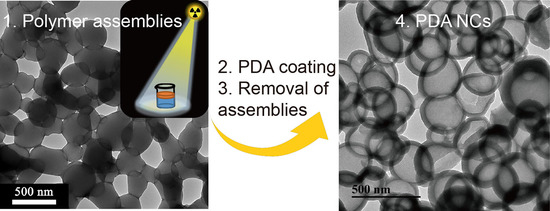
Using γ-Ray Polymerization-Induced Assemblies to Synthesize Polydopamine Nanocapsules
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
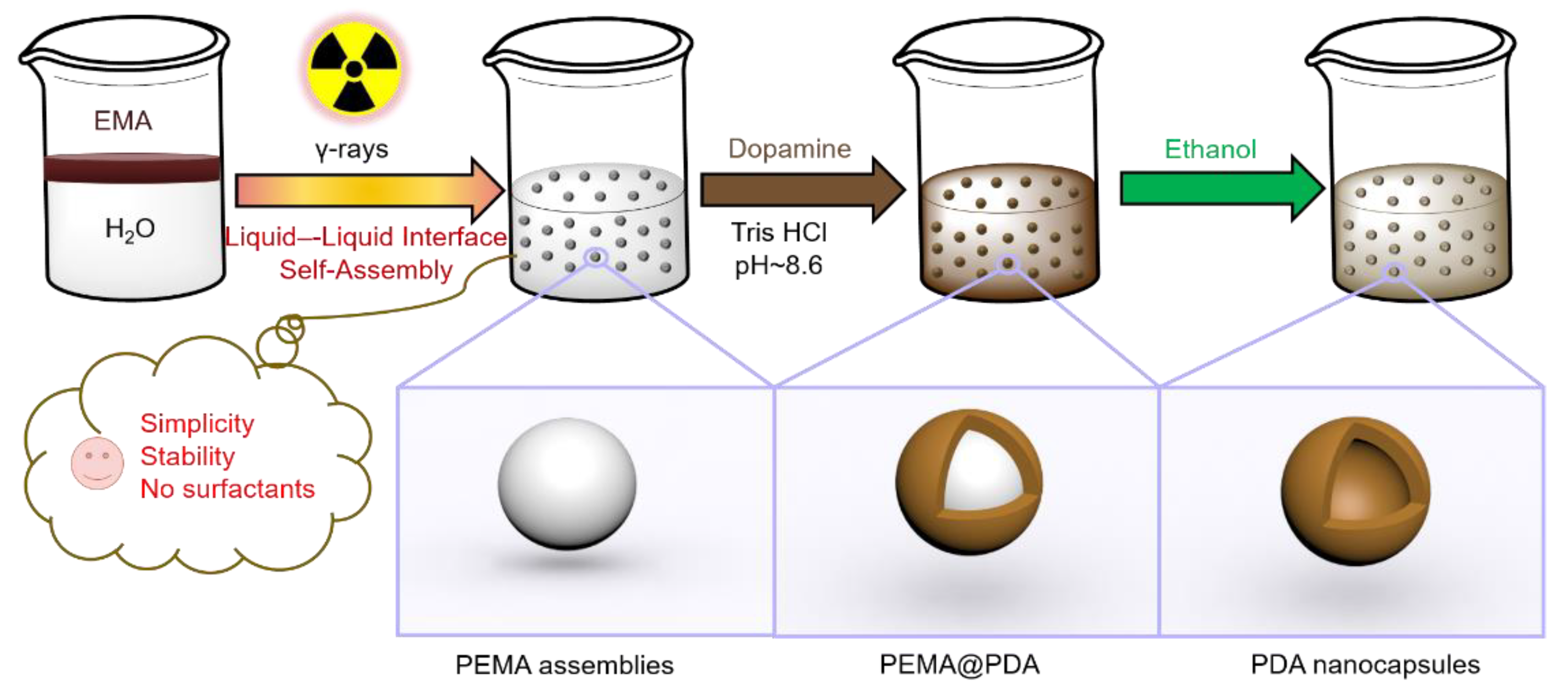
2.2. Synthesis of Polyacrylate Assemblies
2.3. Synthesis of Polydopamine Nanocapsules (PDA NCs)
2.4. Characterizations
2.5. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
2.6. Loading CIP into the PDA NCs
2.7. Releasing CIP from CIP-PDA
2.8. Antibacterial Evaluation of CIP-PDA
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waite, J.H. Mussel Power. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-Inspired Surface Chemistry for Multifunctional Coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryu, J.H.; Messersmith, P.B.; Lee, H. Polydopamine Surface Chemistry: A Decade of Discovery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7523–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Polydopamine and Its Derivative Materials: Synthesis and Promising Applications in Energy, Environmental, and Biomedical Fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrowzynski, R. Polydopamine-Based Multifunctional (Nano)Materials for Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7541–7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Gao, S.; Ding, X.; Wang, D.; Jiang, J.; Jin, J.; Jiang, L. Photothermal-Responsive Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Based Ultrathin Membranes for on/Off Switchable Separation of Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsions. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4835–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.C.; Waldman, R.Z.; Wu, M.B.; Hou, J.W.; Chen, L.; Darling, S.B.; Xu, Z.K. Dopamine: Just the Right Medicine for Membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.W.; Wang, Y.J.; Postma, A.; Hao, J.C.; Hosta-Rigau, L.; Caruso, F. Monodisperse Polymer Capsules: Tailoring Size, Shell Thickness, and Hydrophobic Cargo Loading Via Emulsion Templating. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zheng, W.; Wang, L.; Jin, Z. Scalable Fabrication of Polydopamine Nanotubes Based on Curcumin Crystals. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, A.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Zelikin, A.N.; Tjipto, E.; Caruso, F. Self-Polymerization of Dopamine as a Versatile and Robust Technique to Prepare Polymer Capsules. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3042–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shang, B.; Liu, M.; Shi, F.; Peng, B.; Deng, Z. Hollow Polydopamine Colloidal Composite Particles: Structure Tuning, Functionalization and Applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 513, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; He, B.; Zhang, X.Q.; Lu, A.H. Engineering of Hollow Core-Shell Interlinked Carbon Spheres for Highly Stable Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 8504–8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.W.; Chen, M.; Zhou, S.X.; You, B.; Wu, L.M. A Novel Method for the Fabrication of Monodisperse Hollow Silica Spheres. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6403–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Ha, H. Fabrication of Hollow Polystyrene Nanospheres in Microemulsion Polymerization Using Triblock Copolymers. Langmuir 2002, 18, 5613–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, C.; Feldmann, C.; Wanner, M.; Gerthsen, D. Nanoscale Gold Hollow Spheres through a Microemulsion Approach. Small 2007, 3, 1347–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinger, C.J.; Bruggeman, P.P.; Misra, A.; Borenstein, J.T.; Langer, R. Biocompatibility of Biodegradable Semiconducting Melanin Films for Nerve Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3050–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.L.; Feng, L.Z.; Hao, Y.; Chen, M.C.; Gao, M.; Chao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, W.W.; Liu, J.J.; Liang, C.; et al. Chemistry-a European Journalsynthesis of Hollow Biomineralized Caco3-Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Multimodal Imaging-Guided Cancer Photodynamic Therapy with Reduced Skin Photosensitivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2165–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.X.; Su, C.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, J.F.; Zhang, W.B.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J.; Yang, S.G. Responsive Complex Capsules Prepared with Polymerization of Dopamine, Hydrogen-Bonding Assembly, and Catechol Dismutation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 513, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, D.L.; Xu, T.; Xing, W.S.; Ge, X.; Fang, L.M.; Wang, K.F.; Ren, F.Z.; Lu, X. Mussel-Inspired Contact-Active Antibacterial Hydrogel with High Cell Affinity, Toughness, and Recoverability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1805964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, Y.; Mullner, M.; van Koeverden, M.P.; Noi, K.F.; Zhu, W.; Caruso, F. Engineering Fluorescent Poly(Dopamine) Capsules. Langmuir 2014, 30, 2921–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.M.; Serpe, M.J. Versatile Method for Coating Surfaces with Functional and Responsive Polymer-Based Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 27547–27553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, S.; Jia, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z. Anisotropic Polydopamine Capsules with an Ellipsoidal Shape That Can Tolerate Harsh Conditions: Efficient Adsorbents for Organic Dyes and Precursors for Ellipsoidal Hollow Carbon Particles. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 21686–21696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jia, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, J. Facile Fabrication of Robust Polydopamine Microcapsules for Insulin Delivery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 487, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Wang, D.A.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Robust Polydopamine Nano/Microcapsules and Their Loading and Release Behavior. Chem. Commun. 2009, 44, 6789–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nador, F.; Guisasola, E.; Baeza, A.; Angel, M.; Villaecija, M.; Vallet-Regi, M.; Ruiz-Molina, D. Synthesis of Polydopamine-Like Nanocapsules Via Removal of a Sacrificial Mesoporous Silica Template with Water. Chem.-Eur. J. 2017, 23, 2753–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohri, M.; Nannichi, Y.; Kohma, H.; Abe, D.; Kojima, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Kishikawa, K. Size Control of Polydopamine Nodules Formed on Polystyrene Particles During Dopamine Polymerization with Carboxylic Acid-Containing Compounds for the Fabrication of Raspberry-Like Particles. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 449, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Song, X.; Ai, Q.; Tian, C. Polydopamine Microcapsules with Different Wall Structures Prepared by a Template-Mediated Method for Enzyme Immobilization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 9991–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Su, H.; Bi, X.; Bai, Y.; Chen, L.; Ge, D.; Shi, W.; Sun, Y. Polydopamine Nanocapsule: A Theranostic Agent for Photoacoustic Imaging and Chemo-Photothermal Synergistic Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, D. Interfacial Basicity-Guided Formation of Polydopamine Hollow Capsules in Pristine O/W Emulsions − toward Understanding of Emulsion Template Roles. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 5105–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.Z.; Jiang, W.F.; Tong, G.S.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, J.; Li, H.M.; Yu, C.Y.; Huang, X.H.; Zhou, Y.F. Preparation of Polydopamine Nanocapsules in a Miscible Tetrahydrofuran-Buffer Mixture. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeroslavsky, G.; Richman, M.; Dawidowicz, L.-O.; Rahimipour, S. Sonochemically Produced Polydopamine Nanocapsules with Selective Antimicrobial Activity. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5721–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, M.J.; Chu, L.Y. Functional Polymeric Microparticles Engineered from Controllable Microfluidic Emulsions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; van der Wee, E.; Imhof, A.; van Blaaderen, A. Synthesis of Monodisperse, Highly Cross-Linked, Fluorescent Pmma Particles by Dispersion Polymerization. Langmuir 2012, 28, 6776–6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S. Estimation of the Critical Surface Tension for Polymers from Molecular Constitution by a Modified Hildebrand-Scott Equation. J. Phys. Chem. 1968, 72, 3332–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Luan, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, H.; Li, D.; Hu, L. Using γ-Ray Polymerization-Induced Assemblies to Synthesize Polydopamine Nanocapsules. Polymers 2019, 11, 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111754
Jiang W, Zhang X, Luan Y, Wang R, Liu H, Li D, Hu L. Using γ-Ray Polymerization-Induced Assemblies to Synthesize Polydopamine Nanocapsules. Polymers. 2019; 11(11):1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111754
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Wenwen, Xinyue Zhang, Yafei Luan, Rensheng Wang, Hanzhou Liu, Dan Li, and Liang Hu. 2019. "Using γ-Ray Polymerization-Induced Assemblies to Synthesize Polydopamine Nanocapsules" Polymers 11, no. 11: 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111754
APA StyleJiang, W., Zhang, X., Luan, Y., Wang, R., Liu, H., Li, D., & Hu, L. (2019). Using γ-Ray Polymerization-Induced Assemblies to Synthesize Polydopamine Nanocapsules. Polymers, 11(11), 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111754