Effects of Mn and Co Doping on the Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of Cu2ZnSnS4
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Models and Calculation Methods
2.1. Theoretical Models
2.2. Calculation Methods
2.3. Calculation Methods for Optical Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Geometric Structure Analysis
3.2. Electronic Structure Analysis
3.2.1. Band Structure Analysis
3.2.2. Density of States Analysis
3.3. Mulliken Population Analysis
3.4. Optical Properties Analysis
3.4.1. Complex Dielectric Function
3.4.2. Absorption and Reflection Spectra
3.4.3. Complex Refractive Index
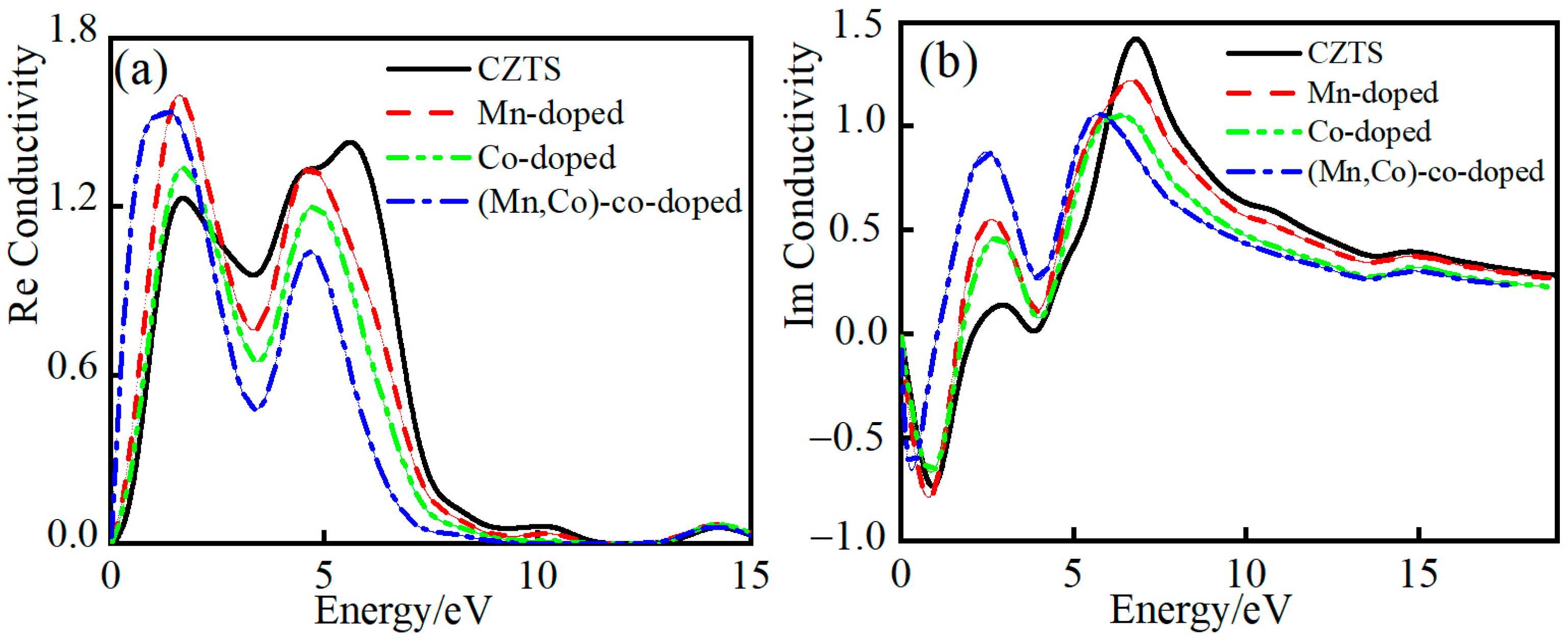
3.4.4. Complex Conductivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, D.W.; Peng, H.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Sa, R.J. First-principles calculations to investigate the electronic and optical properties of Cu2ZnSnS4 with Ag and Se cooping. Chem. Phys. 2022, 554, 111418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashebir, G.Y.; Chao, D.; Wan, Z.Y.; Qi, J.J.; Chen, J.W.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Chen, W.M.; Wang, M.T. Solution-processed Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoparticle film as efficient hole transporting layer for stable perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 129, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.F.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, N.; Hou, J.S.; Zhao, G.Y.; Fang, Y.Z. Fabrication of Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 thin film solar cell devices based on printable nano-ink. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2019, 42, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.H.; Liang, G.X.; Fan, P.; Luo, J.T.; Zheng, Z.H.; Xie, Z.G.; Wang, W.; Chen, S.; Hu, J.G.; Wei, Y.D.; et al. Device Postannealing Enabling over 12% Efficient Solution-Processed Cu2ZnSnS4 Solar Cells with Cd2+ Substitution. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.G.; Ma, D.; Yao, B.; Li, Y.F.; Ding, Z.H.; Wang, C.K.; Luan, H.M.; Zhu, C.J. Mechanism of improvement of the power conversion efficiency of Cu2ZnSn(S, Se)4 solar cells through changing Ag and Cd co-doping form from uniform to non-uniform. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 515, 163564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Sun, Q.Z.; Deng, H.; Xie, W.H.; Zhang, C.X.; Wu, J.H.; Zheng, Q.; Cheng, S.Y. Enhancing carrier transport in flexible CZTSSe solar cells via doping Li strategy. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 75, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, R.A.; Latha, M.; Velumani, S.; Salazar, J.S.; Cruz, J.S. Telescoping synthesis and goldilocks of CZTS nanocrystals. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 111, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Jia, Z.J.; Zhao, Z.Y. Secondary phases in Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film solar cell: The role of interfaces. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2022, 626, 413539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Ma, H.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, B.; Wang, H.R.; Sun, L.; Chen, Y. Defect regulation enhances the efficiency of Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cells by solution engineering. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2025, 285, 113555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prima, E.C.; Manopo, J.; Suhendi, E.; Setiawan, A.; Shukri, G.; Agusta, M.K.; Yuliarto, B. The effect of CuZn+ZnCu defect complex on Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film solar cell: A density functional theory study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 296, 127192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Chen, S.; Su, Z.H.; Wang, Z.; Luo, P.; Zheng, Z.H.; Luo, J.T.; Ma, H.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Liang, G.X. Heat treatment in an oxygen-rich environment to suppress deep-level traps in Cu2ZnSnS4solar cell with 11.51% certified efficiency. Nat. Energy 2025, 10, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Walsh, A.; Gong, X.G.; Wei, S.H. Classification of Lattice Defects in the Kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 and Cu2ZnSnSe4 Earth-Abundant Solar Cell Absorbers. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1522–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.L.; Han, L.T.; Chu, L.L.; Han, M.T.; Jian, Y.; Chi, J.J.; Zhong, X.Y.; Liu, T.; Kou, D.X.; Zhou, W.H.; et al. Passivation of Deep-Level Defects through Chemical Environment Regulation for Efficient CZTSSe Solar Cells Based on Active Selenium Adsorption–Desorption Process. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2414940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangsabanik, M.; Sinha, S.; Maity, P.; Chowdhury, J.; Manna, S.; Gayen, R.N. Partial Substitution of Copper with Silver in Cu2ZnSnS4: An Efficient Strategy to Boost the Performance of Self-Powered Broadband Photodetectors in Superstrate Configuration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 5101–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Xu, J.X.; Yang, Y.Z.; Xie, Z.W. Influence of pre-sulfurization temperature on properties of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film in two-step sulfurization process. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2019, 11, 023501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muska, K.; Timmo, K.; Pilvet, M.; Kaupmees, R.; Raadik, T.; Mikli, V.; Kuusk, M.G.; Krustok, J.; Josepson, R.; Lange, S.; et al. Impact of Li and K co-doping on the optoelectronic properties of CZTS monograin powder. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2023, 252, 112182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.; Ylmaz, S.; Polat, İ.; Bacaksı, E.; Zan, R.; Olgar, M.A. Unveiling Improvements in Structural, Optical, and Photodetection Characteristics of CZTS Thin Films Through Ag-Doping. Opt. Mater. 2025, 163, 117006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzougui, M.; Antoni, F.; Rabeh, M.B.; Kanzari, M. Synthesis and study of microstructural, optical and electrical properties of Na-doped Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films via thermal evaporation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, s10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digraskar, R.V.; Mali, S.M.; Tayade, S.B.; Ghule, A.V.; Sathe, B.R. Overall noble metal free Ni and Fe doped Cu2ZnSnS4(CZTS) bifunctional electrocatalytic systems for enhanced water splitting reactions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 8144–8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.F.; Qin, X.M.; Yan, W.J.; Zhang, C.H.; Zhang, D.X. Effects of Fe and Ni Doping on the Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of Cu2ZnSnS4. Crystals 2023, 13, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Yadav, P.; Kumar, P.; Singh, M.K. Synthesis, morphological and optical properties of hydrothermally synthesized Bi and Mn co-doped Cu2ZnSnS4(CZTS). Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 82, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunavathy, K.V.; Rangasami, C.; Arulanantham, A.M.S.; Merlin, B.F.; Reddy, C.P.; Khan, A. Enhancing the optoelectronic performance of CZTS thin films through cobalt doping via nebulizer-assisted spray pyrolysis technique. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 366, 114941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous Electron Gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-Consistent Equations Including Exchange and Correlation Effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, A1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, T.; Goto, Y.; Kamihara, Y.; Matoba, M.; Yasuoka, K.; Burton, L.A.; Walsh, A. From kesterite to stannite photovoltaics: Stability and band gaps of the Cu2(Zn,Fe)SnS4 alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Han, M.M.; Zeng, Z.; Duan, Y.H. The role of Sb in solar cell material Cu2ZnSnS4. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 6606–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdillah, N.; Ayukaryana, N.R.; Agusta, M.K.; Rusydi, F.; Shukri, G. On the thermodynamic of Cu-Zn disorder formation and electronic structure changes of alkaline-earth M-doped kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 (M = Be, Mg, Ca). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2025, 332, 130262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Nakamura, S.; Wada, T. First-Principles Study on Cd Doping in Cu2ZnSnS4 and Cu2ZnSnSe4. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 51, 10NC11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, M.D.; Lindan, P.; Probert, M.J.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Clark, S.J.; Payne, M.C. First-principles simulation: Ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 2717–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbilt, D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 7892–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennangod, S.; Ray, S.; Subrahmanya, P.A.; Tarafder, K.; Bhat, T.N. Temperature-dependent in situ Cd substitution at Zn sites in Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films via sol-gel method: Experimental and DFT insights. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 712, 164166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raad, N.H.; Karimmirza, E.; Yousefizad, M.; Nouri, N.; Sharifpour, H.; Nadimi, E.; Zeidabadi, M.A.; Manavizadeh, N. Improving the electronic and optical properties of chalcogenide Cu2ZnSnS4 compound with transition metal dopants: A first-principles investigation. Thin Solid Film. 2023, 766, 139653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Xia, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.P.; Dou, M.L.; Ji, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, J.J.; Wang, F. First-principle study on phase stability of kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 for thin film solar cells with off-stoichiometric composition. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 768, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Qi, H. Electronic and optical properties of Ti3AC2 (A=Sn, Ge, Si) MAX phases by first-principles calculations. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2025, 706, 417140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Tahir, M.B.; Dahshan, A.; Ahmed, B.; Sagir, M. Lithium doping effect on structural, electronic and optical properties of KCaF3 fluoroperovskite: DFT insights using GGA-PBE. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 158, 111475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.F.; Wu, J. Third generation photovoltaics. Laser Photonics Rev. 2009, 3, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H.T.; He, J.L.; Tian, Y.J. Ab initio investigations of optical properties of the high-pressure phases of Zno. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paier, J.; Asahi, R.; Nagoya, A.; Kresse, G. Cu2ZnSnS4 as a potential photovoltaic material: A hybrid hartree-fock density functional theory study. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 115126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlido, P.; Schmidt, J.; Huran, A.W.; Tran, F.; Marques, M.A.L.; Botti, S. Exchange-correlation functionals for band gaps of solids: Benchmark, reparametrization and machine learning. NPJ Comput. Mater. 2020, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebègue, S.; Arnaud, B.; Alouani, M. Calculated quasiparticle and optical properties of orthorhombic and cubic Ca2Si. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 085103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Gao, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.C.; Wang, C.C.; Ji, H.D. Insights on selective pb adsorption via O 2p orbit in uio-66 containing rich-zirconium vacancies. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, A.S.; Sharma, I. Dielectric properties, Optoelectrical parameters and electronic polarizability of thermally evaporated a-Pb-Se-Ge thin films. Phys. B Phys. Condens. Matter 2021, 622, 413330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, A.S. Intensive linear and nonlinear optical studies of thermally evaporated amorphous thin Cu-Ge-Se-Te fflms. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2022, 586, 121563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, D.R. Wave-Number-Dependent Dielectric Function of Semiconductors. Phys. Rev. 1962, 128, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.M.; Chhetri, S.K.; Acharya, G.; Graf, D.; Upreti, D.; Dahal, S.; Nabi, M.R.U.; Rahman, S.; Sakon, J.; Churchill, H.O.H.; et al. Quantum oscillation studies of the nodal line semimetal Ni3In2S2-xSex. Acta Mater. 2025, 289, 120884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
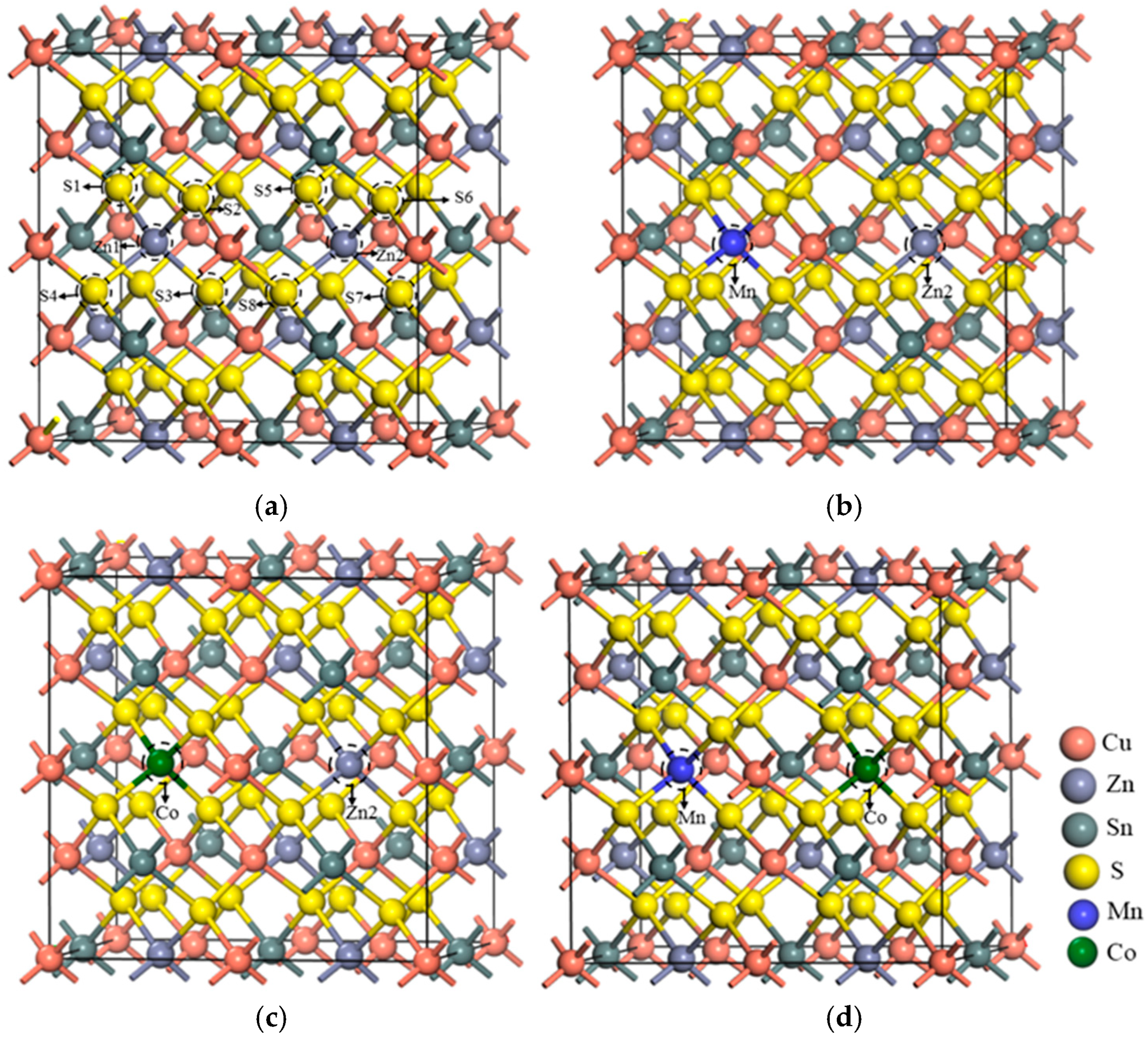
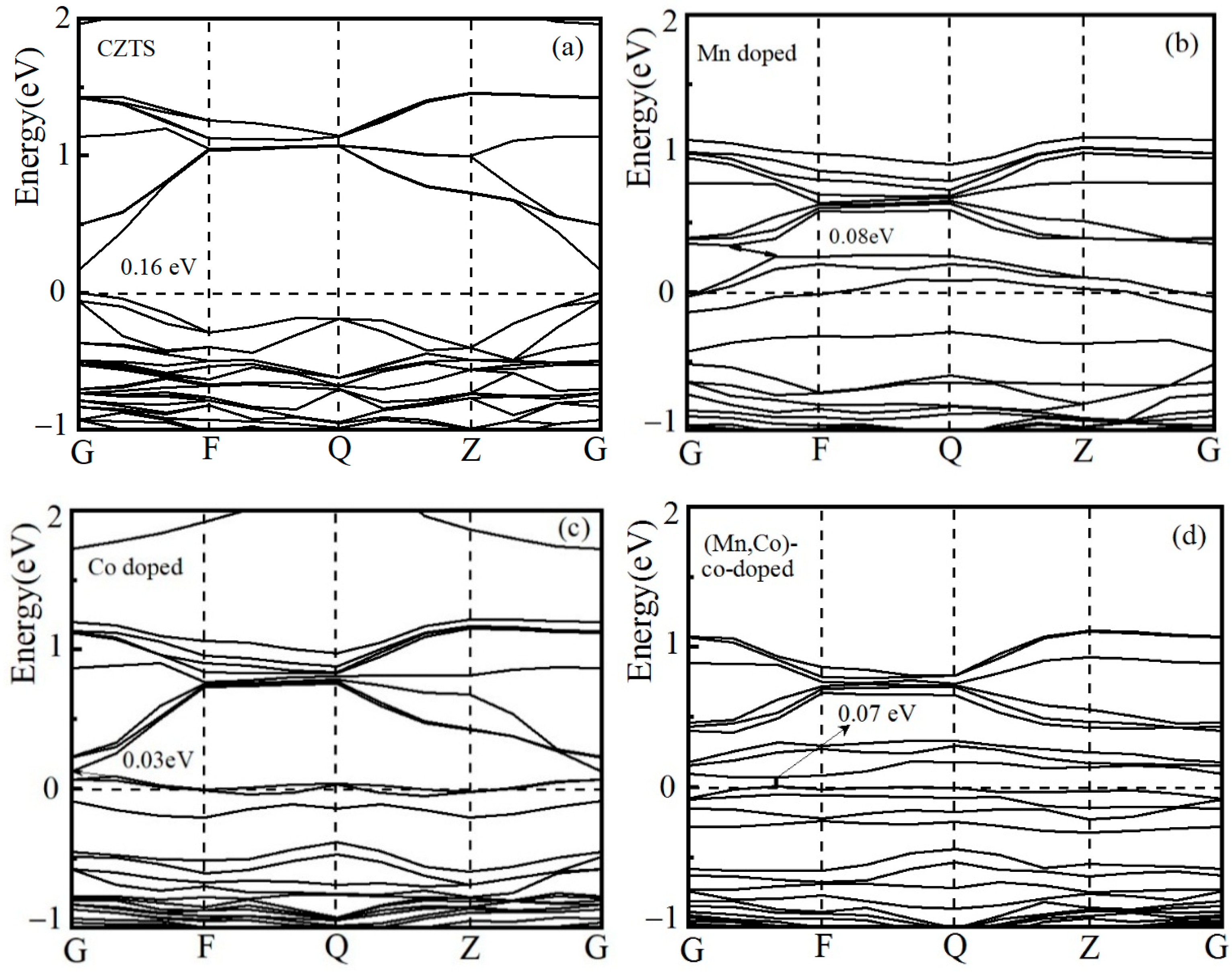


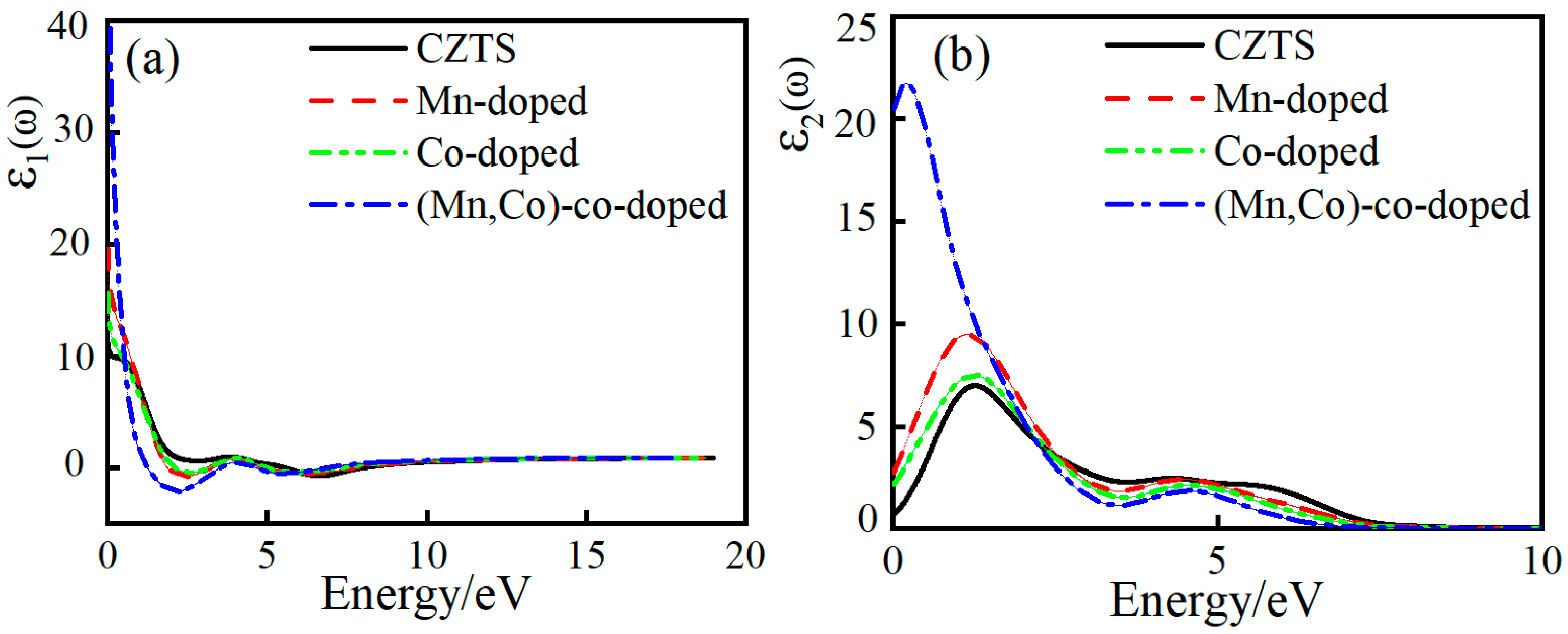

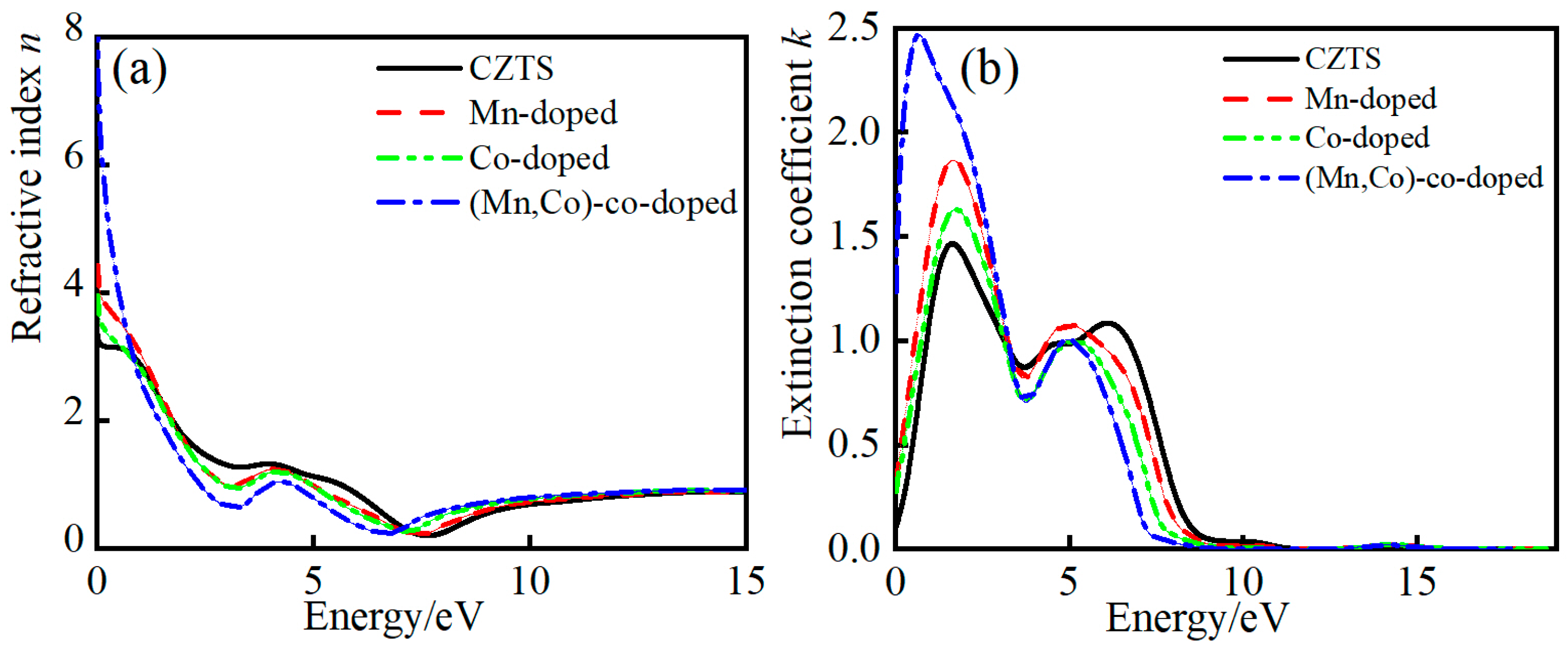
| Sample | a/Å | a% | c/Å | c% | v/Å3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2ZnSnS4(experiment) [25] | 5.428 | — | 10.864 | — | — |
| Cu2ZnSnS4(calculated) [40] | 5.466 | — | 10.929 | — | — |
| Undoped Cu2ZnSnS4 | 5.471 | — | 10.941 | — | 654.854 |
| Mn-doped Cu2ZnSnS4 | 5.460 | −0.20% | 10.950 | 0.08% | 652.877 |
| Co-doped Cu2ZnSnS4 | 5.455 | −0.29% | 10.934 | −0.06% | 650.893 |
| (Mn,Co)-co-doped Cu2ZnSnS4 | 5.435 | −0.66% | 10.936 | −0.05% | 648.674 |
| Sample | Atom | s | p | d | Total Charge/e | Charge Population/e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2ZnSnS4 | Zn1 | 0.42 | 0.95 | 9.98 | 11.34 | 0.66 |
| S1, S2, S3, S4 | 1.84 | 4.54 | 0.00 | 6.37 | −0.37 | |
| Zn2 | 0.42 | 0.95 | 9.98 | 11.34 | 0.66 | |
| S5, S6, S7, S8 | 1.84 | 4.54 | 0.00 | 6.37 | −0.37 | |
| Mn-doped Cu2ZnSnS4 | Mn | 0.38 | 0.50 | 6.05 | 6.93 | 0.07 |
| S1, S2, S3, S4 | 1.83 | 4.42 | 0.00 | 6.25 | −0.25 | |
| Co-doped Cu2ZnSnS4 | Co | 0.46 | 0.63 | 7.89 | 8.98 | 0.02 |
| S1, S2, S3, S4 | 1.84 | 4.44 | 0.00 | 6.28 | −0.28 | |
| (Mn,Co)-co-doped Cu2ZnSnS4 | Mn | 0.38 | 0.50 | 6.03 | 6.91 | 0.09 |
| S1, S2, S3, S4 | 1.83 | 4.42 | 0.00 | 6.25 | −0.25 | |
| Co | 0.45 | 0.63 | 7.90 | 8.99 | 0.01 | |
| S5, S7 | 1.83 | 4.44 | 0.00 | 6.27 | −0.27 | |
| S6, S8 | 1.84 | 4.45 | 0.00 | 6.28 | −0.28 |
| Sample | Bond | Population | Length (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2ZnSnS4 | S1—Zn1 | 0.48 | 2.366 |
| S2—Zn1 | 0.48 | 2.366 | |
| S3—Zn1 | 0.48 | 2.366 | |
| S4—Zn1 | 0.48 | 2.366 | |
| Mn-doped Cu2ZnSnS4 | S1—Mn | 0.61 | 2.191 |
| S2—Mn | 0.61 | 2.191 | |
| S3—Mn | 0.61 | 2.191 | |
| S4—Mn | 0.61 | 2.193 | |
| Co-doped Cu2ZnSnS4 | S1—Co | 0.56 | 2.196 |
| S2—Co | 0.56 | 2.196 | |
| S3—Co | 0.56 | 2.196 | |
| S4—Co | 0.56 | 2.196 | |
| (Mn,Co)-co-doped Cu2ZnSnS4 | S1—Mn | 0.62 | 2.188 |
| S2—Mn | 0.60 | 2.197 | |
| S3—Mn | 0.62 | 2.188 | |
| S4—Mn | 0.60 | 2.198 | |
| S5—Co | 0.56 | 2.179 | |
| S6—Co | 0.55 | 2.199 | |
| S7—Co | 0.56 | 2.180 | |
| S8—Co | 0.55 | 2.198 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Qin, X.; Yan, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, D. Effects of Mn and Co Doping on the Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of Cu2ZnSnS4. Crystals 2025, 15, 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090781
Yang X, Qin X, Yan W, Zhang C, Zhang D. Effects of Mn and Co Doping on the Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of Cu2ZnSnS4. Crystals. 2025; 15(9):781. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090781
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiufan, Xinmao Qin, Wanjun Yan, Chunhong Zhang, and Dianxi Zhang. 2025. "Effects of Mn and Co Doping on the Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of Cu2ZnSnS4" Crystals 15, no. 9: 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090781
APA StyleYang, X., Qin, X., Yan, W., Zhang, C., & Zhang, D. (2025). Effects of Mn and Co Doping on the Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of Cu2ZnSnS4. Crystals, 15(9), 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090781






