Transport Properties of One-Step Compression Molded Epoxy Nanocomposite Foams
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Carbon Nanoparticles
2.3. Preparation of ER Foams
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
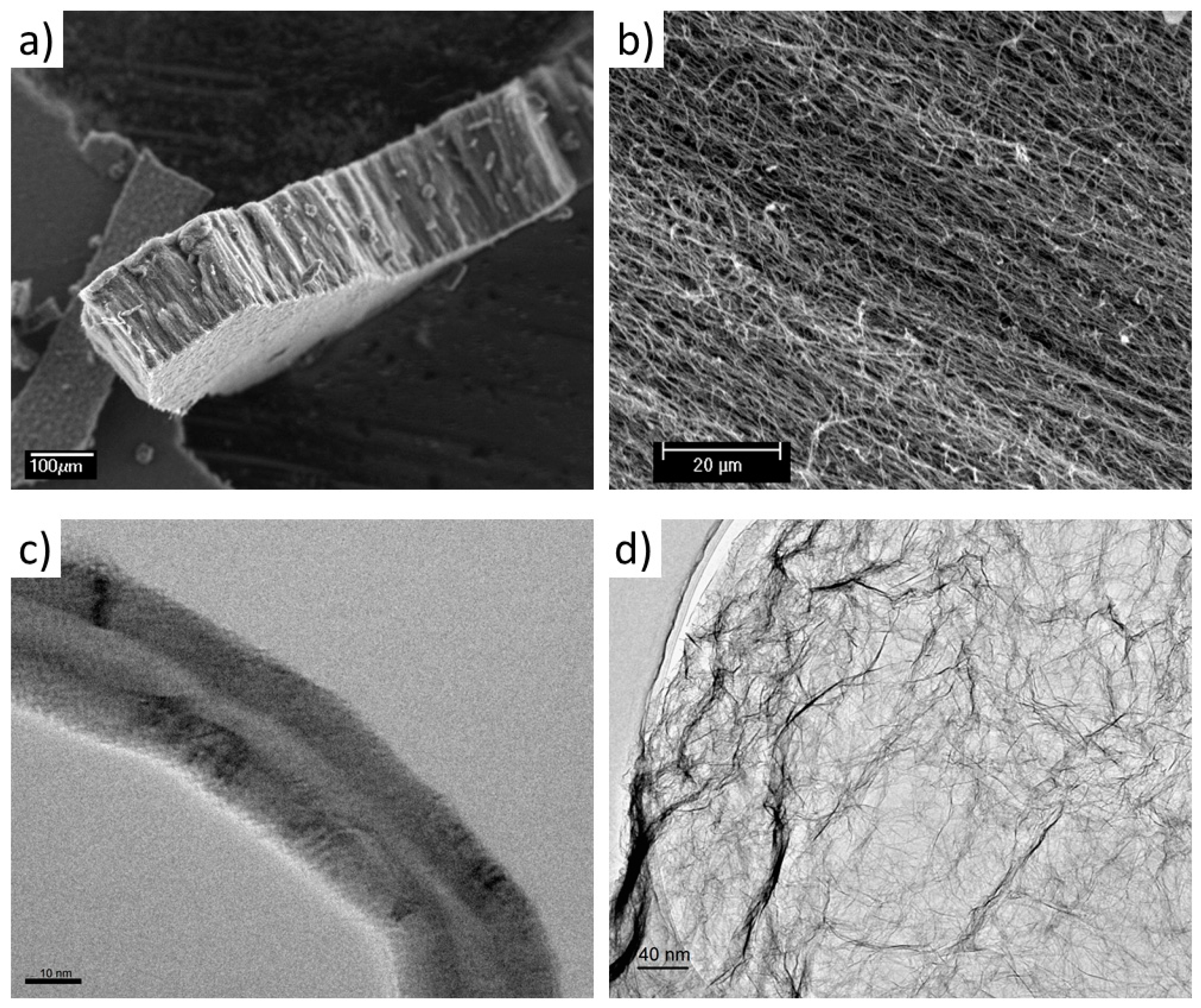
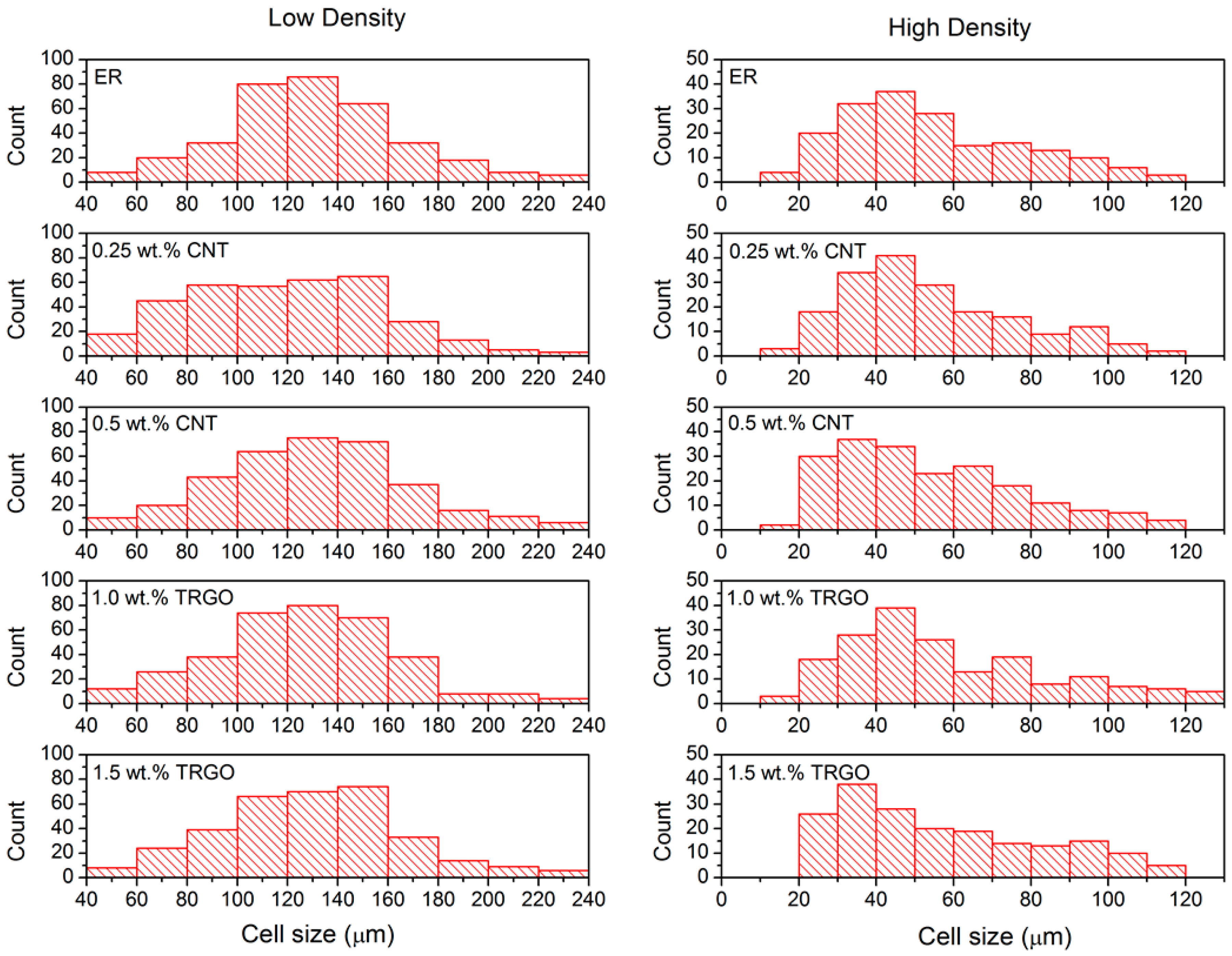
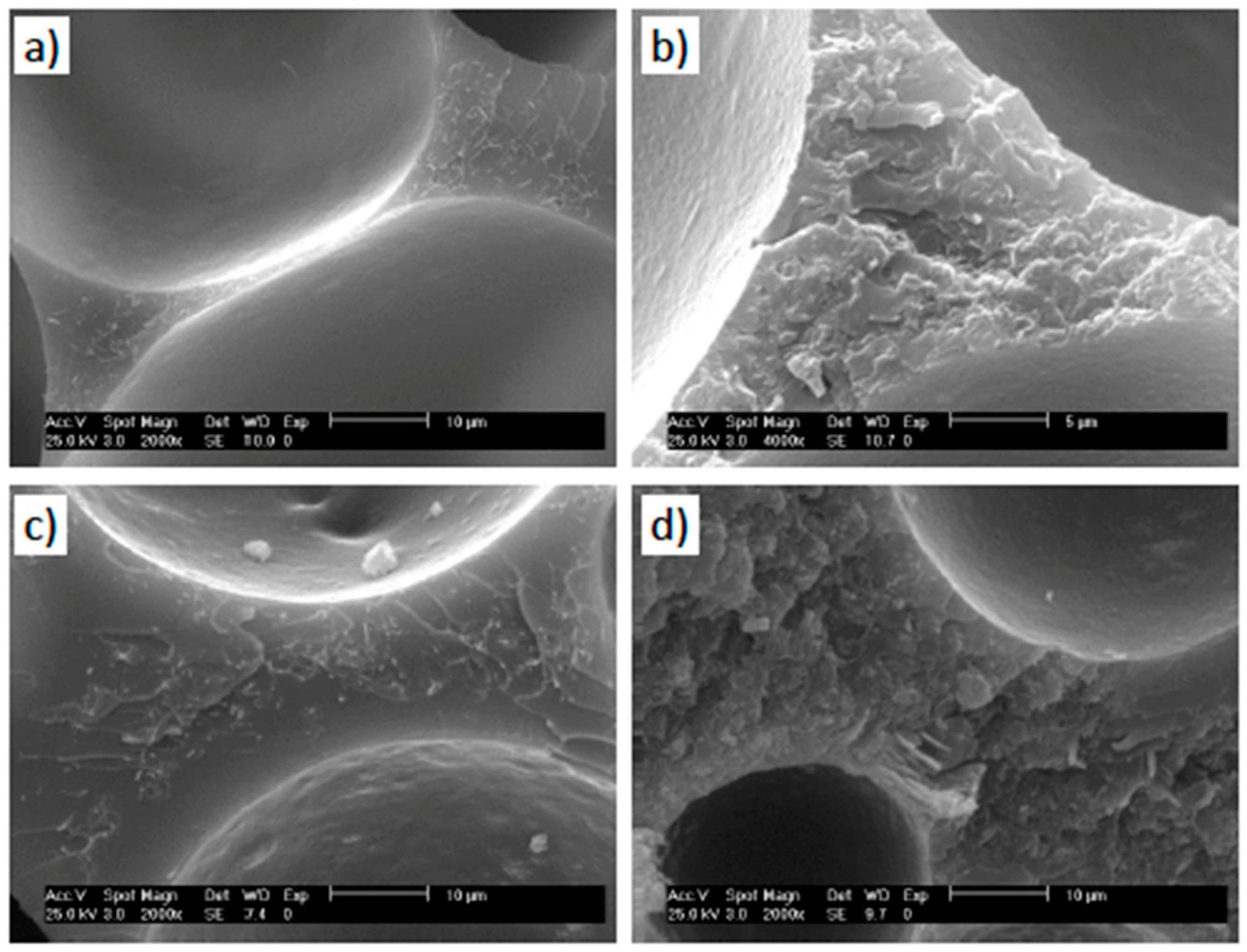
3.1. Morphology
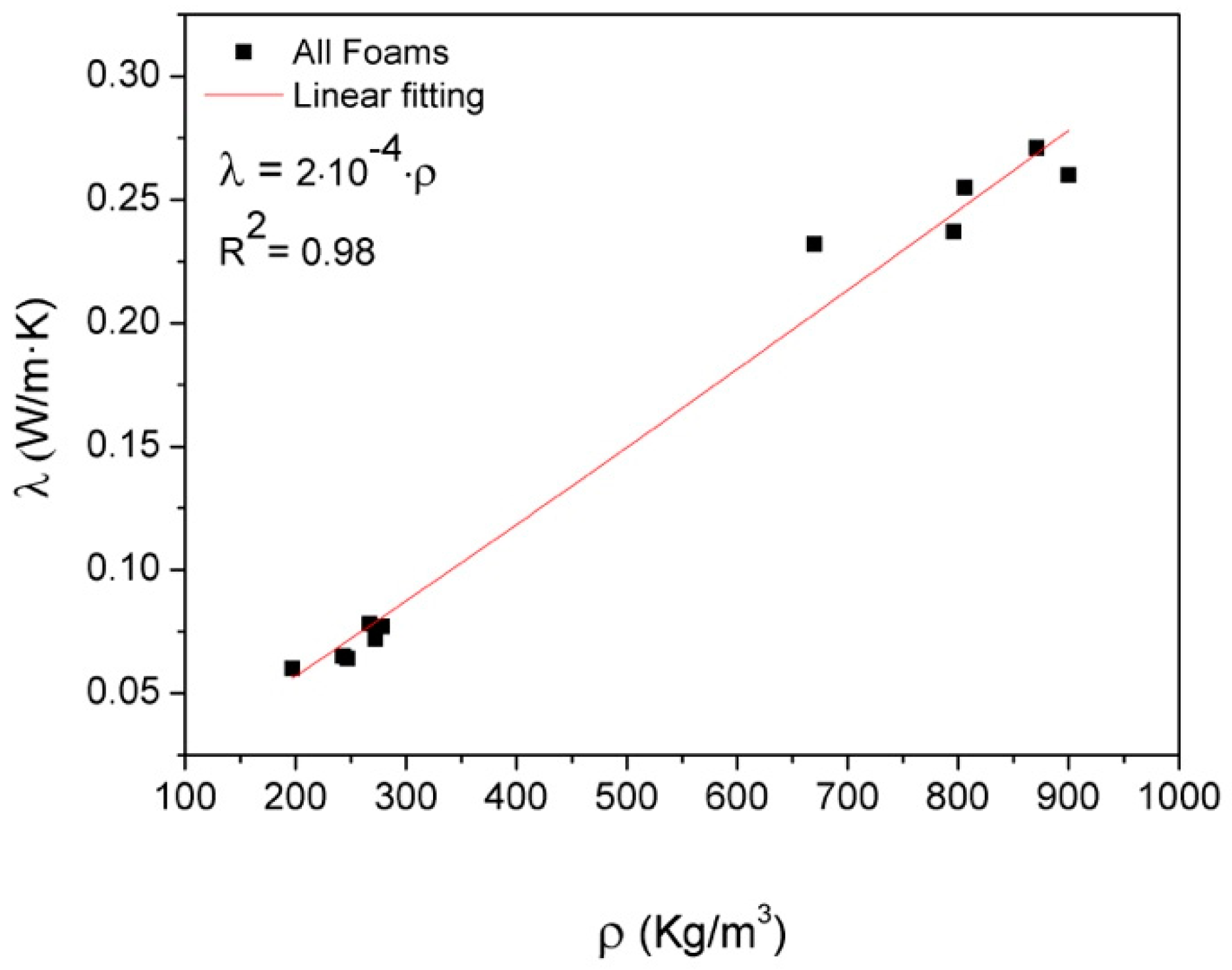
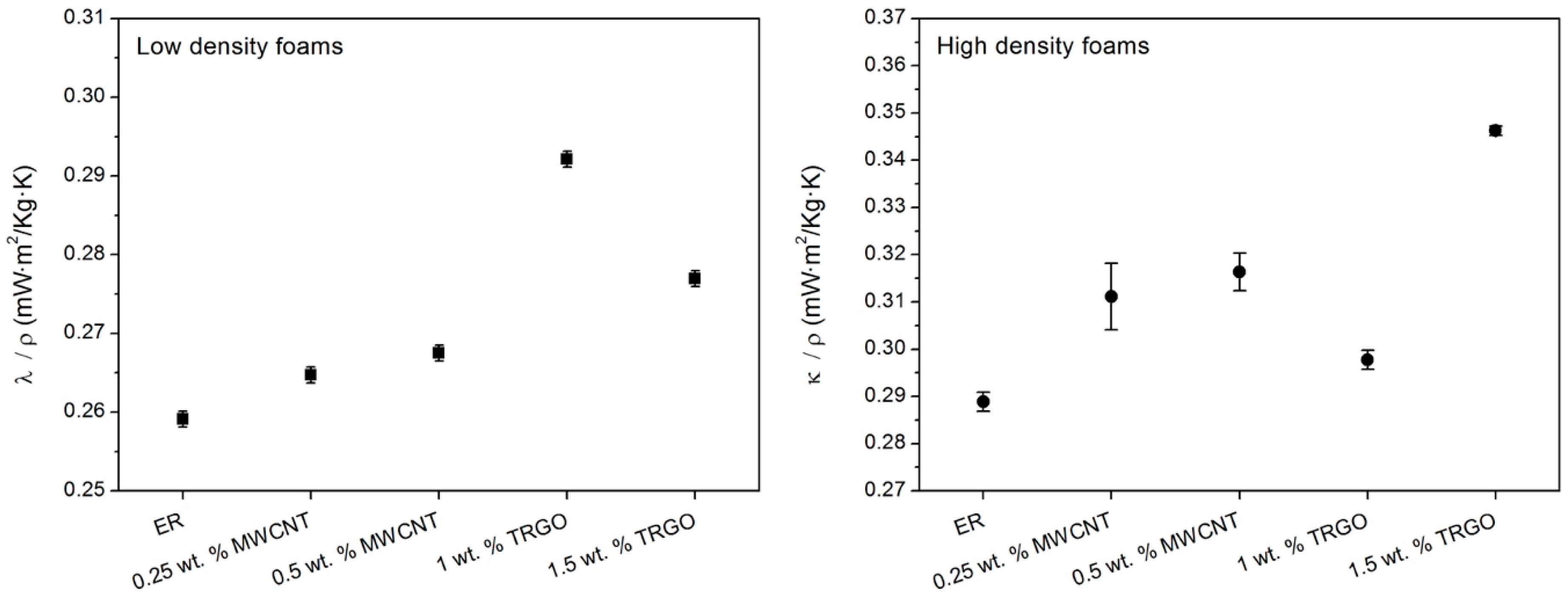
3.2. Thermal Conductivity
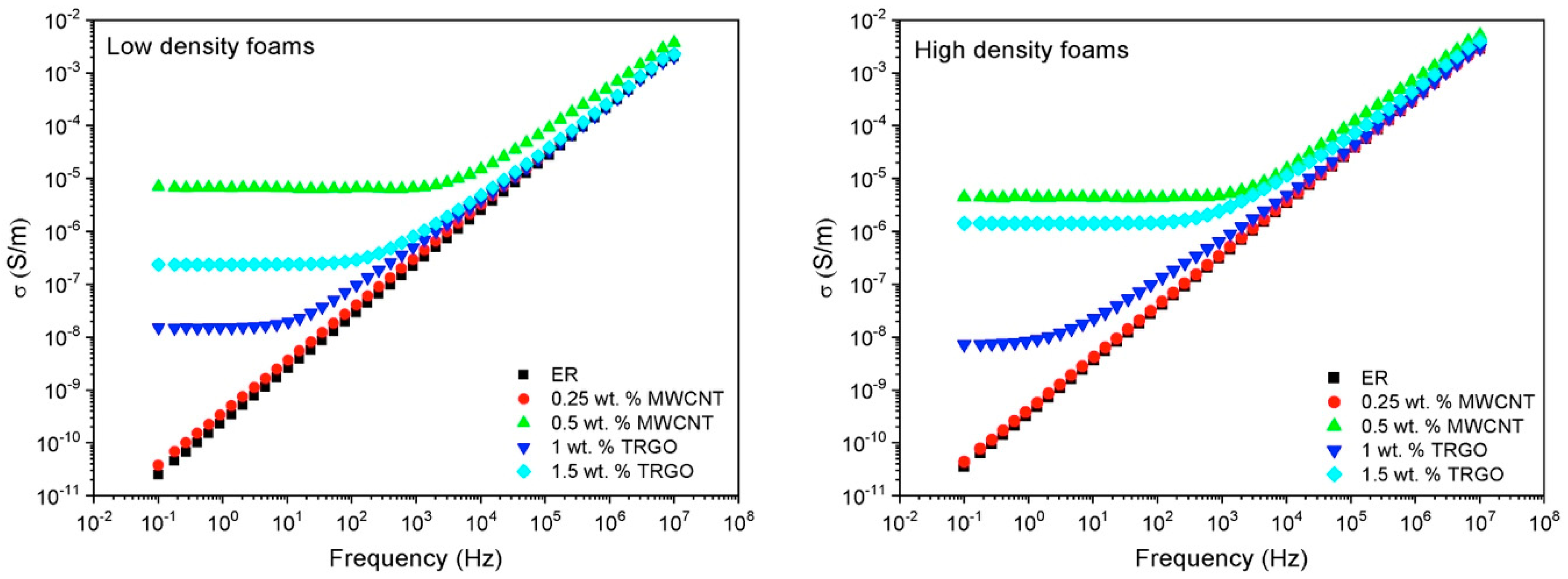
3.3. Electrical Conductivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- John, B.; Reghunadhan Nair, C.P. Syntactic foams. In Handbook of Thermoset Plastics; Dodiuk, H., Goodman, S.H., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 511–554. [Google Scholar]
- Klempner, D.; Sendijarevi’c, V.; Aseeva, R.M. Handbook of Polymeric Foams and Foam Technology; Hanser Publishers: Munich, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Zeltmann, S.E.; Shunmugasamy, V.C.; Pinisetty, D. Applications of Polymer Matrix Syntactic Foams. JOM 2014, 66, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Kim, H.S. Toughening method and mechanisms for thermosets. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; He, L. The compressive properties of expandable microspheres/epoxy foams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 56, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Zeng, L.; Li, R.; Tian, H.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W. A review of the electrical and mechanical properties of carbon nanofiller-reinforced polymer composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 1036–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, P.; Verdejo, R.; Wöllecke, F.; Altstädt, V.; Sandler, J.K.W.; Shaffer, M.S.P. Carbon nanofibers allow foaming of semicrystalline poly(ether ether ketone). Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 2864–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo, R.; Barroso-Bujans, F.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.A.; Antonio de Saja, J.; Arroyo, M.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A. Carbon nanotubes provide self-extinguishing grade to silicone-based foams. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3933–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Rende, D.; Schadler, L.S.; Ozisik, R. Polymer nanocomposite foams. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 3837–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.; Velasco, J.I. Multifunctional polymer foams with carbon nanoparticles. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 486–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, E.F.; Woldesenbet, E. Processing and mechanical characterization of carbon nanotube reinforced syntactic foams. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2012, 31, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, M.E.; Rodriguez, A.J.; Minaie, B.; Violette, M. Processing and properties of syntactic foams reinforced with carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 2383–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimchev, M.; Caeti, R.; Gupta, N. Effect of carbon nanofibers on tensile and compressive characteristics of hollow particle filled composites. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colloca, M.; Gupta, N.; Porfiri, M. Tensile properties of carbon nanofiber reinforced multiscale syntactic foams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 44, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, E.; Ghamsari, A.K.; Woldesenbet, E. Mechanical properties of graphene platelets reinforced syntactic foams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 60, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, R.L.; Dorogokupets, G.; Gupta, N. Carbon nanofiber reinforced syntactic foams: Degradation mechanism for long term moisture exposure and residual compressive properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2041–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, R.; Gupta, N. Carbon-nanofiber-reinforced syntactic foams: compressive properties and strain rate sensitivity. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2014, 66, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Bao, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, A. Rigid thermosetting epoxy/multi-walled carbon nanotube foams with enhanced conductivity originated from a flow-induced concentration effect. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 37710–37720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hua, W.; Zhang, A.; Bao, J. Light-Weight Silver Plating Foam and Carbon Nanotube Hybridized Epoxy Composite Foams with Exceptional Conductivity and Electromagnetic Shielding Property. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24131–24142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Xu, Y.; Bao, J. Epoxy composite foams with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding and heat-resistance performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Bao, J. Epoxy foams with tunable acoustic absorption behavior. Mater. Lett. 2017, 194, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Y. Acoustically and Thermally Insulating Epoxy Foams Prepared by Non-traditional Expandable Microspheres. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Xu, Y.; Bao, J. Epoxy–carbon black composite foams with tunable electrical conductivity and mechanical properties: Foaming improves the conductivity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo, R.; Barroso Bujans, F.; Rodriguez Perez, M.; de Saja, J.; Lopez Manchado, M. Functionalized graphene sheet filled silicone foam nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2221–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 22007-2:2015. Determination of Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Diffusivity—Part 2: Transient Plane Heat Source (Hot Disc) Method; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Gallego, M.; Bernal, M.M.; Hernandez, M.; Verdejo, R.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A. Comparison of filler percolation and mechanical properties in graphene and carbon nanotubes filled epoxy nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gallego, M.; González-Jiménez, A.; Verdejo, R.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Valentin, J.L. Epoxy resin curing reaction studied by proton multiple-quantum NMR. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2015, 53, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gallego, M.; Verdejo, R.; Khayet, M.; de Zarate, J.M.O.; Essalhi, M.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A. Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotubes and graphene in epoxy nanofluids and nanocomposites. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Hidalgo, R.; Yuste-Sanchez, V.; Verdejo, R.; Blanco, C.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Menéndez, R. Main structural features of graphene materials controlling the transport properties of epoxy resin-based composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 101, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.M.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Verdejo, R. In situ foaming evolution of flexible polyurethane foam nanocomposites. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011, 212, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo, R.; Bernal, M.M.; Romasanta, L.; Lopez Manchado, M. Graphene filled polymer nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3301–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo, R.; Saiz-Arroyo, C.; Carretero-Gonzalez, J.; Barroso-Bujans, F.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.A.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A. Physical properties of silicone foams filled with carbon nanotubes and functionalized graphene sheets. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 2790–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo, R.; Tapiador, F.J.; Helfen, L.; Bernal, M.M.; Bitinis, N.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A. Fluid dynamics of evolving foams. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 10860–10866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botas, C.; Álvarez, P.; Blanco, P.; Granda, M.; Blanco, C.; Santamaría, R.; Romasanta, L.J.; Verdejo, R.; López-Manchado, M.A.; Menéndez, R. Graphene materials with different structures prepared from the same graphite by the Hummers and Brodie methods. Carbon 2013, 65, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin Gallego, M. Development of Epoxy Nanocomposites based on Carbon Nanostructures. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Rey Juan Carlos, Móstoles, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Xu, L.; Chen, C.; Tang, J.; Ji, X.; Li, Z. Enhanced mechanical and thermal properties of rigid polyurethane foam composites containing graphene nanosheets and carbon nanotubes. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solórzano, E.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.A.; Lázaro, J.; de Saja, J.A. Influence of Solid Phase Conductivity and Cellular Structure on the Heat Transfer Mechanisms of Cellular Materials: Diverse Case Studies. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2009, 11, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojny, F.H.; Wichmann, M.H.G.; Fiedler, B.; Kinloch, I.A.; Bauhofer, W.; Windle, A.H.; Karl, S. Evaluation and identification of electrical and thermal conduction mechanisms in carbon nanotube/epoxy composites. Polymer 2006, 47, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Wu, S.; Sun, Y. Hollow-Structured Materials for Thermal Insulation. Adv. Mater. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Gupta, M.C.; Dudley, K.L.; Lawrence, R.W. Novel carbon nanotube—Polystyrene foam composites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2131–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gupta, M.C.; Dudley, K.L.; Lawrence, R.W. Conductive carbon nanofiber-polymer foam structures. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.B.; Li, Z.M.; Shi, L.; Bian, X.C.; Xiang, Z.D. Ultralight conductive carbon-nanotube-polymer composite. Small 2007, 3, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Nafezarefi, F.; Tai, N.H.; Schlagenhauf, L.; Nüesch, F.A.; Chu, B.T.T. Size and synergy effects of nanofiller hybrids including graphene nanoplatelets and carbon nanotubes in mechanical properties of epoxy composites. Carbon 2012, 50, 5380–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gallego, M.; Hernández, M.; Lorenzo, V.; Verdejo, R.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Sangermano, M. Cationic photocured epoxy nanocomposites filled with different carbon fillers. Polymer 2012, 53, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.; Arjmand, M.; Otero Navas, I.; Zehtab Yazdi, A.; Sundararaj, U. Effect of Nanofiller Geometry on Network Formation in Polymeric Nanocomposites: Comparison of Rheological and Electrical Properties of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube and Graphene Nanoribbon. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 3954–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Protocol | Gap 1 (µm) | Gap 2 (µm) | Speed (rpm) | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | 120 | 40 | 100 | 10 |
| Step 2 | 60 | 20 | 80 | 10 |
| Step 3 | 15 | 5 | 80 | 10 |
| Sample | Cell Size (µm) | ρ (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| ER-LD | 130 ± 29 | 247 ± 3 |
| 0.25 wt.% MWCNT-LD | 118 ± 41 | 272 ± 2 |
| 0.5 wt.% MWCNT-LD | 129 ± 36 | 243 ± 1 |
| 1 wt.% TRGO-LD | 126 ± 35 | 267 ± 3 |
| 1.5 wt.% TRGO-LD | 125 ± 31 | 278 ± 1 |
| ER-HD | 58 ± 27 | 707 ± 1 |
| 0.25 wt.% MWCNT-HD | 53 ± 17 | 871 ± 3 |
| 0.5 wt.% MWCNT-HD | 55 ± 28 | 806 ± 2 |
| 1 wt.% TRGO-HD | 56 ± 17 | 796 ± 1 |
| 1.5 wt.% TRGO-HD | 57 ± 26 | 670 ± 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin-Gallego, M.; Lopez-Hernandez, E.; Pinto, J.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.A.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Verdejo, R. Transport Properties of One-Step Compression Molded Epoxy Nanocomposite Foams. Polymers 2019, 11, 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050756
Martin-Gallego M, Lopez-Hernandez E, Pinto J, Rodriguez-Perez MA, Lopez-Manchado MA, Verdejo R. Transport Properties of One-Step Compression Molded Epoxy Nanocomposite Foams. Polymers. 2019; 11(5):756. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050756
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin-Gallego, Mario, Emil Lopez-Hernandez, Javier Pinto, Miguel A. Rodriguez-Perez, Miguel A. Lopez-Manchado, and Raquel Verdejo. 2019. "Transport Properties of One-Step Compression Molded Epoxy Nanocomposite Foams" Polymers 11, no. 5: 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050756
APA StyleMartin-Gallego, M., Lopez-Hernandez, E., Pinto, J., Rodriguez-Perez, M. A., Lopez-Manchado, M. A., & Verdejo, R. (2019). Transport Properties of One-Step Compression Molded Epoxy Nanocomposite Foams. Polymers, 11(5), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050756









