Fibrin Hydrogels for Endothelialized Liver Tissue Engineering with a Predesigned Vascular Network
Abstract
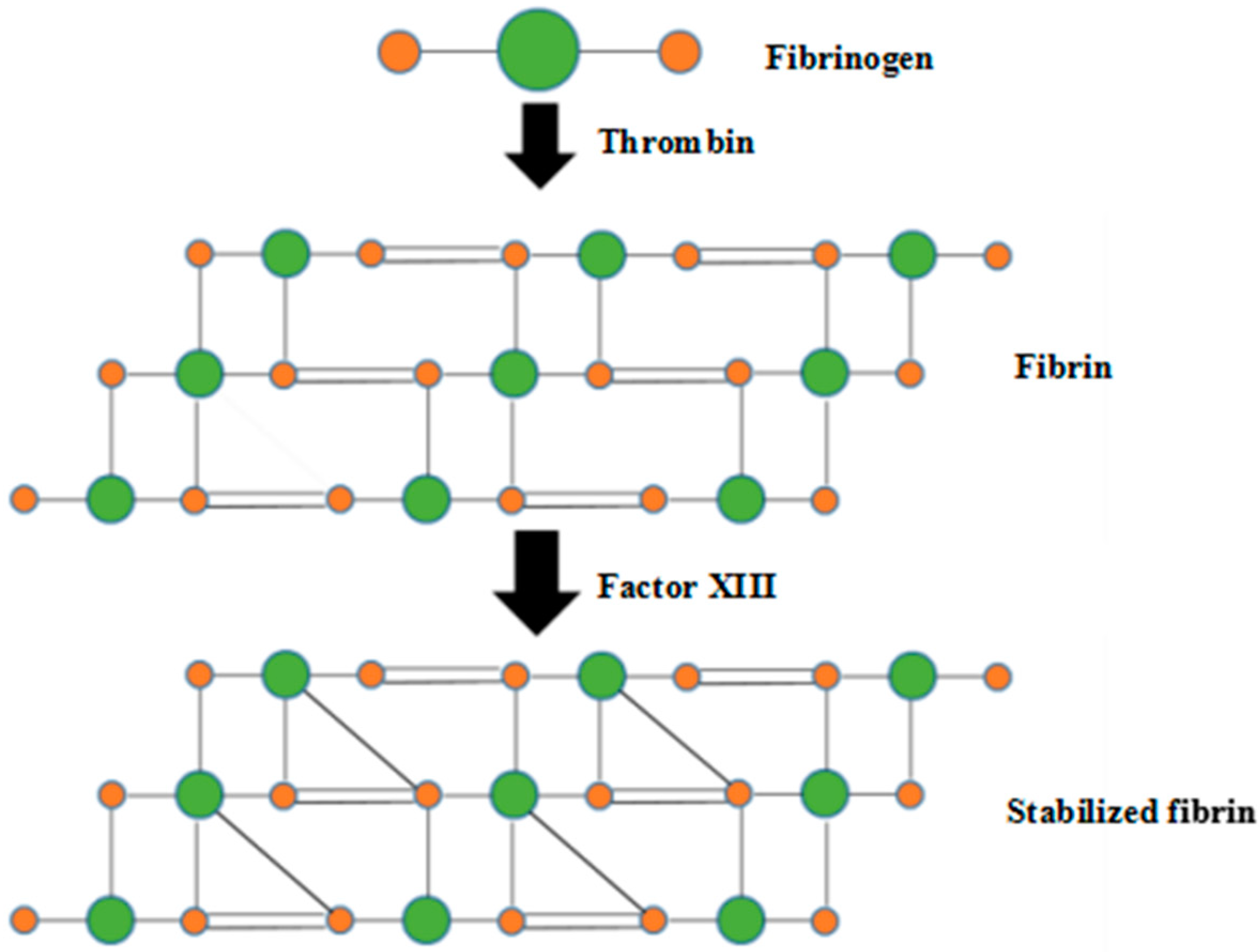
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Hepatocytes and ADSCs
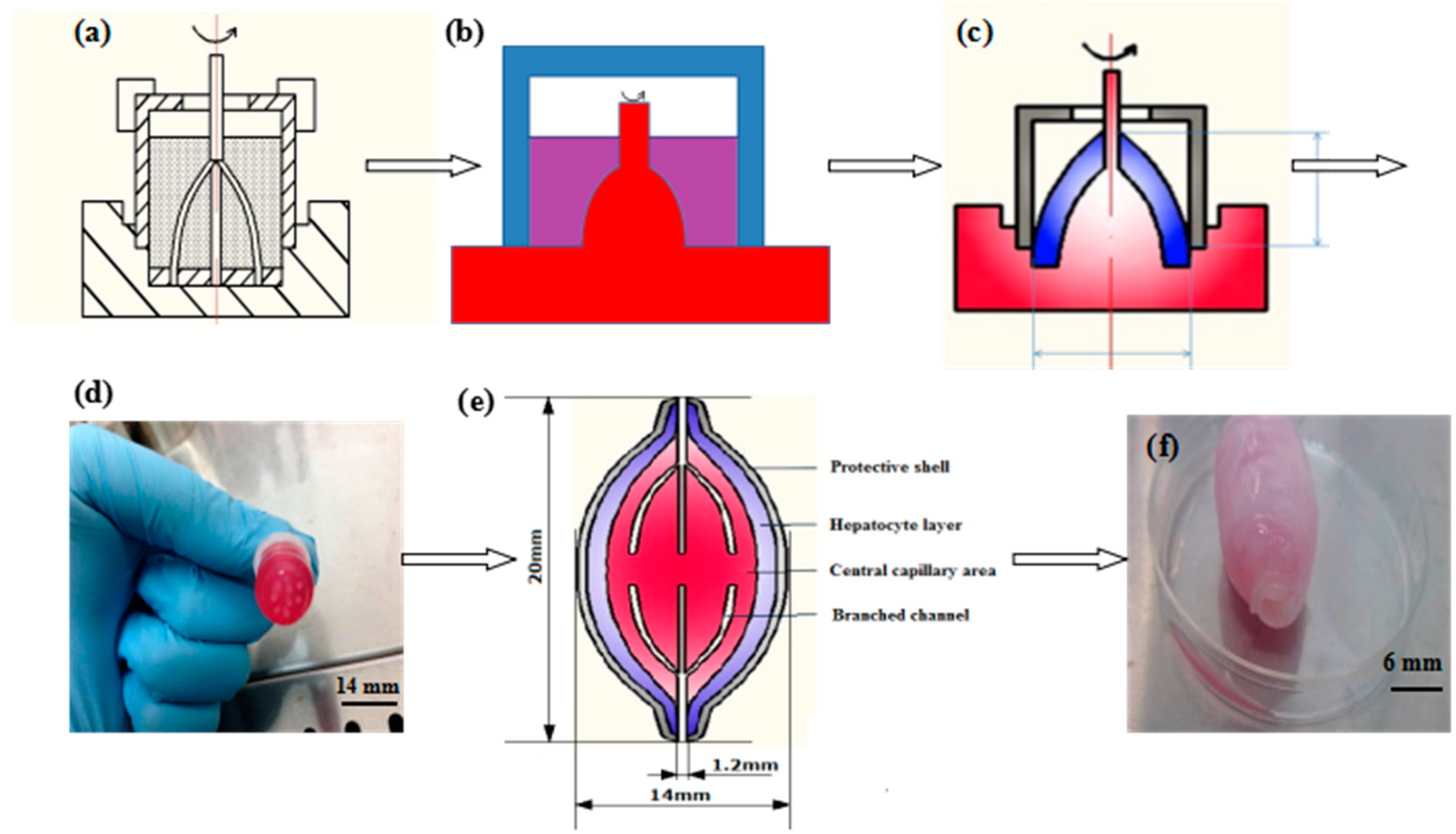
2.3. Construction of a Spindle Endothelialized Liver Tissue
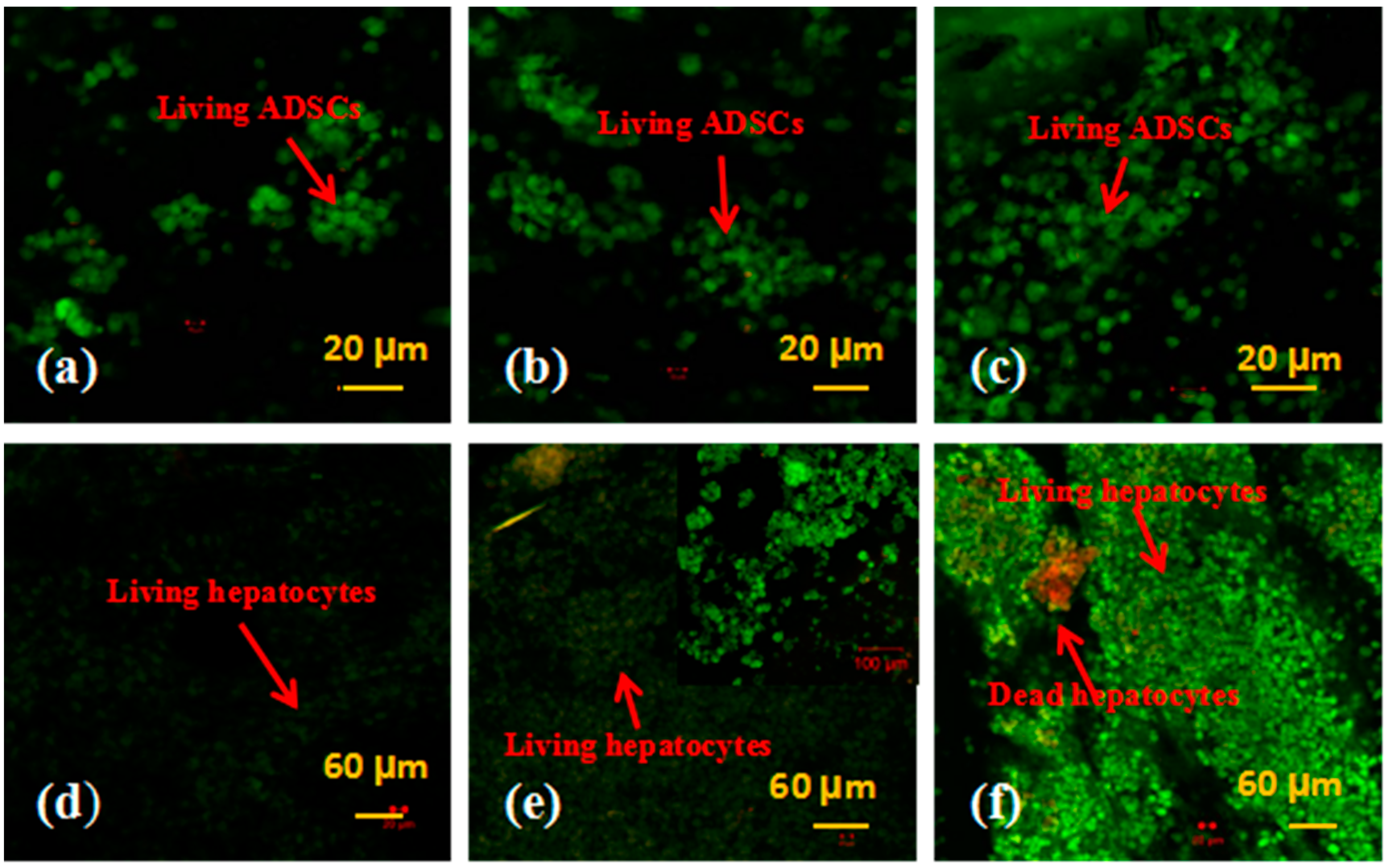
2.4. Cell Viability Tests
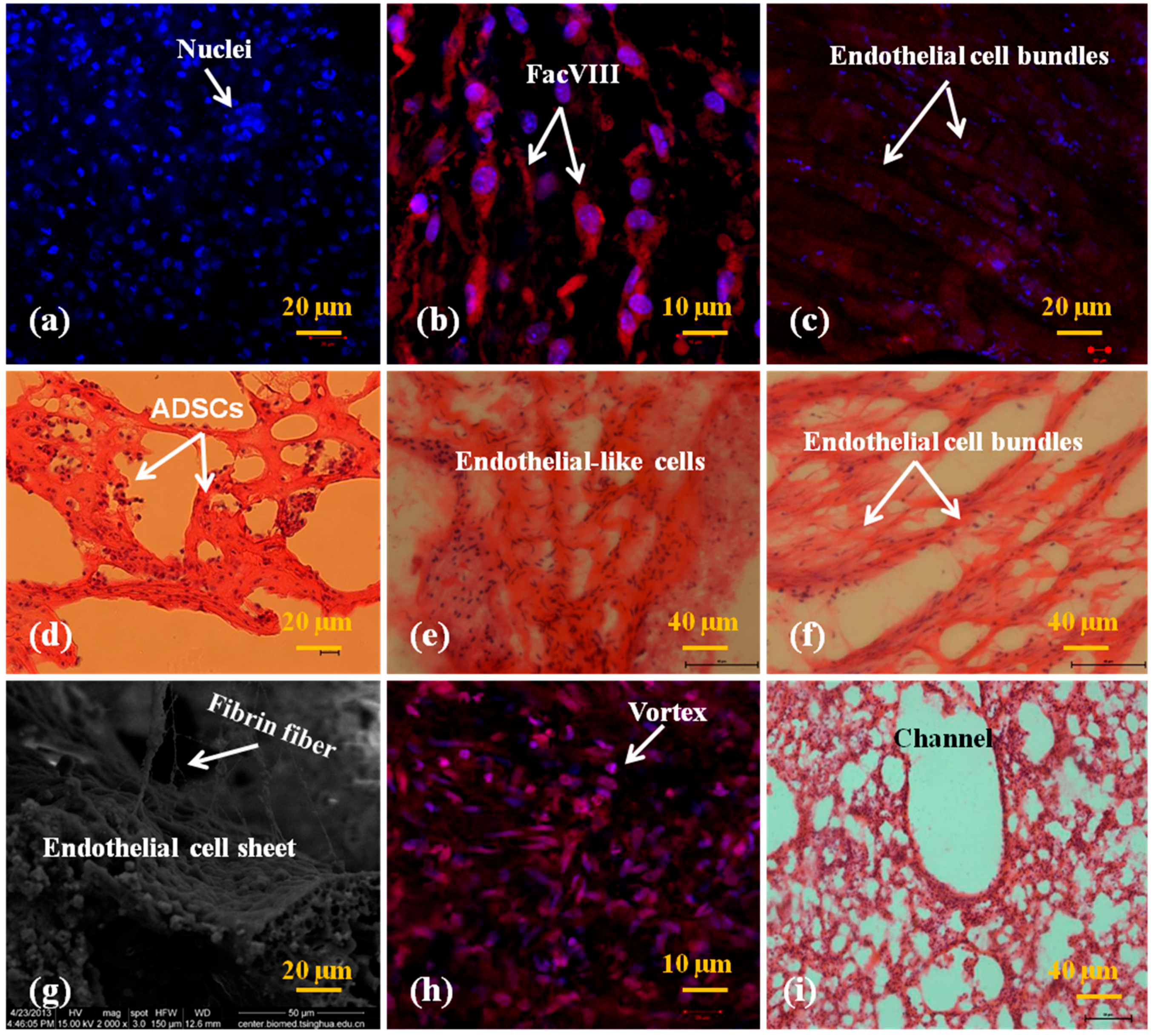
2.5. In Vitro Engagement and Characterization of the Cells
2.6. Permeability of the Spindle Vascularized Liver Tissues
2.7. Mechanical Strength Measurement
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
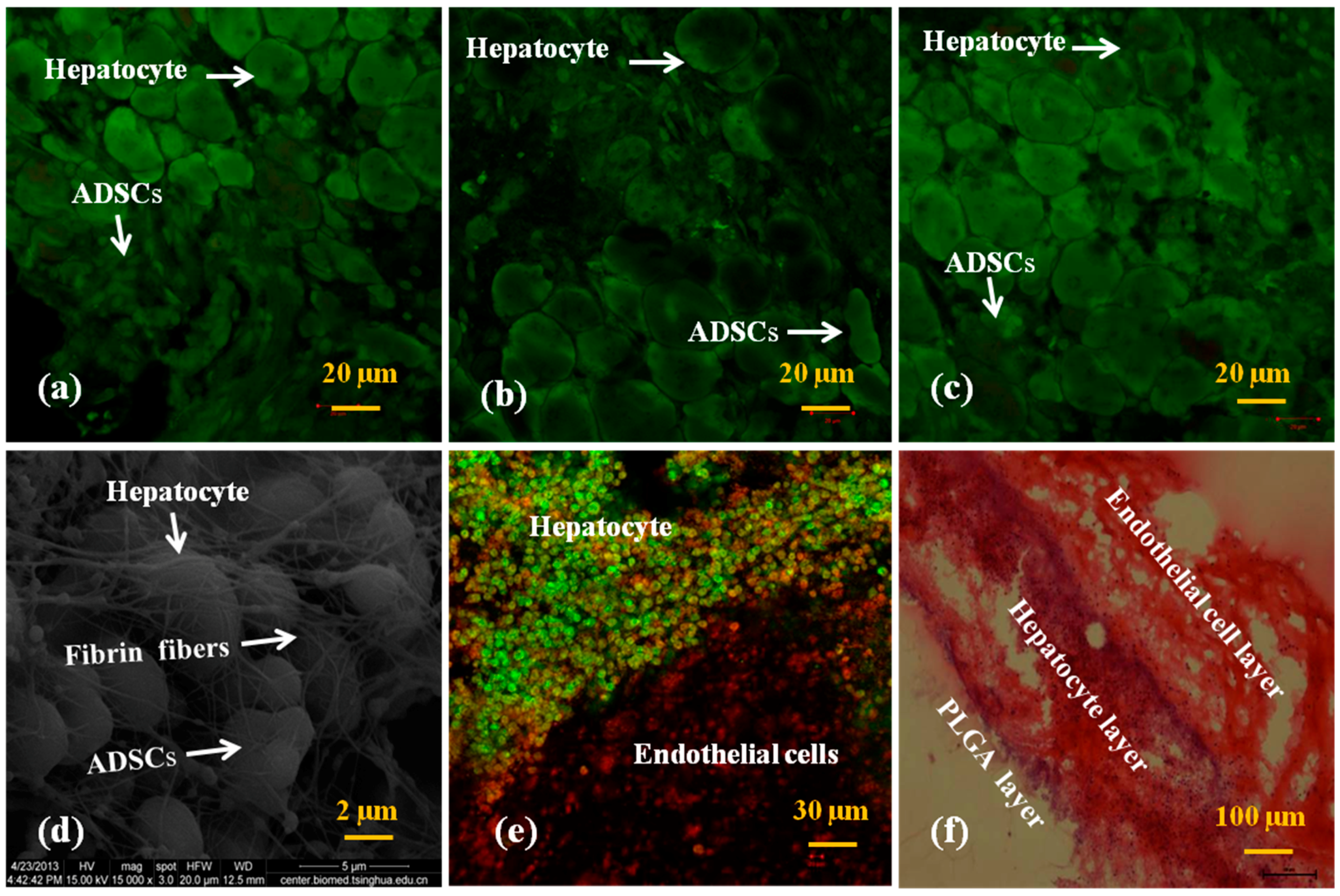
3.1. Generation of the Spindle Cell-Laden Constructs
3.2. Cell Viability in the Spindle Construct
3.3. In Vitro Engagement Effects of ADSCs to ECs and Hepatocytes in the Spindle Constructs
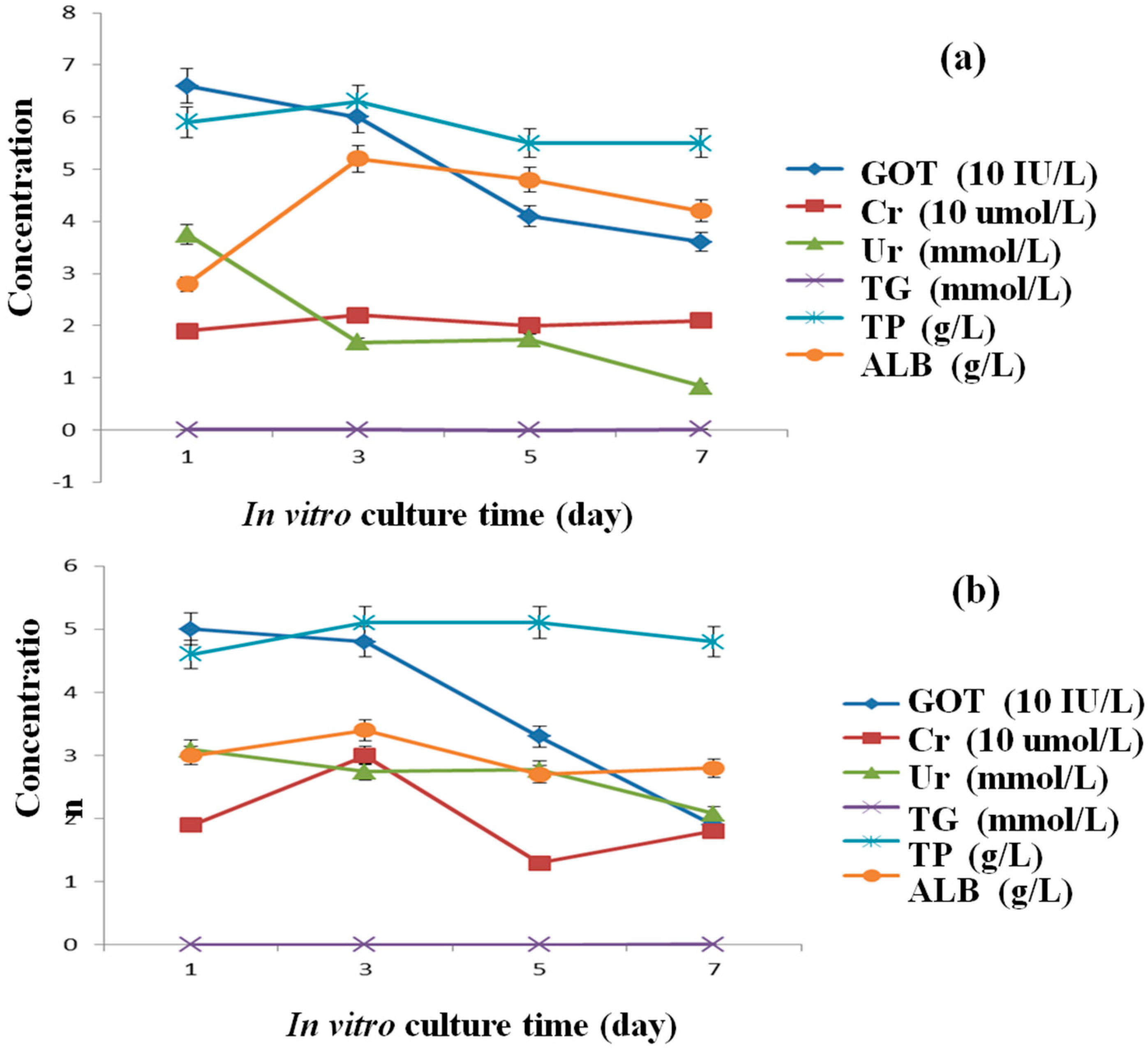
3.4. Secretion Abilities of the Hepatocytes
3.5. Permeability of the Spindle Construct after ADSC Engagement
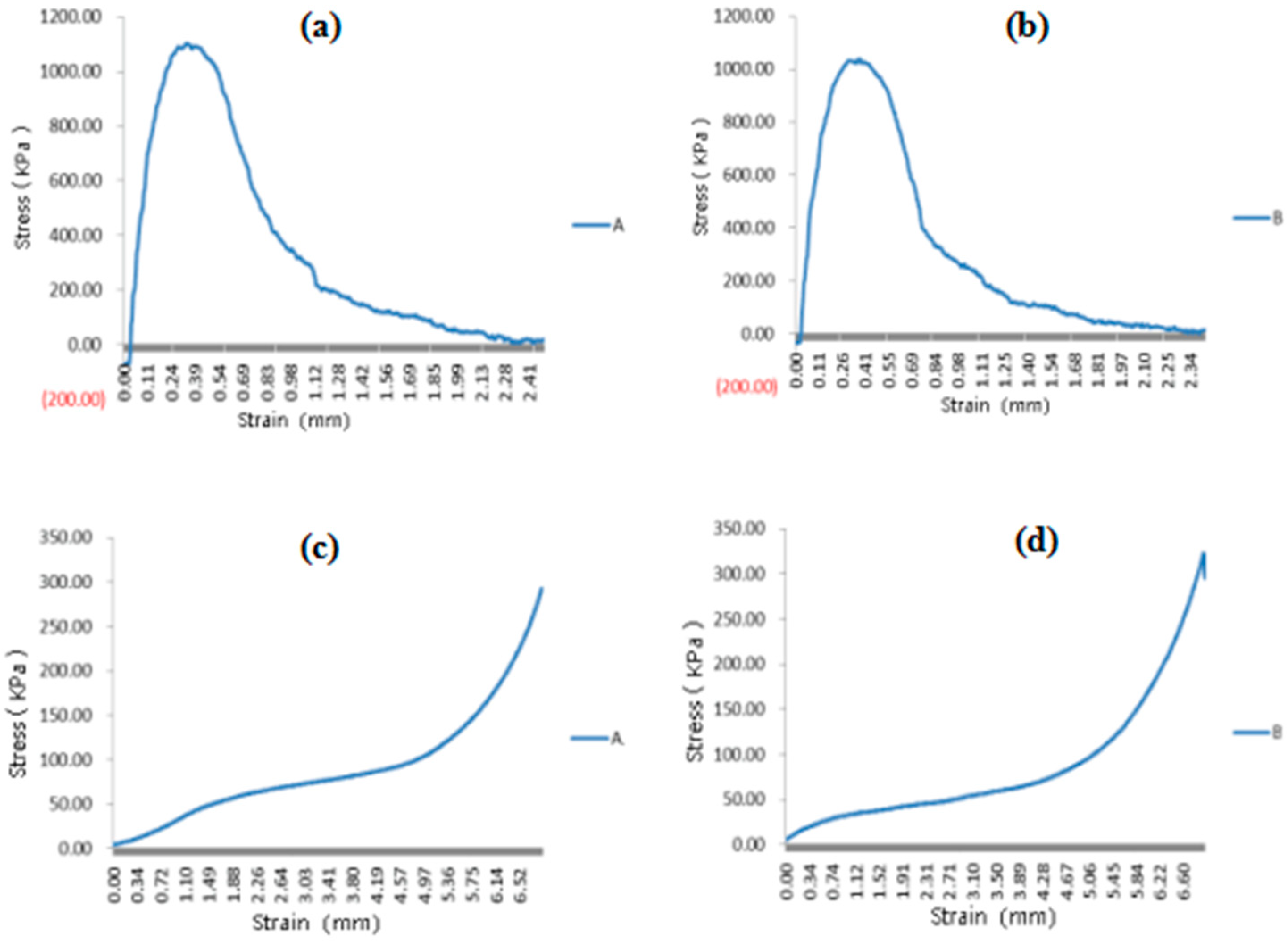
3.6. Mechanical Properties of the Spindle Vascularized Liver Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, F.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q.; Ao, Q.; Tian, X.; Fan, J.; Tong, H.; Wang, X. Progress in organ 3D bioprinting. Int. J. Bioprint. 2018, 4, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. 3D printing of tissue/organ analogues for regenerative medicine. In Handbook of Intelligent Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Regenerative Medicine, 2nd ed.; Khang, G., Ed.; Pan Stanford Publishing: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 557–570. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, L.G.; Naughton, G. Tissue engineering-current challenges and expanding opportunities. Science 2002, 295, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derby, B. Printing and prototyping of tissues and scaffolds. Science 2012, 338, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, R. Rapid prototyping as a tool for manufacturing bioartificial livers. Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, R. Recent trends and challenges in complex organ manufacturing. Tissue Eng. Part B 2010, 16, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X. Intelligent freeform manufacturing of complex organs. Artif. Organs 2012, 36, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, X. Creation of a vascular system for complex organ manufacturing. Int. J. Bioprint. 2015, 1, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takiwa, T.; Kano, J.; Kodama, M.; Matsumura, T. Multilayer rat hepatocyte aggregates formed on expanded polytetrafluoroethylene surface. Cytotechnology 1997, 25, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, R.G.; Ahsan, S.; Aizawa, Y.; Maxwell, K.L.; Morshead, C.M.; Shoichet, M.S. Spatially controlled simultaneous patterning of multiple growth factors in three-dimensional hydrogels. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.-H.; Moya, M.L.; Hughes, C.C.W.; George, S.C.; Lee, A.P.A. A microfluidic platform for generating large-scale nearly identical human microphysiological vascularized tissue arrays. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2990–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tuomi, J.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Poloheimo, K.-S.; Partanen, J.; Yliperttula, M. The integrations of biomaterials and rapid prototyping techniques for intelligent manufacturing of complex organs. In Advances in Biomaterials Science and Biomedical Applications; Lazinica, R., Rosario, P., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 437–463. ISBN 978-953-51-1051-4. [Google Scholar]
- Klement, B.J.; Young, Q.M.; George, B.J.; Nokkaew, M. Skeletal tissue growth, differentiation and mineralization in the NASA rotating wall vessel. Bone 2004, 34, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planat-Bénard, V.; Menard, C.; André, M.; Puceat, M.; Perez, A.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.-M.; Pénicaud, L.; Casteilla, L. Spontaneous cardiomyocyte differentiation from adipose tissue stroma cells. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidarsson, H.; Hyllner, J.; Sartipy, P. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to cardiomyocytes for in vitro and in vivo applications. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2010, 6, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoe, H.; Okitsu, T.; Itou, A.; Kato-Negishi, M.; Gojo, R.; Kiriya, D.; Sato, K.; Miura, S.; Iwanaga, S.; Kuribayashi-Shigetomi, K.; et al. Metre-long cell-laden microfibres exhibit tissue morphologies and functions. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Sundback, C.A.; Kaihara, S.; Benvenuto, M.S.; Kim, B.-S.; Mooney, D.J.; Vacant, J.P. Dynamic seeding and in vitro culture of hepatocytes in a flow perfusion system. Tissue Eng. 2004, 6, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levenberg, S.; Rouwkema, J.; Macdonald, M.; Garfein, E.S.; Kohane, D.S.; Darland, D.C.; Marini, R.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Mulligan, R.C.; D’Amore, P.A.; et al. Engineering vascularized skeletal muscle tissue. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, R.-Z.; Qi, H.; Yang, Y.; Bae, H.; Melero-Martin, J.M.; Khademhosseini, A. Functional human vascular network generated in photocrosslinkable gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2017–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Craven, M.; Choi, N.W.; Totorica, S.; Diaz-Santana, A.; Kermani, P.; Hempstead, B.; Fischbach-Teschl, C.; López, J.A.; et al. In vitro microvessels for the study of angiogenesis and thrombosis. PNAS 2012, 109, 9342–9347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlach, J.C. Long-term liver cell cultures in bioreactors and possible application for liver support. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 1997, 13, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadlock, T.; Sundback, C. Multilumen Polymeric Guidance Channel and Method of Manufacturing a Polymeric Prosthesis. U.S. Patent 621, 402, 1B1, 10 April 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.S.; Stevens, K.R.; Yang, M.T.; Baker, B.M.; Nguyen, D.H.; Cohen, D.M.; Toro, E.; Chen, A.A.; Galie, P.A.; Yu, X.; et al. Rapid casting of patterned vascular networks for perfusable engineered three-dimensional tissues. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; DeConinck, A.; Lewis, J.A. Omnidirectional printing of 3D microvasculL.ar networks. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, H178–H183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, X. Liver manufacturing approaches: The thresholds of cell manipulation with bio-friendly materials for multifunctional organ regeneration. In Organ Manufacturing; Wang, X., Ed.; Nova Science Publisher, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 201–225. [Google Scholar]
- Kaihara, S.; Borenstein, J.; Koka, R.; Lalan, S.; Ochoa, E.R.; Ravens, M.; Pien, H.; Cunningham, B.; Vacanti, J.P. Silicon micromachining to tissue engineer branched vascular channels for liver fabrication. Tissue Eng. 2000, 6, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, M.; Breen, A.; Greiser, U.; O’Brien, T.; Pandit, A. Fibrin-lipoplex system for controlled topical delivery of multiple Genes. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahota, P.S.; Burn, J.L.; Heaton, M.; Freedlander, E.; Suvarna, S.K.; Brown, N.J.; Mac Neil, S. Development of a reconstructed human skin model for angiogenesis. Wound Repair Regener. 2003, 11, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Sharma, H.S. Neurorestoratology: One of the most promising new disciplines at the forefront of neuroscience and medicine. J. Neurorestoratol. 2013, 1, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrel, B.E. Blood platelets: biochemistry and physiology. Hamostaseologie 2003, 23, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabst, M.; Bondili, J.S.; Stadlmann, J.; Mach, L.; Altmann, F. Mass retention time structure: a strategy for the analysis of N-glycans by carbon LC-ESI-MS and its application to fibrin N-glycans. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5051–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; He, K.; Wang, X. Rapid prototyping of a hybrid hierarchical polyurethane-cell/hydrogel construct for regenerative medicine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3220–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, R. Direct fabrication of a hybrid cell/hydrogel construct by a double-nozzle assembling technology. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2009, 24, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Khang, G.; Wang, X. In vitro vascularization of a combined system based on a 3D printing technique. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2014, 10, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Yao, R.; Ge, Y. A cell-assembly derived physiological 3D model of the metabolic syndrome, based on adipose-derived stromal cells and a gelatin/alginate/fibrinogen matrix. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3868–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C. A combined rotational mold for manufacturing a functional liver system. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2015, 39, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sui, S. Pulsatile culture of a PLGA sandwiched cell/hydrogel construct fabricated using a step by step mold/extraction method. Artif. Organs 2011, 35, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Paloheimo, K.-S.; Tuomi, J.; Paloheimo, M.; Sui, S.; Zhang, Q. Characterization of a PLGA sandwiched cell/fibrin tubular construct and induction of the adipose derived stem cells into smooth muscle cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sui, S.; Liu, C. Optimizing the step by step forming processes for fabricating a PLGA sandwiched cell/hydrogel construct. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, L.; Xu, W.; Wang, X. Rapid prototyping of a double layer polyurethane-collagen conduit for peripheral nerve regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part C 2009, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; He, K.; Zhang, W. Optimizing the fabrication processes for manufacturing a hybrid hierarchical polyurethane-cell/hydrogel construct. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2013, 28, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Development of a combined 3D printer and its application in complex organ construction. Master’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J. Vascularization and adipogenesis of a spindle hierarchical adipose-derived stem cell/collagen/alginate-PLGA construct for breast manufacturing. IJITEE 2015, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Vert, M.; Doi, Y.; Hellwich, K.-H.; Hess, M.; Hodge, P.; Kubisa, P.; Rinaudo, M.; Schué, F. Terminology for biorelated polymers and applications (IUPAC Recommendations 2012). Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 84, 377–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Rodriguez, G.A.; Beltrán-Hernández, R.I.; Lucho-Constantino, C.A.; Blasco, J.L. A method for measuring the anoxic biodegradability under denitrifying conditions. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischel, L.L.; Young, E.W.K.; Mader, B.R.; Beebe, D.J. Tubeless microfluidic angiogenesis assay with three-dimensional endothelial-lined microvessels. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Santana, A.; Shan, M.; Stroock, A.D. Endothelial cell dynamics during anastomosis in vitro. Integr. Biol. 2015, 7, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, L.L.Y.; Montgomery, M.; Liang, Y.; Liu, H.; Radisic, M. Perfusable branching microvessel bed for vascularization of engineered tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E3414–E3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucukgul, C.; Ozler, B.; Karakas, H.E.; Gozuacik, D.; Koc, B. 3D hybrid bioprinting of macrovascular structures. Procedia Eng. 2013, 59, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macosko, C.W. Rheology: Principles, Measurements, and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1994; ISBN 978-0-471-18575-8. [Google Scholar]
- Urciuolo, A.; Quarta, M.; Morbidoni, V.; Gattazzo, F.; Molon, S.; Grumati, P.; Montemurro, F.; Tedesco, F.S.; Blaauw, B.; Cossu, G.; et al. Collagen VI regulates satellite cell self-renewal and muscle regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, A.P.; Tien, J. Fabrication of microfluidic hydrogels using molded gelatin as a sacrificial element. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, P.; Cao, X.; Frenette, P.S.; Mao, J.J.; Robey, P.G.; Simmons, P.J.; Wang, C.-Y. The meaning, the sense and the significance: Translating the science of mesenchymal stem cells into medicine. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, G.; Gekas, J.; Bertrand, D.F. Amniotic stem cells for cellular cardiomyoplasty: Promises and premises. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 73, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ao, Q.; Tian, X.; Fan, J.; Tong, H.; Hou, W.; Bai, S. Gelatin-based hydrogels for organ 3D bioprinting. Polymers 2017, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, R. Gelatin-based hydrogels for controlled cell assembly. In Biomedical Applications of Hydrogels Handbook; Ottenbrite, R.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Overview on biocompatibilities of implantable biomaterials. In Advances in Biomaterials Science and Biomedical Applications in Biomedicine; Lazinica, R., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 111–155. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Spatial effects of stem cell engagement in 3D printing constructs. J. Stem Cells Res. Rev. Rep. 2014, 1, 5–9. [Google Scholar]


| Group | Permeation Time (s) |
|---|---|
| A | 61.4 ± 8.1 |
| B | 57.1 ± 8.3 |
| C | 47.8 ± 7.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Liu, C. Fibrin Hydrogels for Endothelialized Liver Tissue Engineering with a Predesigned Vascular Network. Polymers 2018, 10, 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101048
Wang X, Liu C. Fibrin Hydrogels for Endothelialized Liver Tissue Engineering with a Predesigned Vascular Network. Polymers. 2018; 10(10):1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101048
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaohong, and Chang Liu. 2018. "Fibrin Hydrogels for Endothelialized Liver Tissue Engineering with a Predesigned Vascular Network" Polymers 10, no. 10: 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101048
APA StyleWang, X., & Liu, C. (2018). Fibrin Hydrogels for Endothelialized Liver Tissue Engineering with a Predesigned Vascular Network. Polymers, 10(10), 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101048





