Poly[oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate]-b-poly[(vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride)] Based Multifunctional Hybrid Nanostructures Encapsulating Magnetic Nanoparticles and DNA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. POEGMA-b-PVBTMAC Block Copolymer Synthesis
2.3. Synthesis of CoFe2O4 NPs
2.4. Self-Assembly of POEGMA-b-PVBTMAC Block Copolymer
2.5. Preparation of MNPs–Hybrid Complexes
2.6. Preparation of Magnetopolyplexes
2.7. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of POEGMA-b-PVBTMAC Diblock Copolymer
3.2. Characterization of CoFe2O4 NPs
3.3. Physicochemical Characterization of the POEGMA-b-PVBTMAC Copolymer
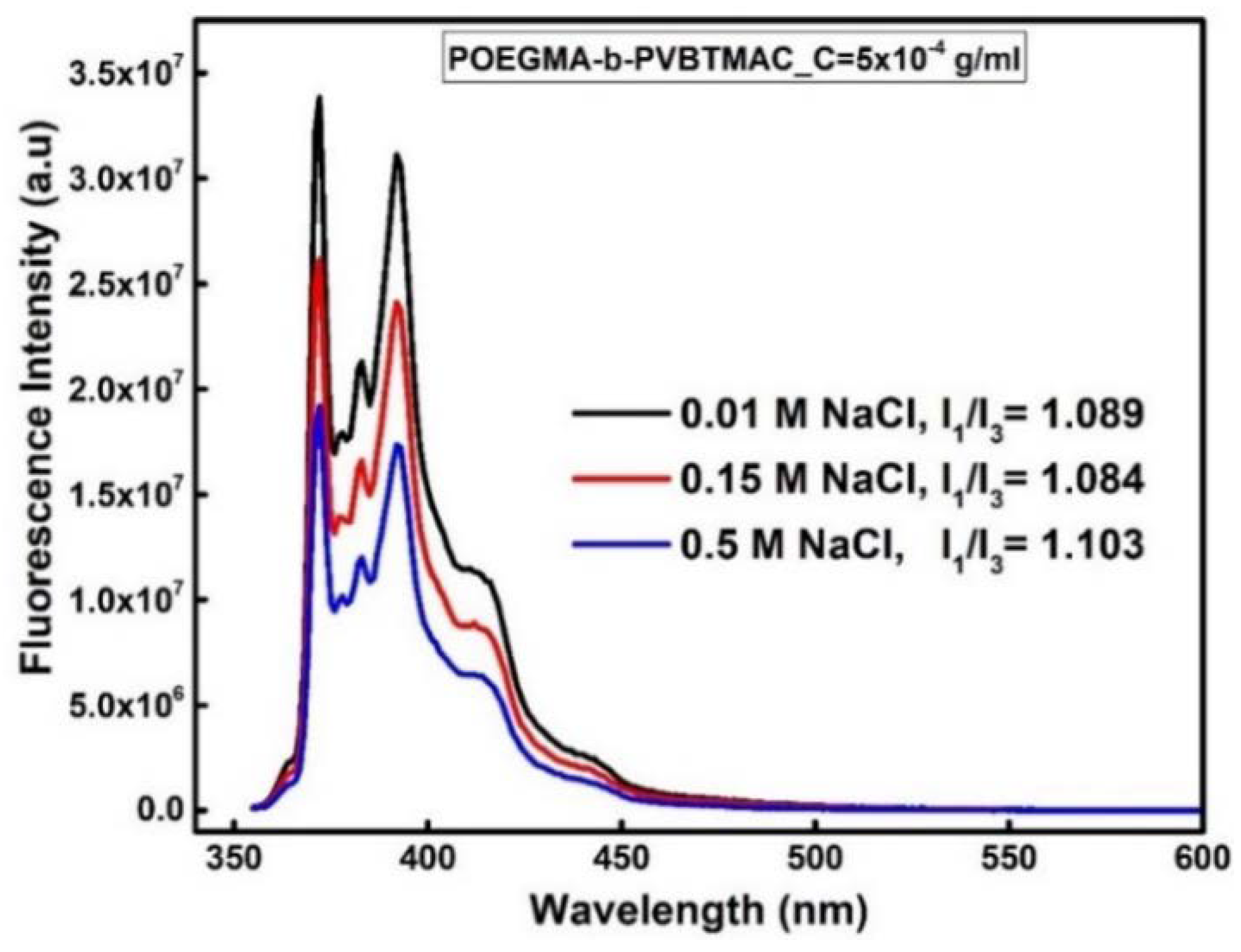
3.4. Effect of Solution Ionic Strength on the Polyelectrolyte Copolymer Behavior
3.5. Electrostatic Complexation of POEGMA-b-PVBTMAC Copolymer with MNPs
3.6. Interaction of BSA with the Diblock/MNPs Hybrid Complexes
3.7. Electrostatic Complexation of POEGMA-b-PVBTMAC Copolymer with MNPs and DNA
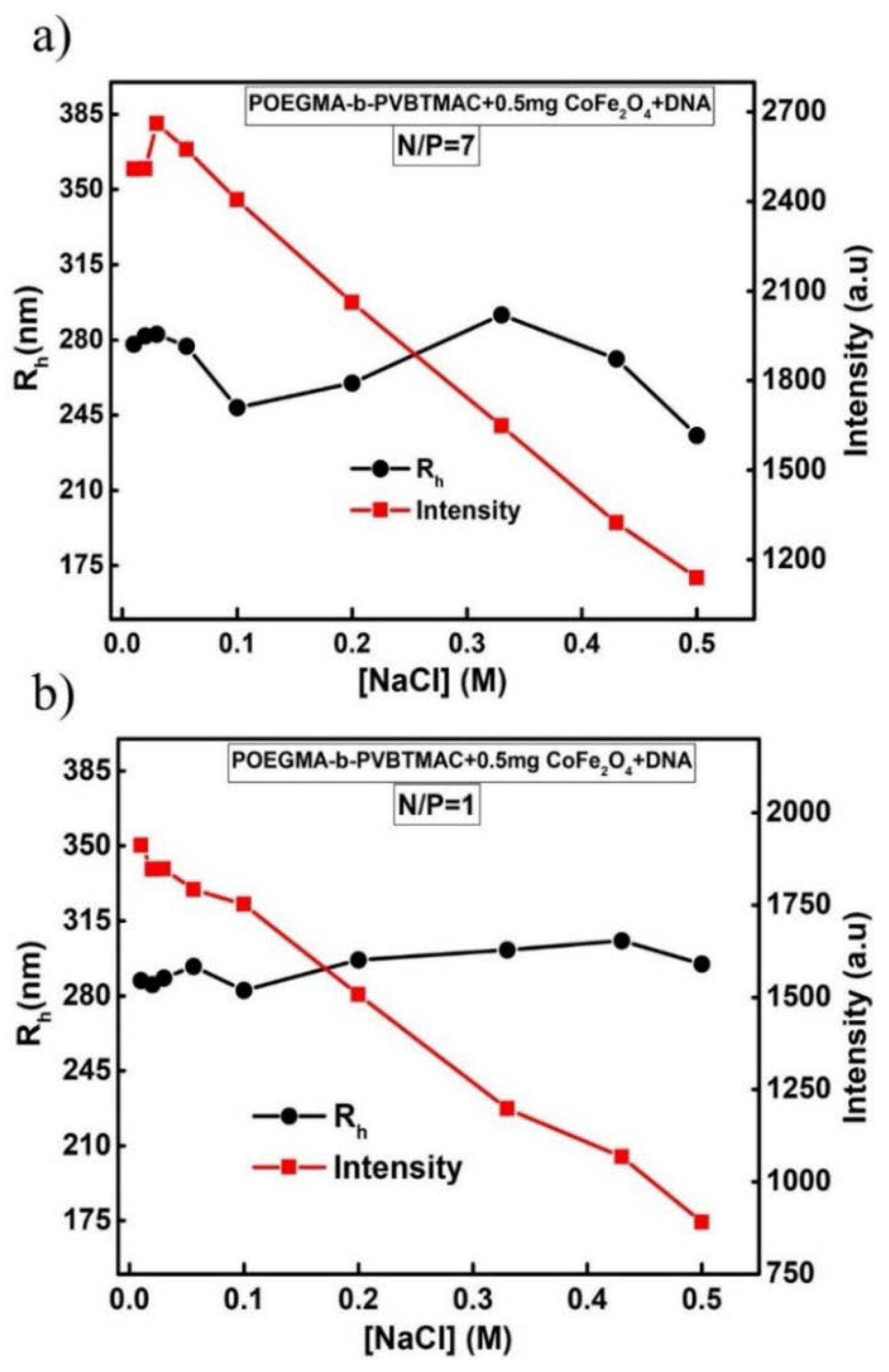
3.8. Behavior of Magnetopolyplexes in the Presence of Salt
3.9. Magnetophoretic Experiments for Diblock/MNPs Hybrid Complexes and Magnetopolyplexes
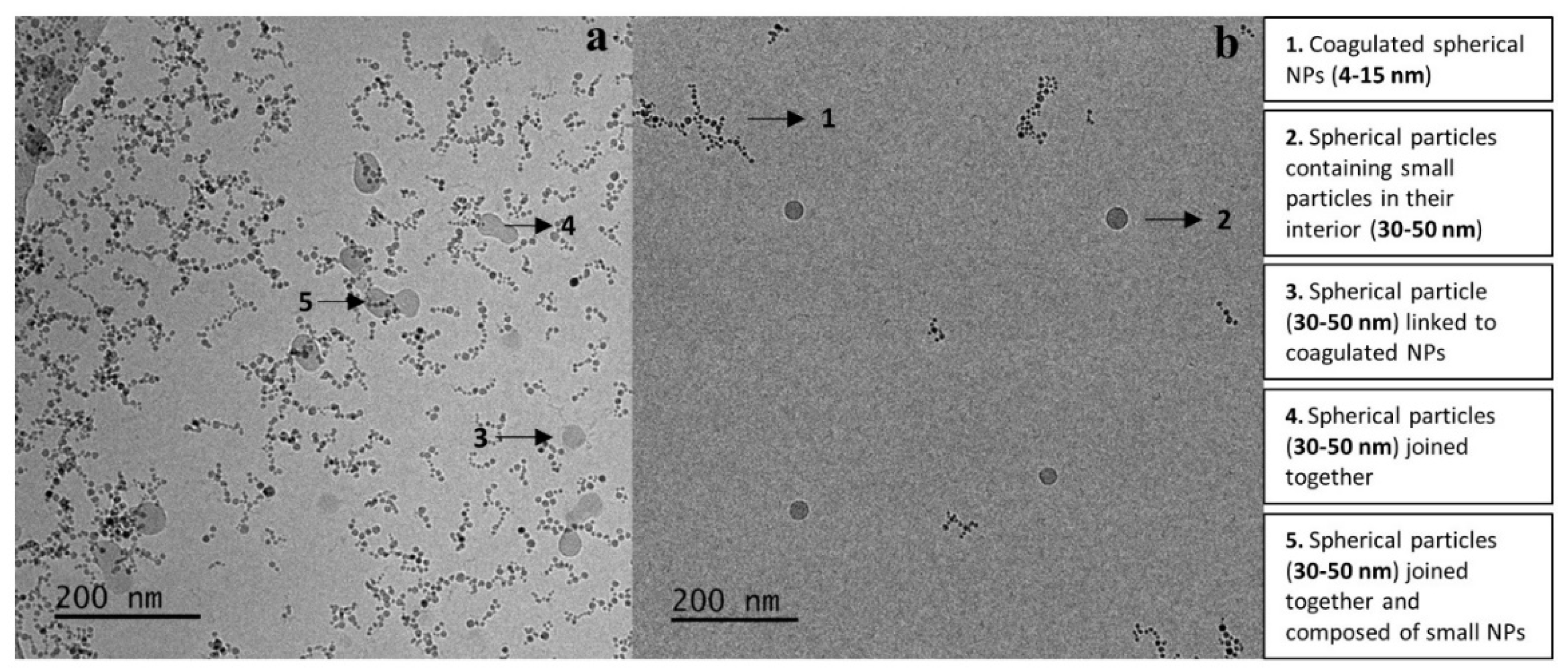
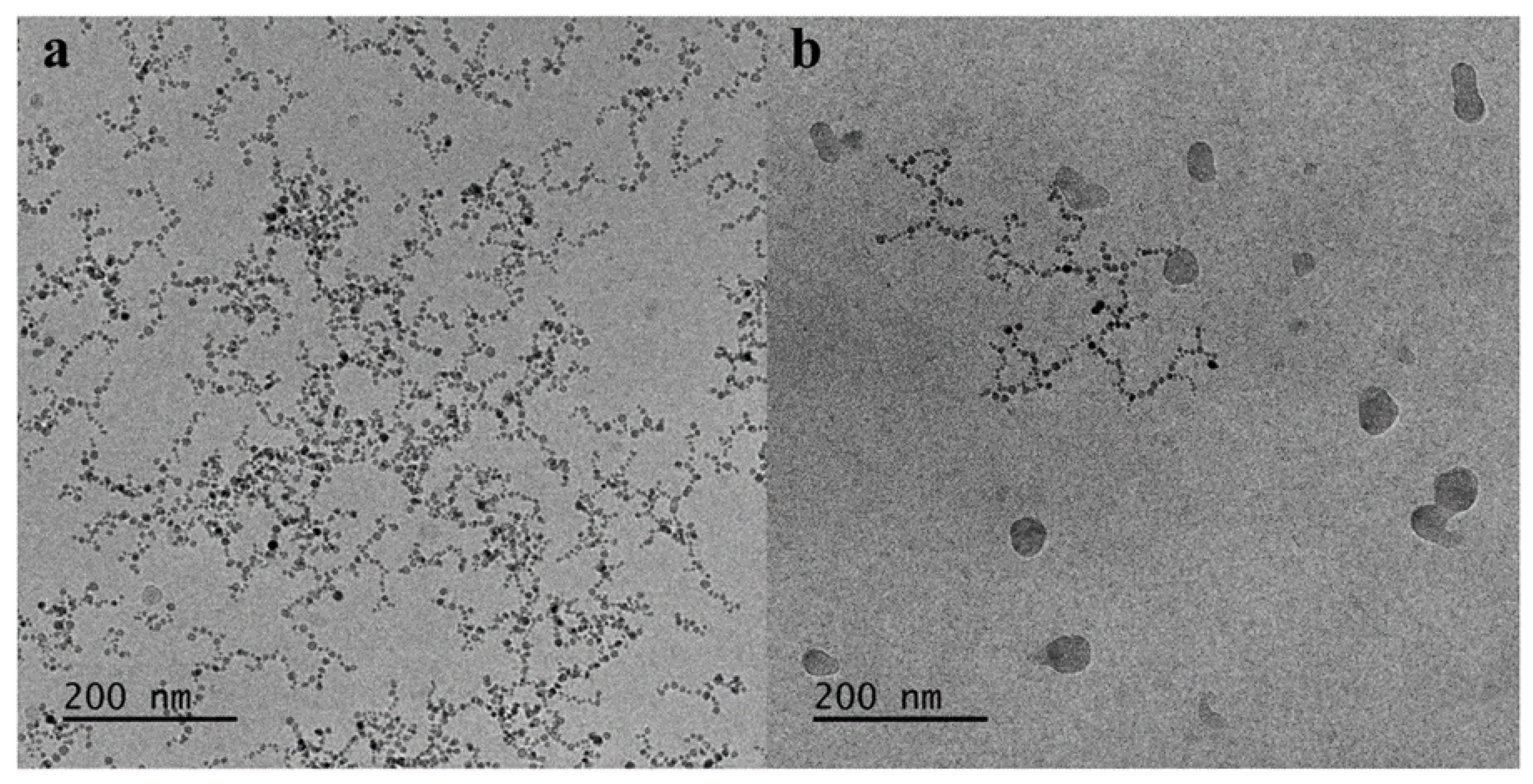
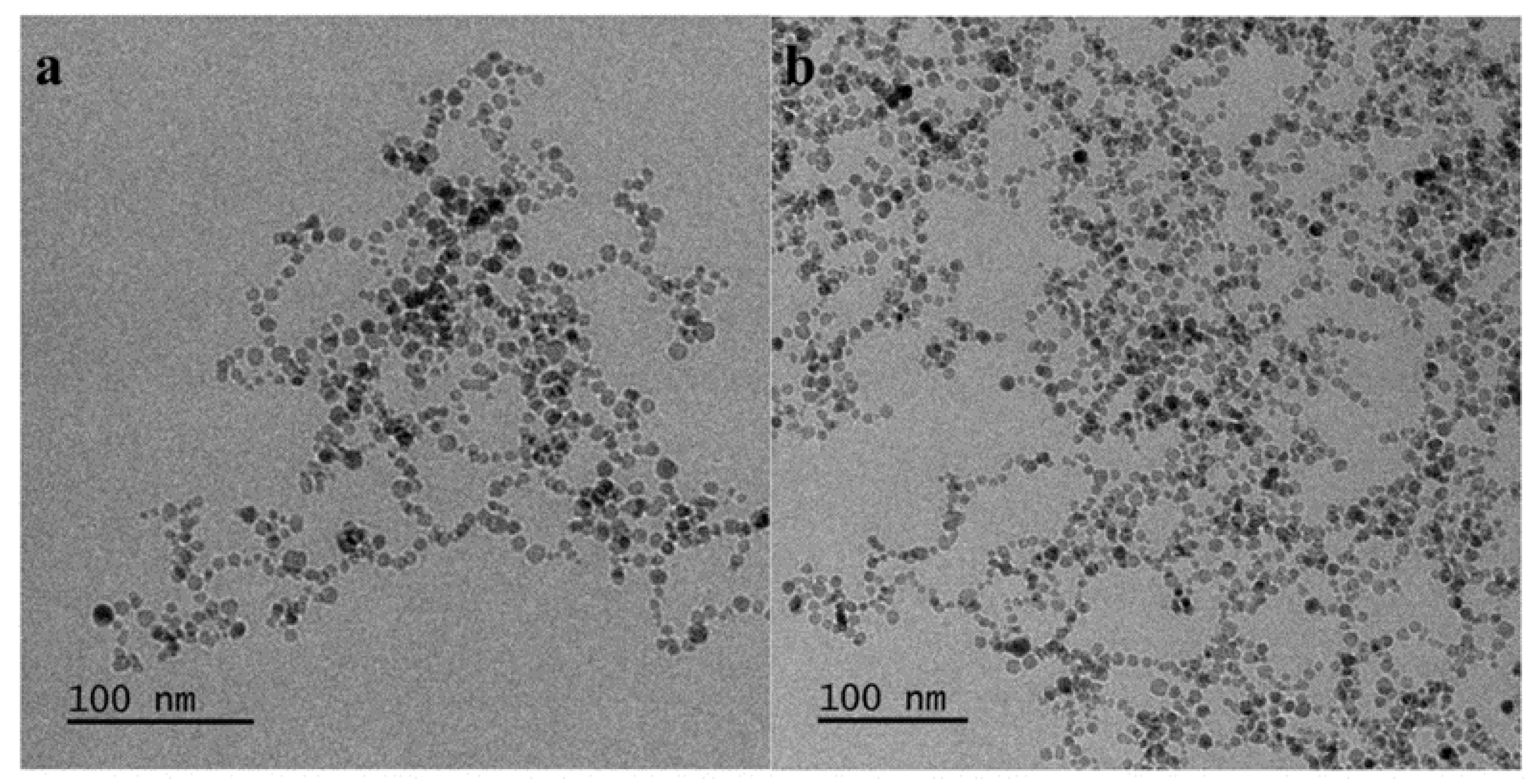
3.10. Cryo-TEM of the MNPs-Hybrid Complexes and DNA-Hybrid Polyplexes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wadajkar, A.S.; Menon, J.U.; Kadapure, T.; Tran, R.T.; Yang, J.; Nguyen, K.T. Design and Application of Magnetic-based Theranostic Nanoparticle Systems. Recent Pat. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 6, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasia-Christoforou, T.; Georgiou, T.K. Polymeric theranostics: Using polymer-Based systems for simultaneous imaging and therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3002–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruebo, M.; Fernández-Pacheco, R.; Ibarra, M.R.; Santamaría, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today 2007, 2, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigit, M.V.; Moore, A.; Medarova, Z. Magnetic nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Gu, H.; Xu, B. Multifunctional Magnetic Nanoparticles: Design, Synthesis, and Biomedical Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-H.; Kuo, T.-R.; Su, H.-J.; Lai, W.-Y.; Yang, P.-C.; Chen, J.-S.; Wang, D.-Y.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-C. Fluorescence-Guided Probes of Aptamer-Targeted Gold Nanoparticles with Computed Tomography Imaging Accesses for in Vivo Tumor Resection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Li, M.; Bratlie, K.M.; Cochran, E.W.; Wang, Q. Polymeric multifunctional nanomaterials for theranostics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6856–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, B.T.; Zhang, L. Current Advances in Polymer-Based Nanotheranostics for Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21859–21873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pispas, S. Double hydrophilic block copolymers of sodium (2-Sulfamate-3-Carboxylate) isoprene and ethylene oxide. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2005, 44, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S.; Gast, A.P.; Bütün, V.; Armes, S.P. Characterizing the Structure of pH Dependent Polyelectrolyte Block Copolymer Micelles. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 4302–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Armes, S.P.; Jin, X.; Zhu, S. Direct Synthesis of Well-Defined Quaternized Homopolymers and Diblock Copolymers via ATRP in Protic Media. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 8268–8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tang, Y.; Billingham, N.C.; Armes, S.P.; Lewis, A.; Lloyd, A.W.; Salvage, J.P. Well-Defined Biocompatible Block Copolymers via Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization of 2-Methacryloyloxyethyl Phosphorylcholine in Protic Media. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 3475–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Armes, S.P. Synthesis and Aqueous Solution Behavior of a pH-Responsive Schizophrenic Diblock Copolymer. Langmuir 2003, 19, 4432–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Armes, S.P. Polymeric surfactants for the new millennium: A pH-Responsive, zwitterionic, schizophrenic diblock copolymer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Billingham, N.C.; Armes, S.P. A Schizophrenic Water-Soluble Diblock Copolymer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2328–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, X.; Zhang, M.; Müller, A.H. Thermo-and pH-Responsive Micelles of Poly (acrylic acid)-block-Poly (N, N-diethylacrylamide). Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2005, 26, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Fang, B.; Drechsler, M.; Müllner, M.; Bolisetty, S.; Ballauff, M.; Müller, A.H.E. Hybrids of Magnetic Nanoparticles with Double-Hydrophilic Core/Shell Cylindrical Polymer Brushes and Their Alignment in a Magnetic Field. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berret, J.-F.; Sehgal, A.; Morvan, M.; Sandre, O.; Vacher, A.; Airiau, M. Stable oxide nanoparticle clusters obtained by complexation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 303, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frka-Petesic, B.; Fresnais, J.; Berret, J.-F.; Dupuis, V.; Perzynski, R.; Sandre, O. Stabilization and controlled association of superparamagnetic nanoparticles using block copolymers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.A.; Kowalczyk, B.; De La Cruz, M.O.; Grzybowski, B.A. Electrostatics at the nanoscale. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1316–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapel, J.-P.; Berret, J.-F. Versatile electrostatic assembly of nanoparticles and polyelectrolytes: Coating, clustering and layer-by-layer processes. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 17, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Nikles, D.E.; Johnson, D.T.; Brazel, C.S. Heat generation of aqueously dispersed CoFe2O4 nanoparticles as heating agents for magnetically activated drug delivery and hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 2390–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Huh, Y.-M.; Jun, Y.-W.; Seo, J.-W.; Jang, J.-T.; Song, H.-T.; Kim, S.; Cho, E.-J.; Yoon, H.-G.; Suh, J.-S.; et al. Artificially engineered magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive molecular imaging. Nat. Med. 2006, 13, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, K.-N.; Kim, K.-M.; Shim, I.-B.; Lee, Y.-K. Temperature change of various ferrite particles with alternating magnetic field for hyperthermic application. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Novosad, V.; Rozhkova, E.A.; Chen, H.; Yefremenko, V.; Pearson, J.; Torno, M.; Bader, S.D.; Rosengart, A.J. Surface Functionalized Biocompatible Magnetic Nanospheres for Cancer Hyperthermia. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 2462–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skandalis, A.; Sergides, A.; Bakandritsos, A.; Pispas, S. PLMA-b-POEGMA Amphiphilic Block Copolymers as Nanocarriers for the Encapsulation of Magnetic Nanoparticles and Indomethacin. Polymers 2017, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berret, J.-F.; Schonbeck, N.; Gazeau, F.; El Kharrat, D.; Sandre, O.; Vacher, A.; Airiau, M. Controlled Clustering of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles Using Block Copolymers: Design of New Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euliss, L.E.; Grancharov, S.G.; O’Brien, S.; Deming, T.J.; Stucky, G.D.; Murray, C.B.; Held, G.A. Cooperative Assembly of Magnetic Nanoparticles and Block Copolypeptides in Aqueous Media. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheparovych, R.; Sahoo, Y.; Motornov, M.; Wang, S.; Luo, H.; Prasad, P.N.; Sokolov, I.; Minko, S. Polyelectrolyte Stabilized Nanowires from Fe3O4Nanoparticles via Magnetic Field Induced Self-Assembly. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, B.; Friedman, G. Magnetic targeting for site-specific drug delivery: Applications and clinical potential. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, H.H.P.; McBain, S.C.; El Haj, A.J.; Dobson, J. A triple-Layer design for polyethyleneimine-Coated, nanostructured magnetic particles and their use in DNA binding and transfection. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 435601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, C.; Schillinger, U.; Scherer, F.; Bergemann, C.; Remy, J.-S.; Krötz, F.; Anton, M.; Lausier, J.; Rosenecker, J. The Magnetofection Method: Using Magnetic Force to Enhance Gene Delivery. Biol. Chem. 2003, 384, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mykhaylyk, O.; Antequera, Y.S.; Vlaskou, D.; Plank, C. Generation of magnetic nonviral gene transfer agents and magnetofection in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2391–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhaylyk, O.; Zelphati, O.; Hammerschmid, E.; Anton, M.; Rosenecker, J.; Plank, C. Recent advances in magnetofection and its potential to deliver siRNAs in vitro. In siRNA and miRNA Gene Silencing; Sioud, M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 487, pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Plank, C.; Rosenecker, J. Magnetofection: The Use of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Nucleic Acid Delivery. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2009, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, S.; Lausier, J.; Gersting, S.W.; Rudolph, C.; Plank, C.; Welsch, U.; Rosenecker, J. Insights into the mechanism of magnetofection using PEI-based magnetofectins for gene transfer. J. Gene Med. 2004, 6, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, S.; Wiehle, S.; Cristiano, R.J. A multifunctional PEI-Based cationic polyplex for enhanced systemic p53-Mediated gene therapy. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 1512–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, A.; Merkel, O.; Fink, L.; Czubayko, F.; Kissel, T.; Aigner, A. In vivo pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and underlying mechanisms of various PEI (–PEG)/siRNA complexes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 236, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haladjova, E.; Mountrichas, G.; Pispas, S.; Rangelov, S. Poly (vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride) Homo and Block Copolymers Complexation with DNA. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 2586–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repko, A.; Vejpravova, J.; Vacková, T.; Zákutná, D.; Nižňanský, D. Oleate-Based hydrothermal preparation of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles, and their magnetic properties with respect to particle size and surface coating. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 390, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Ma, D. Preparation of Co Nanocrystallites by Solvothermal Process and Its Catalytic Activity on the Thermal Decomposition of Ammonium Perchlorate. J. Nanomater. 2010, 2010, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; Mo, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liang, D. Association of Block Copolymer in Nonselective Solvent. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 5339–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Beztsinna, N.; Mountrichas, G.; Van den Dikkenberg, J.B.; Pispas, S.; Hennink, W.E. Small nanosized poly (vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride) based polyplexes for siRNA delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 525, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haladjova, E.; Mountrichas, G.; Pispas, S.; Rangelov, S. Determination of Intimate Composition of Theranostic Polyplexes Based on (Co) Polymers of Poly (vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride). Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2017, 219, 1700428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, D.; Kumar, S.; Banerjee, R.; Maiti, S.; Dhara, D. Polyplex Formation between PEGylated Linear Cationic Block Copolymers and DNA: Equilibrium and Kinetic Studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 7012–7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-W.; Choi, N.H.; Jin, J.-I. Optical, electro-Optic and optoelectronic properties of natural and chemically modified DNAs. Polym. J. 2012, 44, 1191–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | Mn PVBTMAC | Mn POEGMA | % PVBTMAC | PVBTMAC Monomeric Units | POEGMA Monomeric Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVBTMAC | 40,000 | - | 100 | - | - |
| POEGMA-b-PVBTMAC | 4200 | 18,200 | 19 | 20 | 36 |
| Sample | Rh (nm) | PDI | ζpot (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
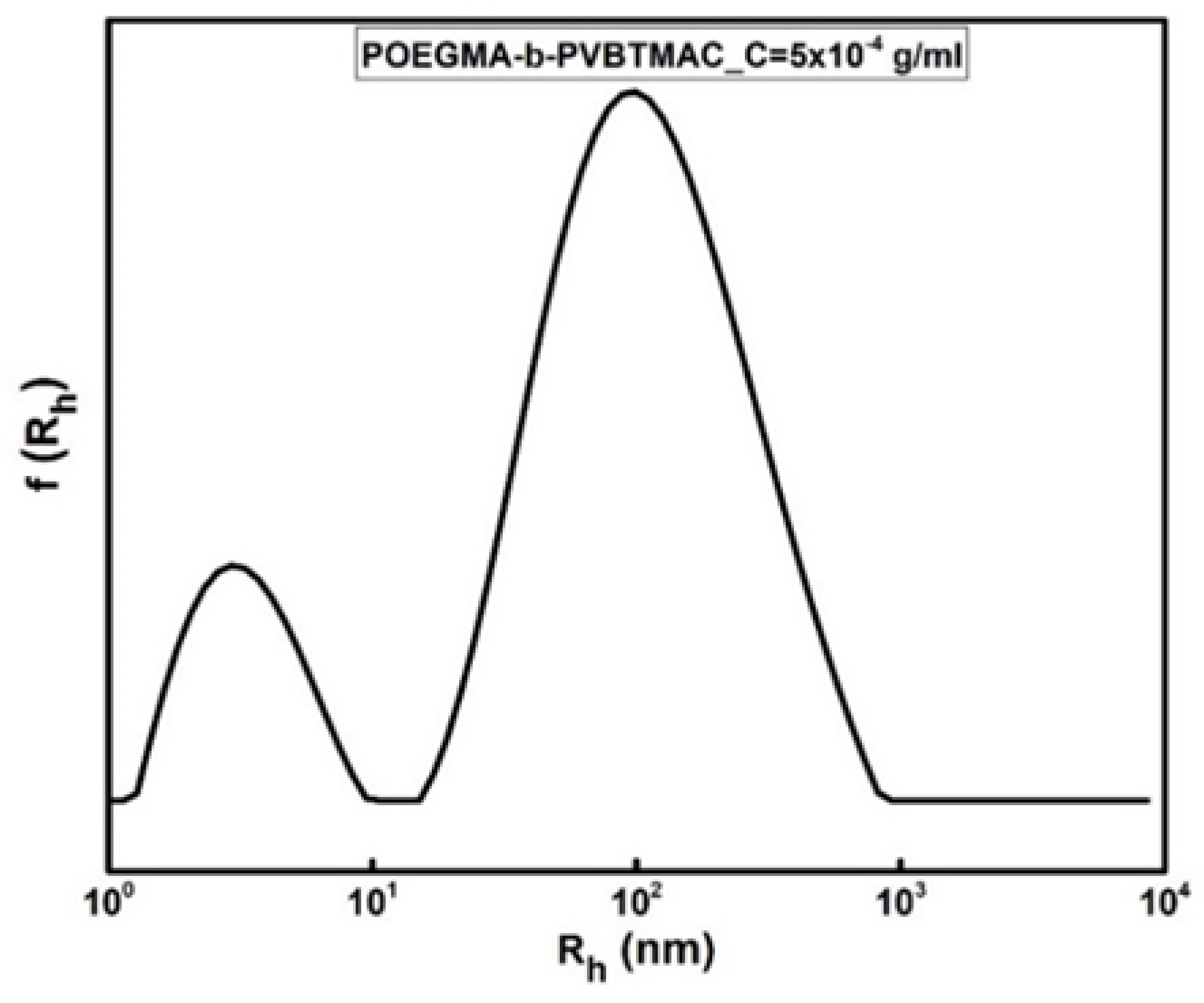
| POEGMA-b-PVBTMAC_C = 5 × 10−4 g/ml | 3/108 | 0.625 | +20 |
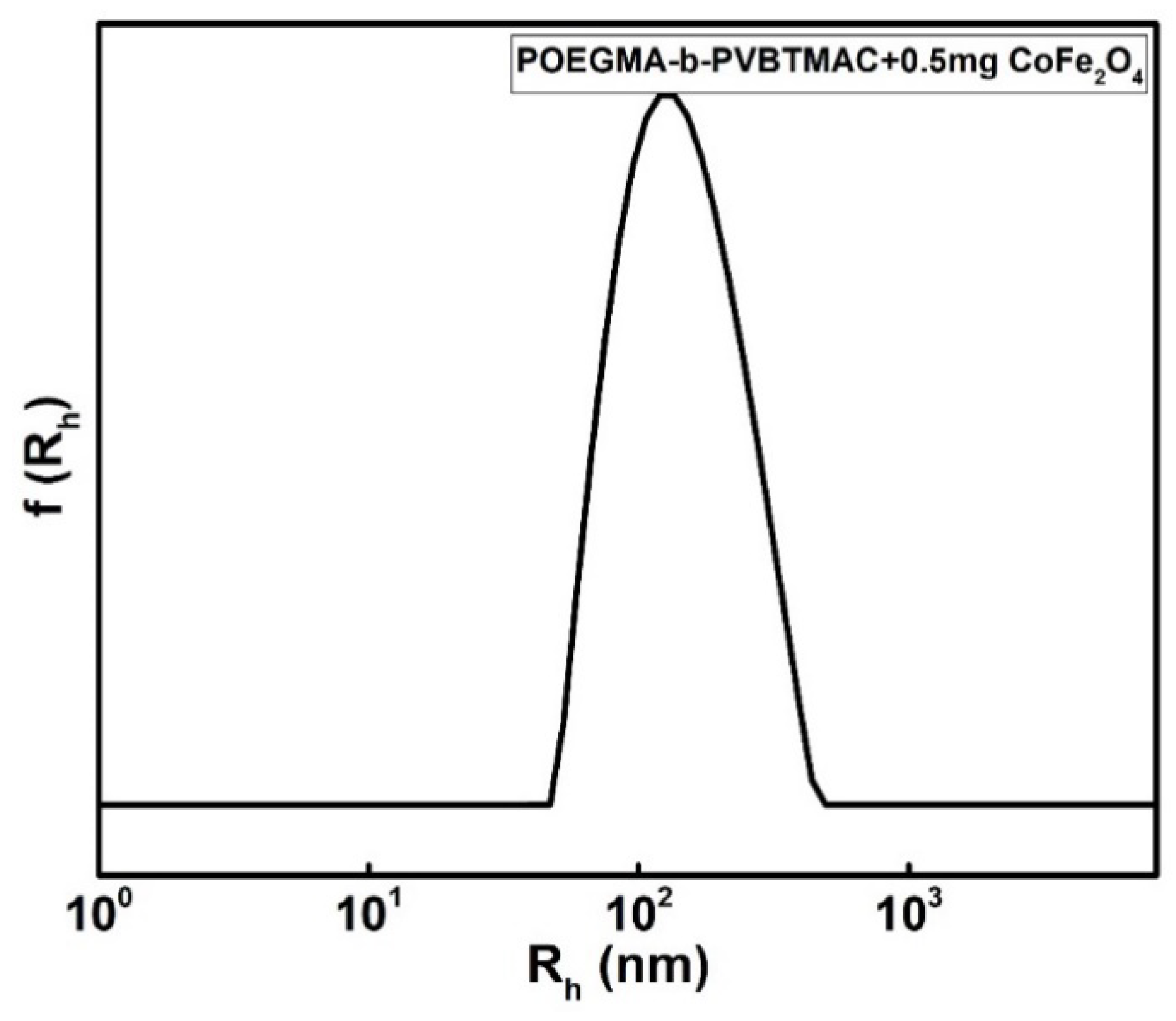
| POEGMA-b-PVBTMAC + 0.5 mg CoFe2O4 | 139 | 0.226 | +14 |
| Sample | Rh (nm) | PDI | Int (kHz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| POEGMA-b-PVBTMAC_C = 5 × 10−4 g/ml | 4/97/469 | 0.5 | 337 |
| POEGMA-b-PVBTMAC + 0.5 mg CoFe2O4 | 300 | 0.340 | 714 |
| POEGMA-b-PVBTMAC + 0.5 mg CoFe2O4 + DNA | 283 | 0.295 | 2143 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chroni, A.; Forys, A.; Trzebicka, B.; Alemayehu, A.; Tyrpekl, V.; Pispas, S. Poly[oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate]-b-poly[(vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride)] Based Multifunctional Hybrid Nanostructures Encapsulating Magnetic Nanoparticles and DNA. Polymers 2020, 12, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061283
Chroni A, Forys A, Trzebicka B, Alemayehu A, Tyrpekl V, Pispas S. Poly[oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate]-b-poly[(vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride)] Based Multifunctional Hybrid Nanostructures Encapsulating Magnetic Nanoparticles and DNA. Polymers. 2020; 12(6):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061283
Chicago/Turabian StyleChroni, Angeliki, Aleksander Forys, Barbara Trzebicka, Adam Alemayehu, Vaclav Tyrpekl, and Stergios Pispas. 2020. "Poly[oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate]-b-poly[(vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride)] Based Multifunctional Hybrid Nanostructures Encapsulating Magnetic Nanoparticles and DNA" Polymers 12, no. 6: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061283
APA StyleChroni, A., Forys, A., Trzebicka, B., Alemayehu, A., Tyrpekl, V., & Pispas, S. (2020). Poly[oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate]-b-poly[(vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride)] Based Multifunctional Hybrid Nanostructures Encapsulating Magnetic Nanoparticles and DNA. Polymers, 12(6), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061283









