Co-Amorphous Andrographolide–Lysine with Unexpectedly Enhanced Solubility
Abstract
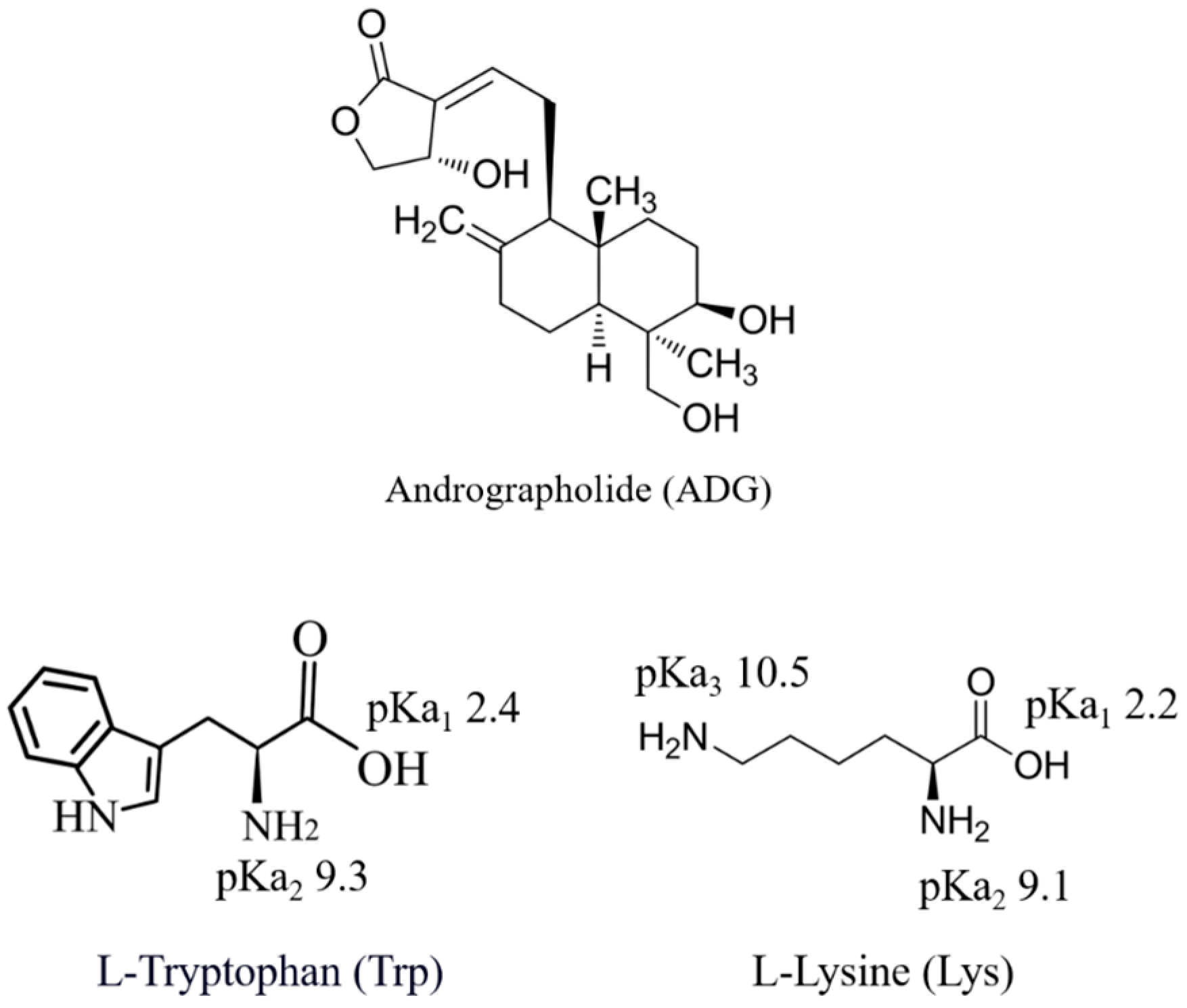
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results
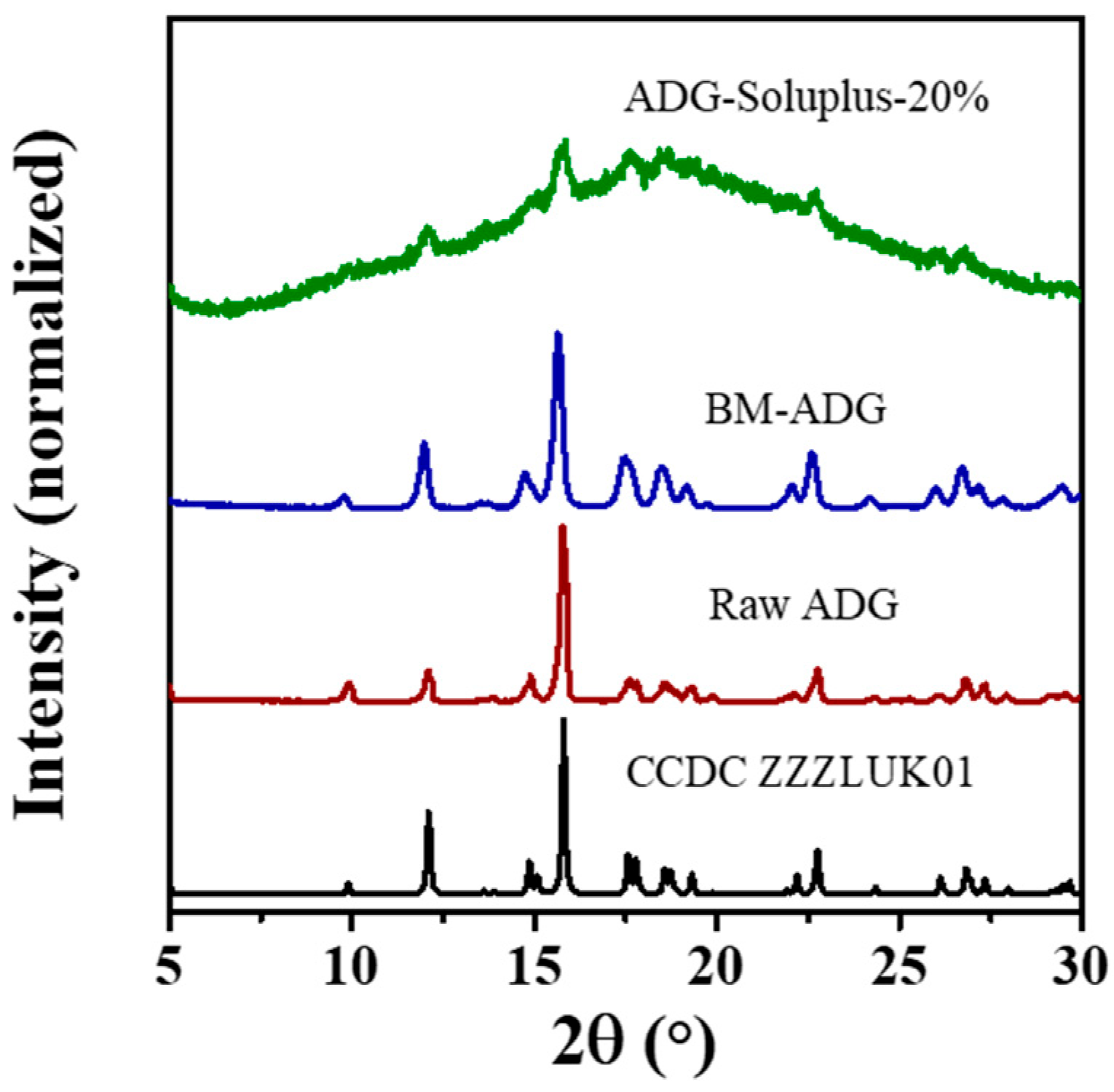
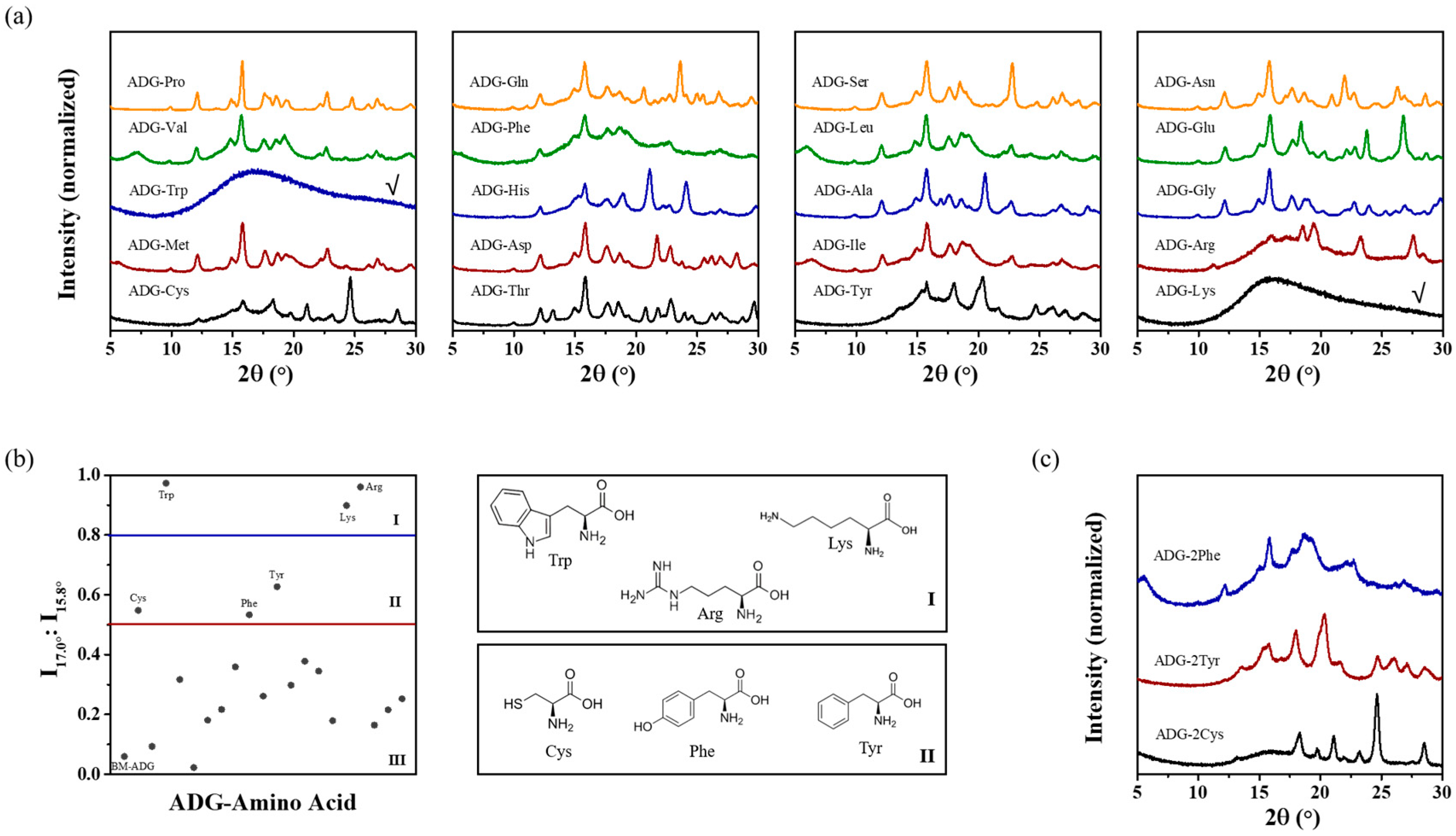
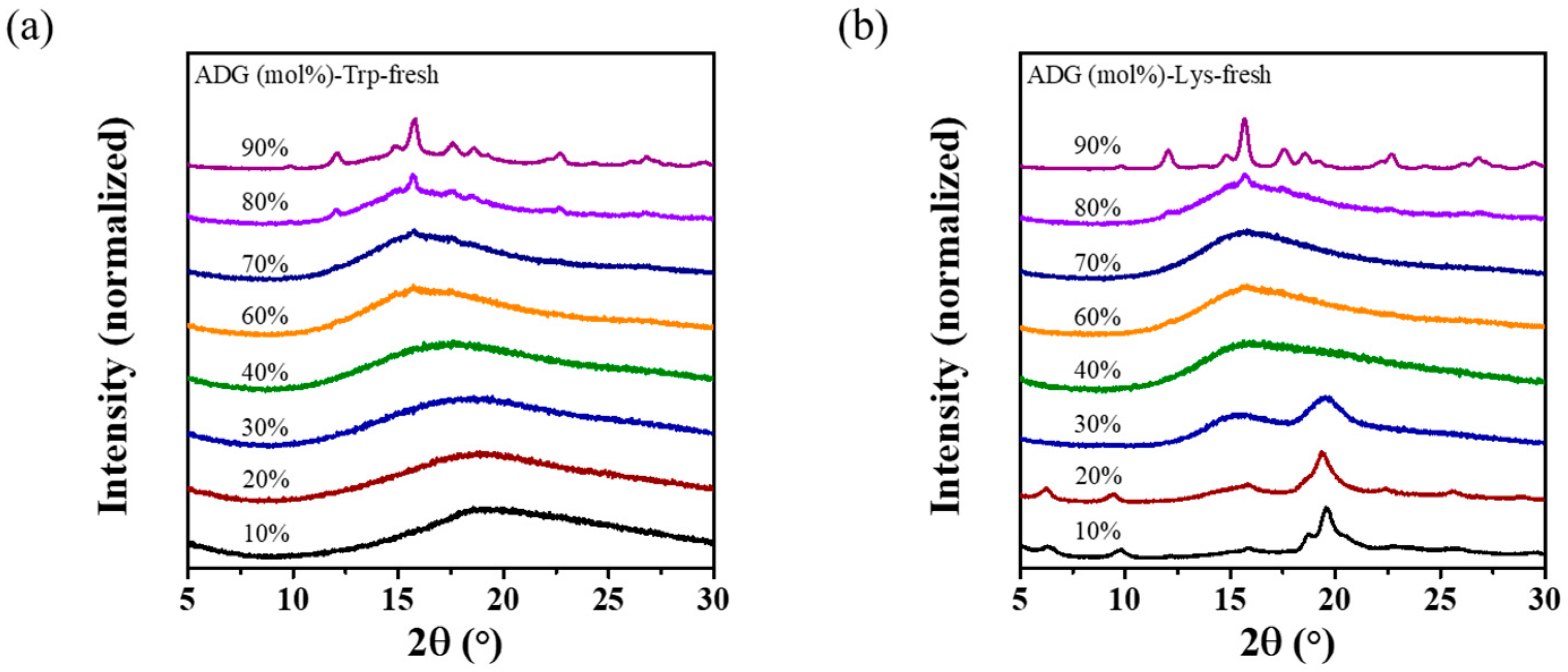
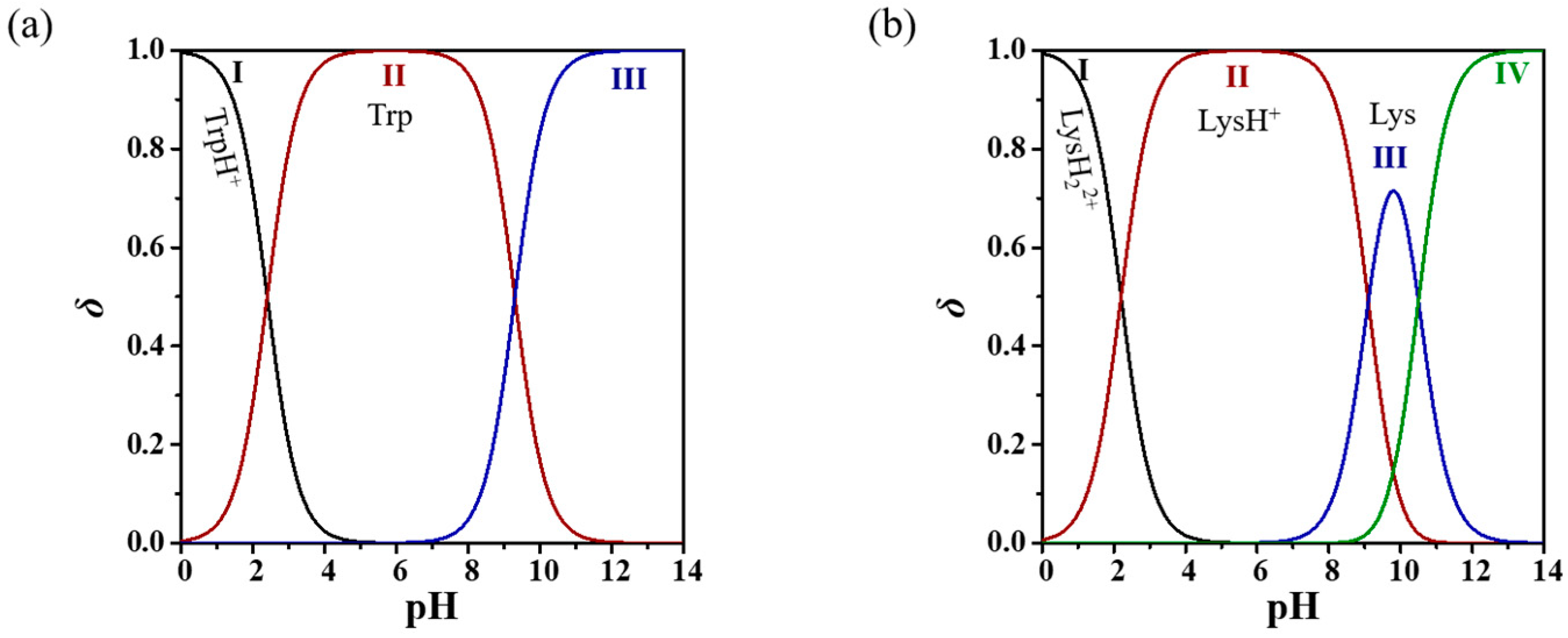
3.1. Co-Amorphous Systems of ADG and Amino Acids
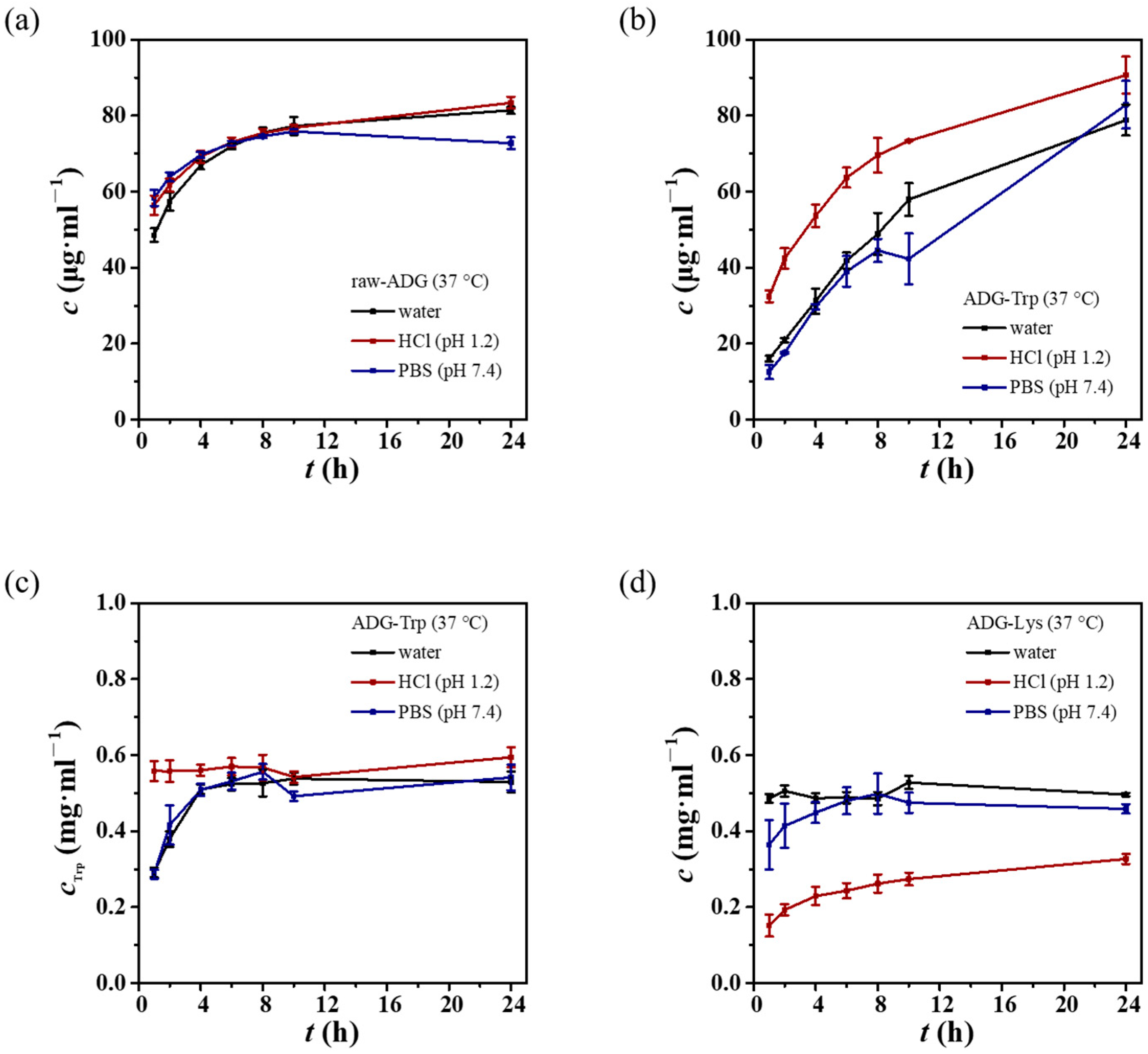
3.2. Dissolution Profiles of ADG-Trp and ADG-Lys
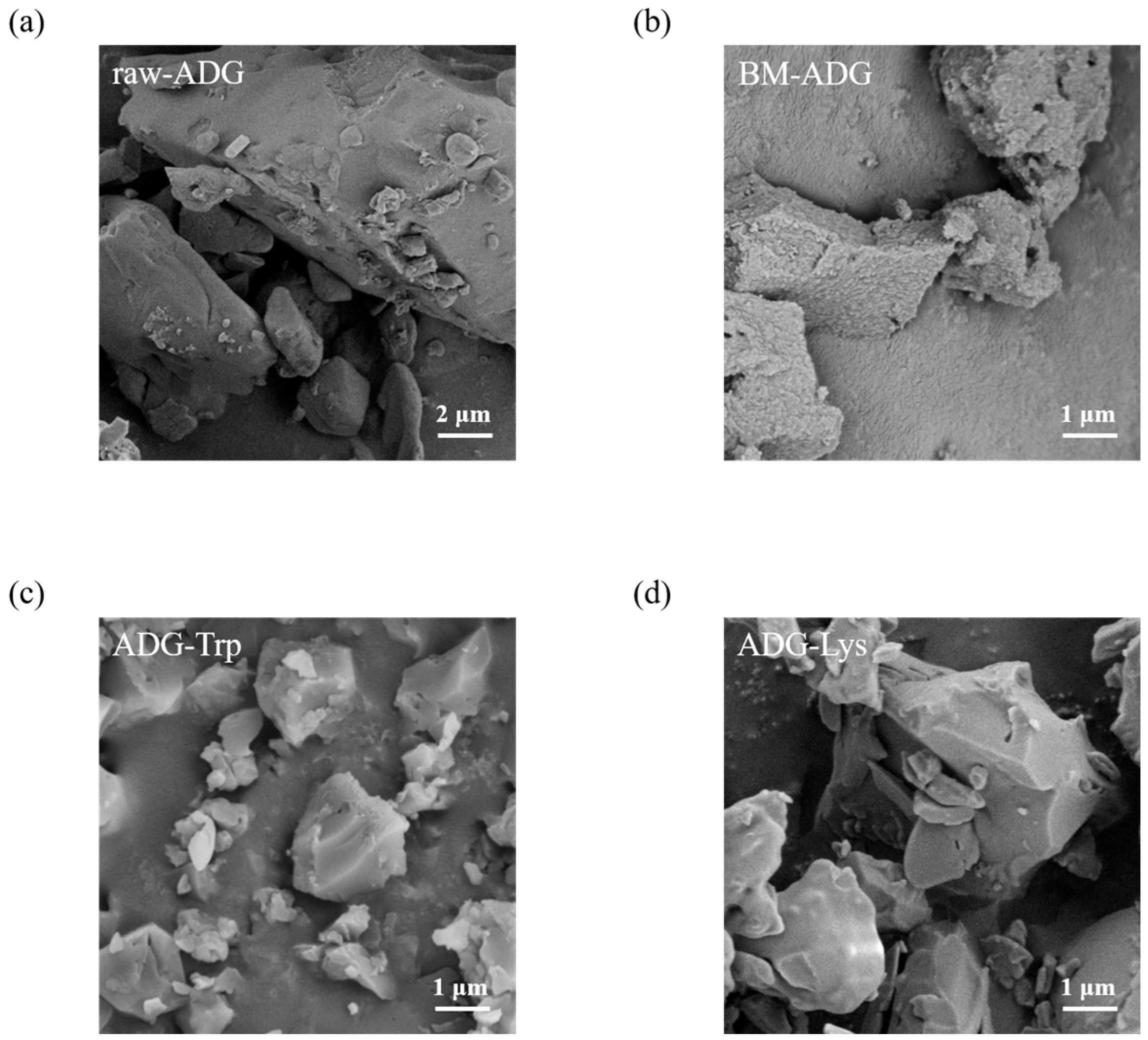
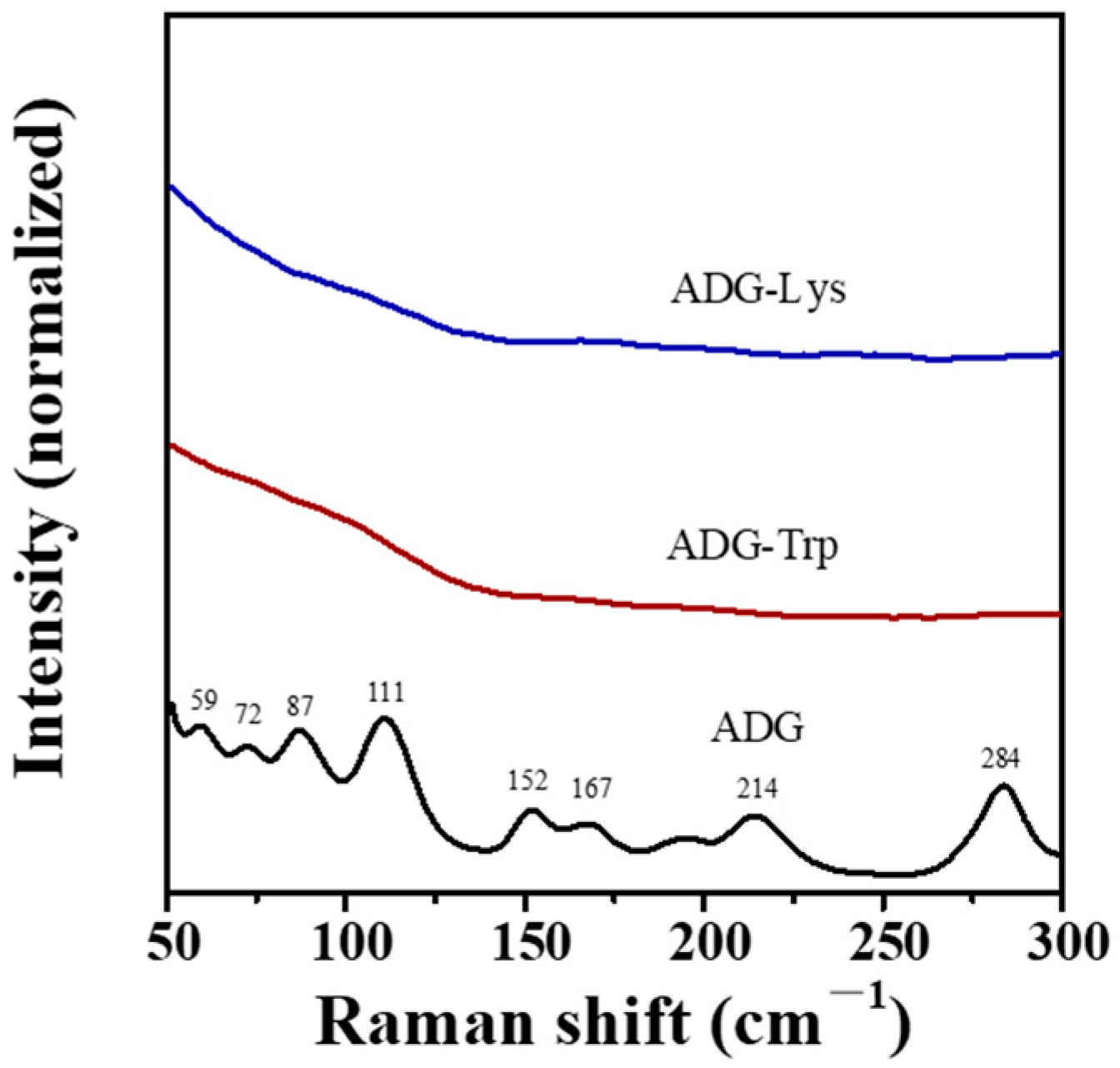
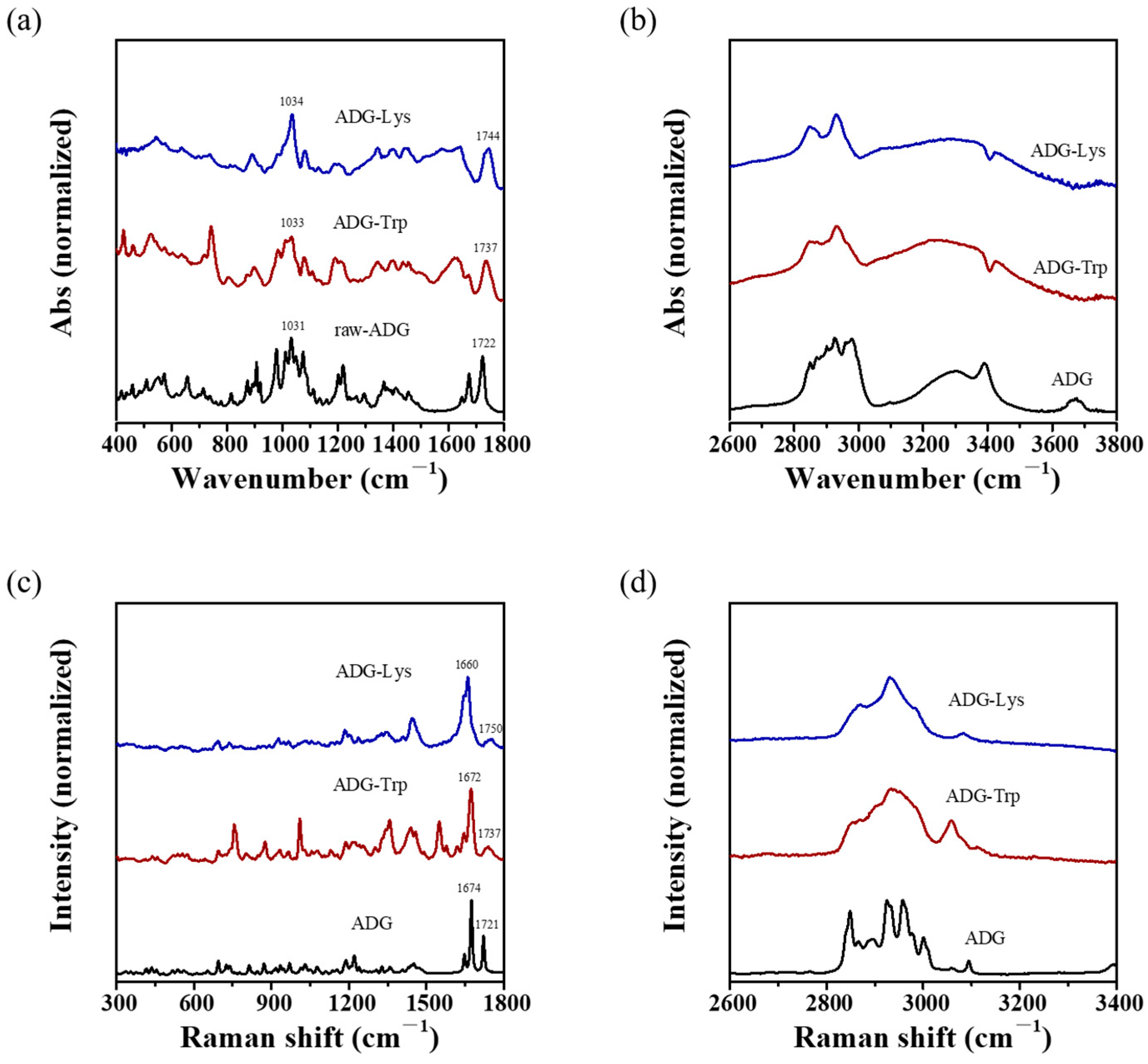
3.3. Morphology and Vibrational Spectroscopic Analysis of ADG-Trp and ADG-Lys
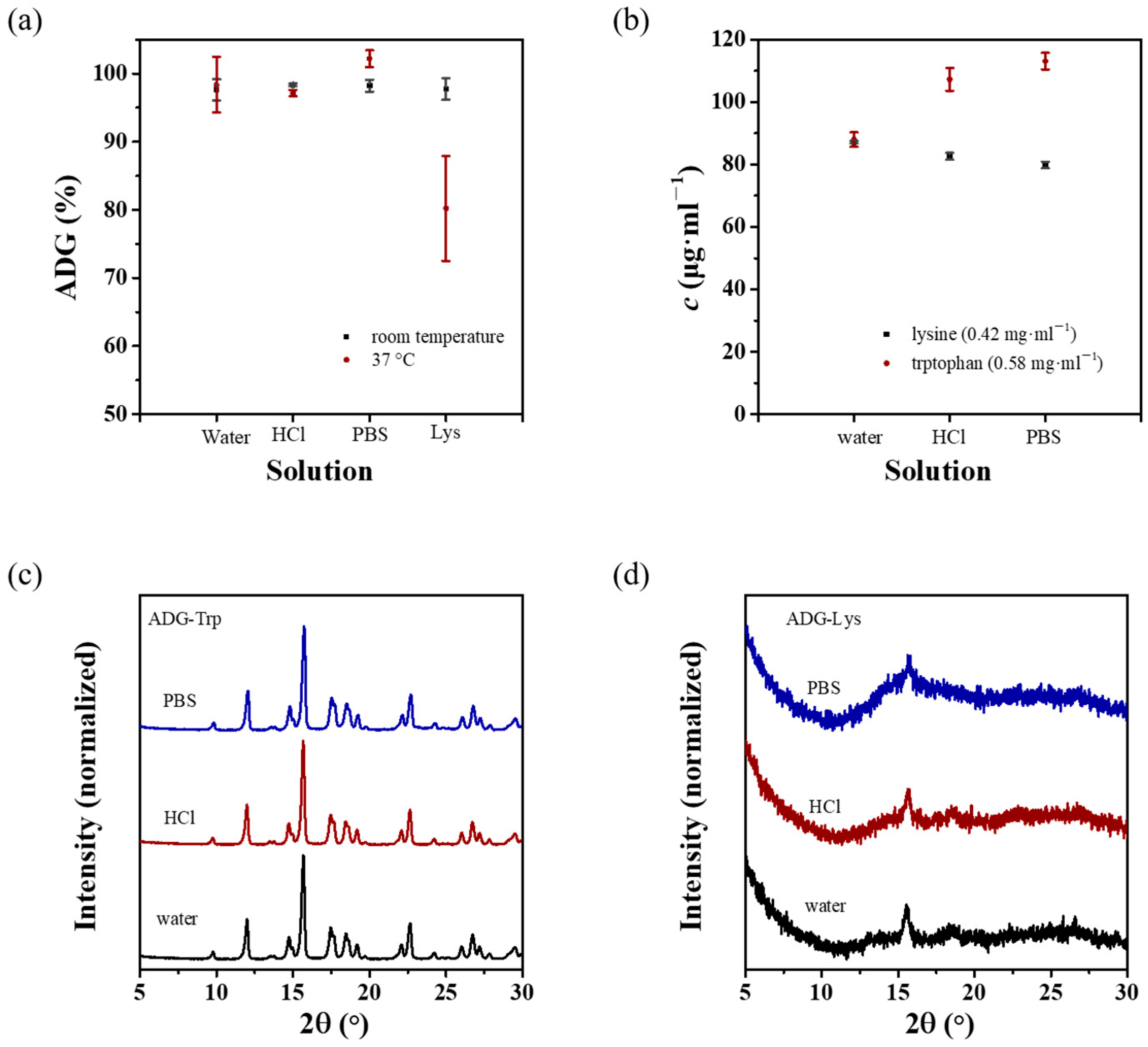
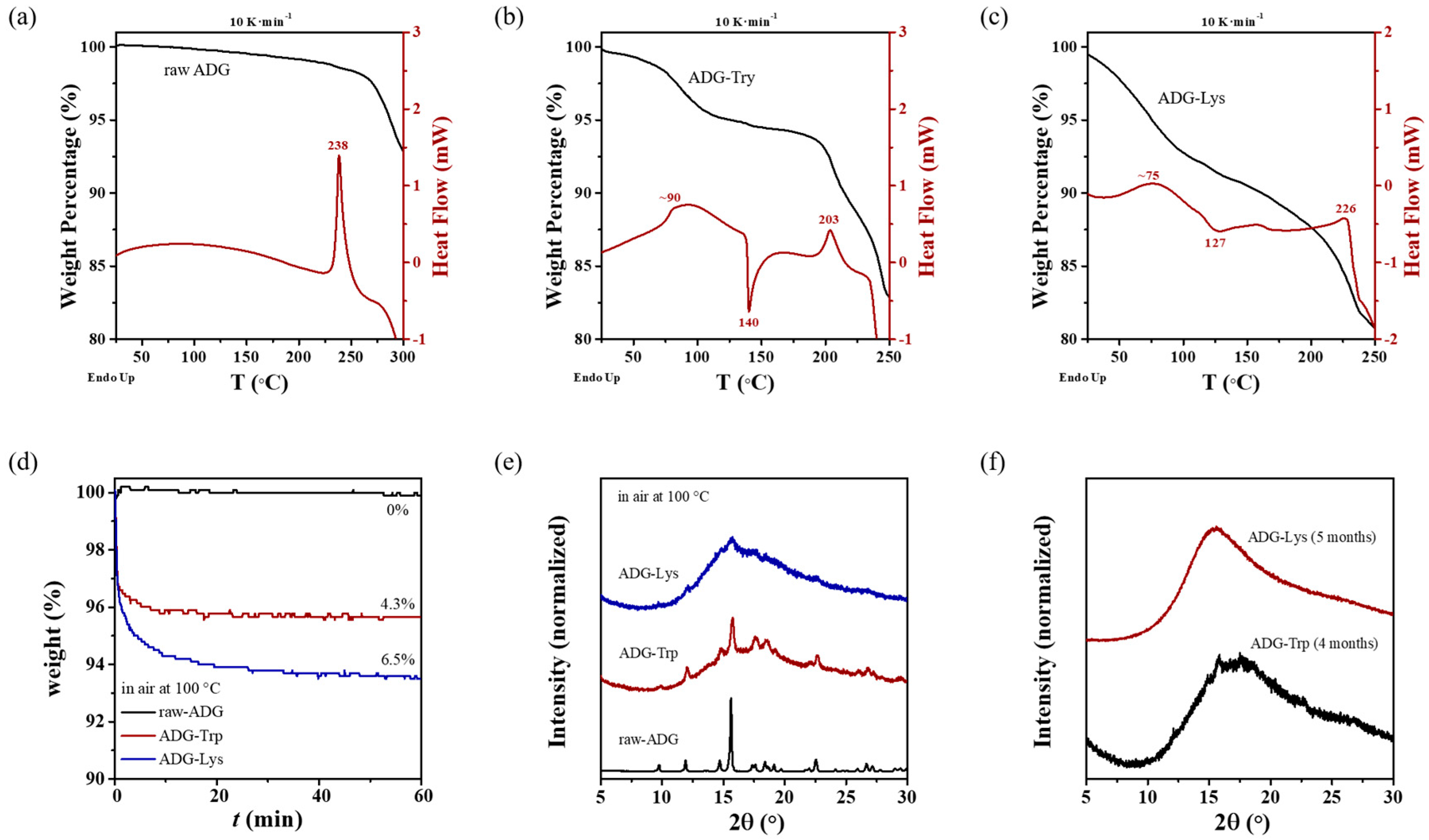
3.4. Stability of ADG-Trp and ADG-Lys
4. Discussion
4.1. Stability of ADG-Lys
4.2. Lysine as a Co-Former
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, Y.; Chen, S.-R.; Ling, C.; Jing, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Overview of pharmacological activities of andrographis paniculata and its major compound andrographolide. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, S17–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppusamy, S.; Pullaiah, T.; Nelson, V.K. Andrographolides—An overview. In Andrographolides; Karuppusamy, S., Nelson, V.K., Pullaiah, T., Eds.; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2024; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Xu, W.; Sun, J.; Dong, B.; Awala, H.; Wang, L. Current trends on repurposing and pharmacological enhancement of andrographolide. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 2346–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Nair, M.S. An insight into the pharmacological and analytical potential of andrographolide. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 36, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Zheng, Z.; Su, J.; Zhou, J.; Xu, S.; Luo, W.; Su, H.; Li, Y.; Xiong, W. Unraveling the impact of stabilizers on nanocrystal preparation and oral absorption: A case study of poorly soluble andrographolide. Nano Lett. 2025, 25, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, P.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Pang, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, L. The comparison of anticrystallization effects of cellulose derivatives with polyvinylpyrrolidone and poloxamer on andrographolide: In vitro and in vivo characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 358, 123510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lv, C.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, T.; Huang, X. An overview on polymorph preparation methods of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Cryst. Growth Des. 2024, 24, 584–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C. Recent advances in drug polymorphs: Aspects of pharmaceutical properties and selective crystallization. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 611, 121320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.B.; Toder, B.H.; Carroll, P.J.; Donohue, J. Andrographolide: An X-ray crystallographic analysis. J. Crystallogr. Spectrosc. Res. 1982, 12, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjula, S.; Kalaiarasi, C.; Pavan, M.S.; Hathwar, V.R.; Kumaradhas, P. Charge density and electrostatic potential of hepatitis C anti-viral agent andrographolide: An experimental and theoretical study. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 2018, 74, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Goud, N.R.; Nangia, A. Andrographolide: Solving chemical instability and poor solubility by means of cocrystals. Chem. Asian J. 2013, 8, 3032–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoulikha, M.; Zou, J.; Yang, P.; Wu, J.; Wu, W.; Hao, K.; He, W. Cocrystal pleomorphism-inspired drug nanoassembly for pulmonary-endothelium targeting and pulmonary hypertension treatment. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, D.; Singh, P.K.; Sajidul, H.; Sheela, M.; Anitha, S.; Rahul, K.; Jitender, M.; Dharmendra, K.; Dua, K. Amorphous systems for delivery of nutraceuticals: Challenges opportunities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1204–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseson, D.E.; Tran, T.B.; Karunakaran, B.; Ambardekar, R.; Hiew, T.N. Trends in amorphous solid dispersion drug products approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration between 2012 and 2023. Int. J. Pharm. X 2024, 7, 100259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, A.; Kouhjani, M.; Yari, D.; Jahani, A.; Asare-Addo, K.; Kamali, H.; Nokhodchi, A. Development, recent advances, and updates in binary, ternary co-amorphous systems, and ternary solid dispersions. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 86, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaval, M.; Dudhat, K.; Soniwala, M.; Dudhrejiya, A.; Shah, S.; Prajapati, B. A review on stabilization mechanism of amorphous form based drug delivery system. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 37, 107411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, R.; Waraya, H.; Hirakura, Y. Application of co-amorphous technology for improving the physicochemical properties of amorphous formulations. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2142–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipduangta, P.; Chansakaow, S.; Tansakul, P.; Meungjai, R.; Dilokthornsakul, P. Polymer matrix and manufacturing methods in solid dispersion system for enhancing andrographolide solubility and absorption: A systematic review. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, Y.; Moinuddin, S.M.; Feng, X.; Ahsan, F. Co-amorphous drug delivery systems: A review of physical stability, in vitro and in vivo performance. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, K.; Maji, I.; Mahajan, S.; Singh, P.K. Unlocking the potential of flavonoid-based co-crystal and co-amorphous systems. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 104050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Han, L.; Li, B.; Lu, S.; Cao, Y. Exploring the formation mechanism of coamorphous andrographolide-oxymatrine based on molecular dynamics and spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 2056–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yang, G.; Shi, W.; Lu, S.; Cao, Y. Improving physicochemical properties and pharmacological activities of ternary co-amorphous systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 181, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, D.U.; Singh, S.; Sharma, P.; Prajapati, B.G. Amorphization of low soluble drug with amino acids to improve its therapeutic efficacy: A state-of-art-review. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, P.; Ma, R.; Jia, J.; Fu, Q. Drug–drug co-amorphous systems: An emerging formulation strategy for poorly water-soluble drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 103883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, M.S.; Elshahat, A.; Hamdy, A.; Fathi, A.M.; Emad-Eldin, M.; Ghazy, F.-E.S.; Chopra, H.; Ibrahim, T.M. Soluplus® as a solubilizing excipient for poorly water-soluble drugs: Recent advances in formulation strategies and pharmaceutical product features. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 84, 104519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.M.; Cruz-Angeles, J.; Vázquez-Dávila, M.; Martínez, E.; Cabada, P.; Navarrete-Bernal, C.; Cortez, F. Mechanical activation by ball milling as a strategy to prepare highly soluble pharmaceutical formulations in the form of co-amorphous, co-crystals, or polymorphs. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, A.L.C.S.; Martins, I.C.B.; Spósito, L.; Morais-Silva, G.; Duarte, J.L.; Rades, T.; Chorilli, M. Indomethacin-omeprazole as therapeutic hybrids? Salt and co-amorphous systems enhancing physicochemical and pharmacological properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 653, 123857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Cabeza, A.J. Acid–base crystalline complexes and the pKa rule. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 6362–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintano, M.; Moura, R.T.; Kraka, E. The pKa rule in light of local mode force constants. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2023, 826, 140654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummanapelli, A.K.; Vasudevan, S. Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations of amino acids in aqueous solutions: Estimating pKa values from metadynamics sampling. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 12249–12255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šebesta, F.; Sovová, Ž.; Burda, J.V. Determination of amino acids’ pKa: Importance of cavity scaling within implicit solvation models and choice of dft functionals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2024, 128, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xie, C.; Liu, L. Solubility of andrographolide in various solvents from (288.2 to 323.2) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 5297–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Xue, R.; Chen, F. Explanation and prediction for the product of trehalose dihydrate selective dehydration process using mid-frequency Raman difference spectra. Vib. Spectrosc. 2024, 130, 103626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assim Haq, S.; Paudwal, G.; Banjare, N.; Iqbal Andrabi, N.; Wazir, P.; Nandi, U.; Ahmed, Z.; Gupta, P.N. Sustained release polymer and surfactant based solid dispersion of andrographolide exhibited improved solubility, dissolution, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacological activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 651, 123786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Nasse, M.J.; Ma, Y.; Qi, L. From synthetic to biogenic Mg-containing calcites: A comparative study using FTIR microspectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Dandan, Y.; Di, D.; Yin, T.; Zhang, S.; Tang, X. Dry state microcrystals stabilized by an HPMC film to improve the bioavailability of andrographolide. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 493, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaidee, W.; Rujanapun, N.; Malee, K.; Chaisawadi, S.; Puttarak, P.; Hiransai, P.; Cordell, G.A.; Sarker, S.D.; Nahar, L.; Charoensup, R. Degradation kinetics of Andrographolide in aqueous solution, product identification and biological activity evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 28856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indulkar, A.S.; Alex, S.; Zhang, G.G.Z. Impact of dissolution medium pH and ionization state of the drug on the release performance of amorphous solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 114, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbmann, K.; Laitinen, R.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T.; Grohganz, H. Amino acids as co-amorphous stabilizers for poorly water-soluble drugs—Part 2: Molecular interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ren, S.; Xiao, W.; Xue, R.; Han, W.; Chen, F. Co-Amorphous Andrographolide–Lysine with Unexpectedly Enhanced Solubility. Crystals 2025, 15, 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090752
Luo H, Zheng Y, Ren S, Xiao W, Xue R, Han W, Chen F. Co-Amorphous Andrographolide–Lysine with Unexpectedly Enhanced Solubility. Crystals. 2025; 15(9):752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090752
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Haifeng, Yuchen Zheng, Shizhao Ren, Wangchuan Xiao, Rongrong Xue, Wei Han, and Fenghua Chen. 2025. "Co-Amorphous Andrographolide–Lysine with Unexpectedly Enhanced Solubility" Crystals 15, no. 9: 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090752
APA StyleLuo, H., Zheng, Y., Ren, S., Xiao, W., Xue, R., Han, W., & Chen, F. (2025). Co-Amorphous Andrographolide–Lysine with Unexpectedly Enhanced Solubility. Crystals, 15(9), 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15090752





