Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifogging Application of Polymer/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Hydrogels with High Strength and Self-Healing Capacity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Hydrogel Synthesis
2.3. Characterizations
2.4. Mechanical Tests
2.5. Swelling Measurements
2.6. Self-Healing Experiments
2.7. Antifogging Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
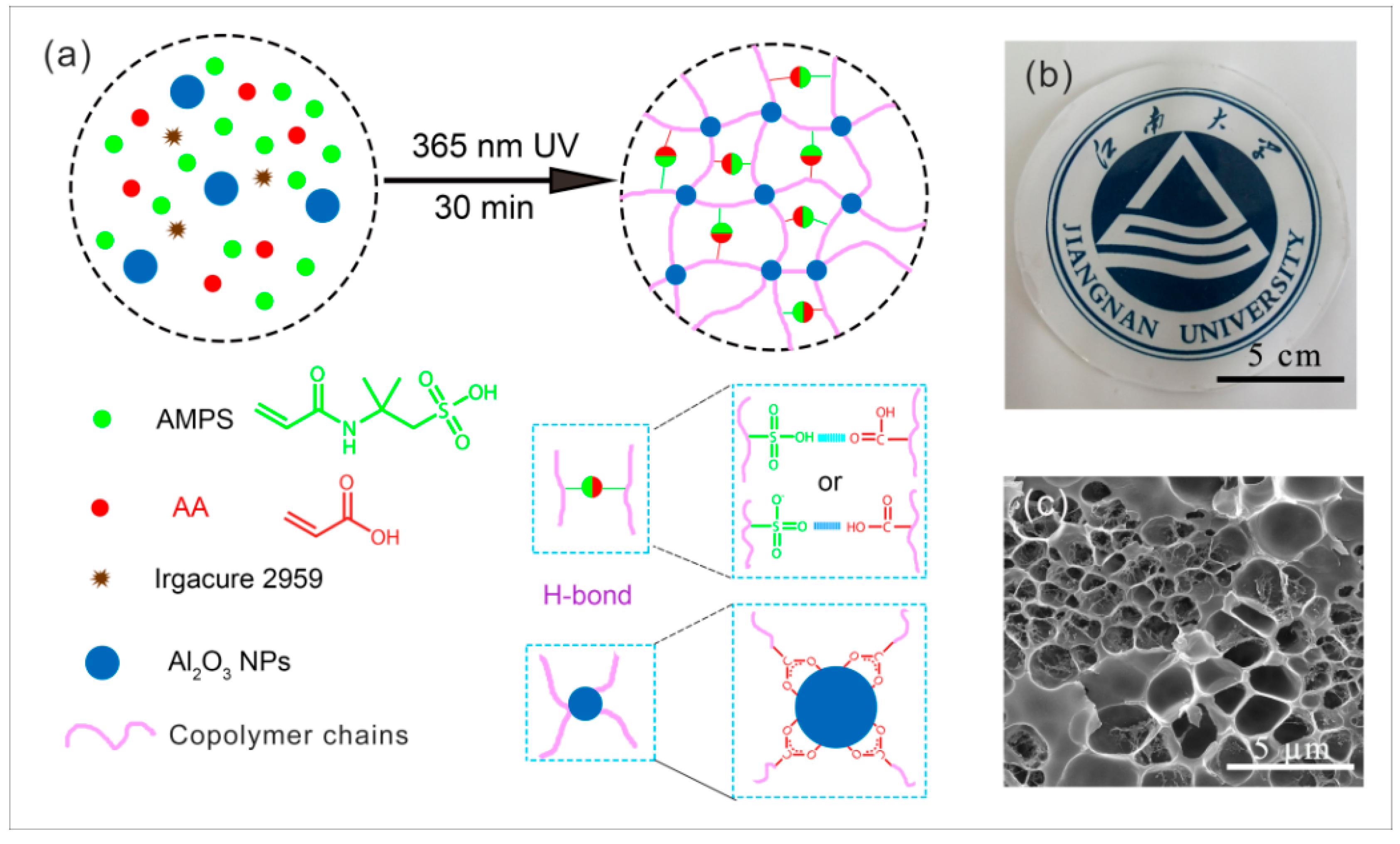
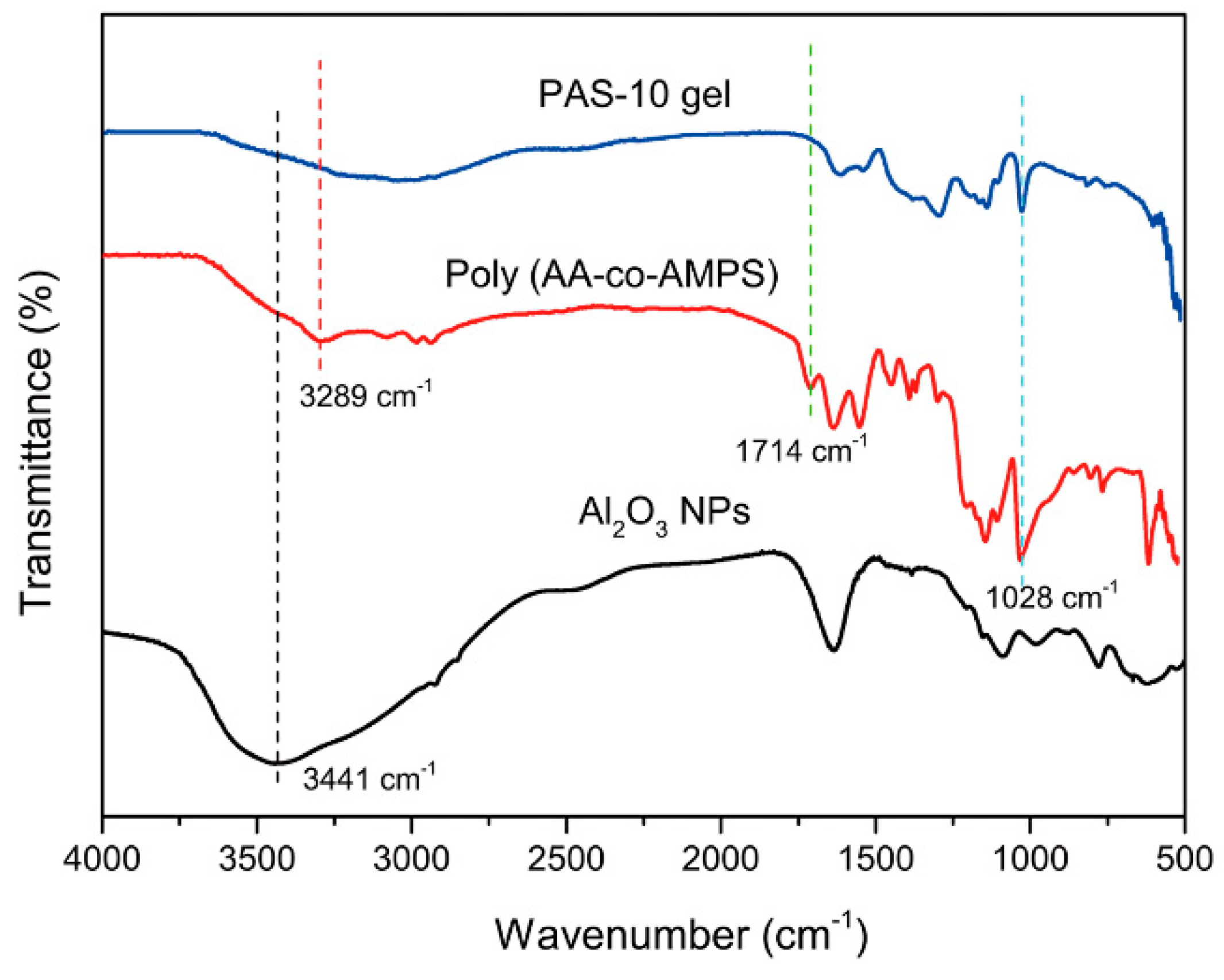
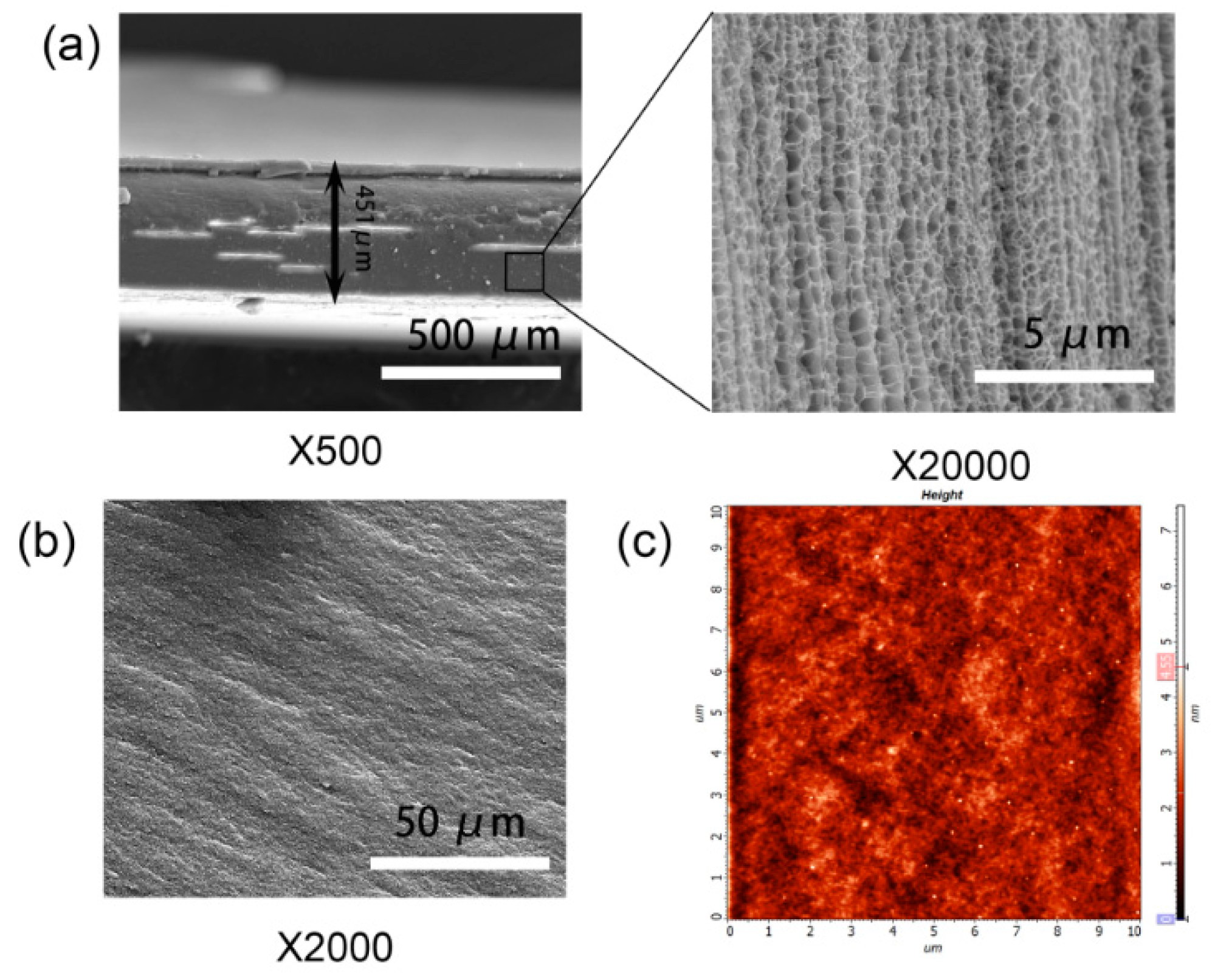
3.1. Formation and Cross-Linking Mechanism of PAS Gels
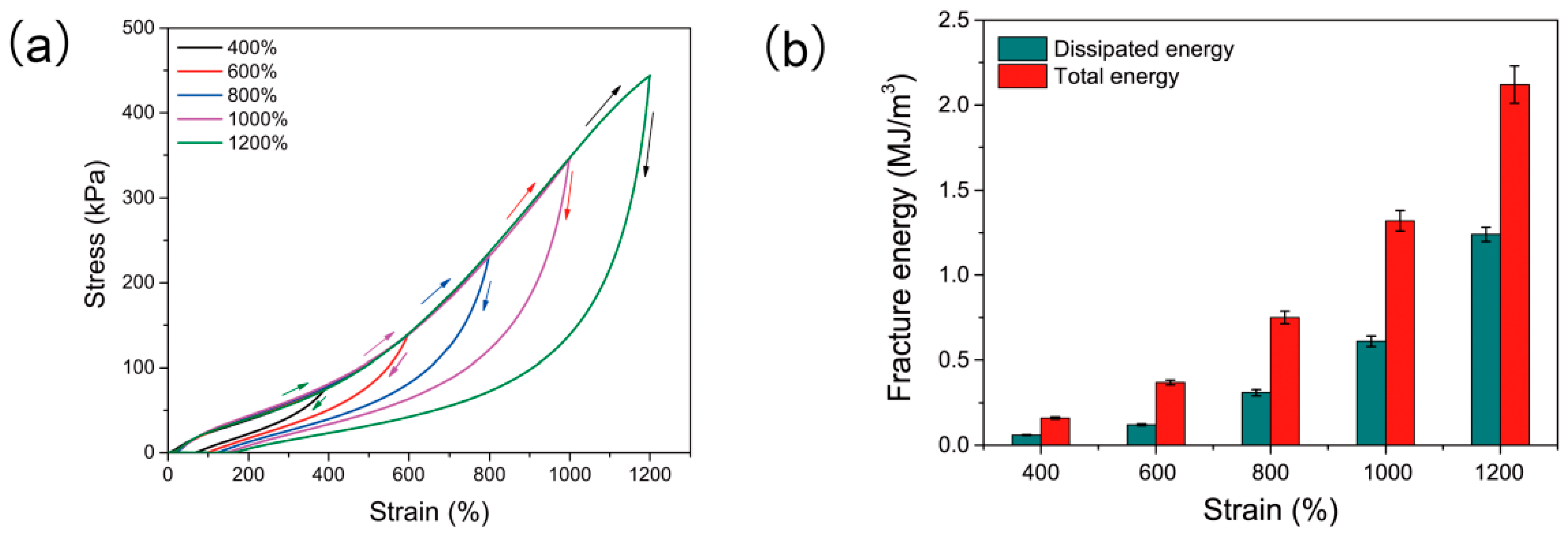
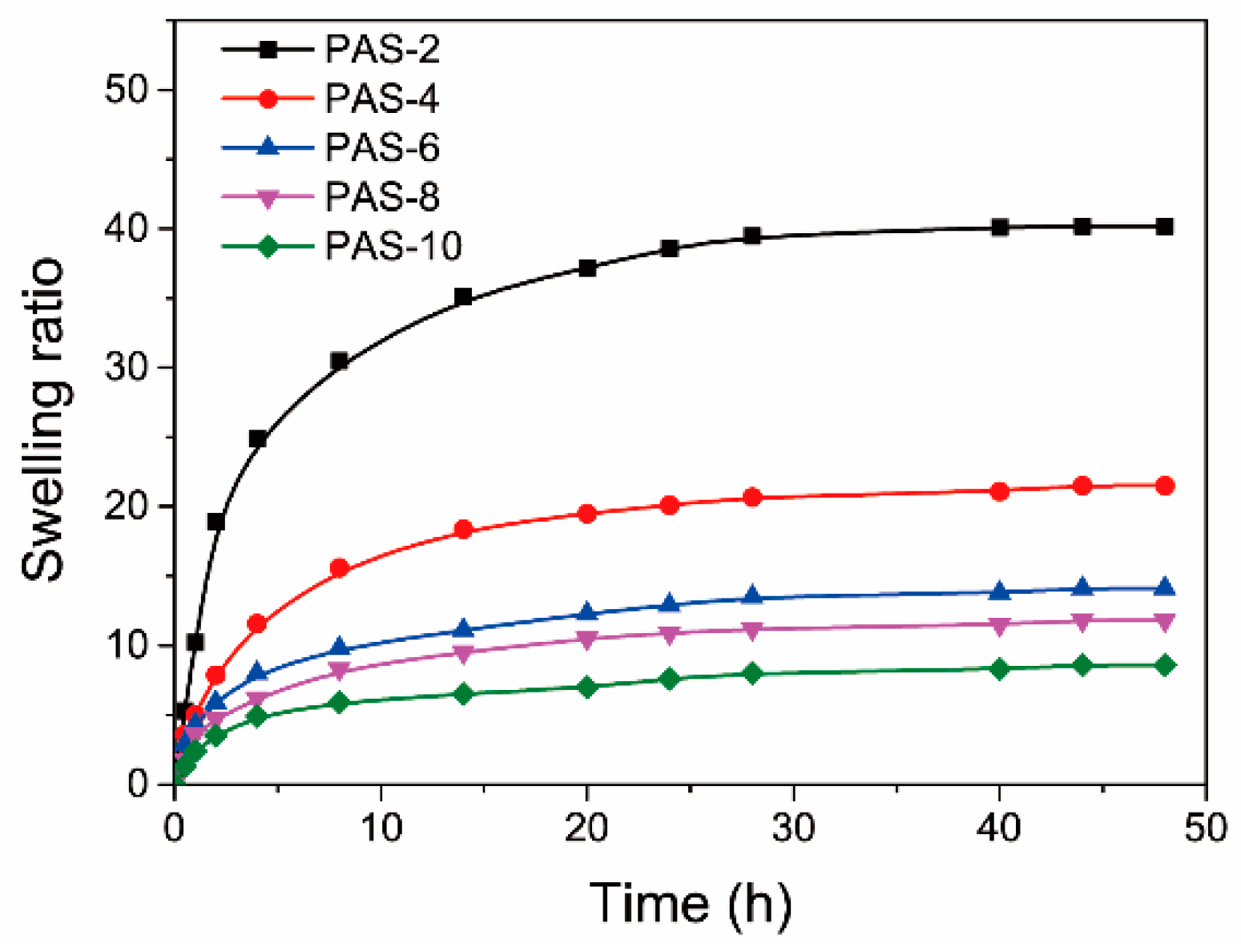
3.2. Mechanical and Swelling Properties of PAS Gels
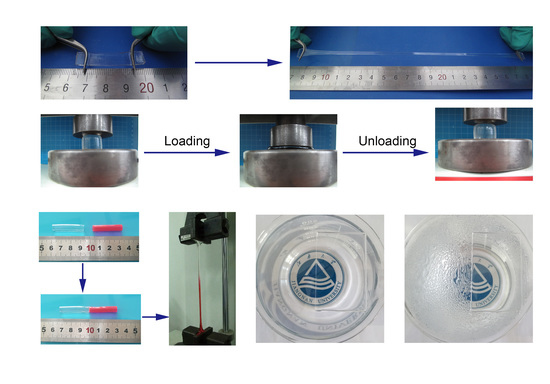
3.3. Self-Healing Ability of PAS Gels
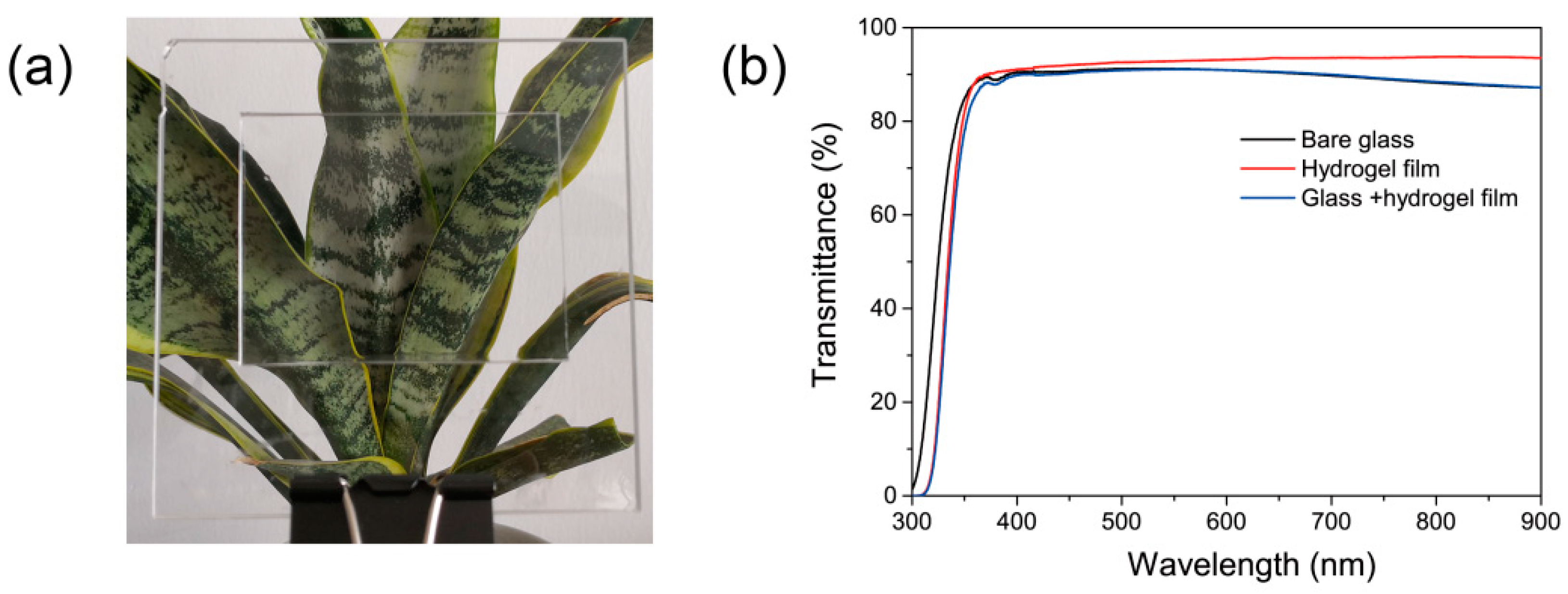
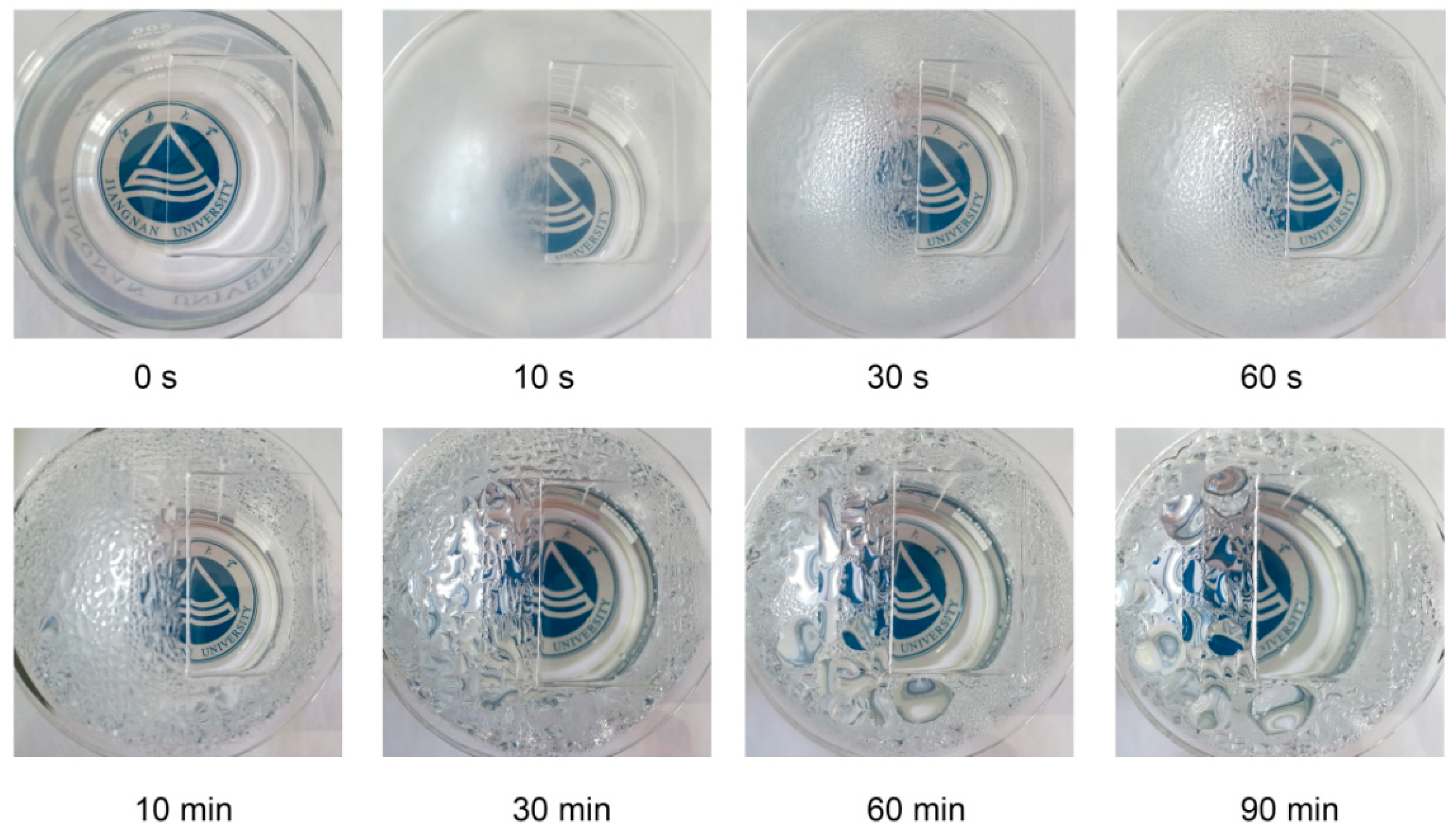
3.4. Antifogging Application of PAS Gels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seliktar, D. Designing Cell-Compatible Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Science 2012, 336, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calo, E.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Biomedical applications of hydrogels: A review of patents and commercial products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomatsu, I.; Peng, K.; Kros, A. Photoresponsive hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annabi, N.; Tamayol, A.; Uquillas, J.A.; Akbari, M.; Bertassoni, L.E.; Cha, C.; Camci-Unal, G.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Peppas, N.A.; Khademhosseini, A. 25th Anniversary Article: Rational Design and Applications of Hydrogels in Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 85–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.A.; Yeom, J.; Hwang, B.W.; Hoffman, A.S.; Hahn, S.K. In situ-forming injectable hydrogels for regenerative medicine. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1973–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Banerjee, R. Biopolymer-Based Hydrogels for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 4453–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.L.; Mauck, R.L.; Burdick, J.A. Hydrogel design for cartilage tissue engineering: A case study with hyaluronic acid. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8771–8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Park, K. Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tao, L.; Li, S.; Wei, Y. Synthesis of Multiresponsive and Dynamic Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Controlled Release of Bioactive Molecules. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2894–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, D.; Liu, B.; Shi, Y.; Pan, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, R.; Yu, G. Highly Sensitive Glucose Sensor Based on Pt Nanoparticle/Polyaniline Hydrogel Heterostructures. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3540–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buenger, D.; Topuz, F.; Groll, J. Hydrogels in sensing applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1678–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GhavamiNejad, A.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. In Situ Synthesis of Antimicrobial Silver Nanoparticles within Antifouling Zwitterionic Hydrogels by Catecholic Redox Chemistry for Wound Healing Application. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghobril, C.; Grinstaff, M.W. The chemistry and engineering of polymeric hydrogel adhesives for wound closure: A tutorial. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1820–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madaghiele, M.; Demitri, C.; Sannino, A.; Ambrosio, L. Polymeric hydrogels for burn wound care: Advanced skin wound dressings and regenerative templates. Burns Trauma 2014, 2, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, P. Hydrogels for Soft Machines. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirthl, D.; Pichler, R.; Drack, M.; Kettlguber, G.; Moser, R.; Gerstmayr, R.; Hartmann, F.; Bradt, E.; Kaltseis, R.; Siket, C.M.; et al. Instant tough bonding of hydrogels for soft machines and electronics. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, H.; Lin, S.; Ma, C.; Takaffoli, M.; Fang, N.X.; Zhao, X. Hydraulic hydrogel actuators and robots optically and sonically camouflaged in water. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Toguchida, J.; Oka, M. Preliminary study of polyvinyl alcohol-hydrogel (PVA-H) artificial meniscus. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Cheng, C.; Teng, Y.; Nie, C.; Zhao, C. Mussel-inspired post-heparinization of a stretchable hollow hydrogel tube and its potential application as an artificial blood vessel. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 2266–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. Multi-scale multi-mechanism design of tough hydrogels: Building dissipation into stretchy networks. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 672–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, Y.; Ito, K. The polyrotaxane gel: A topological gel by figure-of-eight cross-links. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karino, T.; Shibayama, M.; Ito, K. Slide-ring gel: Topological gel with freely movable cross-links. Phys. B 2006, 385, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.P.; Katsuyama, Y.; Kurokawa, T.; Osada, Y. Double-network hydrogels with extremely high mechanical strength. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.P. Why are double network hydrogels so tough? Soft Matter 2010, 6, 2583–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, K.; Takehisa, T. Nanocomposite hydrogels: A unique organic-inorganic network structure with extraordinary mechanical, optical, and swelling/de-swelling properties. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Fang, R.; Rong, Q.; Liu, M. Bioinspired Nanocomposite Hydrogels with Highly Ordered Structures. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hager, M.D.; Greil, P.; Leyens, C.; van der Zwaag, S.; Schubert, U.S. Self-Healing Materials. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 5424–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wool, R.P. Self-healing materials: A review. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 400–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.L.; Panhuis, M.I.H. Self-Healing Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9060–9093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phadke, A.; Zhang, C.; Arman, B.; Hsu, C.-C.; Mashelkar, R.A.; Lele, A.K.; Tauber, M.J.; Arya, G.; Varghese, S. Rapid self-healing hydrogels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4383–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesilyurt, V.; Webber, M.J.; Appel, E.A.; Godwin, C.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G. Injectable Self-Healing Glucose-Responsive Hydrogels with pH-Regulated Mechanical Properties. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraguchi, K.; Uyama, K.; Tanimoto, H. Self-healing in Nanocomposite Hydrogels. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Liu, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, G. Tough, Stretchable, Compressive Novel Polymer/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Hydrogels with Excellent Self-Healing Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 38052–38061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q. Tough and Self-Healable Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Repeatable Water Treatment. Polymers 2018, 10, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, G.; Feng, X.; Liu, H.; Li, F.; Wang, M.; Li, H. Room-temperature self-healing tough nanocomposite hydrogel crosslinked by zirconium hydroxide nanoparticles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 140, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ge, X.; Fu, M.; Wang, P.; Wang, Q. High-Strength Nanocomposite Hydrogels with Swelling-Resistant and Anti-Dehydration Properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Q. Preparation of high strength and transparent nanocomposite hydrogels using alumina nanoparticles as cross-linking agents. Mater. Lett. 2018, 228, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, A.R. The interaction of carboxylic acids with aluminium oxides: Journeying from a basic understanding of alumina nanoparticles to water treatment for industrial and humanitarian applications. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 8127–8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, N.; Fu, M.; Wang, P.; Wang, Q. High strength and anti-fatigue nanocomposite hydrogels prepared via self-initiated free radical polymerization triggered by daylight. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 11796–11803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, G. Novel Nanocomposite Hydrogels Consisting of Layered Double Hydroxide with Ultrahigh Tensibility and Hierarchical Porous Structure at Low Inorganic Content. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5950–5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Xia, Y.; Jin, X.; Feng, X.; Li, H. A self-healable and tough nanocomposite hydrogel crosslinked by novel ultrasmall aluminum hydroxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 15470–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraguchi, K.; Farnworth, R.; Ohbayashi, A.; Takehisa, T. Compositional effects on mechanical properties of nanocomposite hydrogels composed of poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) and clay. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 5732–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, K.; Takehisa, T.; Fan, S. Effects of clay content on the properties of nanocomposite hydrogels composed of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and clay. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 10162–10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.Y.; Chang, H.L.; Wang, M.; Xu, F.; Yang, J. High-Strength, Tough, and Self-Healing Nanocomposite Physical Hydrogels Based on the Synergistic Effects of Dynamic Hydrogen Bond and Dual Coordination Bonds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28305–28318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, N.; Alizadeh, E.; Salehi, R.; Khalandi, B.; Davaran, S.; Akbarzadeh, A. Nanocomposite hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering: A review. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.Y.; Wang, M.; Meng, L.; Chang, H.L.; Wang, B.; Xu, F.; Wang, J.; Wan, P.B. Mussel-Inspired Cellulose Nanocomposite Tough Hydrogels with Synergistic Self-Healing, Adhesive, and Strain-Sensitive Properties. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 3110–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chiappone, A.; Roppolo, I.; Shao, F.; Fantino, E.; Lorusso, M.; Rentsch, D.; Dietliker, K.; Pirri, C.F.; Gruetzmacher, H. All-in-One Cellulose Nanocrystals for 3D Printing of Nanocomposite Hydrogels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2353–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, B.; Sun, J. Highly Transparent and Water-Enabled Healable Antifogging and Frost-Resisting Films Based on Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Nafion Complexes. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 6975–6984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, S.; Sun, J. Antifogging and Frost-Resisting Polyelectrolyte Coatings Capable of Healing Scratches and Restoring Transparency. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 8058–8065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, S.; Jang, D.H.; Lee, H.S.; Park, C.H. Anti-fogging behavior of water-absorbing polymer films derived from isosorbide-based epoxy resin. Mater. Lett. 2016, 180, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, M.W.; Urata, C.; Dunderdale, G.J.; Hozumi, A. Anti-Fogging/Self-Healing Properties of Clay-Containing Transparent Nanocomposite Thin Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4318–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Al2O3 Content | Tensile Strength/kP | Elongation at Break/% | Tensile Modulus/kPa | Compressive Strength/MPa | Compressive Modulus/kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2% | 243.5 ± 12.3 | 1916.3 ± 105.5 | 4.6 ± 0.21 | 2.29 ± 0.11 | 20.4 ± 1.03 |
| 4% | 352.3 ± 15.8 | 1848.5 ± 103.7 | 6.7 ± 0.35 | 3.30 ± 0.15 | 36.6 ± 1.98 |
| 6% | 417.9 ± 24.3 | 1904.5 ± 104.7 | 8.6 ± 0.41 | 4.31 ± 0.18 | 65.3 ± 3.30 |
| 8% | 572.5 ± 27.9 | 1793.8 ± 90.6 | 14.1 ± 0.78 | 6.27 ± 0.32 | 78.5 ± 3.62 |
| 10% | 659.3 ± 30.6 | 1784.9 ± 92.5 | 20.1 ± 1.02 | 8.30 ± 0.42 | 110.1 ± 5.51 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, Q. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifogging Application of Polymer/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Hydrogels with High Strength and Self-Healing Capacity. Polymers 2018, 10, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121362
Xu B, Liu Y, Yuan J, Wang P, Wang Q. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifogging Application of Polymer/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Hydrogels with High Strength and Self-Healing Capacity. Polymers. 2018; 10(12):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121362
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Bo, Yuwei Liu, Jiugang Yuan, Ping Wang, and Qiang Wang. 2018. "Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifogging Application of Polymer/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Hydrogels with High Strength and Self-Healing Capacity" Polymers 10, no. 12: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121362
APA StyleXu, B., Liu, Y., Yuan, J., Wang, P., & Wang, Q. (2018). Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifogging Application of Polymer/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Hydrogels with High Strength and Self-Healing Capacity. Polymers, 10(12), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121362