Abstract
Oil spills and the emission of oily wastewater have triggered serious water pollution and environment problems. Effectively separating oil and water is a world-wide challenge and extensive efforts have been made to solve this issue. Interfacial super-wetting separation materials e.g., sponge, foams, and aerogels with high porosity tunable pore structures, are regarded as effective media to selectively remove oil and water. This review article reports the latest progress of polymeric three dimensional porous materials (3D-PMs) with super wettability to separate oil/water mixtures. The theories on developing super-wetting porous surfaces and the effects of wettability on oil/water separation have been discussed. The typical 3D porous structures (e.g., sponge, foam, and aerogel), commonly used polymers, and the most reported techniques involved in developing desired porous networks have been reviewed. The performances of 3D-PMs such as oil/water separation efficiency, elasticity, and mechanical stability are discussed. Additionally, the current challenges in the fabrication and long-term operation of super-wetting 3D-PMs in oil/water separation have also been introduced.
1. Introduction
The rapid development of textile, steel, metallurgy, petrochemical, and other industries has produced a large amount of oily wastewater, causing serious pollution to rivers, lakes, and other water bodies [1,2,3,4]. Among which, oil spillage during mining, transportation, and storage in the petroleum industry are the primary sources of oily wastewater emission [5,6]. For instance, the rapid spreading of the oil slick and the emulsified oil that occurred during mining in the Gulf of Mexico in 2010 (Figure 1) [7,8] and the Bohai Bay in 2011 [9] have caused a devastating blow to marine life and brought disasters to the ecosystem. The spilled oil floated on sea (Figure 1a) [10] threatens the living of sea creatures e.g., oil covered turtle (Figure 1c) [11] and brown pelican (Figure 1d) [12], and trapped them in the spilled oils preventing their swimming or flying while the burned oil released heavy smoke, which caused serious air pollution (Figure 1b) [13]. Oil spills to water not only threats the safety of the ecosystem and human society but also is a great waste of resources [3]. For this world-wide environmental problem, scientists are constantly exploring new and effective technologies and materials to separate oil/water mixtures and recycle oil from oily wastewater efficiently.

Figure 1.
Gulf of Mexico oil spill event [7]: (a) marine ecosystems are polluted [10], (b) preventing the rapid spread of oil via oil fences and burning, and wide range of smoke causing serious air pollution [13]; reproduced with permission from the public domain in the United States. (c and d) the turtle [11] and brown pelican [12] contaminated with leaked crude oil on the sea; reproduced with permission from the Thinkstock and the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic.
Traditional methods including gravity-driven separation, filtration, flocculation, flotation, adsorption, biodegradation, etc. [14,15,16] have been widely utilized to purify oily wastewater. These methods show unique advantages in oily wastewater treatment. Gravity-driven separation can effectively separate oil from water by using the density difference between oil and water [17]. Traditional membrane filtration allows the penetration of small water molecules while prohibiting the passing through of oils under the assistance of pressure or electrical potential achieving oil/water separation [18,19]. Flocculants are commonly used agents to eliminate floated, dispersed, and emulsified oils in water through coagulating oils into large precipitates to achieve oil/water separation [20]. Floatation separates the oil/water mixtures via pushing oil droplets to the surface by bubbling [21]. The mixed oils in water can also be removed by adsorbing. Many adsorbents e.g., wood sheets, zeolites, fabrics, cotton, and linen etc. with large surface area and porosity are easy to obtain from nature and widely used for oil adsorption to separate oil from water [22,23]. Small amounts of oils can be biodegraded into small molecule or CO2 and water by the microorganisms in water to purify oily waste water [24,25]. Nevertheless, the significant shortcomings of these methods, for instance, low separation efficiency and large space occupation of gravity separation, fouling and poor oil/water selectivity of membrane separation, difficulty in reuse/recycling of adsorbents and flocculants, low adsorption capacity and secondary pollution, etc., restrict their practical applications in oily wastewater treatment [6,26,27,28].
Since 1997, the German botanist Baethlott [31] reported that water droplets sit on lotus leaves with water contact angle larger than 150° and roll off easily carrying away the dust when tilting and this phenomenon is defined as the “lotus effect”. This extraordinary property is named as superhydrophobicity and self-cleaning [32,33,34]. Further investigation showed that lotus leaf is comprised of nano/microhierarchical structures and they are coated with low surface energy wax to reduce surface energy, thereby delivery superhydrophobicity and self-cleaning property (Figure 2a) [29,30]. This unique property can be used to design superhydrophobic membranes to eliminate oil from water achieving oil/water separation. In 2004, Feng et al. [35] developed superhydrophobic-superoleophilic copper mesh by dip-coating hydrophobic polytetrafluoroethylene and oil was removed from water through this membrane under gravity-driven separation. Another example learning from nature is mimicking the superhydrophilic-underwater superoleophobic structures from fish scales (regular fan-shaped microstructures (Figure 2b)) to fabricate oil/water separation membranes to remove water from oil/water mixture and keep cleaning from oils [36]. In 2011 Xue et al. [36] fabricated superhydrophilic polyacrylamide (PAM) mesh, which allows water penetration while repelling oil, thereby reduces oil pollution. Dunderdale et al. [37] prepared a more advanced amphiphilic stainless steel mesh which was modified by hydrophilic polymethacrylic acid (PMAA) and hydrophobic poly(ethylhexylmethacrylate)(PEHMA) and can switch its surface wettability in response to various stimulations to effectively separate oil/water mixtures. After that, oil/water separation material with biomimetic super-wettability has undergone rapid development [38,39]. However, the issues of membrane fouling and weak intrusion pressure restrict the long-term operation. Recently, two meshes with opposite wettability were modified by polymer brush and combined to treat oil/water solutions, resulting in high efficiency under high flux and keeping surfaces free from oil contamination [40,41]. Nevertheless, membranes cannot be used to adsorb or store the spilled oils. Therefore, designing a new type of oil/water separation material with high selectivity, adsorption capacity, anti-fouling property, and recyclability is essential for long–term oily wastewater treatment.
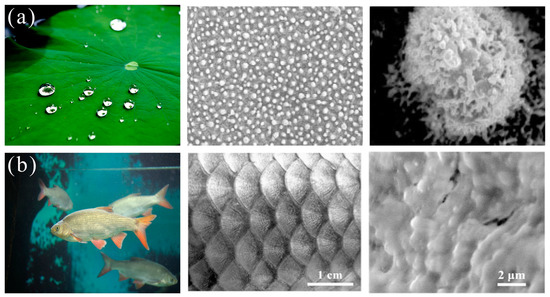
Figure 2.
Biological surfaces with super-wettability and their structures: (a) lotus leaf [29]; reproduced with permission from Wiley. (b) fish scales [30]; reproduced with permission from Wiley.
To increase the penetration channel and separation efficiency, there are some attempts at using inorganic and metal-based 3D-PMs (normally are ceramic foams or copper/nickel foams etc.) [42,43,44,45]. However, their significant disadvantages such as brittle, lack of elasticity, ease of corrosion in acid/base environment, unable to be reused, and difficulty in surface modification restrict the application in oily wastewater treatment. Recently, polymer-based three-dimensional porous materials (3D-PMs) (such as sponge [46,47,48], foam [49,50,51,52], and aerogel [53,54,55]) with multi-layered network structure, higher porosity, adsorption capability, long penetration channel, and tunable pore structure are regarded as promising alternates for effectively oil/water separation after being functionalized with special wettability [56,57,58,59,60]. This is because polymers are always light in weight, ease of processability, resistance to corrosion, chemical stability, and the abundant functional groups on the surface which can be modified with a variety of materials easily [53,61,62,63,64,65]. Especially, the excellent flexibility of polymers enables the high elasticity of polymer 3D-PMs. The elastic 3D-PMs can be compressed and recycled under a certain pressure to discharge the adsorbed oil by compression, which simplifies the separation process [65,66]. Therefore, polymers have been widely used in developing 3D-PMs and polymeric 3D-PMs have become one of the research hotspots in oil/water separation. The published articles on superwetting polymeric oil/water separation 3D-PMs (from 2011 to February 2019) are shown in Figure 3, indicating that polymeric 3D-PMs have undergone rapid development. Interfacial superwetting 3D-PMs are mainly divided into four categories according to their surface wettability and their functions in dealing with different types of oil/water mixtures: (i) superhydrophobic-superoleophilic 3D-PMs are used to absorb oil; (ii) superhydrophilic-underwater superoleophobic 3D-PMs are used to eliminate the layered oil/water mixture and oil-in-water emulsions; (iii) superhydrophilic-superoleophobic 3D-PMs are used to remove water from oily wastewater and eliminate water from water-in-oil emulsion; (iv) 3D-PMs with switchable super-wettability, which can change wettability and remove oil or water by responding to the external stimulation. In this feature article, firstly, the theoretical mechanism of oil/water separation of super-wetting 3D-PMs is reviewed. Then, the design routes, techniques, the applications in different oil/water mixtures treatment, the current challenges existed in 3D-PMs oil/water separation such as oil contamination, relatively weak mechanical robust under certain pressure, difficulties in oil-desorption, and the adsorption or separation efficiency, were also discussed. Finally, the perspective of the future development on fabrication 3D-PMs to meet the practical requirements is briefly discussed.
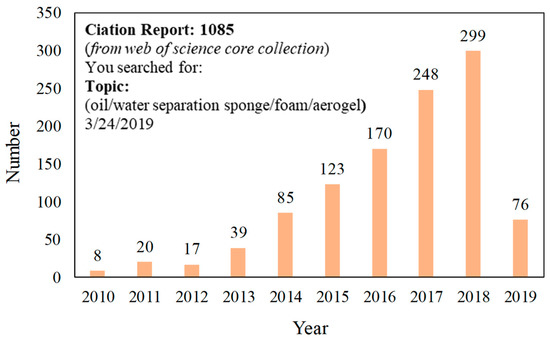
Figure 3.
The published articles from 2010 to February 2019 indexed in ISI Web of Science by searching “oil/water separation sponge/foam/aerogels”.
2. Theoretical Background
Surface wettability is the fundamental property of 3D-PMs for the applications in oil/water separation. Either hydrophilic or hydrophobic 3D-PMs cannot be directly used because both oil and water can wet and pass through the porous structure [62,67,68,69]. Thus, developing the 3D-PMs with selectively oil/water separation property is critical and can be achieved by creating special wettability [60]. The classic theories of Wenzel [70] and Cassie–Baxter indicated that surface wetting is dominated by the chemical composition and surface structure [33]. Thus, the modification of surface energy and the construction of proper pore structure are vital to super-wetting 3D-PMs. Besides, the wettability and surface structure are also an important parameter to determine the separation efficiency and the surface fouling.
2.1. Wetting on Porous Surface
2.1.1. Contact Angle in Air
Wetting behaviors on solid surface is mostly reflected by measuring the water contact angle (WCA) [71]. For an ideal smooth surface, WCA refers to the results of interactions between gas, liquid, and solid phases (Figure 4). Usually, the WCA can be obtained by Young’s equation [72]:
where θ represents the intrinsic contact angle, and γgs, γsl, γgl are the surface energy of gas-solid, solid-liquid, and gas-liquid interfaces, respectively. When θ < 90°, the surface is hydrophilic (Figure 4) while the surface is hydrophobic when θ > 90° (Figure 4).
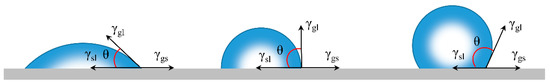
Figure 4.
Schematic illustration of Young’s model [73]; the contact angles (θ) formed by liquid droplets on a smooth homogeneous solid surface in air (left). A hydrophilic (middle) surface with θ < 90° and a hydrophobic surface with the θ > 90°(right); reproduced with permission from Springer.
Since the surface of 3D-PMs is composed of micro/nanopores and is not smooth [74], its wettability cannot be obtained directly from Young’s equation [70,75]. The wetting behaviors of water on porous or rough surfaces can be illustrated by Wenzel and Cassie–Baxter theories [70,76] that the wettability of real surface is the synergetic effects of the surface energy and the surface structure. Wenzel systematically investigated the effects of roughness on wettability, showing that the wettability can be enlarged by surface roughness. In this model, water contacts the solid surface and completely wets and fills into the rough structure resulting in the larger actual contact compared to the apparent contact of the smooth surface (Figure 5a). Therefore, WCA can be calculated from Wenzel equation [70]:
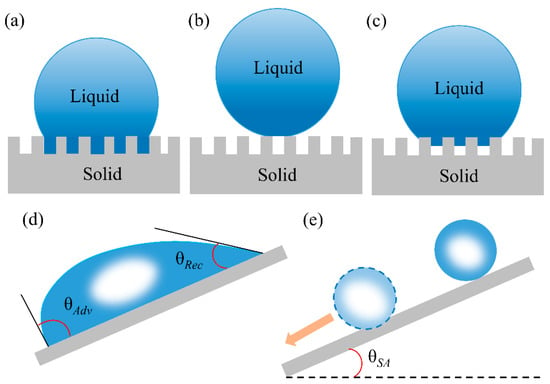
Figure 5.
Effect of solid surface structure on wetting behavior: (a) Wenzel mode [70], (b) Cassie–Baxter mode [76], (c) intermediate states between the Wenzel and the Cassie modes [33]; reproduced with permission from Wiley. (d) Illustration of the “tilted plate” method to measure advancing/receding angle, respectively when the drop just starts to move [73]; reproduced with permission from Springer. (e) Illustration of the sliding angle [83]; reproduced with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry.
In which θ*W and θ are the apparent contact angle and contact angle on ideal flat surface, respectively; r is the ratio of the practical contact area of the solid-liquid interface to the ideal flat surface (r > 1). The Wenzel equation shows that surface roughness is important for the enhancement of the solid surface wettability [77]. However, extremely high roughness or regular porous structure results in cos θ*W larger than 1 or less than −1, which is mathematically unacceptable. To illustrate this phenomena, Cassie–Baxter proposed [76] that the trapped air-pockets under water droplets are considered as the superhydrophobic medium, which repels water wetting and penetration. Thus, the liquid–solid interface is replaced by the air-liquid interface resulting in superhydrophobicity (Figure 5b). The contact angle is defined as Equation (4) [76]:
where φs is the ratio between the contacted solid and liquid. θ*CB represents the apparent contact angle of composite surface. The Cassie–Baxter state is metastable and can easily transit into stable state by breaking the air-pockets and filling with water under. This process can occur by the stimulating of external factors such as pressure [78], electric field [79] etc., the liquid may overcome the energy barrier to transition from Cassie–Baxter state to Wenzel state (Figure 5c) [80,81,82].
2.1.2. Contact Angle Hysteresis
In actual oil–water separation, low surface tension oils tend to adhere to the separation materials causing the surface contamination and the reduction of oil/water separation efficiency [29,71,75,84]. Thus, the self-cleaning performance is a great concern of super-wetting materials and is normally characterized by contact angle hysteresis (CAH) [71]. The intrinsic meaning of CAH is the interactions between liquid droplets and the contacted solid surface. CAH reflects the smallest energy that the droplet needs to overcome to slide off. The smaller the CAH the less energy the liquid droplet has to overcome. CAH is the result of the difference between advancing contact angle (adv, Figure 5d) and the receding contact angle (rec, Figure 5d), in which adv and rec are is the largest and smallest angle contact angle at the starting point of droplet sliding [29,71,75,84]. The tilting angle of the solid surface when the water droplet started to roll off is defined as sliding-off angle which illustrates the adhesion between and liquid droplet [75,84]. The CAH, adv, rec and sliding-off angle (Figure 5e) reflects the motion behavior of water droplets on a surface and the self-cleaning property of solid surface that the smaller the CAH and sliding-off angle the smaller adhesion of surface and better self-cleaning property.
2.1.3. Contact Angles in Water or Oil Phases
As illustrated above the liquid contact angle in air can be predicted from Yong’s equation, the contact angle of liquid a (la) in liquid b (lb) cannot be calculated from Young’s equation. In order to explain the wetting behaviors of liquid a on solid surface in liquid b and calculate the liquid a contact angle under liquid b (θLaCA), the following equation has been derived from Young’s equation [30,85,86]:
where γla-g, γlb-g and γla-lb are interface tensions of liquid a-gas, liquid b-gas and liquid a-liquid b interface, respectively. θa and θb are the contact angle of liquid a and liquid a in air, respectively. (Figure 6a)
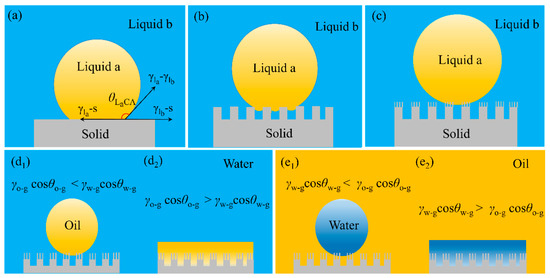
Figure 6.
(a–c) Illustration of the behavior wetting effect by surface structure of the solid substrates in oil/water [30]. (a) smooth surface, (b) microstructure surface, (c) micro/nanohierarchical surface in liquid b; reproduced with permission from Wiley. (d,e) Illustration of the theoretical extreme wettability of solid substrate surface in water/oil [87]. The substrate exposed in the water or oil shows four oil–water states: (d1) superoleophobic, (d2) superoleophilic, (e1) superhydrophobic, (e2) superhydrophilic. o-g: oil and gas interface, w-g: water and gas interface; reproduced with permission from American Chemical Society.
If a surface is hydrophilic, the contact angle of oil and water are less than 90° and θwater-air is larger than θoil-air. Thus, the value of cosθoil-air and cosθwater-air are positive and an oleophobic surface in water is reached when γoil-aircosθoil-air is smaller than γwater-aircosθwater-air (because the surface tension of water is larger than oil). When water contacts with solid surface in oil phase, cosθwater-oil is positive and oil is replaced by water showing hydrophilicity in water. The value of cosθwater-air and cosθoil-air of a hydrophobic-oleophilic surface in air are negative and positive, respectively, such surface shows underwater hydrophilicity and underoil hydrophobicity correspondingly which can be calculated from Equation (5) (Figure 6d,e).
Cassie–Baxter mode is also available for a rough surface in water/oil environment and the wettability of the solid surface can be expressed as the following equation [30,76,88] (Figure 6b):
where φs is the ratio between the contacted solid and liquid a, θLaCA is the intrinsic liquid a contact angle in liquid b. In water phase, water molecules are trapped in the nano/microstructures and forms water-solid interface which prohibits the contact between oil and solid surface showing superoleophobicity (Figure 6c).
2.2. Oil/Water Separation Theory Analysis
To better explain the oil/water separation behaviors of superwetting 3D-PMs and make the separation process more clearly, it is hypothesized that the surface or any section is idealized as a mesh plane according to the Yong-Laplace equation [74,89]. Usually, the surface of the liquid is horizontal which generates the external pressure on porous surface. Before the liquid completely wets and touches the bottom of pores, an intrusion pressure Δpit have to be overcome, which is described as [90,91,92,93]:
where γ is interface tension of water/oil, R is the sedi-diameter of the meniscus, θA is advancing contact angle of the liquid, and d is the average diameter of the pore. Equation (7) shows that when θA < 90°, i.e., the intrusion pressure , the intrusion pressure is broken and oil spontaneously permeates through the pores driven by gravity. Conversely, when θA > 90°, i.e., the intrusion pressure , means that the hole can sustain pressure to some extent, and the water is blocked outside [92,93].
For a surface with θA,water > 150°, the water intrusion pressure Δp,water > 0 while the oil intrusion pressure Δp,oil < 0 (θA,oil < 30°) (Figure 7a,b) that water is prevented while the oil can easily break through the porous structure driven by the gravity achieving oil/water separation. On the contrary, for a porous surface with θA,water < 30° which is superhydrophilic allowing water passing through. This is because such superhydrophilic porous materials must be firstly wetted by water to form the water films [74] under capillary force thereby repel the penetration of oil pass through. However, in long-term operation the water film tends to move to the bottom of the hole and oil starts to fill the pores under the effect of gravity, causing the reduction of oil repellency. As time goes by, the water-solid interface in the pore is replaced by oil-air interface gradually resulting in the decrease of Δp,oil (Figure 7c) [89].
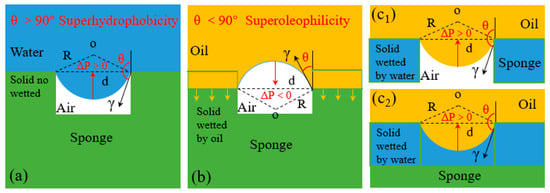
Figure 7.
Schematic illustration of liquid-wetting modes of 3D materials [74,89,90]; (a) because Δp is positive, the superhydrophobic 3D material repels the water penetration by the trapped air. (b) because Δp is negative, the oil can permeate the superhydrophobic 3D material spontaneously. (c) there are two states of the oil supported by superhydrophilic 3D materials: (c1) the oil layer supported by the trapped air in cavities, (c2) the oil layer supported by the trapped water in cavities; reproduced with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry.
The oil/water separation efficiency of 3D-PMs can be evaluated by oil absorption capacity k and separation efficiency R following equations [94,95]:
where mo is initial mass of porous material, me is the total mass of the porous material and the absorbed liquid [36].
where C0 and Cp are the oil concentrations in oily wastewater mixture before and after de-oiling.
3. Fabrication Special-Wettable Oil/Water Separation Three Dimensional Porous Materials (3D-PMs)
The fabrication of super-wetting 3D-PMs follows the classical theories by the combination of creating hierarchical structures (nano/microstructure) and surface chemistry modification. The surface structure can be fabricated via many methods such as etching, nanomaterials modification while the surface chemistry can be tubed through low or high surface energy molecules. During the past decades, a variety of research articles have been published on fabricating special wettable 3D-PMs through post-modification, self-assembly, phase separation etc. (Table 1). The post-modification is the technique to modify on commercial polyurethane (PU) [96], melamine foam [97], polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) sponge/foam [51,98] with inorganic nanomaterial or inorganic-organic composite as modification agents through vapor deposition, dip-coating, chemical etching, and solution immersion. Self-assembly includes polymerization, freeze-drying, sol−gel process, electrospinning, phase separation, etc. and aerogel and sponge with ultralight, large specific surface area and porosity can be fabricated through this method. The common used techniques to develop different type of super-wetting 3D-PMs are summarized in Table 1. The following sections review the design routes, techniques and materials which are used in developing special wettable 3D-PMs, their performances in oil/water separation and the current challenges.

Table 1.
The techniques reported to develop different super-wetting 3D porous materials and the treated specific type of oil/water mixtures.
3.1. Superhydrophobic-Superoleophilic Oil/Water Separation 3D-PMs
3D-PMs with superhydrophobicity-superoleophilicity repel water while it can be wetted by oils allowing the passing through of oils to remove oil from water. Nowadays, three types of superhydrophobic-superoleophilic 3D-PMs e.g., sponge, foams and aerogels have been developed to adsorb light oil from water surface [67,99,122,123]. The adsorption capacity of oils can reach as high as around more than one hundred times of the original weight of 3D-PMs and the separation efficiency can reach to 99% [124]. Currently, two common ways are employed to prepare superhydrophobic 3D-PMs porous materials: (a), utilize the inherent pore structures of commercial PU/melamine/PMMA sponges to achieve superhydrophobicity through surface modification e.g., dip-coating [117], solution-immersion [125] or vapor deposition [126]; (b), use the polymer, graphene, polymer composite as precursor to construct hydrophobic porous 3D structures through self-assembly approach such as foaming technology [105], freeze-drying [127] or electrospinning [128] methods.
3.1.1. Preparation Superhydrophobic 3D-PMs on Commercial Foam/Sponge
Commercial sponge/foams (polyurethane, melamine, polyethylene, polystyrene, poly(melamine formaldehyde)) are inexpensive porous materials with high porosity (typically > 95%), low density (<18 mg/cm3), regular skeleton, elasticity, high mechanical property and chemical stability which are widely used in industry and daily life such as, thermal insulation, sound absorption and shock absorption [67,125,140]. These outstanding properties of commercial sponge/foam enable they can be used for oil/separation after proper modifications. Generally, both water and oil can wet and pass through commercial sponges which is lack of selectivity and oil/water separation performances [112]. However, designing superhydrophobicity to repel water penetration via different types of materials including organic, inorganic, and composite agents by changing surface energy or surface structure is regarded as an easy and feasible way.
Organic Agents
Commercial sponges/foams have abundant microporous structures and can reach superhydrophobicity after surface energy reduction and surface roughness increment. During the past decades, a variety of organic polymers with low surface energy such as hydrophobic organosilanes [108,125] and long-chain alkanes (i.e., fluorine/amine/thiol) [56,141] are extensively used to modify commercial sponges/foams by dip coating, solution-immersion, vapor deposition, situ-polymerization, chemical bonding, and crosslinking (Table 2). Zhang et al. [124] firstly etched the original polyurethane (PU) foam by CrO3 and H2SO4 solution to create rough structures on skeleton. The water contact angle on the sponge decreased from 56° to 0° and the sponge became superhydrophilc after etching. Then the hydrophobic fluoroalkylsilane (FAS) was grafted onto the sponge to reduce the surface energy and the water contact angle was larger than 155° with the sliding-off angle less than 5° via solution immersion. The self-cleaning property is very important for the foam and can be used to remove dust from the foam surface avoiding the blocking of pores (Figure 8e). The obtained superhydrophobic foam can selectively eliminate gasoline, crude oil, and petroleum ether from oily wastewater and the separating efficiency is above 95%. Methyltrichlorosilane with low surface energy was also reported to modify the PU sponge to reduce surface energy to delivery superhydrophobicity (Figure 8b) [108]. However, fluorosilane and chlorosilanes are usually toxic, with ease of deliquescent and hydrolysis to generate hydrogen fluoride or hydrogen chloride causing adverse effects to the environment. Organosiloxane is non-toxic organic matter with hydrophobicity, which can anchor to the surface firmly through cross-linking or situ-polymerization. Chen et al. [125] dip-coated the diluted polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and hexane precursor onto a melamine sponge to fabricate superhydrophobic sponge (WCA > 150°) for oil/water separation. This superhydrophobic sponge can absorb 45–75 times oils or organic solvents of its initial weight and maintains stable oil adsorption capacity after 20 cycles of oil absorption and squeezing. Xiong et al. [140] grafted the hydrolyzed 3-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (KH-570) onto PU foam through the reaction between alkoxysilane molecules and the isocyanate groups on PU foam and reached superhydrophobicity, which can absorb about 100 times its initial weight oil (lubricating oil, diesel oil, crude oil etc.) from oil/water mixture showing excellent oil adsorption property (Figure 8d). To increase the stability of the coated organic coatings, chemical bonding is regarded as an effective way. Oribayo et al. [57] firstly coated dopamine onto melamine sponge to form PDA coating via self-polymerization of PDA. Strong covalent and noncovalent bonds are formed during the polymerization of dopamine, which increased the durability of the coating resulting in long term operation. The superhydrophobicity of PDA-coated melamine sponge was achieved via grafting with low surface tension 1H, 1H, 2H, 2H perfluorodecanethiol (PFD) or octadecylamine (ODA) agents. PFD and ODA are chemically bonded to PDA surface through Michael or Schiff-base reaction via dipping-coating method [142]. The as-prepared superhydrophobic sponge can absorb about 90 times oil (engine oil, silicone oil etc.) of its original weight. Besides, the strong PDA chemical bonds enable robust hydrophobicity and adsorption property after 50 cycles of oil adsorption. Liu et al. [62] used the aniline to suit-polymerization onto melamine sponge and grafted with low surface energy dodecyl mercaptan to delivery superhydrophobicity (Figure 8a). After coating, the skeleton became rough while the coated polyaniline (PANI) showed negligible effect on decreasing the pore size (Figure 8c). The obtained superhydrophobic PANI-sponge can adsorb different types of oil or organic solvents about 51–121 times of its initial weight. Moreover, PANI-sponge also was used in oil-in-water emulsion separation. The etching/polymerization can only randomly increase the roughness of the sponge, which may cause the differences in hydrophobicity at different positions on the surface or internal skeleton. However, post-modification on commercial sponge/foam using organic agents makes it difficult to creating uniformity and desired roughness and surface structure. Besides, the mechanical property of the modified sponge/foam is still a concern after several times of oil desorption under compression due to the weak mechanical robustness of the original commercial sponge/foam.

Table 2.
Summary and comparison of typical examples of the superhydrophobic-superoleophilic oil/water separation 3D-PMs.
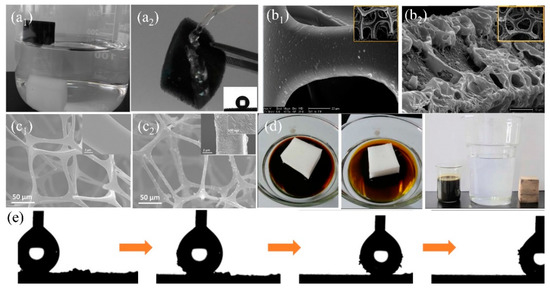
Figure 8.
(a) The photograph of (a1) original melamine sponge (sinking under the water) and PANI-melamine sponge (floating on the water), (a2) the surface of modified sponge rebounding water (the insert is water contact angle (WCA) image) [62]; reproduced with permission from Wiley. (b) SEM images of (b1) the original polyurethane (PU) sponge and (b2) the PU sponges modified with methyltrichlorosilane [108]; reproduced with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry. (c) SEM images of (c1) original sponge and (c2) the PANI-melamine sponge [62]. (d) Photograph of the KH-570 PU foam absorbs the crude oil [140]. (e) Optical images of the water droplet (5 µL) removing carbon black particles from the surface of FAS-PU sponge [124]; reproduced with permission from Wiley.
Organic–Inorganic Composite Modification Agents
Dispersing inorganic nanomaterials into organic precursors significantly increase the surface roughness and forms the secondary nanostructure after application onto the sponge, which enhances the surface wettability and self-cleaning property [132,143]. Except this, the incorporated inorganic nanomaterials can improve the mechanical performance and the organic agents can bind inorganic nanomaterials onto the skeleton through chemical bonds, resulting in durable hydrophobicity and oil/water separation performance. The widely used inorganic nanomaterials mainly include carbon material (activated carbon [22], graphene oxide (GO) [61,144], graphene (GN) [145,146], carbon nanotubes (CNT) [147], carbon soot (CS) [148], etc.), metal oxide (Al2O3 [132,149], TiO2 [117,150,151], SiO2 [122,152], Fe3O4 [153,154], etc.), and metal organic frameworks (MOFs) [59,155]. Carbon materials have been extensively used in the field of adsorption due to ultra-light, high specific surface area and non-toxicity. Recently, carbon materials have been utilized in 3D-PMs to enhance the adsorption capacity in oily wastewater treatment. Wu et al. [61] prepared the hydrophobic GO-PU sponge with WCA of 133.4° via solution immersion and thermal reduction, which can separate different type oil–water mixtures (bromobenzene, carbon tetrachloride, hexane, etc.) and the separation efficiency is higher than 90%. To increase the oil/water separation efficiency, Li et al. [60] used the γ-methacryloxypropyl trimethoxy silane (KH-570) to modify GO and coated onto PU sponge via dip-coating to prepare the superhydrophobic-superoleophilic sponge. WCA increased from 129° to 161° after modified with KH-570 and the oil absorption capacity was enhanced to more than 39 times of its initial weight, which was improved nearly two times compared to the pure PU sponge. Nguyen et al. [156] used the hydrophobic graphene nanosheets (WCA:132°) and PDMS as cements to increase the bonding force between graphene coating and the commercially sponge via solution immersion method. The WCA of the fabricated sponge was 162°, which was superhydrophobic. The oil or organic solvents adsorption capacity of graphene-based sponge was around 54–165 times its original weight and showed relatively stable solvent adsorption performances after 5 cycles of adsorption-desorption However, the oil adsorption capacity dropped nearly 80% in the second cycle of oil adsorption-desorption (Figure 9a) because the oil adhered to the skeleton, and was difficult to squeeze out via compression. To address this issue, Ge et al. [157] fabricated hydrophobic and conductive GO-wrapped-melamine sponge (MS) via dip coating. This conductive GO-wrapped-MS significantly lower the viscosity of crude oil when the sponge was heated up to 90 °C through applying DC voltage showing fast and large oil adsorption (adsorb 3.87 g crude oil in 6 s) comparing to the original sponge (adsorb 1.5 g crude oil in 8 min) (Figure 9b). Chang et al. [158] mixed the carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with PDMS to modify the PU sponge via dip-coating method obtaining superhydrophobic CNTs-PU sponge and lowered the viscosity of heavy oil under light irradiation which effectively enhanced oil adsorption capacity and self-cleaning performances. 3D-PMs are easily contaminated and adhered by high viscosity oil which is difficult to squeeze out the oil residues and caused surface contamination. Electrically induced joule heating and the light irradiation heating can significantly decrease the viscosity of oils resulting in quick adsorption and surface cleaning, showing high promising in practical oil/water separation. However, the large energy input with relatively low energy utilization, and the thermal stability of the polymer sponge under high temperature are needed to be solved in the future.
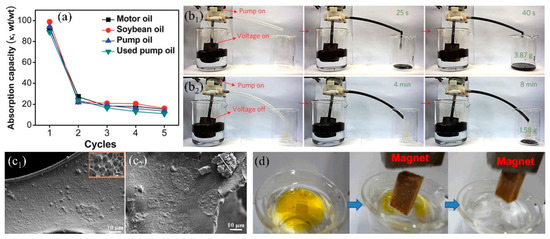
Figure 9.
(a) Absorption recyclability of the sponge modified with graphene for oils [156]. (b) Comparison of efficiency of the viscous crude oil continuous collection device: (b1) applied voltages of 17 V, (b2) applied voltages of 0 V [157]. (c) SEM images of the PU sponge modified by hydrophobic SiO2, (c1) and un-hydrophobic SiO2 (c2) [130]; reproduced with permission from Springer. (d) Photograph of the Fe3O4 melamine sponge absorbs the oil (yellow) by magnetic driven [69]; reproduced with permission from Elsevier.
Inorganic oxides (SiO2, TiO2, Fe3O4, etc.) are sort of important materials in polymer composites due to the high chemical and mechanical stability with relatively low cost [152,159,160]. Thus, they can be utilized to enhance the wettability and mechanical performance of sponges/foams. Ge et al. [161] synthesized hydrophobic SiO2 from chlorotrimethylsilane and mixed with polyfluorowax (PFW) to firmly coat onto PU sponge via dip-coating. The incorporation of SiO2 nanoparticles made the surface rough and PFW reduced surface energy resulting in superhydrophobicity. Besides, the utilization of PFW fixed SiO2 nanoparticles strongly onto PU sponge after curing and delivered robust superhydrophobicity (WCA was only dropped 5° (original: 156°)). The composite sponge showed relatively high mechanical stability by adding certain amount of SiO2 nanoparticles after 400 cycles of compression tests under the strain of about 75%. However, chlorotrimethylsilane is inflammable and is easily hydrolyzed into hydrogen chloride, which is unsafe and caused the loss of hydrophobicity and oil/water selectivity. To avoid this, Salehabadi et al. [130] utilized octylsilane to modify SiO2 nanoparticles showing that PU sponge reached superhydrophobic state after coating with 2 vol % modified SiO2 nanoparticles (Figure 9c1). As comparison, the obtained superhydrophobic SiO2-coated PU sponge can absorb 61–72 times of its initial weight oils showing high adsorption capacity. However, the un-hydrophobized SiO2 tend to agglomerate on the PU sponge at high concentration (3 vol %) (Figure 9c2), causing the decrease of wettability and the oil adsorption capacity dropped more than 5 times. Lei et al. [69] firstly deposited Fe3O4 nanoparticles onto melamine sponge and then coated with lignin by dip-coating to prepare the superhydrophobic composite sponge, which can be driven under magnetic field to quickly separate from oil/water mixture after absorbed the oil (Figure 9d), thereby increasing the separation efficiency. Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) are a sort of metal–organic framework (MOF) in which porosity and specific surface area are relatively high, showing the potential in adsorption organic compounds [59,155,162]. Kim et al. [155] first carbonized melamine sponge under Ar atmosphere and then the zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) was nucleated and grew onto the composite surface in Zn2+ and 2-methylimidazole (MIM) solution at room temperature. The obtained ZIF-8 modified sponge showed highly hydrophobic (WCA: 135°) and high specific surface area (BET: 211 m2/g) which can absorb 55–136 times oil (pump oil, chloroform etc.) of its initial weight. Inorganic-polymer composite coating increases the hydrophobicity, roughness and the durability of the sponge comparing with only using single inorganic/organic modifications. The incorporated inorganic nanomaterials with unique property can equip the sponge with multifunctional properties such as electrical conductivity, magnetic, photoresponse, which broadens the development of 3D-PMs.
3.1.2. Preparation of Superhydrophobic 3D-PMs by Self-Assembly
Though the superhydrophobicity can be easily obtained by surface modification with organic/inorganic compounds, the modification layer generates adverse effects on the flexibility and adsorption capacity of the sponge. Moreover, the pore structure (e.g., diameter, porosity) cannot be precisely adjusted through this method [163] and the initial elasticity of the commercial sponge is significantly reduced (Figure 10a,b) [108]. Especially, the incorporated nanomaterials tend to aggregate and cause the generation of cracks at high loading (Figure 10c,d) [108,143]. In order to well-tune the porous structure and improve the mechanical robustness of the sponge, the superhydrophobic sponge can be prepared through assembling of the polymers via freeze-drying, electrospinning, or polymer foaming.
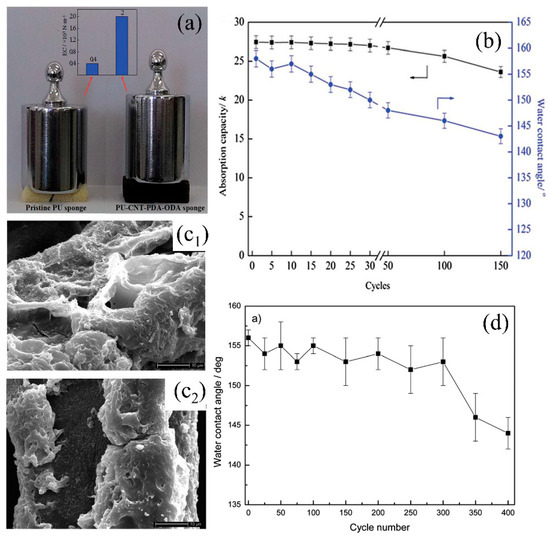
Figure 10.
(a) Photograph of the elasticity comparison of original sponge and CNT–PDA–ODA PU sponge, (b) variation of the CNT–PDA–ODA PU sponge’s WCA and absorption capacity with cycles [143]. (c) SEM images of the methyltrichlorosilane-PU sponge for 300 (c1) and 400 (c2) cycles after water/oil separation, (d) variation of the methyltrichlorosilane-PU sponge’s WCA with cycles [108]; reproduced with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry.
Sponge
Foaming is broadly used to fabricate sponges/foams due to the mass production, ease of fabrication, and abundant pore structures using foaming agents [164,165]. The widely used inorganic foaming agents to fabricate oil/water separation foams are sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), ammonium carbonate, ammonium nitrite, etc. Among which, NaHCO3 is more favorable due to non-toxicity and the formation of uniform and dense pore structures by decomposing into carbon dioxide under thermal heating [166]. Kong et al. [105] utilized polyether polyol, isophorone diisocyanate, and dibutyltin dilaurate as raw materials and NaHCO3 as foaming agent to fabricate flexible PU sponge at 100 °C via pyrolysis. Since PU sponge is hydrophilic, by adding a certain amount of hydrophobic γ-(methacryloyloxy)propyltrimethoxysilane (KH-570) modified Al2O3 hollow spheres during foaming to increase the surface roughness and reduce the surface energy correspondingly, which resulted in highly hydrophobicity (WCA: 144°) (Figure 11b). The obtained composite sponge can absorb 5–37 times oil of its own weight and the oil adsorption capacity is significantly improved (10–50%) compared to PUF without Al2O3 modification. Besides, Al2O3-modified PUF showed relatively high oil adsorption stability after 20 times of cycling oil/water separation. However, the fabrication process is relatively complex and requires harsh environmental parameters to foam. Recently, sugar/salt particles and sodium bicarbonate are reported as a pore-forming template to simplify the fabrication of foams/sponge because they can be easily removed through immersing in water/solvent or decomposition under thermal heating without secondary pollution or pore structure damage. Choi et al. [134] used the cube sugar as template to fabricate polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sponge with highly hydrophobicity (WCA) (Figure 11c), which can absorb 5 times its initial weight oils (silicone oil, motor oil, transformer oil). The oil (chloroform) adsorption capacity was slightly improved from 9 to 11 times of its original weight while using different size (several hundred micrometers or even centimeters) of sugar particles (granulated + sanding and granulated + black sugar particles) as a template (Figure 11d). Similarly, Zhao et al. [102] used NaCl microparticles as template to prepare the hydrophobic PDMS sponge and h can absorb 5–20 times oil or organic solvents. However, hydrophobic PDMS sponge prevents water from entering and dissolving the sugar/salt microparticles causing sugar or salt residues left into the sponge affecting pore structure, wettability and elasticity. Yu et al. [107] reported that they used the citric acid monohydrate (CAM) as a hard template to create pore structures and fabricate PDMS sponge. CAM can be easily removed by dissolving in ethanol within 6 h because ethanol completely wets the porous PDMS sponge. The PDMS sponge can absorb 7–15 times oil or organic solvents and the separation efficiency reached up to 99.8%. However, the pore size and porosity of the as-prepared 3D-PMs via foaming or templating methods are much larger and smaller than the commercial sponge, correspondingly (Figure 11a) leading to the relatively lower hydrophobicity and oil adsorption capacity. Besides, the pore structure and pore size rely on the size of template with which it is difficult to fabricate uniform and smaller pores. To solve this shortcoming, Wang et al. [167] used the thermally-impacted phase separation method to prepare the low density and high porosity polymer foam by firstly mixing the thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), dioxane, and deionized water together to form a homogeneous solution and then removing the dioxane and water from the TPU by decreasing the temperature. The superhydrophobic PU foam was successfully prepared via freeze-drying after 24 h. The foam shows highly porosity (91%) and excellent mechanical properties, which only reduced approximately 25% after 1000 compression cycling test at 80% strain. The PU foam can absorb 10–32 times its initial weight in different types of oils or organic solvents. To reduce the cost and achieve eco-friendliness, Wang et al. [52] used biodegradable poly (lactic acid) (PLA) to fabricate the superhydrophobic polymer foam via phase separation and freeze-drying. The result had a large number of mesopores and high surface area (>96.7 m2/g by BET test), which could absorb 23 times engine/silicone oil of its original weight.
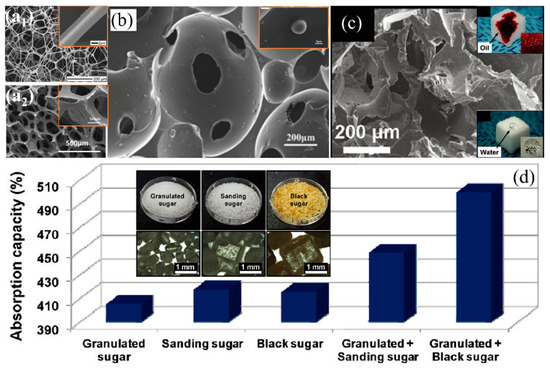
Figure 11.
(a) SEM images of (a1) the melamine sponge [168] and (a2) polyurethane sponge [132]; reproduced with permission from American Chemical Society and Springer. (b) SEM images of the pure PUF sponge (the insert is the Al2O3/PUF sponge) [105]; reproduced with permission from Elsevier. (c) SEM images of the PDMS sponge (the inserts are photograph of the sponge hydrophobicity and oleophilicity), (d) the effects of sugar templates on absorption capacity of PDMS sponges with various (the insert is images of the sugar particles with different size) [134]; reproduced with permission from American Chemical Society.
Aerogel
Super-wetting aerogel is reported to treat oily wastewater with the advantages of ultra-light, large specific surface area, large porosity, and relatively large adsorption capacity [127,169,170]. Currently the oil/water separation aerogels included silicon aerogel [171,172,173], carbon aerogel [174,175,176], fiber cellulose aerogel [177,178,179] and composite aerogel [180,181,182] have been reported for oil/water separation because of the unique properties of ultra-light and relatively high specific surface area. However, conventional silicon aerogels such as tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) aerogels are easy to crack under a certain pressure, causing the collapse of the 3D porous structure [183,184]. Gurav et al. [185] used a two-step sol–gel method to fabricate superhydrophobic TEOS-based silica aerogel (WCA:153°) in which firstly dissolved tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) to form sol and added NH4F/NH4OH to form gel and obtained a 3D structure after a certain period of aging. The superhydrophobicity originated from the utilization of hexamethyldisilazane. Such superhydrophobic aerogel can absorb about 10 times its initial weight in petrol oil. However, the silica aerogel shrinks by nearly 50% and the 3D structure collapsed after compression to squeeze the adsorbed oils (Figure 12a). In order to improve the mechanical properties and maintain its pore structure. Yu et al. [137] used organosilane dimethyldiethoxylsilane (DMDES) and methyltriethoxysilane (MTMS) as co-precursors, which dissolved in ethanol to fabricate the silicon aerogels (density: 0.0897 g/cm3) via the sol-gel. The obtained aerogel showed excellent elasticity, which was due to non-polar methyl groups in backbones and the reduction of the inter-chain cohesion (Figure 12b). The abundant hydrophobic methyl groups on MTMS contributes to the superhydrophobicity (WCA 153.6°) of the composite aerogel, thereby the as-prepared aerogel absorbed 6–17 times its own weight in oil or organic solvents and maintained its structure after 10 cycles of oil adsorption and desorption at 60% strain (Figure 12c). Recently, bridged silsesquioxane aerogels are more favorable due to the significantly improved mechanical strength through the formation of covalent bonding between inorganic siloxane and organic functional groups [186]. Chen et al. [187] used terephthalaldehyde (TPAL) and 3-aminopropyl-triethoxysilane (APTES) as a bridging silsesquioxane precursor and MTMS to fabricate the highly hydrophobic silicon composite aerogel (142°) via the catalytic reaction of acetic acid and freeze-drying. The bridged silsesquioxane aerogel can absorb 8–23 times oil or non-polar organic solvents of its initial weight, and are stable after more than 10 times cycling compression at 50% strain. The BET indicates the specific surface area of the bridged silsesquioxane aerogel was 26.7 m2/g, which was relatively low, leading to the poor adsorption capacity. To further improve the oil adsorption capacity, varied types of carbon aerogels were fabricated such as graphene, CNTs, cellulose, etc. by hydrothermal reaction [188], chemical reduction [189], and thermal reduction [190]. Ren et al. [191] mixed GO nanosheets with melamine to prepare N-doped graphene aerogel via self-assembly and thermal annealing process (900 °C), and showed highly hydrophobic (WCA: 137.2°). Especially, the specific surface area of graphene aerogel was 852 m2/g, and it can absorb 52.6–111.6 times organic solvents of its initial weight. Li et al. [192] used sodium chlorite (SC)-activated poplars catkin (PC) as precursor to prepare PC aerogel, and then carbonized at 1000 °C and successfully obtained the superhydrophobic carbon aerogel with outstanding oil absorption capacity. It can absorb 81–161 times oil (pump oil petroleum ether, etc.) of its initial weight and the adsorption performance remains stable after more than 10 cycles of oil adsorption and desorption. Moreover, PC sponge shows excellent mechanical performance, and can retain its original shape without breaking or collapsing after 500 cycles at 50% strain. Nevertheless, the hydrothermal or carbonization process of preparation aerogels needs relatively high temperatures and the fabrication process of aerogels is always under harsh environment such as supercritical drying, acidic/basic solution, a long period of maintenance, freeze-drying, and relatively high pressure, and produces organic wastewater, which leads to the high cost and may cause secondary pollution.
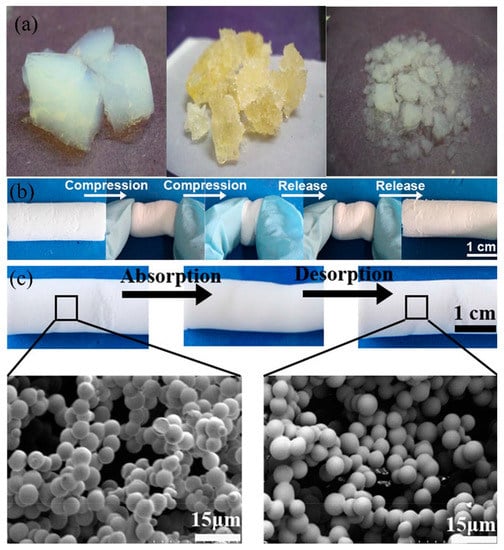

Figure 12.
(a) Photographs of the various stages of tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) aerogel, before absorption (left), during desorption (middle and right) [185]. (b) Photograph of the compression/recovery process of the dimethyldiethoxylsilane–methyltriethoxysilane (DMDES–MTMS) aerogel. (c) SEM images of the adsorption (before) and the desorption (after) of aerogel [137]; reproduced with permission from Springer.
To reduce the fabrication cost and minimize the adverse effects on the environment, using nature materials such as cellulose is an alternative way to develop oil/water separation aerogels [54,123,191]. Cellulose originates from natural resources e.g., natural plants, household waste paper, etc., showing the advantages of low cost, high mechanical property, environmentally friendly, biodegradable materials which can be used to fabricate aerogels via freeze-drying [54,193,194]. However, cellulose is hydrophilic and, thus, can be easily wetted by water and needs hydrophobic modification. Mi et al. [64] used bidirectional freeze-drying (control the growth of ice crystals on the y and z axes) and siliconization, obtaining ultra-light (bulk density: 0.0059 g/cm3) and superhydrophobic (WCA: 150.3°) cellulose-graphene composite aerogels (Figure 13a). The as-prepared composite aerogel can float on dandelion and shows excellent oil adsorption capacity (80–197 times oil or organic solvents of its own weight) due to multi-layered sheet structure, larger porosity and high BET surface area (47.3 m2/g) (Figure 13b). Besides, the composite cellulose aerogel shows high mechanical stability that it recovered to the original size under 50% strain after 100 times cycling compression tests (Figure 13c). However, the irregularity and discontinuity of cellulose leads to the difficulty in precisely controlling the mechanical properties and large scale fabrication [195]. Si et al. [196] used polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibers as the main precursor and crosslinked by the bifunctional benzoxazine (BA-a) to construct elastic networks, and then introduced rigid SiO2 nanofibers to enhance its mechanical strength, successfully preparing the nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels (Figure 13d). The 3D porous structure is relatively stable even after 1000 cycling compressive fatigue test with 60% strain. The nanofibre aerogels can rapidly and effectively separate oil/water emulsions under gravity driven with much higher separation flux comparing with other pressure-driven separation materials due to the numerous multi-level microchannels. By combining with pump, it shows continuous oil/water emulsion separation (Figure 13e,f). Though the aerogels have attracted extensive attentions and the fabrication techniques promote the progress of developing oil/water separation 3D porous materials, its complicated fabrication procedures and the high requirement on temperature and pressure restrict its further application.
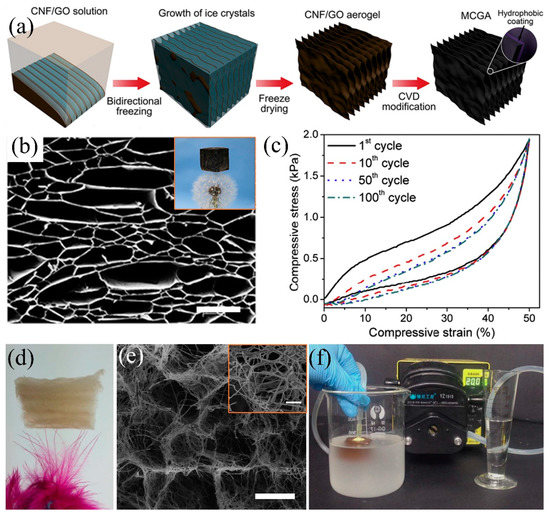
Figure 13.
(a) Schematic diagram of the bidirectional freeze-drying process to prepare the cellulose-graphene composite aerogel, (b) SEM image of the cellulose-graphene aerogel (the insert is the photograph of aerogel on the dandelion), (c) elastic cycle performance of aerogels by 100 cycles [64]; reproduced with permission from Elsevier. (d) Photograph of the cellular aerogel on the feather, (e) SEM image of the cellular aerogels, (f) illustration of continuous oil-in-water emulsion separation by cellular aerogel [196]; reproduced with permission from Nature.
3.2. Superhydrophilic-Underwater Superoleophobic 3D-PMs
Though superhydrophobic 3D PMs have certain advantages (e.g., large adsorption capacity, high efficiency, recyclable) in oil/water separation from oceans, rivers and lakes, oil easily adheres to the skeleton leading to surface contamination, reduction of hydrophobicity and even loss oil/water separation property [197]. Superhydrophilic-underwater superoleophobic 3D porous materials were developed to overcome oil adhesion by the formed density water film. Oil was prevented to contact with the 3D PMs by the water film thereby keeping the surface clean [198,199]. Moreover, the multi-level interactive three-dimensional porous structures show high efficiency in separating stratified oil/water mixture and oil-in-water emulsion avoiding the secondary pollution which was caused by the utilization of demulsification surfactants. Lv et al. [113] dip-coated different amount of SiO2 nanofibers onto melamine formaldehyde (PMF) sponge to adjust the pore size, resulting in the formation of hierarchical pore structures (such as major pores: 100~200 µm, nanoscrolls: 30 nm~2 µm). The obtained sponge with hierarchical pore structure shows highly efficiency (the oil rejection rate is around 99.46%) on demulsification of n-hexane emulsions. Superhydrophilicity-underwater superoleophobicity (OCA: 162.57°) of PMF composite sponge are tuned via the in-situ growth of hydroxide by depositing polydopamine (PDA) and polyethyleneimine (PEI). Water droplets quickly wet the sponge within 25 ms while the underwater oil contact angle (1,2-dichloroethane) is measured of 162.57°. The superhydrophilicity-underwater superoleophobicity enables the quick separation of light oil from water surface and oil from oil-in-water emulsions under gravity driven. However, the double-layered hydroxide (LDH) is positively charged which is not suitable for the separation of negatively charged emulsion due to the neutralization reaction between positive surfaces and negative liquid causing oil contamination and the reduction of flux, and the preparation process is complicated. To solve this problem, Wang et al. [89] mixed cellulose powder with pore-forming agent (Na2SO4·10H2O) and then regenerated the fibers to fabricate superhydrophilic-underwater superoleophobic cellulose sponge via foaming and freeze drying. The cellulose sponge has excellent demulsification performances by gravity driven (Figure 14a) and maintains high-flux (91 L m−2 h−1) and separation efficiency (99.94%) after more than six cycles. The FTIR (Figure 14b4) and UV-VIS analyses (Figure 14b5) illustrate that the oil was removed completely after the emulsion passing through the sponge (Figure 14b). Due to the strong hydrogen bonding affinity between water molecules and cellulose sponges, oil is replaced by the strong competitive adsorbed water showing excellent self-cleaning and anti-pollution ability when the oil-contaminated sponge was immersed into water (Figure 14c).
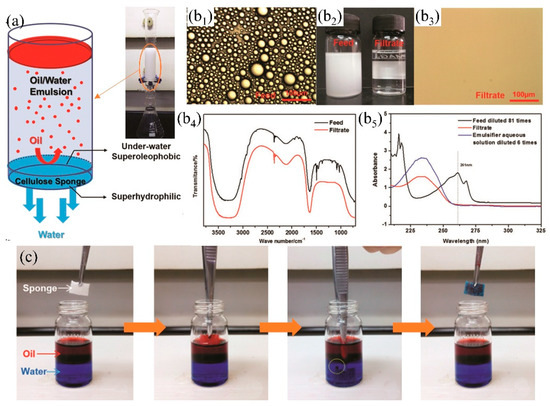
Figure 14.
(a) Schematic diagram of the cellulose sponge separates oil/water (toluene-in water emulsion), (b) the emulsion separation result: (b2) comparison of the emulsion before (left) and after (right) filtration, photograph (b1) and (b3), FTIR (b4) and UV-VIS (b5) of emulsion before and after filtration, (c) self-cleaning and resistance to oil pollution of cellulose sponge [89]. reproduced with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry.
3.3. Superhydrophilic-Superoleophobic 3D-PMs
In oil mining industry, water droplets disperse into oil and water-in-oil emulsions cause the impure of oil. Thus, removing water from the bulk oil is critical for oil purification. The superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic-underwater superoleophobic 3D-PMs are oleophilic which cannot remove minor water from oil/water mixture or water-in-oil emulsion. A new type of superhydrophilic-superoleophobic 3D-PMs have been developed by changing the structure of the super-wetting coating. The mechanisms of designing this unique surface are widely investigated. Okada et al. [200] uniformly coats the fluoroalkylated acrylic oligomer (FAAO) on the resin substrate and successfully prepared the surface with hydrophilic and oil-repellent properties. When water contacts the composite surface, the hydrophilic unit (–COOH) of FAAO is attracted by water molecules causing surface wetting. On the contrary, the hydrophilic unit is flattened by contacting with oils while the fluoroalkyl unit exhibits erect state showing oil repellency. Brown et al. [201] designed a new type flip-flop coating by the layer-by-layer deposition and each layer was interacted by the strong electrostatic interaction. Cationic polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride (PDDA) is chosen as the base layer to bind strongly onto negatively charged glass surface and SiO2 nanoparticles via electrostatic interactions. Then the second (negatively charged SiO2 nanoparticles) and third layers (cationic PDDA) are assembled onto the surface strongly by the electrostatic force. Finally, the fluorosilane were deposited on the last layer to deliver hydrophilic-oleophobicity (WCA < 5°, OCA = 157°). The mechanism of delivering such unique wettability can be explained as follow that the –COOH group of perfluorooctanoic acid is more polar than CFx which preferentially adheres to the surface of the substrate while the fluorinated tail heading out to form low surface energy interface showing oil repellency [201]. Pan et al. [202] utilized sodium atoms (Na) to replace the hydrogen atoms in –COOH group thereby molecules with low surface energy tails and high surface energy heads were formed resulting in superhydrophilicity and oil repellency (Figure 15a).
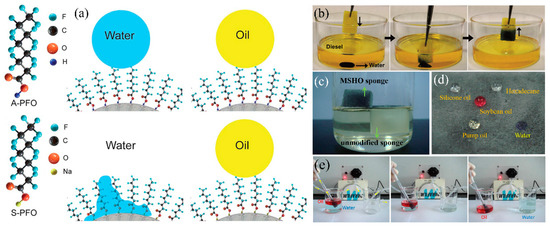
Figure 15.
(a) Schematic diagram of superhydrophobic/superoleophobic conversion to superhydrophilic/superoleophobic [202]; reproduced with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry. (b) Photograph of the superhydrophilic/oleophobic sponge removes the water from oil [115]; reproduced with permission from Wiley. (c) Photograph of the original sponge (sinking under the oil) and magnetic superhydrophilic/oleophobic (MSHO) sponge (floating on the oil), (d) photograph of water and different oil placed on the MSHO sponge, (e) photograph of the MSHO sponge with pump to quickly separate oil/water [116]; reproduced with permission from Elsevier.
Following the above mechanisms, a series of superhydrophilic-superoleophobic sponge/foams have been developed for oily wastewater treatment. Xu et al. [115] dip-coated heptafluoroantimonic acid modified TiO2 sol and SiO2 NPs onto PU sponge to increase surface roughness. After that, the composite polyurethane (PU) sponge was treated by ammonia vapor to transfer superhydrophilicity-superoleophobicity to superhydrophobic-superoleophobicity. The modified PU sponge can easily remove water from the bottom of the diesel oil without any oil residues left in water (Figure 15b). Su et al. [116] fabricated superhydrophilic-superoleophobic melamine sponge (Figure 15c,d) by using sodium perfluorononanoate (PFNA) and Fe3O4 nanoparticels via dip-coating approach obtaining highly oleophobicity (OCA: 144°).The obtained sponge can eliminate water from oil/water mixtures by gravity driven with the separation efficiency reach to 97.6% (pump oil) and 94% (pump oil). This method does not require pretreatment (wet by water) or the formation of oil repellent water films. Moreover, combining with the peristaltic pump, the superhydrophilic-superoleophobic sponge can continuously remove large amounts of water pollutants from bulk oil by (Figure 15e).
3.4. 3D PMs with Switschable Super-Wettabilityunder External Stimulation
Either superhydrophobic or superhydrophilic 3D PMs, they only have one single wetting property and can only absorb or separate specific liquids. In addition, oils, especially the high viscos oil (e.g., crude oil) are easily adhering onto the superhydrophobic surface causing the reduction of adsorption capacity and difficult to desorb [203]. Smart 3D porous materials with switchable wettability are receiving more and more attention due to the advantages of responding to external stimulation, ease of adsorb-desorption, self-cleaning, multi-functional oil/water separation under varied environment. A series of 3D-PMs have been reported to utilize in oil/water separation which can switch their wettability under the stimulation of light [204], heat [205], pH [206] showing ease of desorption after oil absorption and self-cleaning (Table 3). Li et al. [204] reported to fabricate light responding PU sponge through immersing into octadecanoic acid and titanium dioxide (TiO2) solution under ultrasonication and obtained coral-like cluster rough structures with superhydrophobicity (WCA: 151°). The superhydrophobic composite sponge (151.1°) was switched into superhydrophilic (0°) under UV irradiation by from the generation of Ti3+, oxygen vacancy and the formation of hydrogen bonds. This smart TiO2 PU sponge can absorb 27–60 times oil or organic solvents of its original weight and shows certain antifouling and self-cleaning properties. The adhered oil on the sponge skeleton causing the decreasing of separation efficiency which can be released under UV irradiation attributing to the conversion of hydrophobicity to hydrophilicity. Kim et al. [117] further investigated the mechanisms of oil desorption under UV irradiation indicating that the oil desorption was attributed to the growth and diffusion of the generated bubbles from the dissolved oxygen and nitrogen under the catalysis of TiO2. The bubbles wrapped oil to increase its diffusion power and thus desorb from porous materials surface into water (Figure 16a,b).

Table 3.
Summary and comparison of typical examples of the polymeric three dimensional (3D) porous materials with switchable super-wettability.
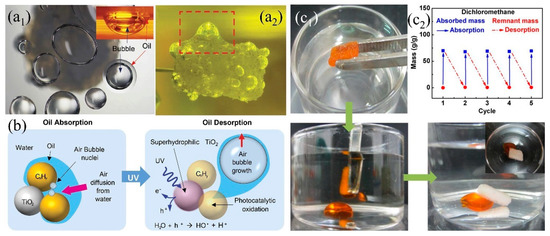
Figure 16.
(a) Photograph of (a1) top view of desorbed oil/bubbles (the inset shows the side view), (a2) oil/bubble desorption (about 24 h), (b) schematic diagram of oil desorption under UV light response [117]; reproduced with permission from Nature. (c1) Photograph of rapid desorption of oil by slightly squeezing the sponge at 20 °C, (c2) cycling performance of OTS/PNIPAAm sponge adsorption/desorption at different temperatures [205], reproduced with permission from American Chemical Society.
Comparing with UV irradiation which requires the generation of UV light, thermal and pH response can also be utilized to tune the super-wetting property of surfaces relatively simply. Poly (N-isopropyl acrylamide) (PNIPAAm) is a type of thermal response material with relatively low hydrophilic and hydrophobic transition temperature (LCST) of 32 °C [205]. When the temperature is less than the LCST, PNIPAAm forms hydrogen bonds with water molecule to hydrate, swell and outstretch resulting in hydrophilicity; when the temperature is higher than the LCST, the C=O group combines with the N-H group to form intramolecular hydrogen bond resulting in hydrophobicity [205]. Lei et al. [205] grafted hydrophobic octadecyltrichlorosilane (OTS) modified PNIPAAm onto melamine sponge to artificial control wettability by changing temperature. Water contact angle increased from 0° to 150° when the temperature rises from 25 to 40 °C showing superhydrophobicity. Oil can be quickly adsorbed at 37 °C (the modified sponge can absorb about 35 times pump oil/peanut oil/gasoline of its initial weight) while the oil can be quickly and completely discharged after applying a slightly pressure at 20 °C (Figure 16c1). Furthermore, the thermal response performance was stable after 5 adsorption/desorption cycles (Figure 16c2). pH responded and switchable super-wetting melamine sponge was developed by grafting poly-4-vinylpyridine (PVP) [206]. Water contact angle gradually rises from 0° to 137° when pH increases from 1 to 7. When pH = 7, WCA reached to 137°, achieving a transition between superhydrophilicity and superhydrophobicity. PVP deprotonated and agglomerated at pH=7 showing hydrophobicity and it can quickly absorb oil stains; the PVP protonated pyridyl group stretches at pH=1 showing hydrophilicity and rapidly releasing of oil stains. By changing the environmental parameters, the sponge with switchable wettability provides a good solution for the treatment of highly viscous oil e.g., crude oil.
4. Conclusions and Perspective
In this article, we briefly reviewed the typical materials and techniques which are utilized in the recent development of superhydrophobic-superoleophilic, superhydrophilic-superoleophobic, superhydrophilic-underwater superoleophobic, switchable super-wetting polymeric oil/water separation three dimensional (3D) porous materials such as sponge, foam and aerogels. By reviewing the effects of wettability on oil/separation, the desired wettability on dealing the specific oil/water mixtures was developed correspondingly. There are a variety of polymers can be used to fabricate super-wettable 3D-PMs through similar techniques. However, the requirements of wettability are not the same due to their unique roles in separating specific oil/water mixtures. Surface wettability be tuned through the low surface energy polymers and nanomaterials. The utilized nanomaterials significantly enhanced the roughness to improve the wettability and separation efficiency. Moreover, the incorporated nanomaterials can also be applied to improve the mechanical stability of 3D-PMs. The organic–inorganic nanomaterials modification coatings show great potential in developing high performance 3D-PMs to meet the advanced requirements in current and the future oily wastewater treatment.
However, there are some challenges in developing polymeric 3D-PMs and their utilization in oil/water separation in the following aspects: (i) materials and technologies that are suitable for large-scale, simple and low-cost production, environmentally friendly, and avoid secondary pollution; (ii) the actual oily wastewater is complicated, especially with high adhesion and high density oils, one of the significant shortcomings that restricts the application in oil/water separation is oil contamination, thus developing superwetting polymeric 3D-PMs with anti-oil-pollution is critical; (iii) squeezing the adsorbed liquid after long-term filtration or adsorption is a fundamental requirement for cycling oil/water separation, thus, developing 3D-PMs with excellent mechanical stability and elasticity is crucial; (iv) the stability of superwetting coating determines the efficient selectivity of 3D-PMs, but they are easily peeled off from the surface, leading to the loss of super-wettability. We expect that, in the near future, the above issues can be solved gradually to promote the applications of super-wetting 3D-PMs in oily wastewater treatment with high efficiency, anti-fouling, and mechanical robust performance.
Author Contributions
Z.P. conceived of the content of the article; Z.P. and F.C. designed the structure of this work; Y.G. wrote the paper.
Funding
The authors acknowledge National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.21808131) and (Grant No. U1610222), Funding for the Project of Supporting the Development of Talants, Central government of China (228545025 and 228545046).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ge, J.; Ye, Y.D.; Yao, H.B.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.L.; Ding, H.; Yong, N.; He, L.H.; et al. Pumping through porous hydrophobic/oleophilic materials: An alternative technology for oil spill remediation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 3612–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Purkait, M.K.; Das, C. Cross-Flow Microfiltration of Industrial Oily Wastewater: Experimental and Theoretical Consideration. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Huo, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Hou, X. Oil/water separation based on natural materials with super-wettability: Recent advances. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 25140–25163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Craig, V.S.J.; Wang, C.; Li, L.H.; Chen, Y. Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic Porous Boron Nitride Nanosheet/Polyvinylidene Fluoride Composite Material for Oil-Polluted Water Cleanup. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2, 1400267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugham, T.; Kaleekkal, N.J.; Rana, D.; Doraiswamy, M. Separation of oil/water emulsions using nano MgO anchored hybrid ultrafiltration membranes for environmental abatement. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Guo, Z. Recent advances in biomimetic thin membranes applied in emulsified oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15749–15770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deepwater_Horizon_oil_spill (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Schrope, M. Oil spill: Deep wounds. Nature 2011, 472, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2011_Bohai_Bay_oil_spill (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Defense.gov_photo_essay_100506-N-6436W-023.jpg (accessed on 12 April 2019).
- Available online: http://www.discovery.com/dscovrd/wildlife/five-years-later-gulf-coast-wildlife-still-reeling-f rom-deepwater-horizon-spill/ (accessed on 12 April 2019).
- Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Oiled_Pelicans.jpg (accessed on 12 April 2019).
- Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Defense.gov_photo_essay_100506-N-6070S-819.jpg?uselang=en (accessed on 12 April 2019).
- Hanafy, M.; Nabih, H.I. Treatment of Oily Wastewater Using Dissolved Air Flotation Technique. Energy Sources 2007, 29, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, W.T.; Park, K.; Han, S.D.; Yoon, S.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Bae, W.; Rhee, Y.W. Investigation of water separation from water-in-oil emulsion using electric field. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2010, 16, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.K.; Saint, C. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2997–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G.; Kota, A.K.; Li, Y.; Sohani, A.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. On-Demand Separation of Oil–water Mixtures. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3666–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padaki, M.; Murali, R.S.; Abdullah, M.S.; Misdan, N.; Moslehyani, A.; Kassim, M.A.; Hilal, N.; Ismail, A.F. Membrane technology enhancement in oil–water separation. A review. Desalination 2015, 357, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, B.; Ghoshal, A.K.; Purkait, M.K. Ultrafiltration of stable oil-in-water emulsion by polysulfone membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, H.; Huang, M.; Yang, H.; Li, A. A review on chitosan-based flocculants and their applications in water treatment. Water Res. 2016, 95, 59–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, J. Methods And apparatus for Oil Demulsification and Separation of Oil and Suspended Solids from Produced Water. U.S. Patent 6,875,351, 5 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bayat, A.; Aghamiri, S.F.; Moheb, A.; Vakili-Nezhaad, G.R. Oil Spill Cleanup from Sea Water by Sorbent Materials. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2005, 28, 1525–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakovic, V.; Aleksic, G.; Radetic, M.; Rajakovic, L. Efficiency of oil removal from real wastewater with different sorbent materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, F.J.; Gimeno, O.; Portela, J.R.; de la Ossa, E.M.; Beltrán, F.J. Supercritical Water Oxidation of Olive Oil Mill Wastewater. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 3670–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.P.; Ollis, D.F. Integration of chemical and biological oxidation processes for water treatment: Review and recommendations. Environ. Prog. 1995, 14, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Chen, Y.; Na, L.; Cao, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Lin, F. In-situ ultrafast separation and purification of oil/water emulsions by superwetting TiO2 nanocluster-based mesh. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 8525–8529. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty, B.; Ghoshal, A.K.; Purkait, M.K. Preparation, characterization and performance studies of polysulfone membranes using PVP as an additive. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 315, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, A.; Cambiella, Á.; Benito, J.M.; Pazos, C.; Coca, J. Ultrafiltration of oil-in-water emulsions with ceramic membranes: Influence of pH and crossflow velocity. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-Hydrophobic Surfaces: From Natural to Artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Wei, Z.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Design of a Superoleophobic and Low Adhesive Water/Solid Interface. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, B. Bio-Inspired Polymeric Structures with Special Wettability and Their Applications: An Overview. Polymers 2017, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.J.; Jiang, L. Design and creation of superwetting/antiwetting surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2010, 18, 3063–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Feng, X.Q.; Wang, G.; Yu, S.W. Mechanisms of superhydrophobicity on hydrophilic substrates. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 356002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. A Super-Hydrophobic and Super-Oleophilic Coating Mesh Film for the Separation of Oil and Water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2012–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. A novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunderdale, G.J.; England, M.W.; Sato, T.; Urata, C.; Hozumi, A. Programmable Oil/Water Separation Meshes: Water or Oil Selectivity Using Contact Angle Hysteresis. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 301, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhu, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, L.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Guo, X.; Zheng, G.; Guo, Z. Superhydrophobic Shish-kebab Membrane with Self-Cleaning and Oil/Water Separation Properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9866–9875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Dai, F.; Lin, L.; An, Z.; He, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y. Simplified and robust adhesive-free superhydrophobic SiO2-decorated PVDF membranes for efficient oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunderdale, G.J.; Urata, C.; Sato, T.; England, M.W.; Hozumi, A. Continuous, High-Speed, and Efficient Oil/Water Separation using Meshes with Antagonistic Wetting Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18915–18919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, C.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Kong, W.; Pan, D.; Guan, G.; Hao, X. A novel 3D porous modified material with cage-like structure: Fabrication and its demulsification effect for efficient oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 5895–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Cheng, J. Fabrication of robust surfaces with special wettability on porous copper substrates for various oil/water separations. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, R.; Zhao, Y. Facile preparation of superhydrophobic metal foam for durable and high efficient continuous oil–water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.-Y.; Lyu, S.-S.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Mo, D.-C. Fluorine-Induced Superhydrophilic Ti Foam with Surface Nanocavities for Effective Oil-in-Water Emulsion Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.-Y.; Chen, K.-X.; Wang, J.-H.; Mo, D.-C.; Lyu, S.-S. Hierarchical nanoparticle-induced superhydrophilic and under-water superoleophobic Cu foam with ultrahigh water permeability for effective oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 10566–10574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Men, X.; Zhu, X. Facile Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Sponge with Selective Absorption and Collection of Oil from Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 9411–9416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-H.; Liu, W.-C.; Hong, J.-L. Superhydrophobic Melamine Sponge Modified by Cross-Linked Urea Network as Recyclable Oil Absorbent Materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 8449–8459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, X.; Hu, Y.; Hao, G.; Li, X.; Jiang, W. Design of Recyclable Superhydrophobic PU@Fe3O4@PS Sponge for Removing Oily Contaminants from Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 3249–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, Y. One-Step Synthesis of Carbon-Hybridized ZnO on Polymeric Foams by Atomic Layer Deposition for Efficient Absorption of Oils from Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakhramanly, Y.N.; Azizov, A.G. Mechanism of Crude Oil and Petroleum-Product Sorption from Water Surfaces by Random Polypropylene Based Polymer Foam Sorbents. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2014, 49, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, W. Low-Cost and Superhydrophobic Magnetic Foam as an Absorbent for Oil and Organic Solvent Removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 9498–9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Li, N.; Liu, C.; Schubert, D.W.; Shen, C. Facile Fabrication of Superhydrophobic and Eco-Friendly Poly(lactic acid) Foam for Oil–Water Separation via Skin Peeling. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14362–14367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.-P.; Wang, Z.; Ren, J.; Lv, Y.-K. Highly compressible polyimide/graphene aerogel for efficient oil/water separation. J. Mater.Sci. 2019, 54, 5918–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J. Compressible and conductive carbon aerogels from waste paper with exceptional performance for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 14858–14864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Mei, T.; He, X.; Zhong, W.; Liu, K.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, D. A facile route to the production of polymeric nanofibrous aerogels for environmentally sustainable applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3692–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Geng, G. Highly efficient oil-in-water emulsion and oil layer/water mixture separation based on durably superhydrophobic sponge prepared via a facile route. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oribayo, O.; Feng, X.; Rempel, G.L.; Pan, Q. Modification of Formaldehyde-Melamine-Sodium Bisulfite Copolymer Foam and its application as Effective Sorbents for Clean Up of Oil Spills. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 160, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, M.; Hejazi, I.; Seyfi, J.; Ghiyasi, S.; Ghorashi, S.S.; Khonakdar, H.A.; Davachi, S.M. Investigating the effect of surface composition and morphology on oil/water separation efficiency of sponges coated with polymer nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, E431–E439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Deng, Y.; Wang, C. Multiphase surface growth of hydrophobic ZIF-8 on melamine sponge for excellent oil/water separation and effective catalysis in a Knoevenagel reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3258–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.; Chai, W.; Xu, J. Oil-absorbent polyurethane sponge coated with KH-570-modified graphene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, X.; Wu, X.; Qian, R.; Jiang, P. Mechanically flexible and multifunctional polymer-based graphene foams for elastic conductors and oil–water separators. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5658–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Meng, K.; Ding, K.; Wang, Y. A Superhydrophobic Sponge with Hierarchical Structure as an Efficient and Recyclable Oil Absorbent. Chempluschem 2015, 80, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Zhao, Z.; Kang, R.; Yan, Z.; Lv, W.; Li, M.; Jia, R.; Luo, L. Robust superhydrophobic candle soot and silica composite sponges for efficient oil/water separation in corrosive and hot water. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 817–826. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, H.-Y.; Jing, X.; Politowicz, A.L.; Chen, E.; Huang, H.-X.; Turng, L.-S. Highly compressible ultra-light anisotropic cellulose/graphene aerogel fabricated by bidirectional freeze drying for selective oil absorption. Carbon 2018, 132, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Su, D.; Zhang, F.; Ji, H.; Liu, R. Superelastic and superhydrophobic bacterial cellulose/silica aerogels with hierarchical cellular structure for oil absorption and recovery. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 346, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Jin, Y.; Jiang, P.; Yu, J. Oil/Water Separation Performances of Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic Sponges. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13137–13142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, J. A two-step hydrophobic fabrication of melamine sponge for oil absorption and oil/water separation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 339, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J. Furfuryl alcohol modified melamine sponge for highly efficient oil spill clean-up and recovery. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 21893–21897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Zhang, G.; Ouyang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, C. Simple fabrication of multi-functional melamine sponges. Mater. Lett. 2017, 190, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracco, G.; Holst, B. Surface Science Techniques. Vacuum 2013, 45, 647. [Google Scholar]
- Young, T. An Essay on the Cohesion of Fluids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1805, 95, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lee, T.R. Contact Angle and Wetting Properties. In Surface Science Techniques; Bracco, G., Holst, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, M.; Zhuang, J.; Chen, L. A robust salt-tolerant superoleophobic aerogel inspired by seaweed for efficient oil–water separation in marine environments. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 25394–25400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darband, G.B.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Khorsand, S.; Sokhanvar, S.; Kaboli, A. Science and Engineering of Superhydrophobic Surfaces: Review of Corrosion Resistance, Chemical and Mechanical Stability. Arab. J. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.; Baxter, S. Wettability of Porous Surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Patterning of controllable surface wettability for printing techniques. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5184–5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuma, A.; Quéré, D. Superhydrophobic states. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Su, B. Electricity-driven wettability with a low threshold voltage. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 082106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Jiang, L. Bio-Inspired, Smart, Multiscale Interfacial Materials. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2842–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Definition of Superhydrophobic States. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3423–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, A.; Yeomans, J.M. Modeling Droplets on Superhydrophobic Surfaces: Equilibrium States and Transitions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 2624–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Biomimetic polymeric superhydrophobic surfaces and nanostructures: From fabrication to applications. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3338–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, R.J. Contact angle, wetting, and adhesion: A critical review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1993, 6, 1269–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.C.; Bhushan, B. Wetting Behavior of Water and Oil Droplets in Three-Phase Interfaces for Hydrophobicity/philicity and Oleophobicity/philicity. Langmuir 2009, 25, 14165–14173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Huo, J.; Hou, X. Superoleophobic surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4168–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Surfaces with Superwettability: New Insight on Theory, Design, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 8230–8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-X.; Chen, Y.-X.; Guo, Z.; Liu, H.-L.; Wang, D.-P.; Huang, X.-J. Bioinspired Multifunctional Hetero-Hierarchical Micro/Nanostructure Tetragonal Array with Self-Cleaning, Anticorrosion, and Concentrators for the SERS Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10633–10642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q.; Peng, S.; Wu, X.; Ren, T.; Zeng, Z.; Xue, Q. A cellulose sponge with robust superhydrophilicity and under-water superoleophobicity for highly effective oil/water separation. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3093–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Photo-induced water–oil separation based on switchable superhydrophobicity–superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity of the aligned ZnO nanorod array-coated mesh films. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 19652–19657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-C.; Xu, Z.-K. Mineral-Coated Polymer Membranes with Superhydrophilicity and Underwater Superoleophobicity for Effective Oil/Water Separation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Cheng, Z.; Lv, T.; Qian, Y.; Liu, Y. Anti-corrosive hierarchical structured copper mesh film with superhydrophilicity and underwater low adhesive superoleophobicity for highly efficient oil–water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13411–13417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Zha, F.; Lei, Z. A prewetting induced underwater superoleophobic or underoil (super) hydrophobic waste potato residue-coated mesh for selective efficient oil/water separation. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wan, W.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y. Controllable and green synthesis of robust graphene aerogels with tunable surface properties for oil and dye adsorption. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X.; Qiu, Z.; Peng, X.; Ying, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G. One-step modification of PU sponges for selective absorption of oil–water mixtures. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kaang, B.K.; Han, N.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, W.S. An anti-overturn Janus sponge with excellent floating stability for simultaneous pollutant remediation and oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 16371–16381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, A.; Le Floch, S.; Reinert, L.; Ramos, S.M.M.; Tuaillon-Combes, J.; Soneda, Y.; Chaudet, P.; Baillis, D.; Blanchard, N.; Duclaux, L.; et al. Melamine-derived carbon sponges for oil–water separation. Carbon 2016, 107, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.S.; Carter, G.T.; Brönstrup, M. Editorial: Are natural products the solution to antimicrobial resistance? Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 685–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, F.; Hu, L.-L.; Gong, L.-X.; Zhao, L.; Li, S.-N.; Tang, L.-C. Facile synthesis of super-hydrophobic, electrically conductive and mechanically flexible functionalized graphene nanoribbon/polyurethane sponge for efficient oil/water separation at static and dynamic states. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 2154–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sileika, T.S.; Barrett, D.G.; Zhang, R.; Lau, K.H.A.; Messersmith, P.B. Colorless Multifunctional Coatings Inspired by Polyphenols Found in Tea, Chocolate, and Wine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10766–10770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.Q.; Yang, W.J.; Neoh, K.-G.; Kang, E.-T.; Fu, G.D. Dopamine-Induced Reduction and Functionalization of Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 8336–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Durable superhydrophobic/superoleophilic PDMS sponges and their applications in selective oil absorption and in plugging oil leakages. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18281–18287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S. The fabrication of 3D porous PDMS sponge for Oil and organic solvent absorption. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2019, 38, S86–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, X.; Jiao, Y.; Shi, J. Fabrication of a Superhydrophobic, Fire-Resistant, and Mechanical Robust Sponge upon Polyphenol Chemistry for Efficiently Absorbing Oils/Organic Solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 1842–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Li, Y.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, D.; Xu, J.; Xue, M. Fabrication of hydrophobic and oleophilic polyurethane foam sponge modified with hydrophobic Al2O3 for oil/water separation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 58, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Lin, Y. A Facile Method for the Fabrication of a Superhydrophobic Polydopamine-Coated Copper Foam for Oil/Water Separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 413, 140–148. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Yu, C.; Cui, L.; Song, Z.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, L. Facile Preparation of the Porous PDMS Oil-Absorbent for Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1600862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, N.; Lin, L.; Liu, F.; Pan, Q. Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Lai, X.; Su, X.; Liang, T.; Zeng, X. Thiolated graphene-based superhydrophobic sponges for oil–water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, K.; Jia, C.; Ding, Y.; Dai, Z. A three-dimensional porous metal foam with selective-wettability for oil–water separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 5371–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Lv, C.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Guo, Z.; Shen, C. Porous Polyethylene Bundles with Enhanced Hydrophobicity and Pumping Oil-Recovery Ability via Skin-Peeling. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12580–12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zha, F.; She, H. Robust superhydrophobic attapulgite coated polyurethane sponge for efficient immiscible oil/water mixture and emulsion separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15546–15553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Mei, Q.; Xiao, J.; Du, M.; Zheng, Q. 3D Multiscale Superhydrophilic Sponges with Delicately Designed Pore Size for Ultrafast Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1704293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Xu, M.; Wang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, L.; Xue, Q. Cellulose Sponge with Superhydrophilicity and High Oleophobicity Both in Air and under Water for Efficient Oil–Water Emulsion Separation. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. A Superamphiphobic Coating with an Ammonia-Triggered Transition to Superhydrophilic and Superoleophobic for Oil–Water Separation. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 4610–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Yang, H.; Song, S.; Lu, B.; Chen, R. A magnetic superhydrophilic/oleophobic sponge for continuous oil–water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.-C.; Chang-Jian, C.-W.; Hsiao, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-C.; Huang, J.-H. Interfacial engineering of melamine sponges using hydrophobic TiO2 nanoparticles for effective oil/water separation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 67, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Jung, M.C.; Cho, S.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.-Y.; Lee, H.J.; Oh, K.H.; Moon, M.-W. UV-responsive nano-sponge for oil absorption and desorption. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, J.; Ma, X.; Peng, X.; Qiu, Z.; Ying, J.; Wang, J. Smart PDMS sponge with switchable pH-responsive wetting surface for oil/water separation. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 8940–8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, P. Smart surfaces with switchable superoleophilicity and superoleophobicity in aqueous media: Toward controllable oil/water separation. NPG Asia Mater. 2012, 4, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Chang, W.; Liao, S.; Qian, Z.; Liu, Y. pH-Responsive Sponges Fabricated by Ag–S Ligands Possess Smart Double-Transformed Superhydrophilic–Superhydrophobic–Superhydrophilic Wettability for Oil–Water Separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 10772–10782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Geng, G. Highly recyclable superhydrophobic sponge suitable for the selective sorption of high viscosity oil from water. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 97, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, F.; Yuan, D. Superhydrophobic, ultralight and flexible biomass carbon aerogels derived from sisal fibers for highly efficient oil–water separation. Cellulose 2018, 25, 3067–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Multifunctional Foam with Self-Cleaning and Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Weibel, J.A.; Garimella, S.V. Continuous Oil–Water Separation Using Polydimethylsiloxane-Functionalized Melamine Sponge. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 3596–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chen, K.; Du, R.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Rümmeli, M.H.; Xie, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Scalable Seashell-Based Chemical Vapor Deposition Growth of Three-Dimensional Graphene Foams for Oil–Water Separation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6360–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, H.; Fu, R.; Xing, L.; Xiang, J.; Li, Z.; Li, F.; Zhang, T. Surface Modification of Bacterial Cellulose Aerogels’ Web-like Skeleton for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 7373–7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Xu, W.; Wu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Fong, H. Ultralight electrospun cellulose sponge with super-high capacity on absorption of organic compounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Z.; Qu, L. Bio-inspired fabrication of fire-retarding, magnetic-responsive, superhydrophobic sponges for oil and organics collection. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 172, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehabadi, S.; Seyfi, J.; Hejazi, I.; Davachi, S.M.; Naeini, A.H.; Khakbaz, M. Nanosilica-decorated sponges for efficient oil/water separation: Role of nanoparticle’s type and concentration. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 7017–7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Hao, G.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, N.; Yu, L. One-pot synthesis of robust superhydrophobic, functionalized graphene/polyurethane sponge for effective continuous oil–water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, N. Robust and Durable Superhydrophobic Polyurethane Sponge for Oil/Water Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 11260–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lei, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Mi, N.; Chen, H.; Huang, D.; Li, N. A facile method to fabricate the superhydrophobic magnetic sponge for oil–water separation. Mater. Lett. 2017, 195, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-J.; Kwon, T.-H.; Im, H.; Moon, D.-I.; Baek, D.J.; Seol, M.-L.; Duarte, J.P.; Choi, Y.-K. A Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Sponge for the Selective Absorption of Oil from Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4552–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanthong, P.; Reubroycharoen, P.; Kongparakul, S.; Samart, C.; Wang, Z.; Hao, X.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Fabrication and evaluation of nanocellulose sponge for oil/water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Bian, Z. Preparation of MCC/MC Silica Sponge and Its Oil/Water Separation Apparatus Application. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 5795–5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wu, X.; Fang, J. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic “sponge-like” aerogels for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 5115–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.-Y.; Jing, X.; Xie, H.; Huang, H.-X.; Turng, L.-S. Magnetically driven superhydrophobic silica sponge decorated with hierarchical cobalt nanoparticles for selective oil absorption and oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lian, M.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Guo, Z.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Continuous fabrication of polymer microfiber bundles with interconnected microchannels for oil/water separation. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 9, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, Y. Direct silanization of polyurethane foams for efficient selective absorption of oil from water. Aiche J. 2017, 63, 2232–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Durable Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Polyurethane Sponges Inspired by Mussel and Lotus Leaf for the Selective Removal of Organic Pollutants from Water. ChemPlusChem 2014, 79, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, E.; Liu, Z.; Gao, D.; Yuan, R.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y. A Novel Carbon Nanotubes Reinforced Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic Polyurethane Sponge for Selective Oil–water Separation through a Chemical Fabrication. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, J.; Chen, K.; Hao, J.; Ji, D. Continuous separation of oil from water surface by a novel tubular unit based on graphene coated polyurethane sponge. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Li, Y.; Fei, T.; Gong, W. Facile one-pot synthesis of superhydrophobic reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge at the presence of ethanol for oil–water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Dashairya, L. Reduced graphene oxide modified melamine formaldehyde (rGO@MF) superhydrophobic sponge for efficient oil–water separation. J. Porous Mater. 2018, 25, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, A.; Zilouei, H.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Asadinezhad, A. Enhancing oil removal from water by immobilizing multi-wall carbon nanotubes on the surface of polyurethane foam. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 157, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Xiong, W.; Wang, M.; Fan, L.; Rabiee-Golgir, H.; Jiang, L.; Hou, W.; Huang, X.; Jiang, L.; et al. Highly Efficient and Recyclable Carbon Soot Sponge for Oil Cleanup. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5924–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Xiong, S.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y. Extremely Efficient and Recyclable Absorbents for Oily Pollutants Enabled by Ultrathin-Layered Functionalization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18816–18823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Yu, Z.; Wu, W.; Fang, L.; Zhu, H. Continuous oil–water separation with surface modified sponge for cleanup of oil spills. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 53514–53519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wu, W.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, H. Facile Preparation and Characterization of Modified Polyurethane Sponge for Oil Absorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 20139–20144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Zulfiqar, U.; Hussain, S.Z.; Zaheer, U.; Hussain, I.; Husain, S.W.; Subhani, T. Fabrication of superhydrophobic filter paper and foam for oil–water separation based on silica nanoparticles from sodium silicate. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anju, M.; Renuka, N.K. Magnetically actuated graphene coated polyurethane foam as potential sorbent for oils and organics. Arab. J. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Tang, Y.; Yin, L.; Tang, H.; Li, C. Versatile fabrication of the magnetic polymer-based graphene foam and applications for oil–water separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 468, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, D.W.; Buyukcakir, O.; Kim, M.-K.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Coskun, A. Highly Hydrophobic ZIF-8/Carbon Nitride Foam with Hierarchical Porosity for Oil Capture and Chemical Fixation of CO2. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Tai, N.-H.; Lee, S.-B.; Kuo, W.-S. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic properties of graphene-based sponges fabricated using a facile dip coating method. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7908–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Shi, L.-A.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Yao, H.-B.; Zhu, Y.-B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.-W.; Wu, H.-A.; Yu, S.-H. Joule-heated graphene-wrapped sponge enables fast clean-up of viscous crude-oil spill. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Shi, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, R.; Shi, L.; Jin, Y.; Qing, W.; Tang, C.; Wang, P. Solar-assisted fast cleanup of heavy oil spills using a photothermal sponge. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 9192–9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Yang, X.B.; Wang, Z.X.; Long, J.; Shao, L. Designing multifunctional 3D magnetic foam for effective insoluble oil separation and rapid selective dye removal for use in wastewater remediation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 7316–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-T.; Lin, B.; Jiang, L.-W.; Lin, E.-C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.-J.; Tang, Y.-W.; He, F.-A.; Li, D.-H. Effective preparation of magnetic superhydrophobic Fe3O4/PU sponge for oil–water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Men, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Z. A superhydrophobic monolithic material with tunable wettability for oil and water separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 2365–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, A. One-step synthesis of the superhydrophobic zeolitic imidazolate framework F-ZIF-90 for efficient removal of oil. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 2372–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Cheng, H.; Fane, A.G.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H. Recent Development of Advanced Materials with Special Wettability for Selective Oil/Water Separation. Small 2016, 12, 2186–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajoie, M.S.; Thomas, M.C. Sodium bicarbonate particle size and neutralization in sponge-dough systems. Cereal Foods World 1994, 39, 684–687. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.S.; Guetzlaff, J.; Hoseney, R.C. Role of sodium bicarbonate and trapped air in extrusion. Cereal Chem. 1989, 66, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio-Avalos, J.C.; Manzano-Ramírez, A.; Yañez-Limón, J.M.; Contreras-García, M.E.; Alonso-Guzmán, E.M.; González-Hernández, J. Development and characterization of an inorganic foam obtained by using sodium bicarbonate as a gas generator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2005, 19, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Shen, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, X. Facile Thermally Impacted Water-Induced Phase Separation Approach for the Fabrication of Skin-Free Thermoplastic Polyurethane Foam and Its Recyclable Counterpart for Oil–Water Separation. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1800635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhai, X.; Xiang, T.; Zhou, M.; Zang, D.; Gao, Z.; Wang, C. Superhydrophobic melamine sponge with excellent surface selectivity and fire retardancy for oil absorption. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; You, T.; Zhang, X.; Xu, F. Superhydrophobic Cellulose Nanofiber-Assembled Aerogels for Highly Efficient Water-in-Oil Emulsions Separation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, P.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, F. Sustainable, Reusable, and Superhydrophobic Aerogels from Microfibrillated Cellulose for Highly Effective Oil/Water Separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6409–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Qian, Z.; Guo, J.; Dong, H.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J. Robust Superhydrophobic Bridged Silsesquioxane Aerogels with Tunable Performances and Their Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolghasemi, M.A.; Motahari, S.; Mohebbi, A. Sol-gel derived flexible silica aerogel as selective adsorbent for water decontamination from crude oil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhou, X.; Hao, G.; Jiang, W.; Wang, T. Property control of graphene aerogels by in situ growth of silicone polymer. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, F.; You, L.; Shen, X.; Li, S. Removal of organic solvents/oils using carbon aerogels derived from waste durian shell. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 78, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, P.; Xia, Y.; Chen, B. Multifunctional carbon aerogels from typha orientalis for oil/water separation and simultaneous removal of oil-soluble pollutants. Cellulose 2018, 25, 5863–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, S.; Ma, Q.; Jia, X.; Ma, P.-C. Preparation of carbon nanotubes/graphene hybrid aerogel and its application for the adsorption of organic compounds. Carbon 2017, 118, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Superelastic and Superhydrophobic Nanofiber-Assembled Cellular Aerogels for Effective Separation of Oil/Water Emulsions. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.-J.; Zhu, P.-L.; Yu, S.-H.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.-P.; Liao, W.-H. Ultralight, super-elastic and volume-preserving cellulose fiber/graphene aerogel for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 2017, 115, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Liu, W.; Dong, Z.; Deng, Y. Underwater superoleophobicity cellulose nanofibril aerogel through regioselective sulfonation for oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Lyu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Facile synthesis of fluorinated polydopamine/chitosan/reduced graphene oxide composite aerogel for efficient oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, P.; Hubbe, M.A.; Lucia, L.; Pal, L. High performance nanocellulose-based composite coatings for oil and grease resistance. Cellulose 2018, 25, 3377–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Han, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Magnetic carbon aerogel pyrolysis from sodium carboxymethyl cellulose/sodium montmorillonite composite aerogel for removal of organic contamination. J. Porous Mater. 2018, 25, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.M.; Carroll, M.K. Hydrophobic Silica Aerogels: Review of Synthesis, Properties and Applications. In Aerogels Handbook; Aegerter, M.A., Leventis, N., Koebel, M.M., Eds.; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 47–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; McLaughlin, E.; Pfeffer, R.; Lin, Y.S. Adsorption of oils from pure liquid and oil–water emulsion on hydrophobic silica aerogels. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 99, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurav, J.L.; Rao, A.V.; Nadargi, D.Y.; Park, H.-H. Ambient pressure dried TEOS-based silica aerogels: Good absorbents of organic liquids. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, D.A.; Shea, K.J. Bridged Polysilsesquioxanes. Highly Porous Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Materials. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Gao, H.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J.; Dong, W.; Huang, X.; Wang, G. Vacuum-Dried Synthesis of Low-Density Hydrophobic Monolithic Bridged Silsesquioxane Aerogels for Oil/Water Separation: Effects of Acid Catalyst and Its Excellent Flexibility. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Guan, J.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R.; He, M.; Jiang, Z. Asymmetric Aerogel Membranes with Ultrafast Water Permeation for the Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 26546–26554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Miao, Y.-E.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Tjiu, W.W.; Liu, T. Ni-Doped Graphene/Carbon Cryogels and Their Applications As Versatile Sorbents for Water Purification. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7584–7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Young, T.M.; Liu, P.; Contescu, C.I.; Huang, B.; Wang, S. Ultralight carbon aerogel from nanocellulose as a highly selective oil absorption material. Cellulose 2015, 22, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Shi, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, L. Facile synthesis of N-doped graphene aerogel and its application for organic solvent adsorption. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 6419–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, T.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Pressure-Sensitive and Conductive Carbon Aerogels from Poplars Catkins for Selective Oil Absorption and Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18001–18007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Li, C.; Liang, H.W.; Chen, J.F.; Yu, S.H. Ultralight, Flexible, and Fire-Resistant Carbon Nanofiber Aerogels from Bacterial Cellulose. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2925–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, C.; Lu, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Jin, C.; Sun, Q.; Li, J. Ultralight and hydrophobic nanofibrillated cellulose aerogels from coconut shell with ultrastrong adsorption properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranford, S.W.; Anna, T.; Pugno, N.M.; Buehler, M.J. Nonlinear material behaviour of spider silk yields robust webs. Nature 2012, 482, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Tang, X.; Ge, J.; Ding, B. Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Removal of Organic Pollutants from Water Using Superwetting Materials. Chem. Rec. 2018, 18, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, J.P.; Nataraj, S.K.; Gogda, A.; Meena, R. Bio-based superhydrophilic foam membranes for sustainable oil–water separation. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4552–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Yang, J.; Zhu, D.; Zheng, J.; Handschuh-Wang, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; et al. Hydrophilic Sponges for Leaf-Inspired Continuous Pumping of Liquids. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1700028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, A.; Nikaido, T.; Ikeda, M.; Okada, K.; Yamauchi, J.; Foxton, R.M.; Sawada, H.; Tagami, J.; Matin, K. Inhibition of biofilm formation using newly developed coating materials with self-cleaning properties. Dent. Mater. J. 2008, 27, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.S.; Bhushan, B. Bioinspired, roughness-induced, water and oil super-philic and super-phobic coatings prepared by adaptable layer-by-layer technique. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, F.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. Coexistence of superhydrophilicity and superoleophobicity: theory, experiments and applications in oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 15057–15063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Dunderdale, G.J.; England, M.W.; Hozumi, A. Oil/water separation techniques: A review of recent progresses and future directions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16025–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, L.; Lei, J.; He, J.; Li, N.; Pan, F. Intelligent sponge with reversibly tunable super-wettability: Robust for effective oil–water separation as both the absorber and filter tolerate fouling and harsh environments. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 12334–12340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Zhang, G.; Deng, Y.; Wang, C. Thermoresponsive Melamine Sponges with Switchable Wettability by Interface-Initiated Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 8967–8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Zhang, G.; Deng, Y.; Wang, C. Surface modification of melamine sponges for pH-responsive oil absorption and desorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 416, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).