Influence of Filler Content and Filler Size on the Curing Kinetics of an Epoxy Resin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Isothermal Kinetic Model
3. Experimental
3.1. Material
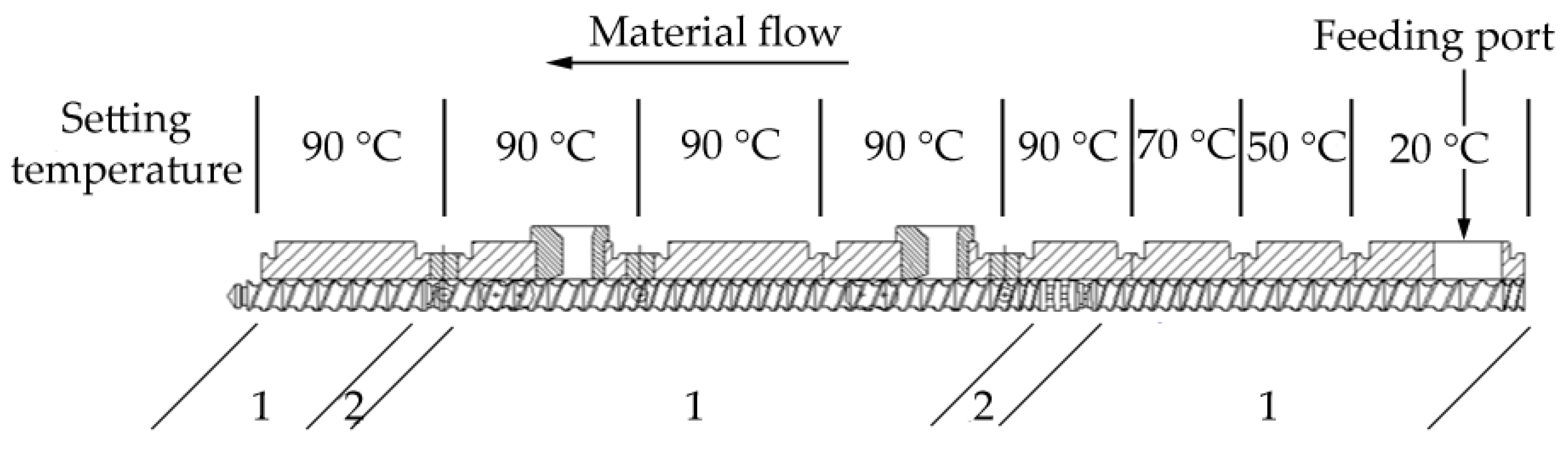
3.2. Sample Preparation
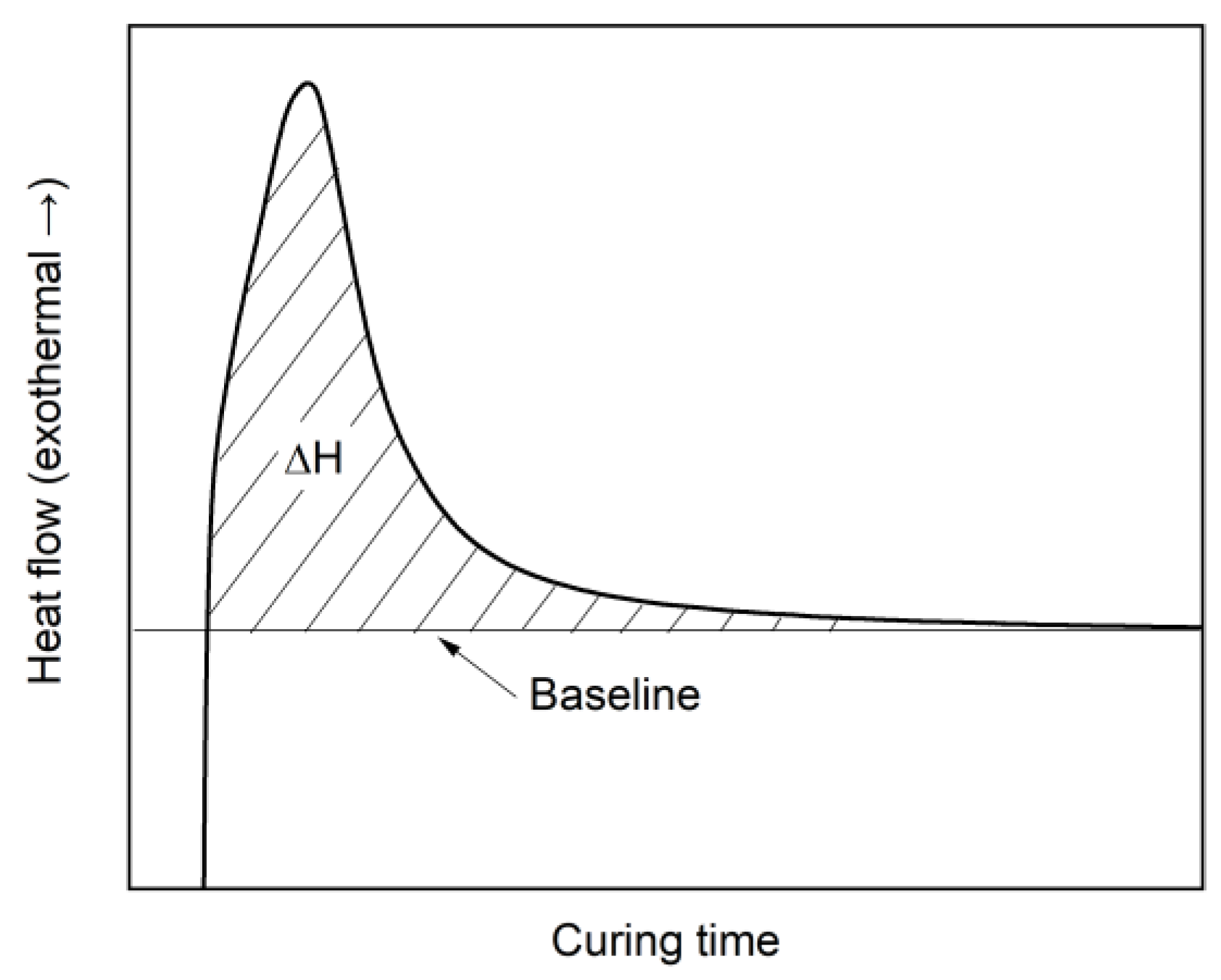
3.3. Testing Methods
4. Results
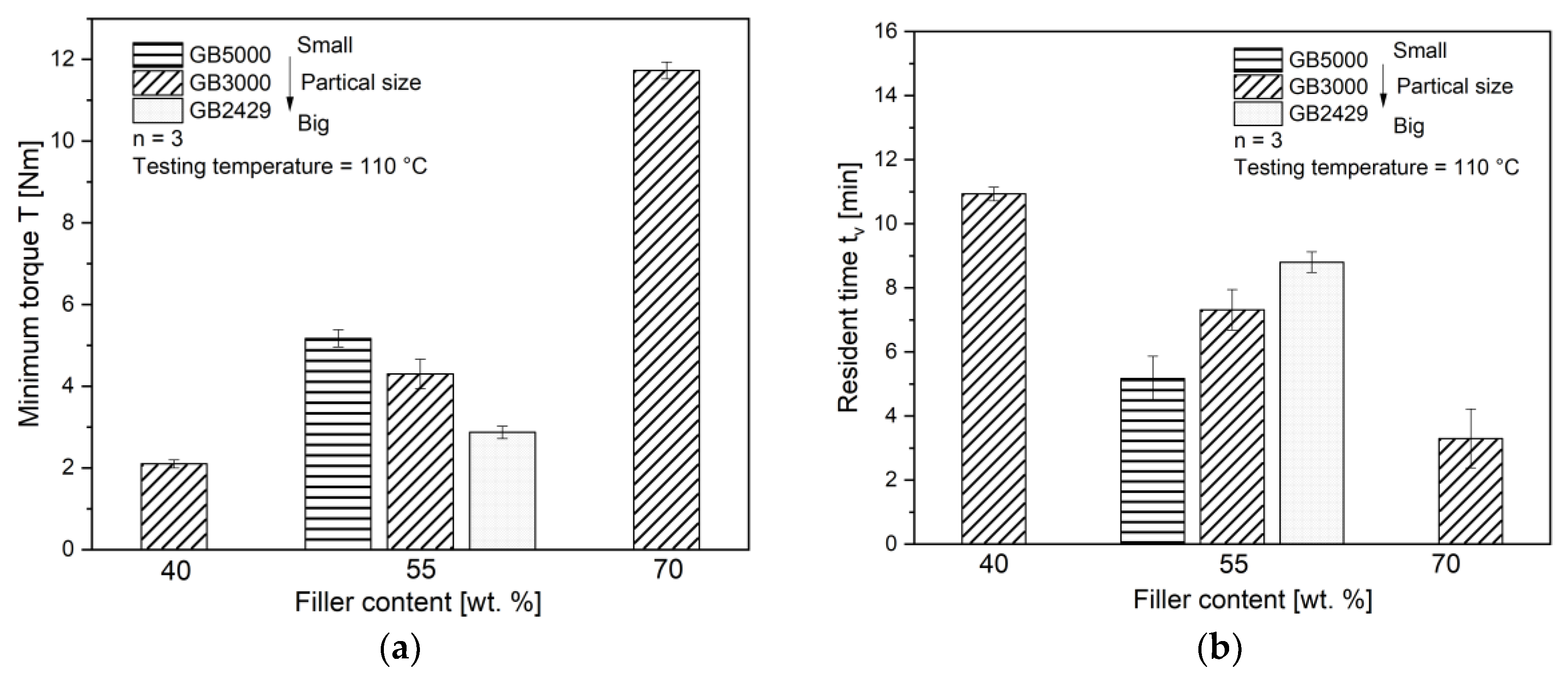
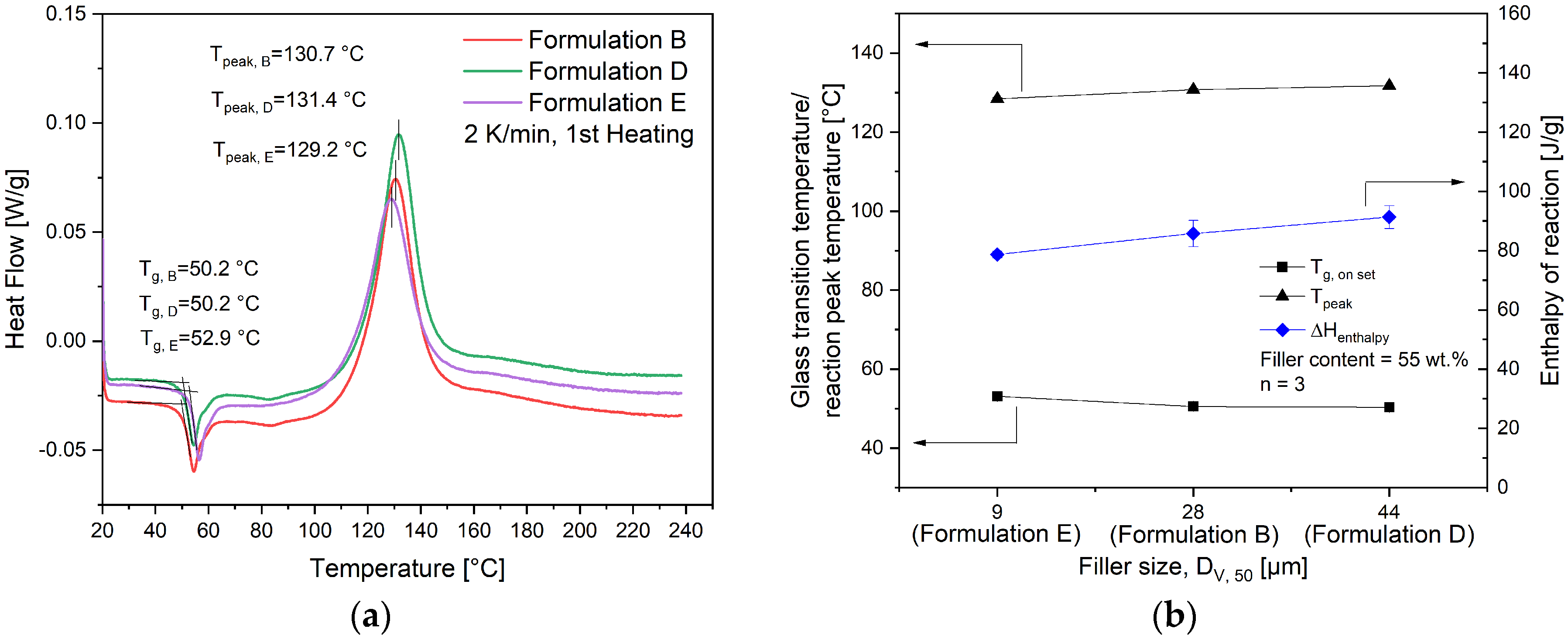
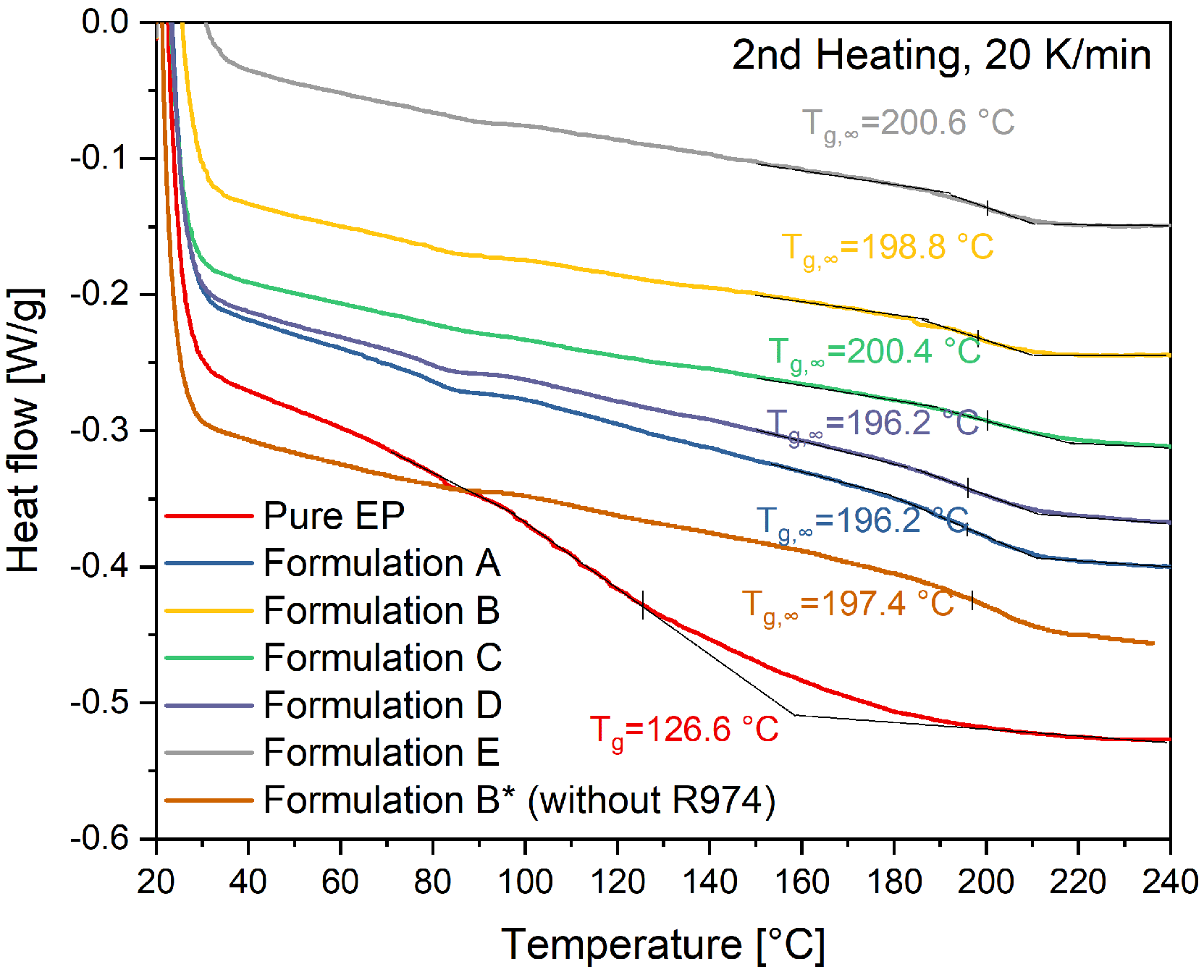
4.1. Characterization of Fillers and Compounds
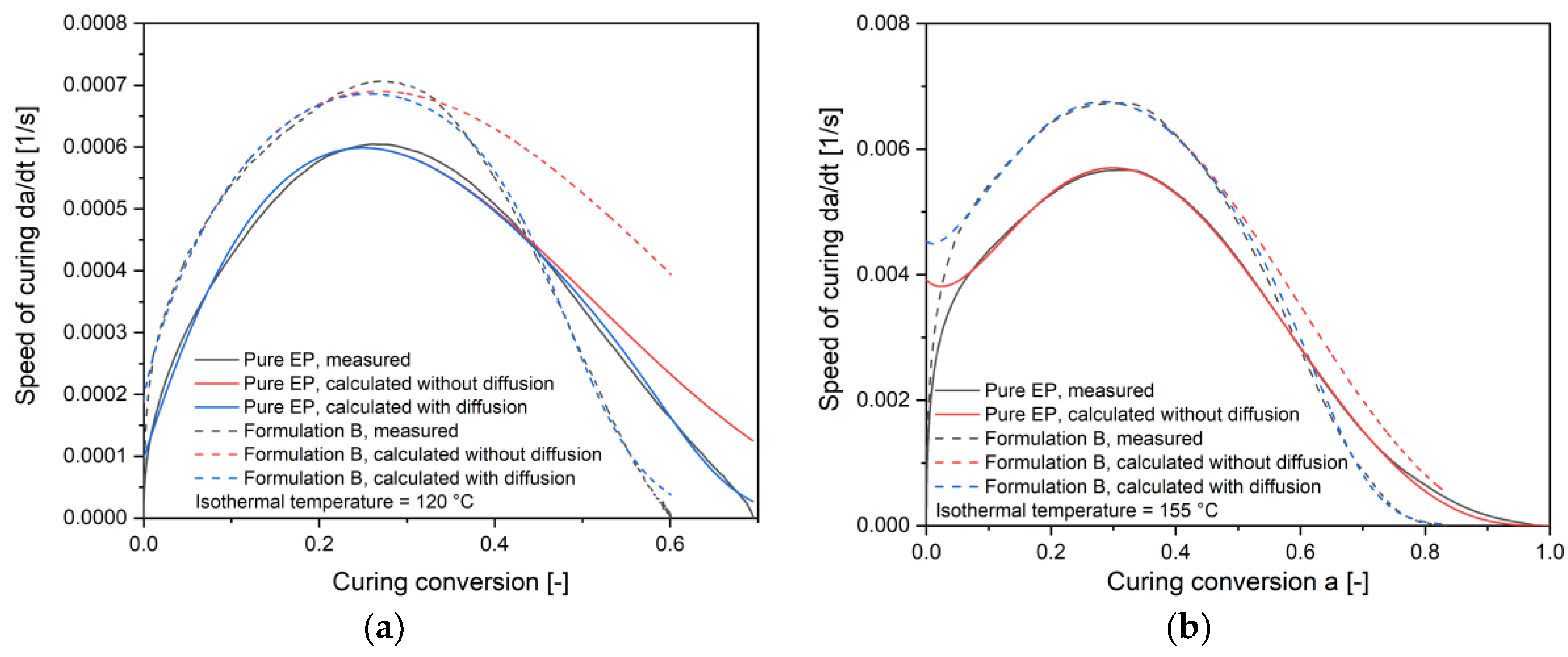
4.2. Calculation of Autocatalytic Kinetic Model Parameters
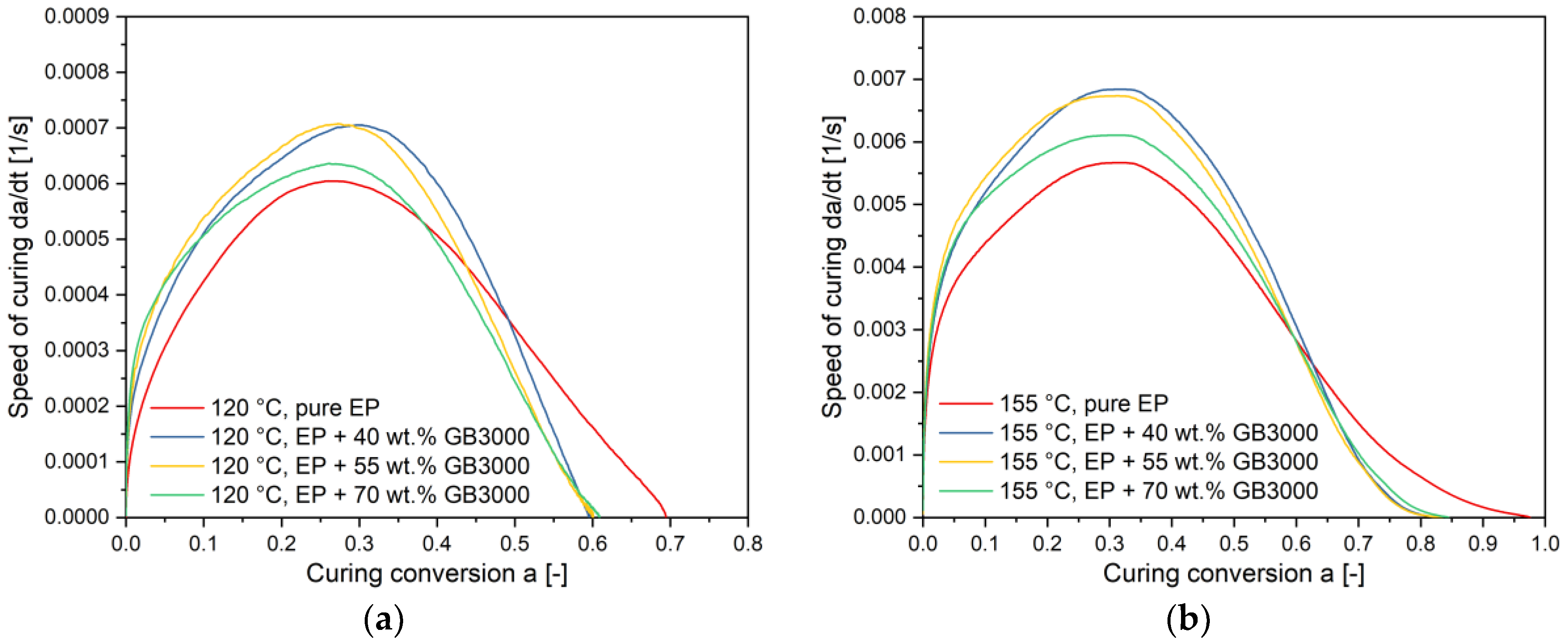
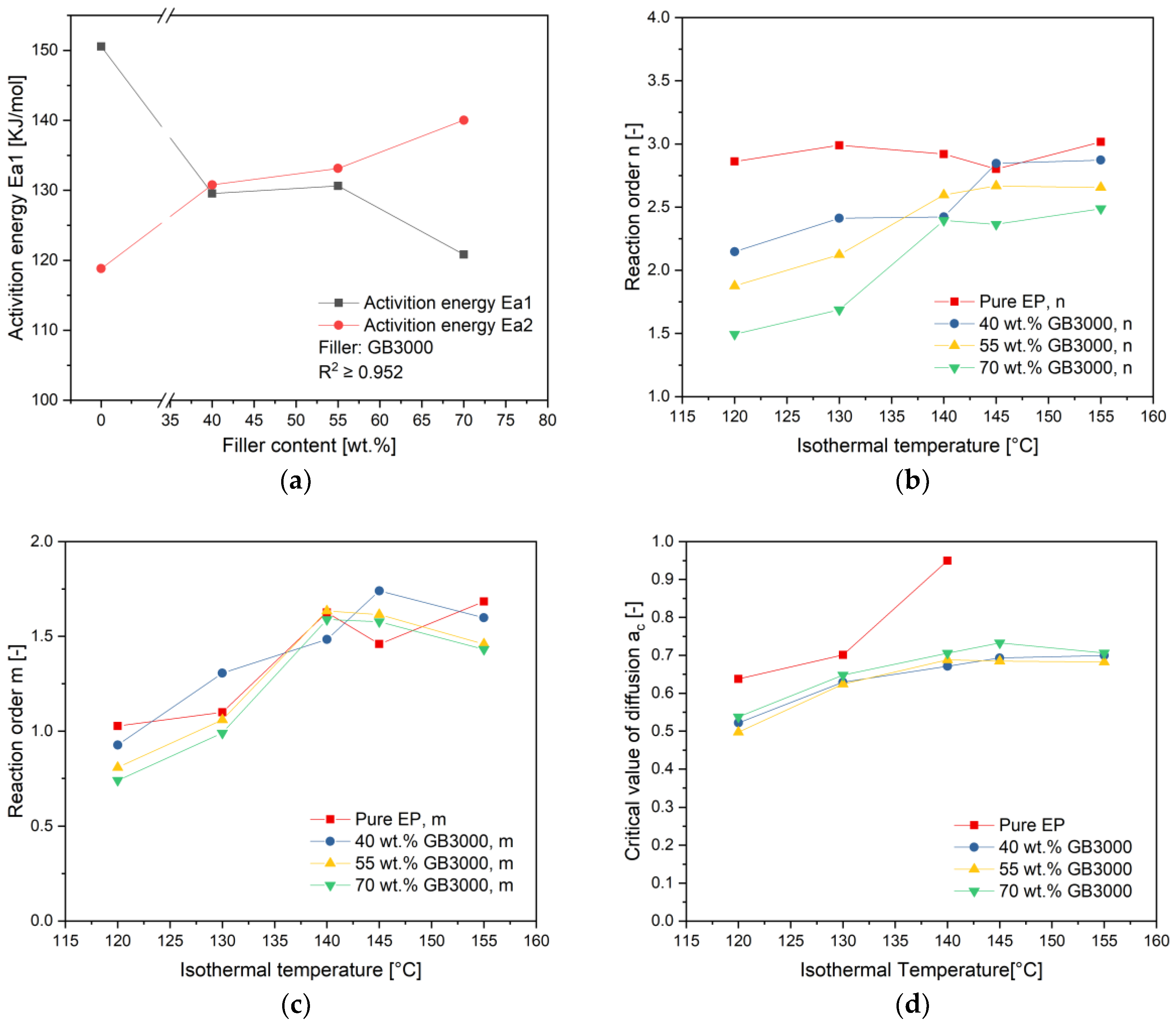
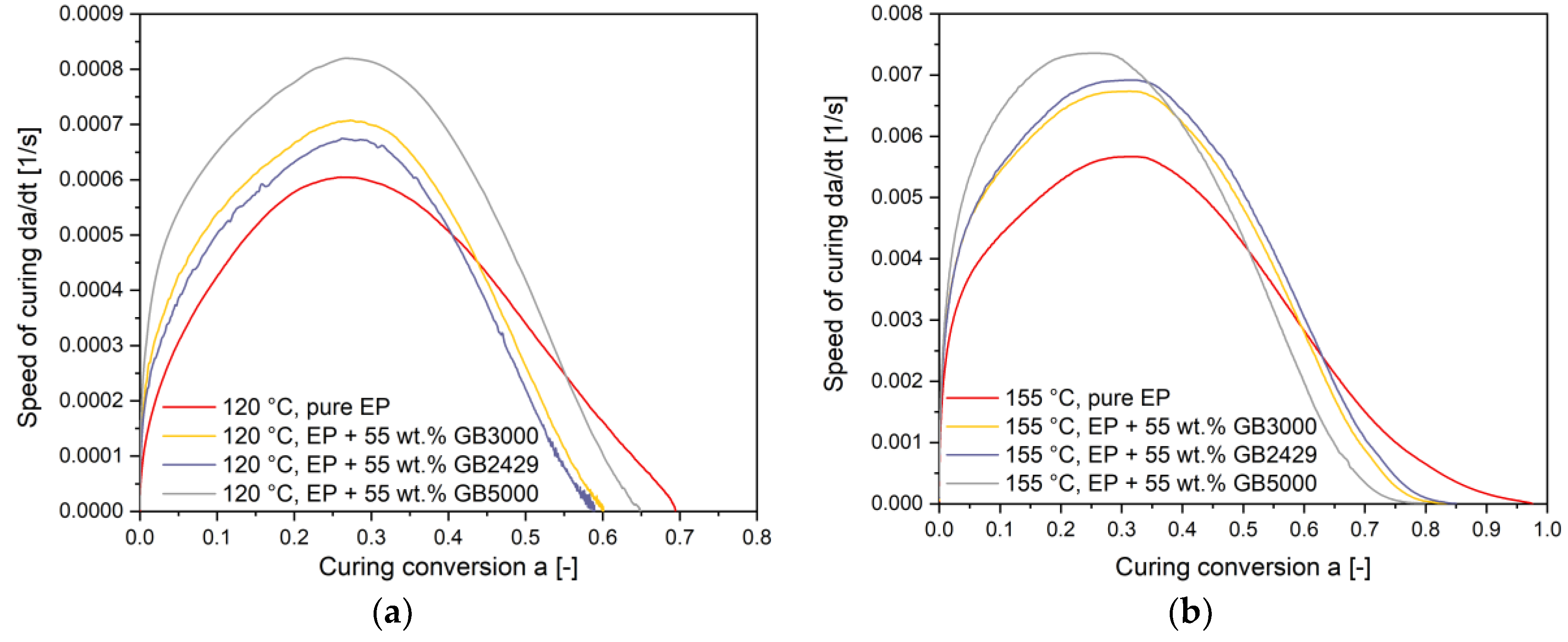
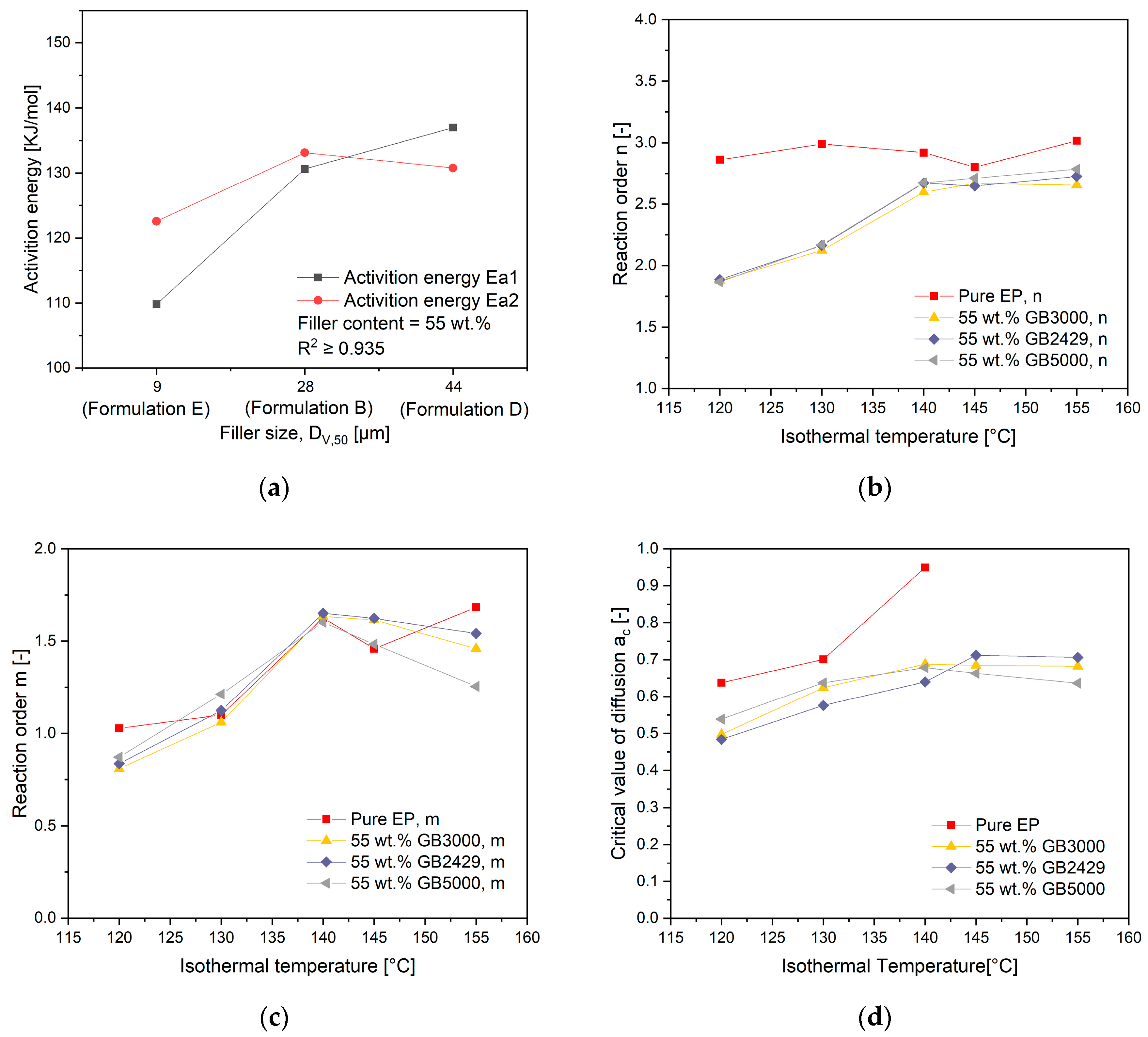
4.3. Influence of Filler Content on the Curing Kinetics
4.4. Influence of Filler Content on the Curing Kinetics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dudek, R.; Vogel, D.; Michel, B. Mechanical failure in COB-technology using glob-top encapsulation. IEEE Trans. Component. Packag. Manuf. Technol. Part C 1996, 19, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Dang, J.; Xie, C. Thermal conductivity epoxy resin composites filled with boron nitride. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhai, Z.; Drummer, D. Thermal Conductivity of Aluminosilicate- and Aluminum Oxide-Filled Thermosets for Injection Molding: Effect of Filler Content, Filler Size and Filler Geometry. Polymers 2018, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, M.; Kinjo, N.; Eguchi, S.; Hozoji, H.; Kawata, T.; Sashima, H. Effects of curing accelerators on physical properties of epoxy molding compound (EMC). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1992, 44, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yoo, S.; Bae, J.-Y.; Yun, H.-C.; Hwang, J.; Kong, B.-S. Thermal stabilities and mechanical properties of epoxy molding compounds (EMC) containing encapsulated red phosphorous. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 81, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hera, D. Leiterplattenbasiertes Packaging zur Systemintegration Mittels Film-Assisted. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, W.; Woebcken, W.; Becker, G.W. Duroplaste; Hanser: Munich, Germany, 1988; ISBN 3446144188. [Google Scholar]
- Rasool, A.; Böhm, H.J. Effects of particle shape on the macroscopic and microscopic linear behaviors of particle reinforced composites. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2012, 58, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linec, M.; Mušič, B. The Effects of Silica-Based Fillers on the Properties of Epoxy Molding Compounds. Materials 2019, 12, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.-W.; Kim, W.; Hwang, S.; Choe, Y.-S.; Lee, S.-H. A low-viscousity, highly thermally conductive epoxy molding compound (EMC). Macromol. Res. 2004, 12, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, N.; Halley, P.J.; Cooper-White, J.; Lange, J. The effects of silica fillers on the gelation and vitrification of highly filled epoxy-amine thermosets. Macromol. Symp. 2001, 169, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Jang, J.; Yoon, S.-H. Cure Behavior of the Liquid-Crystalline Epoxy/Carbon Nanotube System and the Effect of Surface Treatment of Carbon Fillers on Cure Reaction. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2002, 203, 2196–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Ryan, M. Effect of fillers on kinetics of epoxy cure. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1979, 24, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jin, J.; Song, M.; Lin, Y. Effect of graphene oxide sheet size on the curing kinetics and thermal stability of epoxy resins. Mater. Res. Express 2016, 3, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamal, M.; Sourour, S. Kinetics and thermal characterization of thermoset cure. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1973, 13, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, C.-S.; Poehlein, G.W. A kinetic model for curing reactions of epoxides with amines. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1987, 27, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, X. Autocatalytic curing kinetics of thermosetting polymers: A new model based on temperature dependent reaction orders. Polymer 2010, 51, 3814–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsch, M.; Karger-Kocsis, J.; Holst, M. Influence of fillers and additives on the cure kinetics of an epoxy/anhydride resin. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourour, S.; Kamal, M. Differential scanning calorimetry of epoxy cure: Isothermal cure kinetics. Thermochim. Acta 1976, 14, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, F.; Vazquez, E.C.; Rodríguez-Núñez, E.; Martínez-Ageitos, J.M. Curing kinetics of the epoxy system diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A/isophoronediamine by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Durix, S.; Sinturel, C.; Omonov, T.; Goossens, S.; Groeninckx, G.; Moldenaers, P.; Thomas, S. Cure kinetics, morphology and miscibility of modified DGEBA-based epoxy resin—Effects of a liquid rubber inclusion. Polymer 2007, 48, 1695–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garschke, C.; Parlevliet, P.; Weimer, C.; Fox, B. Cure kinetics and viscosity modelling of a high-performance epoxy resin film. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.; Lopez-Bueno, I.; Nogueira, P.; Ramırez, C.; Abad, M.; Barral, L.; Cano, J. Effect of poly (styrene-co-acrylonitrile) on the curing of an epoxy/amine resin. Polymer 2001, 42, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salla, J.M.; Ramis, X. Comparative study of the cure kinetics of an unsaturated polyester resin using different procedures. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 835–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak, M. A relationship between the glass transition temperature and the conversion degree in the curing reaction of the EPY epoxy system. Polimery 2011, 56, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teil, H.; Page, S.A.; Michaud, V.; Månson, J.-A.E. TTT-cure diagram of an anhydride-cured epoxy system including gelation, vitrification, curing kinetics model, and monitoring of the glass transition temperature. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 1774–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.; Manas-Zloczower, I. Chemorheology of unfilled and filled epoxy resins. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1993, 33, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, P.P.; Puglia, D.; Jyotishkumar, P.; Kenny, J.M.; Thomas, S. Effect of nanoclay and carboxyl-terminated (butadiene-co-acrylonitrile) (CTBN) rubber on the reaction induced phase separation and cure kinetics of an epoxy/cyclic anhydride system. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 5241–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


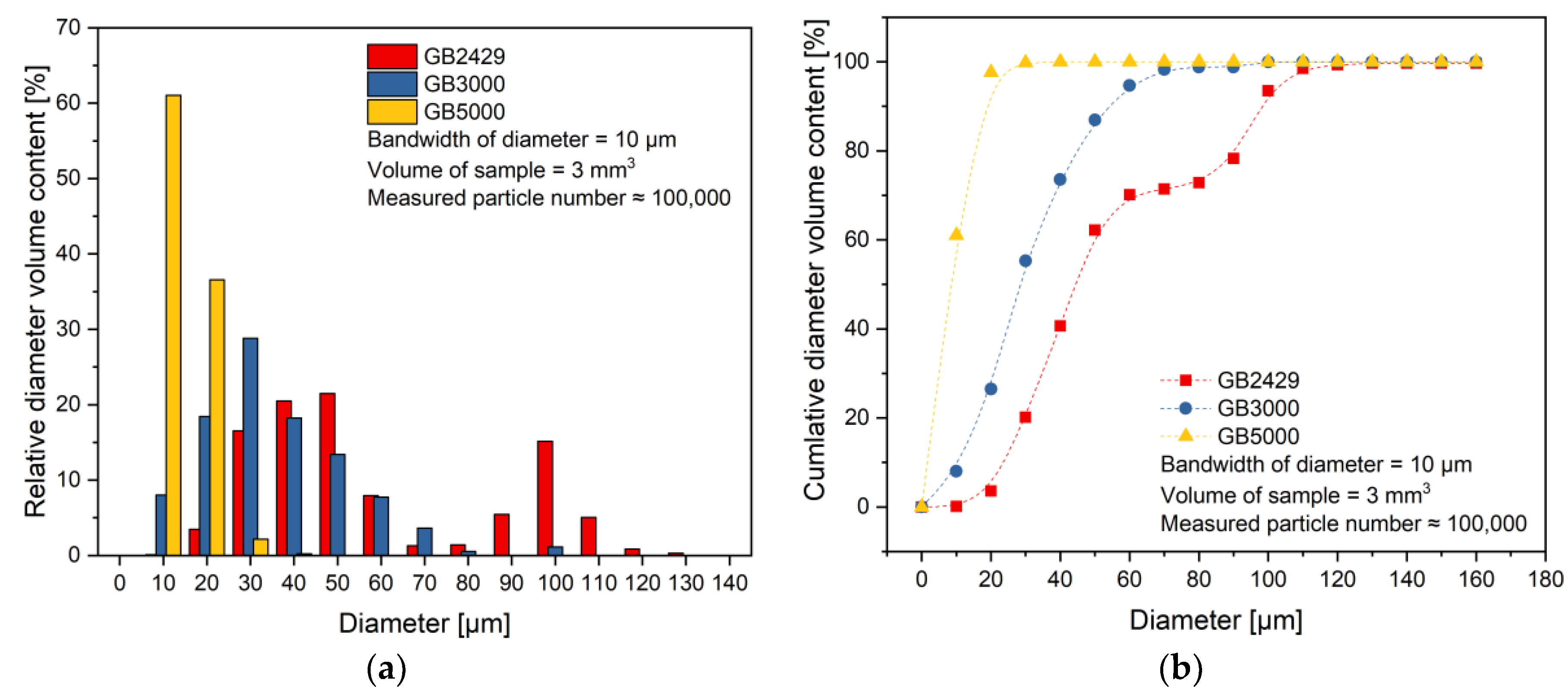

| Product | Particle Size Distribution * [µm] | Bulk Density [g/cm3] ASTM D-3101-78 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Value | Range | Untapped | Tapped | |
| GB2429 | 70–100 | 53–106 | 1.46 | 1.57 |
| GB3000 | 30–50 | - | 1.44 | 1.59 |
| GB5000 | 7–10 | - | 1.28 | 1.62 |
| Formulation | Polymer Matrix | Additive and Content | Filler and Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | EP 246-1 | R974, 5 wt.% | GK3000, 40 wt.% |
| B | EP 246-1 | R974, 5 wt.% | GK3000, 55 wt.% |
| C | EP 246-1 | R974, 5 wt.% | GK3000, 70 wt.% |
| D | EP 246-1 | R974, 5 wt.% | GK2429, 55 wt.% |
| E | EP 246-1 | R974, 5 wt.% | GK5000, 55 wt.% |
| B* | EP 246-1 | - | GK3000, 55 wt.% |
| Filler | Diameter [µm] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DV,10 | DV,50 | DV,90 | |
| Spheriglass GB5000 | 4.77 | 8.89 | 15.75 |
| Spheriglass GB3000 | 10.98 | 25.84 | 56.26 |
| Spheriglass GB2429 | 23.78 | 43.22 | 96.87 |
| Parameter | Temperature [°C] | Pure EP | EP + 40 wt.% GB3000 | EP + 55 wt.% GB2429 | EP + 55 wt.% GB3000 | EP + 55 wt.% GB5000 | EP + 70 wt.% GB3000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 120 | 9.758 × 10−5 | 1.749 × 10−4 | 1.661 × 10−4 | 1.878 × 10−4 | 3.268 × 10−4 | 2.312 × 10−4 |
| k2 | 5.260 × 10−3 | 3.950 × 10−3 | 3.070 × 10−3 | 3.050 × 10−3 | 3.510 × 10−3 | 2.210 × 10−3 | |
| m | 1.027 | 0.928 | 0.836 | 0.809 | 0.871 | 0.740 | |
| n | 2.862 | 2.147 | 1.887 | 1.875 | 1.867 | 1.493 | |
| A | 0.638 | 0.522 | 0.484 | 0.497 | 0.539 | 0.537 | |
| C | 22.707 | 38.189 | 27.170 | 21.550 | 20.532 | 21.921 | |
| R2 | 0.985 | 0.990 | 0.992 | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.993 | |
| k1 | 130 | 3.082 × 10−4 | 6.115 × 10−4 | 5.363 × 10−4 | 5.422 × 10−4 | 8.630 × 10−4 | 6.522 × 10−4 |
| k2 | 1.035 × 10−2 | 1.398 × 10−2 | 9.250 × 10−3 | 9.520 × 10−3 | 1.183 × 10−2 | 6.580 × 10−3 | |
| m | 1.100 | 1.306 | 1.124 | 1.060 | 1.213 | 0.990 | |
| n | 2.990 | 2.413 | 2.163 | 2.123 | 2.169 | 1.688 | |
| Ac | 0.701 | 0.629 | 0.576 | 0.624 | 0.638 | 0.648 | |
| C | 22.594 | 20.759 | 20.374 | 21.485 | 23.270 | 20.313 | |
| R2 | 0.992 | 0.994 | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.995 | 0.996 | |
| k1 | 140 | 1.260 × 10−3 | 1.440 × 10−3 | 1.620 × 10−3 | 1.780 × 10−3 | 2.210 × 10−3 | 1.830 × 10−3 |
| k2 | 4.239 × 10−2 | 2.732 × 10−2 | 3.723 × 10−2 | 3.936 × 10−2 | 4.125 × 10−2 | 2.994 × 10−2 | |
| m | 1.626 | 1.484 | 1.650 | 1.635 | 1.603 | 1.589 | |
| n | 2.920 | 2.423 | 2.671 | 2.596 | 2.675 | 2.394 | |
| Ac | 0.950 | 0.671 | 0.640 | 0.688 | 0.678 | 0.705 | |
| C | 10.390 | 21.060 | 25.584 | 19.635 | 20.854 | 25.008 | |
| R2 | 0.900 | 0.995 | 0.993 | 0.996 | 0.995 | 0.990 | |
| k1 | 145 | 1.640 × 10−3 | 2.440 × 10−3 | 2.440 × 10−3 | 2.480 × 10−3 | 2.87 × 10−3 | 2.650 × 10−3 |
| k2 | 3.707 × 10−2 | 6.220 × 10−2 | 5.461 × 10−2 | 5.201 × 10−2 | 4.905 × 10−2 | 4.126 × 10−2 | |
| m | 1.459 | 1.740 | 1.624 | 1.615 | 1.484 | 1.577 | |
| n | 2.802 | 2.846 | 2.647 | 2.668 | 2.712 | 2.364 | |
| Ac | * | 0.693 | 0.712 | 0.685 | 0.663 | 0.733 | |
| C | * | 17.680 | 23.780 | 23.120 | 24.660 | 26.267 | |
| R2 | * | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.993 | 0.990 | 0.980 | |
| k1 | 155 | 3.920 × 10−3 | 4.390 × 10−3 | 4.850 × 10−3 | 4.520 × 10−3 | 4.860 × 10−3 | 4.370 × 10−3 |
| k2 | 9.715 × 10−2 | 1.008 × 10−1 | 8.653 × 10−2 | 7.468 × 10−2 | 6.612 × 10−2 | 5.883 × 10−2 | |
| m | 1.683 | 1.598 | 1.542 | 1.460 | 1.255 | 1.431 | |
| n | 3.016 | 2.873 | 2.727 | 2.656 | 2.785 | 2.488 | |
| Ac | * | 0.699 | 0.706 | 0.683 | 0.637 | 0.706 | |
| C | * | 25.485 | 22.040 | 21.204 | 24.391 | 21.266 | |
| R2 | * | 0.993 | 0.990 | 0.994 | 0.993 | 0.990 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Drummer, D. Influence of Filler Content and Filler Size on the Curing Kinetics of an Epoxy Resin. Polymers 2019, 11, 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111797
Zhao Y, Drummer D. Influence of Filler Content and Filler Size on the Curing Kinetics of an Epoxy Resin. Polymers. 2019; 11(11):1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111797
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yang, and Dietmar Drummer. 2019. "Influence of Filler Content and Filler Size on the Curing Kinetics of an Epoxy Resin" Polymers 11, no. 11: 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111797
APA StyleZhao, Y., & Drummer, D. (2019). Influence of Filler Content and Filler Size on the Curing Kinetics of an Epoxy Resin. Polymers, 11(11), 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111797





