Microstructure, Hardness and Tribological Characteristics of High-Entropy Coating Obtained by Detonation Spraying
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
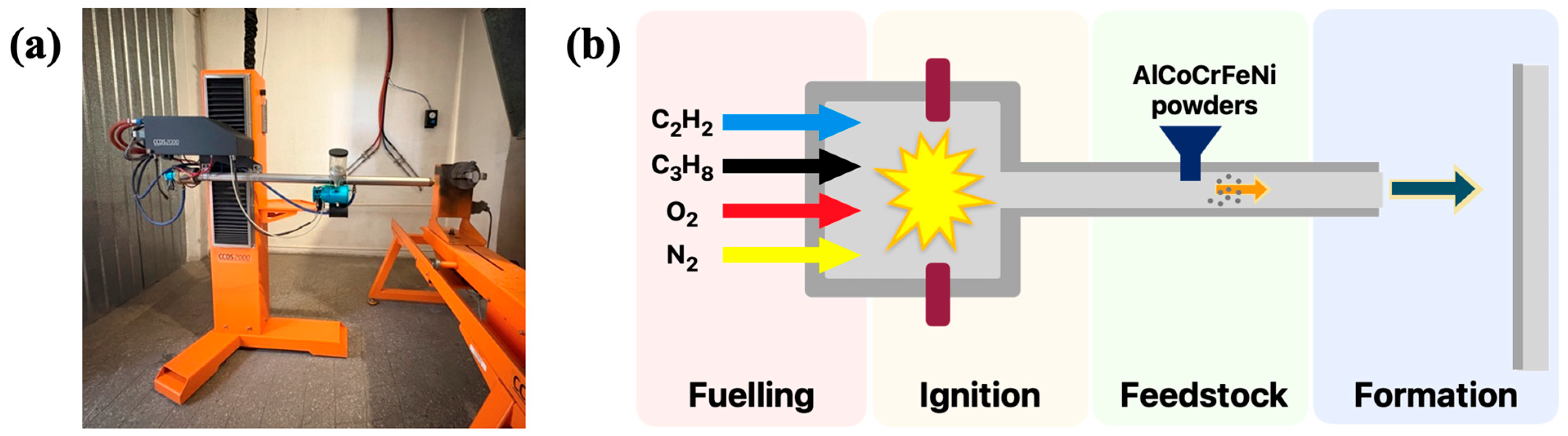
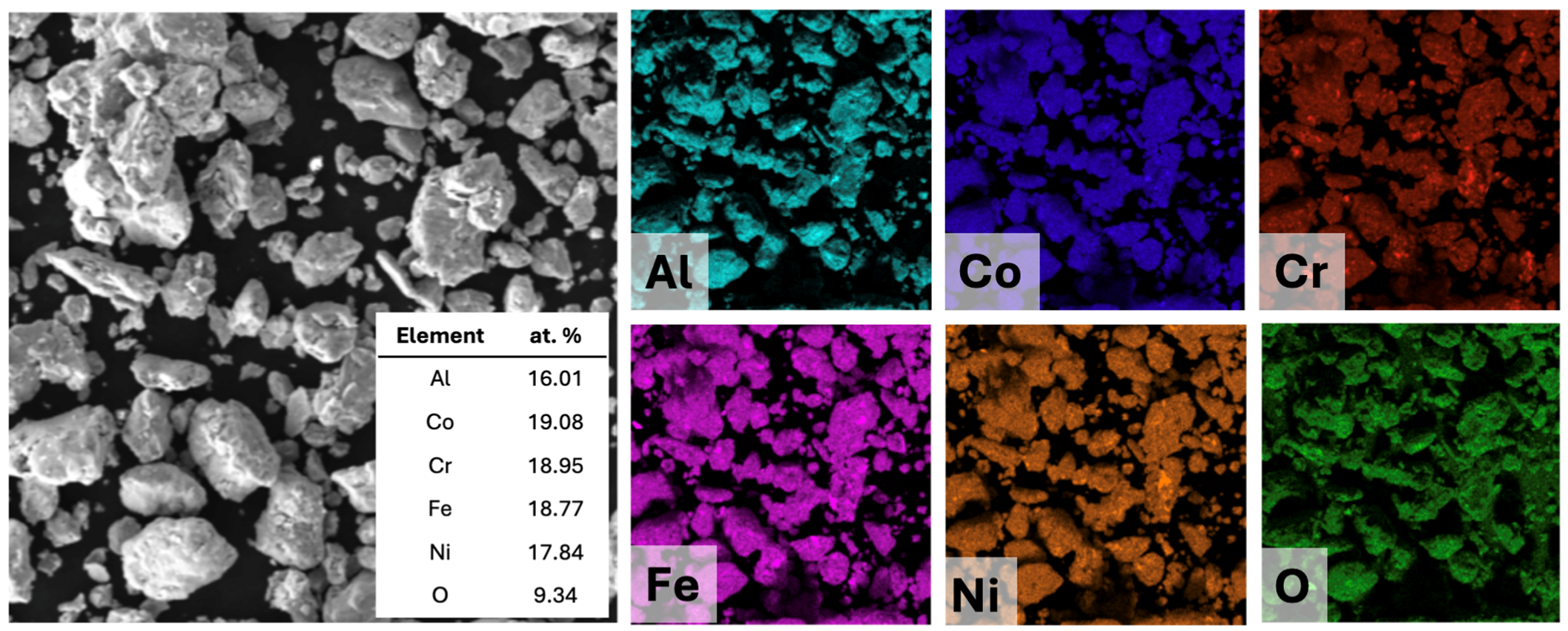
2.1. Preparation of AlCoCrFeNi HEA Coatings
2.2. Predictions Using Thermo-Calc
2.3. Microstructural and Phase Composition Analysis
2.4. Microhardness and Tribological Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Predictions Based on Thermo-Calc Data
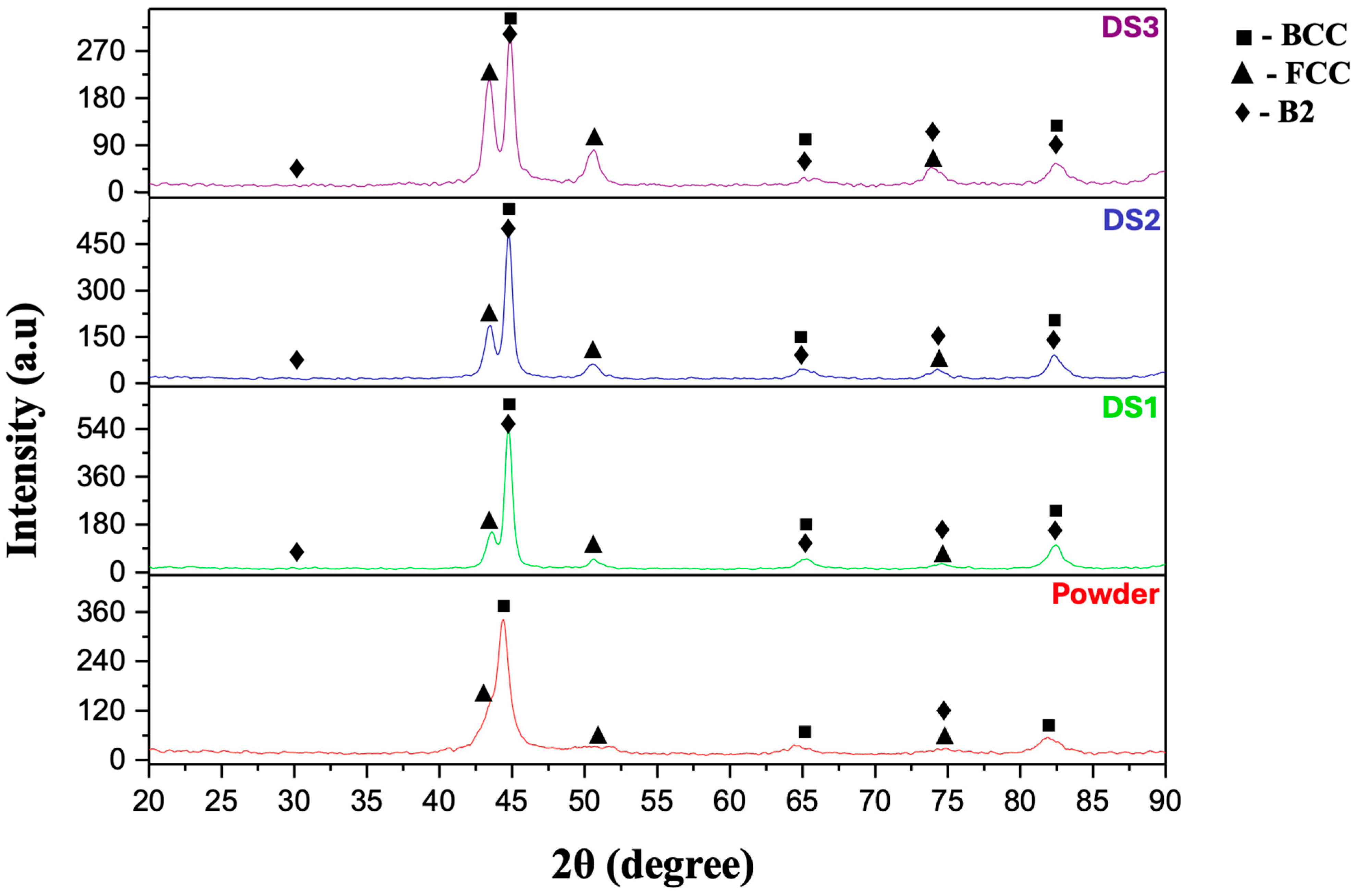
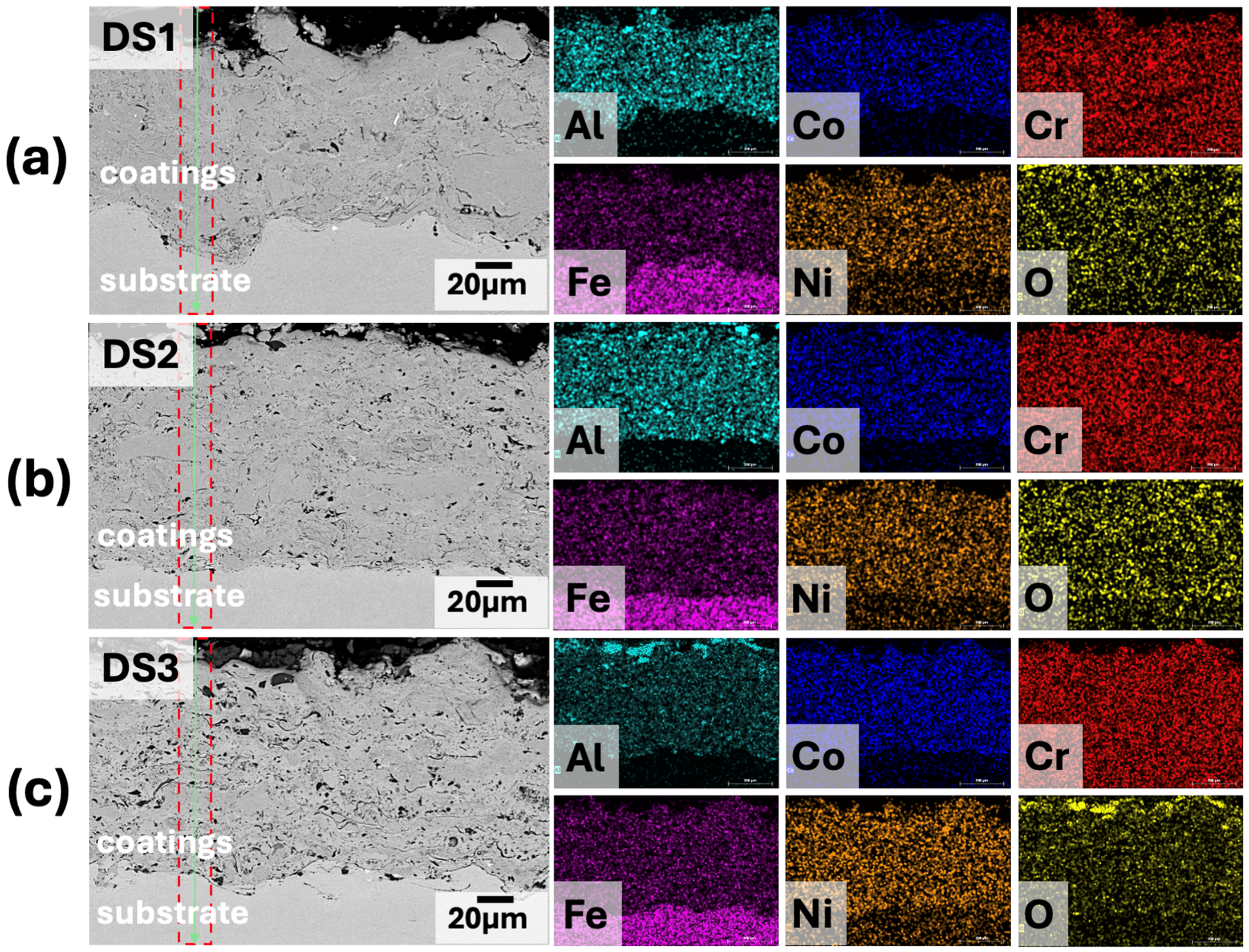
3.2. Phase and Microstructural Analysis
4. Conclusions
- -
- Phase analysis of AlCoCrFeNi HEA showed that the gas-sprayed powder consisted of BCC + B2 + FCC phases. The phase composition of the powder obtained by mechanical alloying and the coating is consistent with the calculated phase predictions obtained using Thermo-Calc modeling under non-equilibrium cooling conditions.
- -
- The microhardness of the AlCoCrFeNi coating increased from DS 1 (234–468 HV) to DS 2 (235–479 HV), reaching a maximum of 648 HV for the DS 3 coating. However, the obtained values are inferior to previously published data for AlCoCrFeNi coatings applied by the HVAF method (~845 HV) [7], which is probably due to the formation of the FCC phase, which reduces hardness.
- -
- Dry friction wear showed differences in the wear resistance of coatings depending on the spraying regime. The DS 1 coating had the lowest volumetric wear (0.0001483 mm3/N × m), while DS 2 and DS 3 had higher values—0.0002829 mm3/N × m and 0.0002497 mm3/N × m, respectively. The increase in wear volume for DS 2 and DS 3 coatings is associated with the presence of oxide inclusions and a possible decrease in the density of the lamellar structure due to more intense particle melting and thermal exposure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W. Recent progress in high entropy alloys. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mat. 2006, 31, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W. Alloy design strategies and future trends in high-entropy alloys. JOM 2013, 265, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S. Alloyed pleasures: Multimetallic cocktails. Curr. Sci. 2003, 85, 1404–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Boer, F.R.; Boom, R.; Mattens, W.C.M.; Miedema, A.R.; Niessen, A.K. Cohesion in Metals: Transition Metal Alloys; North-Holland Physics Publishing, Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; Volume 1, 758p. [Google Scholar]
- Meghwal, A.; Bosi, E.; Anupam, A.; Hall, C.; Björklund, S.; Joshi, S.; Munroe, P.; Berndt, C.C.; Ang, A.S.M. Microstructure, multi-scale mechanical and tribological performance of HVAF sprayed AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coating. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1005, 175962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.B.; Wu, Z.X.; Lu, W.; He, M.; Wang, T.; Guo, Z.; Huang, J. Microstructures and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy coatings by detonation spraying. Intermet. 2021, 132, 107138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwalani, B.; Gorsse, S.; Choudhuri, D.; Zheng, Y.; Mishra, R.S.; Banerjee, R. Tensile yield strength of a single bulk Al0. 3CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy can be tuned from 160 MPa to 1800 MPa. Scr. Mater. 2019, 162, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.M.; Lu, M.W.; Sun, J.F.; Luo, K.Y.; Lu, J.Z. Microstructure and wear resistance of CoCrFeNiMn coatings prepared by extreme-high-speed laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 470, 129821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Haghdadi, N.; Shamlaye, K.; Hodgson, P.; Barnett, M.; Fabijanic, D. The sliding wear behaviour of CoCrFeMnNi and AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys at elevated temperatures. Wear 2019, 428, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Mei, K.; Dong, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, J.; Luo, Z. An investigation on the wear and corrosion resistance of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings enhanced by Ti and Si. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 487, 130949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B.; Chaput, K.J.; Couzinie, J.P. Development and exploration of refractory high entropy alloys—A review. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3092–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.H.; Fu, R.T.; Chen, B.Y.; Zeng, S.C.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Z.; Guo, Y.C.; Liang, M.X.; Li, J.P.; Lu, Y.Q.; et al. Corrosion resistance of CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy coating prepared through plasma transfer arc claddings. Metals 2021, 11, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorr, B.; Schellert, S.; Müller, F.; Christ, H.J.; Kauffmann, A.; Heilmaier, M. Current status of research on the oxidation behavior of refractory high entropy alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2001047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Miracle, D.B.; Chuang, C.P.; Liaw, P.K. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giniyatova, S.G.; Kadyrzhanov, K.K.; Shlimas, D.I.; Borgekov, D.B.; Uglov, V.V.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Zdorovets, M.V. Effects of Structural Radiation Disorder in the Near-Surface Layer of Alloys Based on NbTiVZr Compounds Depending on the Variation of Alloy Components. Crystals 2023, 13, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Comprehensive review on high entropy alloy-based coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 477, 130327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogrebnjak, A.D.; Goncharov, A.; Yunda, A.; Shelest, I.; Swic, A.; Lebedynskyi, I. Structural features of the formation of multicomponent and high-entropy transition metal nitride films. High Temp. Mater. Process. Int. Q. High-Technol. Plasma Process. 2018, 22, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralba, J.M.; Alvaredo, P.; García-Junceda, A. Powder metallurgy and high-entropy alloys: Update on new opportunities. Powder Metall. 2020, 63, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulianitsky, V.Y.; Rybin, D.K.; Ukhina, A.V.; Bokhonov, B.B.; Dudina, D.V.; Samodurova, M.N.; Trofimov, E.A. Structure and composition of Fe-Co-Ni and Fe-Co-Ni-Cu coatings obtained by detonation spraying of powder mixtures. Mater. Lett. 2021, 290, 129498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.P.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.G.; An, Q.Z.; Nie, P.L.; Sun, B.D. Characterisation of detonation sprayed Mo–Co–Cr–B alloy coatings. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulianitsky, V.Y.; Dudina, D.V.; Batraev, I.S.; Kovalenko, A.I.; Bulina, N.V.; Bokhonov, B.B. Detonation spraying of titanium and formation of coatings with spraying atmosphere-dependent phase composition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 261, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.U.; Lan, X.D.; Yong, L.I.U.; Fei, L.I.; Zhang, W.D.; Chen, Z.J.; Zai, X.F.; Han, Z.E.N.G. Fabrication, tribological and corrosion behaviors of detonation gun sprayed Fe-based metallic glass coating. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.Q.; Rhyim, Y.M.; Jin, H.W.; Park, C.G.; Kim, M.C. Application of fractal dimension to optimum deposition of NiCrAlY coating by d-gun spray. Mater. Manuf. Process. 1999, 14, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, D.; Beran, P.; Riekehr, L.; Tseng, J.C.; Harlin, P.; Jansson, U.; Cedervall, J. Structure and phase transformations in gas atomized AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 893, 162060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.M.; Weaver, M.L. Oxidation behavior of arc melted AlCoCrFeNi multi-component high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 674, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosi, E.; Meghwal, A.; Singh, S.; Munroe, P.; Berndt, C.C.; Ang, A.S.M. Empirical and computational-based phase predictions of thermal sprayed high-entropy alloys. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2023, 32, 1840–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitkenov, D.; Nabioldina, A.; Raisov, N. Development of Method for Applying Multilayer Gradient Thermal Protective Coatings Using Detonation Spraying. Coatings 2024, 14, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo-Calc Software. Available online: https://thermocalc.com/products/databases/high-entropy-alloys/ (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Pelton, A.D. Equilibrium and Scheil-Gulliver Solidification. In Phase Diagrams and Thermodynamic Modeling of Solutions, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowski, L. The Science and Engineering of Thermal Spray Coatings, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2008; pp. 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Peng, X.; Hu, N.; Chen, M. Phase, microstructure and mechanical properties evaluation of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy during mechanical ball milling. Intermetallics 2021, 138, 107310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, M.; Prasad, A.; Parakh, A.; Murty, B.S. Influence of sequence of elemental addition on phase evolution in nanocrystalline AlCoCrFeNi: Novel approach to alloy synthesis using mechanical alloying. Mater. Des. 2017, 126, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogal, Ł.; Szklarz, Z.; Bobrowski, P.; Kalita, D.; Garzeł, G.; Tarasek, A.; Kot, M.; Szlezynger, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Co–Cr–Fe–Ni base high entropy alloys obtained using powder metallurgy. Met. Mater. Int. 2019, 25, 930–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.C.; Chen, J.H.; Stadler, S.; Chen, S.H. Properties of atomized AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy powders and their phase-adjustable coatings prepared via plasma spray process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 478, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munitz, A.; Salhov, S.; Hayun, S.; Frage, N. Heat treatment impacts the micro-structure and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 683, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Element | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | N | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | ≤0.03 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.045 | 0.03 | 16.00–18.00 | 10.00–14.00 | 2.00–3.00 | ≤0.10 | Balanced |
| Regimes | Ratio O2/C2H2 | Distance to Substrate, mm | Number of Shots | Delay Time, s | Length of Barrel, mm | Percentage of Gas Filling, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS 1 | 1.026 | 150 | 30 | 0.5 | 1000 | 54 |
| DS 2 | 64 | |||||
| DS 3 | 74 |
| Samples | Phases | Phase Content (wt.%) | Lattice Parameter (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powder | BCC and B2 FCC | 75 ± 1 25 ± 1 | 2.874 3.577 |
| DS 1 | BCC and B2 FCC | 77 ± 1 23 ± 1 | 2.867 3.598 |
| DS 2 | BCC and B2 FCC | 69 ± 1 31 ± 1 | 2.869 3.614 |
| DS 3 | BCC and B2 FCC | 52 ± 1 48 ± 1 | 2.8661 3.6231 |
| Elements (at%) | Al | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS 1 | map | 15.88 ± 0.84 | 11.24 ± 0.42 | 16.77 ± 0.55 | 29.99 ± 1.02 | 12.14 ± 0.48 | 13.98 ± 0.62 |
| line | 15.00 ± 1.26 | 14.63 ± 1.27 | 16.31 ± 1.17 | 27.69 ± 2.18 | 13.60 ± 1.30 | 12.77 ± 1.30 | |
| DS 2 | map | 15.98 ± 0.80 | 12.63 ± 0.46 | 17.42 ± 0.56 | 26.80 ± 0.89 | 12.90 ± 0.49 | 14.27 ± 0.63 |
| line | 12.98 ± 0.95 | 13.52 ± 0.99 | 17.36 ± 1.05 | 30.46 ± 2.00 | 13.82 ± 1.10 | 11.88 ± 1.14 | |
| DS 3 | map | 16.65 ± 0.81 | 10.85 ± 0.40 | 15.04 ± 0.49 | 23.58 ± 0.80 | 10.83 ± 0.42 | 23.06 ± 0.68 |
| line | 11.49 ± 1.04 | 10.85 ± 1.14 | 18.21 ± 1.50 | 30.17 ± 2.75 | 13.35 ± 1.49 | 15.93 ± 1.63 | |
| Samples | Average Porosity, % | Hardness, HV | Volume Wear Rate, ×10−4 mm3 × N−1 × m−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DS 1 | 10.9 ± 0.1 | 468 ± 12 | 1.483 |
| DS 2 | 12.4 ± 0.1 | 479 ± 9 | 2.829 |
| DS 3 | 11.3 ± 0.1 | 648 ± 14 | 2.497 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sagdoldina, Z.; Sulyubayeva, L.; Buitkenov, D.; Kambarov, Y. Microstructure, Hardness and Tribological Characteristics of High-Entropy Coating Obtained by Detonation Spraying. Crystals 2025, 15, 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070625
Sagdoldina Z, Sulyubayeva L, Buitkenov D, Kambarov Y. Microstructure, Hardness and Tribological Characteristics of High-Entropy Coating Obtained by Detonation Spraying. Crystals. 2025; 15(7):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070625
Chicago/Turabian StyleSagdoldina, Zhuldyz, Laila Sulyubayeva, Dastan Buitkenov, and Yedilzhan Kambarov. 2025. "Microstructure, Hardness and Tribological Characteristics of High-Entropy Coating Obtained by Detonation Spraying" Crystals 15, no. 7: 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070625
APA StyleSagdoldina, Z., Sulyubayeva, L., Buitkenov, D., & Kambarov, Y. (2025). Microstructure, Hardness and Tribological Characteristics of High-Entropy Coating Obtained by Detonation Spraying. Crystals, 15(7), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070625





