Electrostatic Potentials, Intralattice Attractive Forces and Crystal Densities of Nitrogen-Rich C,H,N,O Salts
Abstract
:1. Why “Nitrogen-Rich?”
2. Molecular vs. Ionic Crystal Lattices
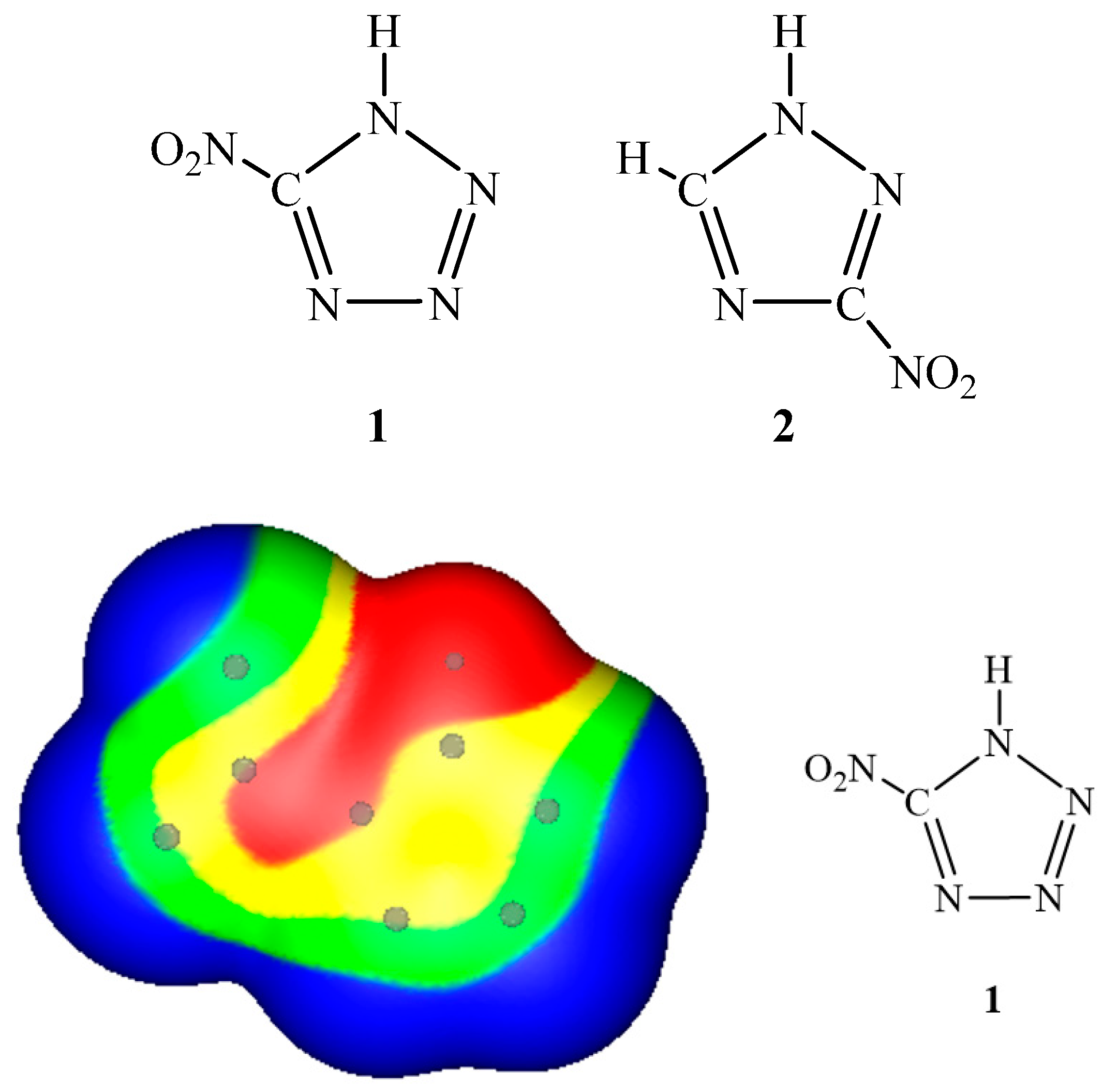
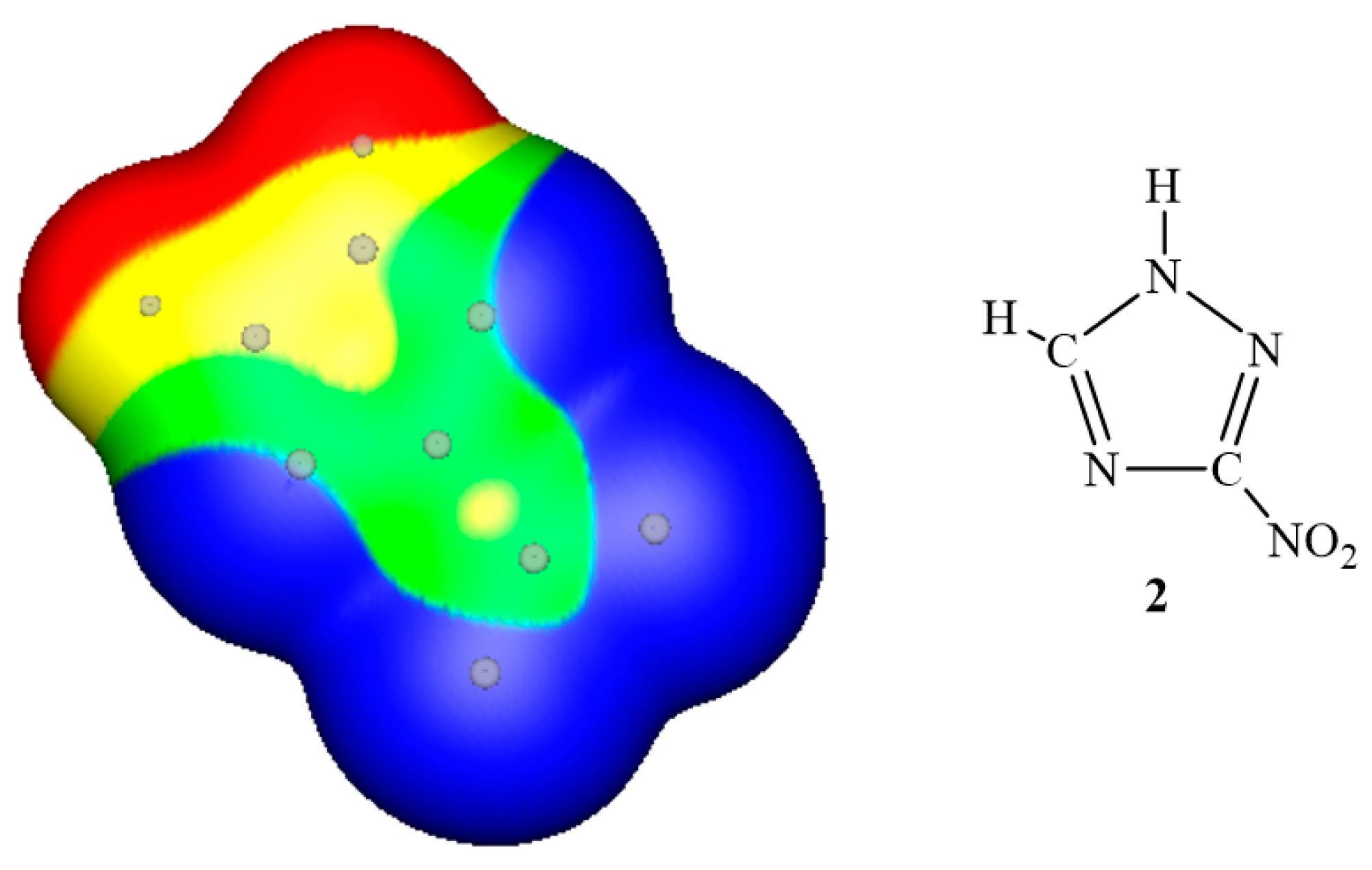
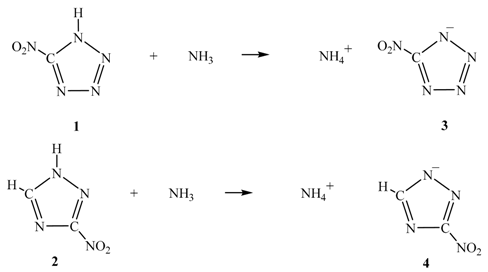
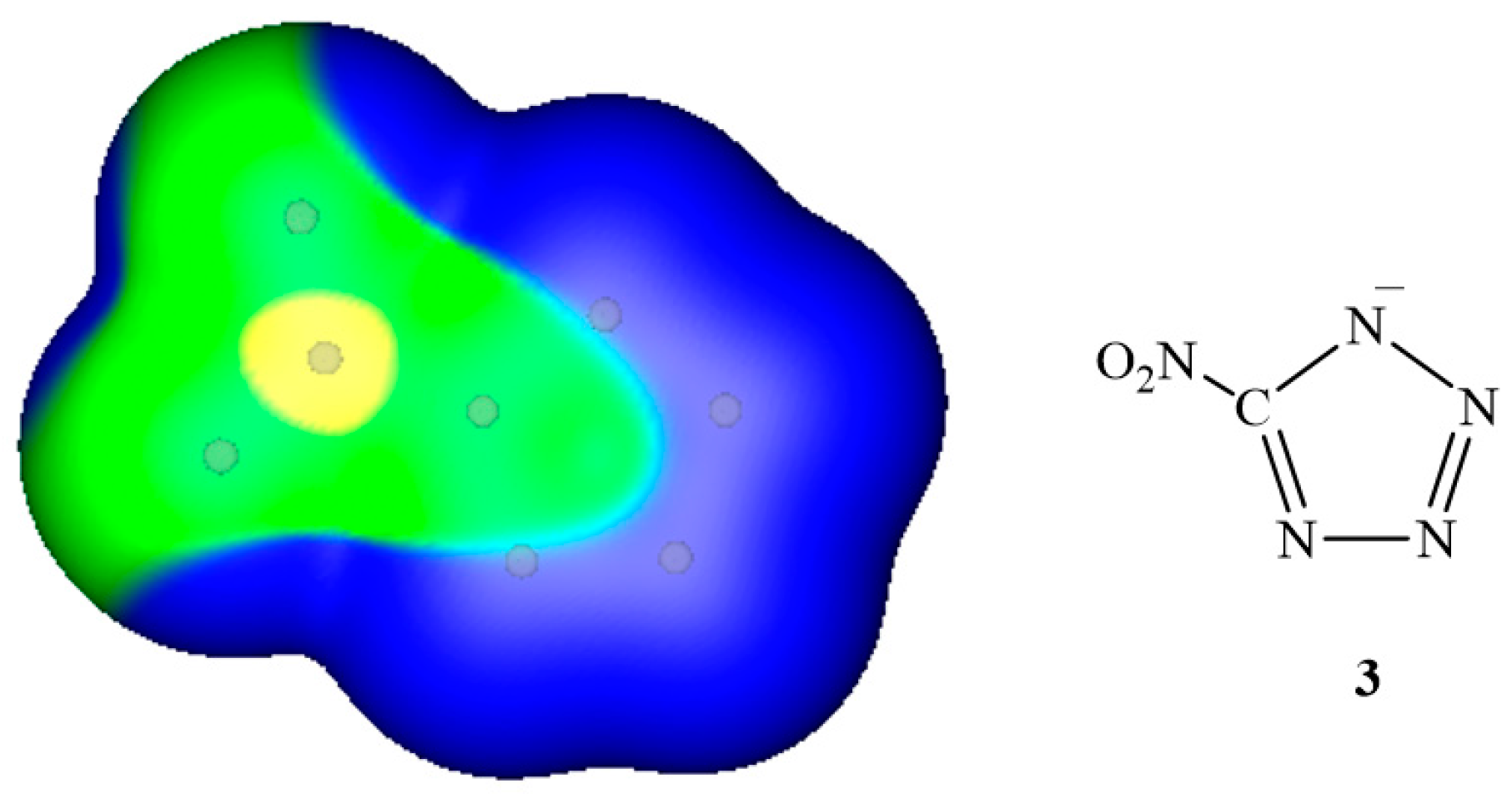
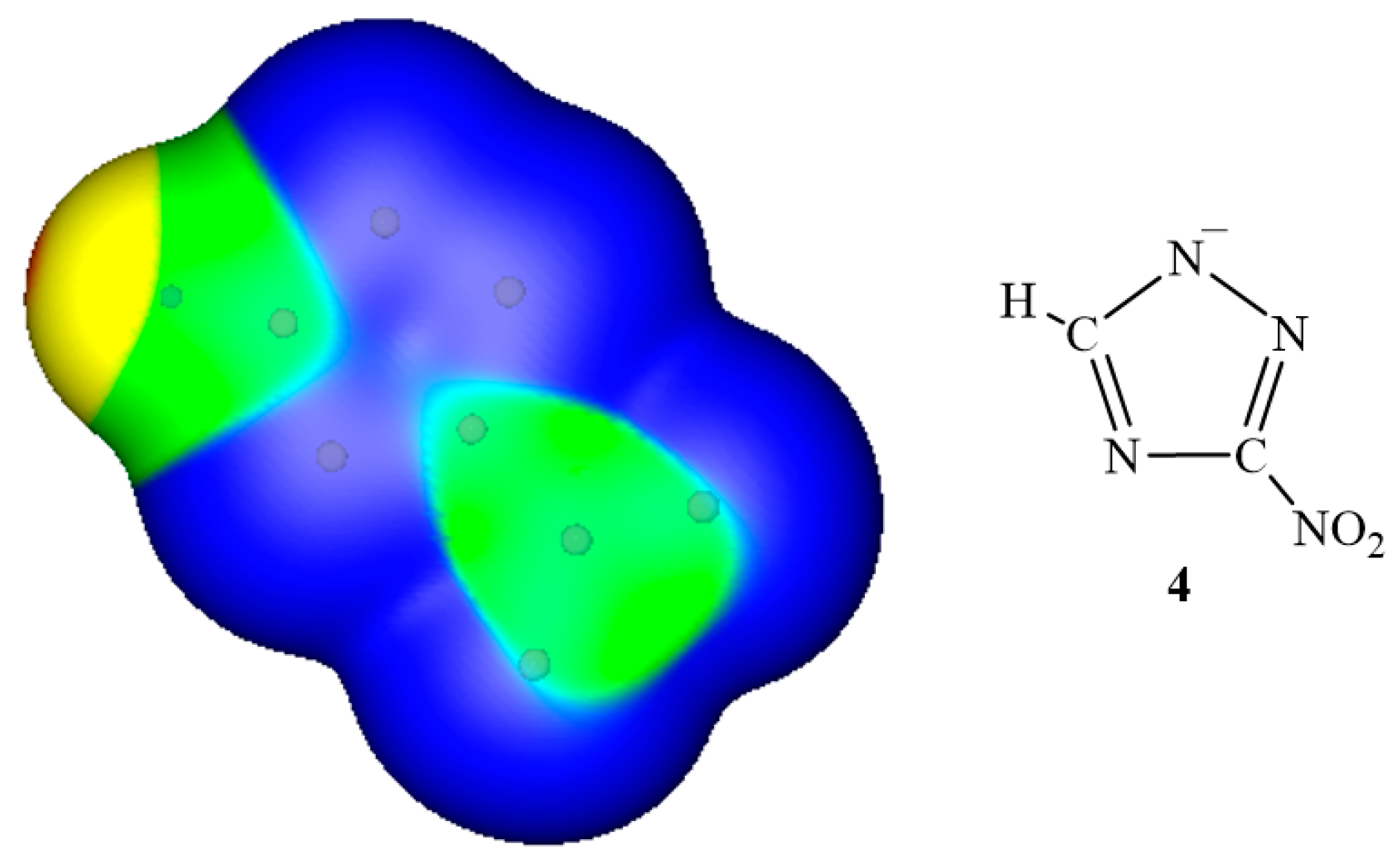
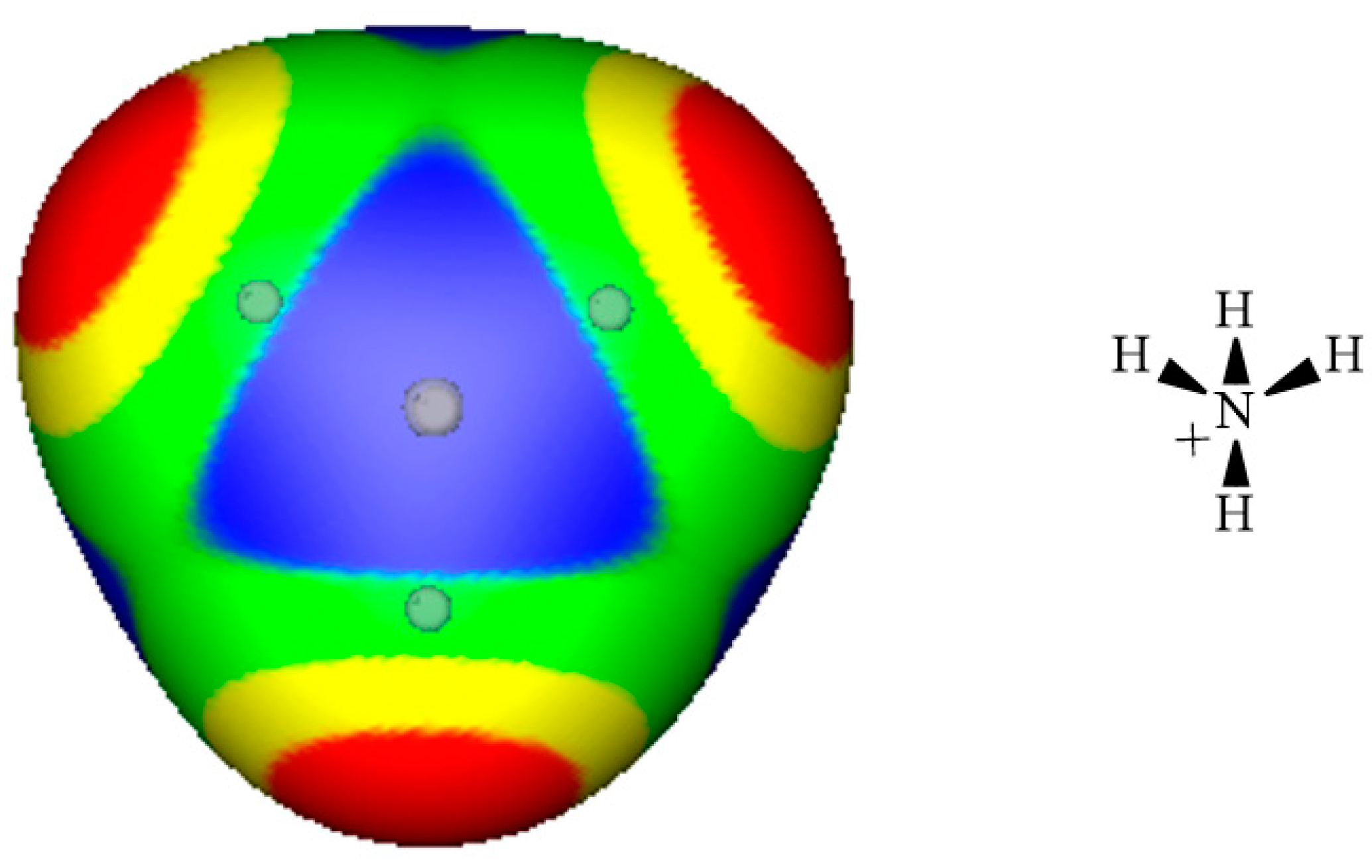
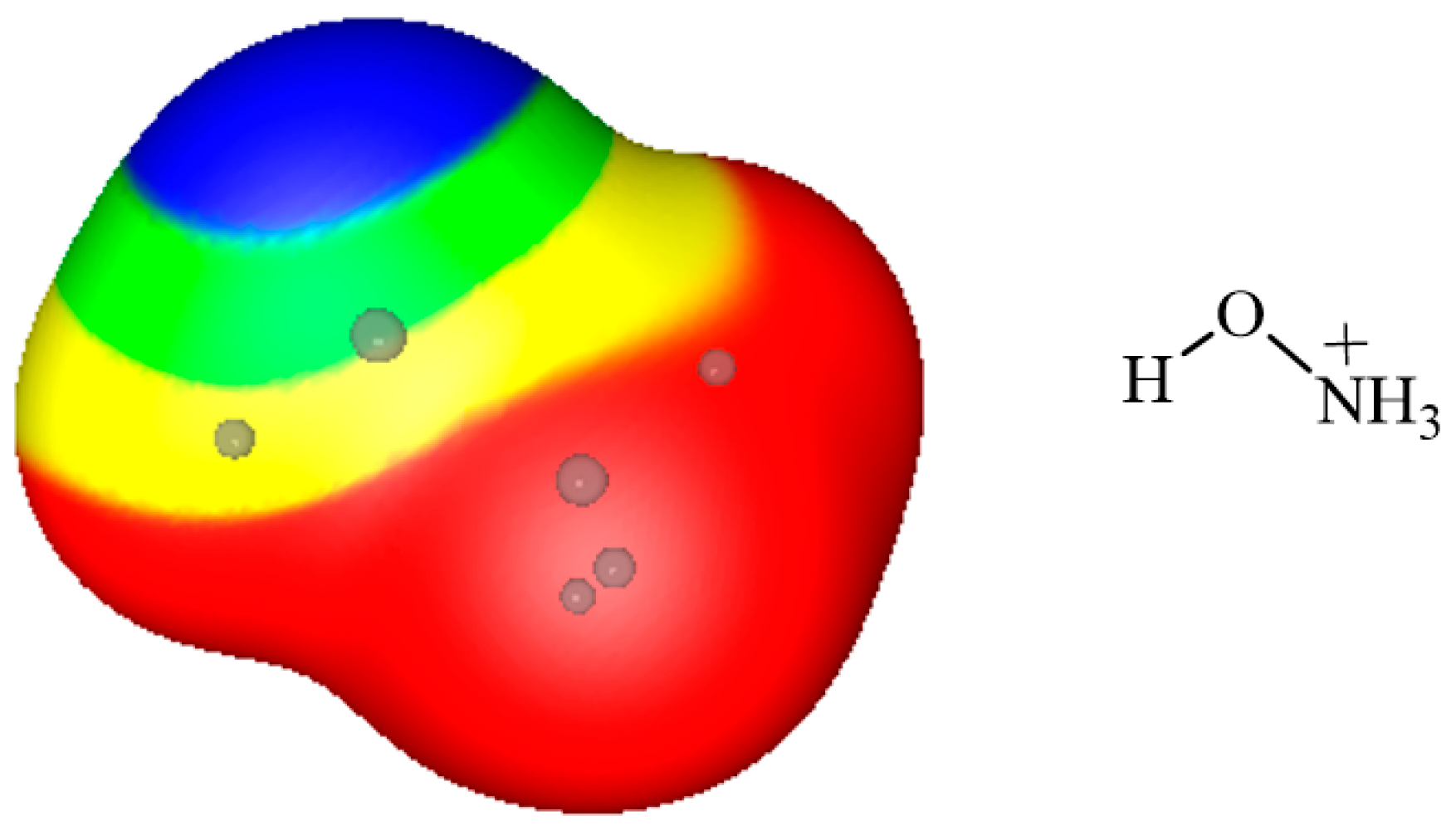
3. Electrostatic Potentials on Ionic Surfaces


4. Crystal Densities and Electrostatic Potentials

| Cation | Most Positive Potentials, kcal/mol |
|---|---|
| hydroxylammonium | 190, 181, 181, 180 |
| ammonium | 181, 181, 181, 181 |
| 5-nitrotetrazolium | 174, 174, 153, 152 |
| hydrazinium | 173, 173, 172 |
| 3,3-dinitroazetidinium | 172, 172 |
| 5-aminotetrazolium | 172, 172 |
| methylammonium | 169, 169, 169 |
| 1,1-dimethylhydrazinium | 164, 164, 156 |
| azidoformadinium | 165, 157, 143 |
| t-butylhydrazinium | 161, 158, 154 |
| 1,5-diaminotetrazolium | 164, 141, 130, 130 |
| 1-isopropyl-3,3-dinitroazetidinium | 158, 158, 143 |
| hydroxyguanidinium | 157, 152, 143, 136 |
| guanidinium | 154, 154, 154 |
| aminoguanidinium | 154, 151 |
| 1,5-diamino-4-methyltetrazolium | 149, 137 |
| N,N,N-trimethylhydrazinium | 142, 142, 130 |
| triaminoguanidinium | 136 |
| Anion | Most Negative Potentials, kcal/mol |
|---|---|
| nitrate | −151, −151, −151 |
| nitroformate | −142, −142, −123, −120, −120 |
| azide | −139, −139 |
| 5-aminotetrazolate | −137, −137, −137 |
| 3-nitro-1,2,4-triazolate | −136, −133 |
| 4-nitro-1,2,3-triazolate | −132, −124, −124, −123 |
| dinitramide | −131, −126, −126, −121, −121 |
| 5-nitrotetrazolate | −126, −126, −118, −118, −116 |
| 4,5-dinitroimidazolate | −125, −125, −119 |
| 3,5-dinitropyrazolate | −123, −123 |
| 3,5-dinitro-1,2,4-triazolate | −119, −119, −119, −119 |
| picrate | −119, −119 |
| 2,4,5-trinitroimidazolate | −116, −116, −115, −114 |
| Salt | Density, g/cm3 | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| oxalhydrazinium dinitrate | 1.945 | 44 |
| 1-amino-3-nitroguanidinium nitrate | 1.91 | 38 |
| oxalhydrazinium nitrate | 1.840 | 44 |
| 5-aminotetrazolium dinitramide 1.833 | 1.833 | 29 |
5. Discussion and Summary
| Compound | Structure | Density a g/cm3 | ΔHf b kcal/mol (cal/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 H-imidazole | 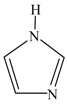 | 1.0303 | 11.9 (175) |
| 1 H-1,2,3-triazole | 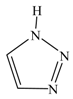 | 1.1861 | --- |
| 1 H-tetrazole | 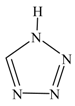 | 1.4060 | 56.4 (805) |
| cyclohexane | 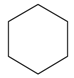 | 0.7739 | −37.68 (−447.7) |
| piperidine |  | 0.8606 | −20.66 (−242.6) |
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dlott, D.D. Fast Molecular Processes in Energetic Materials. In Energetic Materials. Part 2. Detonation, Combustion; Politzer, P., Murray, J.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Chapter 6; pp. 125–191. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, R.; Köhler, J.; Homburg, A. Explosives, 6th ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford, S.A. Role of Thermochemical Decomposition in Energetic Material Initiation Sensitivity and Explosive Performance. Cent. Eur. J. Energ. Mater. 2008, 5, 75–101. [Google Scholar]
- Klapötke, T.M. Chemistry of High Energy Materials; de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S. Some Molecular/Crystalline Factors that Affect the Sensitivities of Energetic Materials: Molecular Surface Electrostatic Potentials, Lattice Free Space and Maximum Heat of Detonation Per Unit Volume. J. Mol. Model. 2015, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Jacobs, S.J. Chemistry of Detonation. I. A Simple Method for Calculating Detonation Properties of C,H,N,O Explosives. J. Chem. Phys. 1968, 48, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, C.L. Numerical Modeling of Explosives and Propellants, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, B.M.; Hare, J. Predicting Heats of Detonation Using Quantum Mechanical Calculations. Thermochim. Acta 2002, 384, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S. Some Perspectives on Estimating Detonation Properties of C,H,N,O Compounds. Cent. Eur. J. Energ. Mater. 2011, 8, 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Klapötke, T.M.; Ang, H.-G. Estimation of the Crystalline Density of Nitramine (N-NO2 Bond) High Energy Density Materials. Propell. Explos. Pyrotech. 2001, 26, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardt, C.J.; Gavezzotti, A. Computer Simulations and Analysis of Structural and Energetic Features of Some Crystalline Energetic Materials. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 3430–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S. Perspectives on the Crystal Densities and Packing Coefficients of Explosive Compounds. Struct. Chem. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagoria, P.F.; Lee, G.S.; Mitchell, A.R.; Schmidt, R.D. A Review of Energetic Materials Synthesis. Thermochim. Acta 2002, 384, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churakov, A.M.; Tartakovsky, V.A. Progress in 1,2,3,4-Tetrazine Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 2601–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Shreeve, J.M. Azole-Based Energetic Salts. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 7377–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, N.; Klapötke, T.M.; Reymann, M.; Stierstorfer, J. Nitrogen-Rich Salts of 1H,1′H-5,5′-Bitetrazole-1,1′-diol: Energetic Materials with High Thermal Stability. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 2167–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S. Detonation Performance and Sensitivity: A Quest for Balance. Adv. Quantum Chem. 2014, 69, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Stine, J.R. Molecular Structure and Performance of High Explosives. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1993, 296, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S. Impact Sensitivity and the Maximum Heat of Detonation. J. Mol. Model. 2015, 21, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, R.F.W.; Carroll, M.T.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Chang, C. Properties of Atoms in Molecules: Atomic Volumes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 7968–7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, Z.P.; Murray, J.S.; Politzer, P. Directional Tendencies of Halogen and Hydrogen Bonding. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2010, 110, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, E.F.C.; Rice, B.M. Improved Prediction of Heats of Formation of Energetic Materials Using Quantum Mechanical Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gálvez-Ruiz, J.C.; Holl, G.; Karaghiosoff, K.; Klapötke, T.M.; Löhnwitz, K.; Mayer, P.; Nöth, H.; Polborn, K.; Rohbogner, C.J.; Suter, M.; et al. Derivatives of 1,5-Diamino-1H-tetrazole: A New Family of Energetic Heterocyclic-Based Salts. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 4237–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, E.F.C.; Rice, B.M. A Comparison of Methods to Predict Solid Phase Heats of Formation of Molecular Energetic Salts. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Xiao, H.; Gong, X.; Ju, X.; Zhu, W. Crystal Density Predictions for Nitramines Based on Quantum Chemistry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, B.M.; Hare, J.J.; Byrd, E.F.C. Accurate Predictions of Crystal Densities Using Quantum Mechanical Molecular Volumes. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 10874–10879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politzer, P.; Martinez, J.; Murray, J.S.; Concha, M.C.; Toro-Labbé, A. An Electrostatic Interaction Correction for Improved Crystal Density Prediction. Mol. Phys. 2009, 107, 2095–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Martinez, J.; Murray, J.S.; Concha, M.C. An Electrostatic Correction for Improved Crystal Density Predictions of Energetic Ionic Compounds. Mol. Phys. 2010, 108, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, B.M.; Byrd, E.F.C. Evaluation of Electrostatic Descriptors for Predicting Crystalline Density. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2146–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Vo, T.T.; Parrish, D.A.; Shreeve, J.M. Energetic Salts with π-Stacking and Hydrogen-Bonding Interaction Lead the Way to Future Energetic Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunitz, J.D.; Filippini, G.; Gavezzotti, A. A Statistical Study of Density and Packing Variations among Crystalline Isomers. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 6595–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.S.; Politzer, P. Correlations Between the Solvent Hydrogen-Bond-Donating Parameter α and the Calculated Molecular Surface Electrostatic Potential. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 6715–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagelin, H.; Murray, J.S.; Brinck, T.; Berthelot, M.; Politzer, P. Family-Independent Relationships between Computed Molecular Surface Quantities and Solute Hydrogen Bond Acidity/Basicity and Solute-Induced Methanol O-H Infrared Frequency Shifts. Can. J. Chem. 1995, 73, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thottempudi, V.; Shreeve, J.M. Synthesis and Promising Properties of a New Family of High-Density Energetic Salts of 5-Nitro-3-trinitromethyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole and 5,5′Bis(trinitromethyl)-3,3′-azo-1H-1,2,4-triazole. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19982–19992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Joo, Y.-H.; Parrish, D.A.; Vo, T.; Shreeve, J.M. 1-Amino-1-hydrazino-2,2-dinitroethene and Corresponding Salts: Synthesis, Characterization, and Thermolysis Studies. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 4613–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapötke, T.M.; Petermayer, C.; Piercey, D.G.; Stierstorfer, J. 1,3-Bis(nitroimido)-1,2,3-triazolate Anion, the N.-Nitroimide Moiety, and the Strategy of Alternating Positive and Negative Charges in the Design of Energetic Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20827–20836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, N.; Fischer, D.; Klapötke, T.M.; Piercey, D.G.; Stierstorfer, J. Pushing the Limits of Energetic Materials—The Synthesis and Characterization of Dihydroxylammonium 5,5′-Bistetrazole-1,1′-diolate. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 20418–20422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, N.; Klapötke, T.M.; Stierstorfer, J. 1-Amino-3-nitroguanidine (ANQ) in High-Performance Ionic Energetic Materials. Z. Naturforsch. 2012, 67b, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, N.; Gao, L.; Klapötke, T.M.; Stierstorfer, J. Energetic Salts of 5,5′Bis(Tetrazole-2-oxide) in a Comparison to 5,5′-Bis(Tetrazole-1-oxide) Derivatives. Polyhedron 2013, 51, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, D.; Klapötke, T.M.; Reymann, M.; Stierstorfer, J. Dense Energetic Nitraminofurazanes. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 6401–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapötke, T.M.; Preimesser, A.; Stierstorfer, J. Energetic Derivatives of 2-Nitrimino-5,6-dinitro-benzimidazole. Propell. Explos. Pyrotech. 2015, 40, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shreeve, J.M. 3,3′-Dinitroamino-4,4′-azoxyfurazan and Its Derivatives: An Assembly of Diverse N-O Building Blocks for High-Performance Energetic Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4437–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapötke, T.M.; Mayr, N.; Stierstorfer, J.; Weyrauther, M. Maximum Compaction of Ionic Organic Explosives: Bis(hydroxylammonium) 5,5′ Dinitromethyl-3,3′-bis(1,2,4-oxadiazolate) and Its Derivatives. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, D.; Klapötke, T.M.; Stierstorfer, J. Oxalylhydrazinium Nitrate and Dinitrate—Efficiency Meets Performance. J. Energ. Mater. 2014, 32, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, D.; Klapötke, T.M.; Stierstorfer, J. 1,5-Di(nitramino)tetrazole: High Sensitivity and Superior Explosive Performance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10299–10302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.; Parrish, D.A.; Shreeve, J.M. Energetic Multifunctionalized Nitraminopyrazoles and Their Ionic Derivatives: Ternary Hydrogen-Bond Induced High Energy Density Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4778–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, A.M.; Jin, P.; Brinck, T.; Murray, J.S.; Politzer, P. The Electrostatic Potential as a Measure of Gas Phase Carbocation Stability. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2006, 106, 2904–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S.; Clark, T. σ-Hole Bonding: A Physical Interpretation. Top. Curr. Chem. 2015, 358, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S.; Clark, T. Mathematical Modeling and Physical Reality in Noncovalent Interactions. J. Mol. Model. 2015, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrić, J.M.; Misini-Ignjatović, M.Z.; Murray, J.S.; Politzer, P.; Zarić, S.D. Hydrogen Bonding Between Metal Ion Complexes and Non-coordinated Water. Electrostatic Potentials and Interaction Energies. ChemPhysChem. submitted for publication.
- Glasstone, S. Text-Book of Physical Chemistry; Van Nostrand: New York, NY, USA, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira-Dias, J.J.C.; Murrell, J.N. The Calculation of Electric Polarizabilities of Hydrocarbons with Particular Attention to the Bond-Additive Property. Mol. Phys. 1970, 19, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, K.M. Theoretical Analysis of Molecular Polarizabilities and Polarizability Derivatives in Hydrocarbons. J. Chem. Phys. 1989, 91, 2424–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidig, K.E.; Bader, R.F.W. Properties of Atoms in Molecules: Atomic Polarizabilities. J. Chem. Phys. 1990, 93, 7213–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinck, T.; Murray, J.S.; Politzer, P. Polarizability and Volume. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 4305–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Murray, J.S.; Politzer, P. Local Ionization Energy and Local Polarizability. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2004, 96, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S.; Janjić, G.V.; Zarić, S.D. σ-Hole Interactions of Covalently-Bonded Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Arsenic: A Survey of Crystal Structures. Crystals 2014, 4, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 87th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.-R.; Zhao, J.-M.; Dong, H.-S. Crystal Structure of 2,4,6-Trinitropyridine and its N-oxide. J. Chem. Cryst. 2005, 35, 943–948. [Google Scholar]
- Linstrom, P.J.; Mallard, W.G. NIST Chemistry Webbook, NIST Standard Reference Database No. 69. Available online: http://www.nist.gov (accessed on 31 December 2015).
- Rice, B.M.; Hare, J.J. A Quantum Mechanical Investigation of the Relation between Impact Sensitivity and the Charge Distribution in Energetic Molecules. J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 1770–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepekin, V.I.; Korsunskii, B.L.; Denisaev, A.A. Initiation of Solid Explosives by Mechanical Impact. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2008, 44, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Politzer, P.; Lane, P.; Murray, J.S. Electrostatic Potentials, Intralattice Attractive Forces and Crystal Densities of Nitrogen-Rich C,H,N,O Salts. Crystals 2016, 6, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst6010007
Politzer P, Lane P, Murray JS. Electrostatic Potentials, Intralattice Attractive Forces and Crystal Densities of Nitrogen-Rich C,H,N,O Salts. Crystals. 2016; 6(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst6010007
Chicago/Turabian StylePolitzer, Peter, Pat Lane, and Jane S. Murray. 2016. "Electrostatic Potentials, Intralattice Attractive Forces and Crystal Densities of Nitrogen-Rich C,H,N,O Salts" Crystals 6, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst6010007
APA StylePolitzer, P., Lane, P., & Murray, J. S. (2016). Electrostatic Potentials, Intralattice Attractive Forces and Crystal Densities of Nitrogen-Rich C,H,N,O Salts. Crystals, 6(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst6010007






