Luminescent and UV-Shielding ZnO Quantum Dots/Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium Nanocomposite Polymer Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of ZnOQD and ZnOQD/CMC Nanocomposites
2.3. Fabrication of ZnOQD/CMC Composites
2.4. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
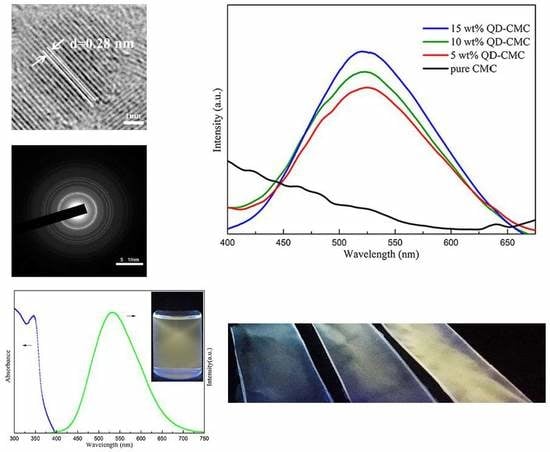
3.1. Morphology and Diffraction Analysis of ZnOQD
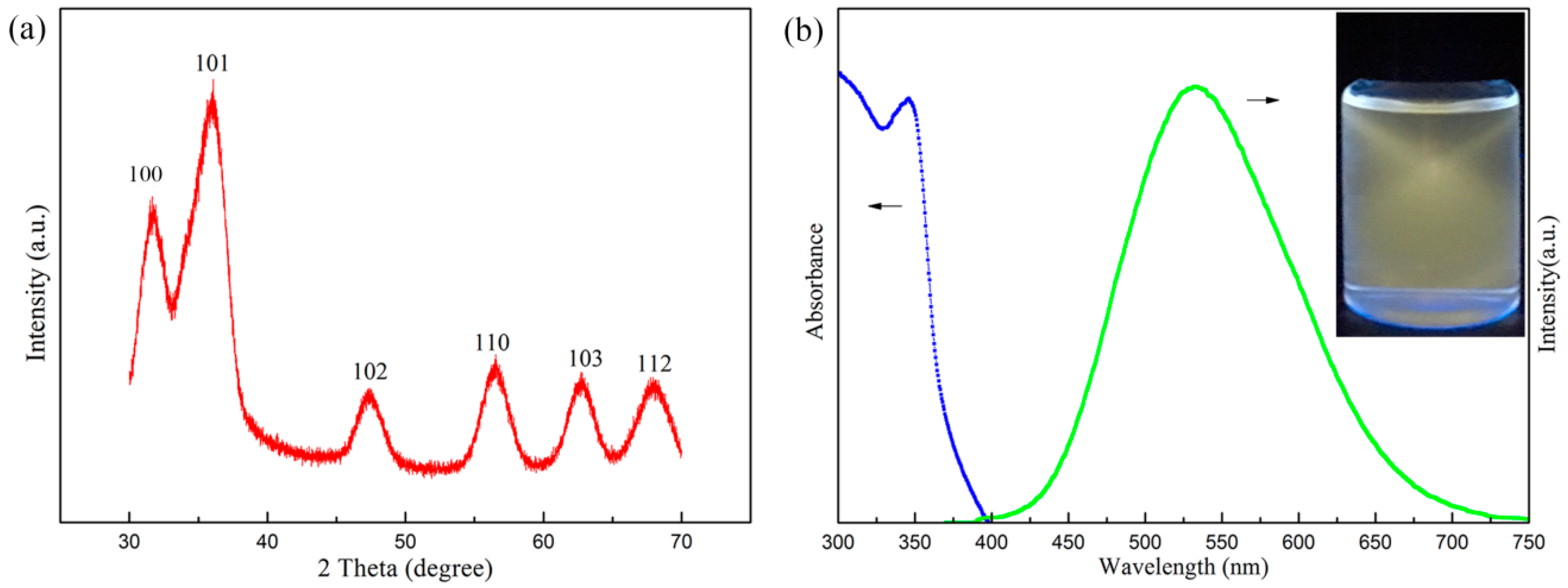
3.2. XRD and Photoluminescence Analysis of ZnOQD
3.3. Morphology Analysis of ZnOQD/CMC Composites
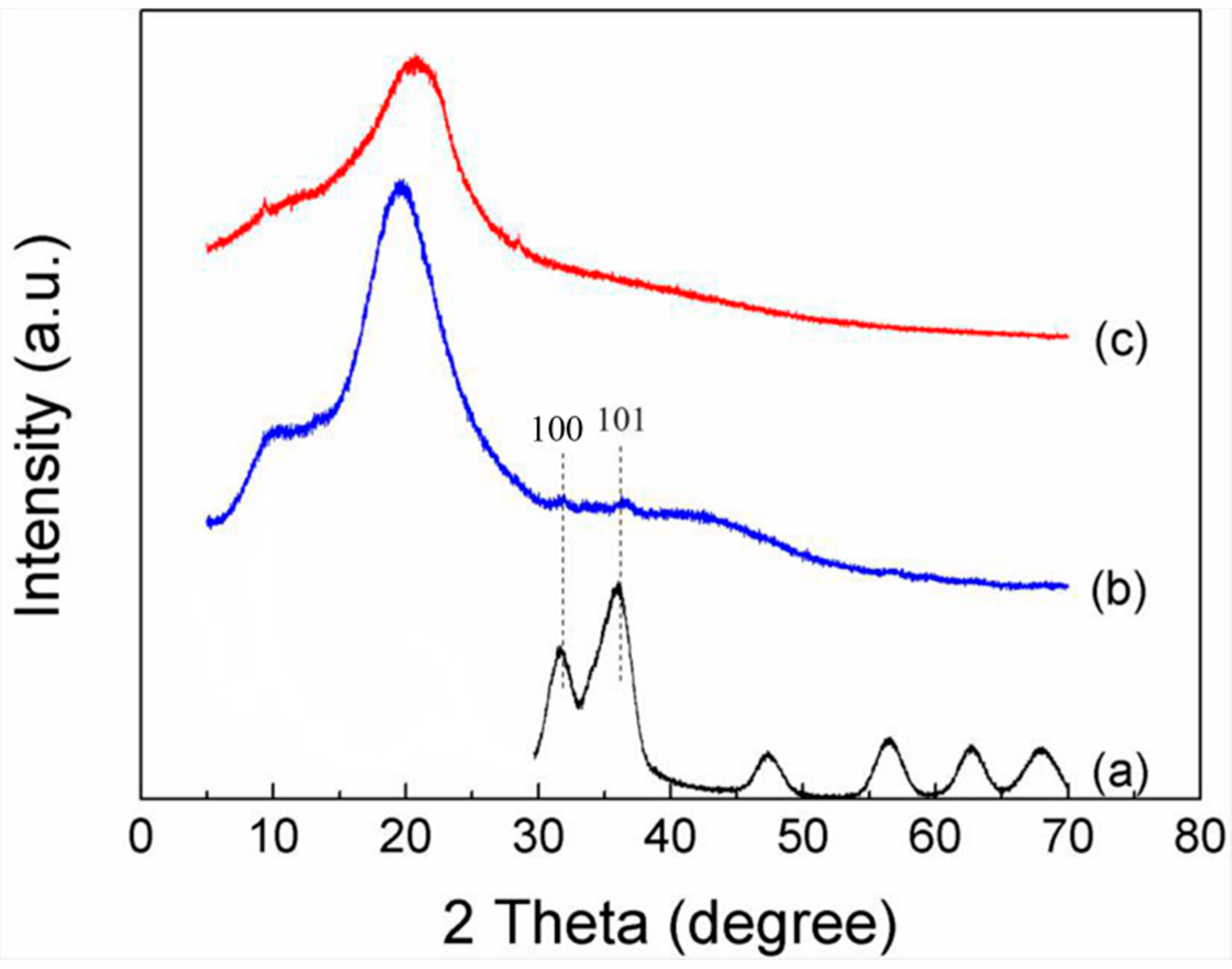
3.4. XRD Analysis of ZnOQD/CMC Composites
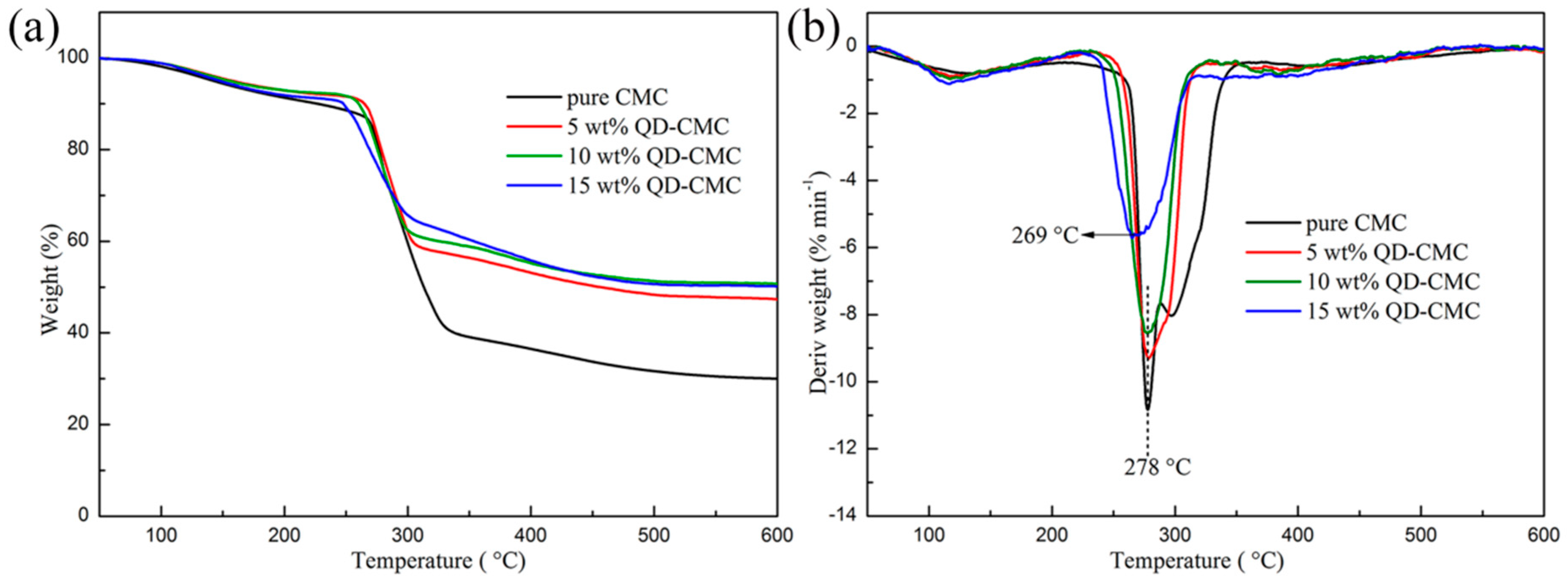
3.5. Thermal Analysis of CMC and Composites
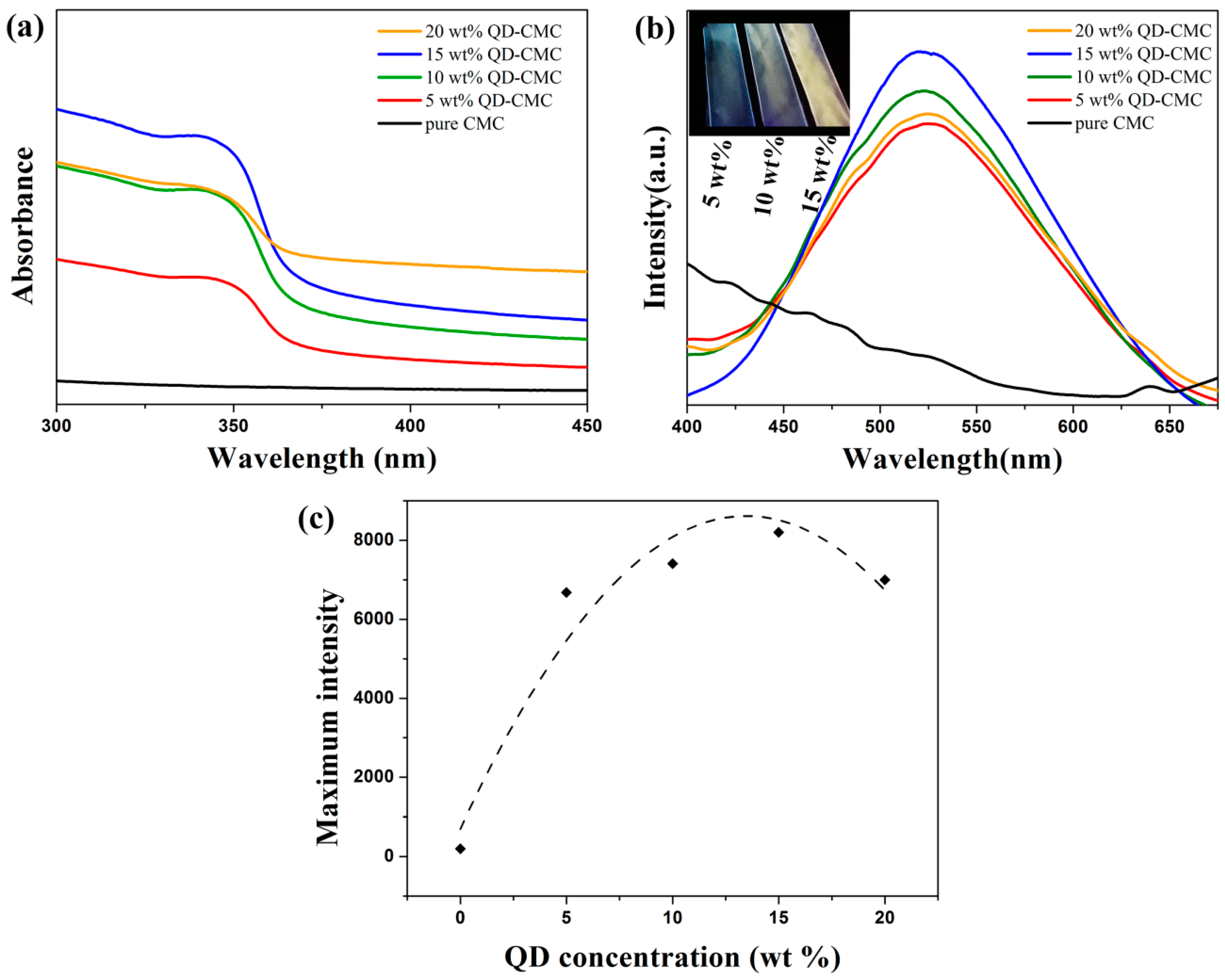
3.6. Photoluminescence Analysis of ZnOQD/CMC Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kovalchuk, A.; Huang, K.; Xiang, C.; Martí, A.A.; Tour, J.M. Luminescent Polymer Composite Films Containing Coal-Derived Graphene Quantum Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 26063–26068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Liu, B.; Chen, T.; Liu, B. Dielectric properties of graphene quantum dot-cobalt ferrite-poly(vinylidene fluoride) ternary composites. Mater. Lett. 2017, 209, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koushesh, S.M.; Amini, R. Nano-ZnO/carboxymethyl cellulose-based active coating impact on ready-to-use pomegranate during cold storage. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, A.M.; Elsayed, S.M.; Elsayed, H.S.; Salama, H.H.; Dufresne, A. Enhancement of Egyptian soft white cheese shelf life using a novel chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose/zinc oxide bionanocomposite film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ying, Q.; Huang, X.; Li, C.; Xue, J. Synthesis of Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes–Chitosan Nanocomposites for the Development of an Electrochemical Biosensor for Serum Leptin Detection. Mater. Lett. 2017, 211, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Yang, C.; Chen, S.; Li, W.; Lou, J.; Wang, J. A facile approach to prepare shell/core nanofibers for drug controlled release. Mater. Lett. 2015, 150, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Tian, J.; Liu, T.; Guo, Z.; Ding, S.; Li, H. Preparation and antibacterial properties of carboxymethyl chitosan/ZnO nanocomposite microspheres with enhanced biocompatibility. Mater. Lett. 2017, 212, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Saha, N.; Kitano, T.; Saha, P. Biodegradation of PVP–CMC hydrogel film: A useful food packaging material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanmani, P.; Rhim, J.W. Properties and characterization of bionanocomposite films prepared with various biopolymers and ZnO nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noshirvani, N.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Mokarram, R.R.; Hashemi, M.; Coma, V. Preparation and characterization of active emulsified films based on chitosan-carboxymethyl cellulose containing zinc oxide nano particles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.S.; Du, X.W.; Kulinich, S.A.; Qiu, J.S.; Qin, W.J.; Li, R.; Sun, J.; Liu, J. Stable Aqueous Dispersion of ZnO Quantum Dots with Strong Blue Emission via Simple Solution Route. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 16029–16033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Xie, S.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, C.; Li, C. The flexible-transparent photosensitive films of cotton cellulose framework of carbon quantum dots/ZnO. Mater. Lett. 2017, 211, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, K.; Mishima, K.; Kato, T.; Irie, K.; Mishima, K. Transparent polymeric hybrid film of ZnO nanoparticle quantum dots and PMMA with high luminescence and tunable emission color. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.M. ZnO Nanoparticles Applied to Bioimaging and Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2013, 44, 5329–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Choo, E.S.G.; Li, L.; Ding, J.; Xue, J. Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles with Tunable Emission Colors and Their Cell Labeling Applications. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 3383–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.-V.; Jiang, S.; He, C.; Lin, Z.; Lin, N.; Nguyen, A.-T.; Kang, L.; Han, M.-Y.; Liu, X.-Y. Elevating Biomedical Performance of ZnO/SiO2@Amorphous Calcium Phosphate–Bioinspiration Making Possible the Impossible. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 6921–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Xu, X.; Hu, J. Transparent and UV-shielding ZnO@PMMA nanocomposite films. Opt. Mater. 2013, 36, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Ansari, Z.A.; Singh, S.P.; Shanker, V. Synthesis and Characterization of Highly Fluorescent Water Dispersible ZnO Quantum Dots. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2009, 2, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, M.; Shi, B.; Li, B. Flame Retardance and Smoke Suppression of CFA/APP/LDHs/EVA Composite. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, B. Thermal Stability, Combustion Behavior, and Mechanical Property in a Flame-Retardant Polypropylene System. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Kawata, A.; Morito, S.; Sato, Y.; Yamaguchi, I. Preparation and properties of polymer/zinc oxide nanocomposites using functionalized zinc oxide quantum dots. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 3430–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shao, C.; Gao, F.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Enhanced ultraviolet emission from highly dispersed ZnO quantum dots embedded in poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) electrospun nanofibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 347, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.P.; Le Rendu, P.; Musa, I.; Yang, S.H.; Dan, Y.; That, C.T.; Nguyen, T.P. Investigation of the optical properties of polyfluorene/ZnO nanocomposites. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 3997–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balen, R.; da Costa, W.V.; de Lara Andrade, J.; Piai, J.F.; Muniz, E.C.; Companhoni, M.V.; Nakamura, T.U.; Lima, S.M.; da Cunha Andrade, L.H.; Bittencourt, P.R.S.; et al. Structural, thermal, optical properties and cytotoxicity of PMMA/ZnO fibers and films: Potential application in tissue engineering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 385, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Li, B.; Ji, Y.; Wang, L. Luminescent and UV-Shielding ZnO Quantum Dots/Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium Nanocomposite Polymer Films. Polymers 2018, 10, 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101112
Li T, Li B, Ji Y, Wang L. Luminescent and UV-Shielding ZnO Quantum Dots/Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium Nanocomposite Polymer Films. Polymers. 2018; 10(10):1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101112
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tianyi, Bin Li, Yali Ji, and Lili Wang. 2018. "Luminescent and UV-Shielding ZnO Quantum Dots/Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium Nanocomposite Polymer Films" Polymers 10, no. 10: 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101112
APA StyleLi, T., Li, B., Ji, Y., & Wang, L. (2018). Luminescent and UV-Shielding ZnO Quantum Dots/Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium Nanocomposite Polymer Films. Polymers, 10(10), 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101112