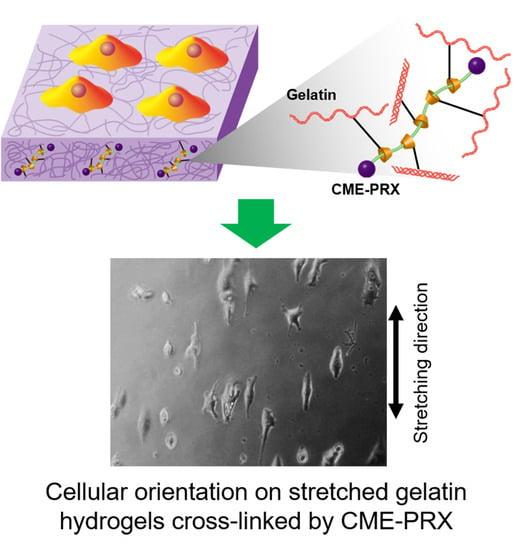
Cellular Orientation on Repeatedly Stretching Gelatin Hydrogels with Supramolecular Cross-Linkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
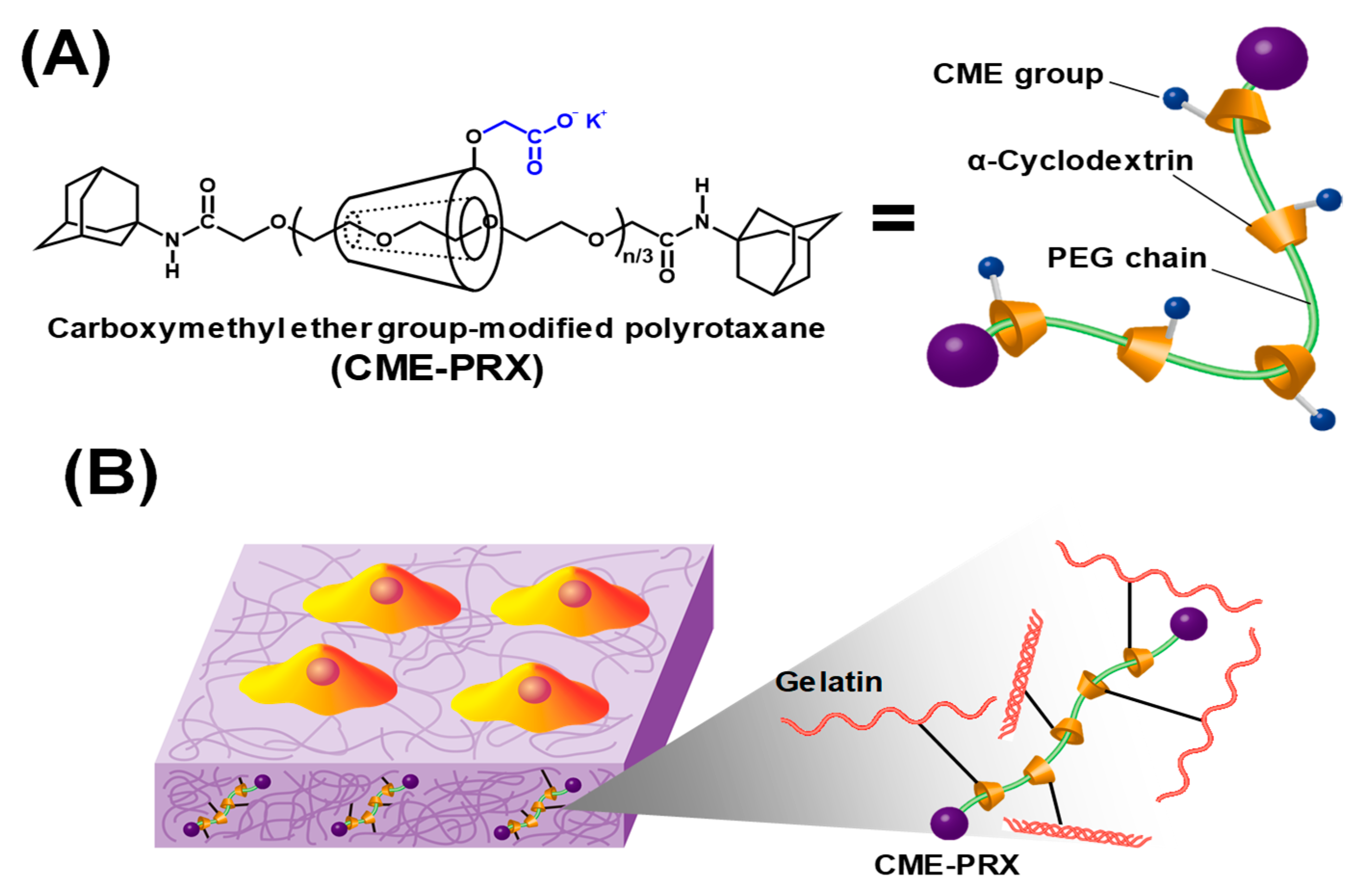
2.2. Preparation of Gelatin Hydrogels Cross-Linked by CME-PRXs
2.3. Characterization of Gelatin Hydrogels Cross-Linked by CME-PRXs
2.4. Preparation of Cell Culture Chambers
2.5. Protein Adsorption Assay
2.6. Fibroblast Cultivation with Gelatin Hydrogels Cross-Linked by CME-PRXs
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
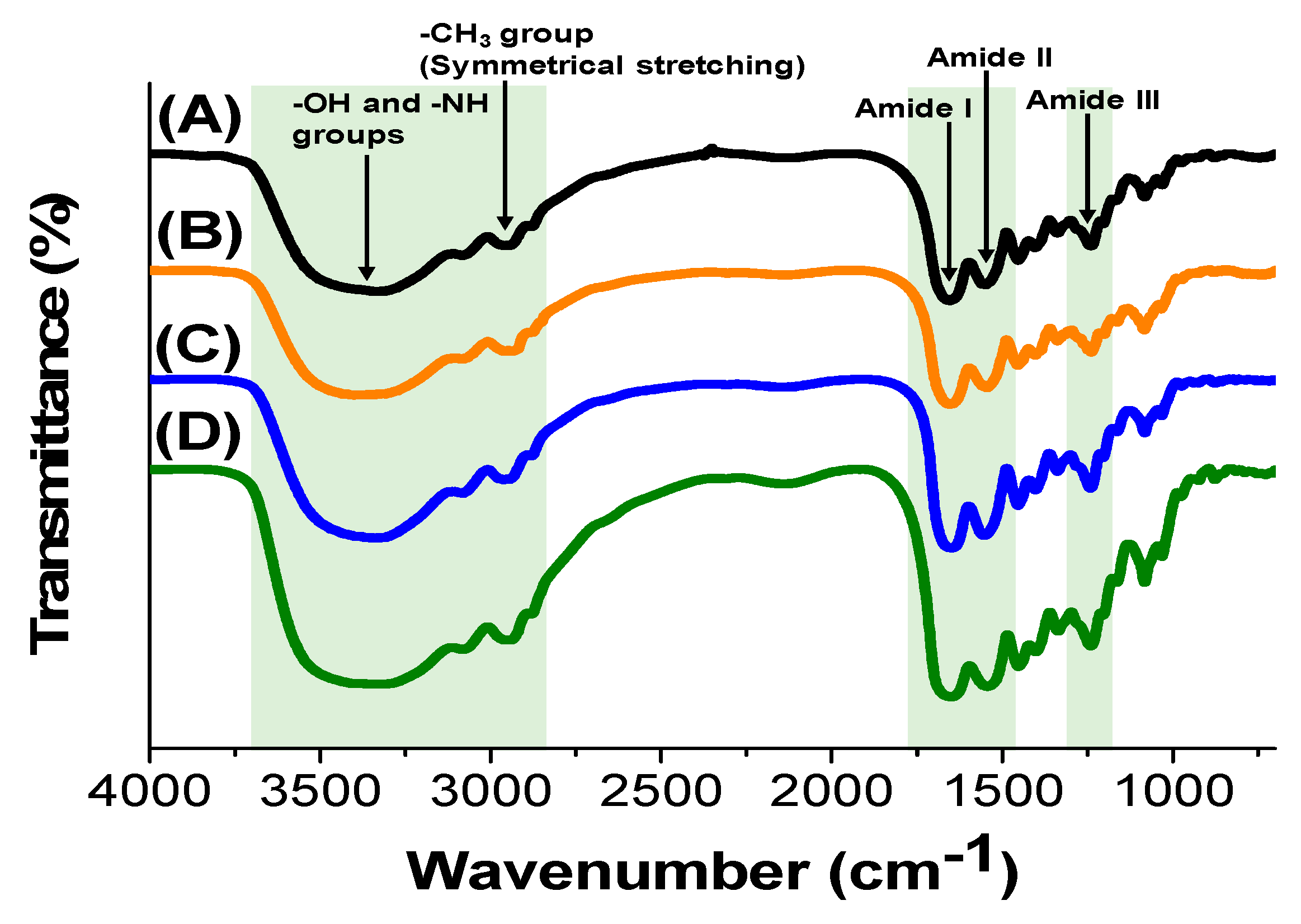
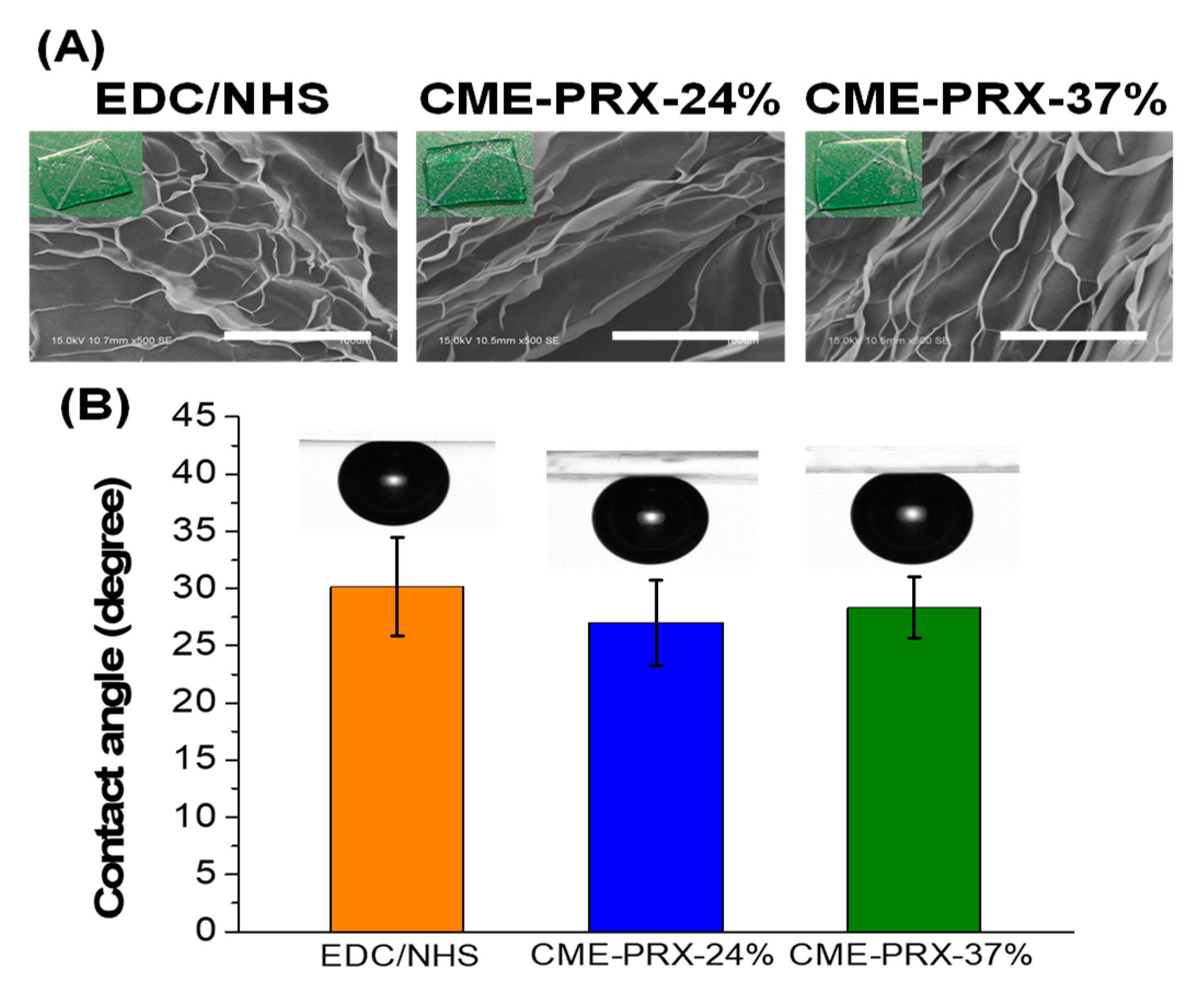
3.1. Characterization of Gelatin Hydrogels Cross-Linked by CME-PRXs
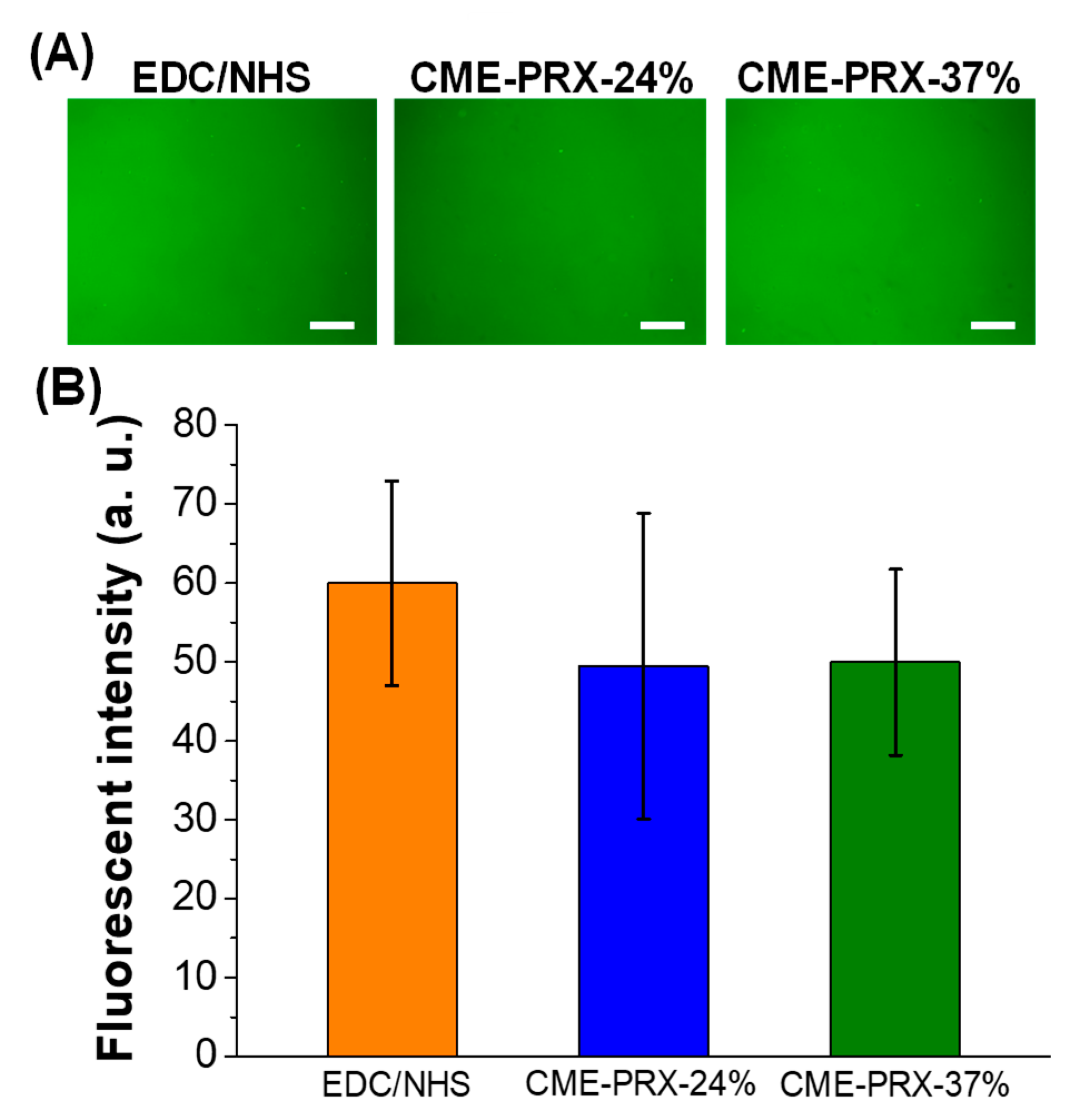
3.2. Protein Adsorption Assay of Gelatin Hydrogels Cross-Linked by CME-PRXs
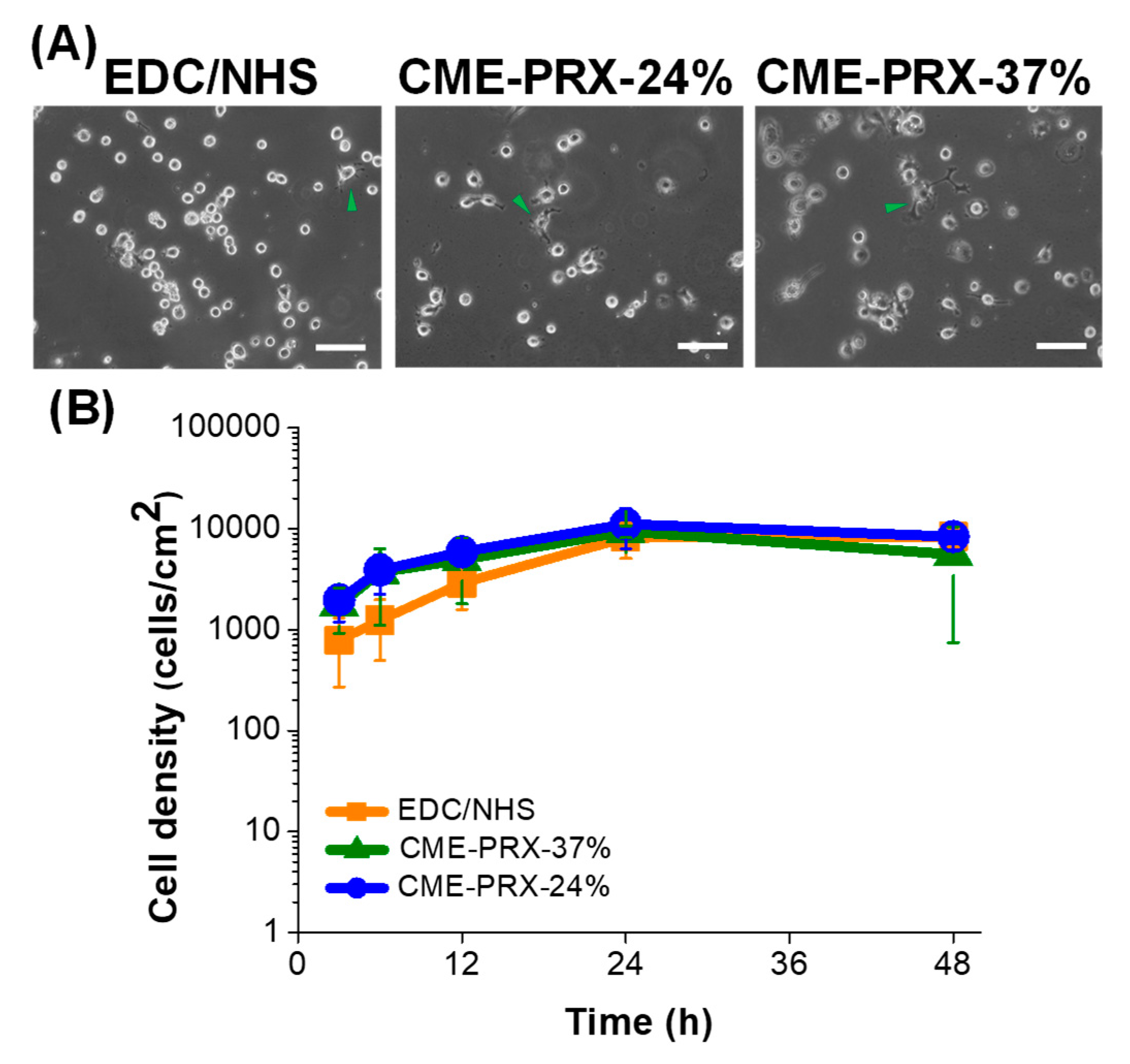
3.3. Cytocompatibility of Gelatin Hydrogels Cross-Linked by CME-PRXs
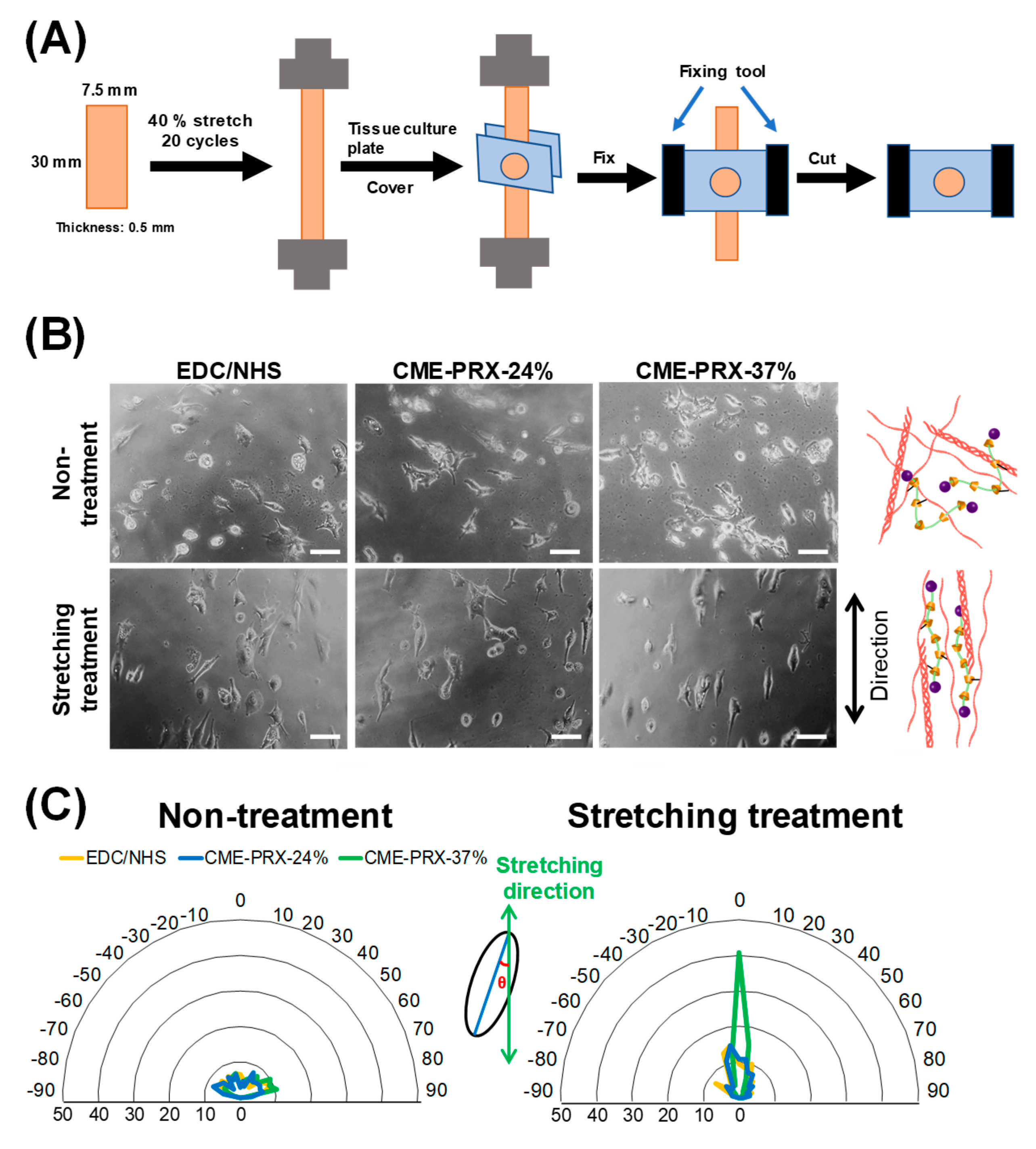
3.4. Orientation of Adhering Cells on Gelatin Hydrogels Cross-Linked by CME-PRXs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanani, Z.A.; Roos, Y.H.; Kerry, J.P. Use and Application of Gelatin as Potential Biodegradable Packaging Materials for Food Products. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 71, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigi, A.; Panzavolta, S.; Roveri, N. Hydroxyapatite-Gelatin Films: A Structural and Mechanical Characterization. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Mase, A.; Takizawa, Y.; Shinkai, M.; Honda, H.; Hata, K.-I.; Ueda, M.; Kobayashi, T. Transglutaminase-Mediated Gelatin Matrices Incorporating Cell Adhesion Factors as a Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 95, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; He, J.; Nichol, J.W.; Wang, L.; Hutson, C.B.; Wang, B.; Du, Y.; Fan, H.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Photocrosslinkable Gelatin and Silk Fibroin Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2384–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushibiki, T.; Tomoshige, R.; Fukunaka, Y.; Kakemi, M.; Tabata, Y. In Vivo Release and Gene Expression of Plasmid DNA by Hydrogels of Gelatin with Different Cationization Extents. J. Control. Release 2003, 90, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanayama, Y.; Aoki, C.; Sakai, Y. Development of Low Endotoxin Gelatin for Regenerative Medicine. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodarzi, H.; Jadidi, K.; Pourmotabed, S.; Sharifi, E.; Aghamollaei, H. Preparation and In Vitro Characterization of Cross-Linked Collagen-Gelatin Hydrogel Using EDC/NHS for Corneal Tissue Engineering Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Wang, S.; Hu, D.; Fu, W.; Wu, J.; Hong, H.; Domian, I.J.; Li, F.; Liu, J. Bioresorbable Electrospun Gelatin/Polycaprolactone Nanofibrous Membrane as a Barrier to Prevent Cardiac Postoperative Adhesion. Acta Biomater. 2019, 83, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, X.G.; Wang, J.W.; Zhou, H.; Dong, J. Treatment of Osteomyelitis Defects by a Vancomycin-Loaded Gelatin/β-Tricalcium phosphate Composite Scaffold. Bone Jt. Res. 2018, 7, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, B.J.; Gawlitta, D.; Rosenberg, A.J.W.P.; Malda, J.; Melchels, F.P.W. Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogels: Biofabrication-Based Tissue Repair. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Do, M.D.; Casey, P.; Sulistio, A.; Qiao, G.G.; Lundin, L.; Lillford, P.; Kosaraju, S. Chemical Modification of Gelatin by a Natural Phenolic Cross-Linker, Tannic Acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6809–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, M.; Spizzirri, U.G.; Iemma, F.; Puoci, F.; Cirillo, G.; Parisi, O.I.; Picci, N. Grafted Thermo-Responsive Gelatin Microspheres as Delivery Systems in Triggered Drug Release. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svachova, V.; Vojtova, L.; Pavlinak, D.; Vojtek, L.; Sedlakova, V.; Hyrsl, P.; Albertum, M.; Jaros, J.; Hampl, A.; Jancar, J. Novel Electrospun Gelatin/Oxycellulose Nanofibers as a Suitable Platform for Lung Disease Modeling. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 67, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, R.; Abke, J.; Schnell, E.; Macionczyk, F.; Gbureck, U.; Mehrl, R.; Ruszczak, Z.; Kujat, R.; Englert, C.; Nerlich, M.; et al. Surface Engineering of Stainless Steel Materials by Covalent Collagen Immobilization to Improve Implant Biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6962–6972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Luyn, M.J.A.; van Wachem, P.B.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Olde Damink, L.H.H.; Feijen, J. Calcification of Subcutaneously Implanted Collagen in Relation to Cytotoxicity, Cellular Interactions and Crosslinking. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1995, 11, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Cojazzi, G.; Panzavolta, S.; Rubini, K.; Roveri, N. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Gelatin Films at Different Degrees of Glutaraldehyde Cross-Linking. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Hirose, K.; Taguchi, K.; Ogushi, Y.; Kawakami, K. An Injectable, In Situ Enzymatically Gellable, Gelatin Derivative for Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3371–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campiglio, C.E.; Negrini, N.C.; Fare, S.; Draghi, L. Cross-Linking Strategies for Electrospun Gelatin Scaffolds. Materials 2019, 12, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canas, A.I.; Delgado, J.P.; Gartner, C. Biocompatible Scaffolds Composed of Chemically Crosslinked Chitosan and Gelatin for Tissue Engineering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K. Slide-Ring Materials Using Topological Supramolecular Architecture. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2010, 14, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, A.; Yui, N. Threaded Macromolecules as a Versatile Framework for Biomaterials. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13433–13446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisaka, Y.; Yui, N. Engineering Molecularly Mobile Polyrotaxane Surfaces with Heparin-Binding EGF-Like Growth Factors for Improving Hepatocyte Functions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2019, 107, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, A.B.; Esaki, K.; Gotoh, H.; Seki, T.; Ito, K.; Sakai, Y.; Takeoka, Y. Extremely Stretchable Thermosensitive Hydrogels by Introducing Slide-Ring Polyrotaxane Cross-Linkers and Ionic Groups into the Polymer Network. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Tamura, A.; Arisaka, Y.; Seo, J.-H.; Yui, N. Mechanically Reinforced Gelatin Hydrogels by Introducing Slidable Supramolecular Cross-Linkers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Ito, K. Polymer Networks Characterized by Slidable Crosslinks and the Asynchronous Dynamics of Interlocked Components. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, D.; Yang, J.; Nishi, T.; Ito, K.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. Novel Slide-Ring Material/Natural Rubber Composites with High Damping Property. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, J. Polyrataxane, Derivatives II. Preparation and Characterization of Ionic Polyrotaxanes and Ionic Slide-Ring Gels. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2011, 49, 2199–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissink, M.J.B.; Beernink, R.; Pieper, J.S.; Poot, A.A.; Engbers, G.H.M.; Beugeling, T.; Aken, W.G.; Feijen, J. Immobilization of Heparin to EDC/NHS-Crosslinked Collagen. Characterization and In Vitro Evaluation. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, S.K. Comparison of 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl) Carbodiimide Based Strategies to Crosslink Antibodies on Amine-Functionalized Platforms for Immunodiagnostic Applications. Diagnostics 2012, 2, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuike, T.; Chaochai, T.; Komoto, D.; Tamura, H. Adsorption and Desorption Behaviors of Bovine Serum Albumin on Gelatin/Chitosan Sponge. J. Chem. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2017, 5, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, C.M.; De Graaf, L.A.; Reis, R.L.; Cunha, A.M. Effect of Crosslinking, Thermal Treatment and UV Irradiation on the Mechanical Properties and In Vitro Degradation Behavior of Several Natural Proteins Aimed to Be Used in the Biomedical Field. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazid, S.; Kolli, M.E.; Medjahed, A.; Doufnoune, R. The Interaction of Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose with Gelatin in the Absence and Presence of NaCl, CaCl2 and glucose. J. Polym. Eng. 2015, 35, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, H.; Tamura, A.; Osawa, M.; Tonegawa, A.; Arisaka, Y.; Matsumura, M.; Miura, H.; Yui, N. Scavenger Receptor A-Mediated Targeting of Carboxylated Polyrotaxanes to Macrophages and the Impacts of Supramolecular Structure. Macromol. Biosci. 2018, 18, 1800059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulogne, F.; Ingremeau, F.; Limat, L.; Stone, H.A. Tuning the Receding Contact Angle on Hydrogels by Addition of Particles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5573–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Stukel, J.M.; Cebull, H.L.; Willits, R.K. Tuning the Mechanical Properties of Poly(ethylene glycol) Microgel-Based Scaffolds to Increase 3D Schwann Cell Proliferation. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 16, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubin, H.; Nichol, J.W.; Hutson, C.B.; Bae, H.; Sieminski, A.L.; Cropek, D.M.; Akhyari, P.; Khademhosseini, A. Directed 3D Cell Alignment and Elongation in Microengineered Hydrogels. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6941–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Barreto-Ortiz, S.F.; Yu, Y.; Ginn, B.P.; De Santis, N.A.; Hutton, D.L.; Grayson, W.L.; Cui, F.-Z.; Korgel, B.A.; et al. Creating Polymer Hydrogel Microfibres with Internal Alignment via Electrical and Mechanical Stretching. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3243–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glamazda, A.Y.; Plokhotnichenko, A.M.; Leontiev, V.S.; Karachevtsev, V.A. DNA-Wrapped Carbon Nanotubes Aligned in Stretched Gelatin Films: Polarized Resonance Raman and Absorption Spectroscopy Study. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2017, 93, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayumi, K.; Nagao, M.; Endo, H.; Osaka, N.; Shibayama, M.; Ito, K. Dynamics of Polyrotaxane Investigated by Neutron Spin Echo. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2009, 404, 2600–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarroux, N.; Guegan, P.; Cheradame, H.; Auvray, L. High Conversion Synthesis of Pyrene End Functionalized Polyrotaxane Based on Poly (ethylene oxide) and α-Cyclodextrins. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 23816–23822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardy, B.L.; Tan, S.; Dam, H.H.; Ejima, H.; Blencowe, A.; Qiao, G.G.; Caruso, F. Nanoparticles Assembled via pH-Responsive Reversible Segregation of Cyclodextrins in Polyrotaxanes. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 15589–15596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.H.; Arisaka, Y.; Tonegawa, A.; Kang, T.W.; Tamura, A.; Yui, N. Cellular Orientation on Repeatedly Stretching Gelatin Hydrogels with Supramolecular Cross-Linkers. Polymers 2019, 11, 2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122095
Lee DH, Arisaka Y, Tonegawa A, Kang TW, Tamura A, Yui N. Cellular Orientation on Repeatedly Stretching Gelatin Hydrogels with Supramolecular Cross-Linkers. Polymers. 2019; 11(12):2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122095
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dae Hoon, Yoshinori Arisaka, Asato Tonegawa, Tae Woong Kang, Atsushi Tamura, and Nobuhiko Yui. 2019. "Cellular Orientation on Repeatedly Stretching Gelatin Hydrogels with Supramolecular Cross-Linkers" Polymers 11, no. 12: 2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122095
APA StyleLee, D. H., Arisaka, Y., Tonegawa, A., Kang, T. W., Tamura, A., & Yui, N. (2019). Cellular Orientation on Repeatedly Stretching Gelatin Hydrogels with Supramolecular Cross-Linkers. Polymers, 11(12), 2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122095