Selective Enrichment of Clenbuterol onto Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microspheres with Tailor-made Structure and Oxygen Functionalities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
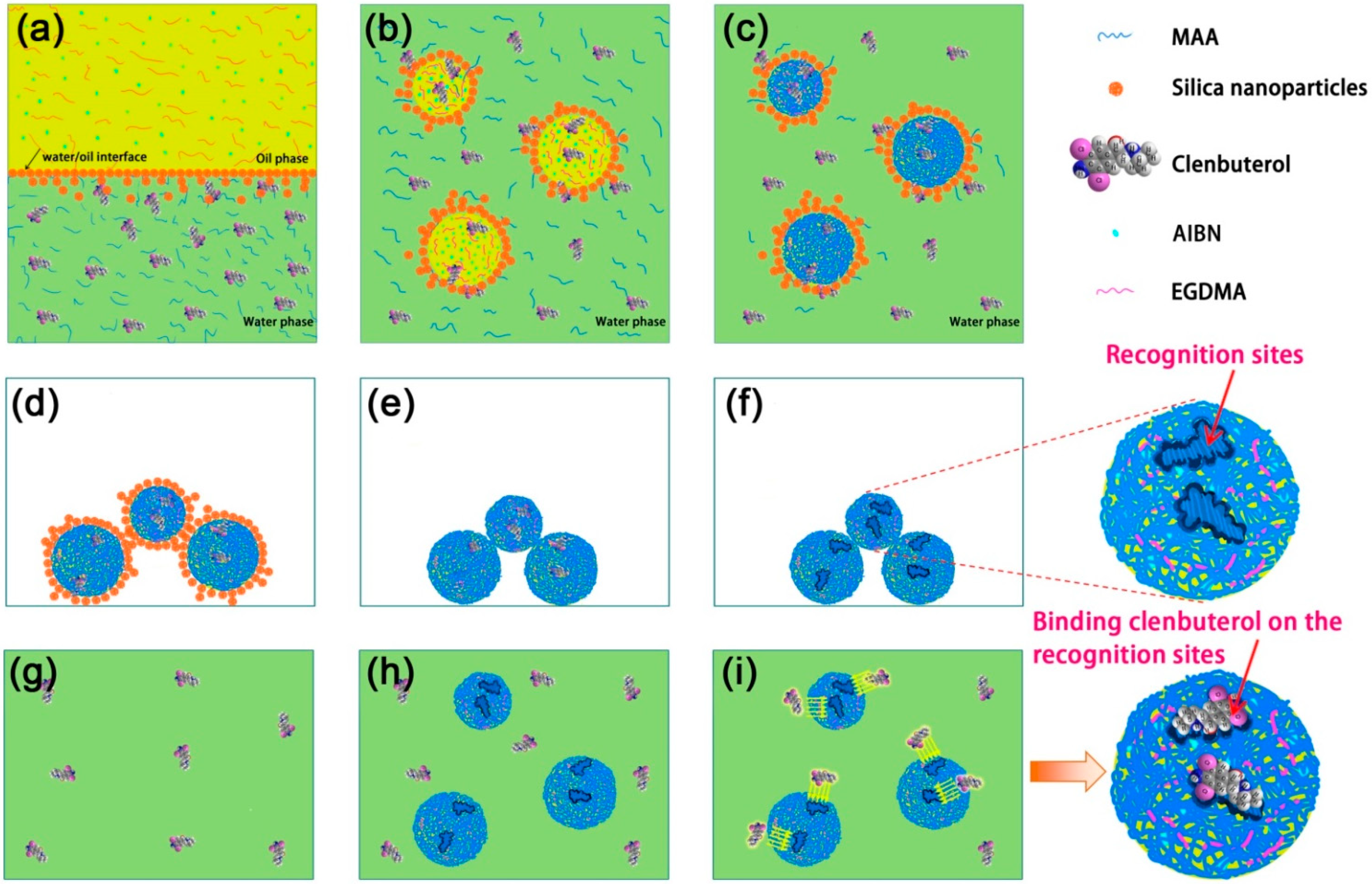
2.2. Synthesis of MIPMs
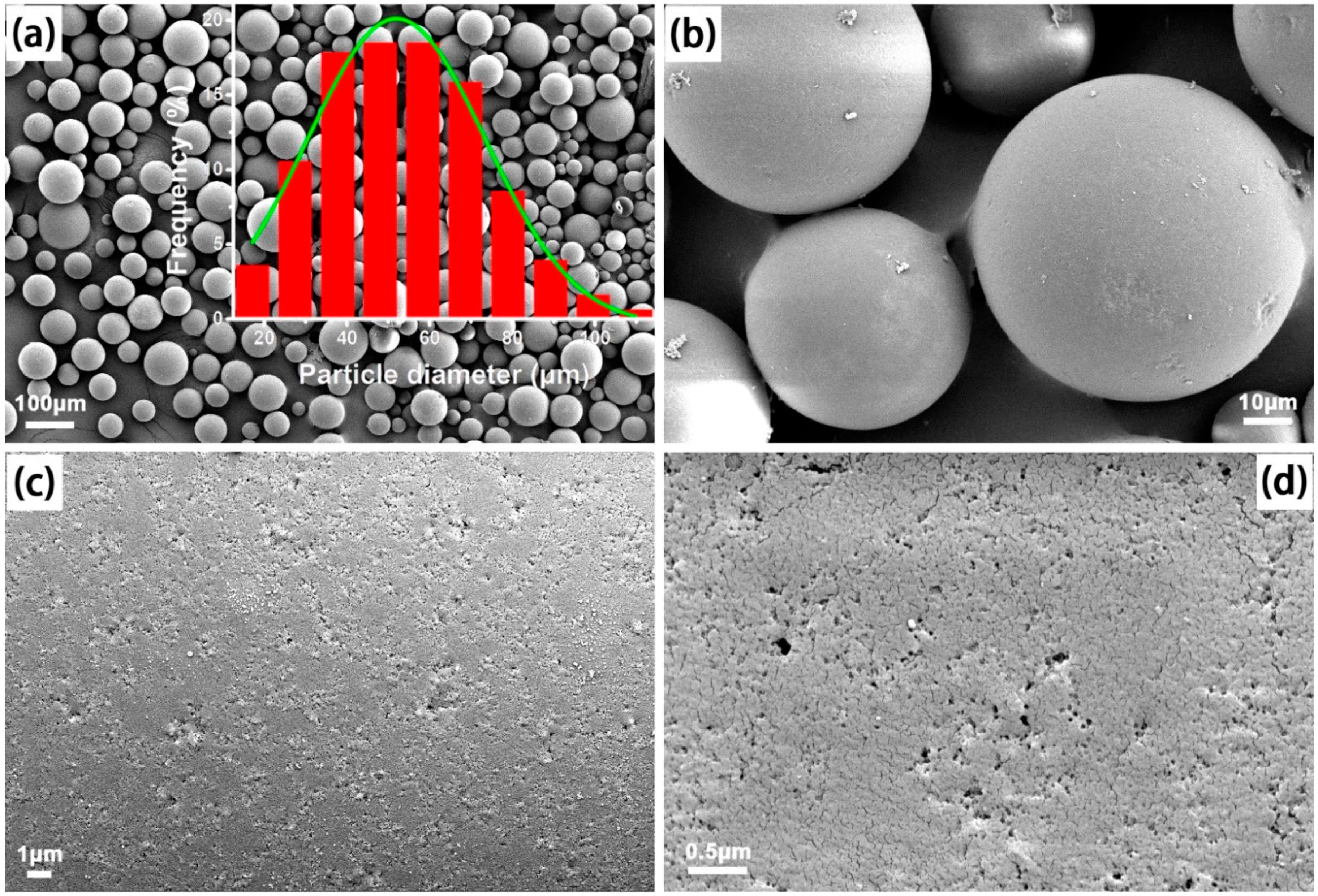
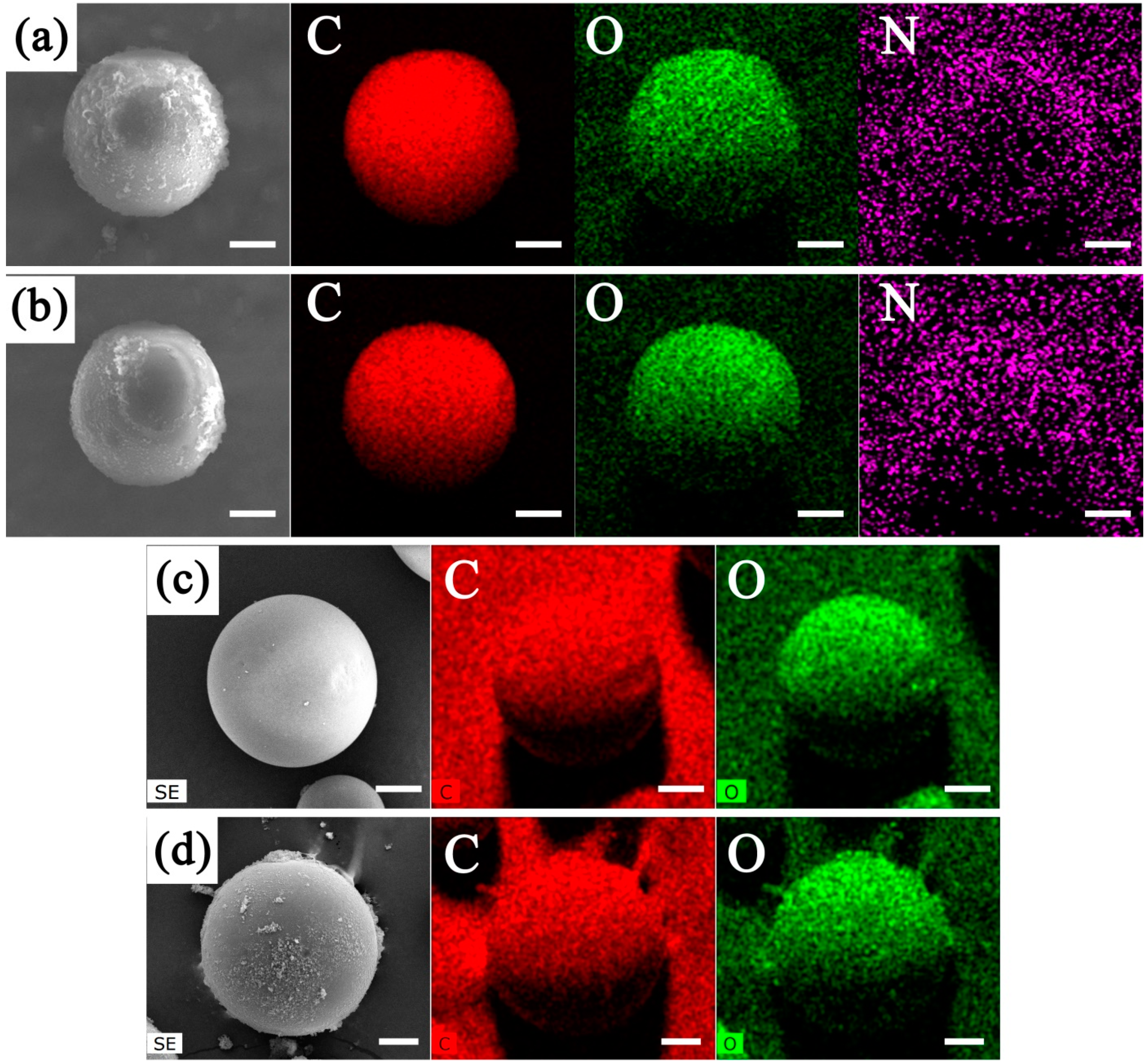
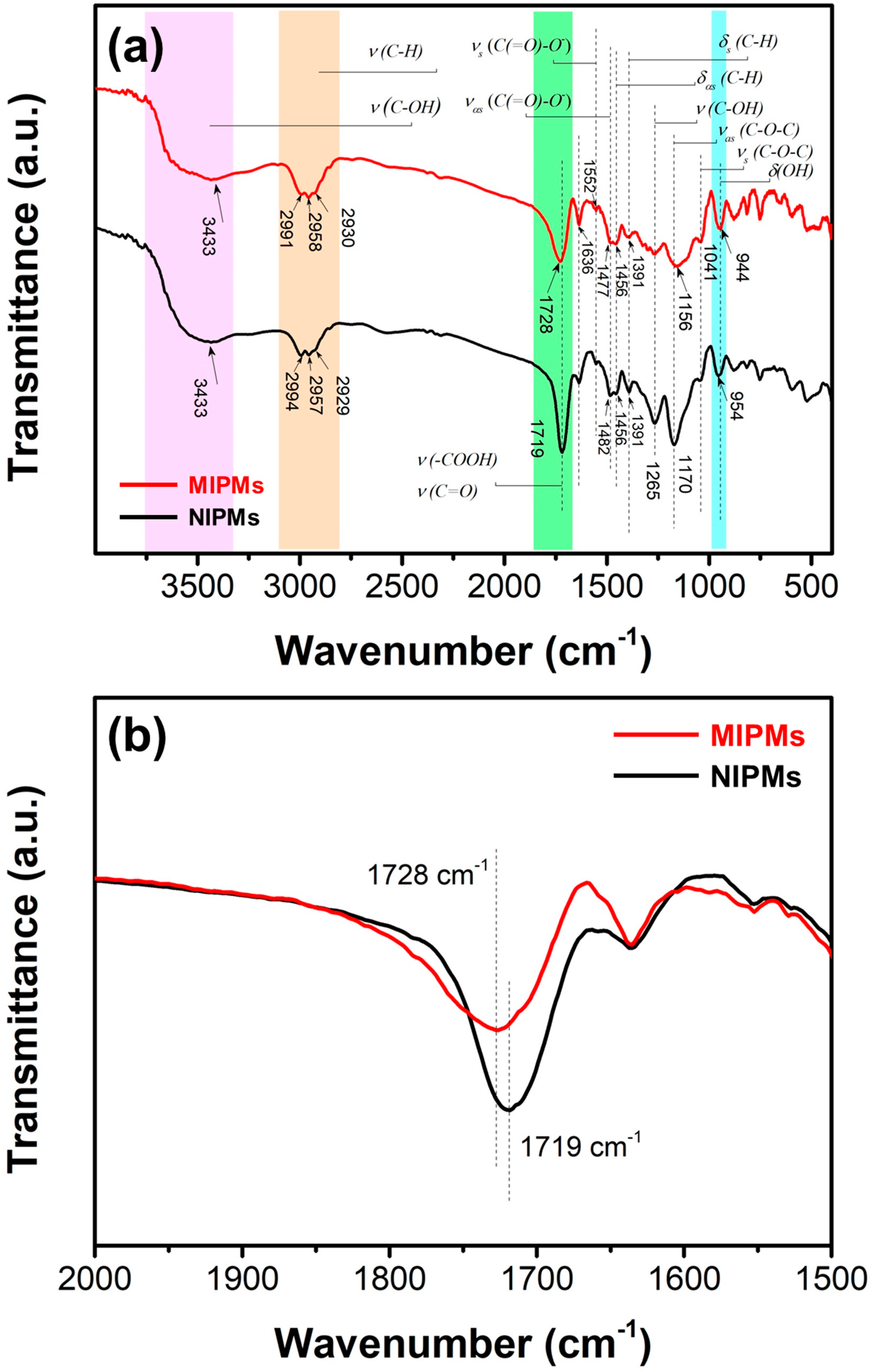
2.3. Characterizations
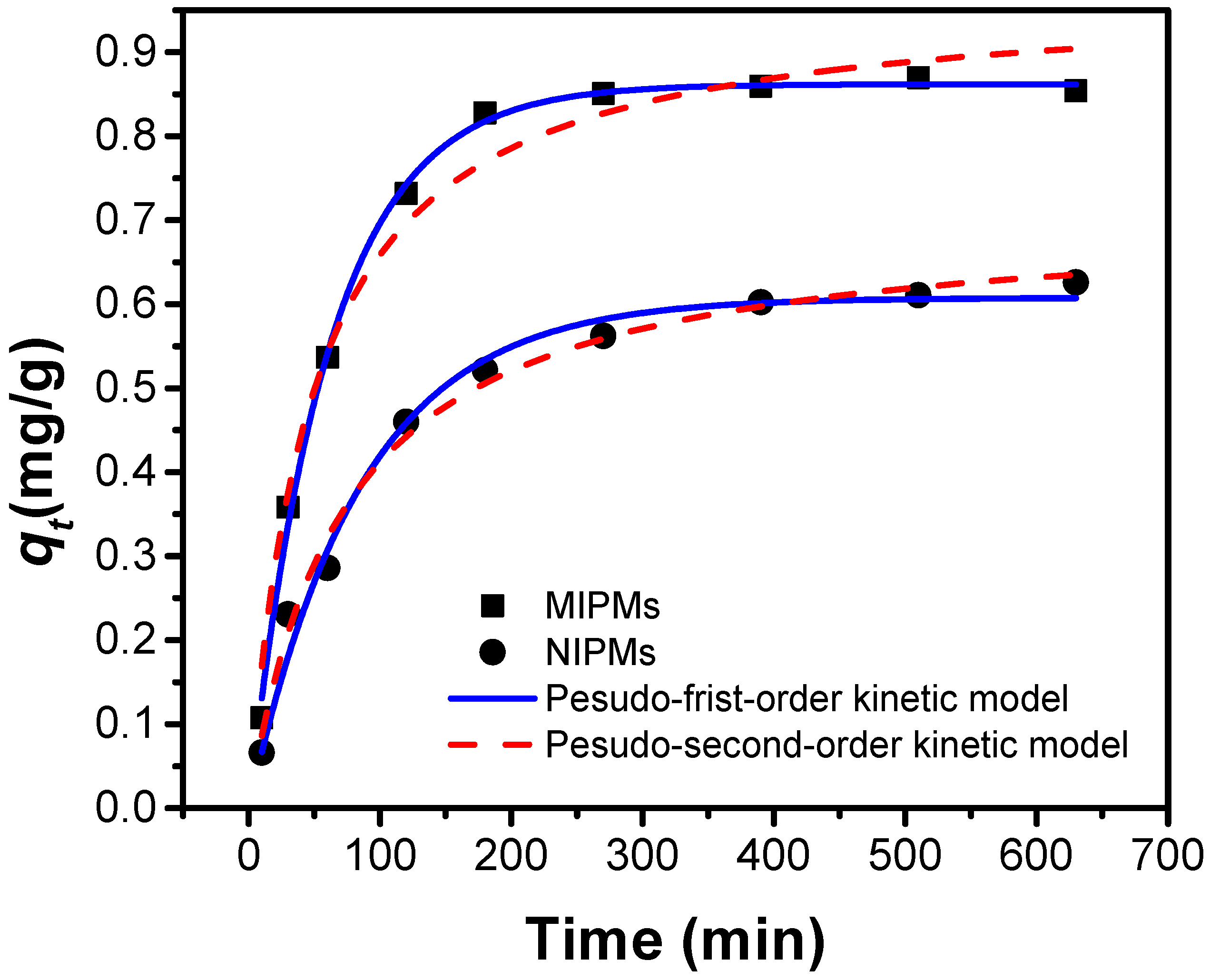
2.4. Adsorption Kinetics
2.5. Adsorption Isotherm
- RL > 1, unfavorable;
- RL < 1, favorable;
- RL = 1, Linear;
- RL = 0, irreversible.
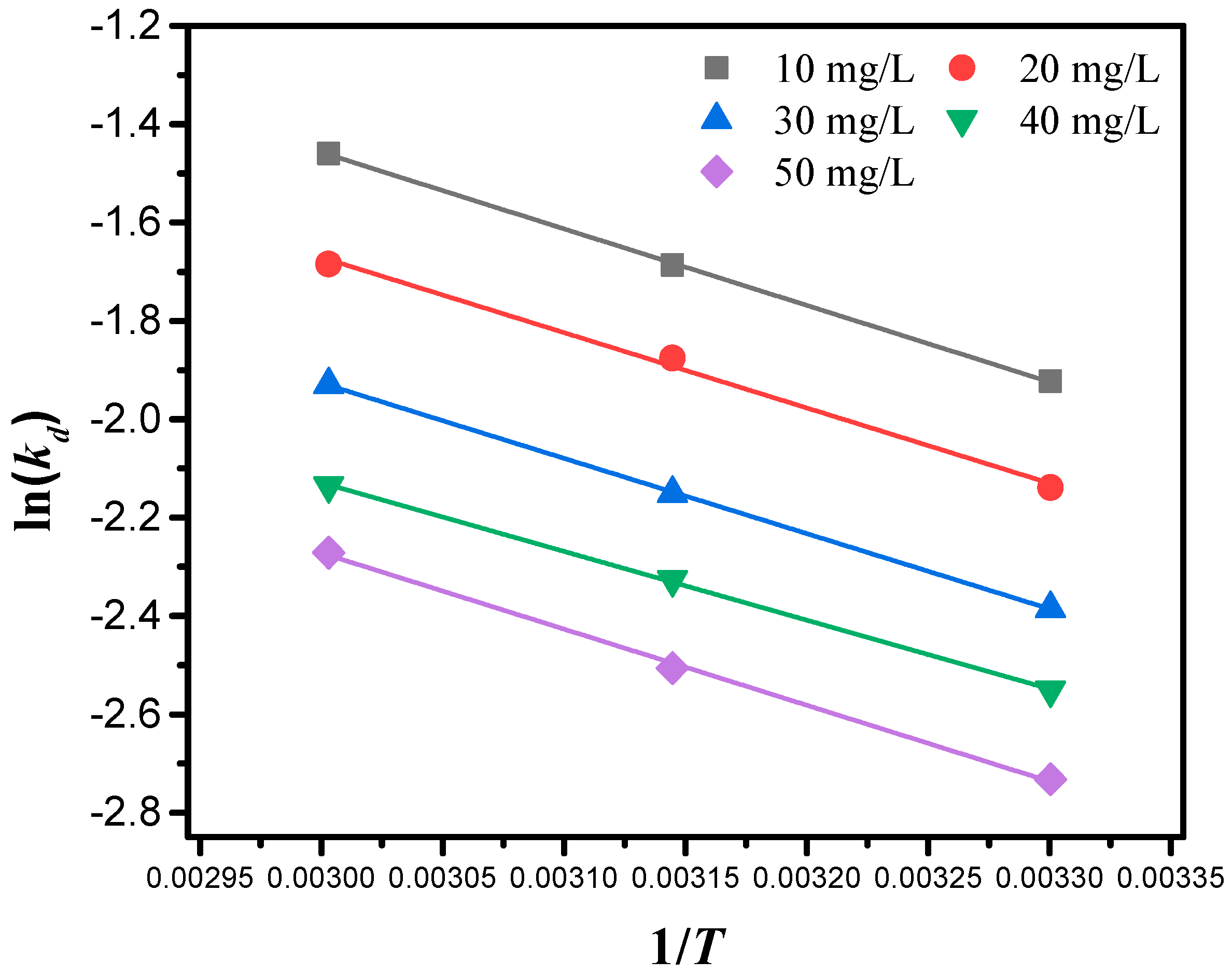
2.6. Adsorption Thermodynamics
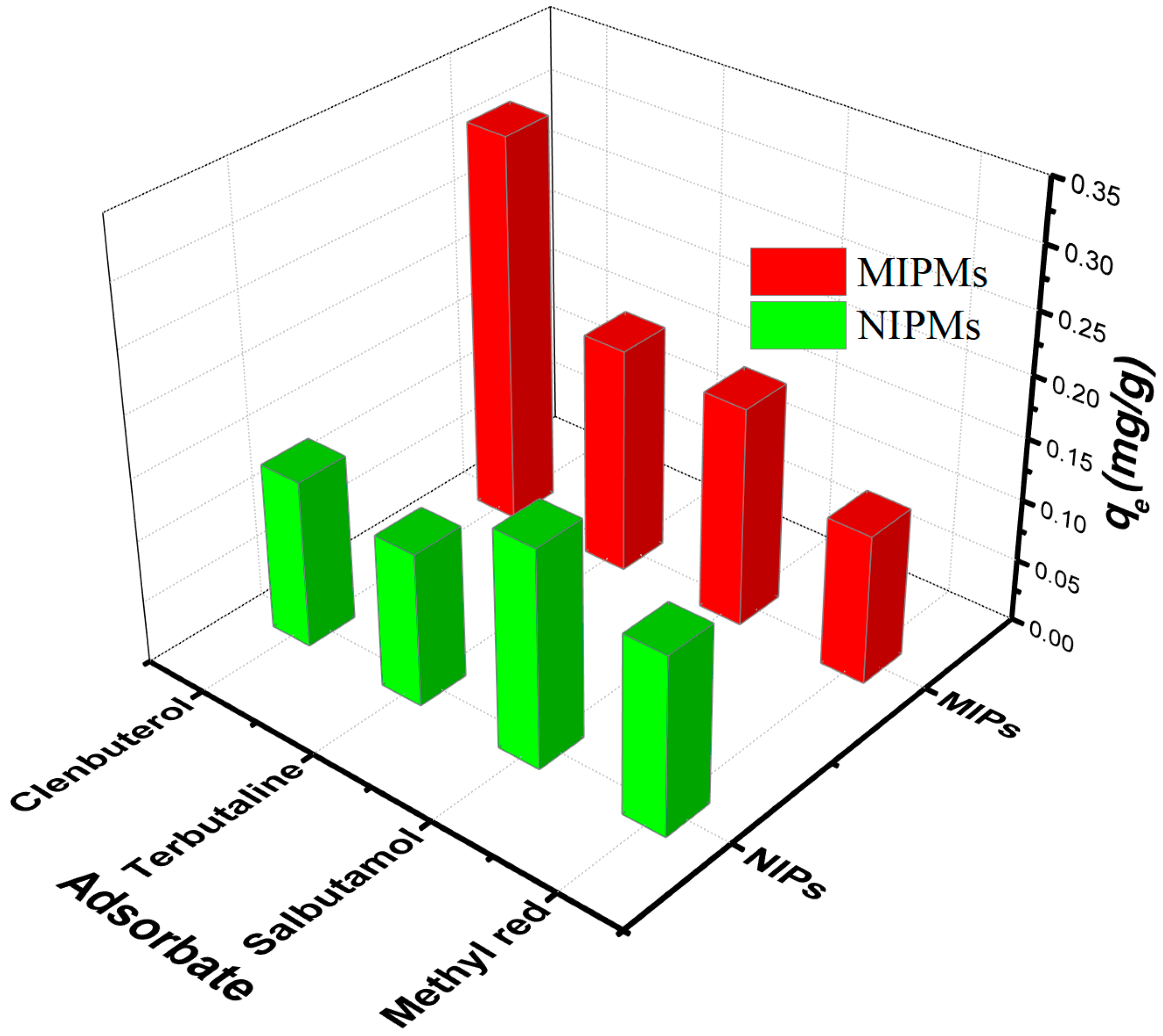
2.7. Competitive Adsorption Tests
2.8. Impact of the Solution as the Medium for the Adsorption of Clenbuterol onto MIPs and NIPMs
2.9. Reliability of the Method Used for the Fabrication of MIPMs
2.10. Test on the Recyclability of the MIPMs
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Özkütük, E.B.; Uğurağ, D.; Ersöz, A.; Say, R. Determination of Clenbuterol by Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Potentiometric Sensors. Anal. Lett. 2015, 49, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Luo, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chang, R.; Du, W.; Chang, C.; Fu, Q. Development of molecular imprinted column-on line-two dimensional liquid chromatography for selective determination of clenbuterol residues in biological samples. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marocolo, M.; Silva-Neto, J.A.; Neto, O.B. Acute interruption of treatment with nandrolone decanoate is not sufficient to reverse cardiac autonomic dysfunction and ventricular repolarization disturbances in rats. Steroids 2018, 132, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, R.; Kang, H.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J. Facile and sensitive detection of clenbuterol in pork using a personal glucose meter. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 6507–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Shen, J.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Jiang, H. Simultaneous determination of chloramphenicol and clenbuterol in milk with hybrid chemiluminescence immunoassays. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zavabeti, A.; Quan, H.; Zhu, W.; Wei, H.; Chen, D.; Ou, J.Z. Recent advances in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides for biological sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, M.; Zhao, K.; Bao, Q.; Pan, P.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wei, J. Adsorption and Electrochemical Detection of Bovine Serum Albumin Imprinted Calcium Alginate Hydrogel Membrane. Polymers 2019, 11, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Duan, M.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Fang, S. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Microspheres as Biomimetic Recognition Material for In Situ Adsorption and Selective Chemiluminescence Determination of Bisphenol A. Polymers 2018, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, B.; Cheng, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Dong, S.; Wei, S.; Wang, P.; Li, J.-R. Determination and removal of clenbuterol with a stable fluorescent zirconium(IV)-based metal organic framework. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.; Sulaiman, R.N.R.; Rahman, H.A.; Noah, N.F.M.; Jusoh, N.; Idroas, M.; Noah, N.F.M. Simultaneous extraction and enrichment of reactive dye using green emulsion liquid membrane system. Environ. Technol. 2018, 40, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlala, A.I.A.; Raman, A.A.A.; Bello, M.M.; Asghar, A. A review of the applications of organo-functionalized magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposites for heavy metal adsorption. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 1004–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, D.; Hu, H.; Xin, J.H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Synthesis and stabilization of metal nanocatalysts for reduction reactions—A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 11157–11182. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Cao, R.; Sun, H.; Huang, C.; Chen, J. Molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres prepared by Pickering emulsion polymerization for selective solid-phase extraction of eight bisphenols from human urine samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 872, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Xin, Q.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Xu, Q. Selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes from aqueous solution on polydopamine microspheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 461, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyola, Y.; Dai, S. High surface-area amidoxime-based polymer fibers co-grafted with various acid monomers yielding increased adsorption capacity for the extraction of uranium from seawater. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 8824–8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Chang, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, D. A new insight into PAM/graphene-based adsorption of water-soluble aromatic pollutants. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 27, 7558–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Liang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Q. Multipurpose Use of a Corncob Biomass for the Production of Polysaccharides and the Fabrication of a Biosorbent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3830–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Adio, S.O.; Asif, M.; Dafalla, H. Statistical analysis of phenols adsorption on diethylenetriamine-modified activated carbon. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzelder, F.; Funck, M.; Schmidt, T.C. Sorption of Heterocyclic Organic Compounds to Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Quan, H.; Zhong, B.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, D. A Reduced Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot-Based Adsorbent for Efficiently Binding with Organic Pollutants. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 6502–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, E.C.; Slaviero, J.C.; Cunha, A.M.; Dotto, G.L.; Hosseini–Bandegharaei, A.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A. Microwave synthesis of silica nanoparticles and its application for methylene blue adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Y. Cellulose-based hydrophobic carbon aerogels as versatile and superior adsorbents for sewage treatment. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45753–45759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Guo, S.; Zeng, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Investigation on efficient adsorption of cationic dyes on porous magnetic polyacrylamide microspheres. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 292, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Xu, X.-Y.; Liang, Y.; Hua, Y.; Guo, H. Fabrication of a molecularly imprinted polymer immobilized membrane with nanopores and its application in determination of β2-agonists in pork samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1429, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Turner, N.W.; Laitenberger, P. Molecularly imprinted polymers in clinical diagnostics—Future potential and existing problems. Med Eng. Phys. 2006, 28, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunath, S.; Panagiotopoulou, M.; Maximilien, J.; Marchyk, N.; Sänger, J.; Haupt, K. Cell and Tissue Imaging with Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Plastic Antibody Mimics. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2015, 4, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Hu, H.; Guo, P.; Ma, Y.; Li, P.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, M. Combining Pickering Emulsion Polymerization with Molecular Imprinting to Prepare Polymer Microspheres for Selective Solid-Phase Extraction of Malachite Green. Polymers 2017, 9, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhu, M.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Piletsky, S.A.; Turner, A.P. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Enzyme-like Catalysis. In Molecularly Imprinted Catalysts; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, S.; Benito-Peña, E.; Navarro-Villoslada, F.; Langer, J.; Sanz-Ortiz, M.N.; Reguera, J.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Multibranched Gold–Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Coated with a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Label-Free Antibiotic Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Analysis. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 7947–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juric, D.; Rohner, N.A.; von Recum, H.A. Molecular Imprinting of Cyclodextrin Supramolecular Hydrogels Improves Drug Loading and Delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, 1800246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koesdjojo, M.T.; Tennico, Y.H.; Remcho, V.T. 18 Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Sorbents for Separations and Extractions. In Separation Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 8, pp. 479–503. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Hu, H.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Guo, P.; Xin, M.; Yu, M.; Lin, H. Functionalization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microspheres for the Highly Selective Removal of Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions and the Analysis of Food-Grade Fish Samples. Polymers 2018, 10, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcer, Y.A.; Demirkurt, M.; Demir, M.M.; Eroglu, A.E. Development of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) as a solid phase extraction (SPE) sorbent for the determination of ibuprofen in water. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 31441–31447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Bao, Y.; Gan, S.; Li, F.; Niu, L. Electrochemical sensor for dopamine based on a novel graphene-molecular imprinted polymers composite recognition element. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, G.; Fiori, M.; Rizzo, B.; Crescenzi, V.; Masci, G. Use of molecularly imprinted polymers in the solid-phase extraction of clenbuterol from animal feeds and biological matrices. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2001, 759, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, B.T.; Seo, M.H.; Zhang, X.; Lee, Y.I. Selective optosensing of clenbuterol and melamine using molecularly imprinted polymer-capped CdTe quantum dots. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 57, 310–316. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, D.; Jiang, Y.; Bi, Y. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the detection of illegal drugs and additives: A review. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.R.; Bajwa, S.Z.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Khan, W.S.; Mujahid, A.; Ihsan, A.; Rehman, A. Molecularly imprinted porous beads for the selective removal of copper ions. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, B.; Boroujeni, M.K.; Ensafi, A.A. Caffeine electrochemical sensor using imprinted film as recognition element based on polypyrrole, sol-gel, and gold nanoparticles hybrid nanocomposite modified pencil graphite electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyazit, S.; Bui, B.T.S.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanomaterials and nanocomposites by controlled/living radical polymerization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 62, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Guan, J.; Xu, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, X. Synthesis and Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Modified TiO2 Nanomaterials: A Review. Polymers 2018, 10, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boitard, C.; Bée, A.; Menager, C.; Griffete, N. Magnetic protein imprinted polymers: A review. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 1563–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertürk, G.; Mattiasson, B. Molecular Imprinting Techniques Used for the Preparation of Biosensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, G.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y. Comparative study of the molecularly imprinted polymers prepared by reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer “bulk” polymerization and traditional radical “bulk” polymerization. J. Mol. Recognit. 2013, 26, 240–251. [Google Scholar]
- Masci, G.; Aulenta, F.; Crescenzi, V. Uniform-sized clenbuterol molecularly imprinted polymers prepared with methacrylic acid or acrylamide as an interacting monomer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 2660–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Kamra, T.; Zhang, K.; Bülow, L.; Ye, L. Preparation of protein imprinted polymer beads by Pickering emulsion polymerization. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Li, L.; Hang, H.; Wu, R.; Dai, X.; Shi, W.; Yan, Y. Fabrication and Evaluation of Magnetic/Hollow Double-Shelled Imprinted Sorbents Formed by Pickering Emulsion Polymerization. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8170–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, H.; Chen, Q.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Qi, X. Selective removal of erythromycin by magnetic imprinted polymers synthesized from chitosan-stabilized Pickering emulsion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 289, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, N.; Frisby, J.; Owens, E.; Hughes, H.; Duggan, P.; McLoughlin, P. The influence of polymer morphology on the performance of molecularly imprinted polymers. Polymers 2010, 51, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Peppas, N.A. Analysis of molecular interactions in poly (methacrylic acid-g-ethylene glycol) hydrogels. Polymers 2003, 44, 3701–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneerung, T.; Liew, J.; Dai, Y.; Kawi, S.; Chong, C.; Wang, C.-H. Activated carbon derived from carbon residue from biomass gasification and its application for dye adsorption: Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G.; Peindy, H.; Gimbert, F.; Robert, C. Removal of C.I. Basic Green 4 (Malachite Green) from aqueous solutions by adsorption using cyclodextrin-based adsorbent: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 53, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahchamani, J.; Mousavi, H.Z.; Behzad, M. Adsorption of methyl violet from aqueous solution by polyacrylamide as an adsorbent: Isotherm and kinetic studies. Desalination 2011, 267, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayesteh, H.; Rahbar-Kelishami, A.; Norouzbeigi, R. Adsorption of malachite green and crystal violet cationic dyes from aqueous solution using pumice stone as a low-cost adsorbent: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

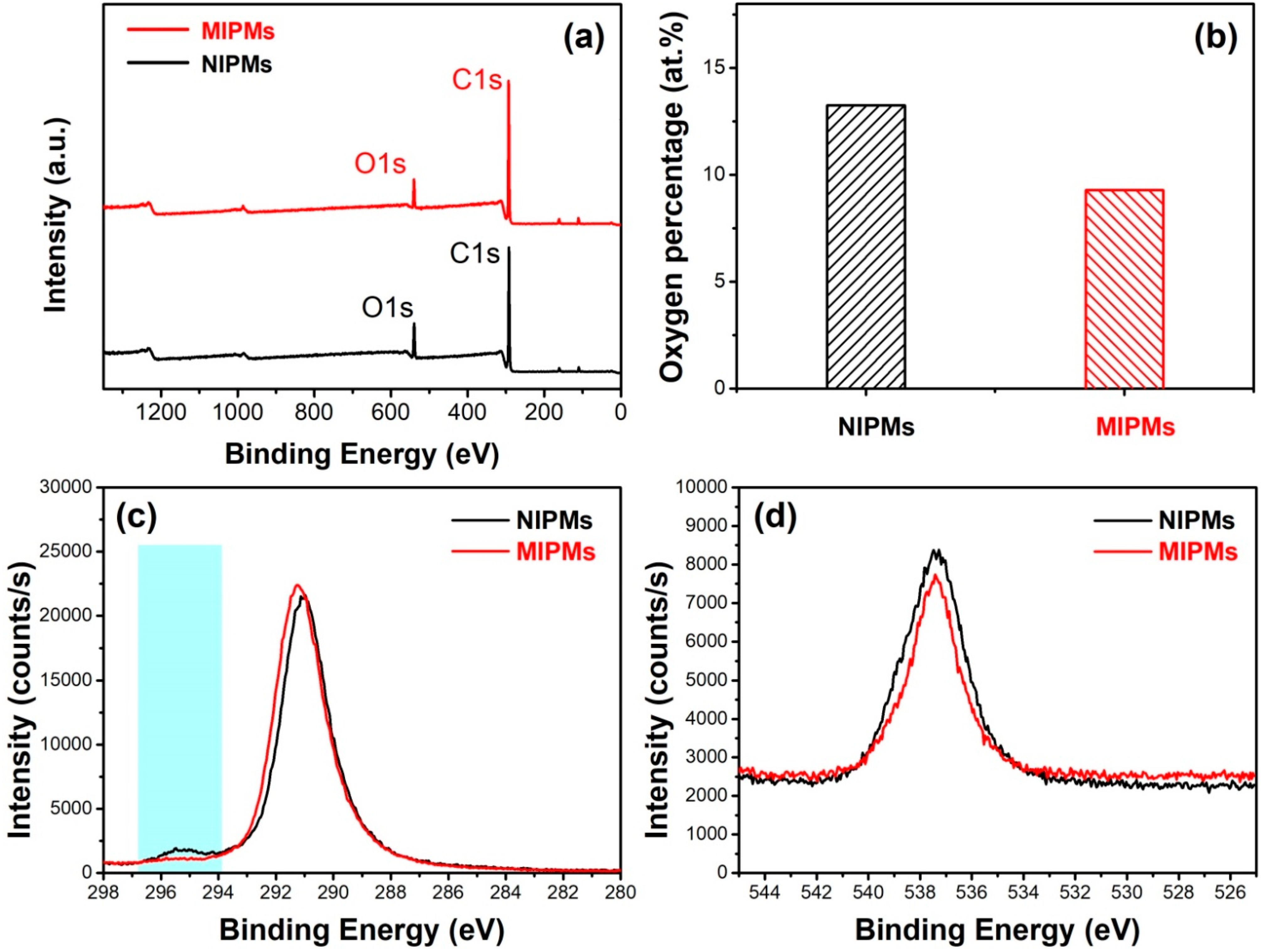

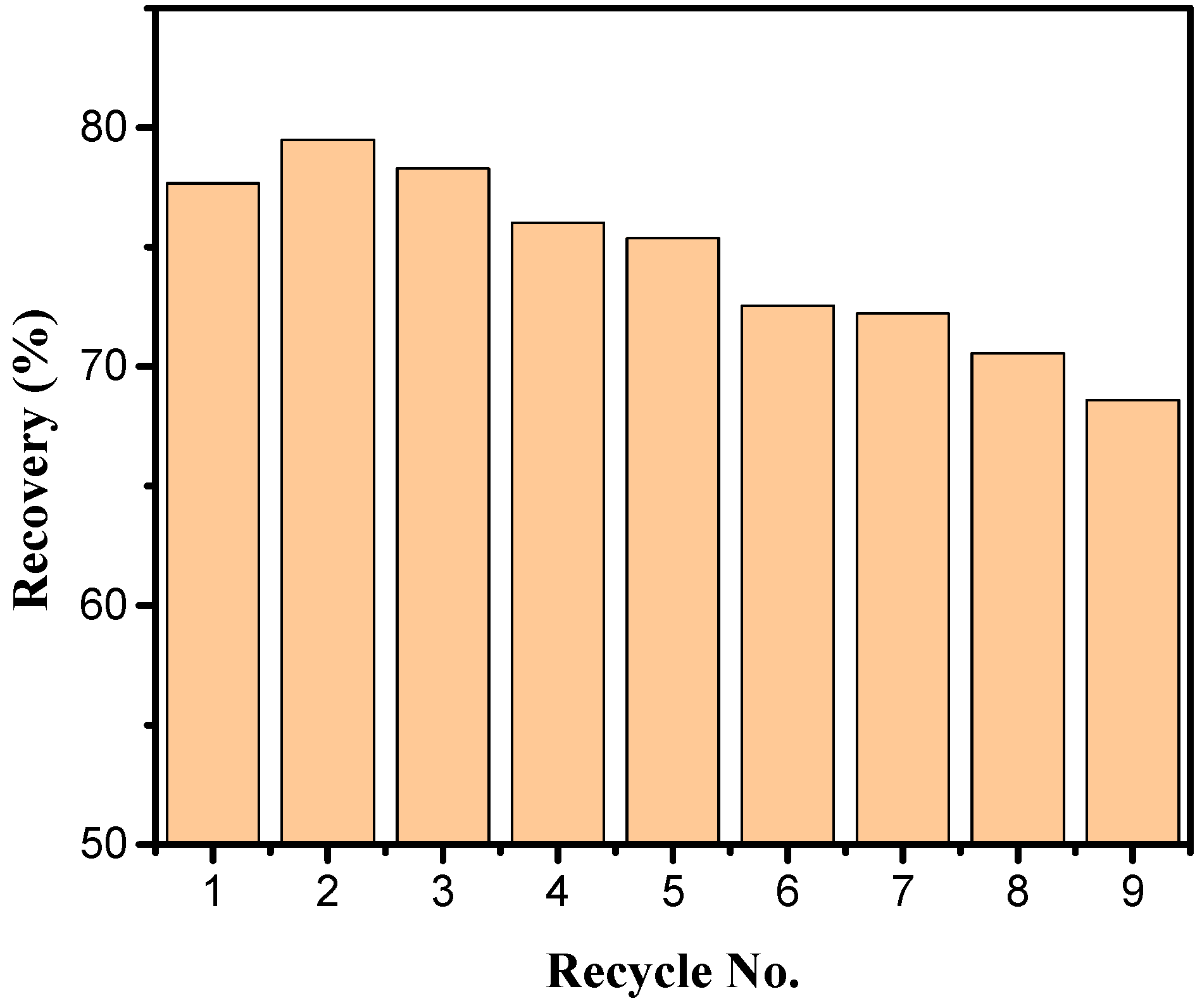
| Sample | BET Surface Area | Volume of Pores | Average Pore Width |
|---|---|---|---|
| m²/g | cm³/g | nm | |
| MIPMs | 14.2265 | 0.029734 | 5.7847 |
| NIPMs | 3.7190 | 0.008051 | 151.0666 |
| Name | Peak BE | FWHM | Area (P) | Atomic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eV | eV | CPS.eV | % | ||
| NIPMs | O1s | 539.37 | 3.3 | 272,588.87 | 13.25 |
| C1s | 292.06 | 2.77 | 739,143.34 | 86.75 | |
| MIPMs | O1s | 539.98 | 2.91 | 194,760.04 | 9.29 |
| C1s | 292.88 | 2.58 | 787,419.49 | 90.71 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Mai, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, M.; Hu, H. Selective Enrichment of Clenbuterol onto Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microspheres with Tailor-made Structure and Oxygen Functionalities. Polymers 2019, 11, 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101635
Zhao X, Mai Y, Chen D, Zhang M, Hu H. Selective Enrichment of Clenbuterol onto Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microspheres with Tailor-made Structure and Oxygen Functionalities. Polymers. 2019; 11(10):1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101635
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiangyun, Yuliang Mai, Dongchu Chen, Min Zhang, and Huawen Hu. 2019. "Selective Enrichment of Clenbuterol onto Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microspheres with Tailor-made Structure and Oxygen Functionalities" Polymers 11, no. 10: 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101635
APA StyleZhao, X., Mai, Y., Chen, D., Zhang, M., & Hu, H. (2019). Selective Enrichment of Clenbuterol onto Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microspheres with Tailor-made Structure and Oxygen Functionalities. Polymers, 11(10), 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101635






