Controlled Preparation of Thermally Stable Fe-Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Composite by Magnetic Induction Heating
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Cured PDMS at Room Temperature
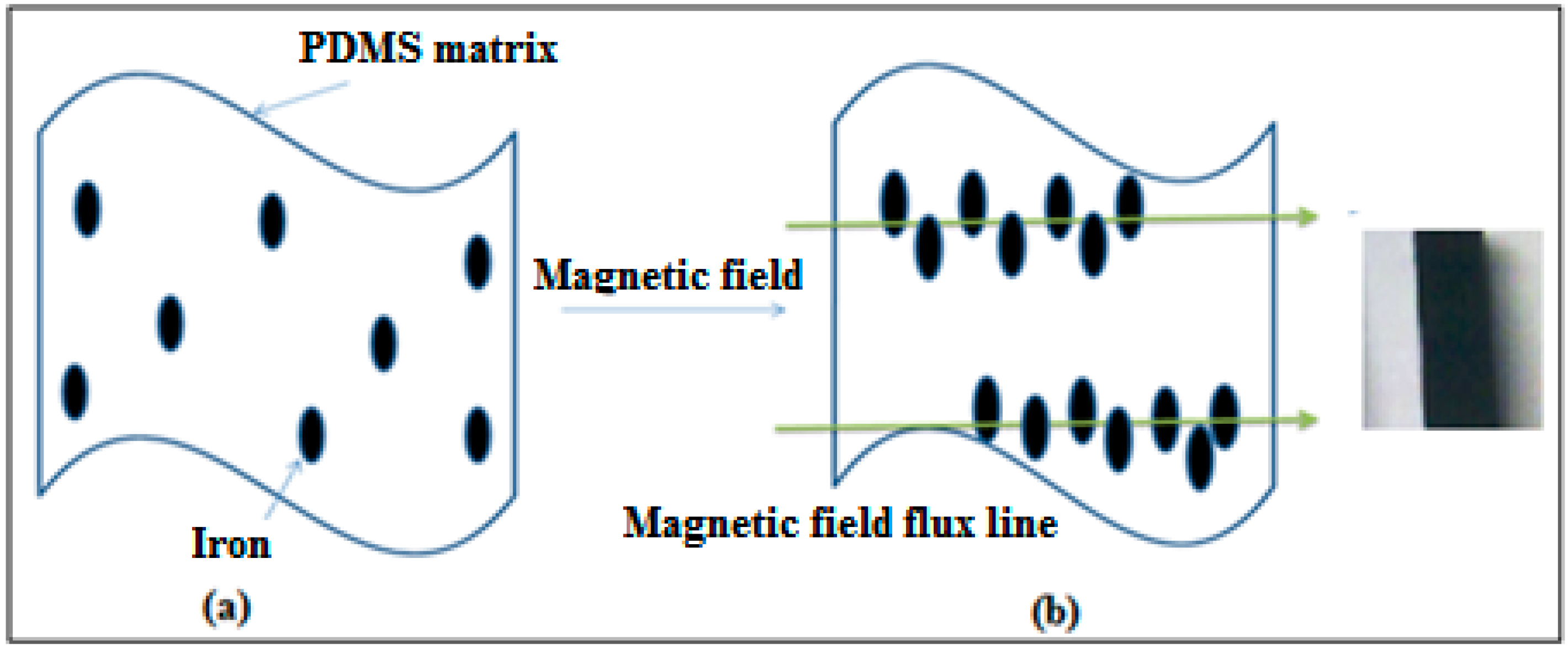
2.3. Preparation of Fe-PDMS Composites via Induction Heating
2.4. Swelling in PDMS Samples
2.5. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
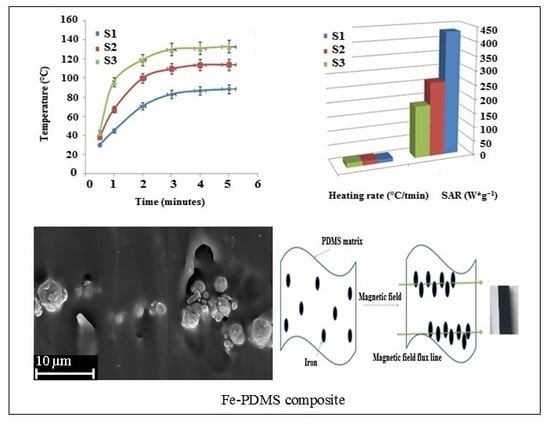
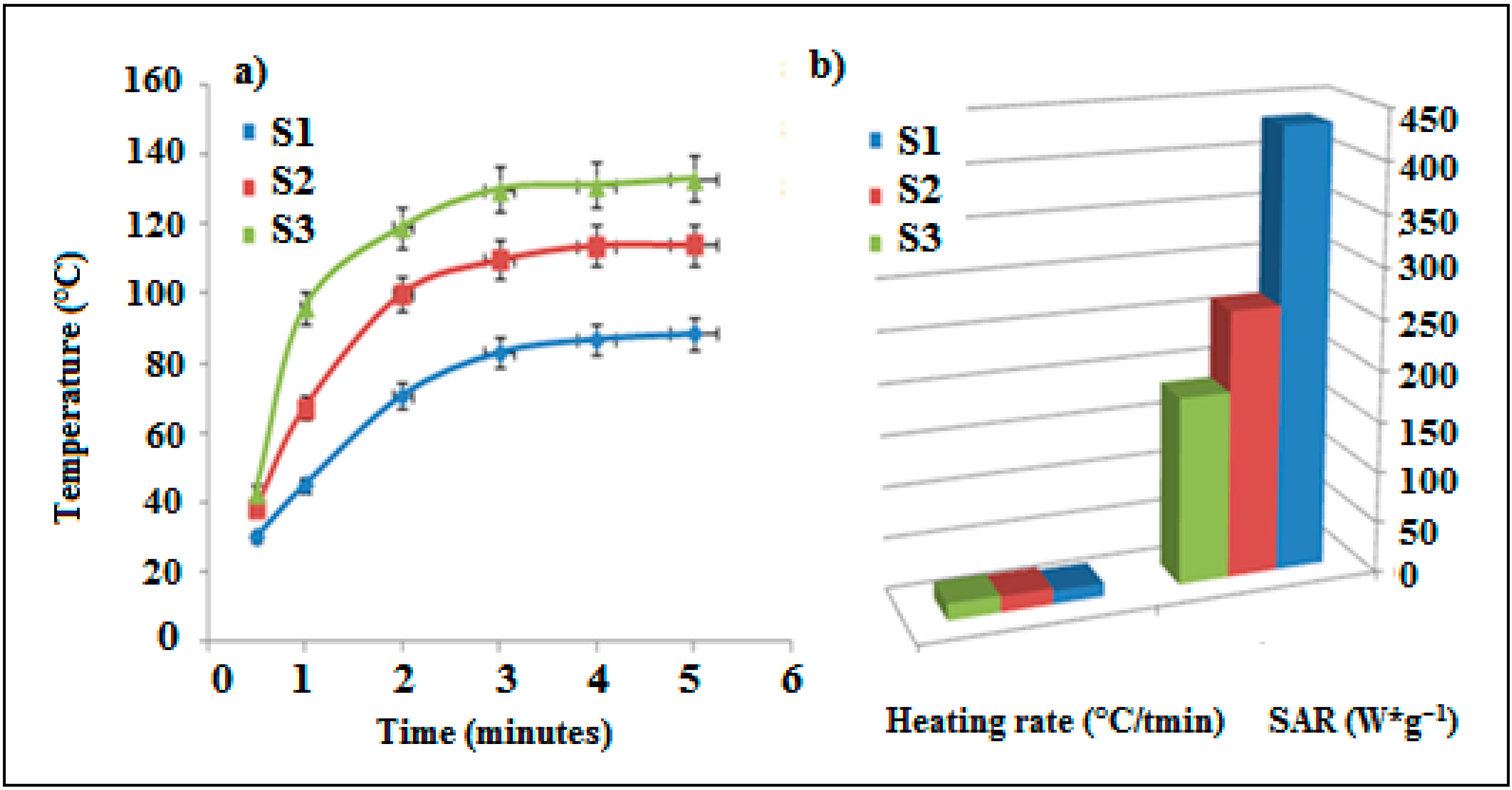
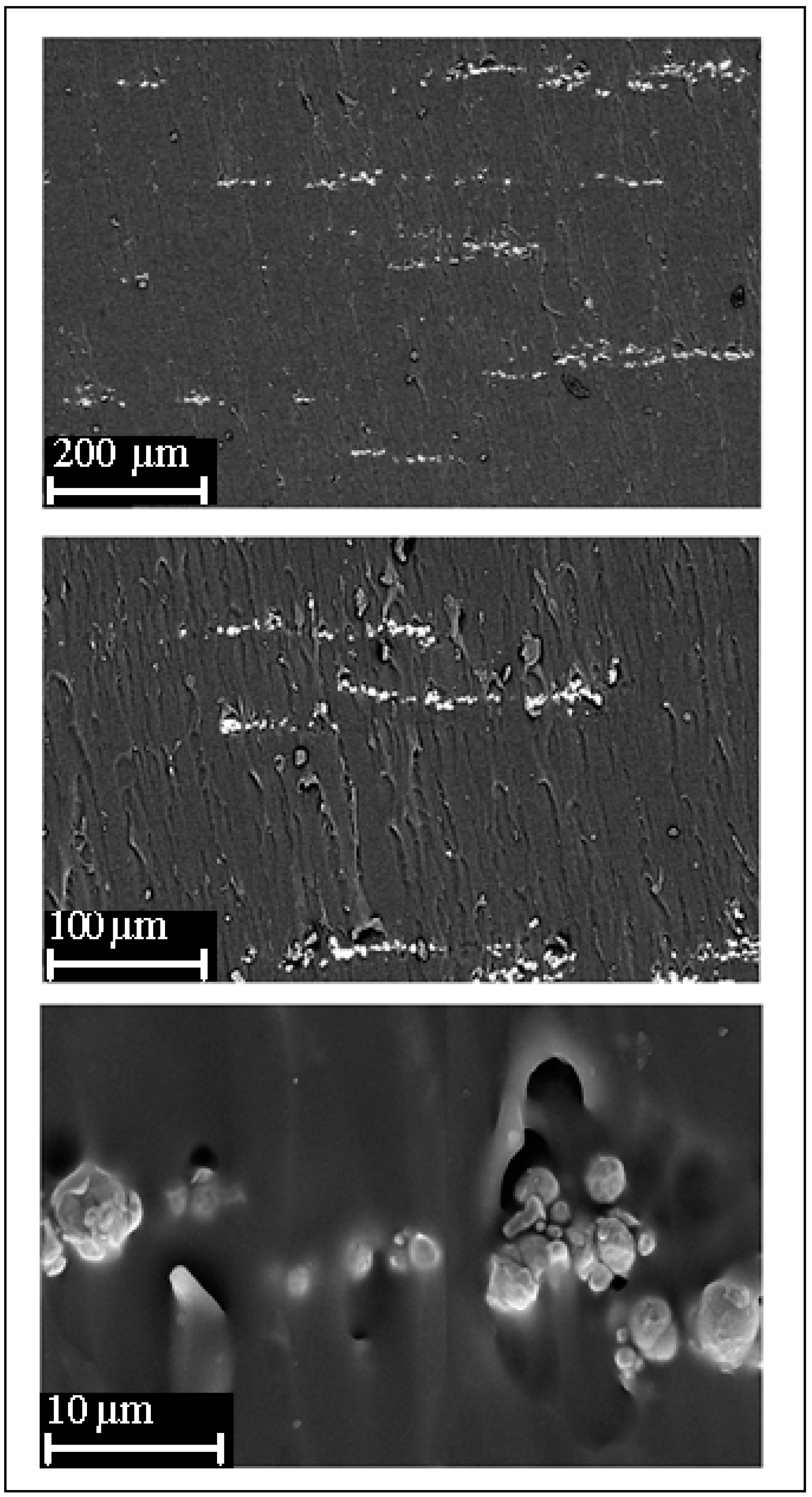
3.1. Heating Properties
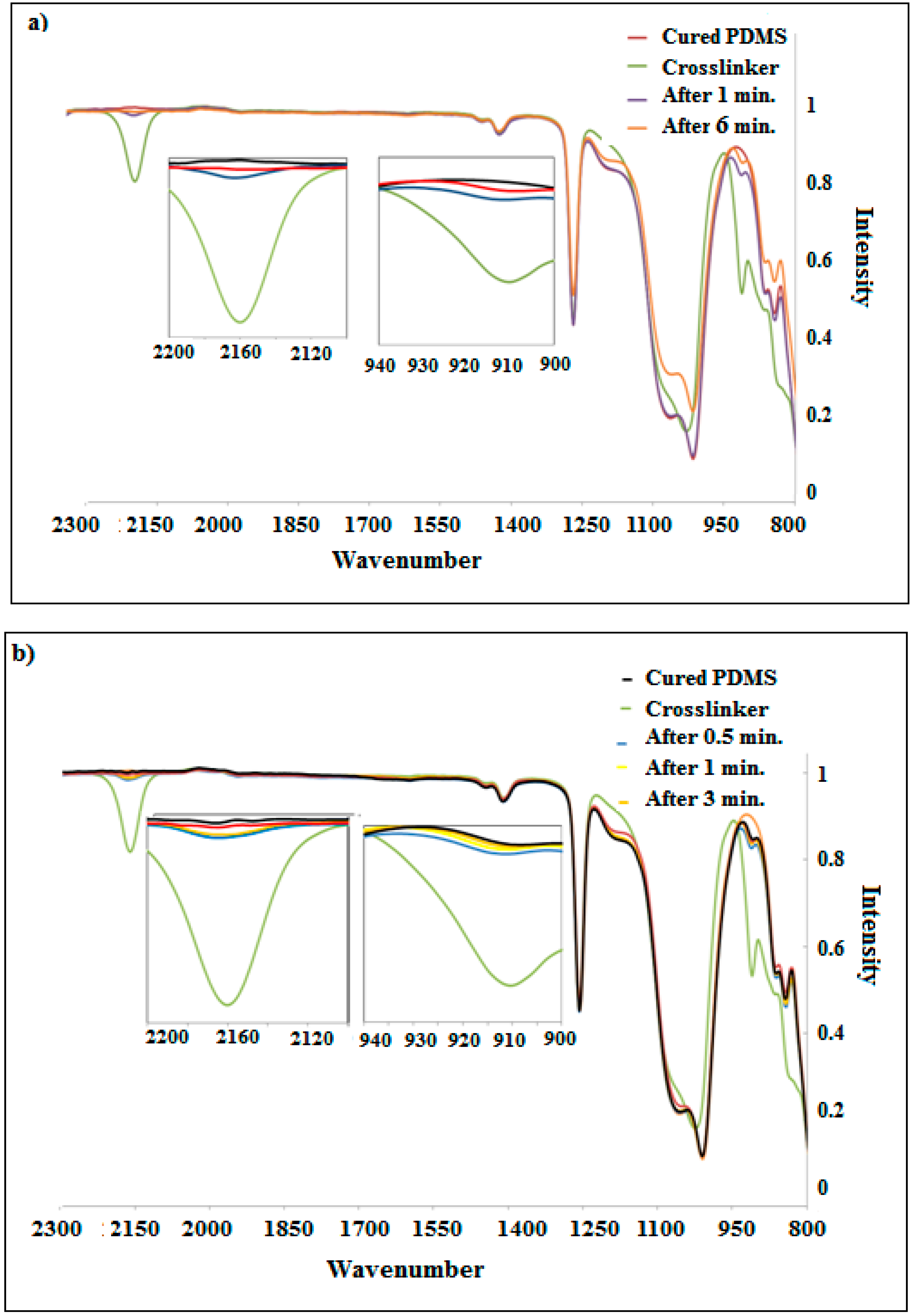
3.2. Curing Process of PDMS Composites
3.3. Swelling Behavior towards Triethylamine
3.4. Effect of Temperature on the Strain Rate
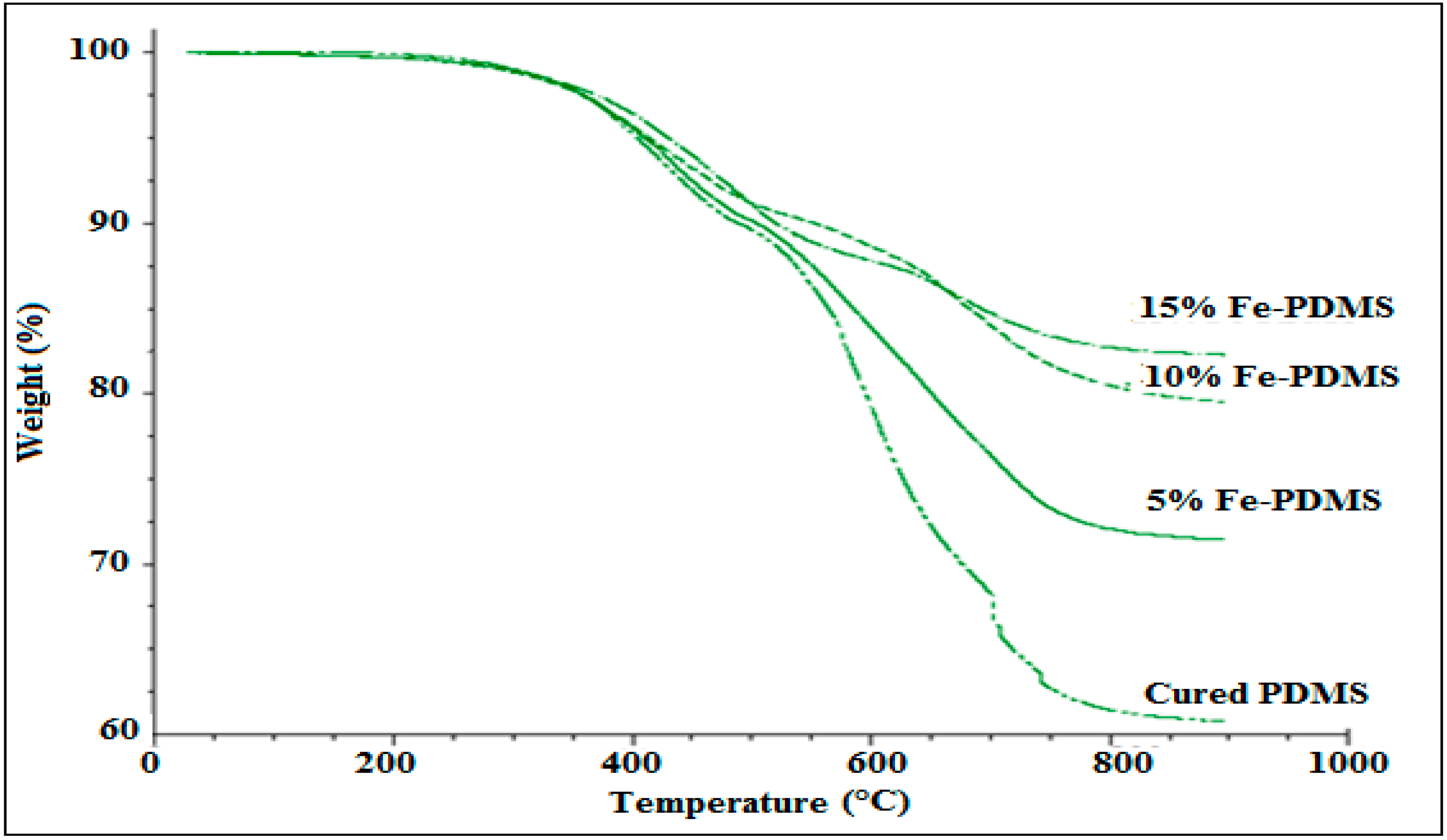
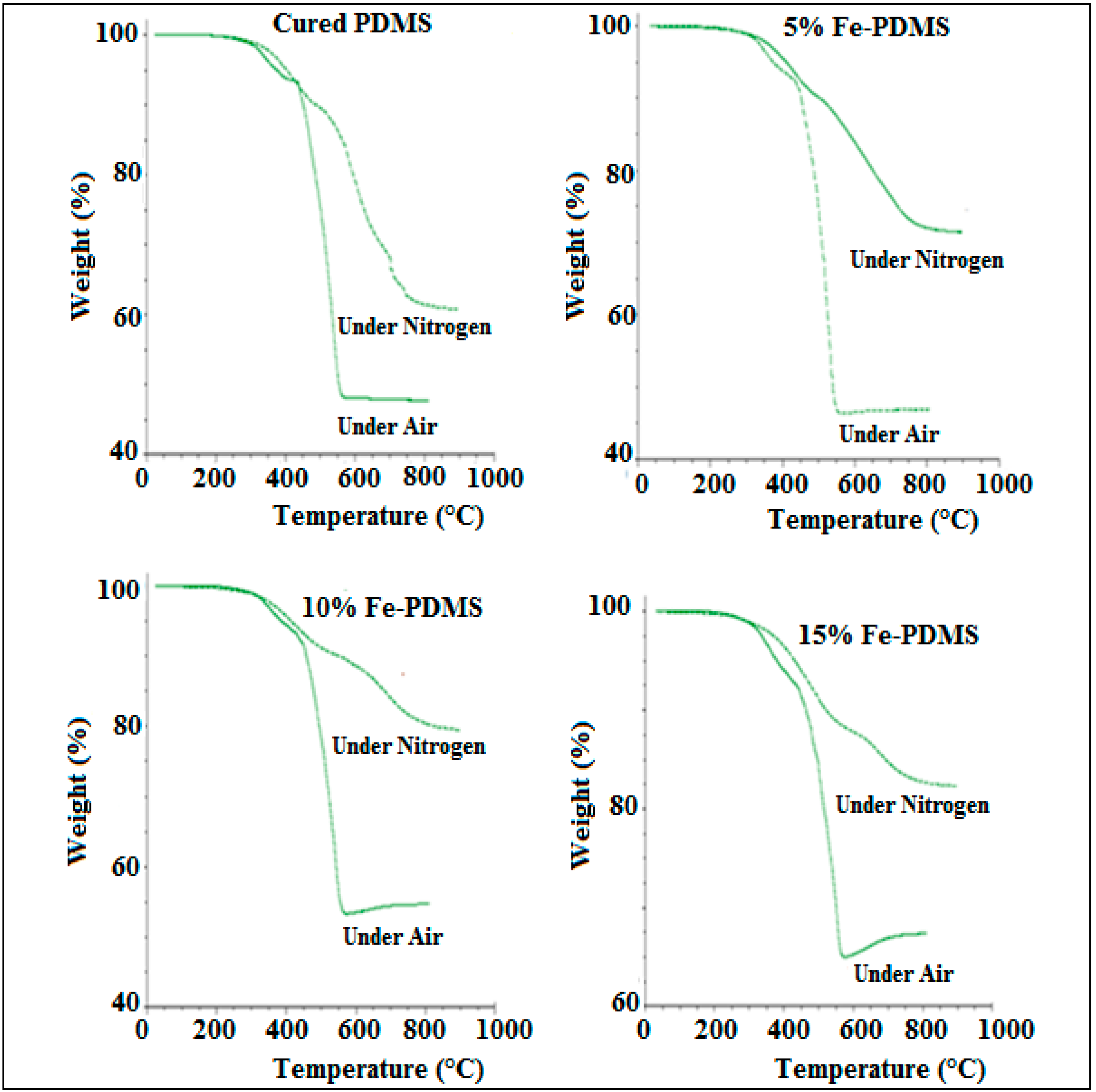
3.5. Thermal Stability of PDMS Composites
3.5.1. Effect of Iron Content on Thermal Stability of PDMS Composites
3.5.2. Effect of Gas Atmosphere Type on Thermal Stability of PDMS Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allan, D.; Radzinski, S.C.; Tapsak, M.A.; Liggat, J.J. The thermal degradation behaviour of a series of siloxane copolymers—A study by thermal volatilisation analysis. Silicon 2016, 8, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, J.; Yeo, J. Fabrication of microfluidic devices using polydimethylsiloxane. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carugo, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Pora, A.; Browning, R.J.; Capretto, L.; Nastruzzi, C.; Stride, E. Facile and cost-effective production of microscale PDMS architectures using a combined micromilling-replica moulding (μMi-REM) technique. Biomed. Microdevices 2016, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleymania, M.; Edrissi, M. Synthesis of bilayer surfactant-coated magnetic nanoparticles for application in magnetic fluid hyperthermia. J. Disp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Stein, G.E.; Cavicchi, K.A.; Vogt, B.D. Unidirectional alignment of block copolymer films induced by expansion of a permeable elastomer during solvent vapor annealing. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bhaway, S.M.; Cavicchi, K.A.; Vogt, B.D. Highly aligned, large pore ordered mesoporous carbon films by solvent vapor annealing with soft shear. Carbon 2015, 82, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Z.; Ye, C.; Lin, K.; Becker, M.L.; Cavicchi, K.A.; Vogt, B.D. Evolution in surface morphology during rapid microwave annealing of PS-b-PMMA thin films. J. Polym. Sci. Part B 2016, 54, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Molla, S.; Albrecht, A.; Cagatay, E.; Mittendorfer, P.; Cheng, G.; Lugli, P.; Salmerón, J.F.; Rivadeneyra, A. Integration of a thin film PDMS-based capacitive sensor for tactile sensing in an electronic skin. J. Sens. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, M.A. Silicon in Organic, Organometallic and Polymer Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Marchi, S.; Sangermano, M.; Meier, P.; Kornmann, X. UV-cured silicone composites obtained via hydrosilation and in-situ generation of inorganic particles. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, S.; Sangermano, M.; Meier, P.; Kornmann, X. Preparation and characterization of PDMS composites by UV-hydrosilation for outdoor polymeric insulators. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow Corning Product Information, “Information about Dow Corning® brand Silicone Encapsulants”. 2005. Available online: http://businessdocbox.com/Green_Solutions/67460800-Information-about-dow-corning-brand-silicone-encapsulants.html (accessed on 7 May 2018).
- Quan, S.X. Properties of post-cured siloxane networks. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1989, 29, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabowo, F.; Wing-Keung, A.L.; Shen, H.H. Effect of curing temperature and cross-linker to pre-polymer ratio on the viscoelastic properties of a PDMS elastomer. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1112, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.F.; Lee, K.F.; Lee, M.Y. Development of a flexible PDMS capacitive pressure sensor for plantar pressure measurement. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 99, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.T.; Cho, M.S.; Jang, I.B.; Choi, H.J. Magnetorheological characterization of carbonyl iron based suspension stabilized by fumed silica. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 282, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Feng, Y.; Xiong, J.; Yang, Y.; Lu, H.X. Microwave absorbing properties of deaggregated flake-shaped carbonyl-iron particle composites at 2–18 GHz. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 42, 1778–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.A.; Hui, W.; Rana, F.; Hawkins, B.G.; Smith, A.E.; Kirby, B.J. Microfluidic devices for terahertz spectroscopy of biomolecules. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdou, M.I.; Abuseda, H. Upgrading offshore pipelines concrete coated by silica fume additive against aggressive mechanical laying and environmental impact. Egypt. J. Petrol. 2016, 25, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, K.; Shioya, T.; Satoh, K. Mechanical properties of silicon impregnated C/C composite material at elevated temperature. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2002, 11, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabli, V.; Aghili, A. The effect of silica nanoparticles, thermal stability, and modeling of the curing kinetics of epoxy/silica nanocomposites. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2015, 24, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Wahab, H.; Saleh, T.S.; Zayed, E.M.; El-Sayed, A.S.; Assaker, R.S.A. Synthesis and evaluation of new anti-microbial additive based on pyrimidine derivative incorporated physically into polyurethane varnish for surface coating and into printing ink paste. Egypt. J. Petrol. 2015, 24, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.S.; Stibor, I. Preparation and characterization of magnetite PDMS composites by magnetic induction heating. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 164, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Sukkary, M.M.; Ismail, D.A.; El Rayes, S.M.; Saad, M.A. Synthesis and evaluation of some derivatives of polysiloxanes. Egypt. J. Petrol. 2014, 23, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.S.; El-Sabbagh, A.; Stibor, I. Hyperthermia properties of magnetic polyethylenimine core/shell nanoparticles: Influence of carrier and magnetic field strength. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Boyed, C.; Luo, W. Two mechanisms and a scaling relation for dynamics in ferrofluids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Bock, C.; Chen, Q. Thickness-dependent mechanical properties of polydimethylsiloxane membranes. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabro, J.D.; Huang, X.; Lewis, B.G.; Ramirez, A.G. Magnetically driven three-dimensional manipulation and inductive heating of magnetic-dispersion containing metal alloys. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4834–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, J.D. Magnetically Curable Composition and Magnetic Cure Process. U.S. Patent 8,206,545 B2, 26 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hajsz, T.; Csetneki, I.; Filipcsei, G.; Zrinyi, M. Swelling kinetics of anisotropic filler loaded PDMS networks. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, A.C.; Brokken-Zijp, J.; Laven, J.; de With, G. Light converter coatings from cross-linked PDMS/particles composite materials. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 68, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, G.; Lomakin, S.M.; Lageard, M. Thermal polydimethylsiloxane degradation. Part 2. The degradation mechanisms. Polymer 2002, 43, 2011–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, S.; Ohtani, H.; Tsuge, S. Characterization of polysiloxanes by high-resolution pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1988, 331, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, G.; Lomakin, S.M.; Lazzari, M. Polydimethylsiloxane thermal degradation Part 1. Kinetic aspects. Polymer 2001, 42, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Harbi, L.M.; Darwish, M.S.A.; Khowdiary, M.M.; Stibor, I. Controlled Preparation of Thermally Stable Fe-Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Composite by Magnetic Induction Heating. Polymers 2018, 10, 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050507
Al-Harbi LM, Darwish MSA, Khowdiary MM, Stibor I. Controlled Preparation of Thermally Stable Fe-Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Composite by Magnetic Induction Heating. Polymers. 2018; 10(5):507. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050507
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Harbi, Laila M., Mohamed S. A. Darwish, Manal M. Khowdiary, and Ivan Stibor. 2018. "Controlled Preparation of Thermally Stable Fe-Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Composite by Magnetic Induction Heating" Polymers 10, no. 5: 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050507
APA StyleAl-Harbi, L. M., Darwish, M. S. A., Khowdiary, M. M., & Stibor, I. (2018). Controlled Preparation of Thermally Stable Fe-Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Composite by Magnetic Induction Heating. Polymers, 10(5), 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050507