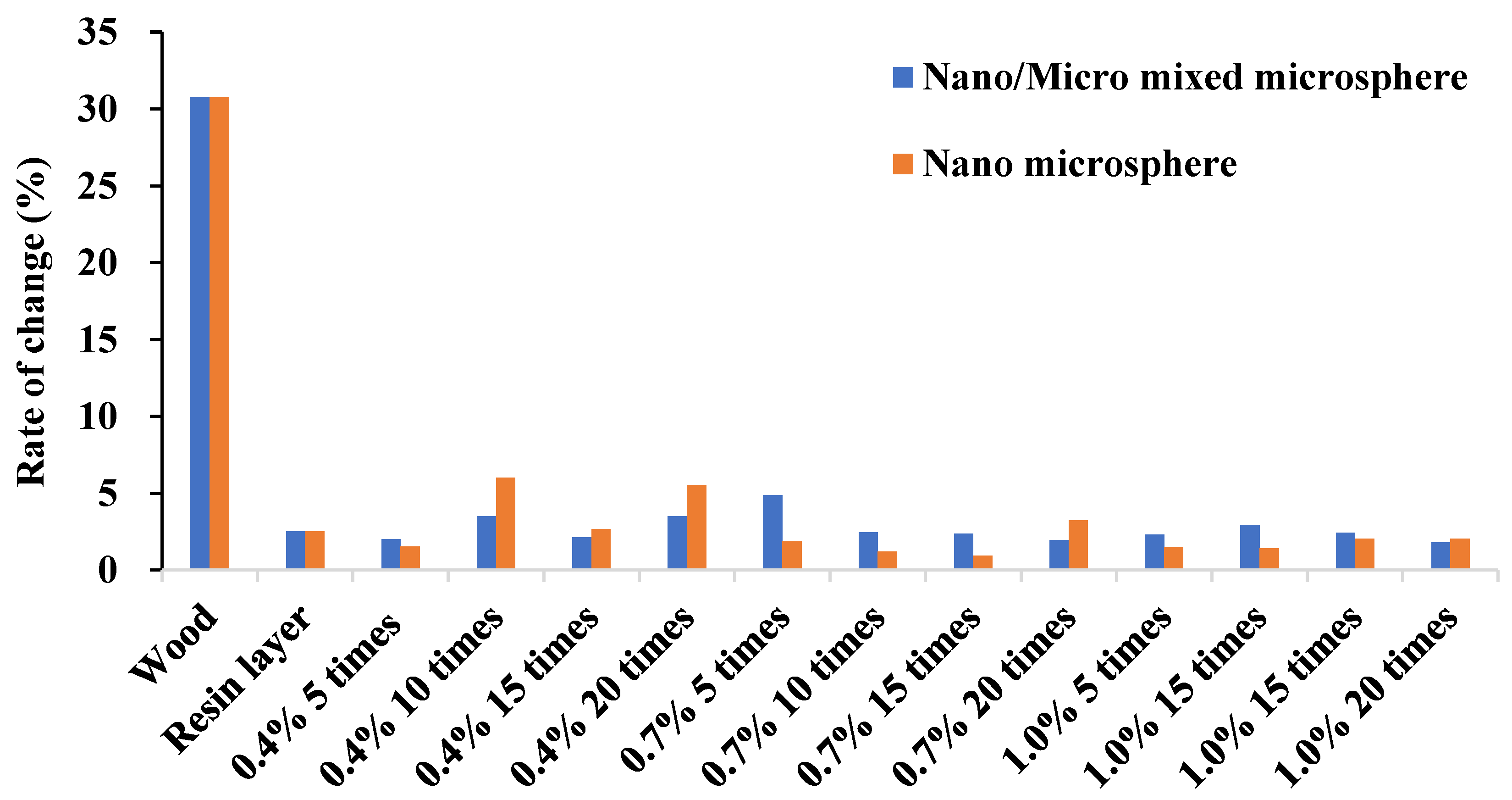


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, R.; Zuo, S.; Song, B.; Mao, H.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Cai, L.; Ge, S.; Lian, H.; Xia, C. Hollow Mesoporous Microspheres Coating for Super-Hydrophobicity Wood with High Thermostability and Abrasion Performance. Polymers 2020, 12, 2856. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122856
Yang R, Zuo S, Song B, Mao H, Huang Z, Wu Y, Cai L, Ge S, Lian H, Xia C. Hollow Mesoporous Microspheres Coating for Super-Hydrophobicity Wood with High Thermostability and Abrasion Performance. Polymers. 2020; 12(12):2856. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122856
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Rui, Shida Zuo, Beibei Song, Haiyan Mao, Zhenhua Huang, Yingji Wu, Liping Cai, Shengbo Ge, Hailan Lian, and Changlei Xia. 2020. "Hollow Mesoporous Microspheres Coating for Super-Hydrophobicity Wood with High Thermostability and Abrasion Performance" Polymers 12, no. 12: 2856. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122856
APA StyleYang, R., Zuo, S., Song, B., Mao, H., Huang, Z., Wu, Y., Cai, L., Ge, S., Lian, H., & Xia, C. (2020). Hollow Mesoporous Microspheres Coating for Super-Hydrophobicity Wood with High Thermostability and Abrasion Performance. Polymers, 12(12), 2856. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122856