Circular Intensity Differential Scattering for Label-Free Chromatin Characterization: A Review for Optical Microscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
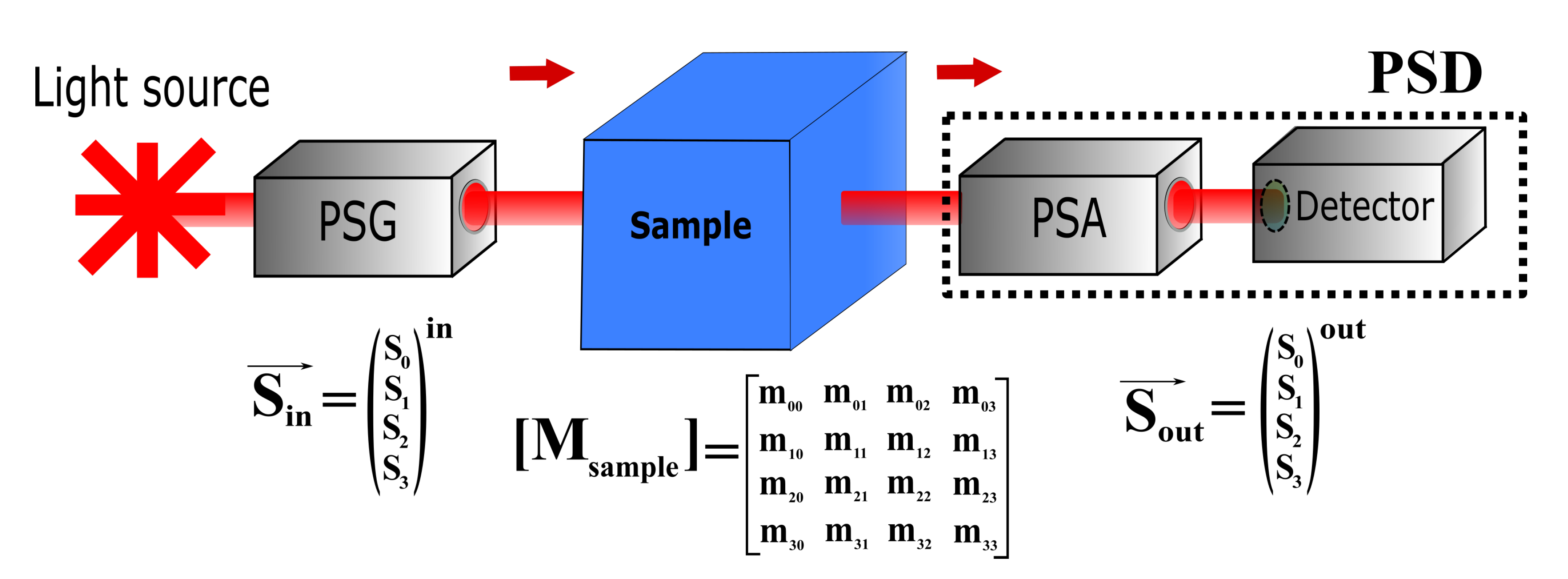
2. CIDS Effect
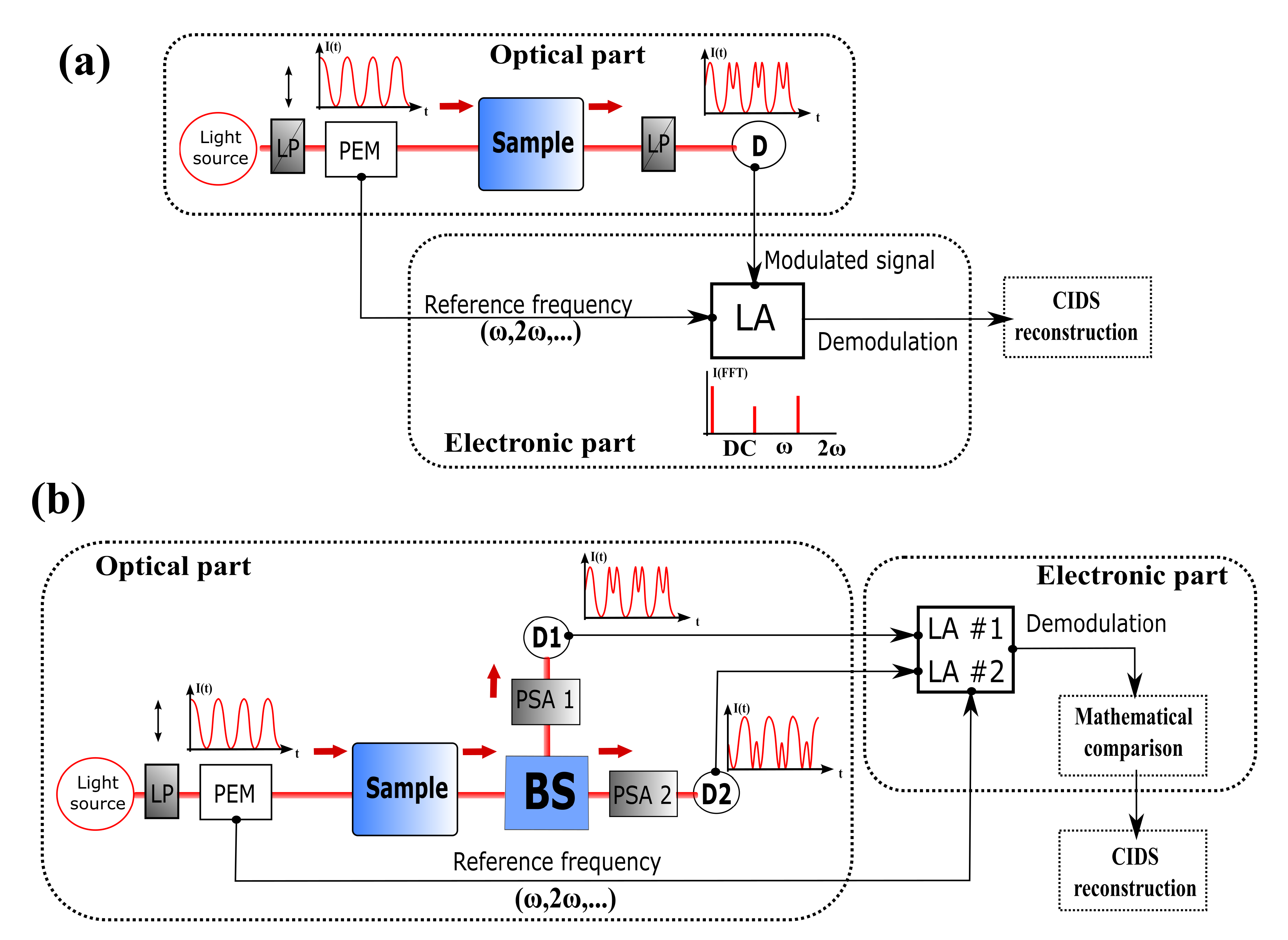
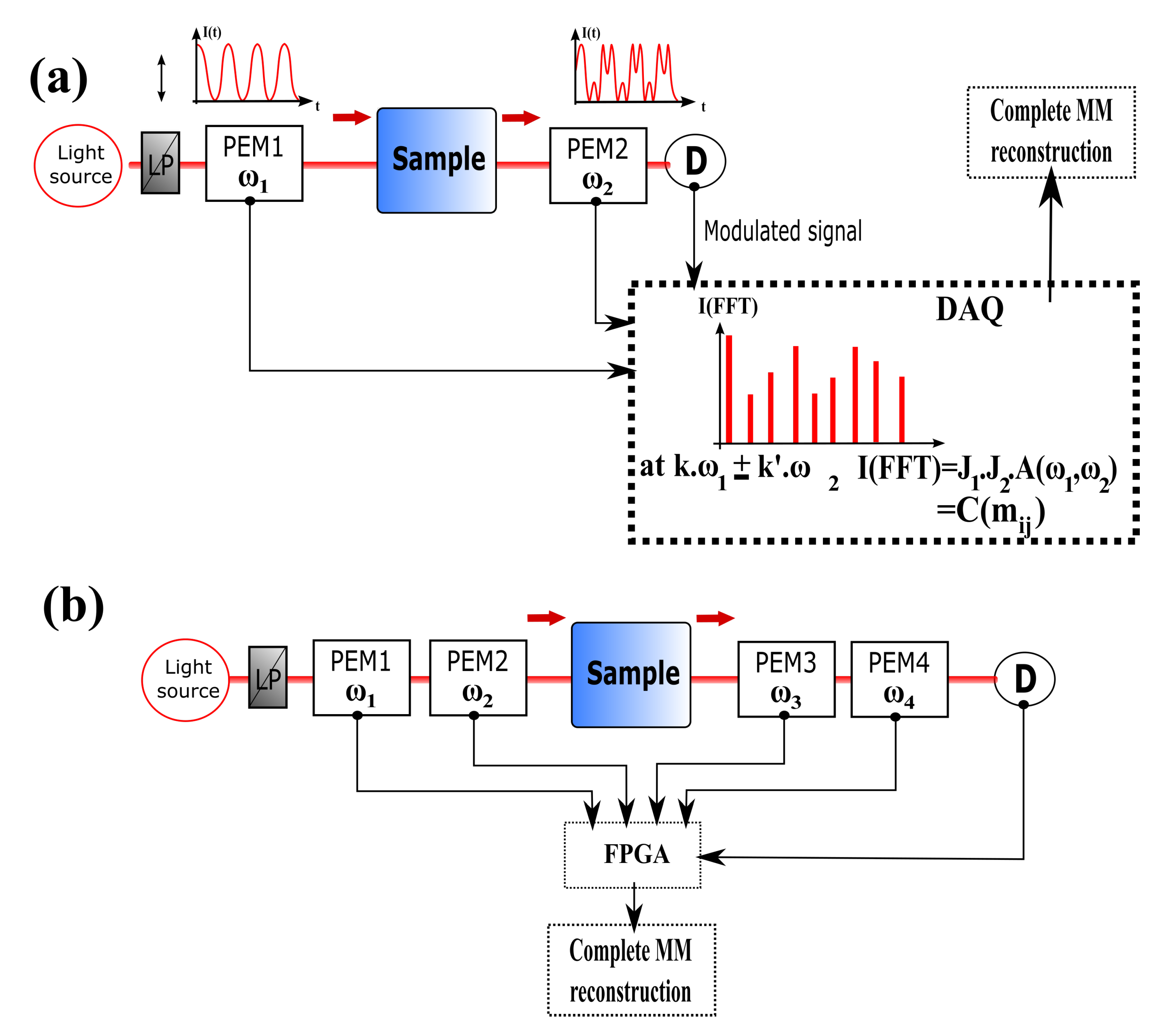
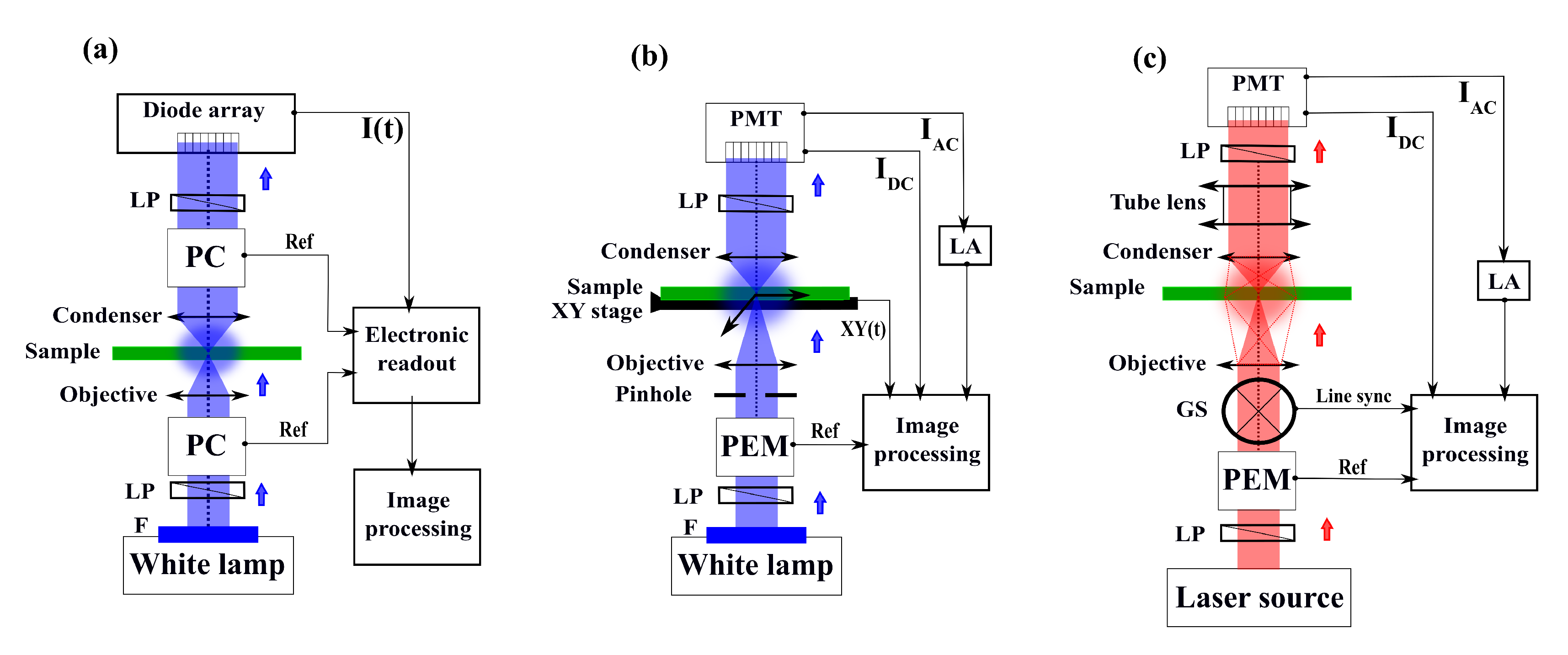
3. CIDS Experimental Architecture
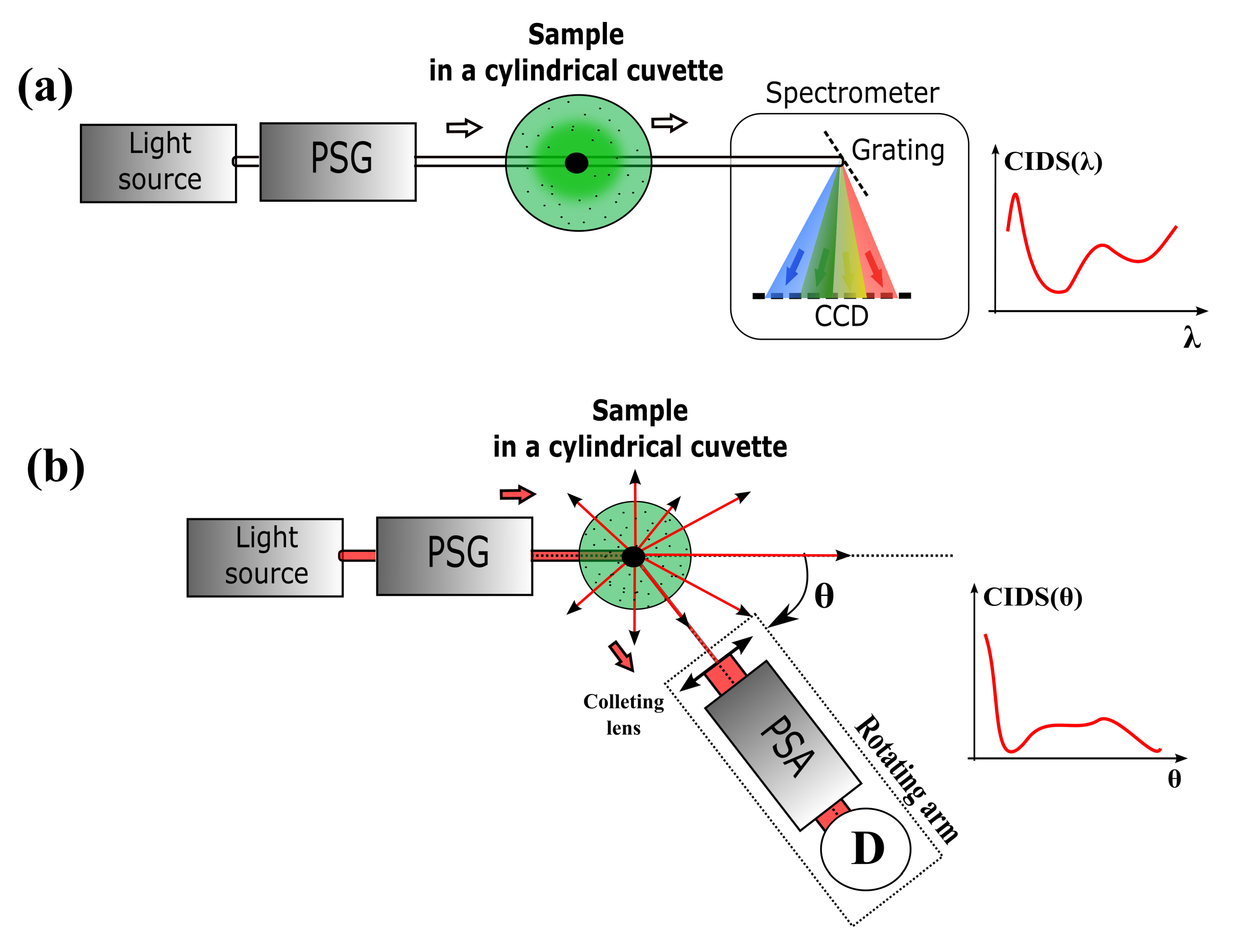
4. CIDS Microscopy Configuration
4.1. Single Point Measurements
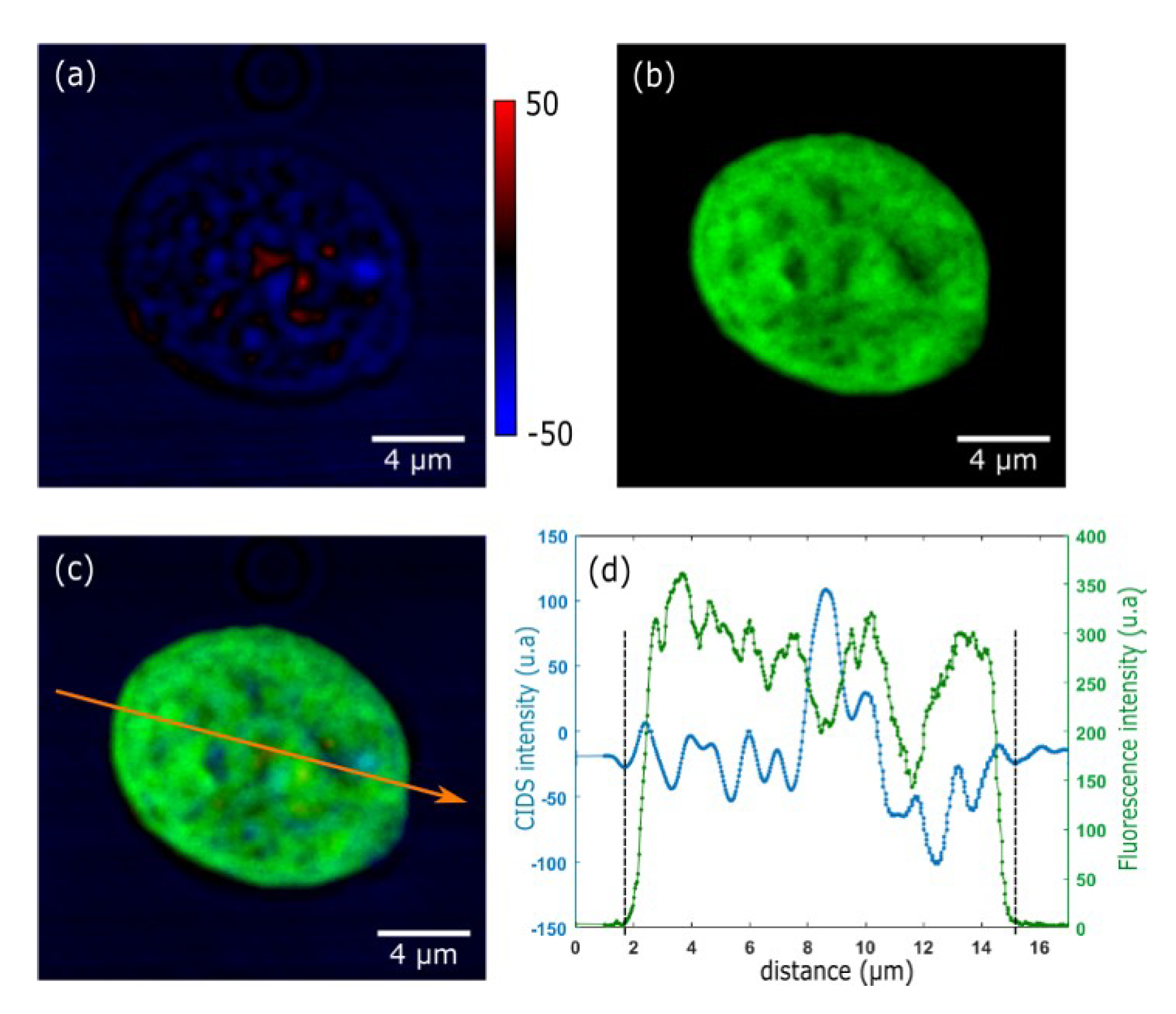
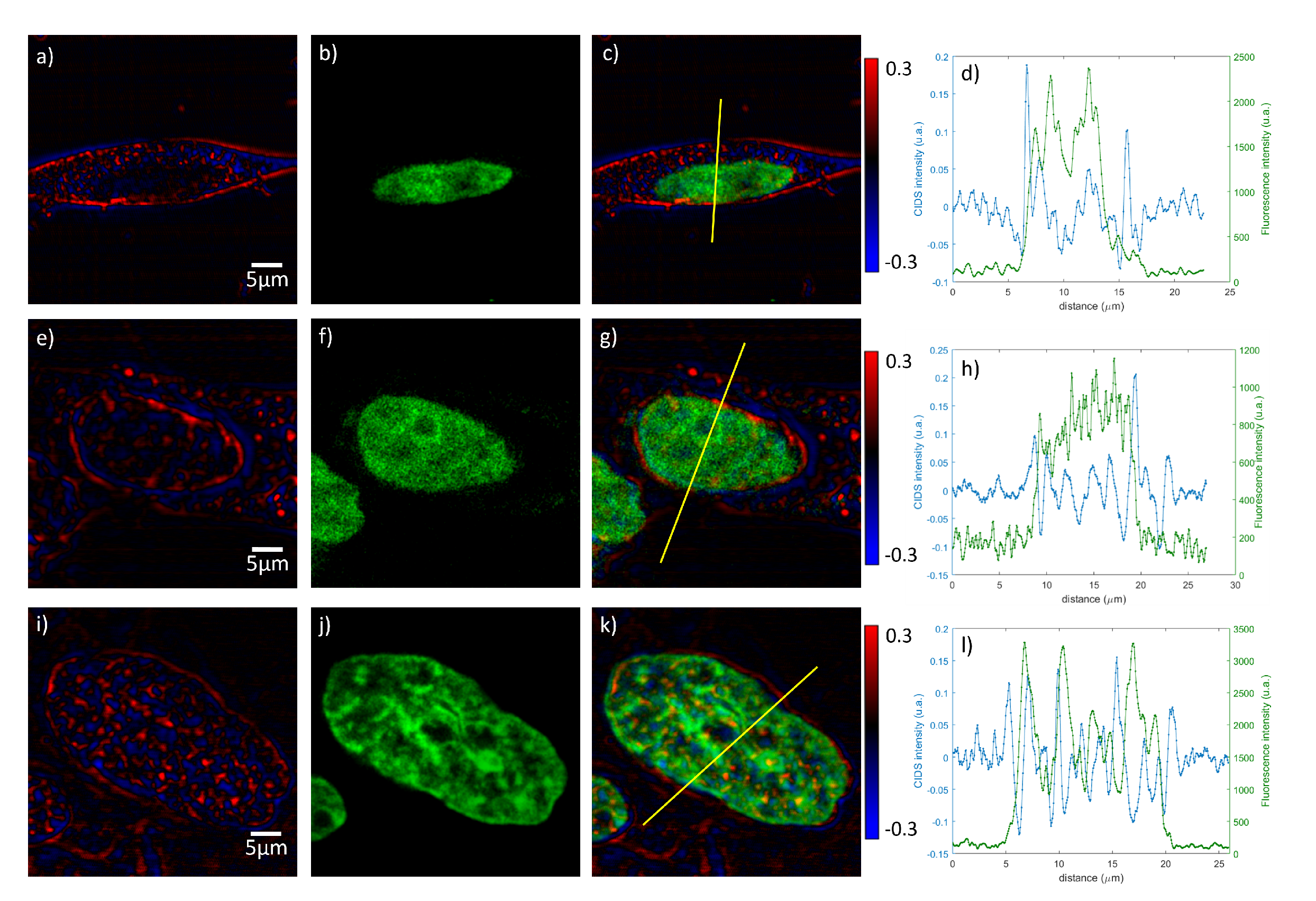
4.2. CIDS Optical Imaging Microscopy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD | Circular Dichroism |
| CIDS | Circular Intensity Differential Scattering |
| 2D | Two-Dimensional |
| 3D | Three-Dimensional |
| MM | Mueller Matrix |
| DDA | Discrete Dipole Approximation |
| SNR | Signal to Noise Ratio |
| PSG | Polarization States Generator |
| PSA | Polarization States Analyzer |
| PSD | polarization States Detector |
| DOP | Degree Of Polarization |
| DOLP | Degree Of Linear Polarization |
| DOCP | Degree Of Circular Polarization |
| PSF | Point Spread Function |
| LP | Linear Polarizer |
| HWP | Half-Waveplate |
| QWP | Quarter-Waveplate |
| PEM | Photoelastic Modulator |
| PC | Pockels Cell |
| LA | Lock-in Amplifier |
| DoA | Division of Amplitudes |
| LD | Linear Dichroism |
| LB | Linear Birefringence |
| CB | Circular Birefringence |
| FOV | Field Of View |
| ExM | Expansion Microscopy |
| SHG | Second Harmonic Generation |
| FLIM | Fluorescence-lifetime imaging microscopy |
| STED | STimulated Emission Depletion |
References
- Kornberg, R.; Lorch, Y. Twenty-five years of the nucleosome, fundamental particle of the eukaryote chromosome. Cell 1999, 98, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phan, H.; Deerinck, T.; Thor, A.; Ellisman, M.; O’Shea, C. ChromEMT: Visualizing 3d chromatin structure and compaction in interphase and mitotic cells. Science 2017, 357, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Schermelleh, L.; Ferrand, A.; Huser, T.; Eggeling, C.; Sauer, M.; Biehlmaier, O. Super-resolution microscopy demystified, Nature Cell Biology. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, F.; Chen, P.; Sun, D.; Wang, M.; Dong, L.; Liang, D.; Xu, R.; Zhu, P.; Li, G. Cryo-em study of the chromatin fiber reveals a double helix twisted by tetranucleosomal units. Science 2014, 344, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huard, S. Polarization of Light. In Polarization of Light, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, H. The foundations of optics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1948, 38, 661–662. [Google Scholar]
- Snik, F.; Craven-Jones, J.; Escuti, M.; Fineschi, S.; Harrington, D.; De Martino, A.; Mawet, M.; Riedi, J.; Tyo, J. An Overview of Polarimetric Sensing Techniques and Technology with Applications to Different Research Fields. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9099, Polarization: Measurement, Analysis, and Remote Sensing XI, Baltimore, MD, USA, 5–9 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga, O.; Canillas, A. Measurement of the optical activity of anisotropic samples by transmission Mueller matrix ellipsometry. EPJ Web Conf. 2010, 5, 03001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Hatit, S.; Foldyna, M.; De Martino, A.; Drévillon, B. Angle-resolved Mueller polarimeter using a microscope objective. Phys. Status Solidi 2008, 205, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aas, L.; Foldyna, M.; De Martino, A.; Drévillon, B. Near infra-red mueller matrix imaging system and application to retardance imaging of strain. Thin Solid Film. 2011, 519, 2737–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyo, J.; Goldstein, D.; Chenault, D.; Shaw, J. Review of passive imaging polarimetry for remote sensing applications. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anna, G.; Goudail, F.; Daniel, D. Polarimetric target detection in the presence of spatially fluctuating Mueller matrices. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 4590–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fade, J.; Panigrahi, S.; Carre, A.; Frein, L.; Hamel, C.; Bretenaker, F.; Ramachandran, H.; Alouini, M. Long-range polarimetric imaging through fog. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 3854–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tuchin, V. Polarized light interaction with tissues. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 071114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Hu, H.; Xiaobo, L.; Guan, Z.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, J.; Liu, T. An Angle of Polarization (AoP) Visualization Method for DoFP Polarization Image Sensors Based on Three Dimensional HSI Color Space. Sensors 2012, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Martino, A.; Pierangelo, A.; Novikova, T.; Validire, P.; Benali, A. Polarimetric Imaging for Cancer Diagnosis and Staging. Opt. Photonics News 2012, 23, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Novikova, T.; Validire, P.; Nazac, A.; Manhas, S.; Pierangelo, A.; De Martino, A.; Antonelli, M.R.; Ibrahim, B.H.; Cohen, H.; Benali, A.; et al. Polarimetric imaging of uterine cervix: A case study. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 14120. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; He, H.; Chang, J.; He, C.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Zeng, N.; Wu, J.; Ma, H. Mueller matrix microscope: A quantitative tool to facilitate detections and fibrosis scorings of liver cirrhosis and cancer tissues. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 071112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubreuil, M.; Babilotte, P.; Martin, L.; Sevrain, D.; Rivet, S.; Le Grand, Y.; Le Brun, G.; Turlin, B.; Le Jeune, B. Mueller matrix polarimetry for improved liver fibrosis diagnosis. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; He, H.; Li, X.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zeng, N.; He, Y.; Ma, H. Quantitatively differentiating microstructures of tissues by frequency distributions of Mueller matrix images. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 105009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.M.; Campbell, M.C.W. Confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy improvement by use of Mueller-matrix polarimetry. Opt. Lett. 2007, 27, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twietmeyer, K.; Chipman, R.; Elsner, A.; Zhao, Y.; VanNasdale, D. Mueller matrix retinal imager with optimized polarization conditions. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 21339–21354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lara, D.; Dainty, C. Axially resolved complete Mueller matrix confocal microscopy. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gratiet, A.; Dubreuil, M.; Rivet, S.; Le Grand, Y. Scanning Mueller polarimetric microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gratiet, A.; D’Amora, M.; Duocastella, M.; Marongiu, R.; Bendandi, A.; Giordani, S.; Bianchini, P.; Diaspro, A. Zebrafish structural development in Mueller-matrix scanning microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.Y.; Chipman, R. Interpretation of Mueller matrices based on polar decomposition. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1996, 13, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, C.; Huffman, D. Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. In Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nafie, L. Circular polarization spectroscopy of chiral molecules. J. Mol. Struct. 1995, 347, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, B.; Gill, P. Circular Dichroism Techniques: Biomolecular and Nanostructural Analyses-A Review. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 74, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, O.; Sancho-Parramon, J.; Nichols, S.; Maoz, B.M.; Canillas, A.; Bosch, S.; Markovich, G.; Kahr, B. Relation between 2D/3D chirality and the appearance of chiroptical effects in real nanostructures. Opt. Exp. 2011, 24, 2242–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, C. Circular Intensity Differential Scattering of Chiral Molecules. Ph.D. Thesis, Berkeley University, Berkeley, CA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante, C.; Tinoco, I.; Maestre, M. Circular differential scattering can be an important part of the circular dichroism of macromolecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 3568–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, M.; Price, N. The use of circular dichroism in the investigation of protein structure and function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 1, 349–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perry, R.; Hunt, A.; Huffman, D. Experimental determinations of Mueller scattering matrices for non-spherical particles. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 2700–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietz, S.; Belmont, A.; Nicolini, C. Differential scattering of circularly polarized light as a unique probe of polynucleosome super-structures. A simulation by multiple scattering of dipoles. Cell Biophys. 1983, 5, 163–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante, C.; Maestre, M.; Keller, D. Expressions for the interpretation of circular intensity differential scattering of chiral aggregates. Biopolymers 1985, 24, 1595–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaspro, A.; Bertolotto, M.; Vergani, L.; Nicolini, C. Polarized light scattering of nucleosomes and polynucleosomes-in situ and in vitro studies. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1991, 38, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, G. On the composition and resolution of streams of polarized light from different sources. Trans. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1992, 9, 339–416. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, J. Piezo-optical birefringence modulators: New use for a long-know effect. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1969, 59, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, O.; Freudenthal, J.; Wang, B.; Nichols, S.; Kahr, B. Circular dichroism with multiple photoelastic modulators. Chim. Oggi 2012, 30, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.; Park, Q.-H. Enhancement of Chiroptical Signals by Circular Differential Mie Scattering of Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre, M.; Salzman, G.; Tobey, R.; Bustamante, C. Circular dichroism studies on single Chinese hamster cells. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 5152–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippers, P.; Dekkers, H. Direct determination of absolute circular dichroism data and calibration of commercial instruments. Anal. Chem. 1981, 53, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, B.; Maestre, M. Experimental differential light-scattering correction to the circular dichroism of bacteriophage T2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wells, K.; Beach, D.; Keller, D.; Bustamante, C. An analysis of circular intensity differential scattering measurements: Studies on the sperm cell of Eledone cirrhosa. Biopolymers 1986, 25, 2043–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Merwe, W.; Li, Z.; Bronk, B.; Czege, J. Polarized light scattering for rapid observation of bacterial size changes. Biophys. J. 1997, 73, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shih, T.Y.; Fasman, G.D. Circular Dichroism Studies of Deoxyribonucleic Acid Complexes with Arginine-Rich Histone IV (f2al). Biochemistry 1970, 10, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinoco, I.J.; Maestre, M.F.; Bustamante, C.; Keller, D. Use of circularly polarized light to study biological macromolecules. Pure Appl. Chem. 1984, 56, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belmont, A.; Zietz, S.; Nicolini, C. Circular Intensity Differential Scattering (CIDS) Measurements in the Soft X-Ray Region of the Spectrum (∼16 eV to 500 eV). In Proceedings of the SPIE 1548, Production and Analysis of Polarized X Rays, San Diego, CA, USA, 21 July 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Livolant, F.; Mickols, W.; Maestre, M. Differential polarization microscopy (CD and linear dichroism) of polytene chromosomes and nucleoli from the dipteran sarcophaga footpad. Biopolymers 1988, 27, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, D.B.; Maestre, M.F.; McClain, W.M.; Hull, P.G.; Shi, Y.; Quinby-Hunt, M.S.; Hearst, J.E.; Hunt, A.J. Determination of the average orientation of DNA in the octopus sperm Eledone cirrhossa through polarized light scattering. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 5733–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Bustamante, C. Differential polarization imaging. IV. Images in higher Born approximations. Biophys. J. 1987, 59, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belmont, A.; Zietz, S.; Nicolini, C.; Nicolini, C. Differential scattering of circularly polarized light by chromatin modeled as a helical array of dielectric ellipsoids within the born approximation. Biopolymers 1985, 24, 1301–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarczyk, A.; Meng, H.; Ordu, O.; Noort, J.V.; Dekker, N.H. Chromatin fibers stabilize nucleosomes under torsional stress. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Draine, B.; Flatau, P. Discrete-dipole approximation for scattering calculations. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1994, 11, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkin, M.; Hoekstra, A. The discrete dipole approximation: An overview and recent developments. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2007, 106, 558–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuh, R. Arbitrary particle shape modeling in ddscat and validation of simulation results. In Proceedings of the DDA-Workshop, Bremen, Germany, 23 March 2007; pp. 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yurkin, M.A.; Hoekstra, A.G. The discrete-dipole-approximation code ADDA: Capabilities and known limitations. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2011, 112, 2234–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, A.; Bustamante, C. Applications of Circularly Polarized Radiation Using Synchrotron and Ordinary Sources. In Applications of Circularly Polarized Radiation Using Synchrotron and Ordinary Sources, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Antti, P.; Zubko, E.; Lumme, K.; Muinonen, K.; Yurkin, M.A.; Draine, B.; Rahola, J.; Hoekstra, A.; Shkuratov, Y. Comparison between discrete dipole implementations and exact techniques. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2007, 106, 417–436. [Google Scholar]
- Konokhova, A.I.; Yurkin, M.A.; Moskalensky, A.E.; Chernyshev, A.V.; Tsvetovskaya, G.A.; Chikova, E.D.; Maltsev, V.P. Light-scattering flow cytometry for identification and characterization of blood microparticles. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 057006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Lee, K.; El-Sayed, I.; El-Sayed, M. Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: Applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7238–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moskalensky, A.; Yurkin, M.A.; Konokhova, A.I.; Strokotov, D.; Nekrasov, V.M.; Chernyshev, A.V.; Tsvetovskaya, G.A.; Chikova, E.; Maltsev, V. Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: Applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 017001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.K.; El-Sayed, M.A. Plasmonic coupling in noble metal nanostructures. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 487, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, K.; Vitkin, I. Optical rotation and linear and circular depolarization rates in diffusively scattered light from chiral, racemic, and achiral turbid media. J. Biomed. Opt. 2002, 7, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, O.; Canillas, A.; Crusats, J.; El-Hachemi, Z.; Llorens, J.; Sorrenti, A.; Ribo, J.M. Flow Effects in Supramolecular Chirality. Isr. J. Chem. 2011, 51, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Campbel, A.; Leoni, J.; Cheng, Y.; Mullner, M.; Lakhwani, G. Circular Intensity Differential Scattering Reveals the Internal Structure of Polymer Fibrils. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 7547–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Simon, R. Characterization of Mueller matrices in polarization optics. Opt. Commun. 1992, 88, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.; Goldbeck, R.; Kliger, D.; Xie, X.; Dunn, R.; Simon, J. Time-resolved circular dichroism spectroscopy: Experiment, theory, and applications to biological systems. J. Phys. Chem. 1992, 96, 5243–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartigalongue, T.; Hache, F. Precise alignment of a longitudinal Pockels cell for time-resolved circular dichroism experiments. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2003, 20, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakberg, T. Modulated interference effects: Use of photoelastic modulators with lasers. Opt. Eng. 1995, 34, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, A.; Huffman, D. A new polarization-modulated light scattering instrument. Rev. Sci. Instruments 1973, 44, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, Y.; Ohmi, Y. Problems of CD spectrometers. 3. Critical comments on liquid crystal induced circular dichroism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 107, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, N.; Oka, K.; Dereniak, E. Snapshot mueller matrix spectropolarimetry. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 2100–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Ise, A. Channeled spectropolarimeter using a wavelength scanning laser and a channeled spectroscopic polarization state generator. In Proceedings of the International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–25 January 2011; Volume 8160. [Google Scholar]
- Alenin, A.; Tyo, J. Generalized channeled polarimetry. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2014, 31, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaspro, A.; Nicolini, C. Circular Intensity Differential Scattering and Chromatin-DNA Structure: A Combined Theoretical Approach. Cell Biophys. 1987, 10, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaspro, A.; Nicolini, C. Changes in DNA superhelical density Monitored by polarized light Scattering. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 177, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Bronk, B.; Druger, S.; Czégé, J.; Van de Merwe, W. Measuring diameters of Rod-Shaped bacteria in vivo with polarized light scattering. Biophys. J. 1995, 69, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jasperson, S.; Schnatterly, S.E. An Improved Method for High Reflectivity Ellipsometry Based on a New Polarization Modulation Technique. Rev. Sci. Instruments 1969, 40, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, E.; Baltzer, N.; von Allmen, M. Polarization modulation ellipsometry: A compact and easy handling instrument. Rev. Sci. Instruments 1985, 56, 2222–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, R. Arrangement of four photodetectors for measuring the state of polarization of light. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1985, 10, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, R.; De, A. Optimal beam splitters for the division-of-amplitude photo- polarimeter. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2003, 20, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jellison, G.; Modine, F.; Chen, C. Calibration procedures for ellipsometer a two-modulator generalized. In Proceedings of the SPIE 3754, Polarization: Measurement, Analysis, and Remote Sensing II, Denver, CO, USA, 25 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Nafie, L.; Stephens, P. Polarization scrambling using a photoelastic modulator: Application to circular dichroism measurement. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1975, 65, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellison, G.; Modine, F. Two-modulator generalized ellipsometry: Experiment and calibration. Appl. Opt. 1997, 65, 8184–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, R. Propagation of partially polarized light through anisotropic media with or without depolarization: A differential 4 × 4 matrix calculus. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1978, 68, 1756–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schellman, R.; Jensen, H. Optical spectroscopy of oriented molecules. Chem. Rev. 1987, 87, 1359–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafie, L. Dual Polarization Modulation: A Real-Time, Spectral-Multiplex Separation of Circular Dichroism from Linear Birefringence Spectral Intensities. Appl. Spectrosc. 2000, 54, 1634–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.; Bottiger, J.; Fry, E. Measurement of polarized light interactions via the Mueller matrix. Appl. Opt. 1980, 19, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga, O.; Freudenthal, J.; Wang, B.; Kahr, B. Mueller matrix polarimetry with four photoelastic modulators: Theory and calibration. Opt. Lett. 2012, 51, 6805–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alali, S.; Gribble, A.; Vitkin, I.A. Rapid wide-field Mueller matrix polarimetry imaging based on four photoelastic modulators with no moving parts. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 1038–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shcherbakov, M.; Vabishchevich, P.; Komarova, V.; Dolgova, T.; Panov, V.; Moshchalkov, V.; Fedyanin, A. Ultrafast Polarization Shaping with Fano Plasmonic Crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 253903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narushima, T.; Okamoto, H. Circular Dichroism Microscopy Free from Commingling Linear Dichroism via Discretely Modulated Circular Polarization. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, O.; El-Hachemi, Z.; Ossikovski, R. Snapshot circular dichroism measurements. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 6746–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre, M.; Katz, J. A circular dichroism microspectrophotometer. Biopolymers 1982, 21, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Schneider, M.J.; Rosenheck, K. Optical Activity of Biological Membranes: Scattering Effects and Protein Conformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 66, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reich, C.; Maestre, M.; Edmondson, S.; Gray, D. Circular dichroism and fluorescence-detected circular dichroism of deoxyribonucleic acid and poly[d(A-C).cntdot.d(G-T)] in ethanolic solutions: A new method for estimating circular intensity differential scattering. Biochemistry 1980, 19, 5208–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, G.; Griffith, J.K.; Gregg, C.T. Rapid identification of microorganisms by circular-intensity differential scattering. Applied and environmental microbiology. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 44, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finzi, L.; Bustamante, C.; Garab, G.; Juand, C. Direct observation of large chiral domains in chloroplast thylakoid membranes by differential polarization microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 8748–8752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, D.; Bustamante, C. Theory of the interaction of light with large inhomogeneous molecular aggregates. II. Psi-type circular dichroism. J. Chem. Phys. 1986, 84, 2972–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Ulibarri, L.; Keller, D.; Maestre, M.; Bustamante, C. The psi-type circular dichroism of large molecular aggregates. III. Calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 1986, 84, 2981–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garab, G.; Wells, S.; Finzi, L.; Bustamante, C. Helically organized macroaggregates of pigment-protein complexes in chloroplasts: Evidence from circular intensity differential scattering. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 5839–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patty, C.; ten Kate, I.; Jan Buma, W.; van Spanning, R.; Steinbach, G.; Ariese, F.; Snik, F. Circular spectropolarimetric sensing of vegetation in the field: Possibilities for the remote detection of extraterrestrial life. Astrobiology 2019, 19, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livolant, F.; Leforestier, A. Condensed phases of DNA: Structures and phase transitions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1996, 21, 1115–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaspro, A.; Radicchi, G.; Nicolini, C. Polarized light scattering: A biophysical method for studying bacterial cells. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1995, 42, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolini, C.; Vergani, L.; Diaspro, A.; Scelza, P. Native Chromatin and damage induced by nuclease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 155, 2981–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hielscher, A.; Eick, A.; Mourant, J.; Shen, D.; Freyer, J.P.; Bigio, I. Diffuse backscattering Mueller matricesof highly scattering media. Opt. Express 1997, 1, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Lu, J.; Brock, R.; McCornell, T.; Ojeda, J.; Jacobs, K.; Hu, X. Angle-resolved Mueller matrix study of light scattering by B-cells at three wavelengths of 442, 633, and 850 nm. J. Biomed. Opt. Express 2007, 12, 034032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, S.; Deshpande, A.; Farrahi, T.; Cambria, T.; Quang, T.; Majeski, J.; Na, Y.; Zervakis, M.; Livanos, G.; Giakos, G. Label-free discrimination of lung cancer cells through mueller matrix decomposition of diffuse reflectance imaging. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 40, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pérez, A.; Gutiérrez-Saiz, O.; Fernández-Luna, J.; Moreno, F.; Saiz, J. Polarimetric detection of chemotherapy-induced cancer cell death. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oldenbourg, R.; Torok, P. Point-spread functions of a polarizing microscope equipped with high -numerical-aperture lenses. Appl. Opt. 2019, 39, 6325–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, A.; Woerdman, J. Role of spatial coherence in polarization tomography. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 1599–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foreman, M.; Romero, C.; Torok, P. Determination of the three-dimensional orientation of single molecules. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.; Yew, E.; Sheppard, C. Polarization conversion in confocal microscopy with radially polarized illumination. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 2147–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, C.; Le Gratiet, A.; Diaspro, A. Factorization of the coherency matrix of polarization optics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2018, 35, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, C.; Castello, M.; Diaspro, A. Three-dimensional polarization algebra. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2016, 33, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, D.; Bustamante, C.; Maestre, M.; Tinoco, I. Imaging of optically active biological structures by use of circularly polarized light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Keller, C.; Bustamante, C. Differential Polarization Imaging I: Theory and Applications. Polariz. Spectrosc. Ordered Syst. 1987, 242, 313–356. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Ulibarri, L.; Bustamante, C. Differential Polarization Imaging. II. Symmetry Properties and Calculations. Biophys. J. 1987, 52, 929–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beach, D.; Bustamante, C.; Wells, K.; Foucart, K. Differential polarization imaging. III. Theory Confirmation. Patterns of polymerization of hemoglobin S in red blood sickle Cells. Biophys. J. 1987, 52, 947–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheppard, C.; Shotton, D. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. In Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy, 1st ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Finzi, L.; Ulibarri, L.; Bustamante, C. Differential polarization imaging. V. Numerical aperture effects and the contribution of preferential scattering and absorption to the circular dichroism images. Biophys. J. 1987, 59, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mickols, W.; Bustamante, C.; Maestre, M.; Tinoco, I.; Embury, S. Differential polarization microscopy: A new imaging technique. Nat. Biotechnol. 1985, 3, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickols, W.; Maestre, M.; Tinoco, I.; Embury, S. Visualization of oriented hemoglobin S in individual erythrocytesby differential extinction of polarized light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 6527–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beach, D.; Wells, K.; Husher, F.; Bustamante, C. Differential polarization microscope using an image dissector camera and phase-lock detection. Rev. Sci. Instruments 1987, 58, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickols, W.; Maestre, M. Scanning differential polarization microscope: Its use to image linear and circular differential scattering. Rev. Sci. Instruments 1988, 59, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Kornfield, J. Polarization modulation laser scanning microscopy: A powerful tool to image molecular orientation and order. Rev. Sci. Instruments 1994, 65, 2823–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garab, G.; Galajda, P.; Pomozi, I.; Finzi, L.; Praznovszky, T.; Ormos, P.; van Amerongen, H. Alignment of biological microparticles by a polarized laser beam. Eur. Biophys. J. 2005, 34, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gratiet, A.; Pesce, L.; Oneto, M.; Marongiu, R.; Zanini, G.; Bianchini, P.; Diaspro, A. Circular intensity differential scattering (CIDS) scanning microscopy to image chromatin-DNA nuclear organization. OSA Contin. 2018, 1, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mickols, W.; Maestre, M.; Tinoco, I. Differential polarization microscopy of changes in structure in spermatocyte nuclei. Nature 1987, 328, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, C.; Finzi, L.; Bustamante, C. Design and application of a computer-controlled confocal scanning differential polarization microscope. Rev. Sci. Instruments 1988, 59, 2399–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Onuki, H.; Yuri, M.; Ishizaka, S. Microscopic imaging of circular dichroism using a polarizing undulator. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 39, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntherland, J.C. Simultaneous Measurement of Circular Dichroism and Fluorescence Polarization Anisotropy. In Proceedings of the SPIE 4625, Clinical Diagnostic Systems: Technologies and Instrumentation, San Jose, CA, USA, 4 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach, G.; Pomozi, I.; Zsiros, O.; Pay, A.; Horvath, G.; Garab, G. Imaging fluorescence detected linear dichroism of plant cell walls in laser scanning confocal microscope. Cytom. A 2008, 73, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, S.; Shribak, M.; Oldenbourg, R. Polarized light imaging of birefringence and diattenuation at high resolution and high sensitivity. J. Opt. 2013, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freudenthal, J.; Hollis, E.; Kahr, B. Imaging chiroptical artifacts. Chirality 2009, 21, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantussi, F.; Fuso, F.; Allegrini, M.; Micali, N.; Occhiuto, I.; Scolaro, L.; Patane, S. Linear and circular dichroism in porphyrin J-aggregates probed by polarization modulated scanning near-field optical microscopy. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10874–10878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patty, C.; Luo, D.; Snik, F.; Ariese, F.; Jan, B.; ten Kate, I.; van Spanning, R.; Sparks, W.; Germer, T.; Garab, G.; et al. Imaging linear and circular polarization features in leaves with complete Mueller matrix polarimetry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2016, 1862, 1350–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
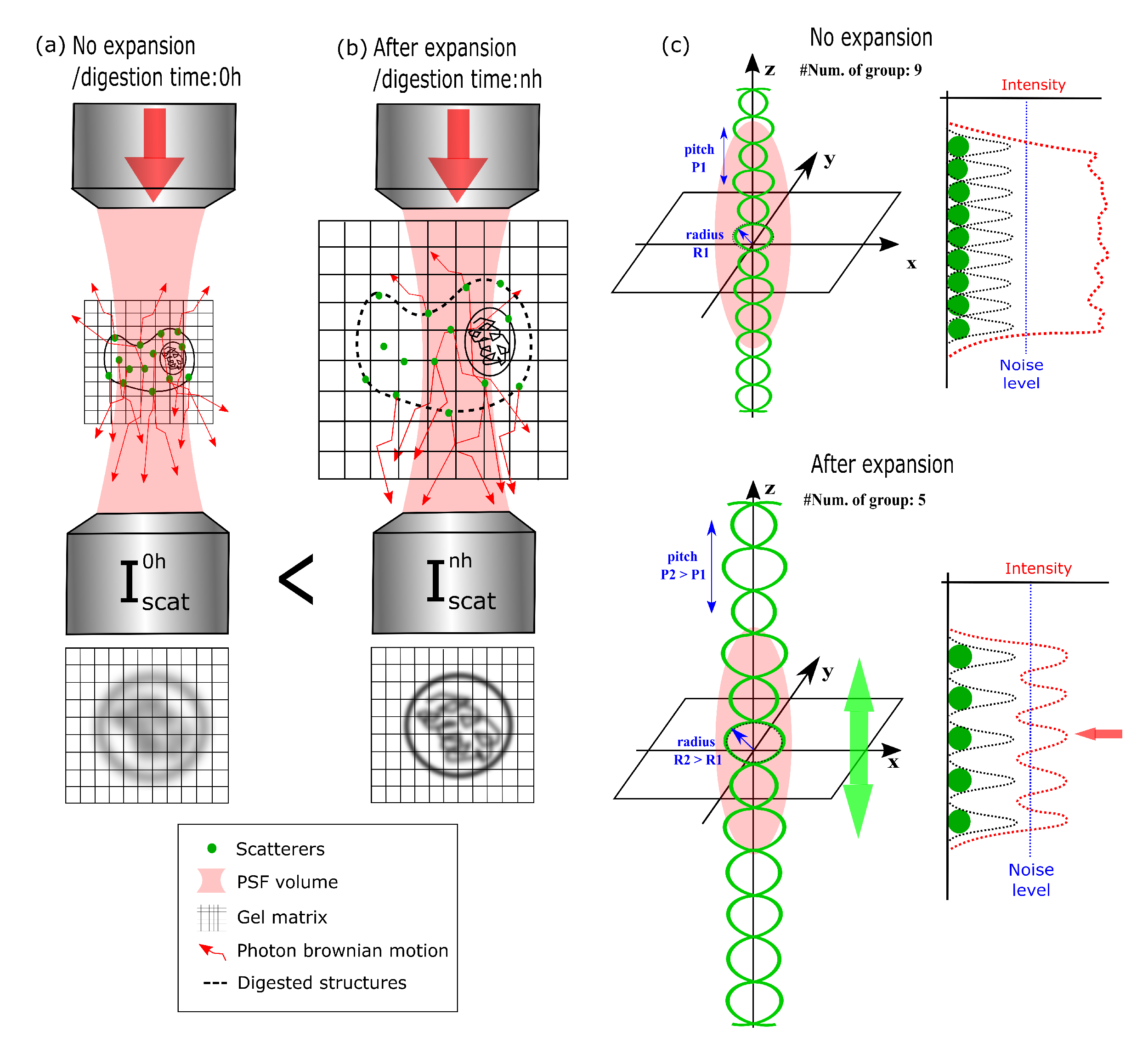
- Marongiu, R.; Le Gratiet, A.; Pesce, L.; Bianchini, P.; Diaspro, A. ExCIDS: A combined approach coupling Expansion Microscopy (ExM) and Circular Intensity Differential Scattering (CIDS) for chromatin-DNA imaging. OSA Contin. 2020, 3, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, N.; Darmanin, C.; Bleackley, M.R.; Parisi, K.; Cadenazzi, G.; Holmes, S.; Anderson, M.A.; Nugent, K.A.; Abbey, B. Ptychographic imaging of NaD1 induced yeast cell death. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 4964–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaspro, A.; Anthony, N.; Bianchini, N.; Cainero, I.; Di Bona, M.; Lanzano, L.; Le Gratiet, A.; Marongiu, R.; Oneto, M.; Pelicci, S.; et al. LIQUITOPY®: A liquid tunable microscope to study chromatin organization in the cell nucleus. Microsc. Microanal. Camb. Univ. Press 2018, 24, 1368–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Speed | Spectral Range | Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotors | ∼ Hz | Wide | Easy and simple Inexpensive | Precise alignment Electronic controls |
| PC | DC—1 GHz | 200 nm to 5 m | High optical quality Very fast modulation Compactness | Temperature control Residual stress Mathematical model Expensive |
| PEM | 20–84 kHz | 170 nm to 19 m | High optical quality High power handling Large acceptance angle Compactness | Mathematical model Expensive |
| Number of Element | Speed | Advantages | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 PEM | 4 | 100 ms | Simple and easy |
| 2 PEMs | 8 | 10 ms | No lock-in detection needed |
| 3 PEMs and 4 PEMs | 16 | 1 ms | No lock-in detection needed No moving parts Wide range of applications |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le Gratiet, A.; Marongiu, R.; Diaspro, A. Circular Intensity Differential Scattering for Label-Free Chromatin Characterization: A Review for Optical Microscopy. Polymers 2020, 12, 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102428
Le Gratiet A, Marongiu R, Diaspro A. Circular Intensity Differential Scattering for Label-Free Chromatin Characterization: A Review for Optical Microscopy. Polymers. 2020; 12(10):2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102428
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe Gratiet, Aymeric, Riccardo Marongiu, and Alberto Diaspro. 2020. "Circular Intensity Differential Scattering for Label-Free Chromatin Characterization: A Review for Optical Microscopy" Polymers 12, no. 10: 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102428
APA StyleLe Gratiet, A., Marongiu, R., & Diaspro, A. (2020). Circular Intensity Differential Scattering for Label-Free Chromatin Characterization: A Review for Optical Microscopy. Polymers, 12(10), 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102428






