Triglycine-Based Approach for Identifying the Substrate Recognition Site of an Enzyme
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. X-Ray Diffraction and Data Processing
2.3. Structure Determination
3. Results
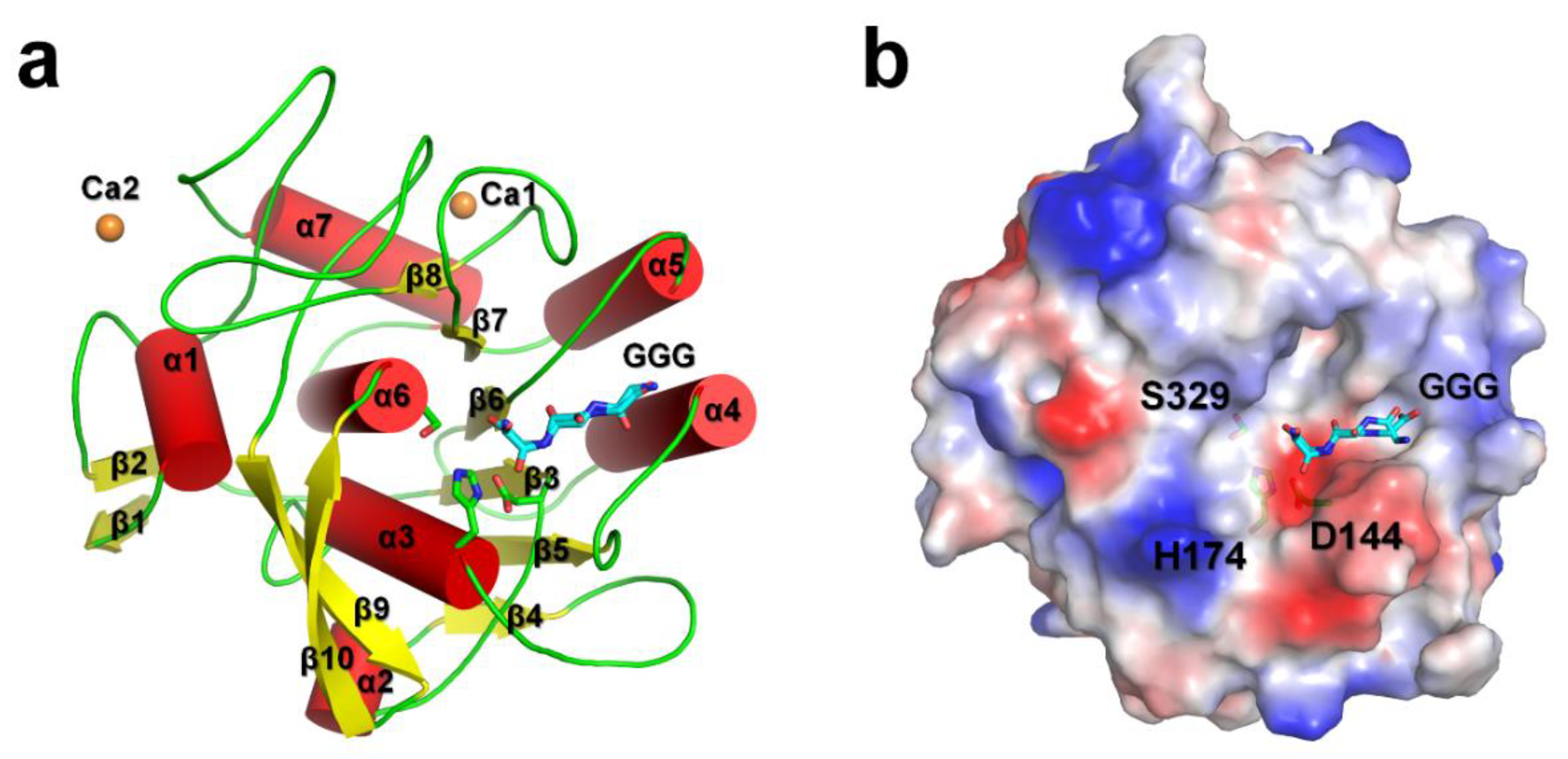
3.1. Overall Structure
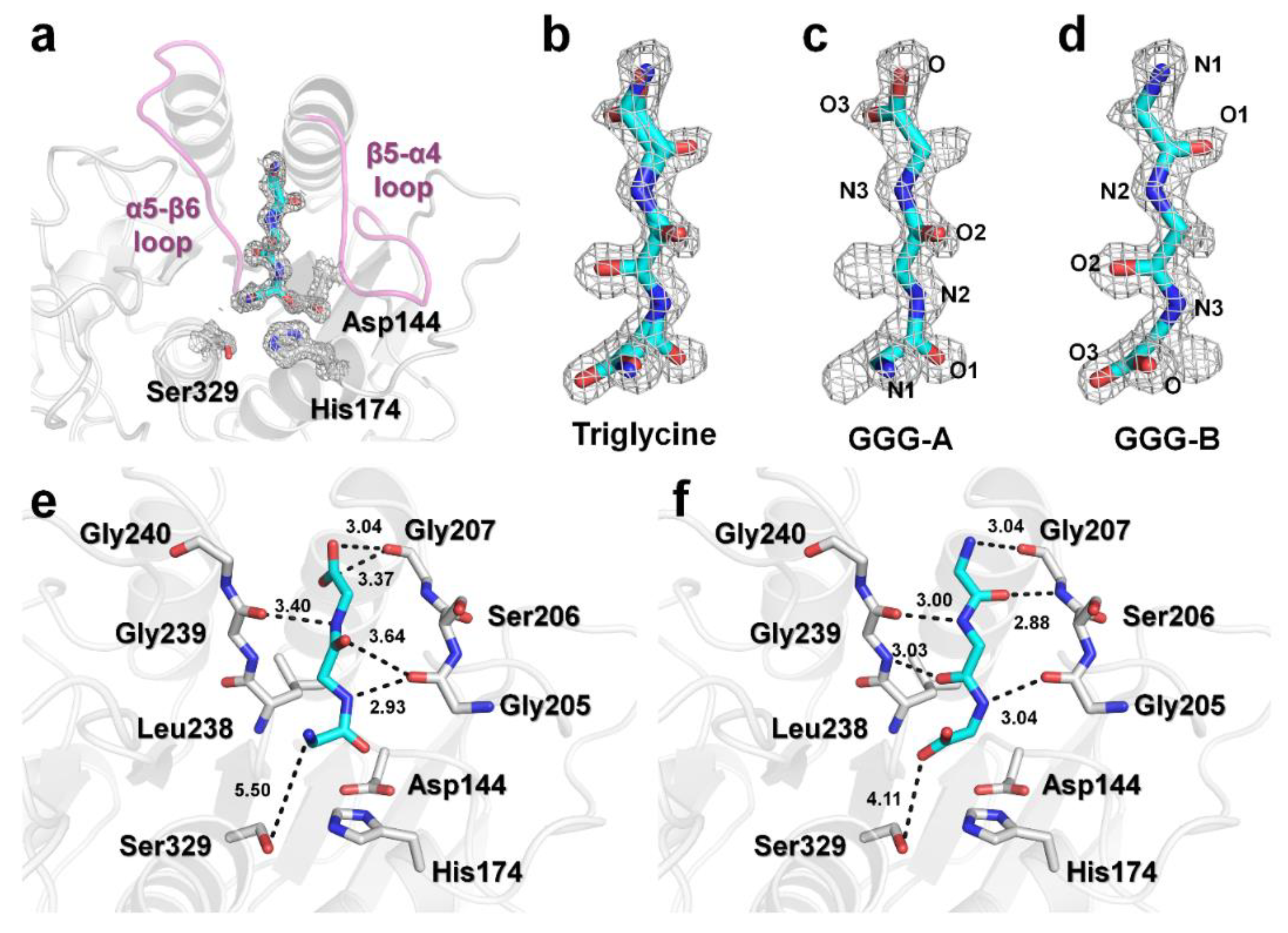
3.2. Triglycine Binding Site on PaProK
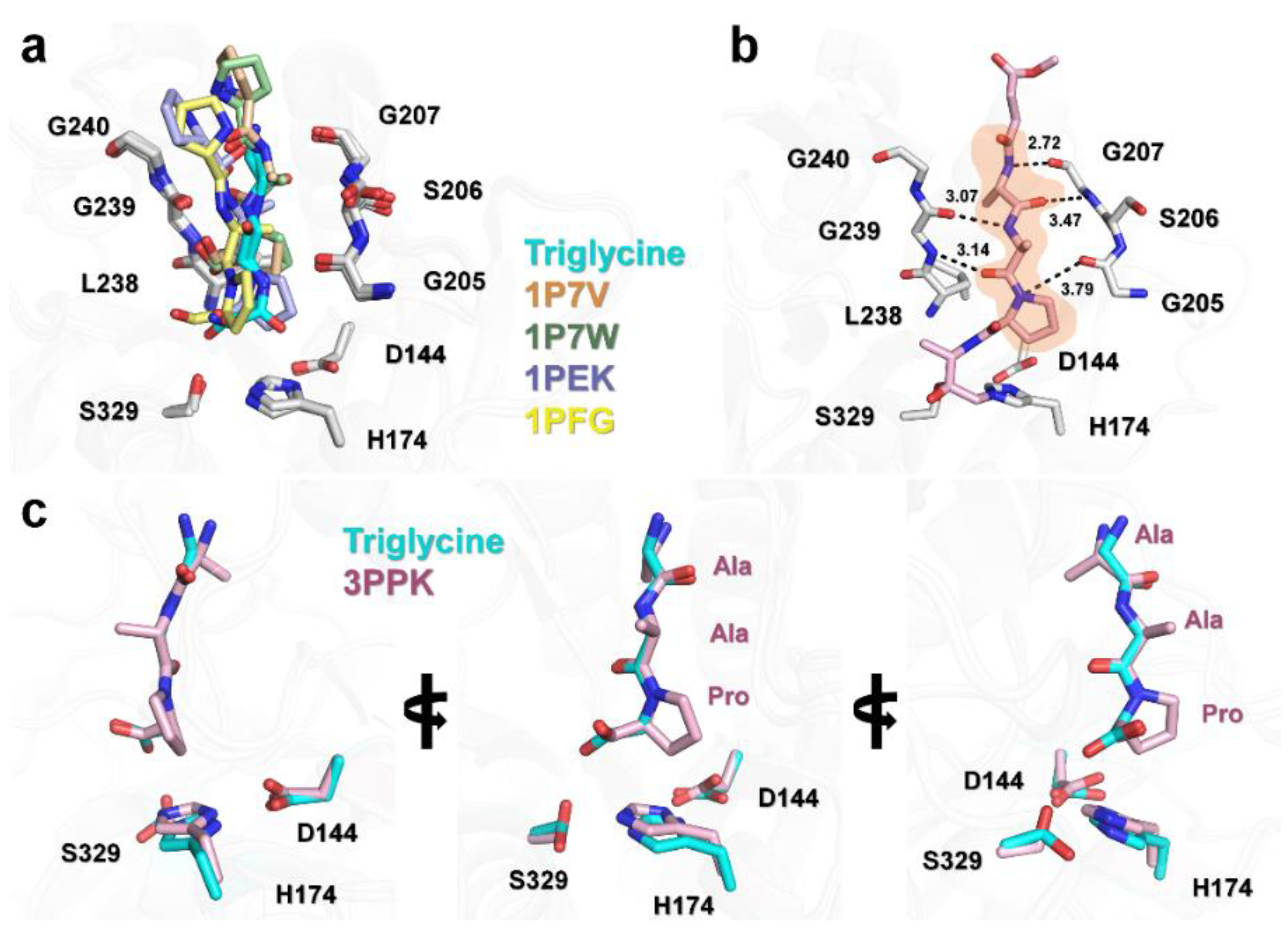
3.3. Structural Comparison of PaProK-Triglycine Complex with Other ProK-Inhibitor Peptide
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pelay-Gimeno, M.; Glas, A.; Koch, O.; Grossmann, T.N. Structure-Based design of inhibitors of protein-protein interactions: Mimicking peptide binding epitopes. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Eng. 2015, 54, 8896–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milroy, L.G.; Grossmann, T.N.; Hennig, S.; Brunsveld, L.; Ottmann, C. Modulators of protein-protein interactions. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4695–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevola, L.; Giralt, E. Modulating protein-protein interactions: The potential of peptides. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2015, 51, 3302–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanfield, R.L.; Wilson, I.A. Protein-Peptide interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1995, 5, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.A.; McClendon, C.L. Reaching for high-hanging fruit in drug discovery at protein-protein interfaces. Nature 2007, 450, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craik, D.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Liras, S.; Price, D. The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosgerau, K.; Hoffmann, T. Peptide therapeutics: current status and future directions. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounge, B.A.; Parker, M.H. Designing a diverse high-quality library for crystallography-based FBDD screening. Methods Enzymol. 2011, 493, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, C.W.; Rees, D.C. The rise of fragment-based drug discovery. Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, R.A.; Congreve, M.; Murray, C.W.; Rees, D.C. Fragment-Based lead discovery: Leads by design. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, W.; Hennrich, N.; Klockow, M.; Metz, H.; Orth, H.D.; Lang, H. Proteinase K from tritirachium album limber. Eur. J. Biochem. 1974, 47, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, A.; Hinrichs, W.; Wolf, W.M.; Saenger, W. Crystal structure of calcium-free proteinase K at 1.5-A resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 23108–23111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Ha, S.C.; Kim, Y.G. The protein crystallography beamlines at the pohang light Source II. Biodesign 2017, 5, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Otwinowski, Z.; Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 1997, 276, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vagin, A.; Teplyakov, A. Molecular replacement with MOLREP. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winn, M.D.; Ballard, C.C. Overview of the CCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betzel, C.; Gourinath, S.; Kumar, P.; Kaur, P.; Perbandt, M.; Eschenburg, S.; Singh, T.P. Structure of a serine protease proteinase K from tritirachium album limber at 0.98 A resolution. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 3080–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-Building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkoczi, G. Phenix: A comprehensive python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8; Schrödinger: New York, NY, USA, 2010. Available online: http://pymol.sourceforge.net/overview/index.htm (accessed on 26 August 2019).
- Williams, C.J.; Headd, J.J.; Moriarty, N.W.; Prisant, M.G.; Videau, L.L.; Deis, L.N. MolProbity: More and better reference data for improved all-atom structure validation. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Priyadarshi, A.; Kwon, S.T.; Koo, B.S.; Yoon, S.H.; Hwang, K. Structural and functional analysis of a novel hormone-sensitive lipase from a metagenome library. Proteins 2009, 74, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Priyadarshi, A.; Lee, W.H.; Hwang, K.Y. Structural and functional analysis of a novel EstE5 belonging to the subfamily of hormone-sensitive lipase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2009, 379, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H.; Kim, S.J.; Priyadarshi, A.; Kim, H.S.; Hwang, K.Y. The crystal structure of an HSL-homolog EstE5 complex with PMSF reveals a unique configuration that inhibits the nucleophile Ser144 in catalytic triads. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 389, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, W.H.; Hwang, K.Y. Biochemical and structural analysis of hormone-sensitive lipase homolog EstE7: Insight into the stabilized dimerization of HSL-Homolog proteins. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 2627–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saxena, A.K.; Singh, T.P.; Peters, K.; Fittkau, S.; Betzel, C. Strategy to design peptide inhibitors: structure of a complex of proteinase K with a designed octapeptide inhibitor N-Ac-Pro-Ala-Pro-Phe-DAla-Ala-Ala-Ala-NH2 at 2.5 A resolution. Protein Sci. 1996, 5, 2453–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzel, C.; Singh, T.P.; Visanji, M.; Peters, K.; Fittkau, S.; Saenger, W.; Wilson, K.S. Structure of the complex of proteinase K with a substrate analogue hexapeptide inhibitor at 2.2-A resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 15854–15858. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, W.M.; Bajorath, J.; Muller, A.; Raghunathan, S.; Singh, T.P.; Hinrichs, W.; Saenger, W. Inhibition of proteinase K by methoxysuccinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Ala-chloromethyl ketone. An x-ray study at 2.2-A resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 17695–17699. [Google Scholar]
| Data Collection | PaProK-Triglcyine |
|---|---|
| Resolution | 50.0–1.40 (1.42–1.40) |
| Space group | P21 |
| Unique reflections | 38738 (1831) |
| Unit cell parameter | |
| a, b, and c (Å) | 38.51, 67.68, and 43.59 |
| α, β, and γ (o) | 90.00, 111.39, and 90.00 |
| Completeness (%) | 94.8 (89.4) |
| Multiplicity | 3.8 (3.7) |
| I/σ(I) | 25.65 (5.17) |
| Rmerge | 0.166 (0.529) |
| Rpim | 0.096 (0.313) |
| Refinement | |
| Resolution | 40.59–1.40 |
| Rfactor | 18.22 |
| Rfree | 21.81 |
| Average B factor (Å2) | |
| Protein | 11.95 |
| Triglycine | 19.00 |
| Calcium | 18.60 |
| Water | 22.03 |
| Real space correlation coefficient | |
| Triglycine form A | 0.83 |
| Triglycine form B | 0.83 |
| R.m.s. deviations | |
| Bonds | 0.008 |
| Angles | 0.993 |
| Ramachandran | |
| Preferred | 96.53 |
| Allowed | 3.09 |
| Outliers | 0.39 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, K.H. Triglycine-Based Approach for Identifying the Substrate Recognition Site of an Enzyme. Crystals 2019, 9, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9090444
Nam KH. Triglycine-Based Approach for Identifying the Substrate Recognition Site of an Enzyme. Crystals. 2019; 9(9):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9090444
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Ki Hyun. 2019. "Triglycine-Based Approach for Identifying the Substrate Recognition Site of an Enzyme" Crystals 9, no. 9: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9090444
APA StyleNam, K. H. (2019). Triglycine-Based Approach for Identifying the Substrate Recognition Site of an Enzyme. Crystals, 9(9), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9090444