Multicompartmental Mesoporous Silica/Polymer Nanostructured Hybrids: Design Capabilities by Integrating Linear and Star-Shaped Block Copolymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SiO2@P2VP-b-PEO Particles
2.3. Encapsulation of Nile Red or Pyrene in PS10-PEO10 Micelles
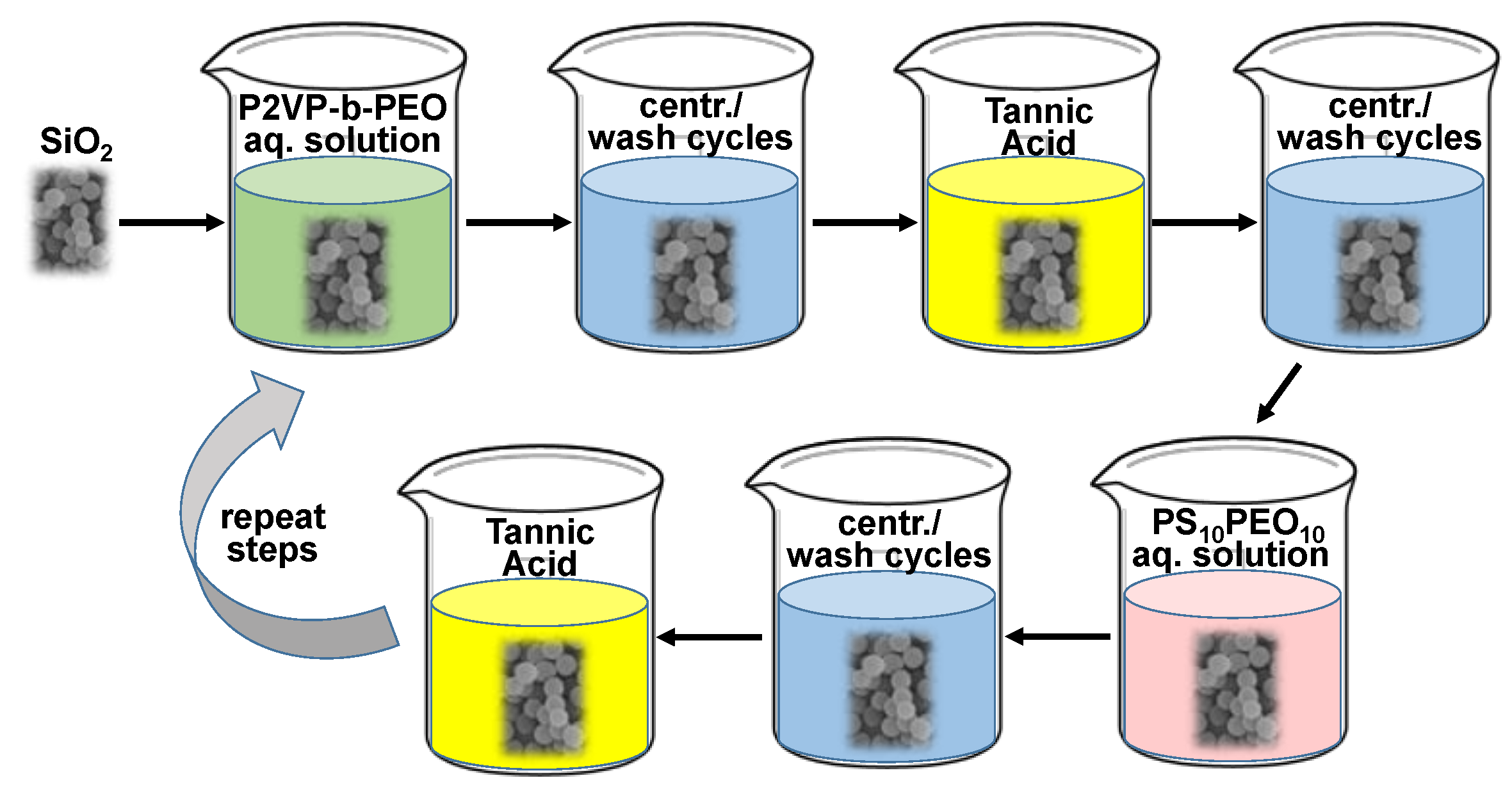
2.4. Preparation of SiO2@P2VP-b-PEO@TA@PS10-PEO10 Particles
2.5. Loading and Release of Calcein in SiO2@P2VP-b-PEO Particles
2.6. Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
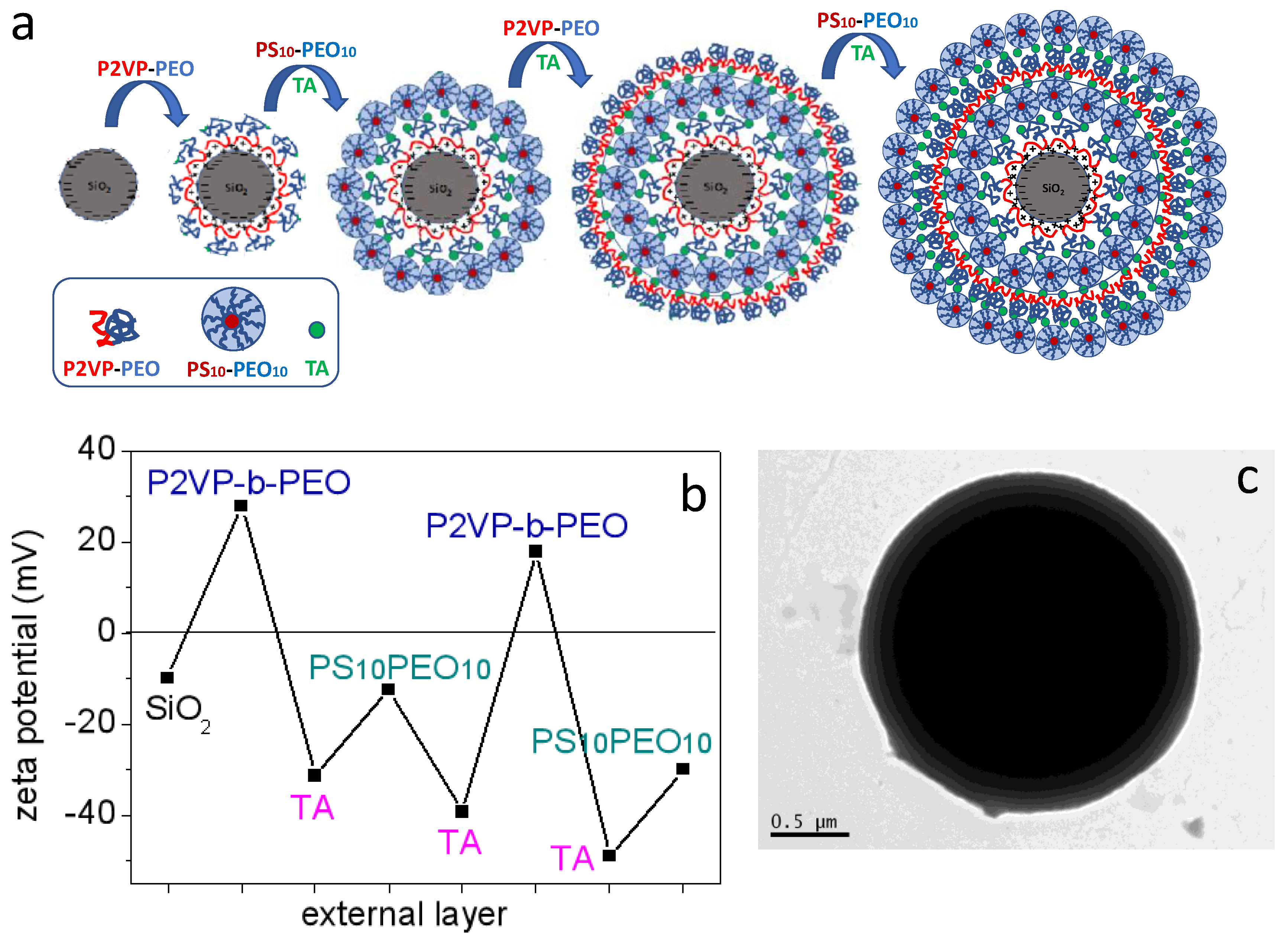
3.1. SiO2@P2VP-b-PEO Hybrids
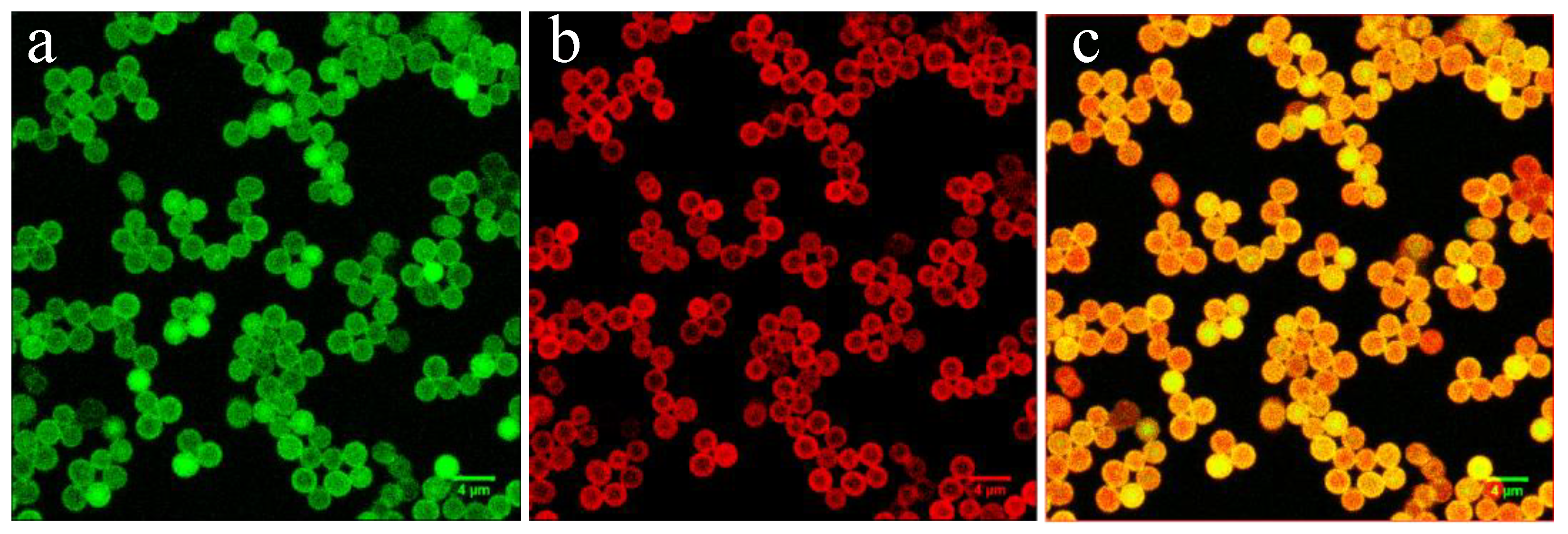
3.2. SiO2@P2VP-b-PEO@TA@PS10-PEO10 Nanostructured Hybrids
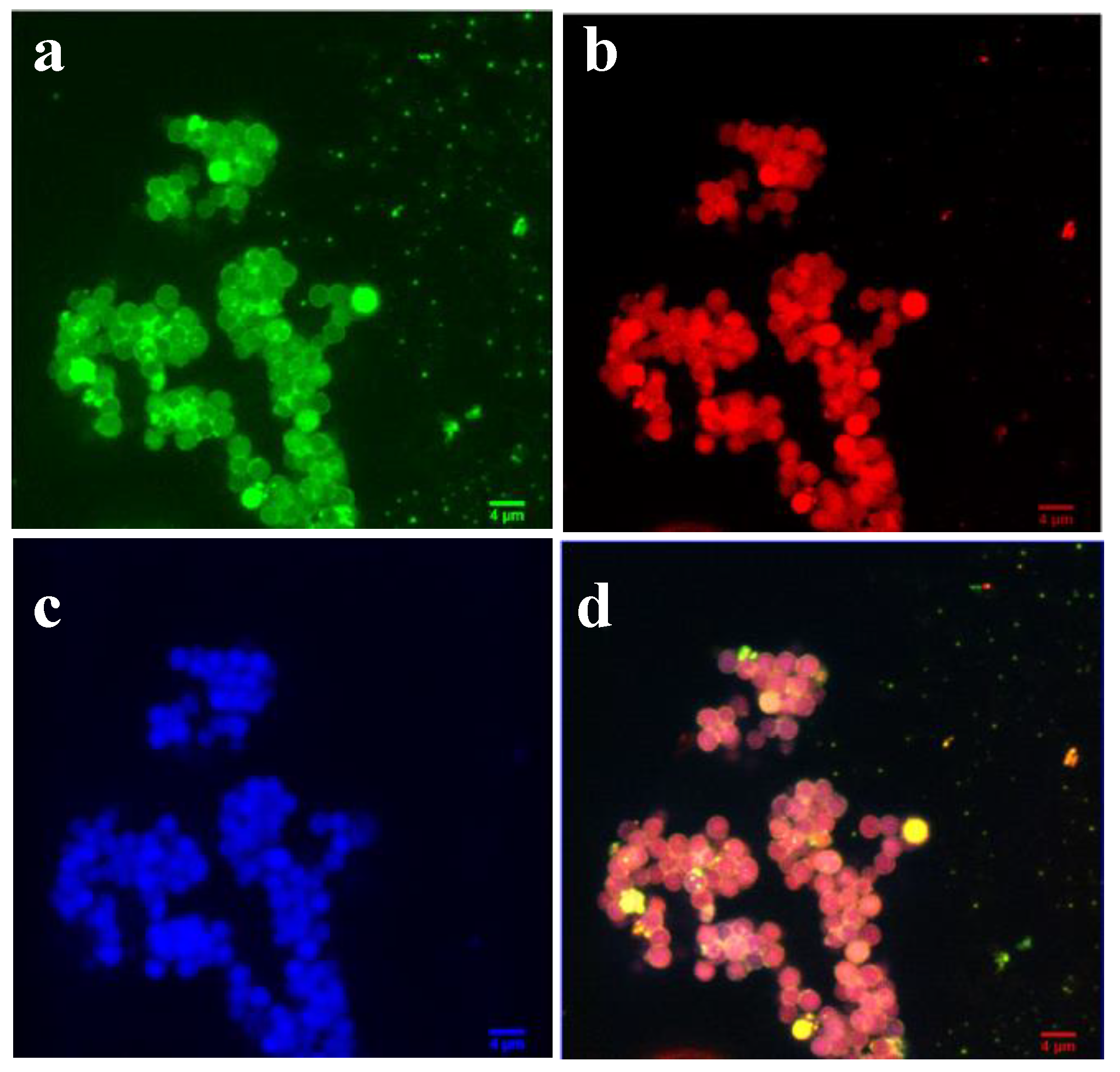
3.3. SiO2 Hybrids with Alternating P2VP-b-PEO and PS10-PEO10 Layers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, N.T.; Cheng, S.H.; Souris, J.S.; Chen, C.T.; Mou, C.Y.; Lo, L.W. Theranostic Applications of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Their Organic/Inorganic Hybrids. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3128–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, D. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Biocompatibility and Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1504–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, S.P.; Padera, R.F.; Langer, R.; Kohane, D.S. The biocompatibility of mesoporous silicates. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4045–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Li, Z.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Biocompatibility, Biodistribution, and Drug-Delivery Efficiency of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy in Animals. Small 2010, 6, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-H.; Hung, Y.; Mou, C.-Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as nanocarriers. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9972–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Shi, J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle based nano drug delivery systems: Synthesis, controlled drug release and delivery, pharmacokinetics and biocompatibility. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 5845–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colilla, M.; Gonzáleza, B.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the design of smart delivery nanodevices. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watermann, A.; Brieger, J. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Vehicles in Cancer. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kango, S.; Kalia, S.; Celli, A.; Njuguna, J.; Habibi, Y.; Kumar, R. Surface modification of inorganic nanoparticles for development of organic–inorganic nanocomposites—A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1232–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shi, S.; Goel, S.; Shen, X.; Xie, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Qin, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Recent advancements in mesoporous silica nanoparticles towards therapeutic applications for cancer. Acta Biomater. 2019, 89, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, S.; Soler-Illia, G.J.A.A.; Azzaroni, O. Gated supramolecular chemistry in hybrid mesoporous silica nanoarchitectures: Controlled delivery and molecular transport in response to chemical, physical and biological stimuli. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6050–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulzar, A.; Gaia, S.; Yanga, P.; Li, C.; Ansaric, M.B.; Linb, J. Stimuli-responsive drug delivery application of polymer and silica in biomedicine. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 8599–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermayer, S.; Weiss, V.; Herrmann, A.; Schmidt, A.; Datz, S.; Müller, K.; Wagner, E.; Bein, T.; Bräuchle, C. Multifunctional polymer-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive targeted drug delivery. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7953–7964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullriede, H.; Abendroth, P.; Ehlert, N.; Doll, K.; Schäske, J.; Winkel, A.; Stumpp, S.N.; Stiesch, M.; Behrens, P. pH-responsive release of chlorhexidine from modified nanoporous silica nanoparticles for dental applications. BioNanoMaterials 2016, 17, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilalis, P.; Tziveleka, L.A.; Varlas, S.; Iatrou, H. pH-Sensitive Nanogates Based on Poly(L-Histidine) for Controlled Drug Release from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairi, V.; Magnolia, S.; Piludu, M.; Nieddu, M.; Caria, C.A.; Sogos, V.; Vallet-Regì, M.; Monduzzi, M.; Salis, A. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with hyaluronic acid. Effect of the biopolymer chain length on cell internalization. Colloid Surf. B 2018, 168, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.; Galiana, I.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Stroeve, P.; Marcos, M.D.; Aznar, E.; Sancenón, F.; Murguía, J.R.; Amorós, P. Poly(N–isopropylacrylamide)–gated Fe3O4/SiO2 core shell nanoparticles with expanded mesoporous structures for the temperature triggered release of lysozyme. Colloid Surf. B 2015, 135, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; Sha, X.; Guo, J.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, W. Thermo and pH dual responsive, polymer shell coated, magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug release. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9239–9247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Y.; Tan, L.; Wu, H.X.; Liu, C.J.; Zhuo, R.X. Dual-stimuli-responsive polymer-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles used for controlled drug delivery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, W.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H. Reversible crosslinking terpolymer shell-based mesoporous silica nanoparticles as on-off nanocarriers for pyrene-releasing application. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 2018, 168, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Shi, J.; Shen, W.; Dong, X.; Feng, J.; Ruan, M.; Li, Y. Stimuli-Responsive Controlled Drug Release from a Hollow Mesoporous Silica Sphere/Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Core–Shell Structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5083–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Shi, J. A mesoporous core-shell structure for pH-controlled storage and release of water-soluble drug. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2007, 103, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamanna, T.; Bulitta, J.B.; Yu, A. Controlling antibiotic release from mesoporous silica nano drug carriers via self-assembled polyelectrolyte coating. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 26, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minati, L.; Antonini, V.; Dalla Serra, M.; Speranza, G.; Enrichi, F.; Riello, P. pH-activated doxorubicin release from polyelectrolyte complex layer coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 180, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Nie, W.; He, C.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Qiu, K.; Wang, W.; Yin, Z. Effect of pH responsive alginate/chitosan multilayers coating on delivery efficiency, cellular uptake and biodistribution of mesoporous silica nanoparticles based nanocarriers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 8447–8460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, J.; Guo, J.; Liu, P. Layer-by-layer engineering fluorescent polyelectrolyte coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as pH-sensitive nanocarriers for controlled release. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 345, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Leng, F.; Zheng, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Huang, C.Z. Autofluorescent and pH-responsive mesoporous silica for cancer-targeted and controlled drug release. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 186, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Sun, H.; Zhao, Q.; Han, N.; Bai, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. Multilayer encapsulated mesoporous silica nanospheres as an oral sustained drug delivery system for the poorly water-soluble drug felodipine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 47, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.D. Layer-by-layer hyaluronic acid/chitosan polyelectrolyte coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as pH-responsive nanocontainers for optical bleaching of cellulose fabrics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Vasantha, C.S.; Sasidharan, A.V. Layer-by-layer assembly of hyaluronic acid/carboxymethylchitosan polyelectrolytes on the surface of aminated mesoporous silica for the oral delivery of 5-fluorouracil. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 93, 572–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsilianis, C.; Papanagopoulos, D.; Lutz, P. Amphiphilic heteroarm star copolymers of polystyrene and poly(ethylene oxide). Polymer 1995, 36, 3745–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennemur, J.G. Poly(vinylpyridine) Segments in Block Copolymers: Synthesis, Self-Assembly, and Versatility. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 1354–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawidjaja, R.; Peleshanko, S.; Genson, K.L.; Tsitsilianis, C.; Tsukruk, V.V. Monomolecular micelles Surface morphologies of Langmuir-Blodgett monolayers of PEOnPSn multiarm star copolymers. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6168–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Ledin, P.A.; Iatridi, Z.; Tsitsilianis, C.; Tsukruk, V.V. Multicompartmental Microcapsules with Orthogonal Programmable Two-Way Sequencing of Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Cargo Release. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4908–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagawa, M.; Suyama, K. Amine oxidase-like activity of polyphenols. Mechanism and properties. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 1953–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutava, T.G.; Balkundi, S.S.; Vangala, P.; Steffan, J.J.; Bigelow, R.L.; Cardelli, J.A.; O’Neal, D.P.; Lvov, Y.M. Layer-by-Layer-Coated Gelatin Nanoparticles as a Vehicle for Delivery of Natural Polyphenols. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daglia, M. Polyphenols as antimicrobial agents. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.T.; Wong, T.Y.; Wei, C.I.; Huang, Y.W.; Lin, Y. Tannins and Human Health: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1998, 38, 421–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutava, T.; Prouty, M.; Kommireddy, D.; Lvov, Y. pH Responsive Decomposable Layer-by-Layer Nanofilms and Capsules on the Basis of Tannic Acid. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 2850–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovskaya, V.; Kharlampieva, E.; Drachuk, I.; Cheng, D.; Tsukruk, V.V. Responsive microcapsule reactors based on hydrogen-bonded tannic acid layer-by-layer assemblies. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3596–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, M.; Tian, L.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Release of Polyphenolic Drugs from Dynamically Bonded Layer-by-Layer Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 3541–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Kozlovskaya, V.; Zavgorodnya, O.; Martinez-Lopez, C.; Catledge, S.; Kharlampieva, E. Encapsulation of anticancer drug by hydrogen bonded multilayers of tannic acid. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 9237–9247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Kozlovskaya, V.; Goins, A.; Campos-Gomez, J.; Saeed, M.; Kharlampieva, E. Biocompatible Shaped Particles from Dried Multilayer Polymer Capsules. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3830–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.S.; Lee, H.I.; Min, Y.; Poon, Z.; Hammond, P.T. Hydrogen-bonded multilayer of pH-responsive polymeric micelles with tannic acid for surface drug delivery. Chem. Commun. 2009, 28, 4194–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Pei, Y.; Li, J.; Xiong, W.; He, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Li, B. pH-Degradable antioxidant nanoparticles based on hydrogen-bonded tannic acid assembly. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 31374–31385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Sosa, C.; Pagels, R.F.; Priestley, R.D.; Prud’homme, R.K. Efficient preparation of size tunable PEGylated gold nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 4813–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmilski, M. pH-dependent surface charging and points of zero charge II. Update. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.; Malak, S.T.; Xu, W.; Heller, W.T.; Tsitsilianis, C.; Tsukruk, V.V. Multicompartmental microcapsules from star copolymer micelles. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
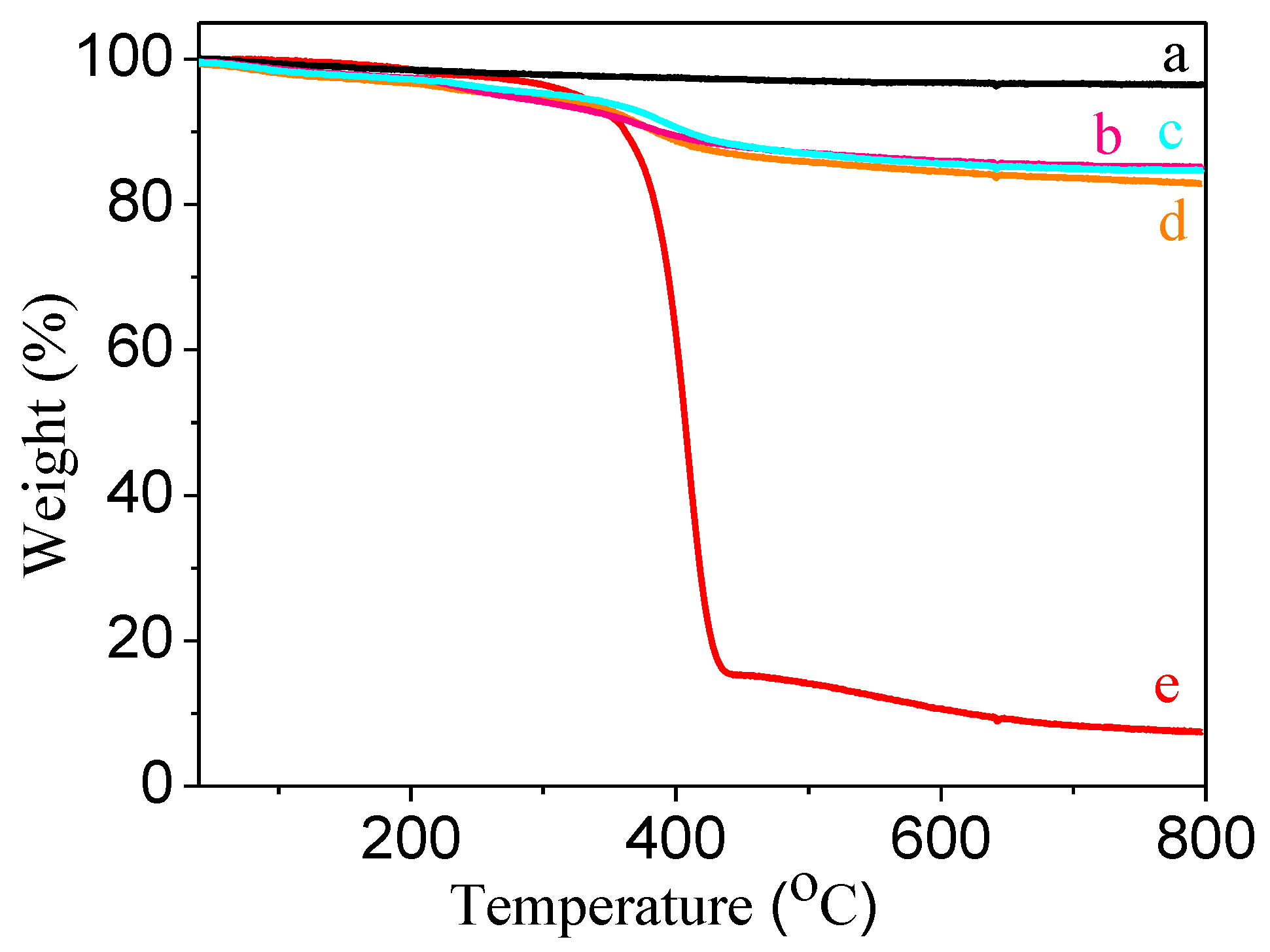
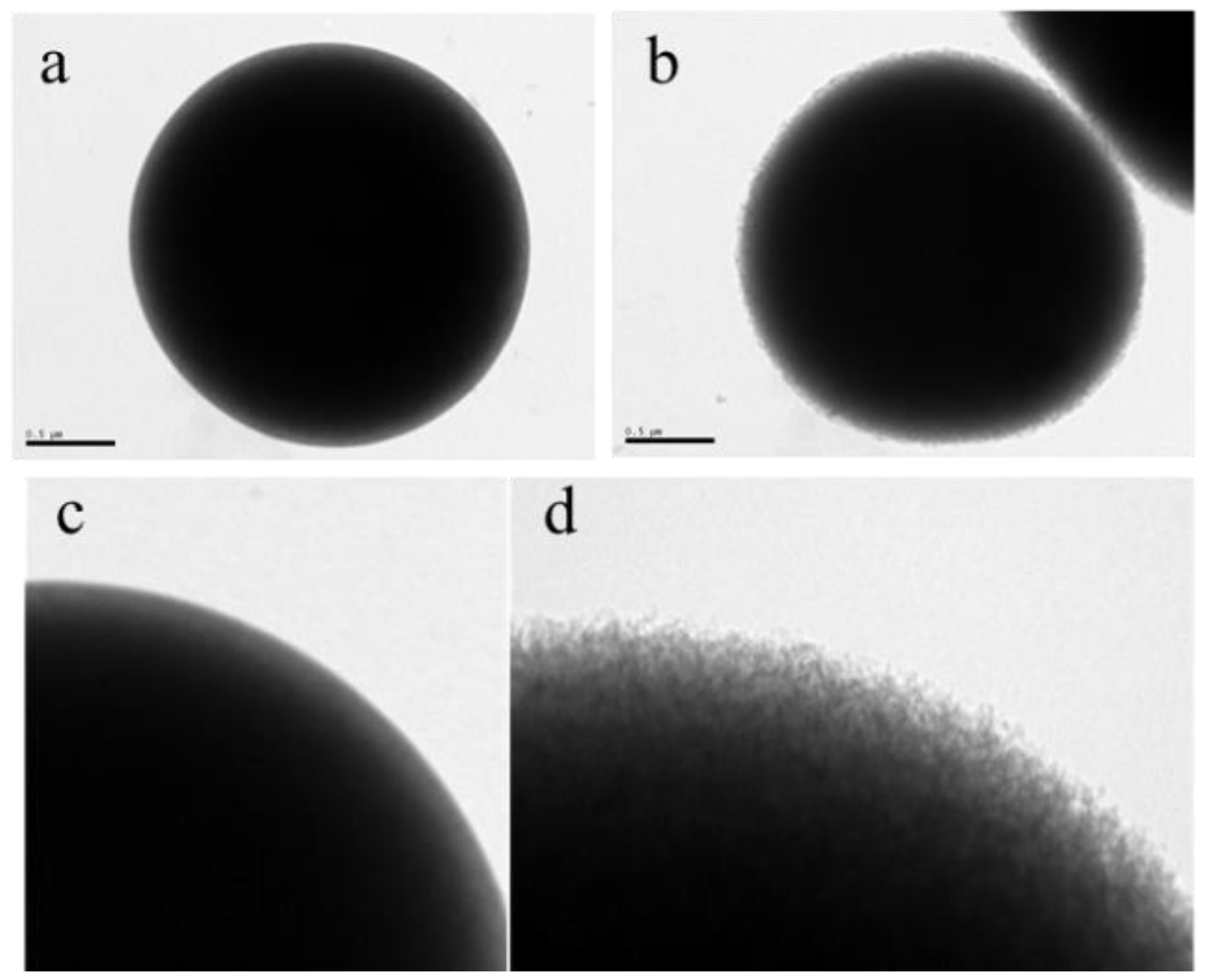
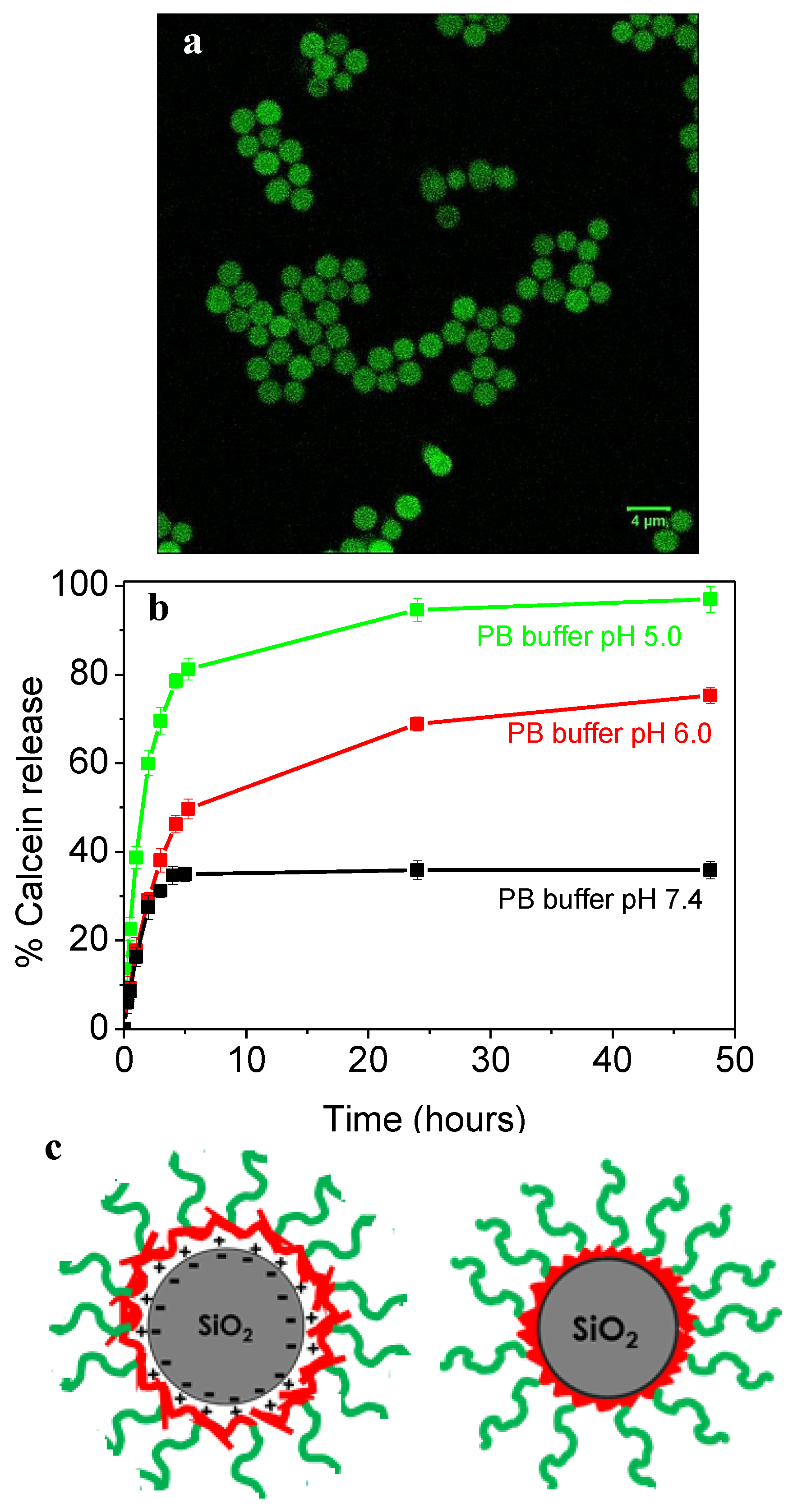
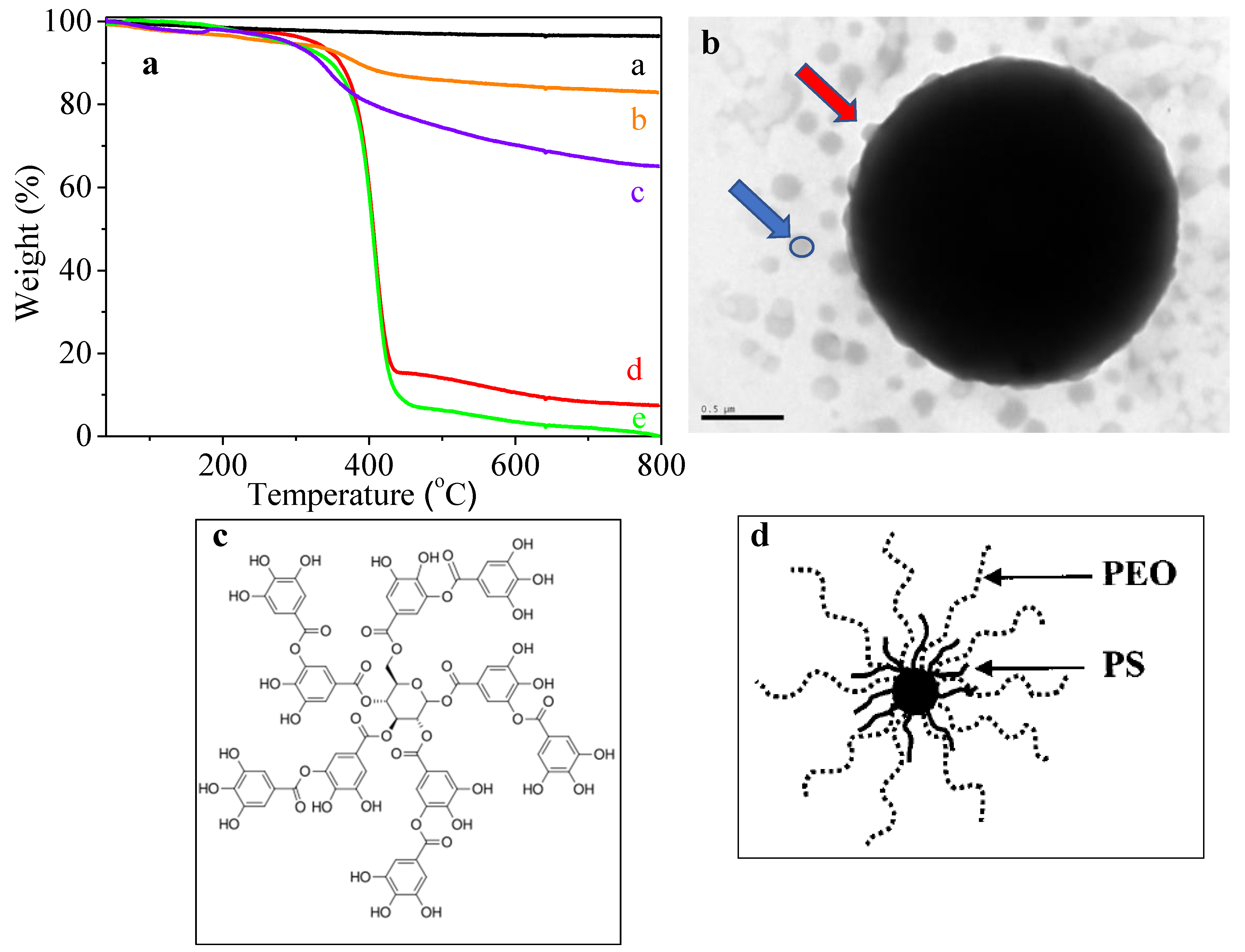
| Sample | Theoretical mpolymer/mSiO2 (%) | mpolymer/mSiO2 (%) from UV–Vis | mpolymer/mSiO2 (%) from TGA |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2@P2VP-b-PEO_1 | 90.66 | 12.35 | 11.7 |
| SiO2@P2VP-b-PEO_2 | 87.66 | 12.87 | 12.2 |
| SiO2@P2VP-b-PEO_3 | 137.33 | 15.2 | 14.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iatridi, Z.; Evangelatou, K.; Theodorakis, N.; Angelopoulou, A.; Avgoustakis, K.; Tsitsilianis, C. Multicompartmental Mesoporous Silica/Polymer Nanostructured Hybrids: Design Capabilities by Integrating Linear and Star-Shaped Block Copolymers. Polymers 2020, 12, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010051
Iatridi Z, Evangelatou K, Theodorakis N, Angelopoulou A, Avgoustakis K, Tsitsilianis C. Multicompartmental Mesoporous Silica/Polymer Nanostructured Hybrids: Design Capabilities by Integrating Linear and Star-Shaped Block Copolymers. Polymers. 2020; 12(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010051
Chicago/Turabian StyleIatridi, Zacharoula, Kyriaki Evangelatou, Nikolaos Theodorakis, Athina Angelopoulou, Konstantinos Avgoustakis, and Constantinos Tsitsilianis. 2020. "Multicompartmental Mesoporous Silica/Polymer Nanostructured Hybrids: Design Capabilities by Integrating Linear and Star-Shaped Block Copolymers" Polymers 12, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010051
APA StyleIatridi, Z., Evangelatou, K., Theodorakis, N., Angelopoulou, A., Avgoustakis, K., & Tsitsilianis, C. (2020). Multicompartmental Mesoporous Silica/Polymer Nanostructured Hybrids: Design Capabilities by Integrating Linear and Star-Shaped Block Copolymers. Polymers, 12(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010051








