Biological Effects of Chitosan-Based Dressing on Hemostasis Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Experimental Dressing
2.1.1. Chitosan Fiber (CF) Preparation
2.1.2. Chitosan Sponge (CP) Preparation
2.2. Physical Characteristics
2.2.1. Raman Measurement
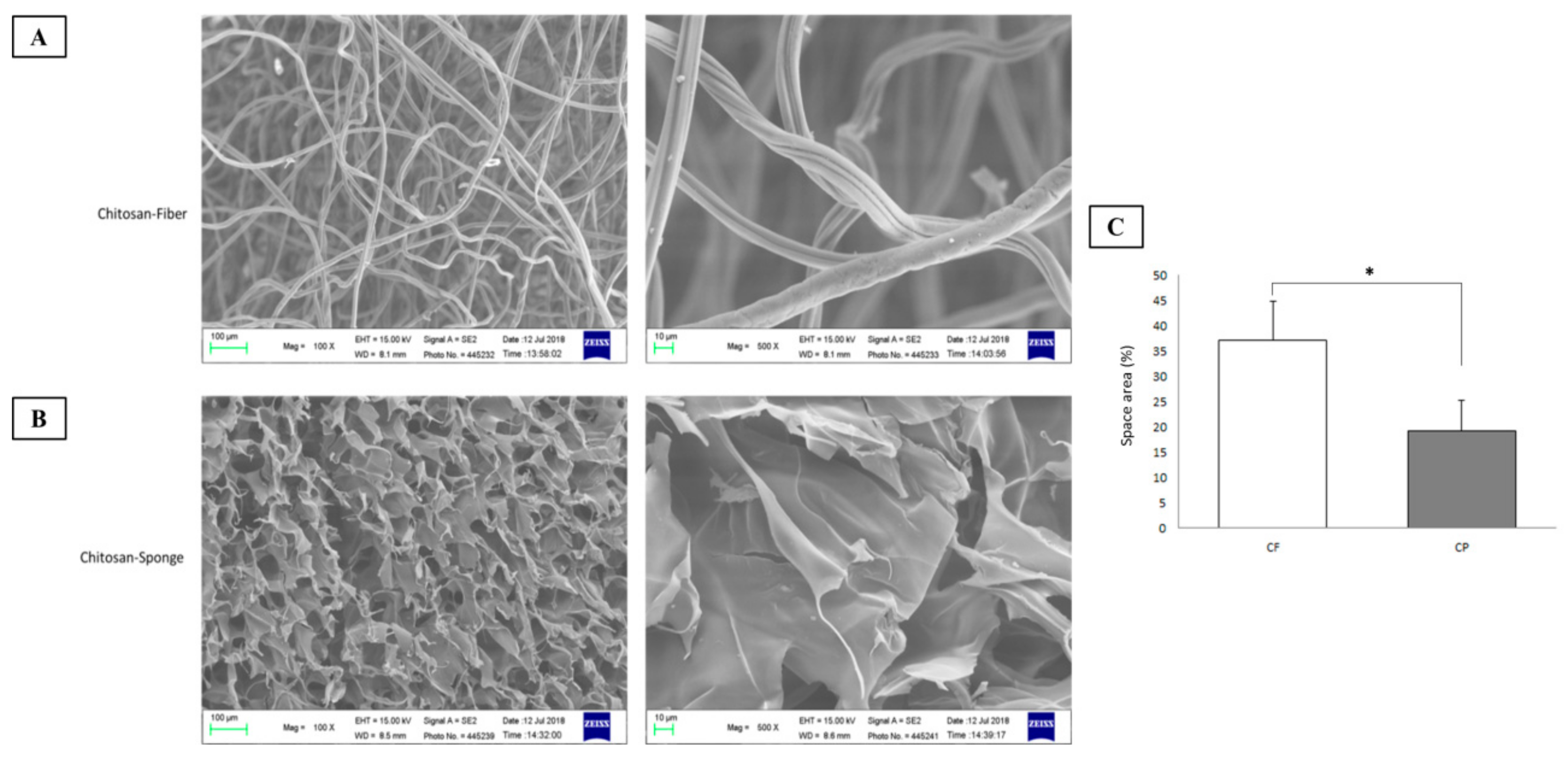
2.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
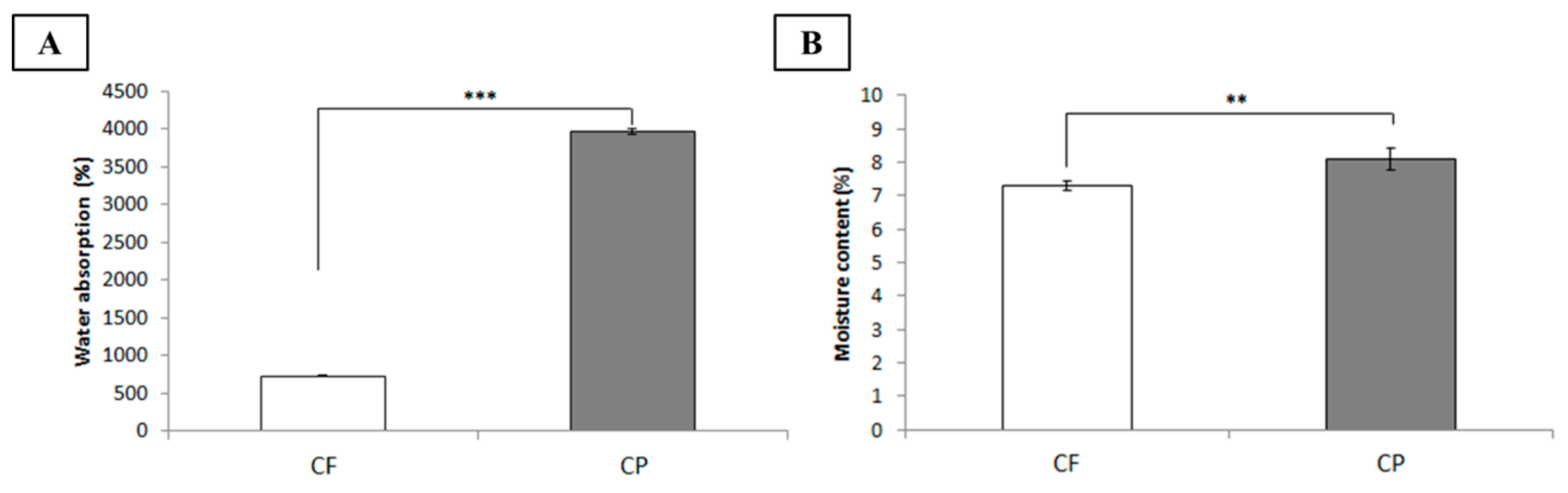
2.3. Water Absorptivity Determination
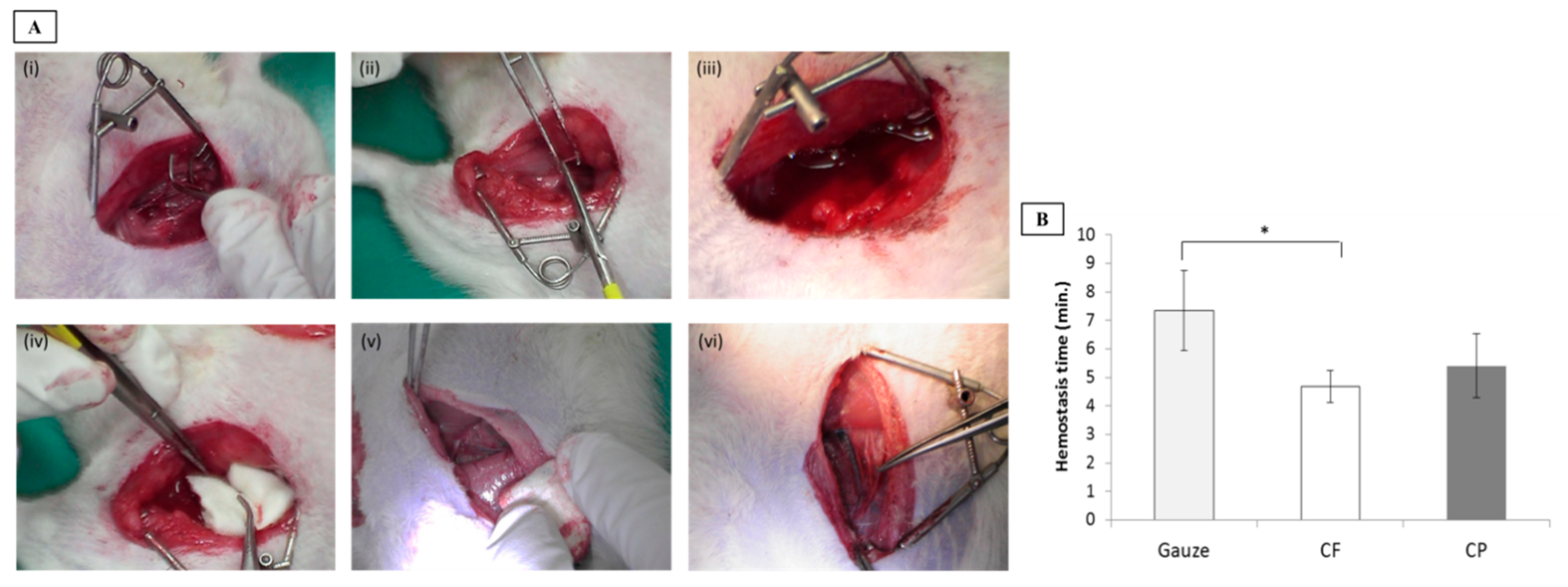
2.4. Animal Model of Femoral Artery Hemorrhage
2.5. Wound Treatment and Hemostasis Time Analysis
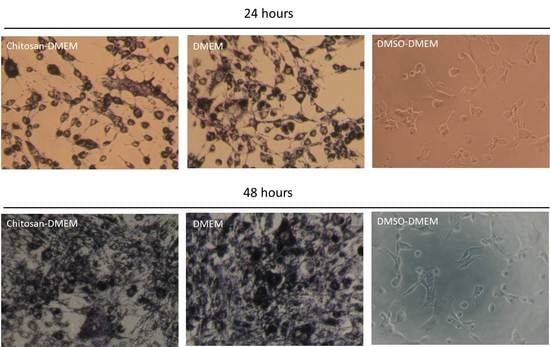
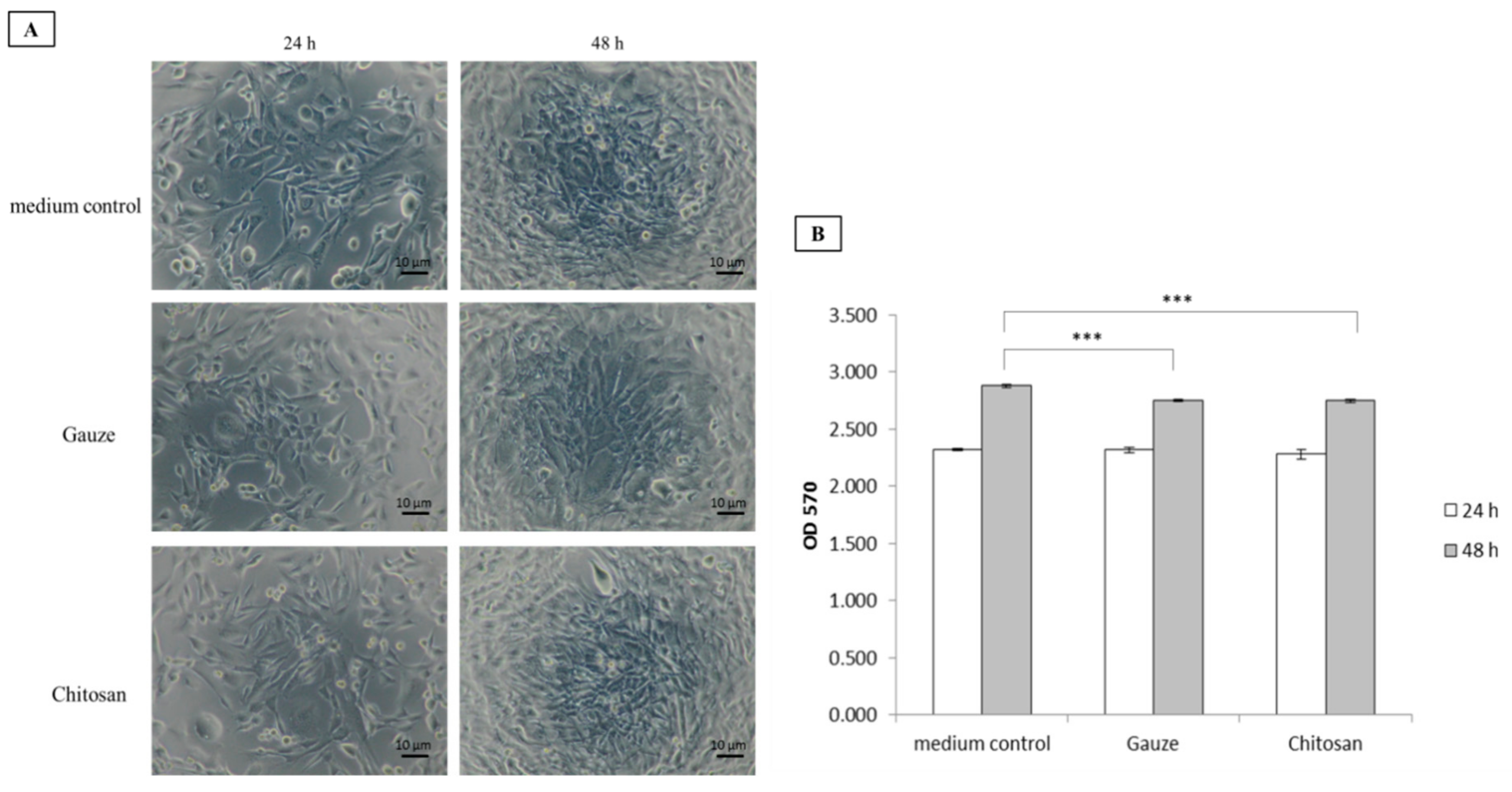
2.6. Cell Viability
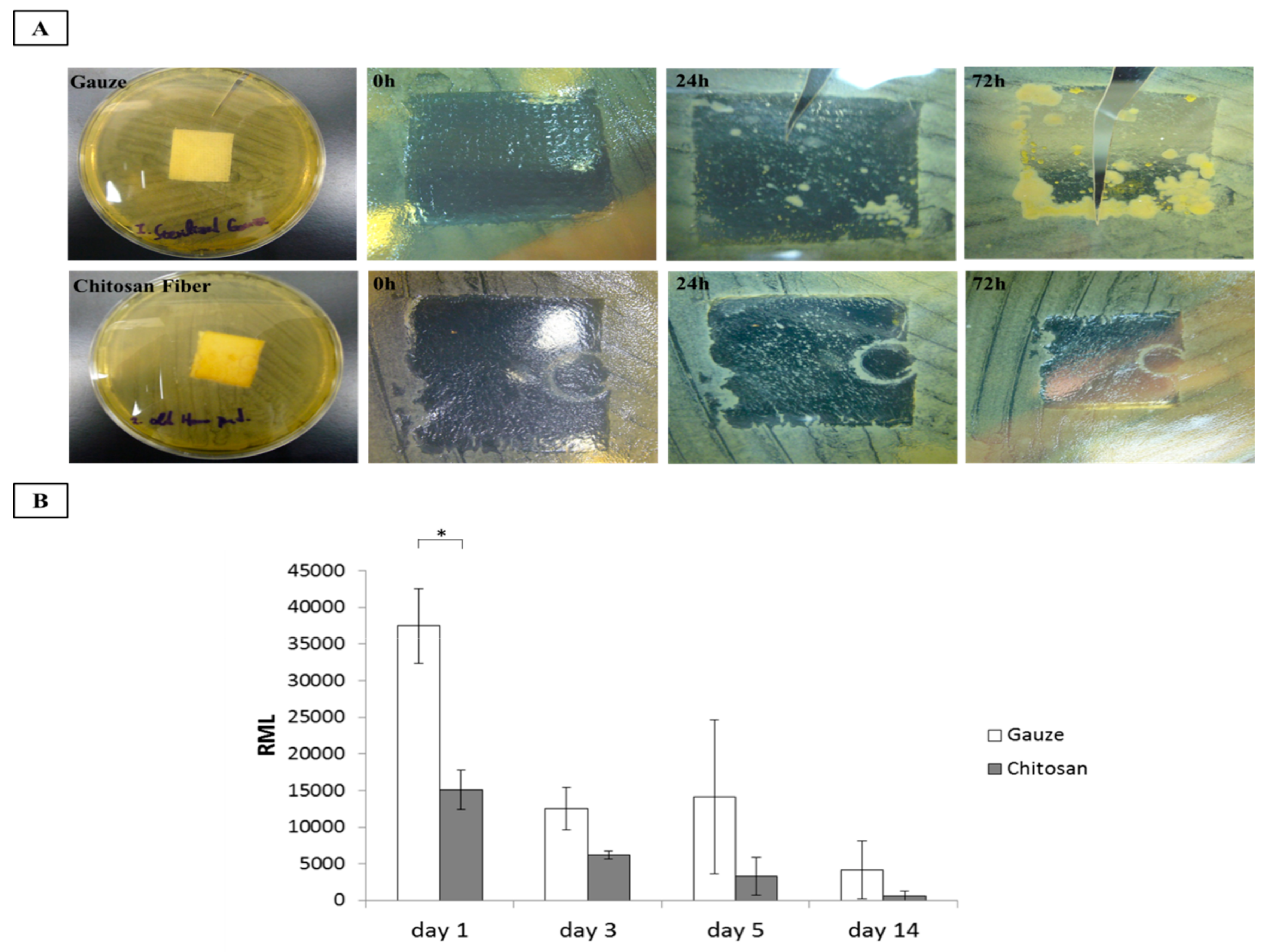
2.7. Antimicrobial Test
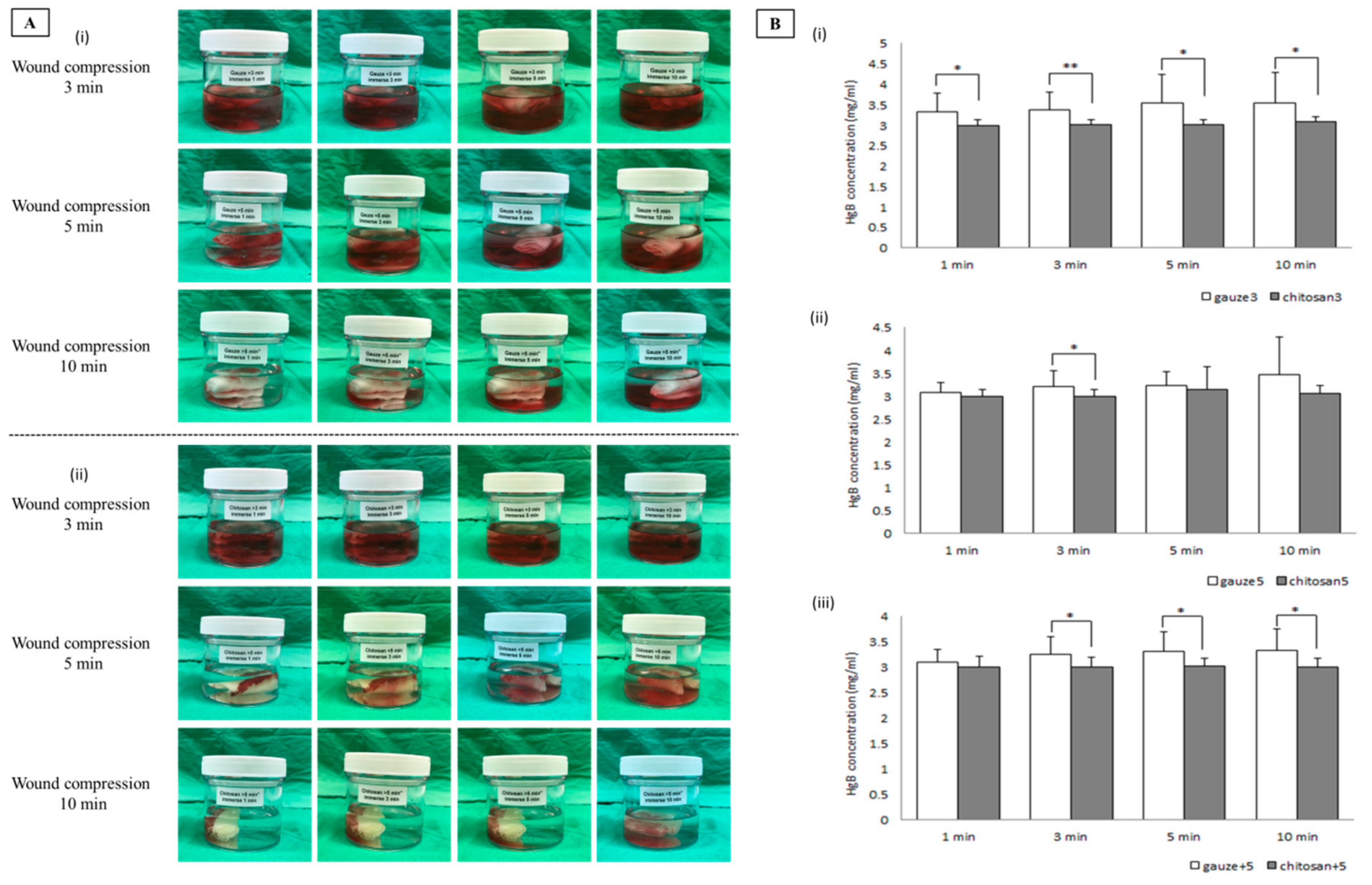
2.8. Measurement of Hemoglobin Absorption by Dressing Applied to Patients with Surgical Wounds
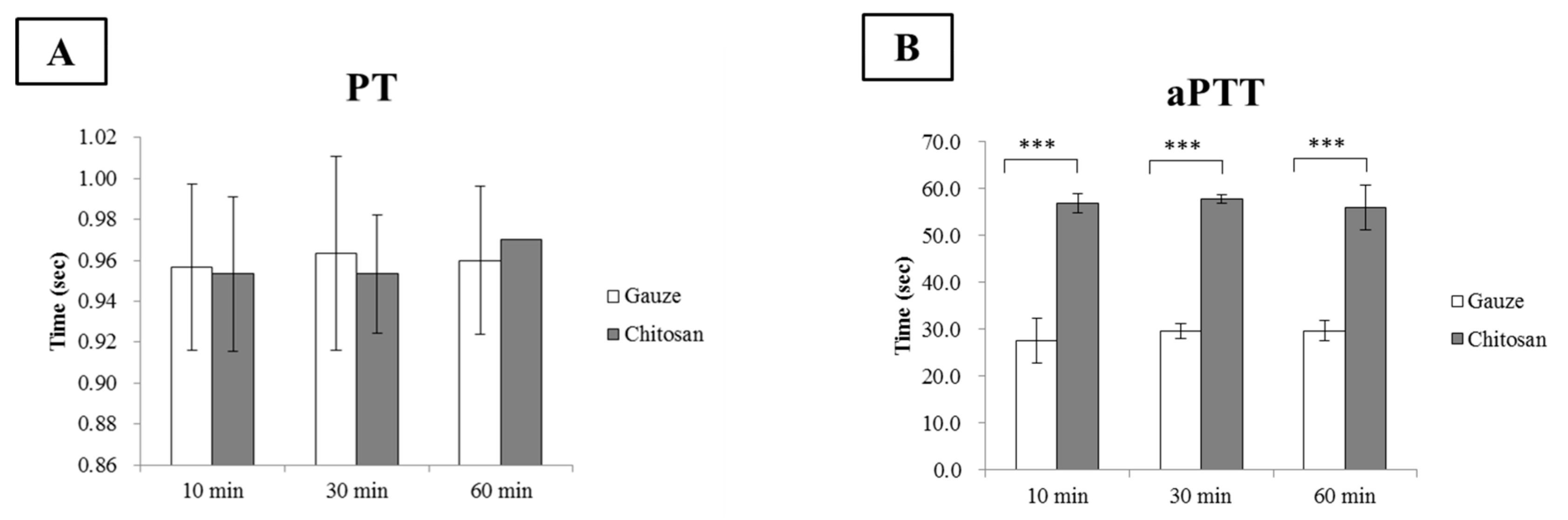
2.9. Prothrombin Time (PT), Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT), and Coagulation Factor Assays
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Chitosan-Based Dressings
3.2. Hemostasis
3.3. Biocompatibility Assessment
3.4. Antimicrobial Activity
3.5. Evaluation of Hemoglobin Absorption
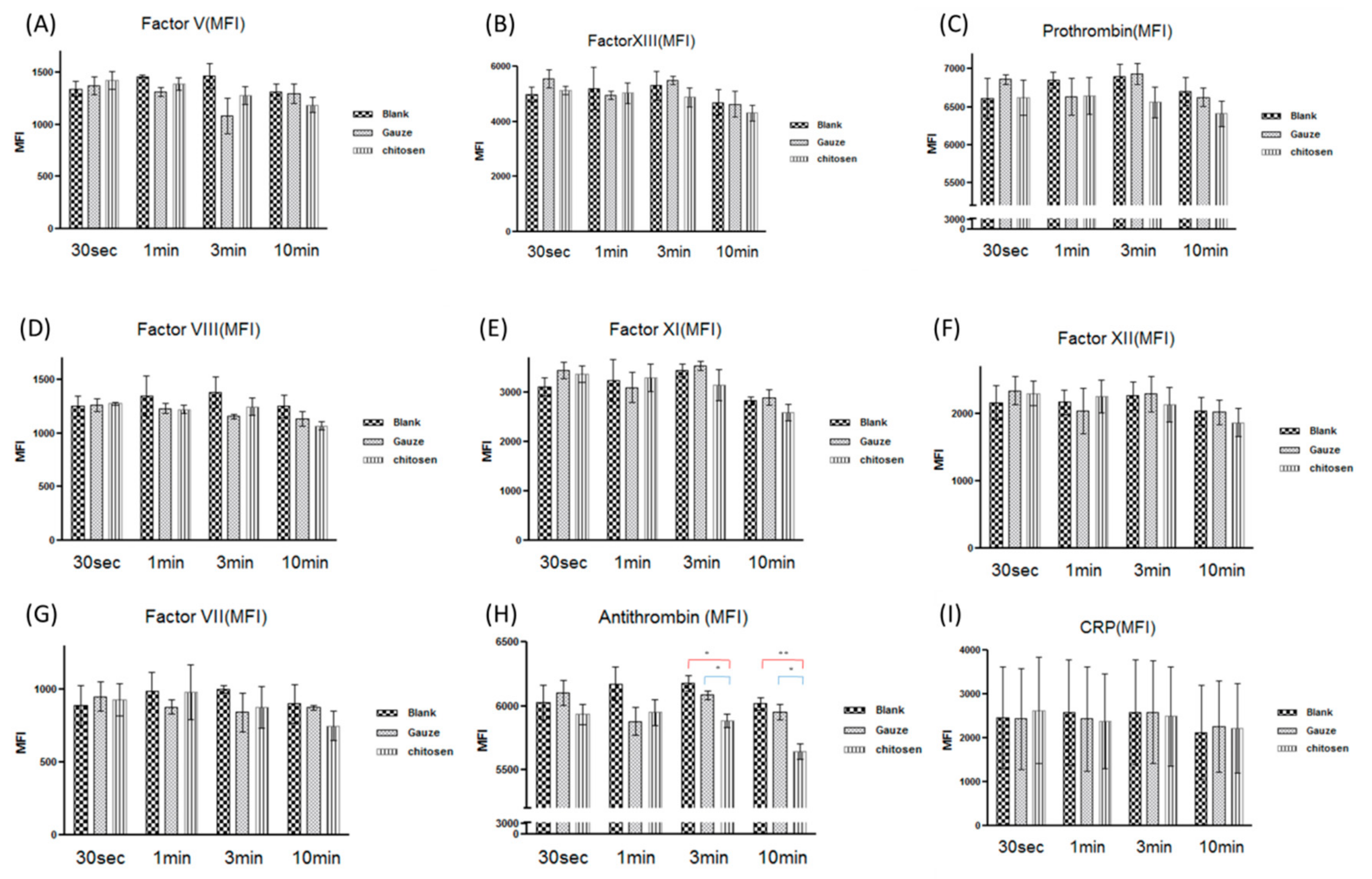
3.6. Chitosan Dressing in the Coagulation Cascade
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Girolami, A.; Santarossa, C.; Ferrari, S.; Cosi, E.; Girolami, B.; Randi, M.L. Clotting factors that may be responsible for both hemorrhagic or thrombotic disorders: The genetic plot has become complex for Factors I, II, V, VII and IX. Rev. Rep. Press. 2018, 2, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyik, Z.; Solak, Y.; Gaipov, A.; Ozbek, O.; Esen, H.; Turk, S. Spontaneous retroperitoneal hemorrhage presenting as hemoperitoneum secondary to renal cyst rupture in a peritoneal dialysis patient with acquired cystic kidney disease. Indian J. Nephrol. 2015, 25, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.Y.; Zeng, B.; Deng, J.B. Massive retroperitoneal hemorrhage secondary to femoral artery puncture. Medicine 2017, 96, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.M.P.; Aguiar, M.I.F.; Rodrigues, A.B.; Miranda, M.D.C.; Araújo, M.A.M.; Rolim, I.L.T.P. The use of nanoparticles in wound treatment: A systematic review. Rev. Esc. Enferm. 2017, 51, e03272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusateri, A.E.; Holcomb, J.B.; Kheirabadi, B.S.; Alam, H.B.; Wade CE, C.E.; Ryan, K.L. Making sense of the preclinical literature on advanced hemostatic products. J. Trauma. 2006, 60, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordy, S.D.; Rhee, P.; Schreiber, M.A. Military applications of novel hemostatic devices. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2011, 8, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirabadi, B.S.; Eden, J.W.; Terrazas, I.B.; Estep, J.S.; Klemcke, H.G.; Dubick, M.A.; Holcomb, J.B. Comparison of new hemostatic granules/powders with currently deployed hemostatic products in a lethal model of extremity arterial hemorrhage in swine. J. Trauma 2009, 66, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Gong, K.; Ao, Q.; Ma, T.; Yan, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, X. Positive charge of chitosan retards blood coagulation on chitosan films. J. Biomater. Appl. 2013, 27, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Kumar, P.T.S.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. A functional chitosan-based hydrogel as a wound dressing and drug delivery system in the treatment of wound healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7533–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.W.; Kim, C.H.; Wang, X.; Pun, S.H.; White, N.J.; Kim, T.H. PolySTAT-modified chitosan gauzes for improved hemostasis in external hemorrhage. Acta Biomater. 2016, 31, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benesch, J.; Tengvall, P. Blood protein adsorption onto chitosan. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2561–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palta, S.; Saroa, R.; Palta, A. Overview of the coagulation system. Indian J. Anaesth. 2014, 58, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatte, H.S.; Zagarins, S.; Khuri, S.F.; Fischer, T.H. Mechanisms of poly-n-acetyl glucosamine polymer-mediated hemostasis: Platelet interactions. J. Trauma 2004, 57, S13–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Kong, S.; Li, S.; Li, C.; Yang, L. Investigation of the effects of molecular parameters on the hemostatic properties of chitosan. Molecules 2018, 23, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krongrad, A.H.S.; Alikhassy, Z.; Matsangos, N.; Sebastian, R.; Marti, G.; Lay, F.; Harmon, J.W. Efficacy of chitosan-based dressing for control of bleeding in excisional wounds. Eplasty 2018, 18, e14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yang, J.; Hu, X.; Liang, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X. Superabsorbent polysaccharide hydrogels based on pullulan derivate as antibacterial release wound dressing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2011, 98, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, G.; Keen, I.; Drew, B.; Rintoul, A.L.; Fredericks, P.; Grøndahl, L. Interactions between alginate and chitosan biopolymers characterized using FTIR and XPS. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2533–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, J.E.S.A.; dos Santosa, H.S.; Ferreira, M.K.A.; Magalhães, F.E.A.; da Silva, D.S.; Bandeira, P.N.; Saraiva, G.D.; Pessoa, O.D.L.; Ricardo, N.M.P.S.; Cruz, B.G.; et al. Preparation, structural and spectroscopic characterization of chitosan membranes containing allantoin. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1199, 126968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersberg, G. Molecular Spectra and Molecular Structure II. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Polyatomic Molecules; Van Nostrand-Reinhold Co. Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1945. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, S.R.; Bhattarai, N.; Yi, H.K.; Hwang, P.H.; Cha, D.I.; Kim, H.Y. Novel biodegradable electrospun membrane: Scaffold for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2595–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Peh, K.; Ch’ng, H. Mechanical, bioadhesive strength and biological evaluations of chitosan films for wound dressing. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 3, 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xia, W.; Liu, P.; Cheng, Q.; Tahirou, T.; Gu, W.; Li, B. Chitosan modification and pharmaceutical/biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1962–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercy, H.P.; Halim, A.S.; Hussein, A.R. Chitosan-derivatives as hemostatic agents: Their role in tissue regeneration. Regen. Res. 2012, 1, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- No, H.K.; Park, N.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Meyers, S.P. Antibacterial activity of chitosans and chitosan oligomers with different molecular weights. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 74, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.J.; Youn, D.K.; Lee, S.H.; No, H.K.; Ha, J.G.; Prinyawiwatkul, W. Antibacterial activity of chitosans with different degrees of deacetylation and viscosities. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Poon, Y.F.; Li, W.; Zhu, H.Y.; Yeap, S.H.; Cao, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhou, C.; Lamrani, M.; Beuerman, R.W.; et al. A polycationic antimicrobial and biocompatible hydrogel with microbe membrane suctioning ability. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Xing, K.; Park, H.J. Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: A state of the art review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 144, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, D.; von Bargen, K.; Haas, A.; Sahl, H.G. Insights into the mode of action of chitosan as an antibacterial compound. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3764–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tianqing, L. Interaction behaviors between chitosan and hemoglobin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhong, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, Q. Effect of chitosan and carboxymethyl chitosan on fibrinogen structure and blood coagulation. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. 2013, 24, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernecky, C.C.; Berger, B.J. Prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR) – blood. In Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures, 6th ed.; Chernecky, C.C., Berger, B.J., Eds.; Elsevier Saunders: St Louis, MO, USA, 2013; pp. 930–935. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, R.C.F.; Ng, T.B.; Wong, J.H.; Chan, W.Y. Chitosan: An update on potential biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Mar. Drugs. 2015, 13, 5156–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.R.; Qin, H.; Nie, S.Q.; Sun, S.D.; Ran, F.; Zhao, C.S. Direct synthesis of heparin-like poly (ether sulfone) polymer and its blood compatibility. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8851–8863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Tian, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, Y.J.; Chen, S.Q. Effect of chitosan molecular weight and deacetylation degree on hemostasis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2007, 84, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kainthan, R.K.; Gnanamani, M.; Ganguli, M.; Ghosh, T.; Brooks, D.E.; Maiti, S.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. Blood compatibility of novel water soluble hyperbranched polyglycerol-based multivalent cationic polymers and their interaction with DNA. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5377–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, C.; Fischer, M.; Maitz, M.F.; Werner, C. Blood coagulation on biomaterials requires the combination of distinct activation processes. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4447–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuck, C.C.; Schiele, U.; Horn, D.; Fronda, D.; Ritz, E. The role of surface charge on the accelerating action of heparin on the antithrombin III-inhibited activity of alpha-thrombin. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 4598–4603. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, S.T.; Bjork, I.; Shore, J.D. Kinetic characterization of heparin-catalyzed and uncatalyzed inhibition of blood coagulation proteinases by antithrombin. Methods Enzymol. 1993, 222, 525–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-W.; Liu, C.-C.; Cherng, J.-H.; Lin, C.-S.; Chang, S.-J.; Hong, Z.-J.; Liu, C.-C.; Chiu, Y.-K.; Hsu, S.-D.; Chang, H. Biological Effects of Chitosan-Based Dressing on Hemostasis Mechanism. Polymers 2019, 11, 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111906
Wang Y-W, Liu C-C, Cherng J-H, Lin C-S, Chang S-J, Hong Z-J, Liu C-C, Chiu Y-K, Hsu S-D, Chang H. Biological Effects of Chitosan-Based Dressing on Hemostasis Mechanism. Polymers. 2019; 11(11):1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111906
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yi-Wen, Chuan-Chieh Liu, Juin-Hong Cherng, Chien-Seng Lin, Shu-Jen Chang, Zhi-Jie Hong, Cheng-Che Liu, Yaw-Kwan Chiu, Sheng-Der Hsu, and Hung Chang. 2019. "Biological Effects of Chitosan-Based Dressing on Hemostasis Mechanism" Polymers 11, no. 11: 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111906
APA StyleWang, Y.-W., Liu, C.-C., Cherng, J.-H., Lin, C.-S., Chang, S.-J., Hong, Z.-J., Liu, C.-C., Chiu, Y.-K., Hsu, S.-D., & Chang, H. (2019). Biological Effects of Chitosan-Based Dressing on Hemostasis Mechanism. Polymers, 11(11), 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111906