Cold-Cured Epoxy-Based Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Resins Containing Deep Eutectic Solvents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
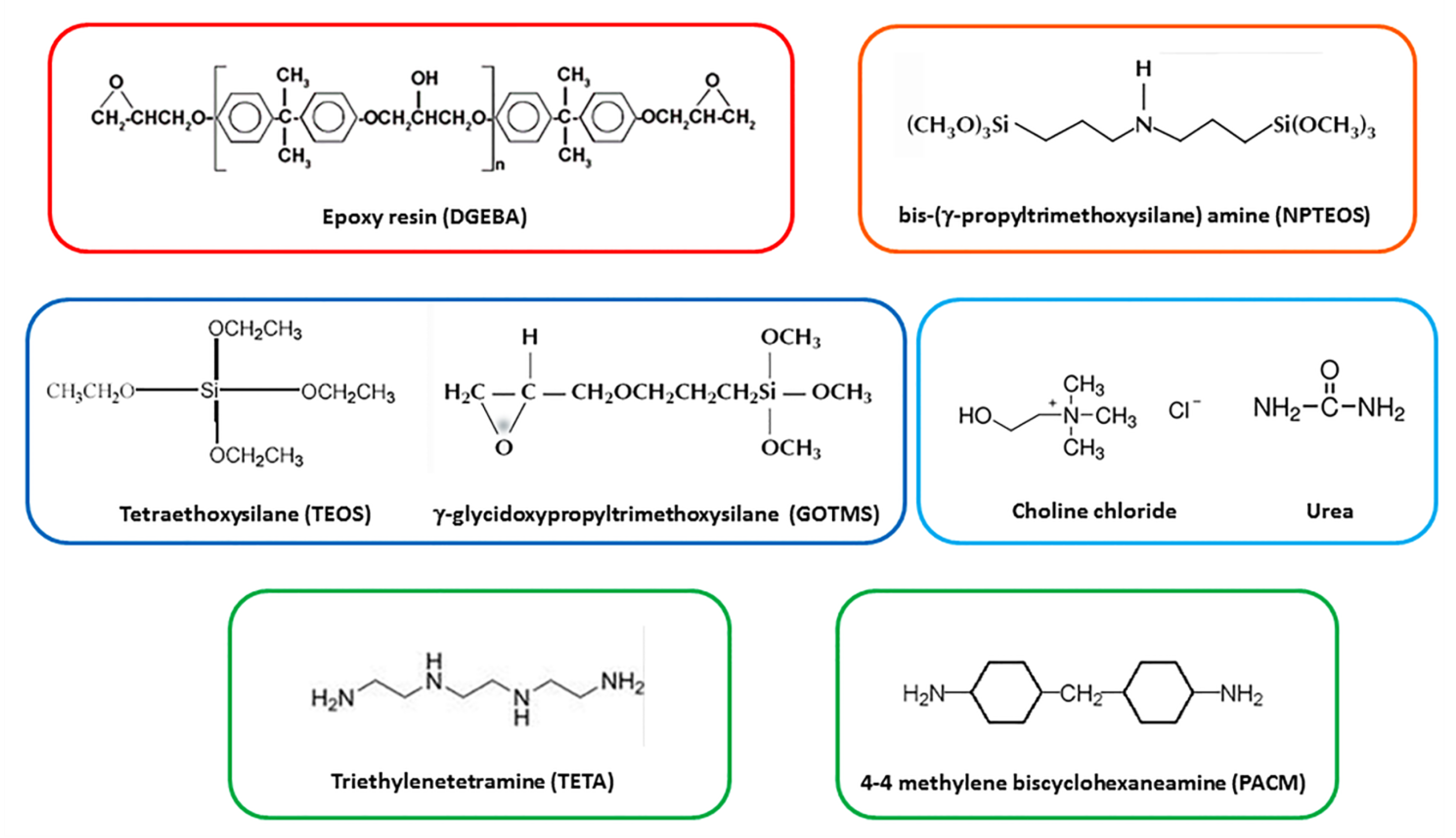
2.1. Materials and Synthesis Procedures
2.2. Production of the Specimens, Curing/Aging Procedures
2.3. Characterization of Fresh Mixtures and Cured/aged Specimens
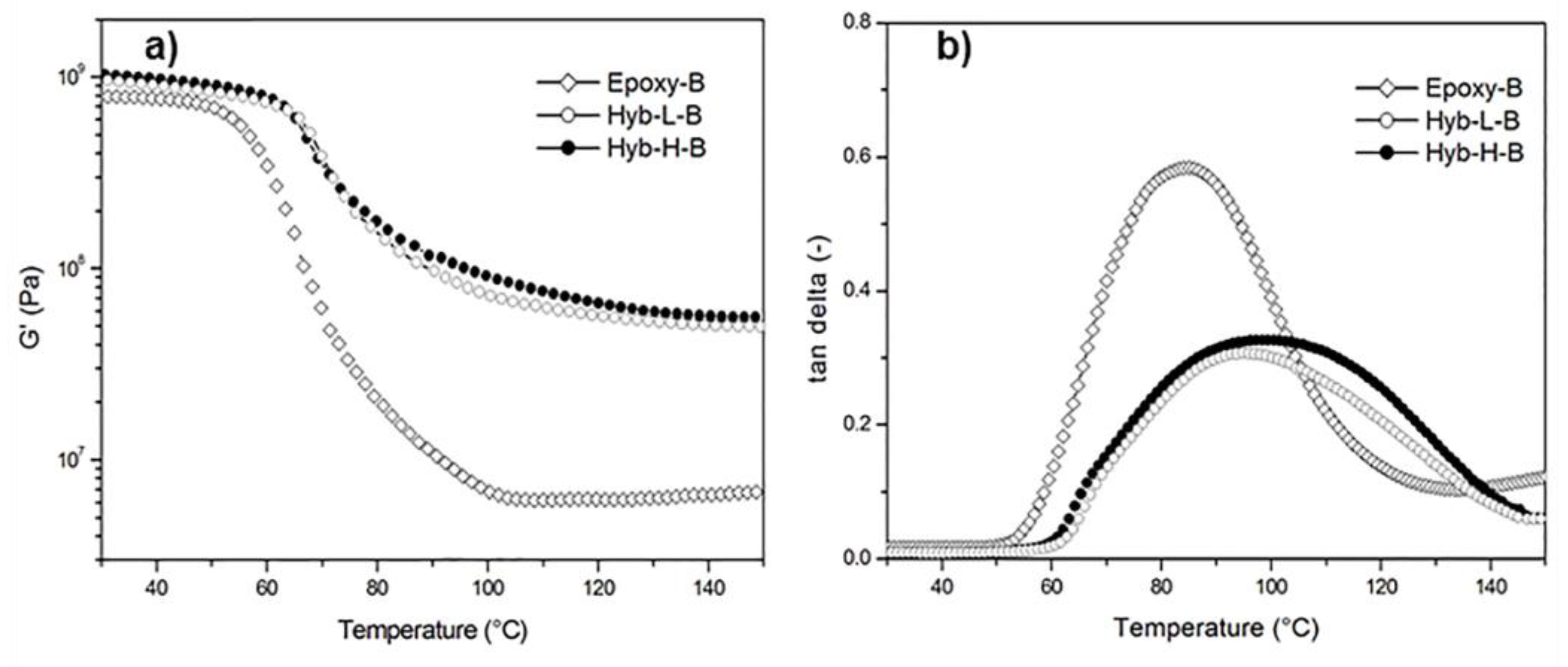
3. Results
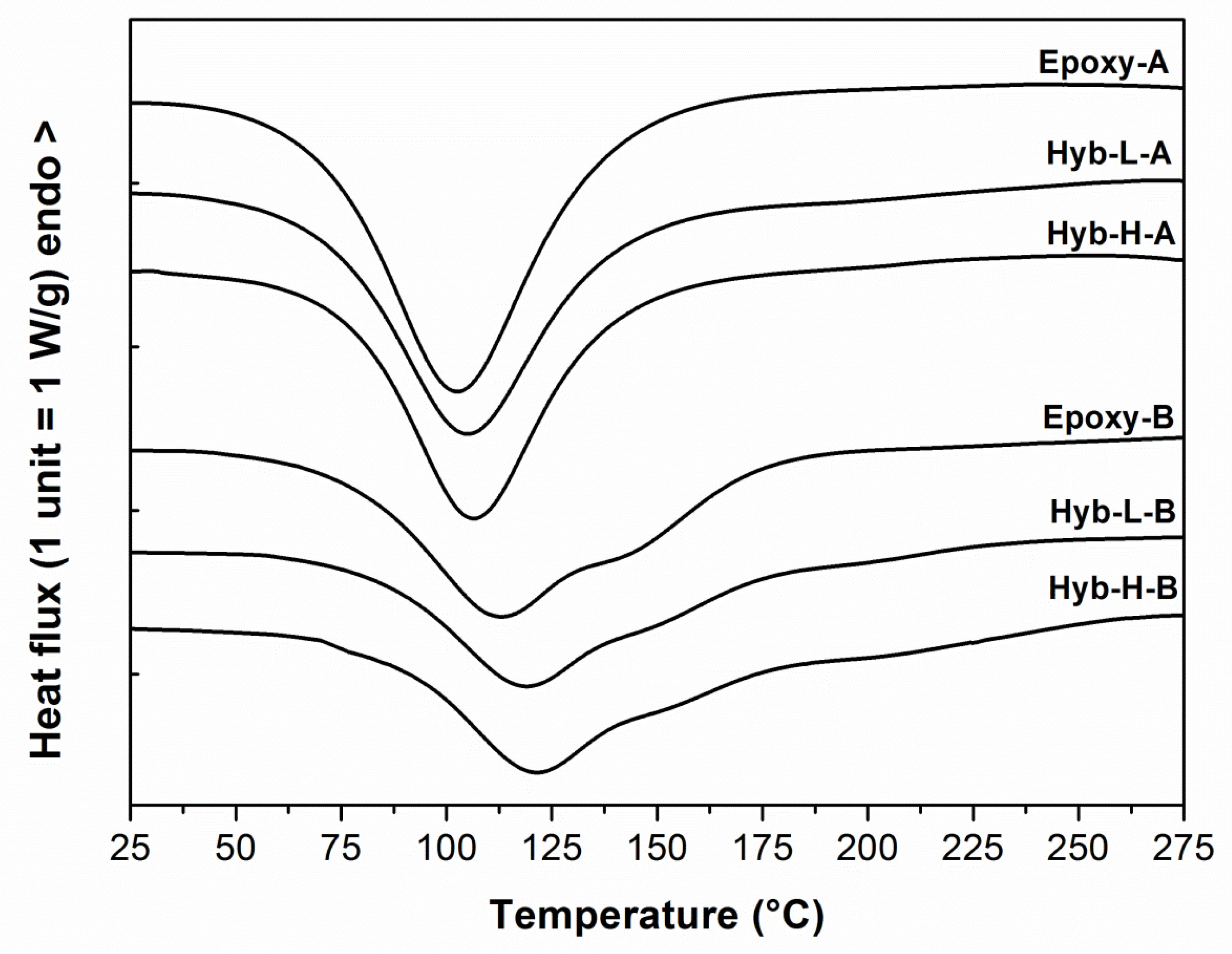
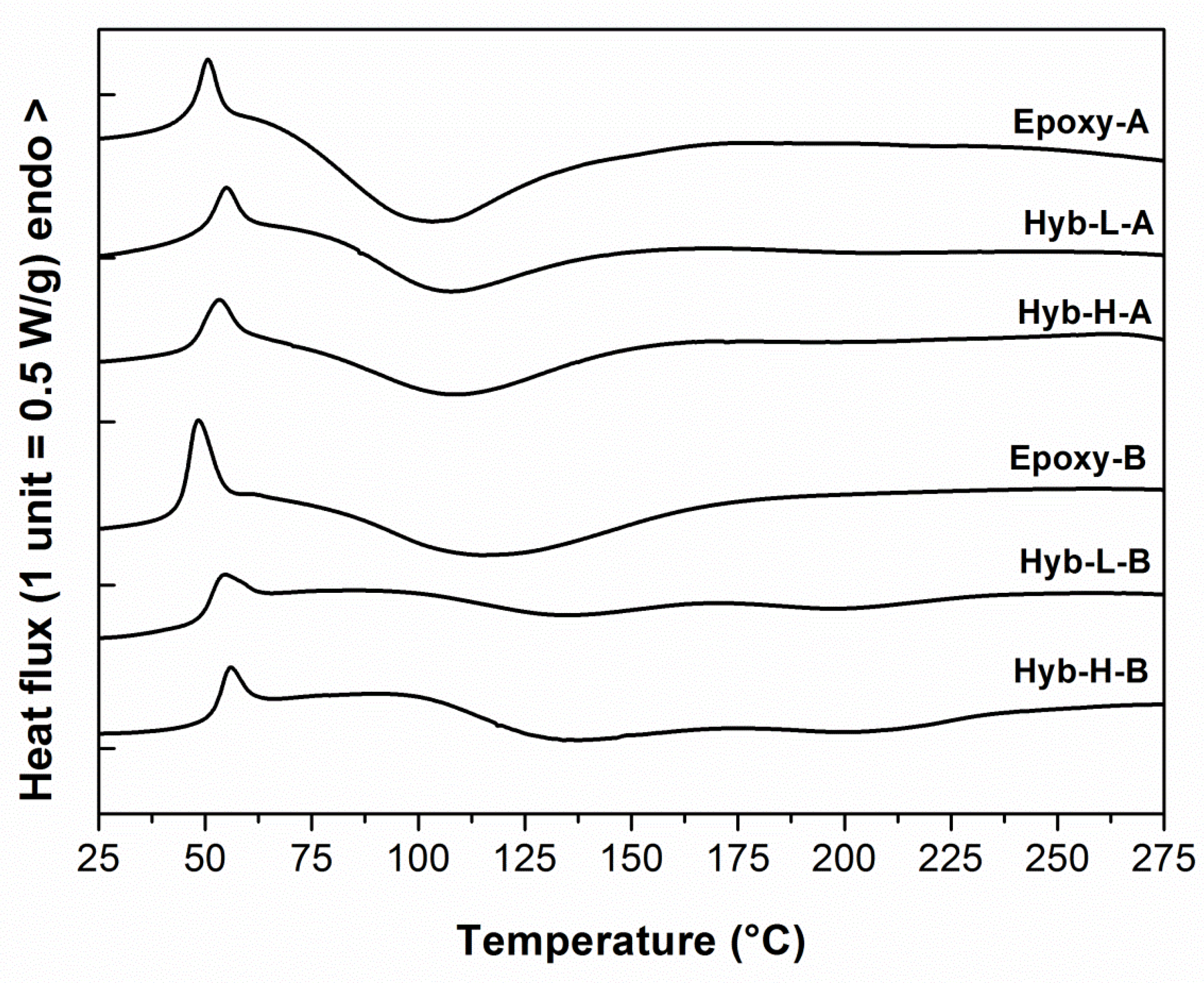
3.1. Cure Kinetics of the Organic Component of the Hybrid Formulation
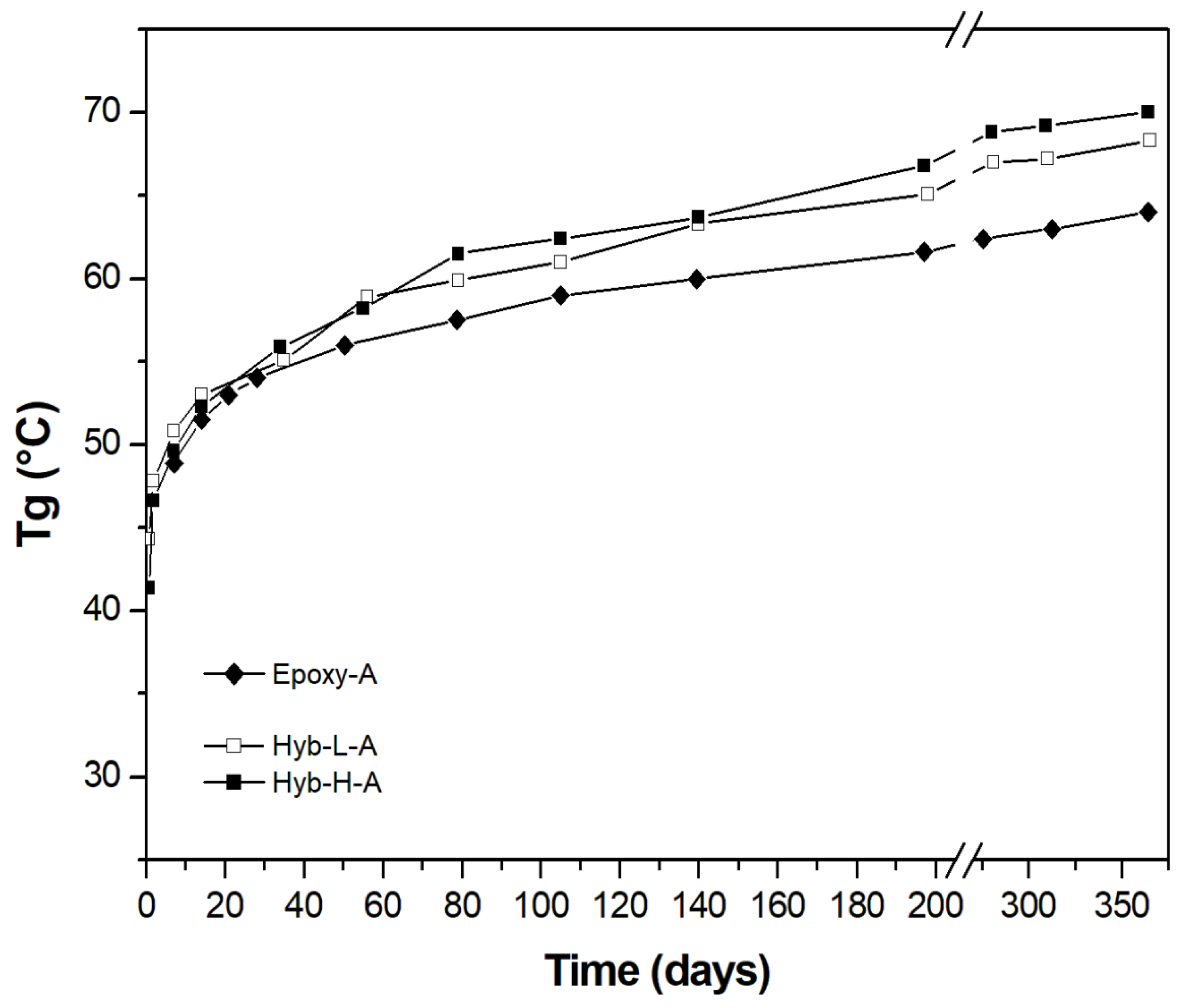
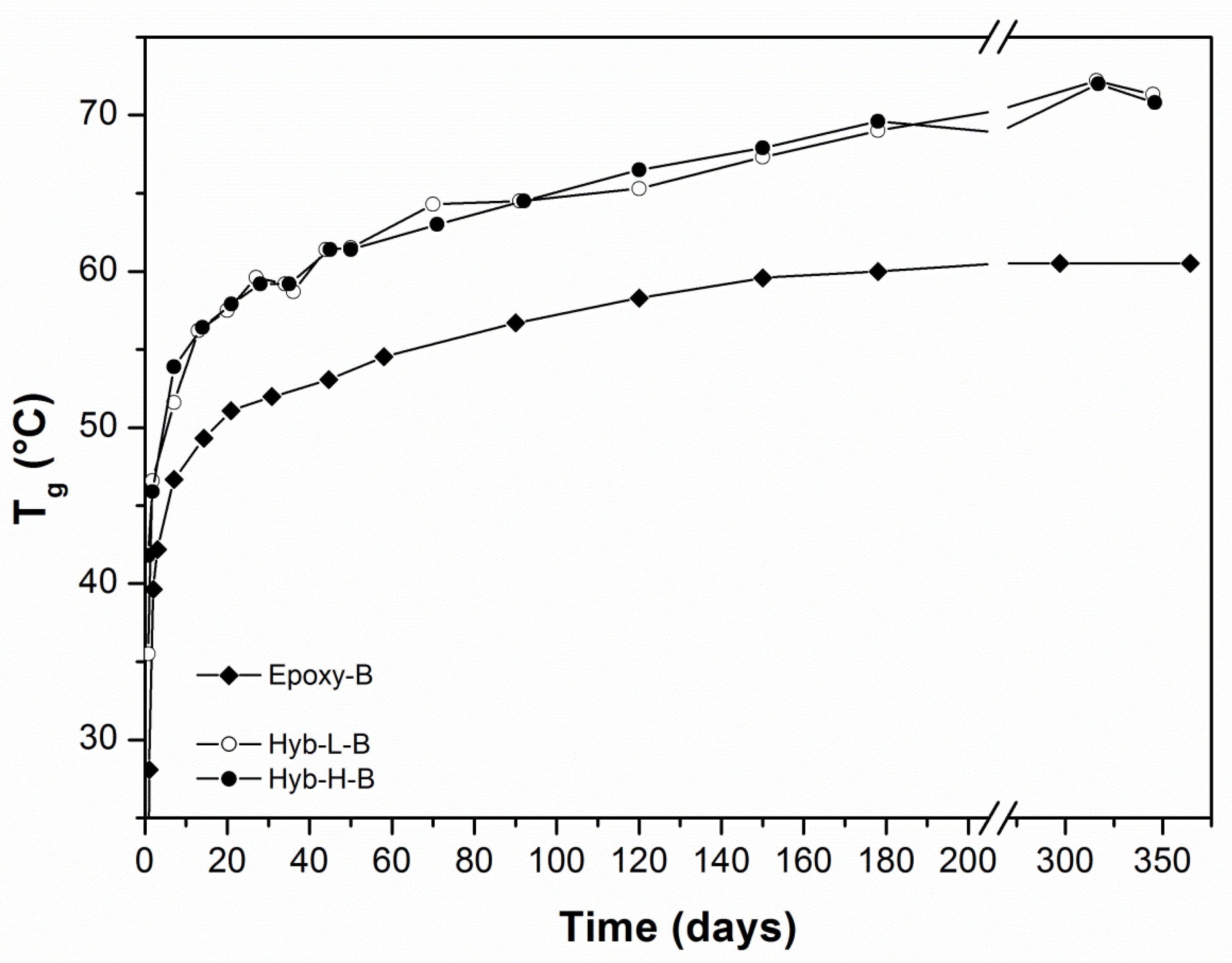
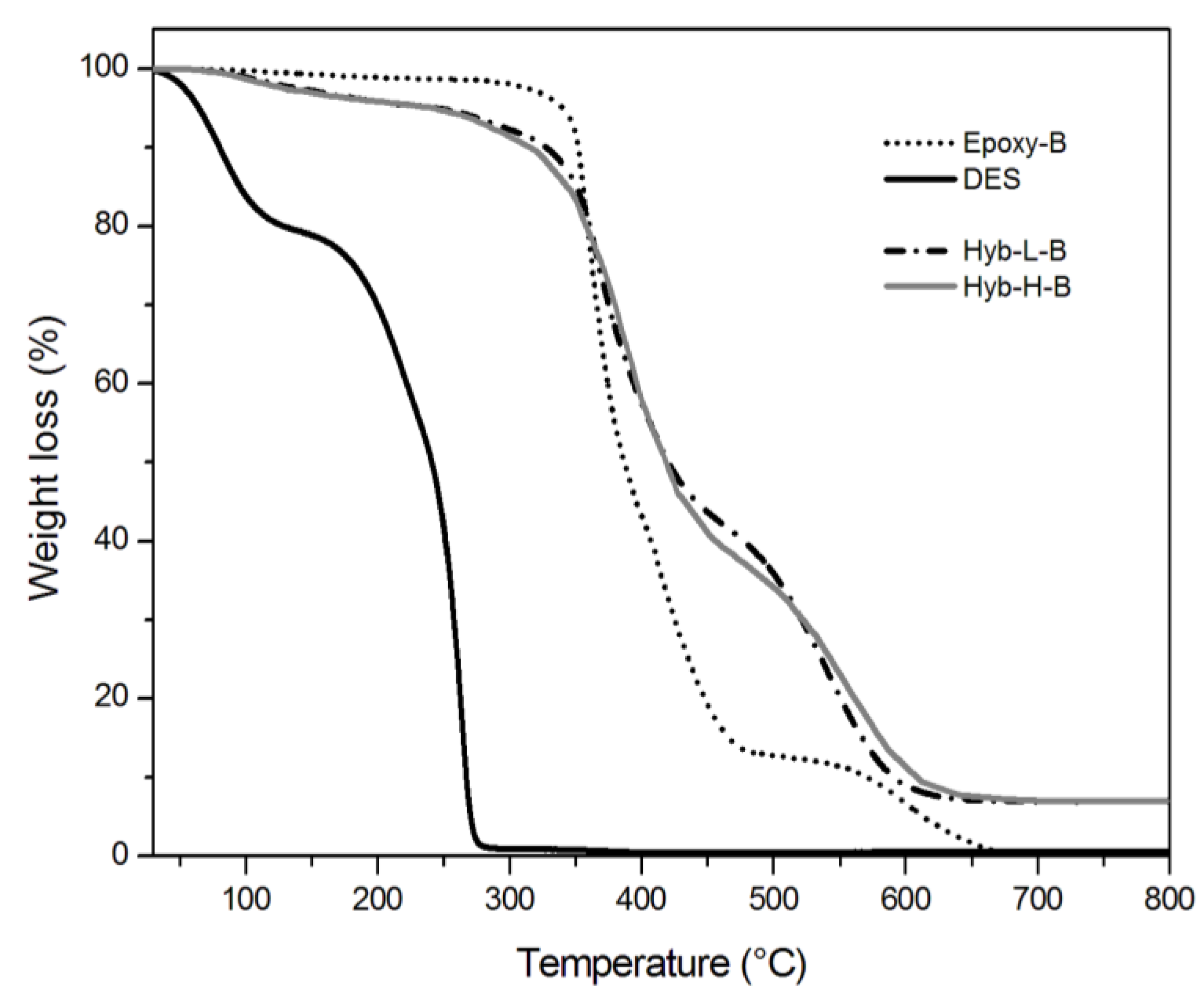
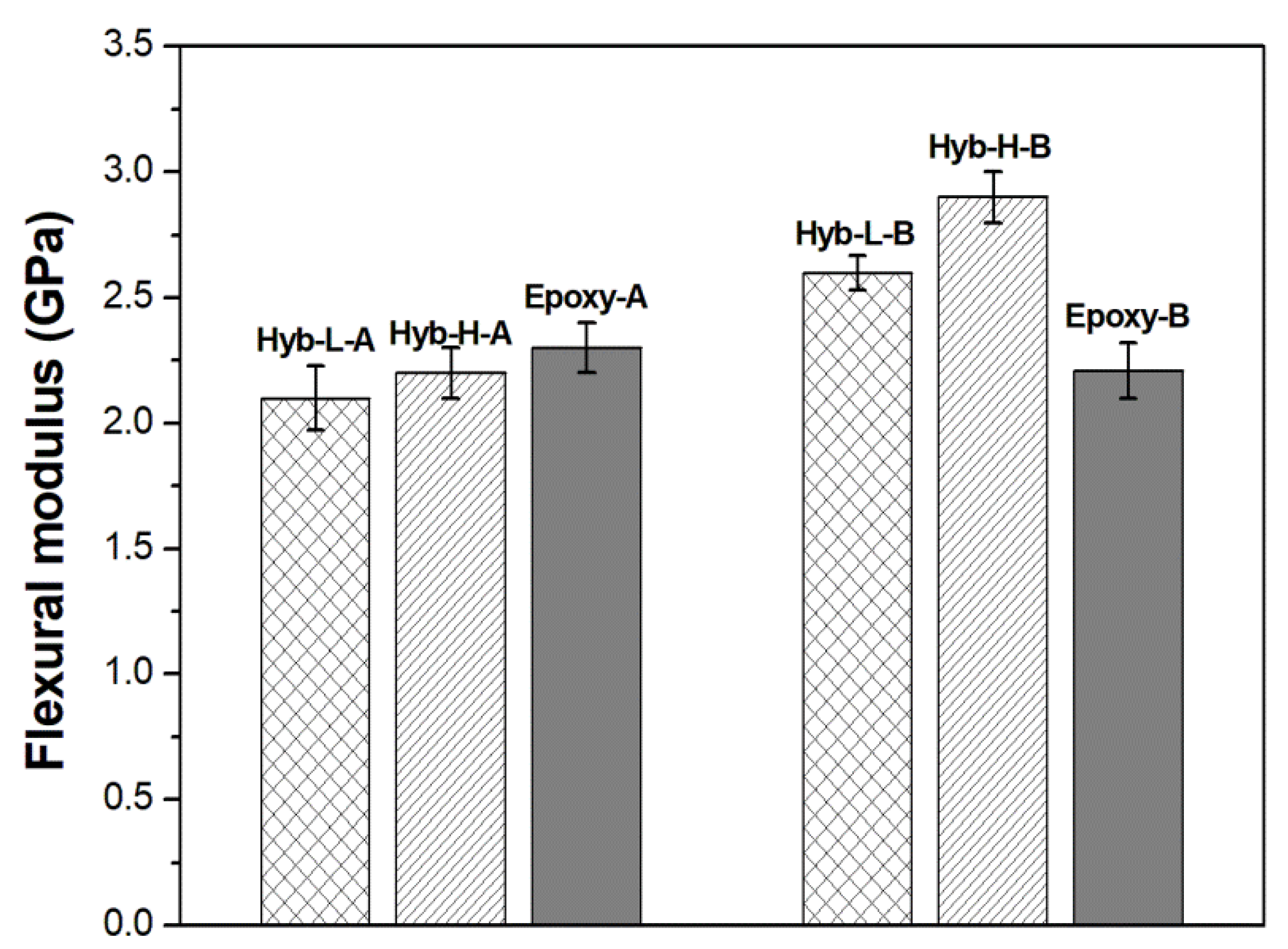
3.2. Characterization of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donadei, V.; Lionetto, F.; Wielandt, M.; Offringa, A.; Maffezzoli, A. Effects of Blank Quality on Press-Formed PEKK/Carbon Composite Parts. Materials 2018, 11, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodhbani, N.; Maréchal, P.; Duflo, H. Ultrasound monitoring of the cure kinetics of an epoxy resin: Identification, frequency and temperature dependence. Polym. Test. 2016, 56, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Anna, R.; Lionetto, F.; Montagna, F.; Maffezzoli, A. Lay-up and consolidation of a composite pipe by in situ ultrasonic welding of a thermoplastic matrix composite tape. Materials 2018, 11, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, F.; Balle, F.; Maffezzoli, A. Hybrid ultrasonic spot welding of aluminum to carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 247, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, F.; Dell’Anna, R.; Montagna, F.; Maffezzoli, A. Modeling of continuous ultrasonic impregnation and consolidation of thermoplastic matrix composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 82, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettieri, M.; Lionetto, F.; Frigione, M.; Prezzi, L.; Mascia, L. Cold-cured epoxy-silica hybrids: Effects of large variation in specimen thickness on the evolution of the Tg and related properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, F.; Frigione, M. Environmental effects on the adhesion properties of nanostructured epoxy-silica hybrids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.M.; Correia, J.R.; Cabral-Fonseca, S. Durability of an epoxy adhesive used in civil structural applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 618–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentano, I.; Puglia, D.; Luzi, F.; Arciola, C.R.; Morena, F.; Martino, S.; Torre, L. Nanocomposites Based on Biodegradable Polymers. Materials 2018, 11, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, A.; Lionetto, F.; Maffezzoli, A. Processing and characterization of amorphous polyethylene terephthalate fibers for the alignment of carbon nanofillers in thermosetting resins. Polym. Compos. 2015, 36, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, L.; Bittolo Bon, S.; Pugno, N.M. Combining living microorganisms with regenerated silk provides nanofibril-based thin films with heat-responsive wrinkled states for smart food packaging. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdolotti, L.; Lavorgna, M.; Lamanna, R.; Di Maio, E.; Iannace, S. Polyurethane-silica hybrid foam by sol–gel approach: Chemical and functional properties. Polymer 2015, 56, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matejka, L. Hybrid Nanocomposites for Nanotechnology; Merhari, L., Ed.; Springer-Verlag US, CBS Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Piscitelli, F.; Lavorgna, M.; Buonocore, G.G.; Verdolotti, L.; Galy, J.; Mascia, L. Plasticizing and Reinforcing Features of Siloxane Domains in Amine-Cured Epoxy/Silica Hybrids. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, M.; Takahashi, R.; Terauchi, A. Phase structure and mechanical and adhesion properties of epoxy/silica hybrids. Polymer 2001, 42, 5151–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, M.; Matsumura, T. Thermomechanical properties and phase structure of epoxy/silica nano-hybrid materials constructed from a linear silicone oligomer. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2005, 43, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.; Wang, H.M.; Akid, R. Effects of the addition of inorganic nanoparticles on the adhesive strength of a hybrid sol–gel epoxy system. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2010, 30, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.; Siddiqi, H.M. A comprehensive study of the bicontinuous epoxy–silica hybrid polymers: I. Synthesis, characterization and glass transition. Polymer 2011, 52, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macan, J.; Ivankovic, H.; Ivankovic, M.; Mencer, H.J. Synthesis and characterization of organic–inorganic hybrids based on epoxy resin and 3-glycidyloxypropyltrimethoxysilane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondioli, F.; Darecchio, M.E.; Luyt, A.S.; Messori, M. Epoxy resin modified with in situ generated metal oxides by means of sol–gel process. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 1792–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, S.K.; Ul Haq, E.; Licciulli, A. Synthesis of silica cryogel-glass fiber blanket by vacuum drying. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 7216–7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, F.; Mascia, L.; Frigione, M. Evolution of transient states and properties of an epoxy-silica hybrid cured at ambient temperature. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 1298–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, R.K.; Donato, K.Z.; Schrekker, H.S.; Matějka, L. Tunable reinforcement of epoxy-silica nanocomposites with ionic liquids. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9939–9948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, R.K.; Lavorgna, M.; Musto, P.; Donato, K.Z.; Jager, A.; Štěpánek, P.; Schrekker, H.S.; Matějka, L. The role of ether-functionalized ionic liquids in the sol-gel process: Effects on the initial alkoxide hydrolysis steps. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 447, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, K.Z.; Donato, R.K.; Lavorgna, M.; Ambrosio, L.; Matějka, L.; Mauler, R.S.; Schrekker, H.S. Ionic liquids as dynamic templating agents for sol–gel silica systems: Synergistic anion and cation effect on the silica structured growth. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 76, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, R.K.; Perchacz, M.; Ponyrko, S.; Donato, K.Z.; Schrekker, H.S.; Beneš, H.; Matějka, L. Epoxy–silica nanocomposite interphase control using task-specific ionic liquids via hydrolytic and non-hydrolytic sol–gel processes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 91330–91339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, A.; Ramis, X.; Fernández-Francos, X. Epoxy Sol-Gel Hybrid Thermosets. Coatings 2016, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzini, B.; Gianoncelli, A.; Kaulich, B.; Kiskinova, M.; Mele, C.; Prasciolu, M. Corrosion of Ni in 1-butyl-1-methyl-pyrrolidinium bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) amide room-temperature ionic liquid: An in-situ X-ray imaging and spectromicroscopy study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 7968–7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzini, B.; Gianoncelli, A.; Kaulich, B.; Mele, C.; Prasciolu, M.; Kiskinova, M. Electrodeposition of manganese oxide from eutectic urea/choline chloride ionic liquid: An in situ study based on soft X-ray spectromicroscopy and visible reflectivity. J. Power Sources 2012, 211, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.O.; Duarte, B.; Granadeiro, C.M.; Balula, S.S. Improving the Catalytic Performance of Keggin [PW12O40] 3-for Oxidative Desulfurization: Ionic Liquids versus SBA-15 Composite. Materials (Basel, Switzerland) 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, B.G.; Riany, N.; Silva, A.A.; Barra, G.M.O.; Livi, S. Dual-role of phosphonium–Based ionic liquid in epoxy/MWCNT systems: Electric, rheological behavior and electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 84, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashchuk, A.; Fainleib, A.M.; Starostenko, O.; Grande, D. Application of ionic liquids in thermosetting polymers: Epoxy and cyanate ester resins. Express Polym. Lett. 2018, 12, 898–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.A.; Livi, S.; Netto, D.B.; Soares, B.G.; Duchet, J.; Gérard, J.-F. New epoxy systems based on ionic liquid. Polymer 2013, 54, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.K.L.; Livi, S.; Soares, B.G.; Pruvost, S.; Duchet-Rumeau, J.; Gérard, J.-F. Ionic liquids: A new route for the design of epoxy networks. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 4, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, F.; Timo, A.; Frigione, M. Curing kinetics of epoxy-deep eutectic solvent mixtures. Thermochim. Acta 2015, 612, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural deep eutectic solvents–solvents for the 21st century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H.; Arab, H.; Mokhtarifar, M.; Maghrebi, M.; Baniadam, M. The effect of choline-based ionic liquid on CNTs’ arrangement in epoxy resin matrix. Mater. Des. 2016, 91, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, R.-R.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.-C.; Lv, X.-Y.; Su, J.; Long, Y.-F.; Wen, Y.-X. Deep Eutectic Solvent Synthesis of LiMnPO4/C Nanorods as a Cathode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries. Materials 2017, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, J.D.M.; Sánchez-Leija, R.J.; Carranza, A.; Pojman, J.A.; del Monte, F.; Luna-Bárcenas, G. Free-radical polymerizations of and in deep eutectic solvents: Green synthesis of functional materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 78, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriazo, D.; Serrano, M.C.; Gutiérrez, M.C.; Ferrer, M.L.; del Monte, F. Deep-eutectic solvents playing multiple roles in the synthesis of polymers and related materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4996–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.; Jia, Y.; Yao, Y.; Sun, J.; Jing, Y. Structure and electrochemical behavior of ionic liquid analogue based on choline chloride and urea. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 65, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, A.-M.; Constantin, V.; Cojocaru, A.; Olteanu, M. Electrochemical behaviour of copper (II) chloride in choline chloride-urea deep eutectic solvent. Rev. Chim. (Buchar.) 2011, 62, 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Vanlandingham, M.R.; Eduljee, R.F.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr. Relationships between stoichiometry, microstructure, and properties for amine-cured epoxies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 71, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloundou, J.P.; Feve, M.; Gerard, J.F.; Harran, D.; Pascault, J.P. Temperature Dependence of the Behavior of an Epoxy−Amine System near the Gel Point through Viscoelastic Study. 1. Low-T g Epoxy−Amine System. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 6907–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, F.; Moscatello, A.; Maffezzoli, A. Effect of binder powders added to carbon fiber reinforcements on the chemoreology of an epoxy resin for composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 112, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. ASTM D790-03, Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Van Assche, G.; Van Hemelrijck, A.; Rahier, H.; Van Mele, B. Modulated differential scanning calorimetry: Non-isothermal cure, vitrification, and devitrification of thermosetting systems. Thermochim. Acta 1996, 286, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Assche, G.; Van Hemelrijck, A.; Rahier, H.; Van Mele, B. Modulated temperature differential scanning calorimetry: Cure, vitrification, and devitrification of thermosetting systems. Thermochim. Acta 1997, 304, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maka, H.; Spychaj, T.; Sikorski, W. Deep eutectic ionic liquids as epoxy resin curing agents. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2014, 19, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmathullah, M.A.M.; Jeyarajasingam, A.; Merritt, B.; VanLandingham, M.; McKnight, S.H.; Palmese, G.R. Room temperature ionic liquids as thermally latent initiators for polymerization of epoxy resins. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 3219–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurín, N.; Sanes, J.; Carrión, F.J.; Bermúdez, M.D. Self-healing of abrasion damage on epoxy resin controlled by ionic liquid. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 37258–37264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigione, M.; Naddeo, C.; Acierno, D. Cold-curing epoxy resins: Aging and environmental effects. I-Thermal properties. J. Polym. Eng. 2001, 21, 23–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M. Fabrication, quality and service-life issues for composites in civil engineering. In Durability of Composites for Civil Structural Applications; Woodhead Publishing Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 13–30. [Google Scholar]
- Savvilotidou, M.; Vassilopoulos, A.P.; Frigione, M.; Keller, T. Effects of aging in dry environment on physical and mechanical properties of a cold-curing structural epoxy adhesive for bridge construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 140, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.-H.; Wu, P.-C.; Bai, Y.-H. Eutectic mixture of choline chloride/urea as a green solvent in synthesis of a coordination polymer: [Zn(O3PCH2CO2)]·NH4. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2005, 8, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Q.; Binder, L. Synthesis and characterization of choline chloride based binary mixtures. ECS Trans. 2010, 33, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito Corcione, C.; Striani, R.; Frigione, M. Microgel Modified UV-Cured Methacrylic-Silica Hybrid: Synthesis and Characterization. Materials 2013, 6, 3805–3825. [Google Scholar]
- Pervin, F.; Zhou, Y.; Rangari, V.K.; Jeelani, S. Testing and evaluation on the thermal and mechanical properties of carbon nano fiber reinforced SC-15 epoxy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 405, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mąka, H.; Spychaj, T.; Zenker, M. High performance epoxy composites cured with ionic liquids. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 31, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.K.L.; Soares, B.G.; Duchet-Rumeau, J.; Livi, S. Dual functions of ILs in the core-shell particle reinforced epoxy networks: Curing agent vs dispersion aids. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 140, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| System | Ionic liquid content [phr] | Curing agent |
|---|---|---|
| Epoxy-A | 0 | aliphatic |
| Hyb-L-A | 2.5 | aliphatic |
| Hyb-H-A | 5 | aliphatic |
| Epoxy-B | 0 | cycloaliphatic |
| Hyb- L-B | 2.5 | cycloaliphatic |
| Hyb- H-B | 5 | cycloaliphatic |
| System | ΔHa (J/g) | Tonseta (°C) | Tpeaka (°C) | Tgb (°C) | Gelation time at 40 °Cc (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy-A | 510.1 ± 14.1 | 63.8 ± 1.0 | 103.2 ± 1.5 | 122.8 ± 2.5 | 48.0 ± 1.5 |
| Hyb-L-A | 461.9 ± 9.2 | 70.3 ± 2.3 | 105.4 ± 2.0 | 110.7 ± 2.3 | 63.2 ± 2.0 |
| Hyb-H-A | 493.9 ± 10.1 | 74.7 ± 1.9 | 107.2 ± 1.6 | 112.2 ± 1.9 | 67.4 ± 1.8 |
| Epoxy-B | 415.9 ± 8.4 | 75.7 ± 1.7 | 113.4 ± 2.0 | 126.5 ± 1.8 | 98.2 ± 2.3 |
| Hyb-L-B | 436.7 ± 7.3 | 78.5 ± 1.9 | 119.3 ± 1.8 | 145.8 ± 2.3 | 116.4 ± 2.6 |
| Hyb-H-B | 472.3 ± 9.1 | 85.4 ± 2.1 | 121.9 ± 1.7 | 152.4 ± 2.1 | 149.0 ± 2.7 |
| System | Residual weight at 800 °C (%) | T0.1a (°C) | T0.5b (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy-A | 0.1 ± 0 | 328.3 ± 1.5 | 362.6 ± 0.9 |
| Hyb-L-A | 5.1 ± 0.03 | 309.0 ± 1.0 | 403.7 ± 1.5 |
| Hyb-H-A | 5.3 ± 0.08 | 297.3 ± 1.0 | 397.2 ± 1.4 |
| Epoxy-B | 0.1 ± 0 | 351.7 ± 0.9 | 386.7 ± 1.1 |
| Hyb-L-B | 7.0 ± 0.07 | 327.3 ± 1.1 | 420.7 ± 1.5 |
| Hyb-H-B | 7.1 ± 0.08 | 316.0 ± 1.2 | 419.5 ± 1.6 |
| DES | 0.1 ± 0 | 80.2 ± 1.0 | 241.3 ± 1.0 |
| SYSTEM | FLEXURAL STRENGHT (MPa) | FLEXURAL STRAIN (%) | FLEXURAL MODULUS (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy-A | 42.5 ± 2.0 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 2.3 ± 0.1 |
| Hyb-L-A | 64.4 ± 4.1 | 3.7 ± 1.6 | 2.1 ± 0.9 |
| Hyb-H-A | 56.3 ± 3.2 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.1 |
| Epoxy-B | 30.9 ± 4.5 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.1 |
| Hyb-L-B | 61.8 ± 2.4 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 2.6 ± 0.1 |
| Hyb-H-B | 37.8 ± 0.9 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 2.9 ± 0.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lionetto, F.; Timo, A.; Frigione, M. Cold-Cured Epoxy-Based Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Resins Containing Deep Eutectic Solvents. Polymers 2019, 11, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010014
Lionetto F, Timo A, Frigione M. Cold-Cured Epoxy-Based Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Resins Containing Deep Eutectic Solvents. Polymers. 2019; 11(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleLionetto, Francesca, Alessia Timo, and Mariaenrica Frigione. 2019. "Cold-Cured Epoxy-Based Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Resins Containing Deep Eutectic Solvents" Polymers 11, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010014
APA StyleLionetto, F., Timo, A., & Frigione, M. (2019). Cold-Cured Epoxy-Based Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Resins Containing Deep Eutectic Solvents. Polymers, 11(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010014