An Electrochemical Sensor for Diphenylamine Detection Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide/Fe3O4-Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with 1,4-Butanediyl-3,3′-bis-l-vinylimidazolium Dihexafluorophosphate Ionic Liquid as Cross-Linker
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
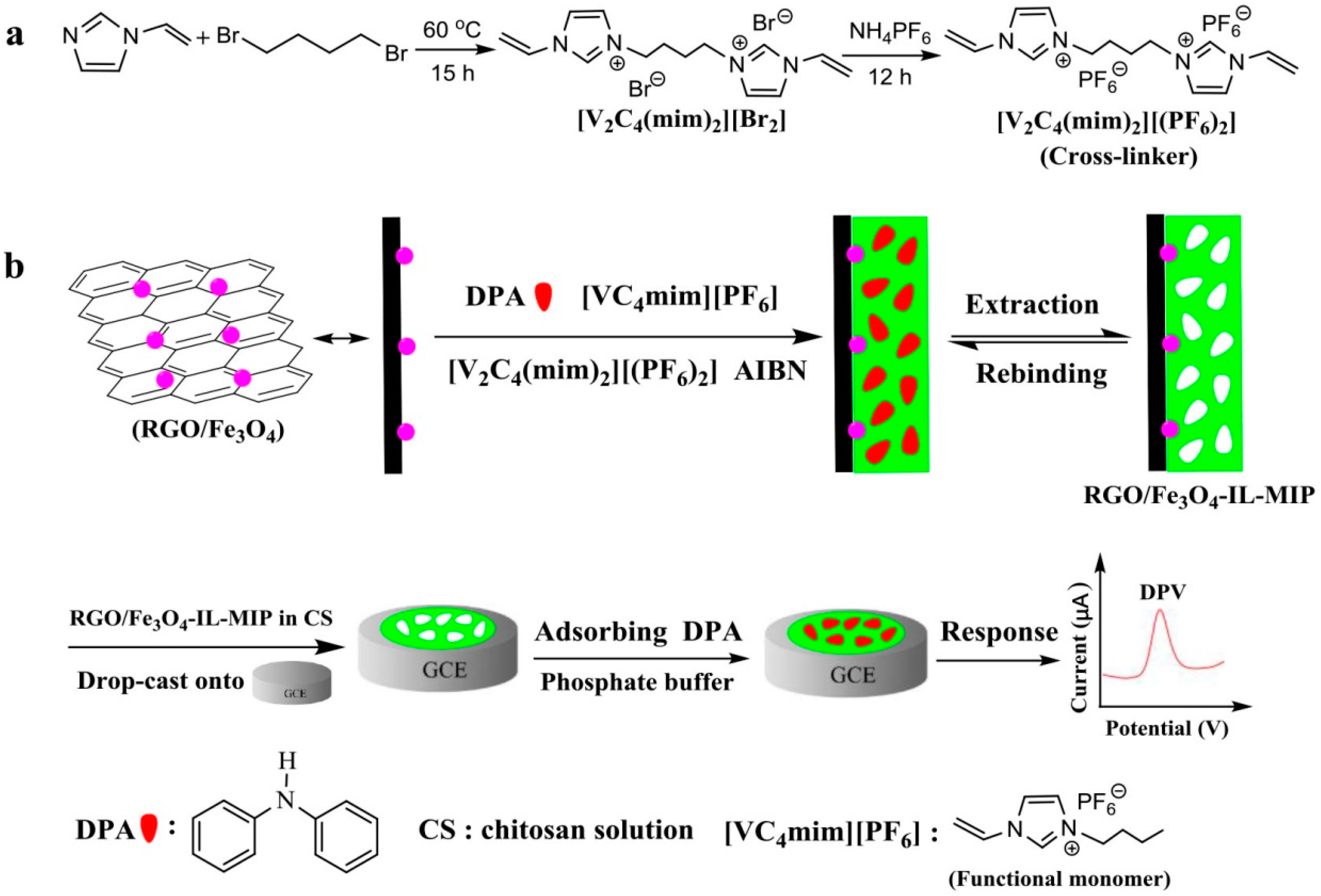
2.3. Preparation of [V2C4(mim)2][(PF6)2]
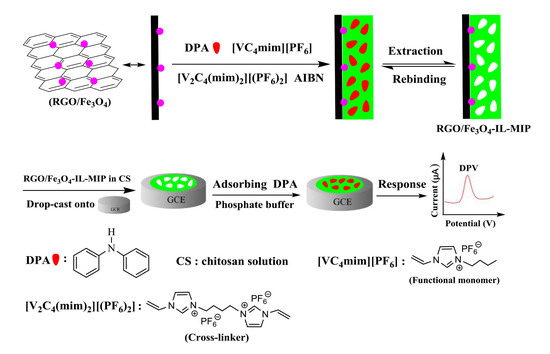
2.4. Synthesis of RGO/Fe3O4-IL-MIP
2.5. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results
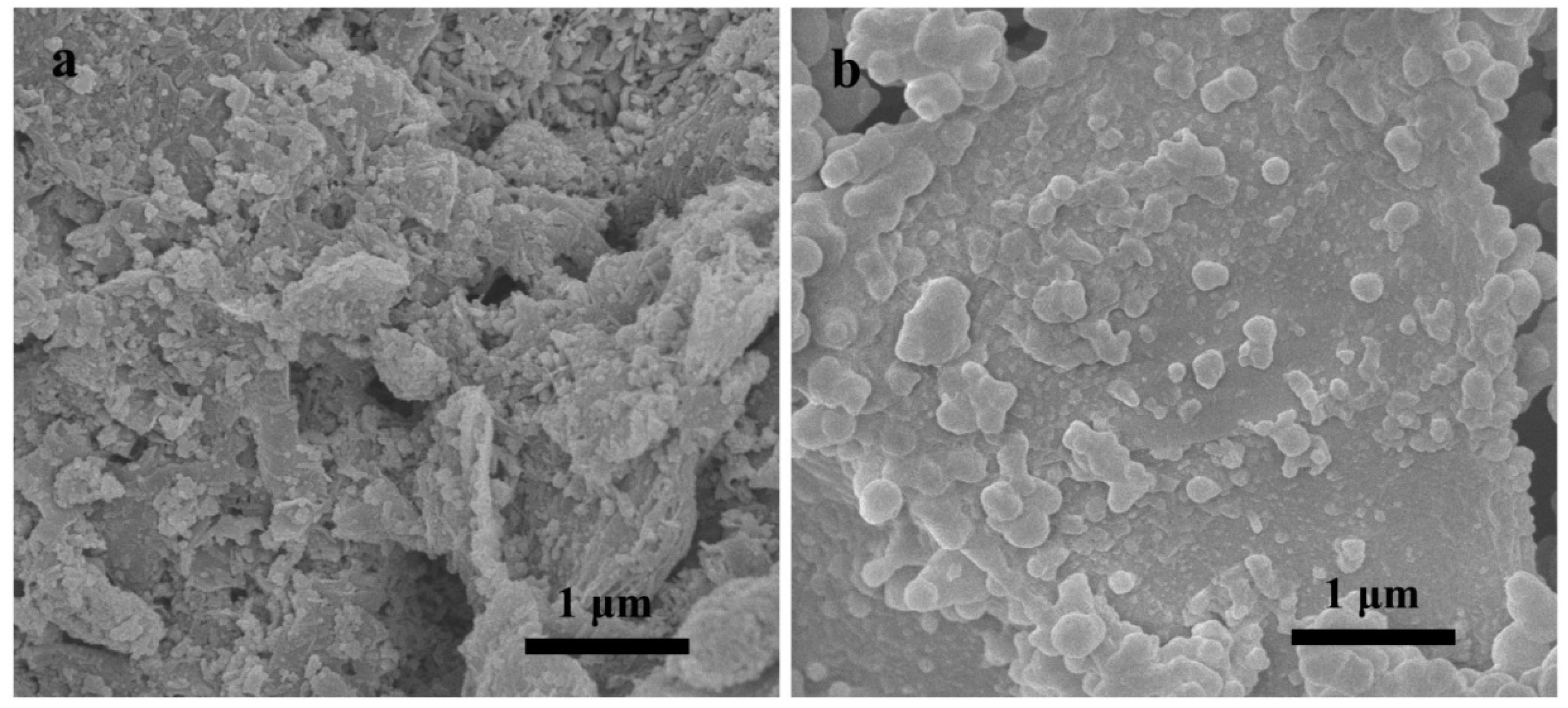
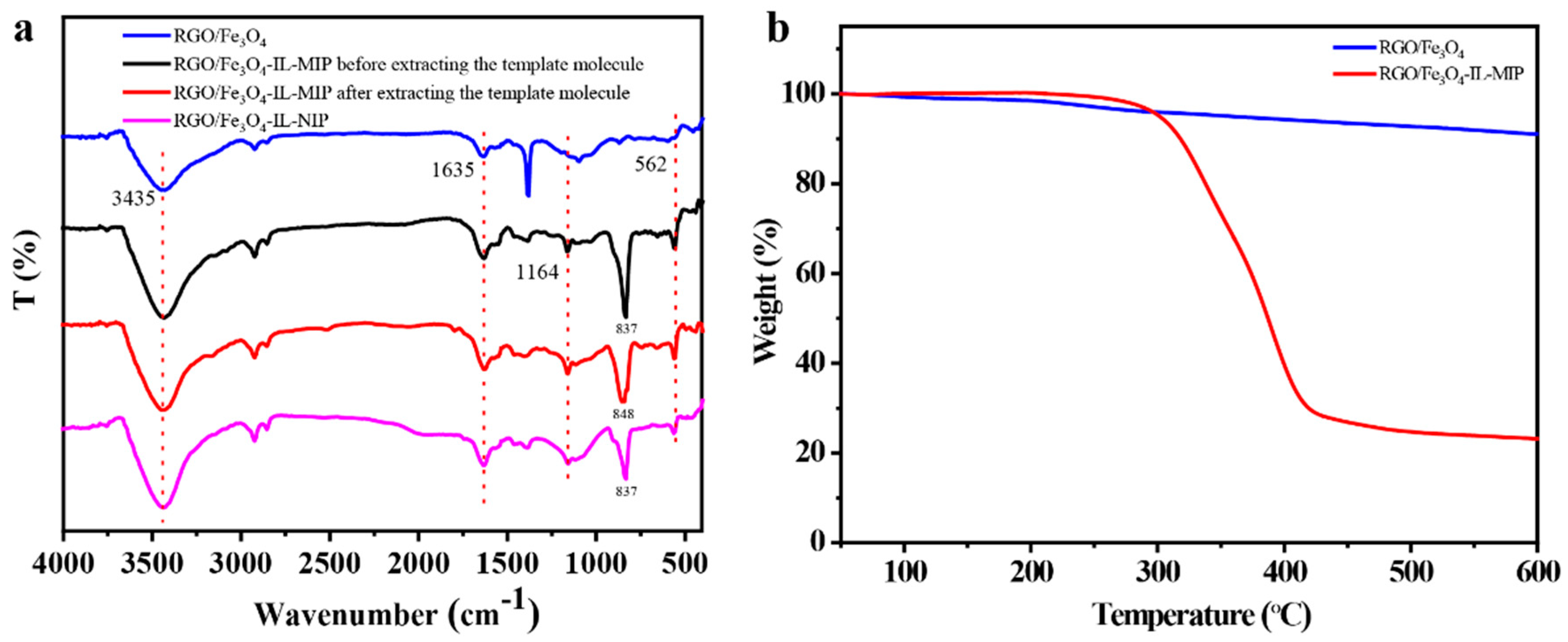
3.1. Characterization of RGO/Fe3O4-IL-MIP
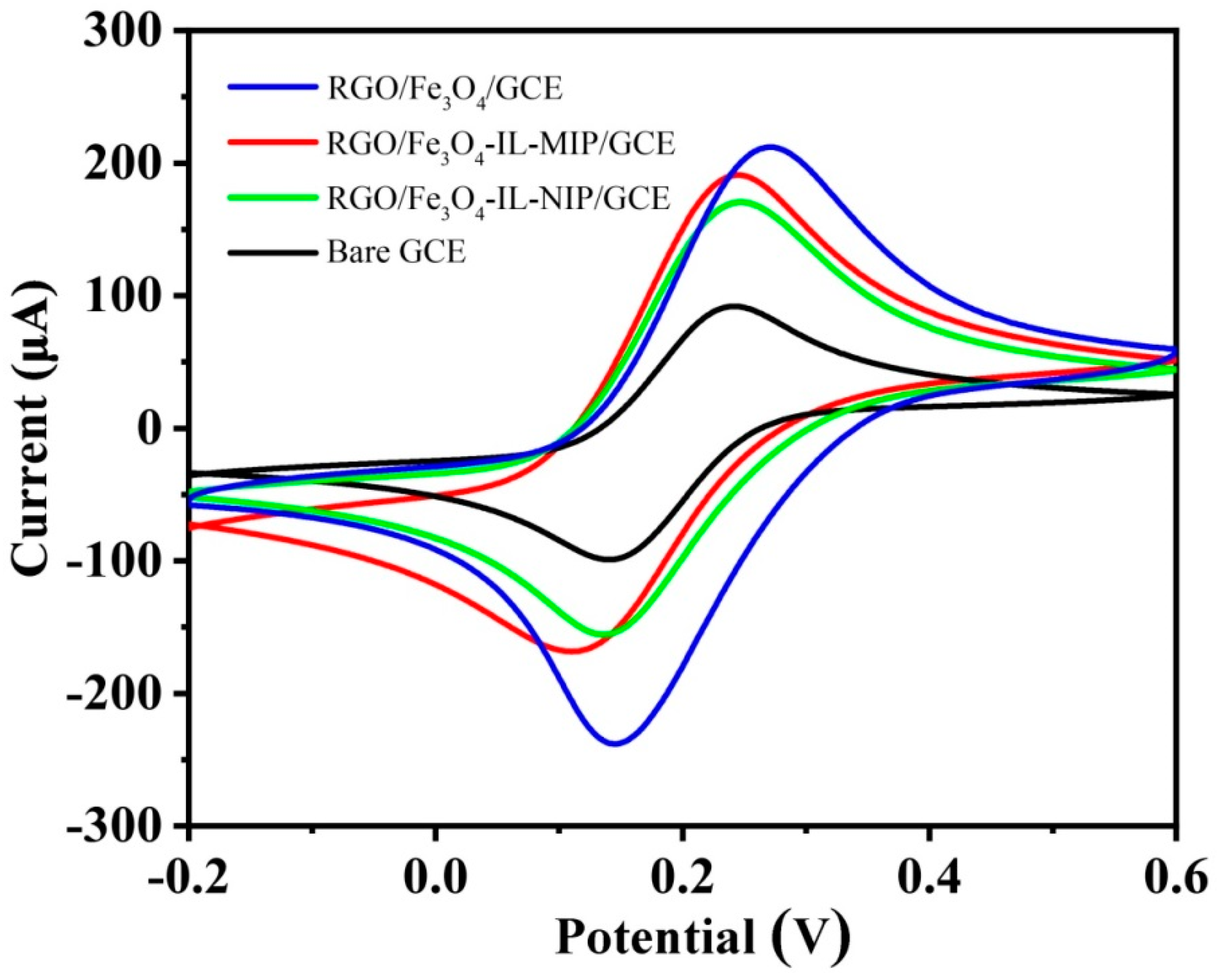
3.2. Electrochemical Behavior of RGO/Fe3O4-IL-MIP/GCE
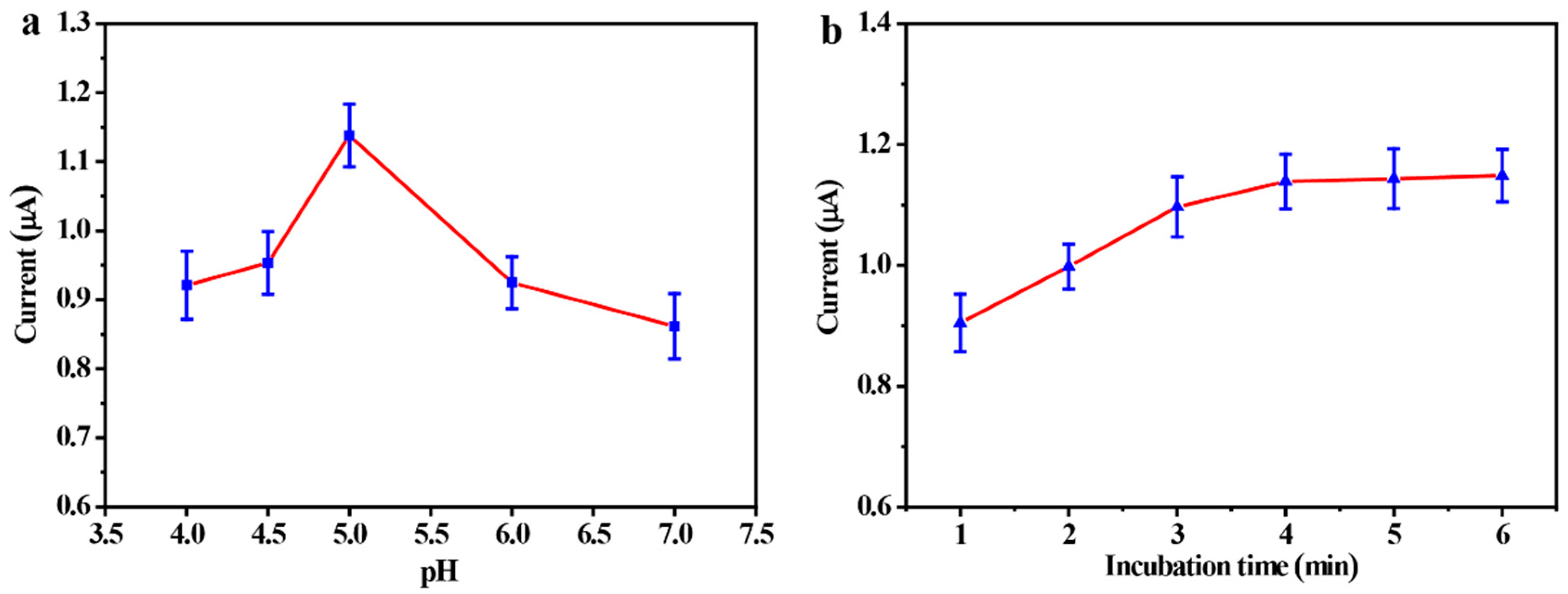
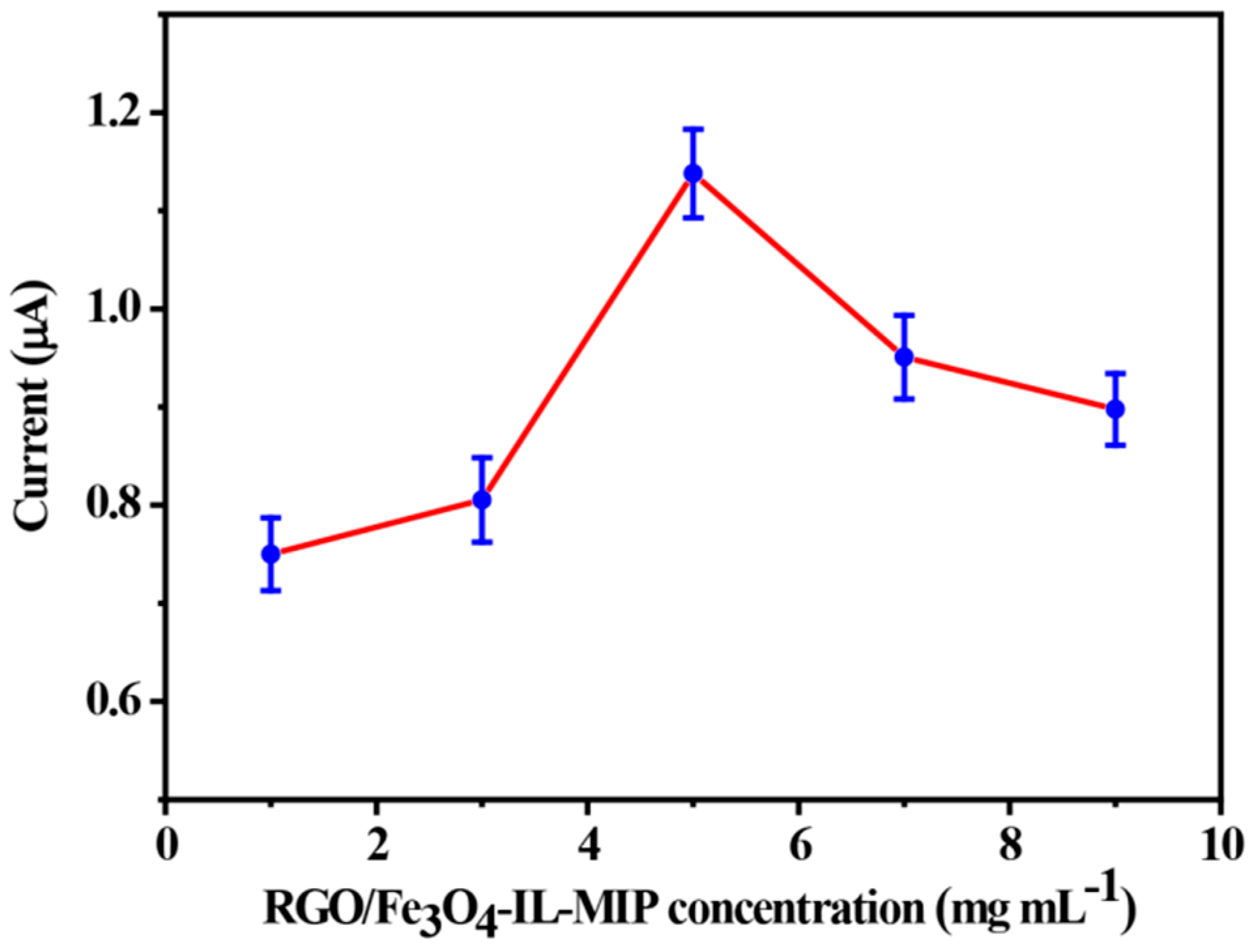
3.3. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
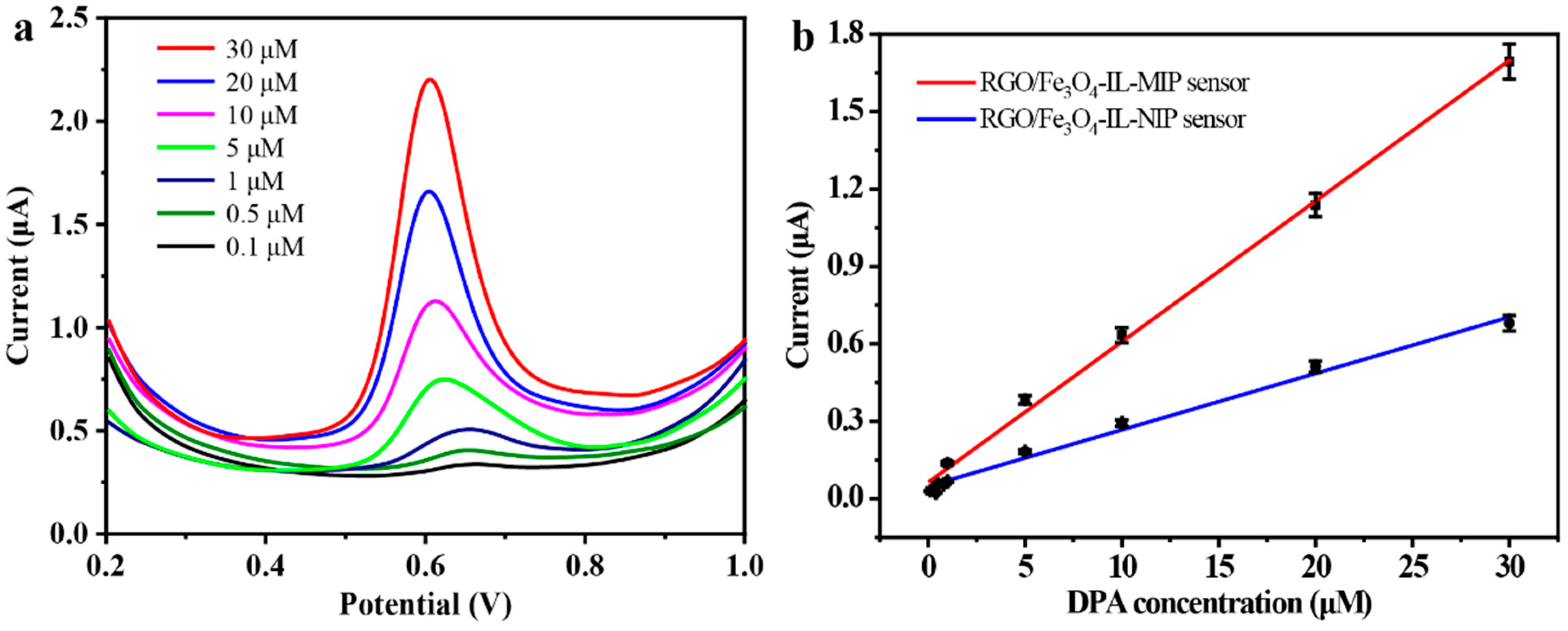
3.4. Analytical Performance and Selectivity of RGO/Fe3O4-IL-MIP Sensor
3.5. Reproducibility and Stability of RGO/Fe3O4-IL-MIP Sensor
3.6. Analytical Application
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alizadeh, N.; Farokhcheh, A. Simultaneous determination of diphenylamine and nitrosodiphenylamine by photochemically induced fluorescence and synchronous fluorimetry using double scans method. Talanta 2014, 121, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drzyzga, O. Diphenylamine and derivatives in the environment: A review. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Yamini, Y.; Asiabi, H.; Moradi, M. Determination of diphenylamine residue in fruit samples by supercritical fluid extraction followed by vesicular based-supramolecular solvent microextraction. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 100, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Pérez, M.L.; Plaza-Bolaños, P.; Romero-González, R.; Martínez-Vidal, J.L.; Garrido-Frenich, A. Comprehensive qualitative and quantitative determination of pesticides and veterinary drugs in honey using liquid chromatography-orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1248, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Forney, C.F.; Jordan, M.A. A method to detect diphenylamine contamination of apple fruit and storages using headspace solid phase micro-extraction and gas chromatography/mass spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granado, V.L.; Gutiérrez-Capitán, M.; Fernández-Sánchez, C.; Gomes, M.T.S.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Jimenez-Jorquera, C. Thin-film electrochemical sensor for diphenylamine detection using molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 809, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Duan, M.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Fang, S. Preparation of molecularly imprinted microspheres as biomimetic recognition material for in situ adsorption and selective chemiluminescence determination of bisphenol A. Polymers 2018, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Tang, C.; Zhu, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, L. Voltammetric determination of 5-hydroxytryptamine based on the use of platinum nanoparticles coated with molecularly imprinted silica. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, I.; Han, H.; Baik, S.; Helms, V.; Kim, Y. Detection of acidic pharmaceutical compounds using virus-based molecularly iImprinted polymers. Polymers 2018, 10, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. Core-shell molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles as synthetic antibodies in a sandwich fluoroimmunoassay for trypsin determination in human serum. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 24476–24483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfarotta, F.; Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S. Solid-phase synthesis of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, G.; Shinde, S.; Yeung, S.Y.; Jakstaite, M.; Li, Q.; Wingren, A.G.; Sellergren, B. An epitope-imprinted biointerface with dynamic bioactivity for modulating cell-biomaterial interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15959–15963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, F.; Peng, H.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Xiong, H. Molecularly imprinted polymer on magnetic graphene oxide for fast and selective extraction of 17β-estradiol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7436–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Hou, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Controlled synthesis various shapes Fe3O4 decorated reduced graphene oxide applied in the electrochemical detection. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 638, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gao, P.; Gai, S.; He, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, P. Ultra small and highly dispersed Fe3O4 nanoparticles anchored on reduced graphene for supercapacitor application. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 190, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yung, K.C.; Ma, R.; Yang, X.; Chui, Y.; Lee, J.M.; Zapien, J.A. Graphene/acid assisted facile synthesis of structure-tuned Fe3O4 and graphene composites as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. Carbon 2015, 86, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, G.J.; Babu, K.J.; Rajan, M.J. Watsonia meriana flower like Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for the highly sensitive and selective electrochemical sensing of dopamine. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Song, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, H. Synthesis of 3D hierarchical Fe3O4/graphene composites with high lithium storage capacity and for controlled drug delivery. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 21567–21573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y. Magnetic-graphene based molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposite for the recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Talanta 2015, 144, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, P.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Highly sensitive Fe3O4 nanobeads/graphene-based molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for 17β-estradiol in water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 884, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, H. Fe3O4@ rGO doped molecularly imprinted polymer membrane based on magnetic field directed self-assembly for the determination of amaranth. Talanta 2014, 123, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Hu, J.; Li, L. A new composite of graphene and molecularly imprinted polymer based on ionic liquids as functional monomer and cross-linker for electrochemical sensing 6-benzylaminopurine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 108, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, F.; Gregorio, V.; Rubio, A.; Garrido, L.; García, N.; Tiemblo, P. Ionic liquid-based thermoplastic solid electrolytes processed by solvent-rree procedures. Polymers 2018, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, S.; Serra, M.; Shinde, S.; Sellergren, B.; De Lorenzi, E. Synthesis and chromatographic evaluation of molecularly imprinted polymers prepared by the substructure approach for the class-selective recognition of glucuronides. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 6961–6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadhirvel, P.; Azenha, M.; Shinde, S.; Schillinger, E.; Gomes, P.; Sellergren, B.; Silva, A.F. Imidazolium-based functional monomers for the imprinting of the anti-inflammatory drug naproxen: Comparison of acrylic and sol–gel approaches. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1314, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, M.; Liu, G.; Hou, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, K.; Li, C. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensing interface based on in-situ-polymerization of amino-functionalized ionic liquid for specific recognition of bovine serum albumin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Tian, Z.; Tong, S.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Xu, R.; Qin, Y.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.; Ouyang, X. A novel molecularly imprinted polymer of the specific ionic liquid monomer for selective separation of synephrine from methanol-water media. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3578–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Hu, X.; Guan, P.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Ding, X.; Du, C. Preparation of surface-imprinted microspheres using ionic liquids as novel cross-linker for recognizing an immunostimulating peptide. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 8027–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Row, K.H. Solid-phase extraction of chlorophenols in seawater using a magnetic ionic liquid molecularly imprinted polymer with incorporated silicon dioxide as a sorbent. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1559, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Antonietti, M. Poly (ionic liquid) latexes prepared by dispersion polymerization of ionic liquid monomers. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zheng, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, W.; Kang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, S.; Xia, J. A non-enzyme hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on Fe3O4/RGO nanocomposite material. ECS Electrochem. Lett. 2014, 3, B26–B29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Luo, C.; Sun, M.; Lu, F.; Fan, L.; Li, X. A chemiluminescence sensor for determination of epinephrine using graphene oxide–magnetite-molecularly imprinted polymers. Carbon 2012, 50, 4052–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Lu, J.; Zhang, W.; He, A.; Yao, S. Ionic liquid-modified silica gel as adsorbents for adsorption and separation of water-soluble phenolic acids from Salvia militiorrhiza Bunge. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 155, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Yi, Y.; Han, Z.; Liu, J.; Gai, Z. 3,4,9,10-Perylene tetracarboxylic acid noncovalently modified multiwalled carbon nNanotubes: Synthesis, characterization, and application for electrochemical determination of 2-aminonaphthalene. Anal. Lett. 2014, 47, 2370–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.; Lee, H.K. Simultaneous electrochemical detection of carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic amines in environmental samples using single-walled carbon nanotube-gold nanoparticle composite. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, M.; Sukanya, R.; Chen, S. Fabrication of europium doped molybdenum diselenide nanoflower based electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of diphenylamine in apple juice. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, R.; Karikalan, N.; Chen, S.M.; Kumar, J.V.; Karuppiah, C.; Muthuraj, V. Assessment of divergent functional properties of seed-like strontium molybdate for the photocatalysis and electrocatalysis of the postharvest scald inhibitor diphenylamine. J. Catal. 2017, 352, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, P.E.; Samui, A.B.; Kulkarni, P.S. An Efficient Method for Determination of the diphenylamine (stabilizer) in propellants by molecularly imprinted polymer based carbon paste electrochemical sensor. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Detection Method | Selective Material | Linear Range (μM) | Detection Limit (μM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEDOT a/MIP/gold electrode | EGDMA b-based MIP | 4.95–115 | 3.9 | [6] |
| EuMoSe2/GCE | NR c | 0.01–243.17 | 0.0088 | [37] |
| SrMoO4/GCE | NR | 0.1–35 | 0.03 | [38] |
| MIP-based CPE d | TRIM e-based MIP | 500–3000 | 100 | [39] |
| RGO/Fe3O4-MIP/GCE | IL-based RGO/Fe3O4-MIP | 0.1–30 | 0.05 | This work |
| Sample | Added DPA (μM) | Found DPA (μM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lake water | 1.0 | 1.039 | 103.9 | 3.6 |
| 5.0 | 4.78 | 95.6 | 4.8 | |
| Pear peel | 1.0 | 0.993 | 99.3 | 4.6 |
| 5.0 | 5.76 | 115.2 | 2.5 | |
| Apple peel | 1.0 | 1.15 | 115.0 | 4.5 |
| 5.0 | 5.32 | 106.4 | 4.7 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Zhu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, L. An Electrochemical Sensor for Diphenylamine Detection Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide/Fe3O4-Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with 1,4-Butanediyl-3,3′-bis-l-vinylimidazolium Dihexafluorophosphate Ionic Liquid as Cross-Linker. Polymers 2018, 10, 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121329
Liu L, Zhu X, Zeng Y, Wang H, Lu Y, Zhang J, Yin Z, Chen Z, Yang Y, Li L. An Electrochemical Sensor for Diphenylamine Detection Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide/Fe3O4-Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with 1,4-Butanediyl-3,3′-bis-l-vinylimidazolium Dihexafluorophosphate Ionic Liquid as Cross-Linker. Polymers. 2018; 10(12):1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121329
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lingyu, Xudong Zhu, Yanbo Zeng, Hailong Wang, Yixia Lu, Jian Zhang, Zhengzhi Yin, Zhidong Chen, Yiwen Yang, and Lei Li. 2018. "An Electrochemical Sensor for Diphenylamine Detection Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide/Fe3O4-Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with 1,4-Butanediyl-3,3′-bis-l-vinylimidazolium Dihexafluorophosphate Ionic Liquid as Cross-Linker" Polymers 10, no. 12: 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121329
APA StyleLiu, L., Zhu, X., Zeng, Y., Wang, H., Lu, Y., Zhang, J., Yin, Z., Chen, Z., Yang, Y., & Li, L. (2018). An Electrochemical Sensor for Diphenylamine Detection Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide/Fe3O4-Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with 1,4-Butanediyl-3,3′-bis-l-vinylimidazolium Dihexafluorophosphate Ionic Liquid as Cross-Linker. Polymers, 10(12), 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121329