A Numerical Analysis of the Fluid Flow in a Slab Mold Considering a SEN with Real Clogging and with Symmetrical Reductions
Abstract
1. Introduction
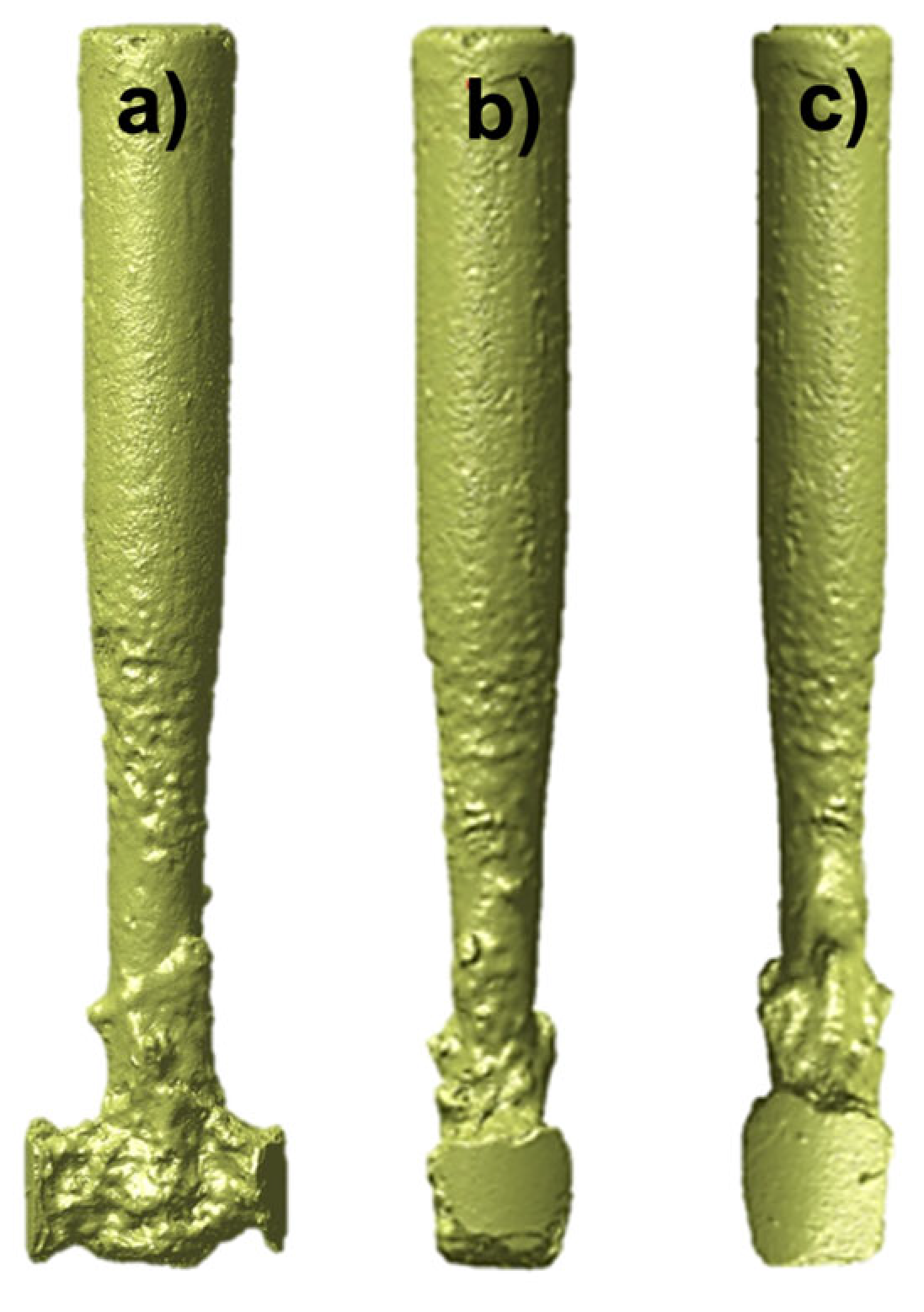
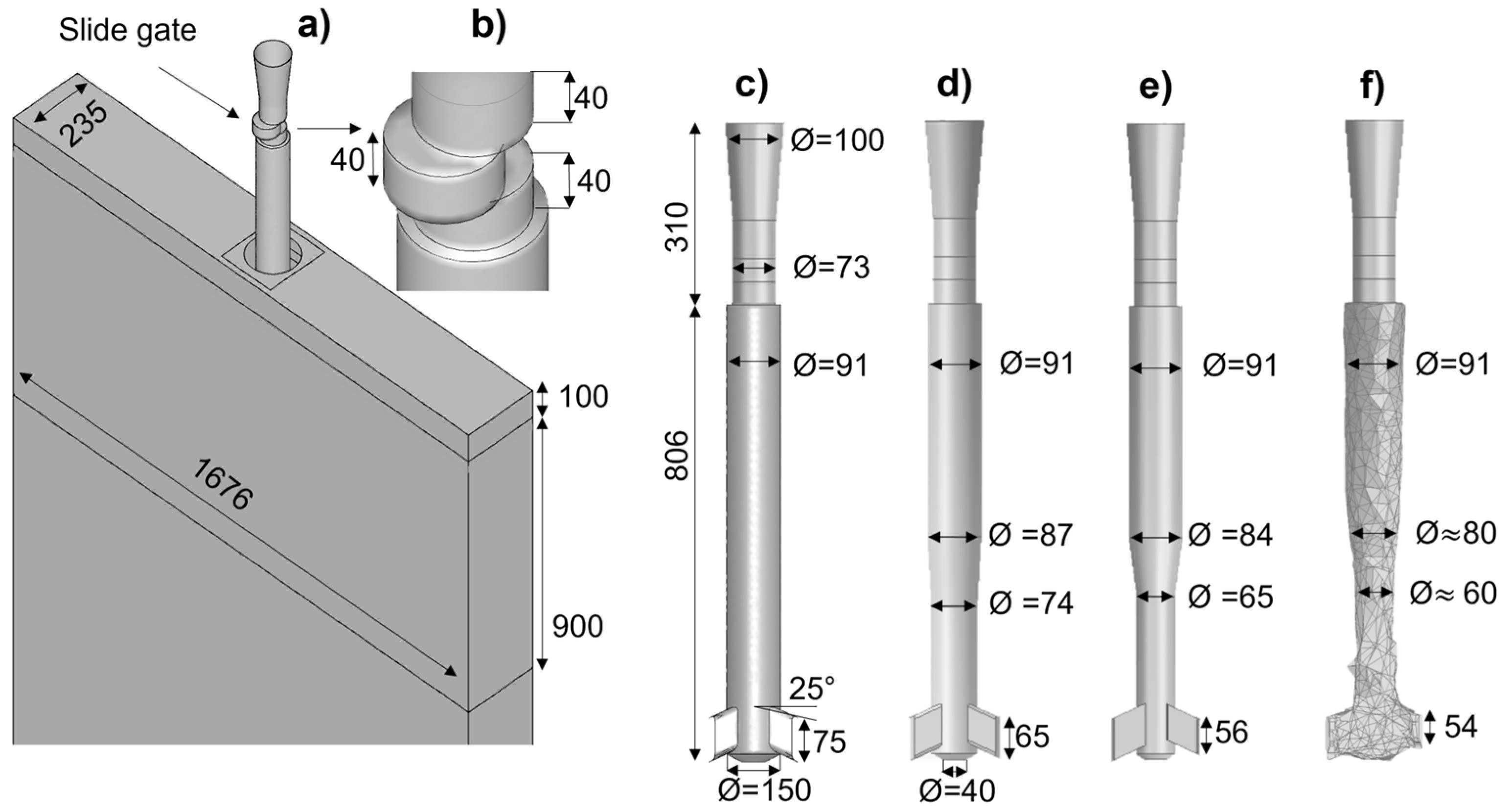
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Main Assumptions
2.2. Fundamental Equations
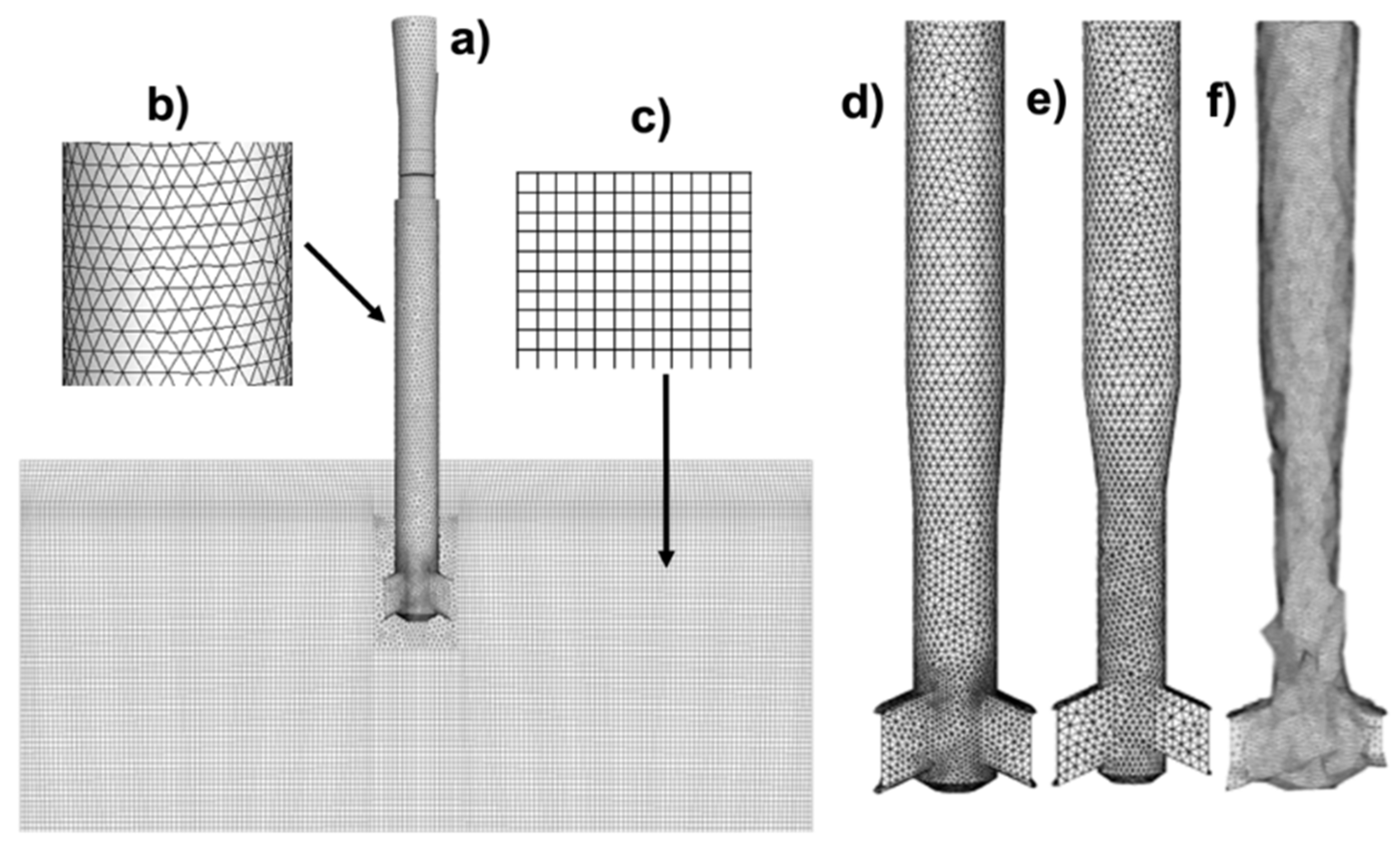
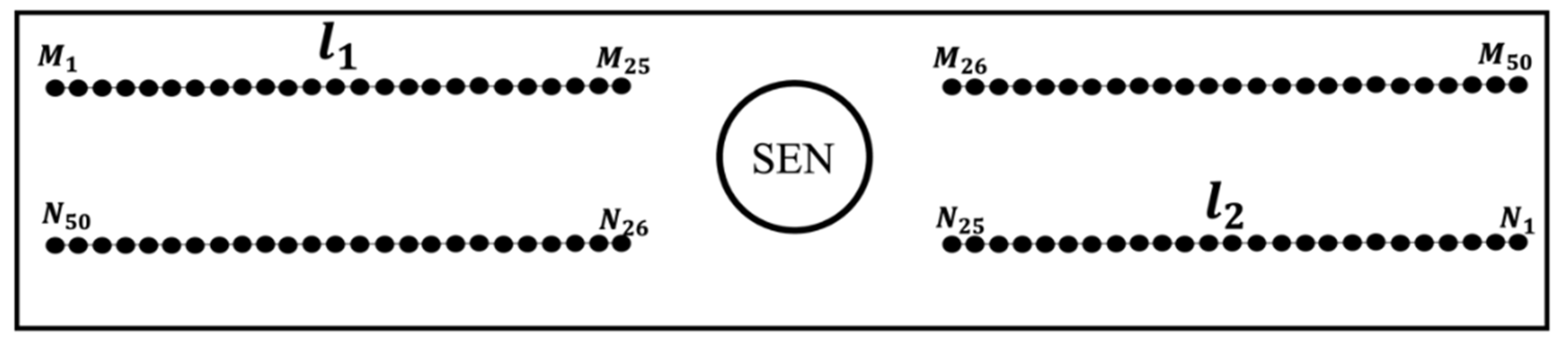
2.3. Numerical Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
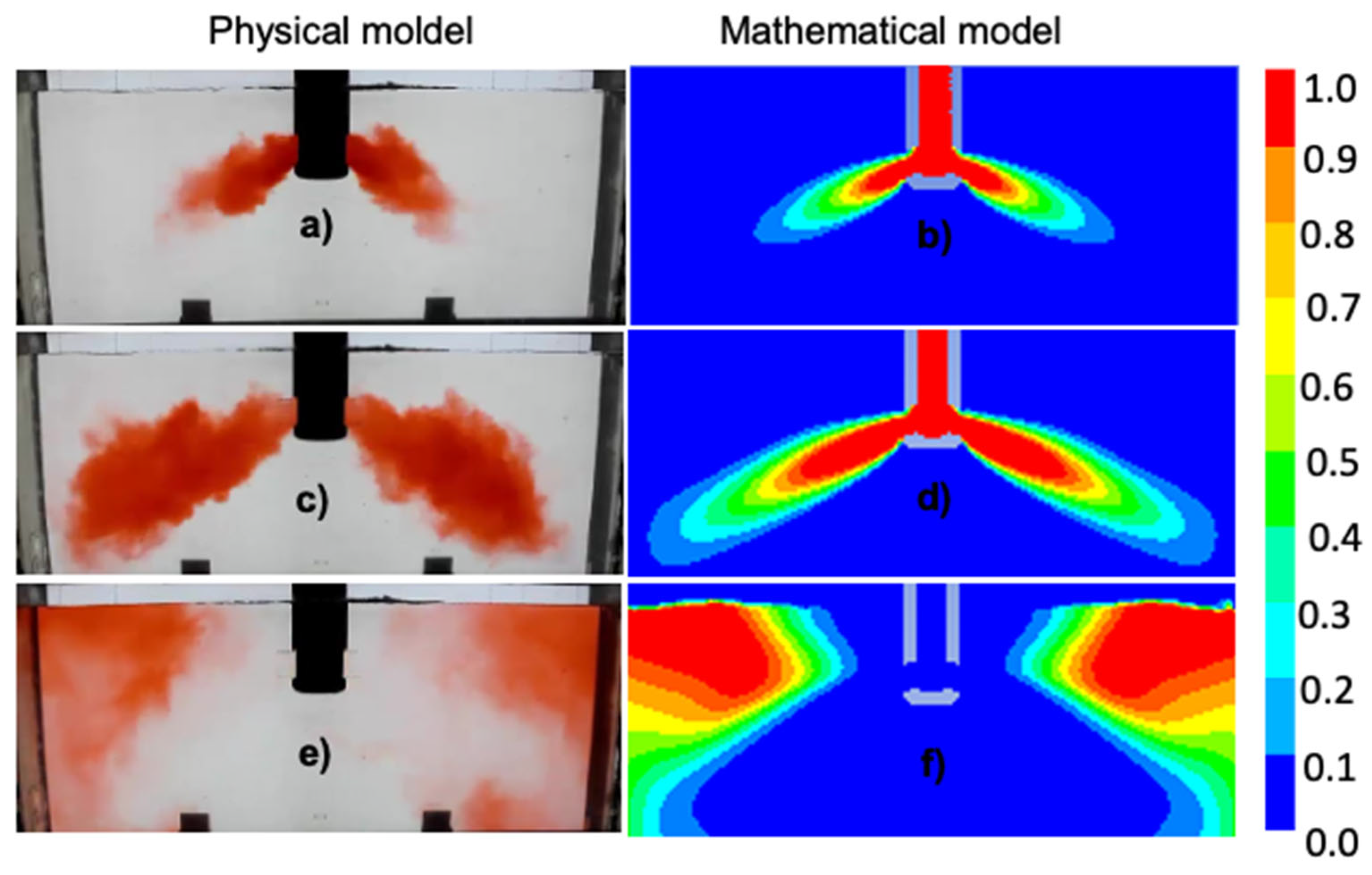
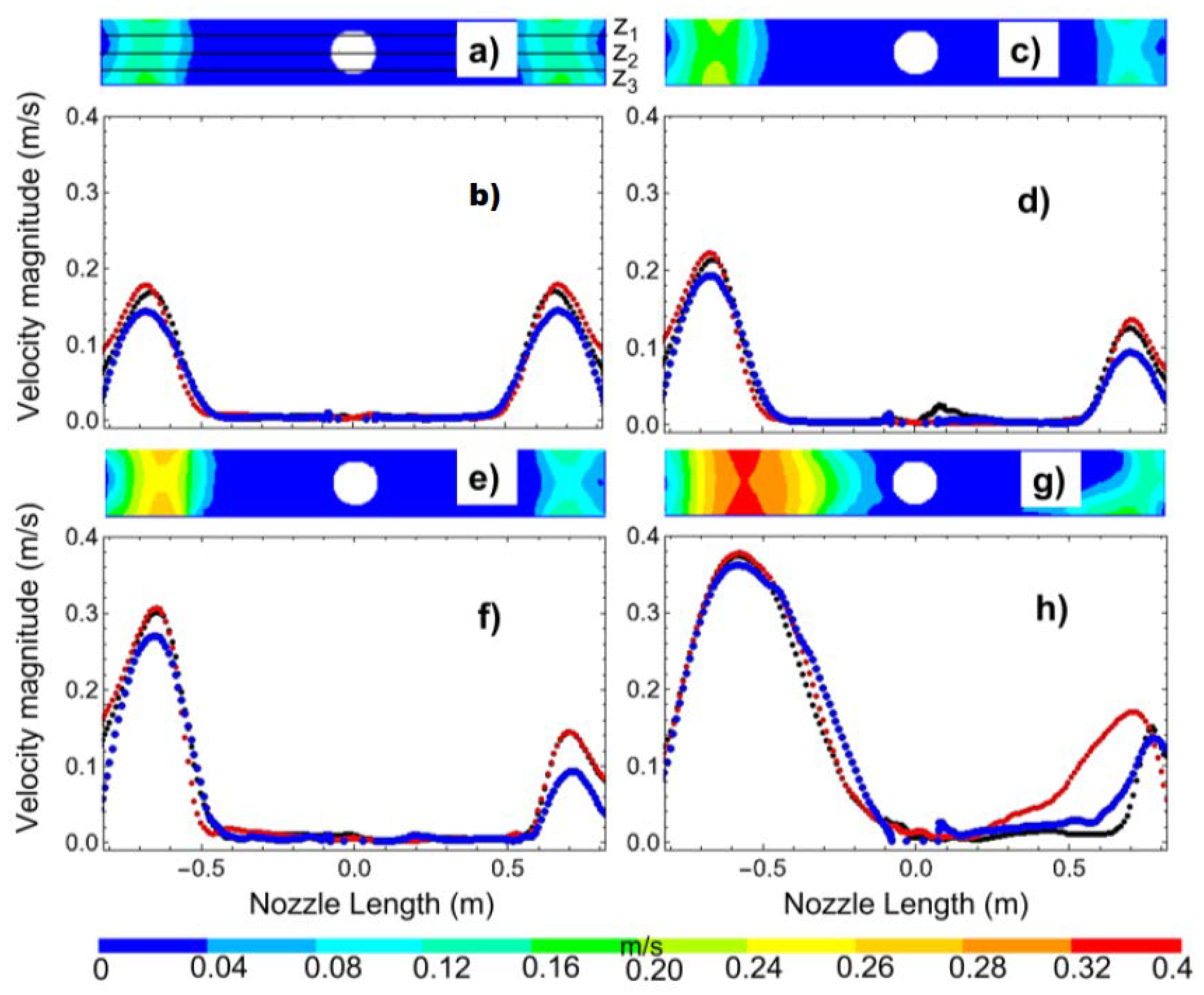
3.1. Mathematical Validation
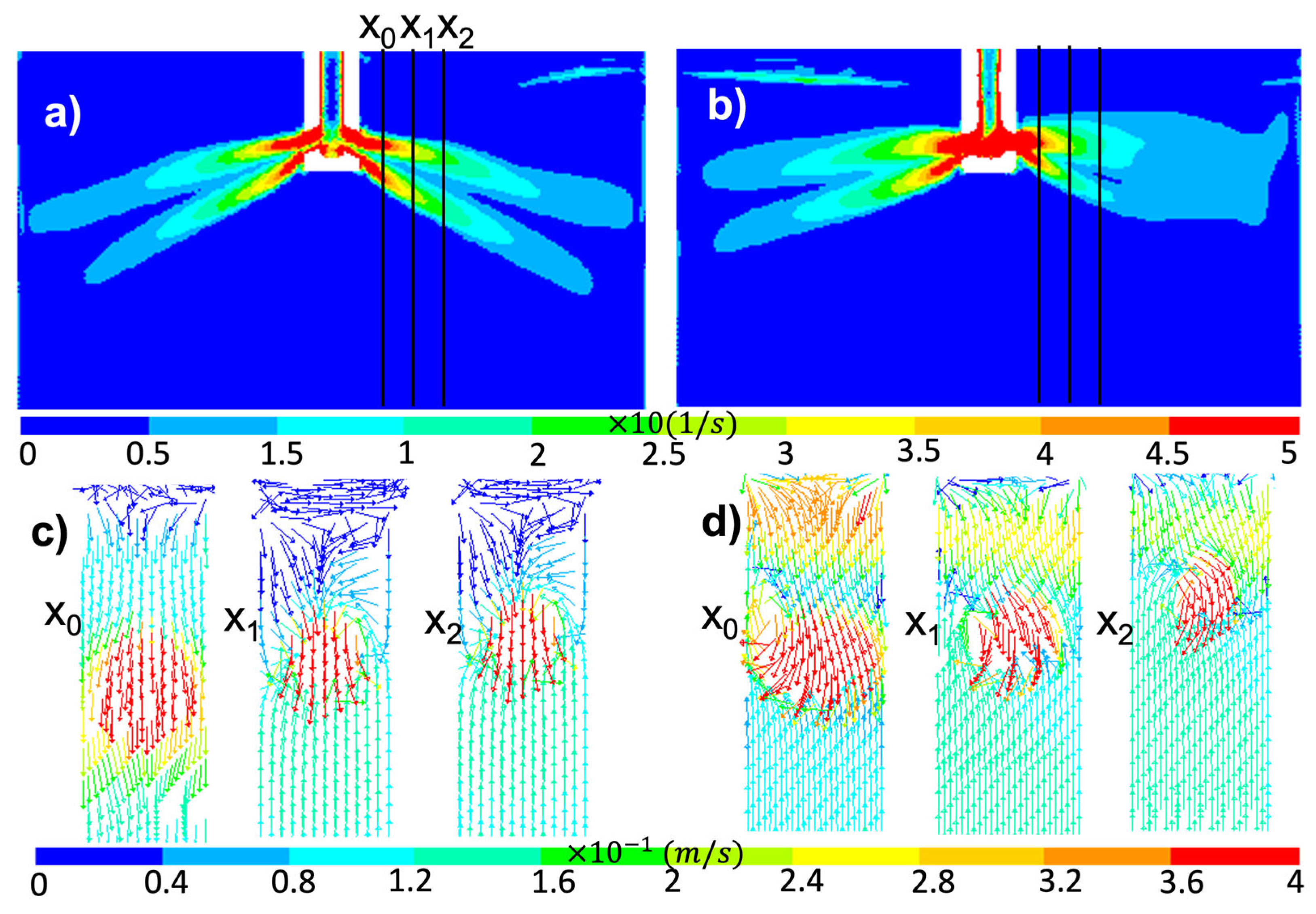
3.2. Comparative Analysis of Flow Behavior Under Different Clogging Stages
3.3. Flow Patterns Inside the Mold
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- When the SEN clogging is too severe, it will modify the fluid dynamics inside the SEN to the point that the effect of the slide gate aperture disappears, as shown in the present research when the real nozzle clogging was applied.
- (2)
- The natural SEN inner wall irregularities, induced by a realistic SEN clogging simulation, produce strong flow rotational movement inside the SEN pool, generating rotational jets and altering the symmetry flow patterns in the mold.
- (3)
- Nozzles with symmetric reductions to simulate real clogging can only qualitatively reflect the expected fluid dynamic patterns. Their estimated results are quantitatively inaccurate given errors of up to 38% in the estimated nozzle velocity and 25% for the meniscus velocities.
- (4)
- The use of symmetric reductions in SEN geometry to simulate real clogging fails to reliably show the fluid dynamics inside it. Such simplification additionally leads to inaccurate predictions of jet behavior, mold flow symmetry, the bath-level velocity magnitudes, and the meniscus stability.
- (5)
- Uniform symmetrically reduced nozzles may be carefully used in studies that require detailed fluid analysis near the internal SEN wall. This is because a SEN with real clogging induces strong velocity variations near the wall due to its natural irregularities.
5. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Bai, H.; Thomas, B.G. Effects of Clogging, Argon Injection, and Continuous Casting Conditions on Flow and Air Aspiration in Submerged Entry Nozzles. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2001, 32, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Kumar, S.; Girase, N.U. Nozzle Clogging Behaviour of Ti-bearing Al-killed Ultra Low Carbon Steel. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.G.; Bai, H. Tundish Nozzle Clogging—Application of Computational Models. In Proceedings of the 18° Process Technology Division Conference Proceedings, Iron and Steel Society, Warrendale, PA, USA, 25–28 March 2001; Volume 18, pp. 895–912. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Zhu, M.; Zhong, B.; Sichen, D. Attachment of Liquid Calcium Aluminate Inclusions on Inner Wall of Submerged Entry Nozzle during Continuous Casting of Calcium-Treated Steel. ISIJ Int. 2014, 54, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Yu, J.; Jin, E.; Wen, T.; Jia, D.; Liu, Z.; Fu, P.; Yuan, L. Effect of Interfacial Reaction Behaviour on the Clogging of SEN in the Continuous Casting of Bearing Steel Containing Rare Earth Elements. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 792, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, C.; Wu, M.; Kharicha, A.; Ludwig, A. Role of Solidification in Submerged Entry Nozzle Clogging during Continuous Casting of Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2010, 91, 2000230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadif, M.; Lehmann, J.; Burty, M.; Domgin, J.F. Control of Steel Reoxidation and CC Nozzle Clogging: An Overview. Metall. Res. Technol. 2007, 104, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, F. Formation and Prevention of Nozzle Clogging during the Continuous Casting of Steels: A Review. ISIJ Int. 2024, 64, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojola, N.; Ekerot, S.; Jönsson, P. Pilot Plant Study of Clogging Rates in Low Carbon and Stainless-Steel Grades. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2011, 38, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojola, N.; Ekerot, S.; Andersson, M.; Jönsson, P. Pilot Plant Study of Nozzle Clogging Mechanisms during Casting of REM Treated Stainless Steels. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2011, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, E.; García-Hernández, S.; de Jesús Barreto, J. Mathematical Analysis of the Dynamic Effects on the Deposition of Alumina Inclusions Inside the Upper Tundish Nozzle. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Jonsson, L.; Ersson, M.; Jönsson, P. Transport and Deposition of Non-Metallic Inclusions in Steel Flows—A Comparison of Different Model Predictions to Pilot Plant Experiment Data. Steel Res. Int. 2017, 88, 1700155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, K.; Mizukami, Y. Mechanism of Alumina Adhesion to Continuous Caster Nozzle with Reoxidation of Molten Steel. ISIJ Int. 2001, 41, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, H.; Wu, M.; Holzmann, T.; Kharicha, A.; Ludwig, A. Simulation of Non-metallic Inclusion Deposition and Clogging of Nozzle. In Proceedings of the Minerals, Metals & Materials Series, Modeling and Simulation in Materials Processing 2018, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 11–15 March 2018; pp. 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, Y.; Coletti, B.; Blanpain, B.; Wollants, P.; Vleugels, J. Material Evaluation to Prevent Nozzle Clogging during Continuous Casting of Al Killed Steels. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Zuo, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D. Kinetic Modeling on Nozzle Clogging during Steel Billet Continuous Casting. ISIJ Int. 2010, 50, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Mathematic Model of SEN Clogging During Continuous Casting of Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2010, 17, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.N. Mechanism of Alumina Buildup in Tundish Nozzles During Continuous Casting of Aluminum-Killed Steels. Metall. Trans. 1974, 5, 2165–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavers, J.D.; Kadar, L. Application of Electromagnetic Forces to Reduce Tundish Nozzle Clogging. Appl. Math. Model. 2004, 28, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, E.; Garcia-Hernandez, S.; Barreto, J.d.J.; Morales, R.; Gonzáles-Solorzano, M.G. Decrease of Nozzle Clogging through Fluid Flow Control. Metals 2020, 10, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzáles-Solorzano, M.G.; Morales, R.; Gutiérrez, E.; Guarneros, J.; Chattopadhyay, K. Analysis of Fluid Flow of Liquid Steel Through Clogged Nozzles: Thermodynamics Analysis and Flow simulation. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 91, 2000049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha Roy, P.D.; Tiwari, P.K. Knowledge Discovery and Predictive Accuracy Comparison of Different Classification Algorithms for Mould Level Fluctuation Phenomenon in thin Slab Caster. J. Intell. Manuf. 2016, 30, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Mishra, P.; Roy, A. Experimental Optimization of Submerged Entry Nozzle Submergence Depth to Reduce Meniscus Fluctuations: A Water Model Study. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 41, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.J.; Sung, H.J.; Lee, S. Flow Oscillations and Meniscus Fluctuations in a Funnel-Type Water Mold Model. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2010, 41, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shan, Q.; Cui, H.; Pan, H.; Lu, B.; Shi, X.; Wen, J. Characteristic Analysis of Mold Level Fluctuation during Continuous Casting of Ti-Bearing IF Steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 31, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Wang, M.; Senk, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhi, J.; Bao, Y. Cone Clogging of Submerged Entry Nozzle in Rare Earth Treated Ultra-Low Carbon Al-Killed Steel and Its Effect on the Flow Field and Vortex in the Mold. Metals 2021, 11, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, P.S.; Singh, A.; Korath, J.M.; Jana, A.K. A Water-Model Experimental Study of Vortex Characteristics Due to Nozzle Clogging in Slab Caster Mould. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2016, 44, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbeler, L.C.; Thomas, B.G. Mold Slag Entrainment Mechanisms in Continuous Casting Molds. Iron Steel Technol. 2013, 10, 121–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Li, Q.; Kuang, S.; Zou, Z. Mathematical Modeling of Liquid Slag Layer Fluctuation and Slag Droplets Entrainment in a Continuous Casting Mold Based on VOF-LES Method. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2017, 36, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Malfliet, A.; Wollants, P.; Blanpain, B.; Guo, M. Effect of Alumina Morphology on the Clustering of Alumina Inclusions in Molten Iron. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girase, N.U.; Basu, S.; Choudhary, S.K. Development of Indices for Quantification of Nozzle Clogging during Continuous Slab Casting. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2007, 34, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, H.; Guerra, F.; Cathcart, C.; Chattopadhyay, K. Predicting Quantitative Indices for SEN Clogging in Continuous Casting Using Long Short-term Memory Time-series Model. ISIJ Int. 2022, 62, 2311–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Thomas, B.G. Turbulent Flow of Liquid Steel and Argon Bubbles in Slide-Gate Tundish Nozzles: Part I. Model Development and Validation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2001, 32, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Thomas, B.G. Turbulent Flow of Liquid Steel and Argon Bubbles in Slide-Gate Tundish Nozzles: Part II. Effect of Operation Conditions and Nozzle Design. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2001, 32, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, H. Effect of Argon Blowing Rate on Multiphase Flow and Initial Solidification in a Slab Mold. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Solorzano, M.G.; Morales, R.; Guarneros, J.; Calderon-Ramos, I.; Muñiz-Valdes, C.R.; Najera-Bastida, A. Unsteady Fluid Flows in the Slab Mold Using Anticlogging Nozzles. Fluids 2022, 7, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, Y.; Kitaoka, H.; Sakuraya, T.; Fujii, T. Mechanism for Separating Inclusions from Molten Steel Stirred with a Rotating Magnetic Field. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, H.; Shen, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhong, Y.; Ren, Z.; Lei, Z. Physical Modeling of Asymmetrical Flow in Slab Continuous Casting Mold due to Submerged Entry Nozzle Clogging with the Effect of Electromagnetic Stirring. ISIJ Int. 2019, 59, 2264–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, X. Flow Transport and Inclusion Motion in Steel Continuous-Casting Mold under Submerged Entry Nozzle Clogging Condition. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2008, 39, 534–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, H.; Zhong, Y.; Ren, Z.; Lei, Z. Influence of EMS on Asymmetric Flow with Different SEN Clogging Rates in a Slab Continuous Casting Mold. Metals 2019, 9, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Mishra, P.; Roy, A. Influence of Submerged Entry Nozzle Port Blockage on the Meniscus Fluctuation Considering Various. Metals 2020, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kim, J.G.; Jung, J.; Huh, K.Y. Prediction of Nozzle Clogging through Fluid–Structure Interaction in the Continuous Steel Casting Process. Steel Res. Int. 2021, 92, 2000549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launder, B.E.; Spalding, D.B. The numerical computation of turbulent flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1974, 3, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Inc. FLUENT 12.0, User’s Guide; Centerra Resource Park, Cavendish Court: Lebanon, NH, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.; Ni, P.; Ersson, M.; Zhang, T.; Jönsson, P.G. Effect of swirling flow tundish submerged entry nozzle outlet design on multiphase flow and heat transfer in mould. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2019, 46, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, S. Hydrodynamics and Collisions of Small Particles in a Turbulent Metallic Melt with Special Reference to Deoxidation of Steel. Scand. J. Metall. 1974, 3, 137–150. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, N.; Funagane, H.; Toh, T. Numerical Analysis Study for Clogging Behavior of Immersion Nozzle (Technical Report). Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 2020, 124, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Barati, H.; Wu, M.; Kharicha, A.; Ludwig, A. A transient model for nozzle clogging. Powder Technol. 2018, 329, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

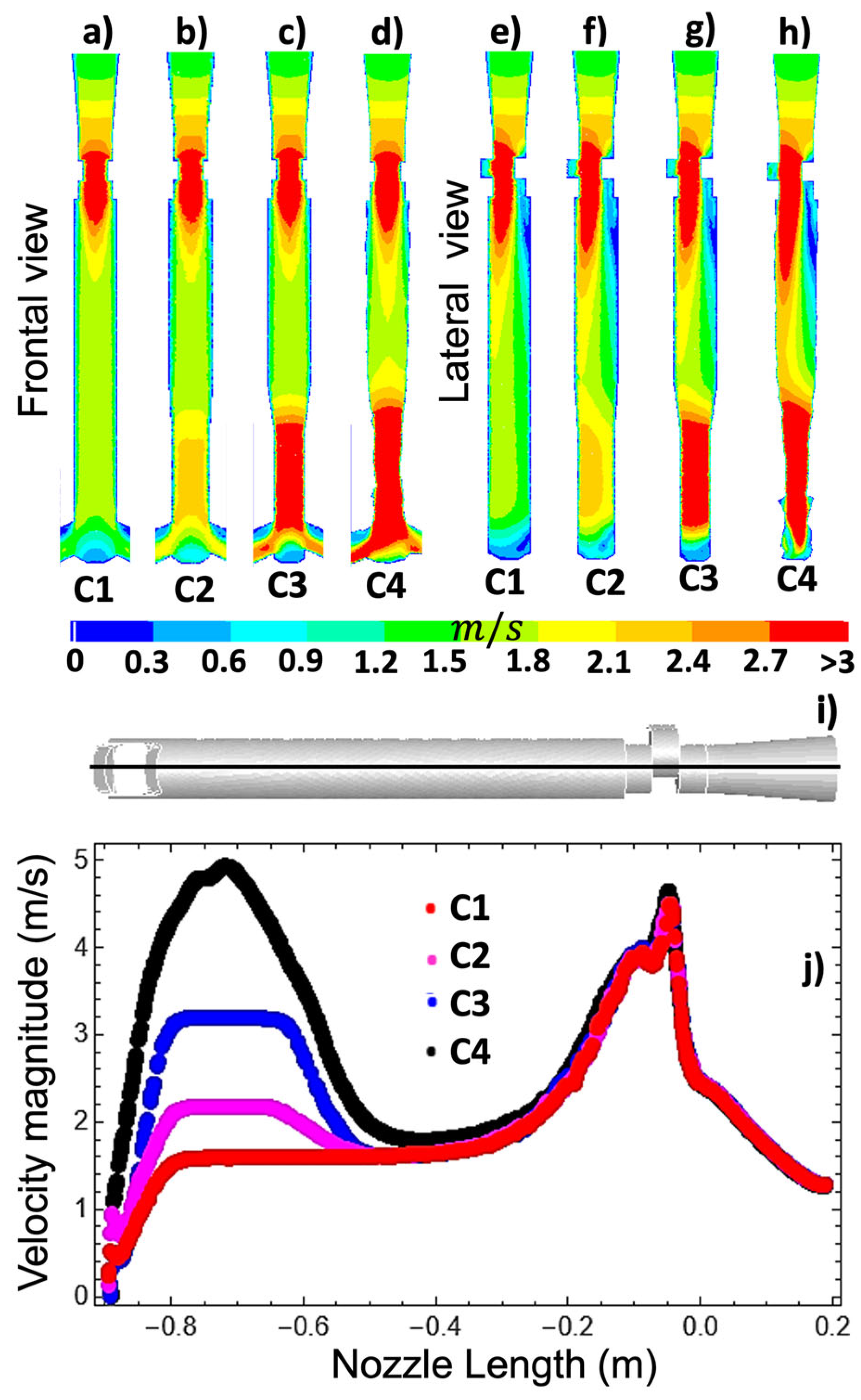
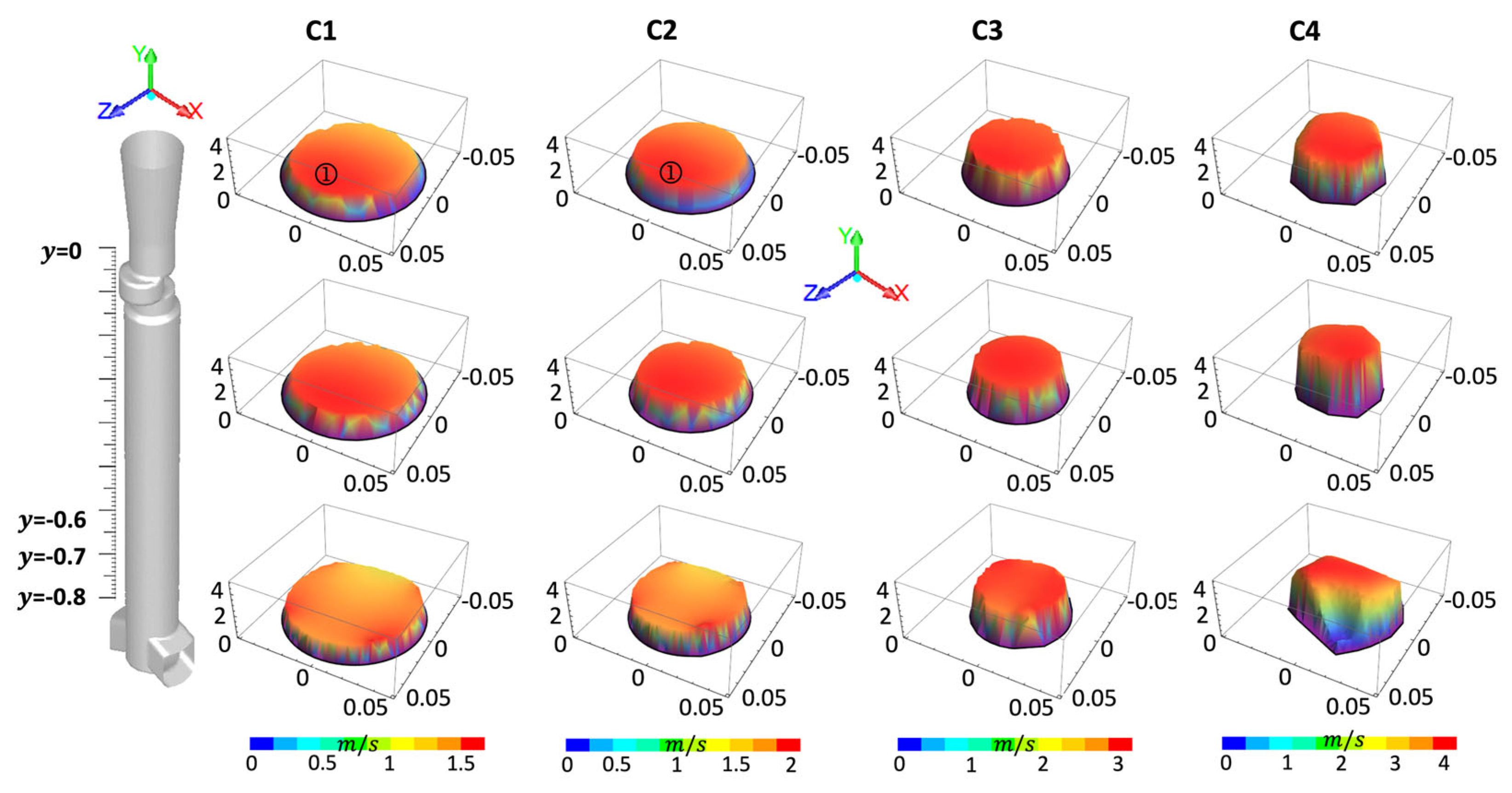

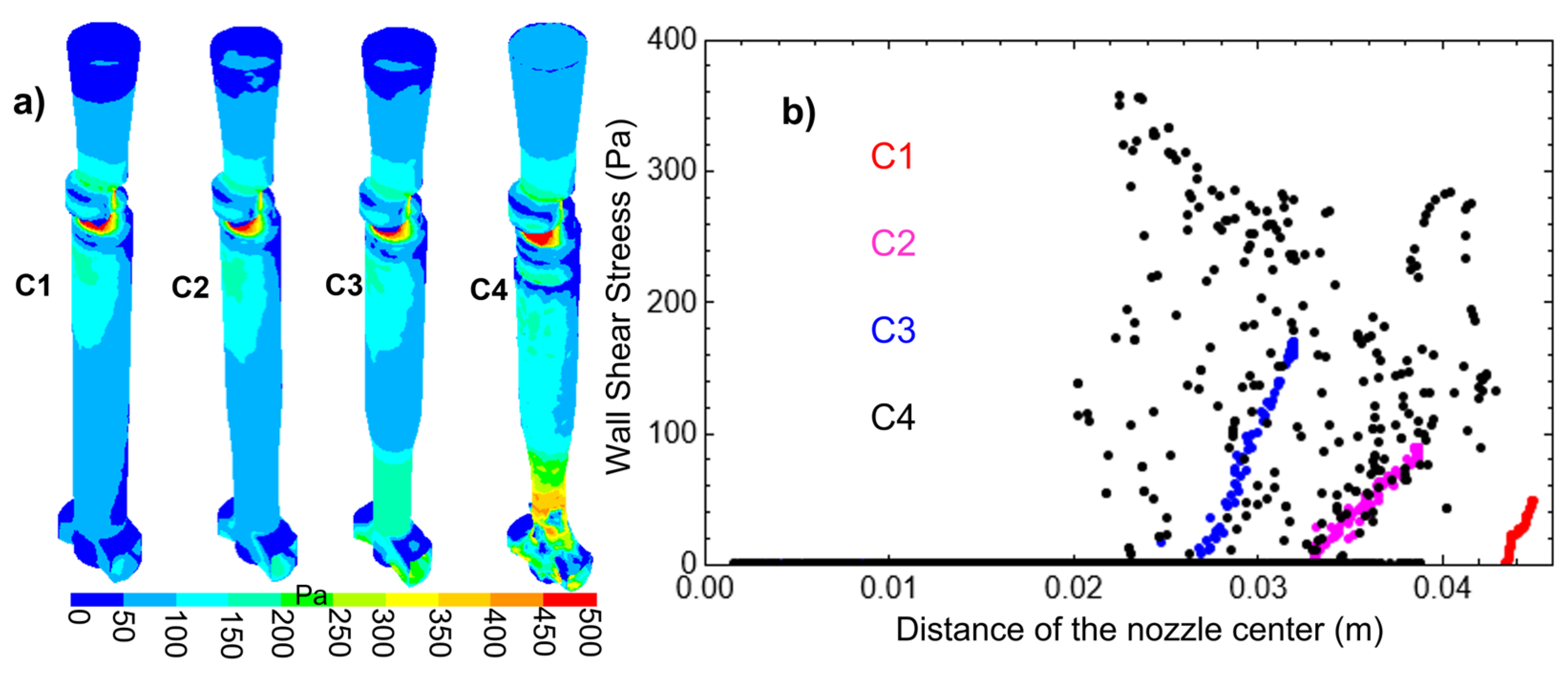
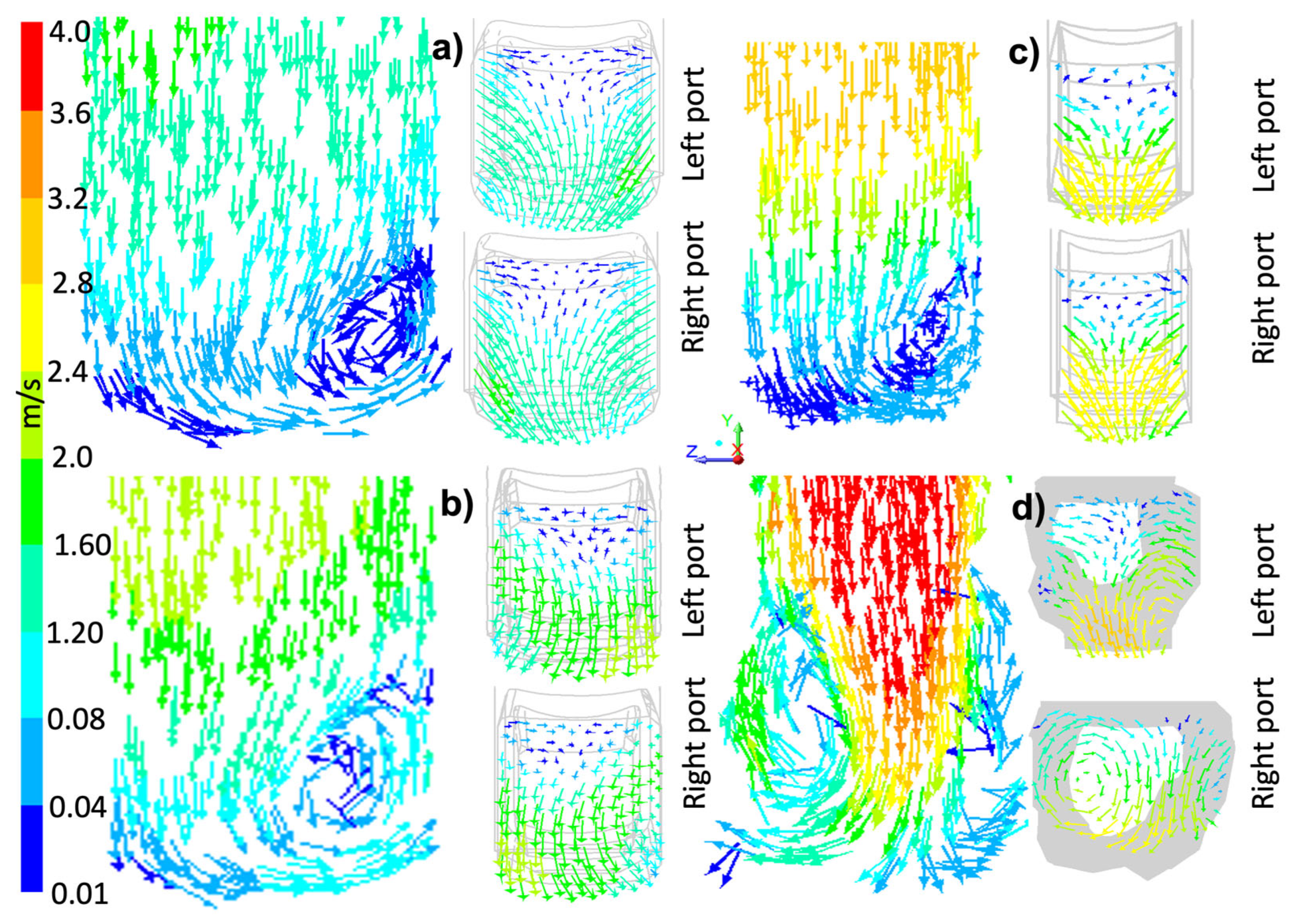
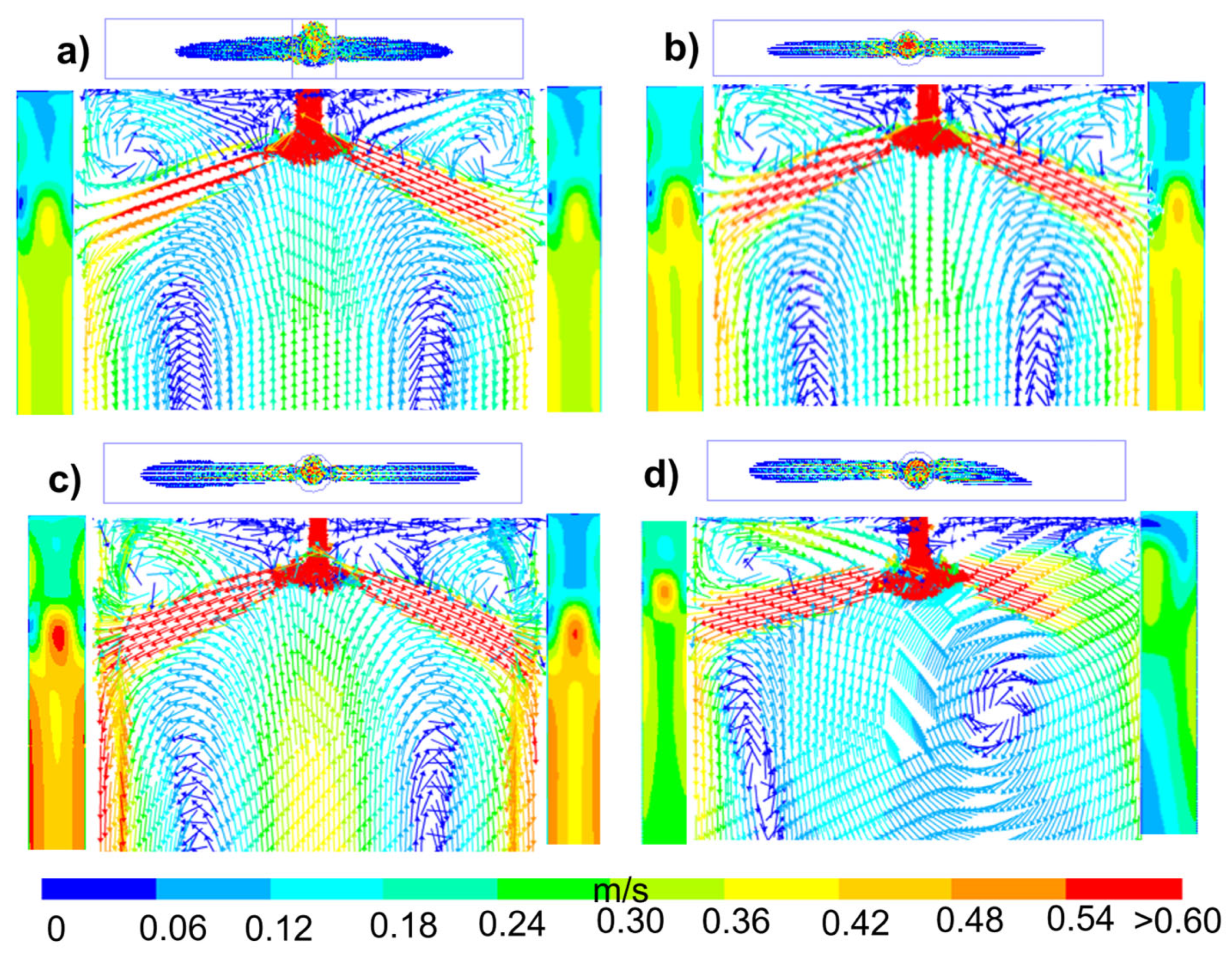
| Case | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.29 | 0.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López, A.; Gutiérrez, E.; Garcia-Hernandez, S.; Morales-Dávila, R.; Barreto, J.d.J. A Numerical Analysis of the Fluid Flow in a Slab Mold Considering a SEN with Real Clogging and with Symmetrical Reductions. Crystals 2025, 15, 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090777
López A, Gutiérrez E, Garcia-Hernandez S, Morales-Dávila R, Barreto JdJ. A Numerical Analysis of the Fluid Flow in a Slab Mold Considering a SEN with Real Clogging and with Symmetrical Reductions. Crystals. 2025; 15(9):777. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090777
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez, Ariana, Enif Gutiérrez, Saul Garcia-Hernandez, Rodolfo Morales-Dávila, and Jose de Jesus Barreto. 2025. "A Numerical Analysis of the Fluid Flow in a Slab Mold Considering a SEN with Real Clogging and with Symmetrical Reductions" Crystals 15, no. 9: 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090777
APA StyleLópez, A., Gutiérrez, E., Garcia-Hernandez, S., Morales-Dávila, R., & Barreto, J. d. J. (2025). A Numerical Analysis of the Fluid Flow in a Slab Mold Considering a SEN with Real Clogging and with Symmetrical Reductions. Crystals, 15(9), 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090777








