A Sandwich-Structured Piezoresistive Sensor with Electrospun Nanofiber Mats as Supporting, Sensing, and Packaging Layers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
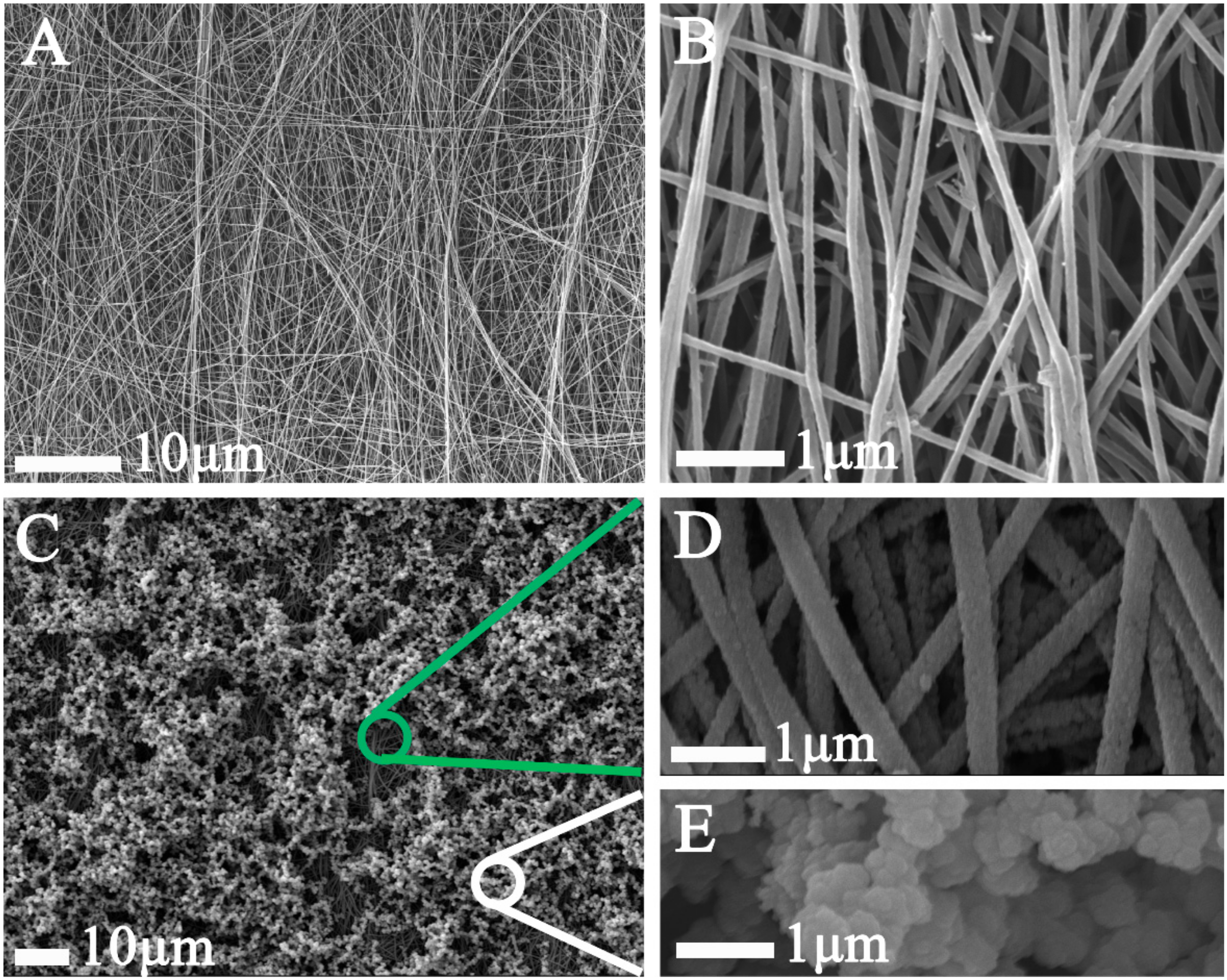
2.2. Preparation of PLA–SF–COL Nanofiber Mats by Electrospinning
2.3. Fabrication of the Conductive Layers
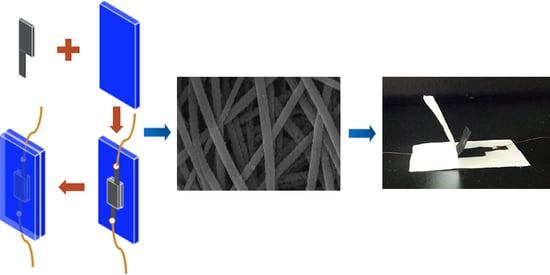
2.4. Construction of Sandwich-Structured Piezoresistive Sensors
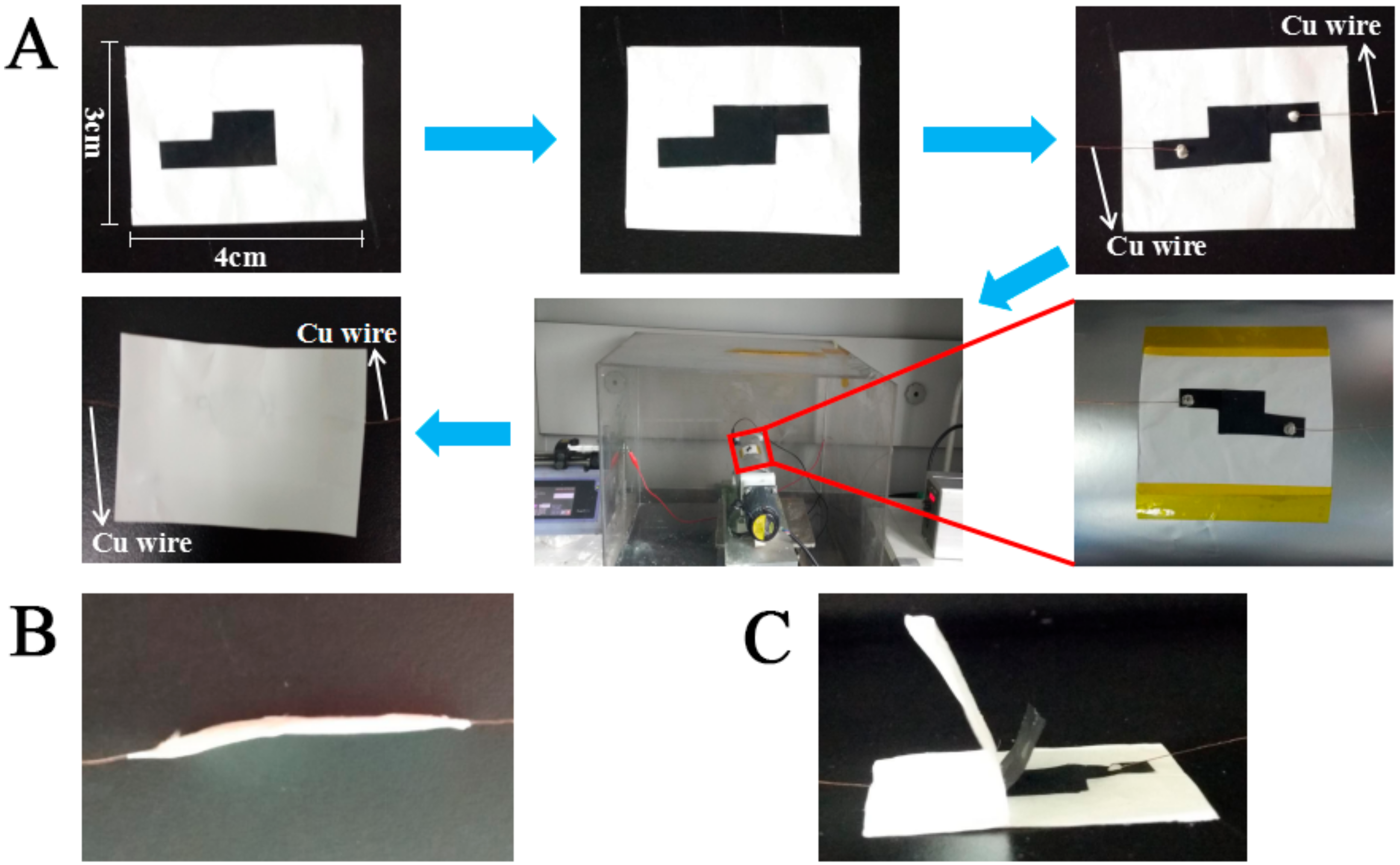
2.5. Characterizations and Measurements
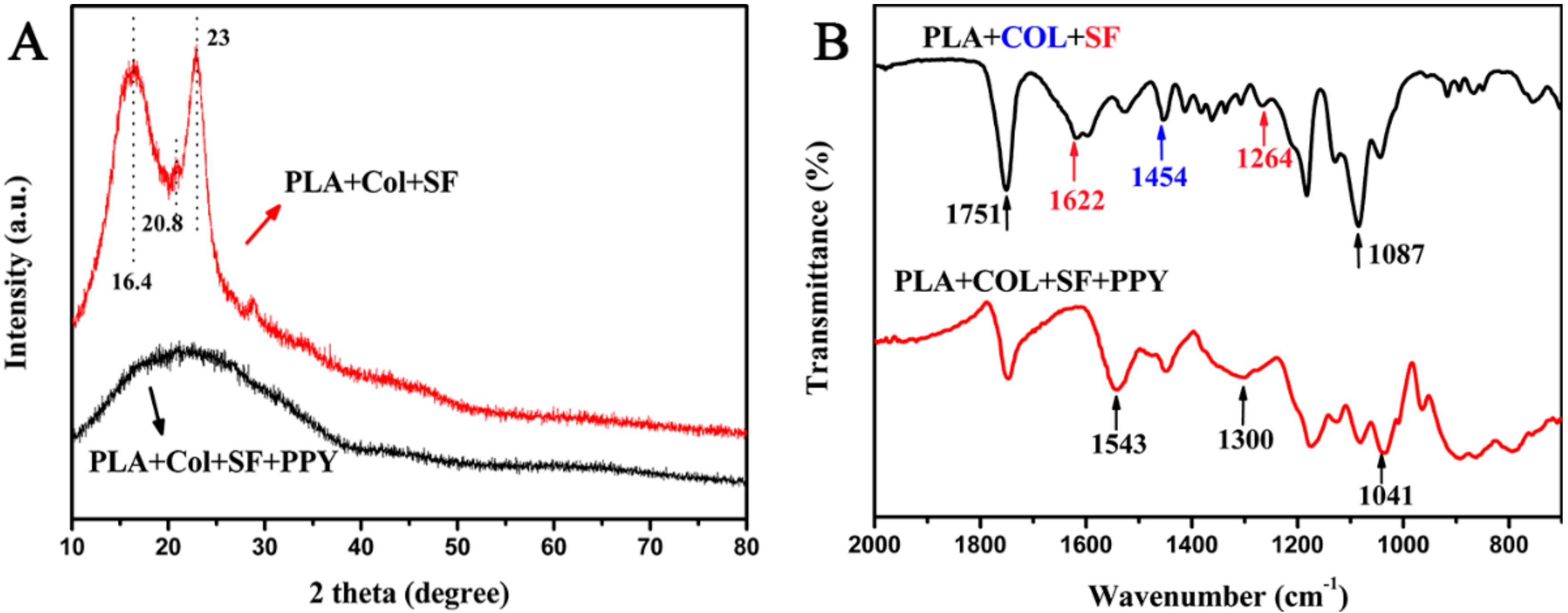
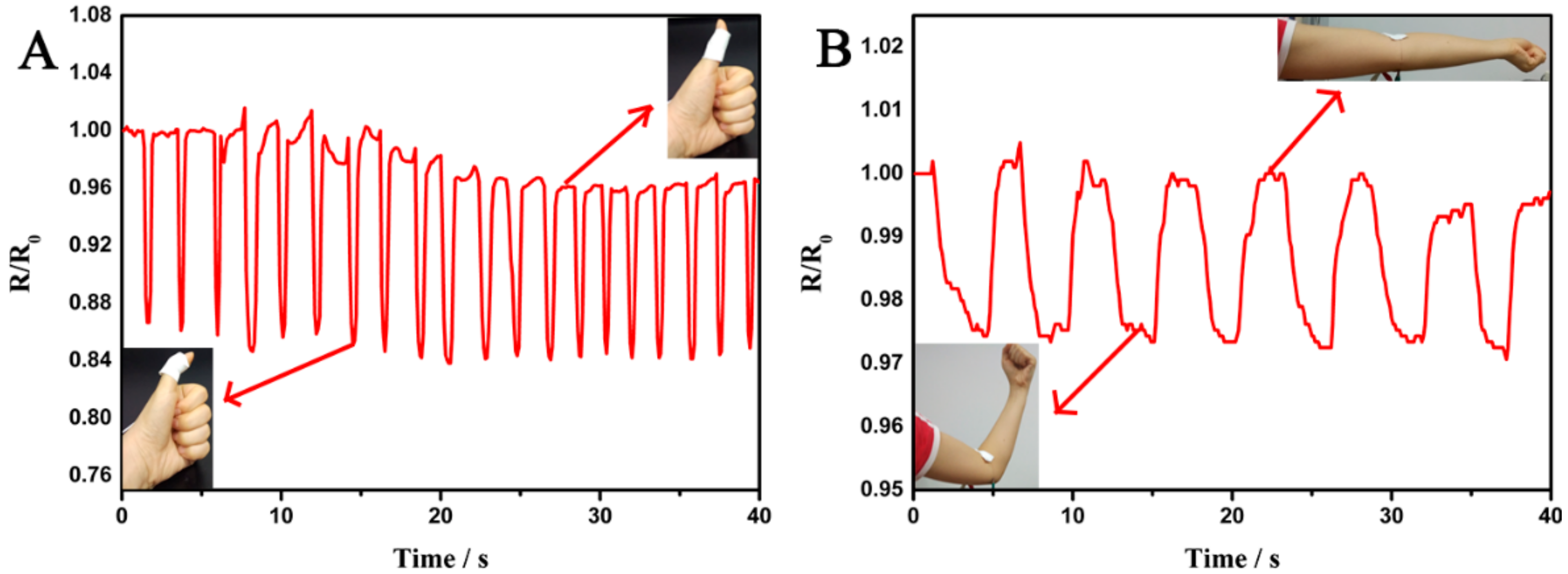
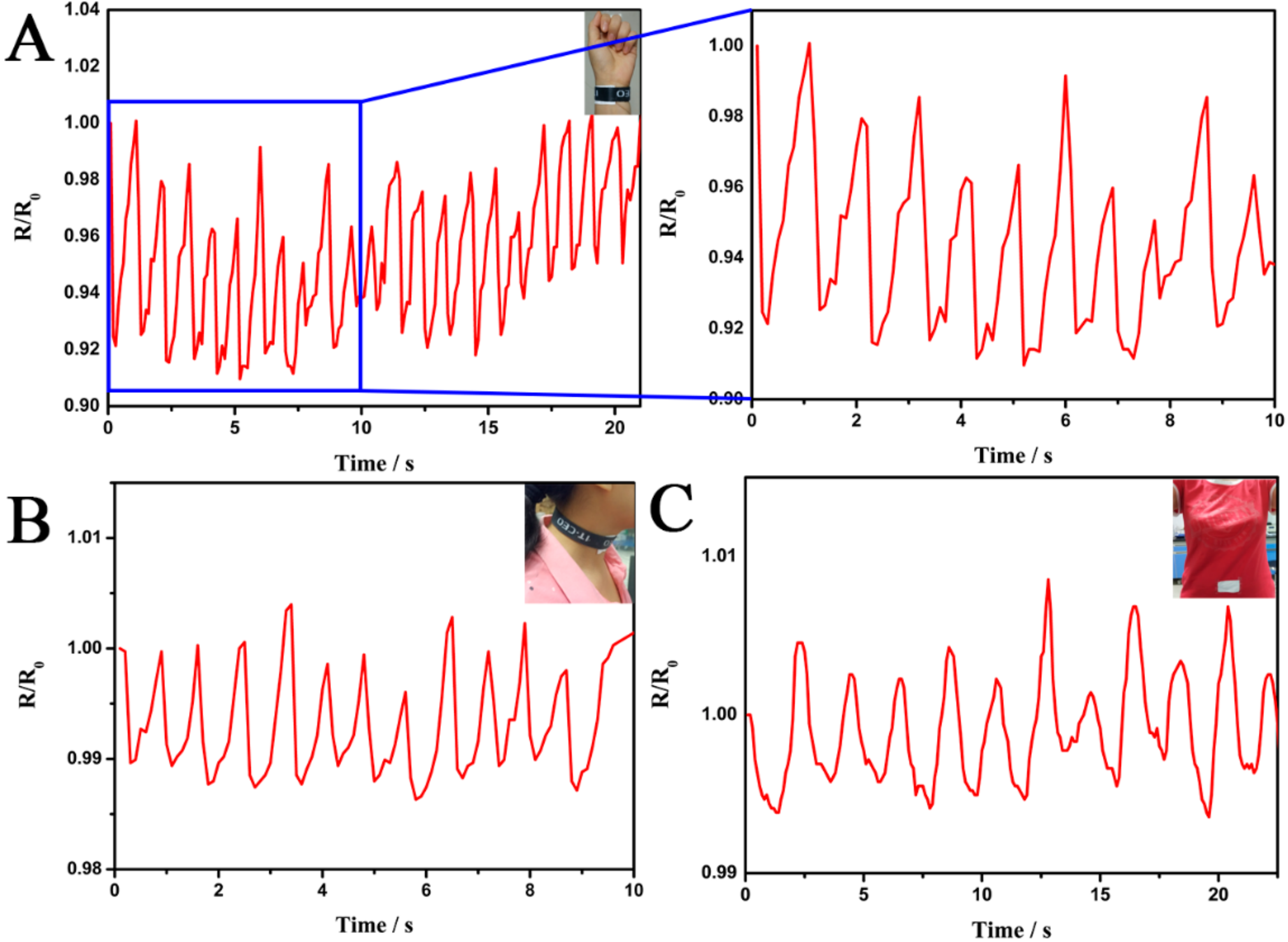
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dagdeviren, C.; Shi, Y.; Joe, P.; Ghaffari, R.; Balooch, G.; Usgaonkar, K.; Gur, O.; Tran, P.L.; Crosby, J.R.; Meyer, M.; et al. Conformal piezoelectric systems for clinical and experimental characterization of soft tissue biomechanics. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Li, X.; Zang, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, K.; Wu, D.; Zhu, H. Wearable and highly sensitive graphene strain sensors for human motion monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4666–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, T. Silk-molded flexible, ultrasensitive, and highly stable electronic skin for monitoring human physiological signals. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, E.; Hwang, B.-U.; Kim, D.; Bo-Yeong, K.; Lee, N.-E. Stretchable, transparent, ultrasensitive, and patchable strain sensor for human-machine interfaces comprising a nanohybrid of carbon nanotubes and conductive elastomers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6252–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Shao, J.; An, N.; Li, X.; Tian, H.; Xu, C.; Ding, Y. Self-powered flexible pressure sensors with vertically well-aligned piezoelectric nanowire arrays for monitoring vital signs. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 11806–11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, C.; Lee, G.Y.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, H.N.; Ahn, S.H.; Suh, K.Y. A flexible and highly sensitive strain-gauge sensor using reversible interlocking of nanofibres. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagdeviren, C.; Su, Y.; Joe, P.; Yona, R.; Liu, Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Huang, Y.; Damadoran, A.R.; Xia, J.; Martin, L.W.; et al. Conformable amplified lead zirconate titanate sensors with enhanced piezoelectric response for cutaneous pressure monitoring. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wei, D.; Tang, L.; Song, X.; Luo, W.; Chu, J.; Gao, T.; Shi, H.; Du, C. Wearable temperature sensor based on graphene nanowalls. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 25609–25615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Mao, C.; Li, C.M. Silk fabric-based wearable thermoelectric generator for energy harvesting from the human body. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hua, Q.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, C. Flexible, stretchable and wearable multifunctional sensor array as artificial electronic skin for static and dynamic strain mapping. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seung, W.; Gupta, M.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Shin, K.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, S.; Lin, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.-W. Nanopatterned textile-based wearable triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3501–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, S.; Cha, S.N.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, J.M.; Chou, L.J.; Wang, Z.L. A hybrid piezoelectric structure for wearable nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Lei, J.; Yang, D.; Yin, B.; Zhang, H.; Bian, J.; Ji, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, Y.; et al. Enhanced performance of wearable piezoelectric nanogenerator fabricated by two-step hydrothermal process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 113903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Jiang, K.; Shen, G. An ultra-sensitive and rapid response speed graphene pressure sensors for electronic skin and health monitoring. Nano Energy 2016, 23, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Z. Flexible and wearable electronic silk fabrics for human physiological monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 095033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, B.C.; Wang, C.; Allen, R.; Bao, Z. An electrically and mechanically self-healing composite with pressure- and flexion-sensitive properties for electronic skin applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.; Gao, E.; Jian, M.; Xia, K.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Ren, T.; Zhang, Y. Carbonized silk fabric for ultrastretchable, highly sensitive, and wearable strain sensors. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6640–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, J.; Tolle, C.R.; Zhu, Z. A highly stretchable strain sensor based on electrospun carbon nanofibers for human motion monitoring. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 79114–79120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Avilés, A.I.; Avilés, F.; Sosa, V. Electrical and piezoresistive properties of multi-walled carbon nanotube/polymer composite films aligned by an electric field. Carbon 2011, 49, 2989–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, J.; Tolle, C.R.; Zhu, Z. Flexible and compressible PEDOT:PSS@melamine conductive sponge prepared via one-step dip coating as piezoresistive pressure sensor for human motion detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16077–16086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Fang, G.; Wan, J.; Zhou, H.; Long, H.; Zhao, X. Electrospun pedot:Pss–pva nanofiber based ultrahigh-strain sensors with controllable electrical conductivity. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 18962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Meguro, H.; Okamoto, S.; Kimura, M. Flexible tactile sensor using the reversible deformation of poly(3-hexylthiophene) nanofiber assemblies. Langmuir 2012, 28, 17593–17596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chronakis, I.S.; Grapenson, S.; Jakob, A. Conductive polypyrrole nanofibers via electrospinning: Electrical and morphological properties. Polymer 2006, 47, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Vepari, C.; Jin, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Electrospun silk-BMP-2 scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3115–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, B.-M.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.H.; Nam, Y.S.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. Electrospinning of silk fibroin nanofibers and its effect on the adhesion and spreading of normal human keratinocytes and fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Zhou, S.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Luo, C.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Weng, J. Osteoblast function on electrically conductive electrospun PLA/MWCNTs nanofibers. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2821–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H. Human bone marrow stromal cell responses on electrospun silk fibroin mats. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2685–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Electrospinning: A fascinating method for the preparation of ultrathin fibers. Angew. Chem. 2007, 46, 5670–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Helfricht, N.; Papastavrou, G.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Low-density self-assembled poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) sponges with ultrahigh and extremely fast water uptake and release. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, e1700838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Multilevel porous structured polyvinylidene fluoride/polyurethane fibrous membranes for ultrahigh waterproof and breathable application. Compos. Commun. 2017, 6, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Duan, G.; Kuhn, U.; Morl, M.; Altstadt, V.; Yarin, A.L.; Greiner, A. Spongy gels by a top-down approach from polymer fibrous sponges. Angew. Chem. 2017, 56, 3285–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainab, G.; Iqbal, N.; Babar, A.A.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Free-standing, spider-web-like polyamide/carbon nanotube composite nanofibrous membrane impregnated with polyethyleneimine for CO2 capture. Compos. Commun. 2017, 6, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W.; Fong, H.; Zhu, Z. Three-dimensional and ultralight sponges with tunable conductivity assembled from electrospun nanofibers for a highly sensitive tactile pressure sensor. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 10288–10294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetia, K.; Schnorr, J.M.; Mannarino, M.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Rutledge, G.C.; Swager, T.M.; Hammond, P.T. Spray-layer-by-layer carbon nanotube/electrospun fiber electrodes for flexible chemiresistive sensor applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Jeong, Y.R.; Yun, J.; Hong, S.Y.; Jin, S.; Lee, S.-J.; Zi, G.; Ha, J.S. Stretchable array of highly sensitive pressure sensors consisting of polyaniline nanofibers and Au-coated polydimethylsiloxane micropillars. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9974–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Hu, X.; Lin, W.; Dong, C.; Wu, H. Electrospun PLGA-silk fibroin-collagen nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2011, 47, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucchi, I.; Boschi, A.; Arosio, C.; Bertini, F.; Freddi, G.; Catellani, M. Bio-based conductive composites: Preparation and properties of polypyrrole (PPy)-coated silk fabrics. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, H.; Tang, T.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jia, J. Facile electrochemical polymerization of polypyrrole film applied as cathode material in dual rotating disk photo fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2016, 324, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Nie, J.; Yang, D. Electrospun poly(lactic acid)/chitosan core-shell structure nanofibers from homogeneous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahab, M.A.; Flynn, A.; Chiou, B.-S.; Imam, S.; Orts, W.; Chiellini, E. Thermal, mechanical and morphological characterization of plasticized PLA–PHB blends. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.J.; Park, J.; Kim, H.J.; Wada, M.; Kaplan, D.L. Three-dimensional aqueous-derived biomaterial scaffolds from silk fibroin. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2775–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, S.-H.; Lee, E.-J.; Wang, P.; Kim, H.-E. Collagen/hydroxyapatite composite nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3055–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, H.; Park, E.J.; Gal, Y.-S.; Lim, K.T. Synthesis and characterization of polypyrrole–TiO2 nanocomposites in supercritical CO2. Colloids Surf. A 2008, 313, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chougule, M.A.; Pawar, S.G.; Godse, P.R.; Mulik, R.N.; Sen, S.; Patil, V.B. Synthesis and characterization of polypyrrole (PPy) thin films. Soft Nanosci. Lett. 2011, 1, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.F.; Senthilkumar, R.; Noel, M.; Kulandainathan, M.A. Polypyrrole microstructure deposited by chemical and electrochemical methods on cotton fabrics. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Dai, L.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J. A facile synthesis of polypyrrole/carbon nanotube composites with ultrathin, uniform and thickness-tunable polypyrrole shells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghoubidoust, F.; Wicaksono, D.H.B.; Chandren, S.; Nur, H. Effect of graphene oxide on the structural and electrochemical behavior of polypyrrole deposited on cotton fabric. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1075, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, W.; Liang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Preparation of chitosan/PLA blend micro/nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 658–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhua, A.; Zhangb, M.; Wua, J.; Shen, J. Covalent immobilization of chitosan/heparin complex with a photosensitive hetero-bifunctional crosslinking reagent on PLA surface. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4657–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, I.C.; Kweon, H.; Park, Y.H.; Hudson, S. Structural characteristics and properties of the regenerated silk fibroin prepared from formic acid. Biomaterials 2001, 29, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belbachir, K.; Noreen, R.; Gouspillou, G.; Petibois, C. Collagen types analysis and differentiation by FTIR spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Li, Q.; Fan, L.; Lan, Z.; Li, P.; Lin, J.; Hao, S. High-performance polypyrrole nanoparticles counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 2008, 181, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Li, B.; Xu, L.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, F.; Xia, Q.; Lu, Z. A Sandwich-Structured Piezoresistive Sensor with Electrospun Nanofiber Mats as Supporting, Sensing, and Packaging Layers. Polymers 2018, 10, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060575
Zhao Z, Li B, Xu L, Qiao Y, Wang F, Xia Q, Lu Z. A Sandwich-Structured Piezoresistive Sensor with Electrospun Nanofiber Mats as Supporting, Sensing, and Packaging Layers. Polymers. 2018; 10(6):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060575
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zicong, Bintian Li, Liqun Xu, Yan Qiao, Feng Wang, Qingyou Xia, and Zhisong Lu. 2018. "A Sandwich-Structured Piezoresistive Sensor with Electrospun Nanofiber Mats as Supporting, Sensing, and Packaging Layers" Polymers 10, no. 6: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060575
APA StyleZhao, Z., Li, B., Xu, L., Qiao, Y., Wang, F., Xia, Q., & Lu, Z. (2018). A Sandwich-Structured Piezoresistive Sensor with Electrospun Nanofiber Mats as Supporting, Sensing, and Packaging Layers. Polymers, 10(6), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060575