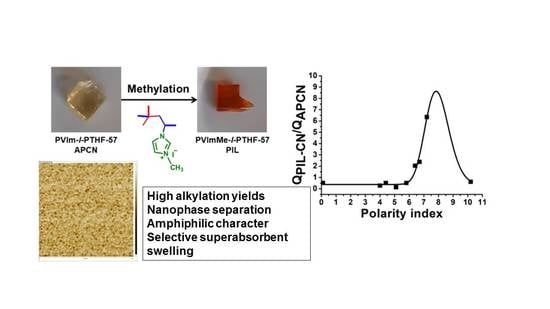
Nanoconfined Crosslinked Poly(ionic liquid)s with Unprecedented Selective Swelling Properties Obtained by Alkylation in Nanophase-Separated Poly(1-vinylimidazole)-l-poly(tetrahydrofuran) Conetworks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Methacrylate-Telechelic Poly(tetrahydrofuran)
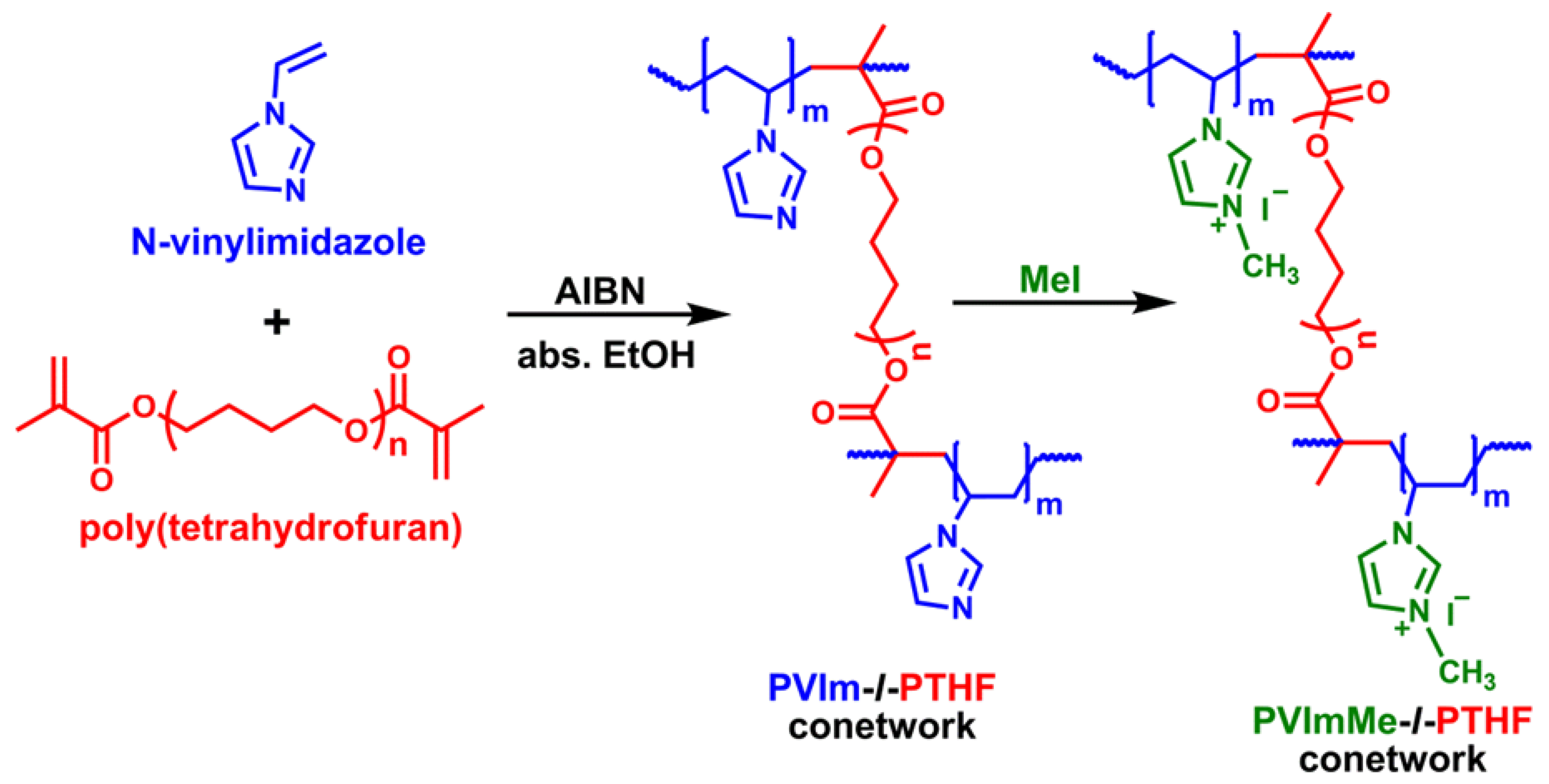
2.3. Synthesis of the PVIm-l-PTHF Polymer Conetworks
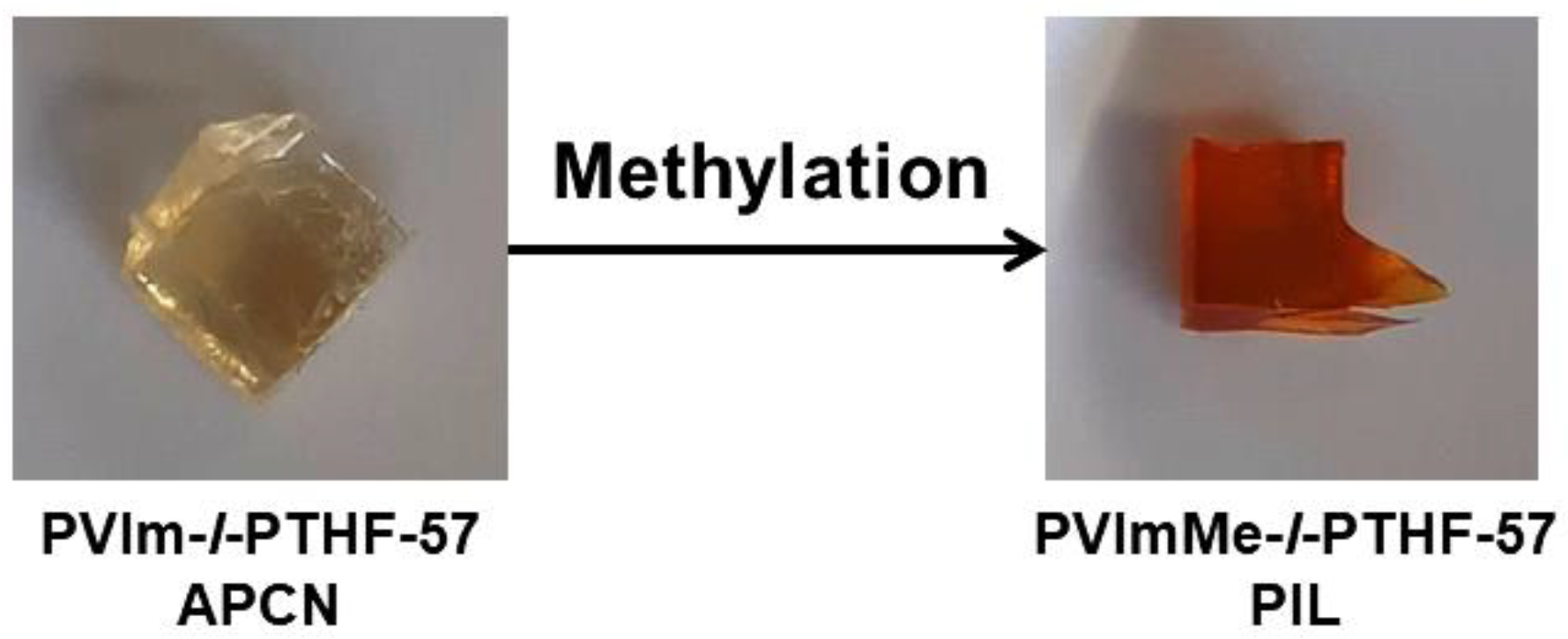
2.4. Alkylation of the Poly(1-vinylimidazole) with Methyl Iodide in the Conetworks
2.5. Elemental Analysis
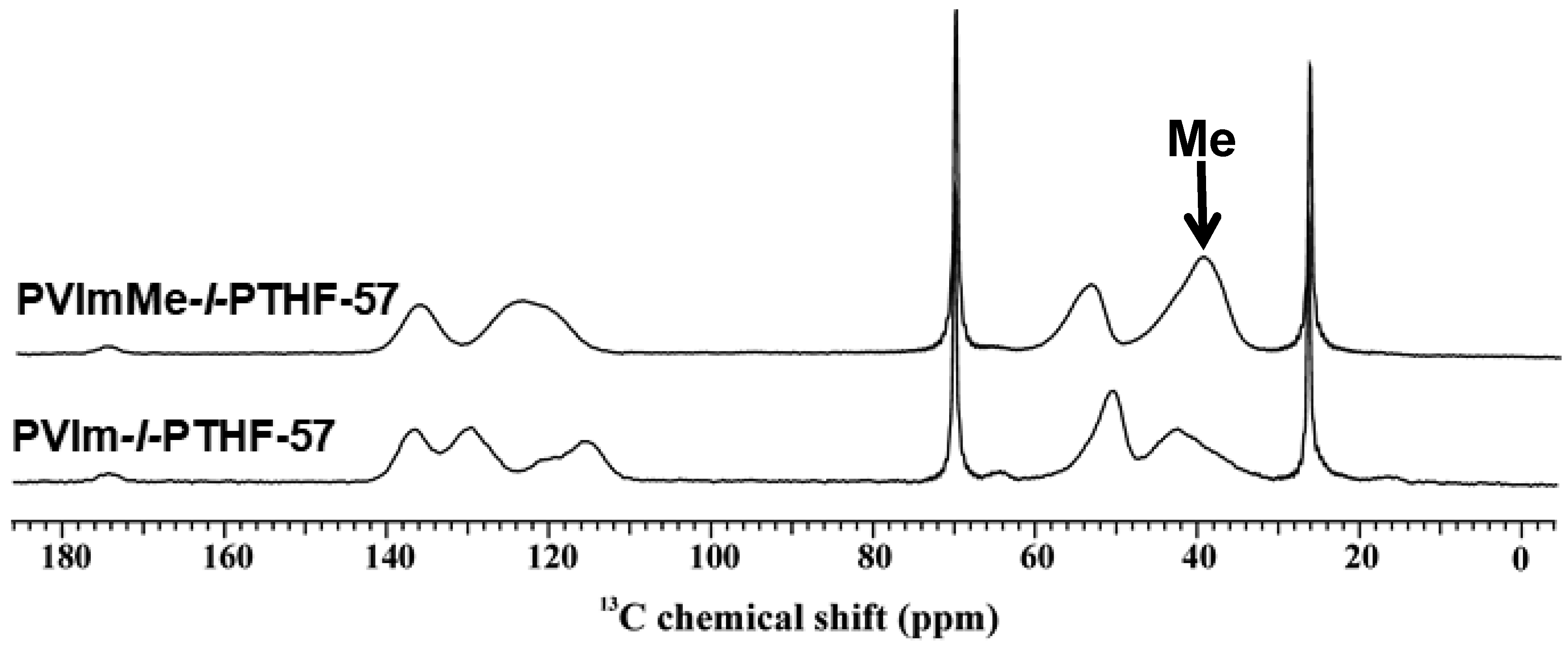
2.6. Solid-State NMR Measurements
2.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.8. Small-Angle X-ray Scattering
2.9. Atomic Force Microscopic Measurements
2.10. Swelling Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
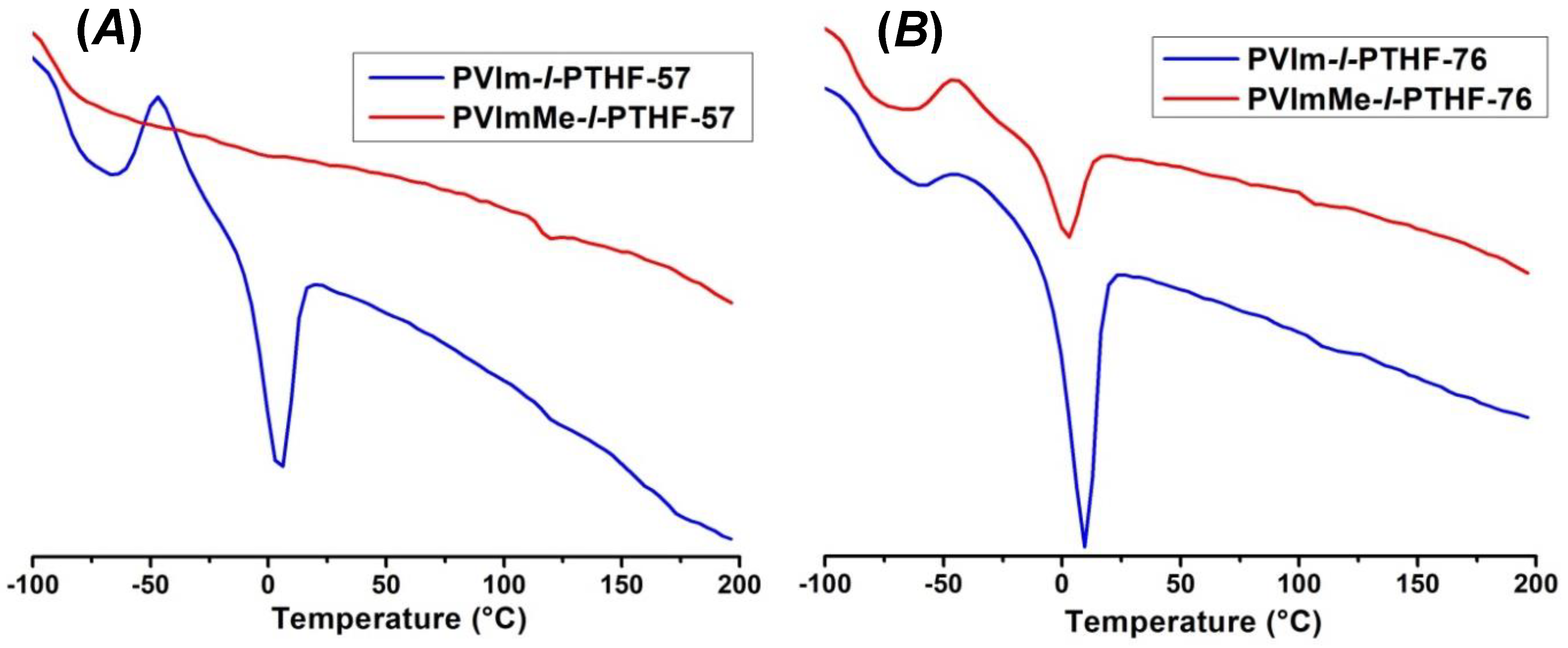
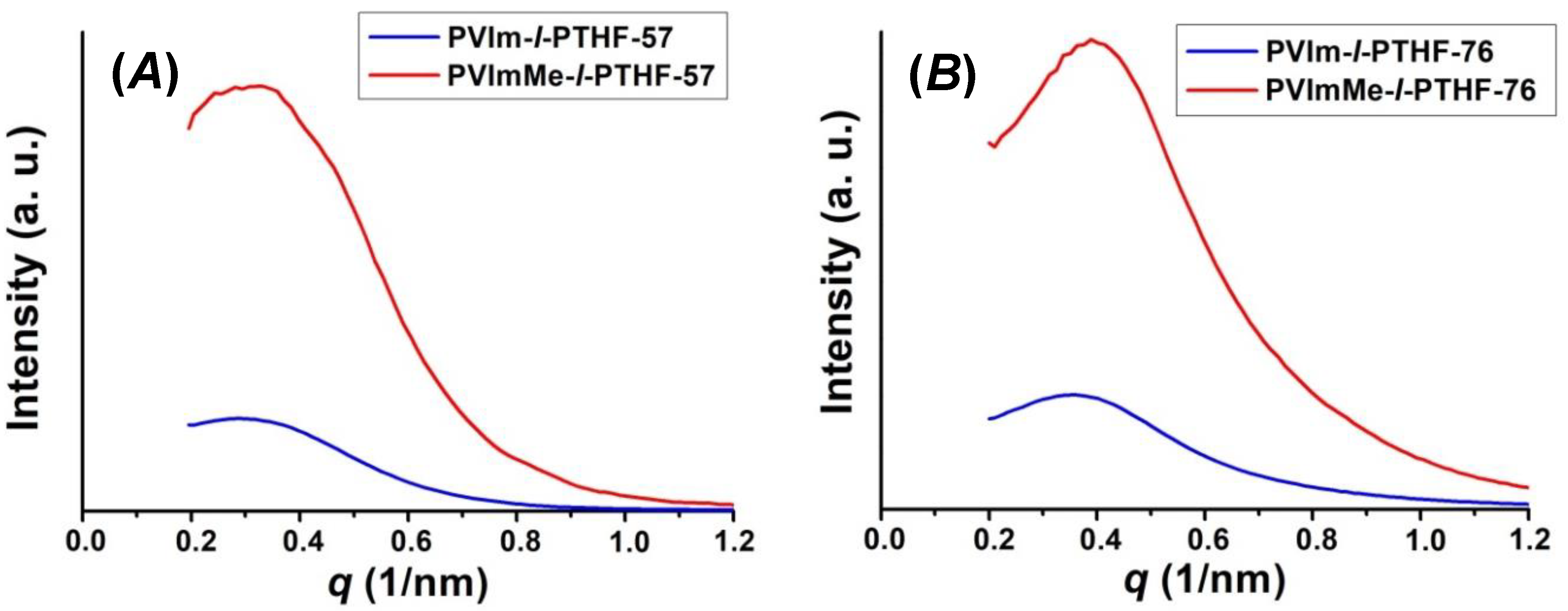
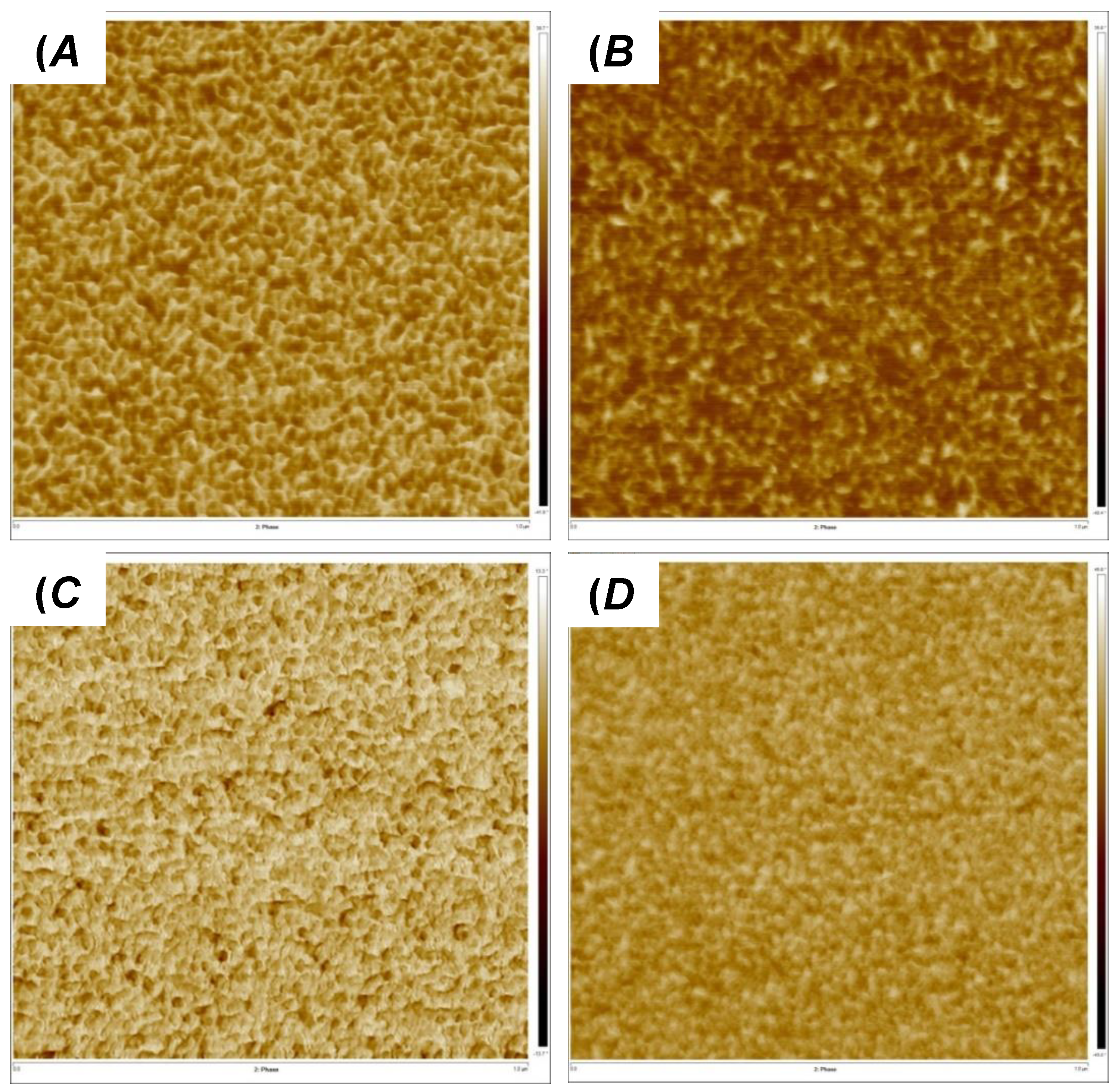
3.1. Synthesis of and Alkylation in PVIm-l-PTHF Conetworks and Structural Characterizations
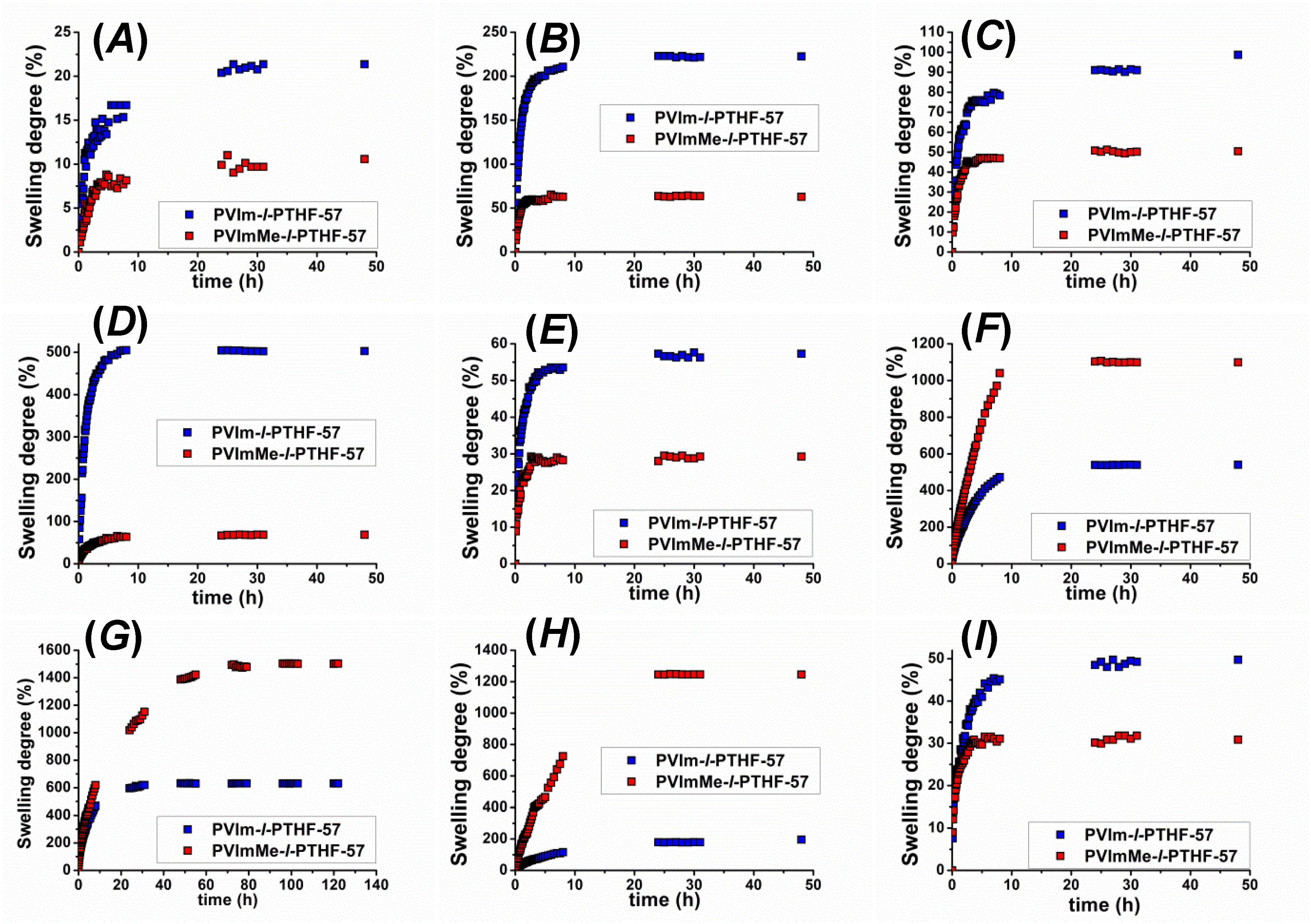
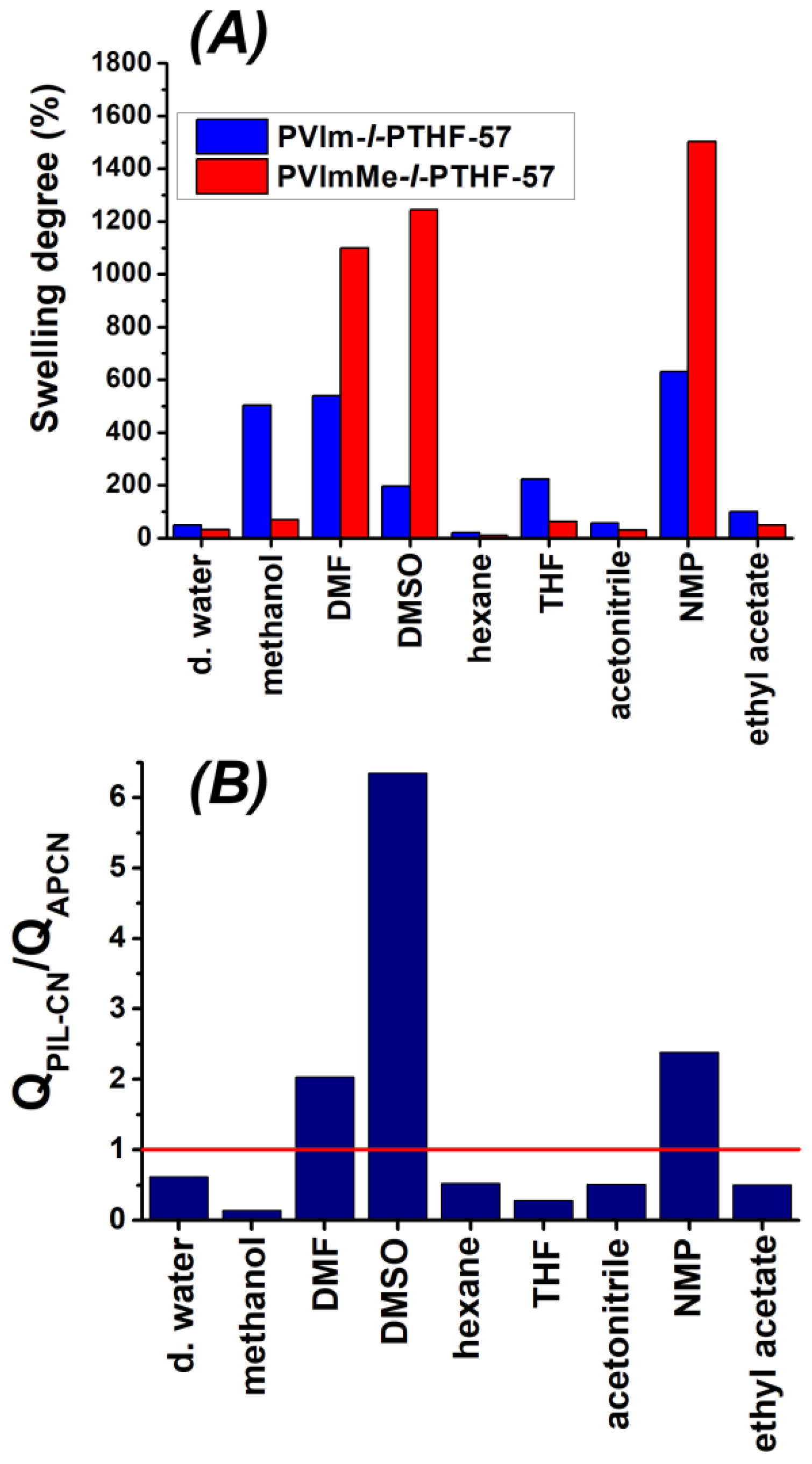
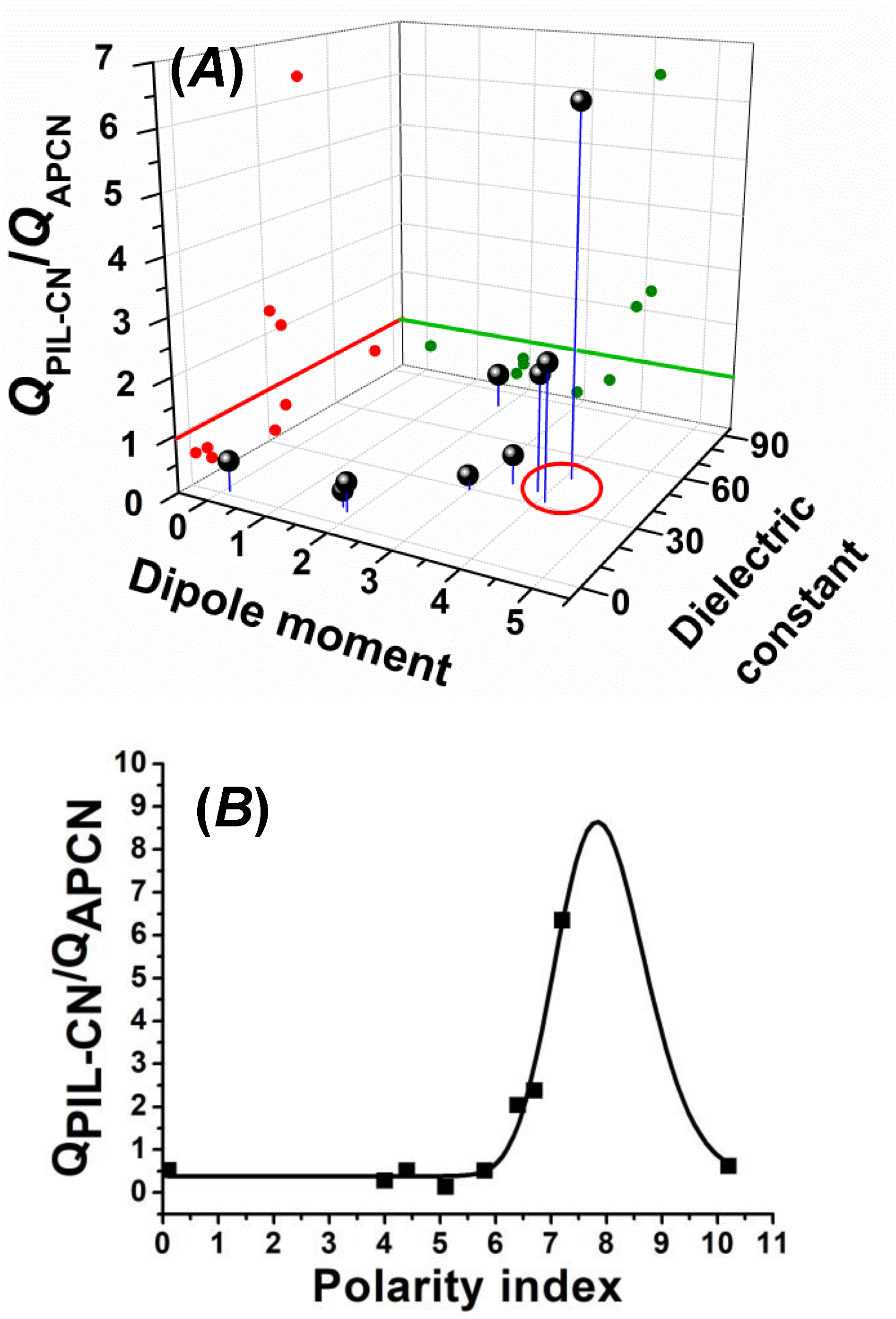
3.2. Swelling Properties of the PVIm-l-PTHF Amphiphilic and PVImMe-l-PTHF Poly(ionic liquid) Conetworks
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, M.C.; Guo, Y.L. Physical Properties of Polymers Under Soft and Hard Nanoconfinement: A Review. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommet, A.B.; Feller, M.; Klajn, R. Chemical Reactivity Under Nanoconfinement. Nat. Nanotech. 2020, 15, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, M.I.; Turkiewicz, A.B.; Darago, L.E.; Oktawiec, J.; Bustillo, K.; Grandjean, F.; Long, G.J.; Long, J.R. Confinement of Atomically Defined Metal Halide Sheets in a Metal-Organic Framework. Nature 2020, 557, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, S. Irreversible Adsorption of Polymer Melts and Nanoconfinement Effects. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 5348–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.; Kim, Y.; Kang, J.S.; Berger, R.; Yoon, H.; Char, K. Charge Transport: Enhanced Vertical Charge Transport of Homo- and Blended Semiconducting Polymers by Nanoconfinement. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2070073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, B.; Zhou, H.; Davis, M.J.; Wang, X.; Priestley, R.D. Effect of Local Chain Conformation in Absorbed Nanolayers on Confined Polymer Molecular Mobility. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 217801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrickios, C.S. (Ed.) Amphiphilic Polymer Co-Networks: Synthesis, Properties, Modelling and Applications; Polym. Chem. Ser. No. 33; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fodor, C.; Stumphauser, T.; Iván, B. Poly(N-vinylimidazole)-Based Nanostructured Amphiphilic Conetworks. In Amphiphilic Polymer Co-Networks: Synthesis, Properties, Modelling and Applications; Polym. Chem. Ser. No., 33; Patrickios, C.S., Ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2020; pp. 15–46. [Google Scholar]
- Mugemana, C.; Grysan, P.; Dieden, R.; Ruch, D.; Bruns, N.; Dubois, P. Self-Healing Metallo-Supramolecular Amphiphilic Polymer Conetworks. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2020, 221, 1900432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, A.; Torras, N.; Castani, A.G.; Garcia-Diaz, M.; Comelles, J.; Pérez-Berezo, T.; Corregidor, C.; Castano, Ó.; Engel, E.; Fernández-Majada, V.; et al. Hydrogel Co-networks of Gelatine Methacrylate and Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Diacrylate sustain 3D Functional in vitro Models of Intestinal Mucosa. Biofabrication 2020, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Song, F.; Gao, W.; Liu, S. Synthesis and Properties of a Temperature-Sensitive Hydrogel Based on Physical Crosslinking via Stereocomplexation of PLLA-PDLA. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 19759–19769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shi, X.; Wang, Z.; Song, F.; Gao, W.; Liu, S. Stereocomplex Poly(Lactic Acid) Amphiphilic Conetwork Gel with Temperature and pH Dual Sensitivity. Polymers 2019, 11, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruycker, K.; Mertens, C.; Du Prez, F.E. Thiolactone Chemistry for the Synthesis of Functional Silicone-Based Amphiphilic Co-Networks. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2019, 57, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizhnyaev, V.N.; Pokatilov, F.A.; Shabalin, A.I.; Zhitov, R.G. Conetworks on the Base of Polystyrene with Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) paired polymers. e-Polymers 2019, 19, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Hayward, R.C. Effects of Randomly End-Linked Copolymer Network Parameters on the Formation of Disordered Cocontinuous Phases. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 2642–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ju, X.J.; Zhang, L.P.; Wang, W.; Faraj, Y.; Zou, L.B.; Xie, R.; Liu, Z.; Chu, L.Y. Transparent Thermo-Responsive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-l-Poly(Ethylene Glycol)Acrylamide Conetwork Hydrogels with Rapid Deswelling Response. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 9507–9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Mondal, R.; Guha, S.; Chatterjee, U.; Jewrajka, S.K. Homogeneous Phase Crosslinked Poly(Acrylonitrile-co-2-Acrylamido-2-Methyl-1-Propanesulfonic Acid) Conetwork Cation Exchange Membranes Showing High Electrochemical Properties and Electrodialysis Performance. Polymer 2019, 180, 121680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbaghi, A.; Rahmani, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Biodegradable Multicomponent Amphiphilic Conetworks with Tunable Swelling Through Combination of Ring--Opening Polymerization and “Click” Chemistry Method as a Controlled Release Formulation for 2,4--Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid Herbicide. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, M.; Dabbaghi, A.; Rahmani, S. Swelling and Drug Delivery Kinetics of Click-Synthesized Hydrogels Based on Various Combinations of PEG and Star-Shaped PCL: Influence of Network Parameters on Swelling and Release Behavior. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 3989–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnava, C.K.; Patrickios, C.S. Model Amphiphilic Polymer Conetworks in Water: Prediction of Their Ability for Oil Solubilization. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 4721–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, S.; Morimura, M.; Kitanaka, H.; Hirokawa, Y.; Kanaoka, S. Swelling and Mechanical Properties of Thermoresponsive/Hydrophilic Conetworks with Crosslinked Domain Structure Prepared from Various Triblock Precursors. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 6122–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalani, D.V.; Jewrajka, S.K. Fouling Resistant Amphiphilic Poly(Dimethylsiloxane)-Linked-Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Network on Ultrafiltration Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Membrane and Effect of Spatial Chain Arrangement on Separation of Oil-Water Emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 583, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, S.; Osypova, A.; Panzarasa, G.; Rossi, R.M.; Bruns, N.; Boesel, L.F. Pyranine--Modified Amphiphilic Polymer Conetworks as Fluorescent Ratiometric pH Sensors. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, 1900360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibayama, M.; Li, X.; Sakai, T. Precision Polymer Network Science with Tetra-PEG Gels—A Decade History and Future. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2019, 297, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Li, X.; Shibayama, M.; Kamata, H.; Sakai, T.; Gilbert, E.P. Insight into the Microscopic Structure of Module-Assembled Thermoresponsive Conetwork Hydrogels. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 6645–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolides, D.E.; Patrickios, C.S.; Sakai, T.; Guerre, M.; Lopez, G.; Améduri, B.; Ladmiral, V.; Simon, M.; Gradzielski, M.; Clemens, D.; et al. Near-Model Amphiphilic Polymer Conetworks Based on Four-Arm Stars of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) and Poly(Ethylene Glycol): Synthesis and Characterization. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 2476–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazani, A.; Dabbaghi, A.; Gouranlou, F. Synthesis of Amphiphilic Co-network Through Click Chemistry Reactions: A Review. Curr. Org. Chem. 2018, 22, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, S.; Sadeghpour, A.; Rossi, R.M.; Bruns, N.; Boesel, L.F. Wide Range of Functionalized Poly(N-Alkyl Acrylamide)-Based Amphiphilic Polymer Conetworks via Active Ester Precursors. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 5267–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pásztor, S.; Iván, B.; Kali, G. Extreme Difference of Polarities in a Single Material: Poly(Acrylic Acid)--Based Amphiphilic Conetworks with Polyisobutylene Cross--linker. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 1818–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, G.; Nugay, T.; Nugay, I.; Nugay, N.; Kennedy, J.P.; Cakmak, M. High Strength Bimodal Amphiphilic Conetworks for Immunoisolation Membranes: Synthesis, Characterization and Properties. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 6251–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasdian, N.; Church, E.; Cottam, A.P.; Hornsby, K.; Leung, M.-Y.; Georgiou, T.K. Novel “Core-First” Star-Based Quasi-Model Amphiphilic Polymer Networks. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 19070–19080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, K.R.; Tew, G.N. Microphase-Separated Thiol-Ene Conetworks from Telechelic Macromonomers with Asymmetric Molecular Weights. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 8042–8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumm, C.; Konieczny, S.; Dropalla, G.J.; Milbradt, M.; Tiller, J.C. Amphiphilic Polymer Conetworks Based on End Group Cross-Linked Poly(2-Oxazoline) Homo- and Triblock Copolymers. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 3234–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, C.; Kali, G.; Iván, B. Poly(N-vinylimidazole)-l-poly(tetrahydrofuran) Amphiphilic Conetworks and Gels: Synthesis, Characterization, Thermal and Swelling Behavior. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4496–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, C.; Iván, B. Poly(N-vinylimidazole)-l-poly(tetrahydrofuran) Amphiphilic Conetworks and Gels II.: Unexpected Dependence of the Reactivity of PTHF Macromonomer Cross-linker on Molecular Weight in Copolymerization with N-vinylimidazole. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2011, 49, 4729–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domján, A.; Fodor, C.; Kovács, S.; Marek, T.; Iván, B.; Süvegh, K. Anomalous Swelling Behavior of Poly(N-vinylimidazole)-l-poly(tetrahydrofuran) Amphiphilic Conetwork in Water Studied by Solid-state NMR and Positron Annihilation Lifetime Spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 7557–7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, C.; Domján, A.; Iván, B. Unprecedented Scissor Effect of Macromolecular Cross-linkers on the Glass Transition Temperature of Poly(N-vinylimidazole), Crystallinity Suppression of Poly(tetrahydrofuran) and Molecular Mobility by Solid State NMR in Poly(N-vinylimidazole)-l-poly(tetrahydrofuran) Conetworks. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 3714–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, C.; Bozi, J.; Blazsó, M.; Iván, B. Unexpected Thermal Decomposition Behavior of Poly(N-vinylimidazole)-l-poly(tetrahydrofuran) Amphiphilic Conetworks, A Class of Chemically Forced Blends. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 17413–17423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, C.; Kali, G.; Thomann, R.; Thomann, Y.; Iván, B.; Mülhaupt, R. Nanophasic Morphologies as a Function of the Composition and Molecular Weight of the Macromolecular Cross-linker in Poly(N-vinylimidazole)-l-poly(tetrahydrofuran) Amphiphilic Conetworks: Bicontinuous Domain Structure in Broad Composition Ranges. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 6827–6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, C.; Stumphauser, T.; Thomann, R.; Thomann, Y.; Iván, B. Poly(N-Vinylimidazole)-l-Poly(Propylene Glycol) Amphiphilic Conetworks And Gels: Molecularly Forced Blends of Incompatible Polymers with Single Glass Transition Temperatures of Unusual Dependence on the Composition. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 5375–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Qian, L.; Gao, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, H.; Miao, Z. Ionic Liquid-Based Amphiphilic Conetwork with Mechanical Toughness: A Promising Candidate for Dye Removal. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 6212–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patinha, D.J.S.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Marrucho, I.M. Poly(Ionic Liquids) in Solid Phase Microextraction: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 98, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J.-K.; Antonietti, M.; Yuan, J. Poly(Ionic Liquid)s with Engineered Nanopores for Energy and Environmental Applications. Polymer 2020, 202, 122640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Gao, Z.; Sun, J.-K.; Yuan, J. Poly(Ionic Liquid) Composites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1726–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshetu, G.G.; Mecerreyes, D.; Forsyth, M.; Zhang, H.; Armand, M. Polymeric Ionic Liquids for Lithium-Based Rechargeable Batteries. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2019, 4, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Weber, J.; Yuan, J. Poly(Ionic Liquid)s: Platform for CO2 Capture and Catalysis. Curr. Opin. Green Sus. Chem. 2019, 16, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; White, B.T.; Kasprzak, C.R.; Long, T.E. Advances in Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids and Poly(Ionic Liquid)s as Conductive Materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 108, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-P.; Ho, K.-C. Poly(Ionic Liquid)s for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: A Mini-Review. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 108, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Mecerreyes, D.; Antonietti, M. Poly(Ionic Liquid)s: An Update. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1009–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapesa, E.U.; Chen, M.T.; Heres, M.F.; Harris, M.A.; Kinsey, T.; Wang, Y.Y.; Long, T.E.; Lokitz, B.S.; Sangoro, J.R. Charge Transport in Imidazolium-Based Homo- and Triblock Poly(Ionic Liquid)s. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigolaeva, L.V.; Bulko, T.V.; Kozin, M.S.; Zhang, W.; Köhler, M.; Romanenko, I.; Yuan, J.; Schacher, F.H.; Pergushov, D.V.; Shumyantseva, V.V. Long-Term Stable Poly(Ionic Liquid)/MWCNTs Inks Enable Enhanced Surface Modification for Electrooxidative Detection and Quantification of dsDNA. Polymer 2019, 168, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Jana, S.; Mandal, T.K. Coulomb Interaction-Driven UCST in Poly(Ionic Liquid) Random Copolymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 133, 109747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerscher, B.; Trötschler, T.M.; Pásztói, B.; Gröer, S.; Szabó, Á.; Iván, B.; Mülhaupt, R. Thermoresponsive Polymer Ionic Liquids and Nanostructured Hydrogels Based Upon Amphiphilic Polyisobutylene-b-Poly(2-Ethyl-2-Oxazoline) Diblock Copolymers. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 3306–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, T.P.; Storey, R.F. Micellization and Adsorption to Carbon Black of Polyisobutylene-Based Ionic Liquids. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 280–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, C.; Akbarzadeh, J.; Stojanovic-Marinow, A.; Peterlik, H.; Binder, W.H. Hierarchically Mesostructured Polyisobutylene-Based Ionic Liquids. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maya, E.M.; Verde-Sesto, E.; Mantione, D.; Iglesias, M.; Mecerreyes, D. New Poly(Ionic Liquid)s Based on Poly(Azomethine-Pyridinium) Salts and Its Use as Heterogeneous Catalysts for CO2 Conversion. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 110, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Q.; Yue, J. Polymerized Imidazolium Ionic Liquids Crosslinking Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) (SPEEK) for High-temperature Proton Exchange Membrane. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 111729–111738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altava, B.; Compan, V.; Andrio, A.; del Castillo, L.F.; Mollá, S.; Burguete, M.I.; García-Verdugo, E.; Luis, S.V. Conductive Films Based on Composite Polymers Containing Ionic Liquids Absorbed on Crosslinked Polymeric Ionic-like Liquids (SILLPs). Polymer 2015, 72, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, T.C.; Wistrom, J.C.; Johnson, R.D.; Miller, K.M. Thermal, Mechanical and Conductive Properties of Imidazolium-containing Thiol-ene Poly(ionic liquid) Networks. Polymer 2016, 100, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, M.; Yang, B.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Veith, G.M.; Sun, X.-G.; Dai, S. Polymerized Ionic Networks with High Charge Density: Quasi-solid Electrolytes in Lithium-metal Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 8088–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, O.F.; Demirci, S.; Sengel, S.B.; Sahiner, N. Highly Regenerable Ionic Liquid Microgels as Inherently Metal-free Green Catalyst for H2 Generation. Polym. Adv. Tech. 2018, 29, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cai, X.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J. Pd Nanoparticles Encapsulated into Mesoporous Ionic Copolymer: Efficient and Recyclable Catalyst for the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol with O2 Balloon in Water. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 189, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Sun, Q.; Fu, Y.; Song, L.; Liang, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Tu, S.; Lu, X.; et al. Sponge-like Quaternary Ammonium-based Poly(ionic liquid)s for High CO2 Capture and Efficient Cycloaddition Under Mild Conditions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 25594–25600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, M.; Zulfiqar, S.; Edhaim, F.; Ruiperez, F.; Rothenberger, A.; Mecerreyes, D. Sustainable Poly(ionic liquids) for CO2 Capture Based on Deep Eutectic Monomers. ACS Sus. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 7200–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xing, L.; Shu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Novel Polymeric Ionic Liquid Microspheres with High Exchange Capacity for Fast Extraction of Plasmid DNA. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 837, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Qiu, T. Stable Poly(Ionic Liquid) with Unique Crosslinked Microsphere Structure as Efficient Catalyst for Transesterification of Soapberry Oil to Biodiesel. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 153, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, A.; Crocella, V.; Maddalena, L.; Barolo, C.; Bordiga, S.; Groppo, E. Spectroscopic Study on the Surface Properties and Catalytic Performances of Palladium Nanoparticles in Poly(ionic liquis)s. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmann, S.; Kerscher, B.; Lienert, C.; Böcherer, D.; Mülhaupt, R. Tailoring Poly(2-Oxazoline)-Based Polymeric Liquids as Thermoresponsive Molecular Brushes and Programmable Dispersants for Silver Nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 6703–6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Elageed, E.H.M.; Qin, L.; Ni, B.; Liu, X.; Gao, G. Swelling Poly(Ionic Liquid)s: Synthesis and Application as Quasi-Homogenous Catalysts in the Reaction of Ethylene Carbonate with Aniline. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gai, H. Design of Novel Poly(Ionic Liquids) for the Conversion of CO2 to Cyclic Carbonates under Mild Conditions without Solvent. ACS Sus. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9489–9497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Wang, X.; Tian, M. Determination of Volatile Water Pollutants Using Cross-Linked Polymeric Ionic Liquid as Solid Phase Micro-Extraction Coatings. Polymers 2020, 12, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, B.; Ding, T.; Ni, B.; Gao, G. Swelling Poly(Ionic Liquid) Supported by Three-Dimensional Wire Mesh for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14347–14353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röchow, E.T.; Coeler, M.; Pospiech, D.; Kobsch, O.; Mechtaeva, E.; Vogel, R.; Voit, B.; Nikolowski, K.; Wolter, M. In Situ Preparation of Crosslinked Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium Ion Batteries: A Comparison of Monomer Systems. Polymers 2020, 12, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, S.-J.; Peng, J.; Li, J.-Q.; Xu, L.; Zhai, M.-L. New Methacrylic Imidazolium Poly(Ionic Liquid) Gel with Super Swelling Capacity for Oil-in-Water Emulsion. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2016, 27, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyazi, T.; Tudor, A.; Diamond, D.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Florea, L.; Benito-Lopez, F. Driving Flows in Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices with a Cholinium Based Poly(Ionic Liquid) Hydrogel. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 261, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Long, M.-C.; Wang, X.-L.; Wu, G.; Wang, Y.-Z. One-Step Preparation of Poly(Ionic Liquid)-Based Flexible Electrolytes by in-situ Polymerization for Dendrite-Free Lithium Ion Batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 122062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Shi, L.; Lu, S.; Sun, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, S. Poly(Ionic Liquid)-Polyethylene Oxide Semi-Inetrpenetrating Polymer Network Solid Electrlyte for Safe Lithium Metal Batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Liu, Z.; Xu, L.; Lou, N.; Li, M.; Liu, L. Controllable Click Synthesis of Poly(Ionic Liquid)s by Surfactant-Free Ionic Liquid Microemulsions for Selective Dyes Reduction. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 147, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammakakam, I.; Bara, J.E.; Jackson, E.M.; Lertxundi, J.; Mecerreyes, D.; Tomé, L.C. Tailored CO2-Philic Anionic Poly(ionic liquid) Composite Membranes: Synthesis, Characterization, and Gas Transport Properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5954–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y. Nanoconfined Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6755–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnacka, M.; Chrobok, A.; Matuszek, K.; Golba, S.; Maksym, P.; Kaminski, K.; Paluch, M. Polymerization of Monomeric Ionic Liquid Confined within Uniaxial Alumina Pores as a New Way of Obtaining Materials with Enhanced Conductivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29779–29790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksym, P.; Tarnacka, M.; Wolnica, K.; Dzienia, A.; Erfurt, K.; Chrobok, A.; Andrzej Zięba, A.; Bielas, R.; Kaminski, K.; Paluch, M. Studies on the Hard Confinement Effect on the RAFT Polymerization of a Monomeric Ionic Liquid. Unexpected Triggering of RAFT Polymerization at 30 °C. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.M.; Sanoja, G.E.; Popere, B.C.; Segalman, R.A. Anhydrous Proton Transport in Polymerized Ionic Liquid Block Copolymers: Roles of Block Length, Ionic Content and Confinement. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacha, A.; Varga, Z.; Bóta, A. CREDO: A New General-purpose Laboratory Instrument for Small-angle X-ray Scattering. J. Appl. Crystal. 2014, 47, 1749–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacha, A. Optimized Pinhole Geometry for Small-Angle Scattering. J. Appl. Crystal. 2015, 48, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaiwi, A.; Hitchcock, P.B.; Seddon, K.R.; Srinivasan, N.; Tan, Y.M.; Welton, T.; Zora, J.A. Hydrogen bonding in imidazolium salts and its implications for ambient-temperature halogenoaluminate (III) ionic liquids. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1995, 3467–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.; Srivastava, N.; Saha, S. Theoretical and spectroscopic studies of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium iodide room temperature ionic liquid: Its differences with chloride and bromide derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 975, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, L.R. Classification of the Solvent Properties of Common Liquids. J. Chromatogr. 1974, 92, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, L.R.; Kirkland, J.J.; Glajch, J.L. Appendix II. Properties of Solvents Used in HPLC, in Practical HPLC Method Development, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA; New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 721–728. [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.M.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PVIm-l-PTHF-57 | PVImMe-l-PTHF-57 | PVIm-l-PTHF-76 | PVImMe-l-PTHF-76 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTHF content (wt%) | 57 | 36 | 76 | 56 |
| PVIm content (wt%) | 43 | 2 | 24 | 1 |
| PVImMe+I− content (wt%) | - | 62 | - | 43 |
| Tg of PTHF (°C) (a) | −86 | −89 | −83 | −87 |
| Tg of PVIm and PVImMe (°C) (b) | 116 | 114 | 106 | 103 |
| Tm of PTHF (°C) (c) | 4.8 | - | 10.0 | 2.7 |
| Xc of PTHF (%) (d) | 9.4 | 0.0 | 13.7 | 5.6 |
| d-spacing by SAXS (nm) | 21.9 | 20.1 | 17.6 | 15.7 |
| dPTHF (nm) (e) | 15.0 | 13.5 | 18.5 | 9.0 |
| dPVIm and dPVImMe (nm) (e) | 7.8 | 8.4 | 7.9 | 8.2 |
| average domain distance (nm) (e) | 22.8 | 21.9 | 26.1 | 17.2 |
| Solvent | QAPCN (%) | QPIL-CN (%) | QPIL-CN/QAPCN | Dipole Moment (D) | Dielectric Constant | Polarity Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| water | 50 | 31 | 0.62 | 1.87 | 80.10 | 10.2 |
| methanol | 503 | 69 | 0.14 | 2.87 | 32.70 | 5.1 |
| DMF | 540 | 1099 | 2.03 | 3.86 | 36.71 | 6.4 |
| DMSO | 196 | 1245 | 6.35 | 4.10 | 46.68 | 7.2 |
| hexane | 21 | 11 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 1.88 | 0.1 |
| THF | 223 | 63 | 0.28 | 1.75 | 7.58 | 4.0 |
| acetonitrile | 57 | 29 | 0.51 | 3.44 | 37.50 | 5.8 |
| NMP | 630 | 1503 | 2.38 | 4.09 | 32.20 | 6.7 |
| ethyl acetate | 99 | 50 | 0.50 | 1.88 | 6.02 | 4.4 |
| Solvent | nAPCN | nPIL-CN |
|---|---|---|
| water | 0.43 | 0.36 |
| methanol | 0.36 | 0.46 |
| DMF | 0.58 | 0.64 |
| DMSO | 0.56 | 0.71 |
| hexane | 0.38 | 0.49 |
| THF | 0.52 | 0.52 |
| acetonitrile | 0.48 | 0.34 |
| N-methylpyrrolidone | 0.58 | 0.63 |
| ethyl acetate | 0.46 | 0.50 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stumphauser, T.; Kasza, G.; Domján, A.; Wacha, A.; Varga, Z.; Thomann, Y.; Thomann, R.; Pásztói, B.; Trötschler, T.M.; Kerscher, B.; et al. Nanoconfined Crosslinked Poly(ionic liquid)s with Unprecedented Selective Swelling Properties Obtained by Alkylation in Nanophase-Separated Poly(1-vinylimidazole)-l-poly(tetrahydrofuran) Conetworks. Polymers 2020, 12, 2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102292
Stumphauser T, Kasza G, Domján A, Wacha A, Varga Z, Thomann Y, Thomann R, Pásztói B, Trötschler TM, Kerscher B, et al. Nanoconfined Crosslinked Poly(ionic liquid)s with Unprecedented Selective Swelling Properties Obtained by Alkylation in Nanophase-Separated Poly(1-vinylimidazole)-l-poly(tetrahydrofuran) Conetworks. Polymers. 2020; 12(10):2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102292
Chicago/Turabian StyleStumphauser, Tímea, György Kasza, Attila Domján, András Wacha, Zoltán Varga, Yi Thomann, Ralf Thomann, Balázs Pásztói, Tobias M. Trötschler, Benjamin Kerscher, and et al. 2020. "Nanoconfined Crosslinked Poly(ionic liquid)s with Unprecedented Selective Swelling Properties Obtained by Alkylation in Nanophase-Separated Poly(1-vinylimidazole)-l-poly(tetrahydrofuran) Conetworks" Polymers 12, no. 10: 2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102292
APA StyleStumphauser, T., Kasza, G., Domján, A., Wacha, A., Varga, Z., Thomann, Y., Thomann, R., Pásztói, B., Trötschler, T. M., Kerscher, B., Mülhaupt, R., & Iván, B. (2020). Nanoconfined Crosslinked Poly(ionic liquid)s with Unprecedented Selective Swelling Properties Obtained by Alkylation in Nanophase-Separated Poly(1-vinylimidazole)-l-poly(tetrahydrofuran) Conetworks. Polymers, 12(10), 2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102292