Magnetic Behavior of Co2+-Doped NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles with Single-Phase Spinel Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
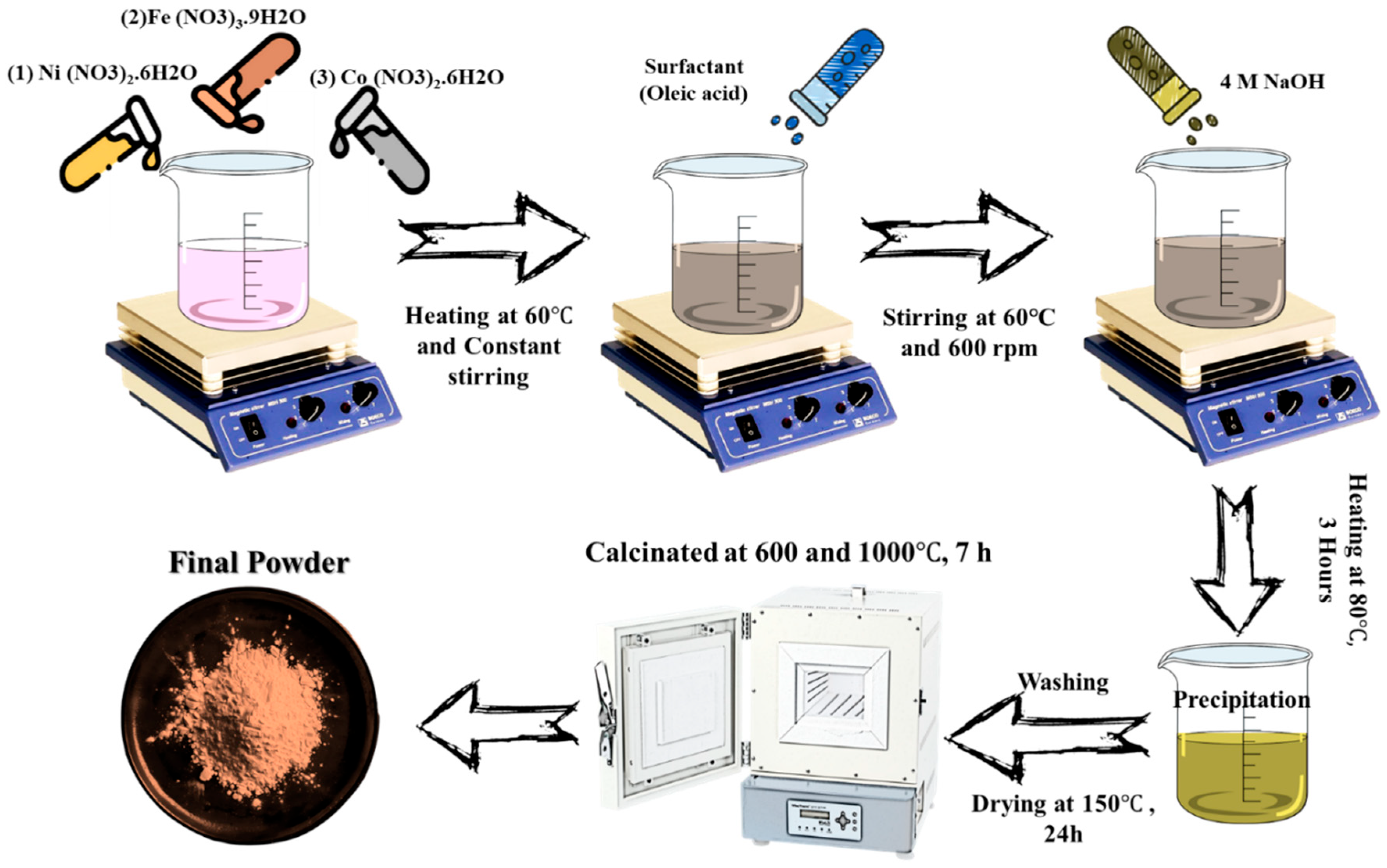
2.2. Synthesis of Co2+-Doped NiFe2O4 Nanocomposite
2.3. Characterization of Co2+-Doped NiFe2O4 Nanocomposites
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermogravimetric (TG) and Differential Thermal (DTA) Analysis
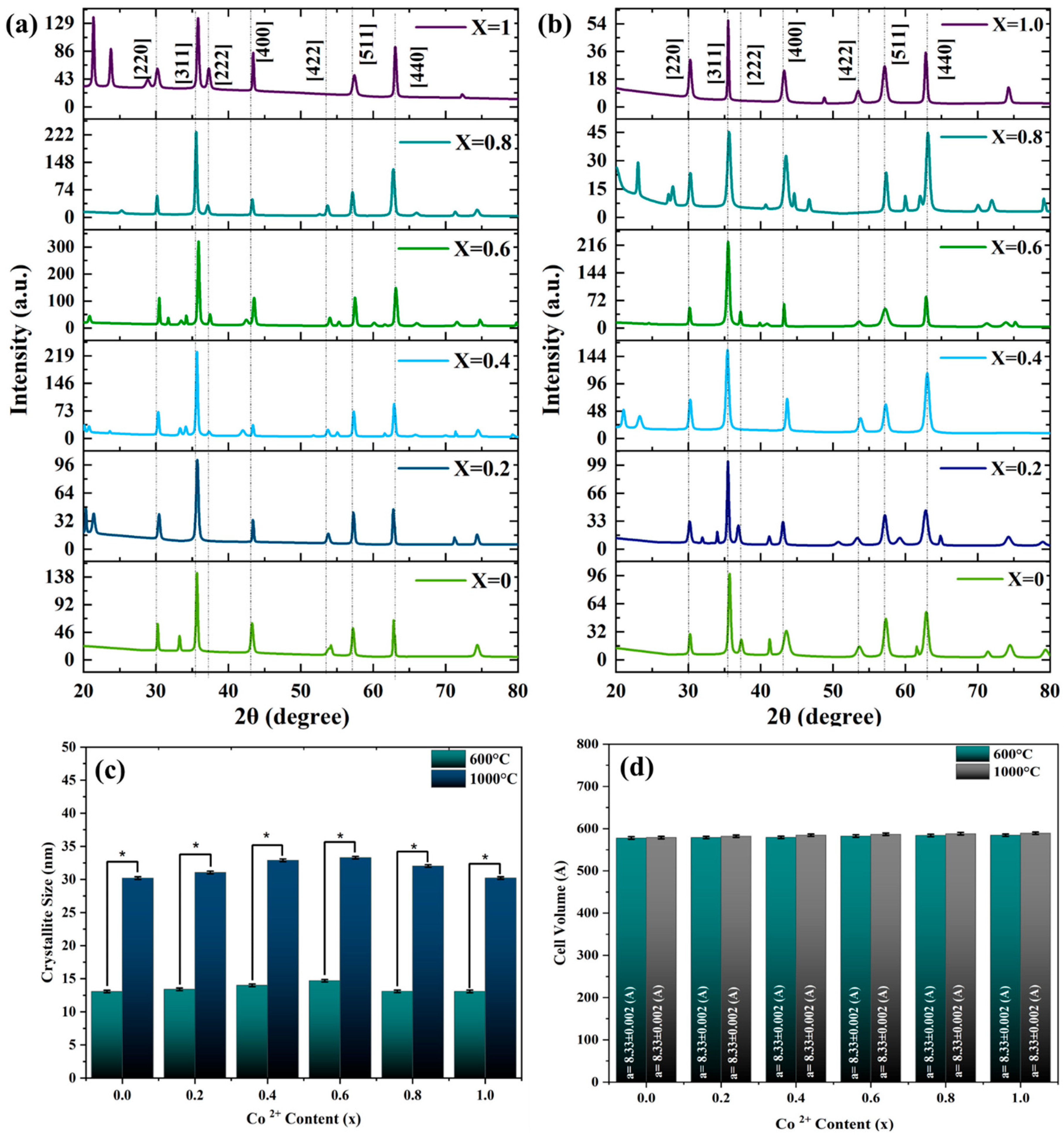
3.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Analysis
3.4. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) Analysis
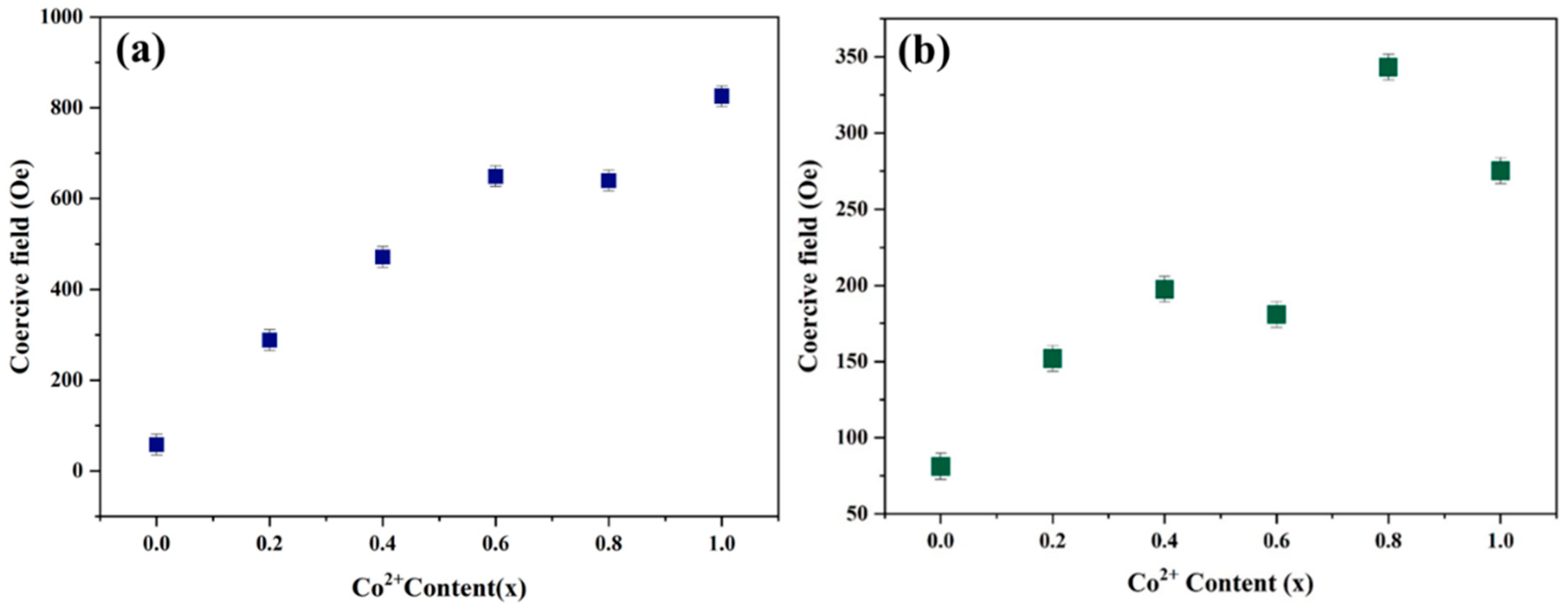
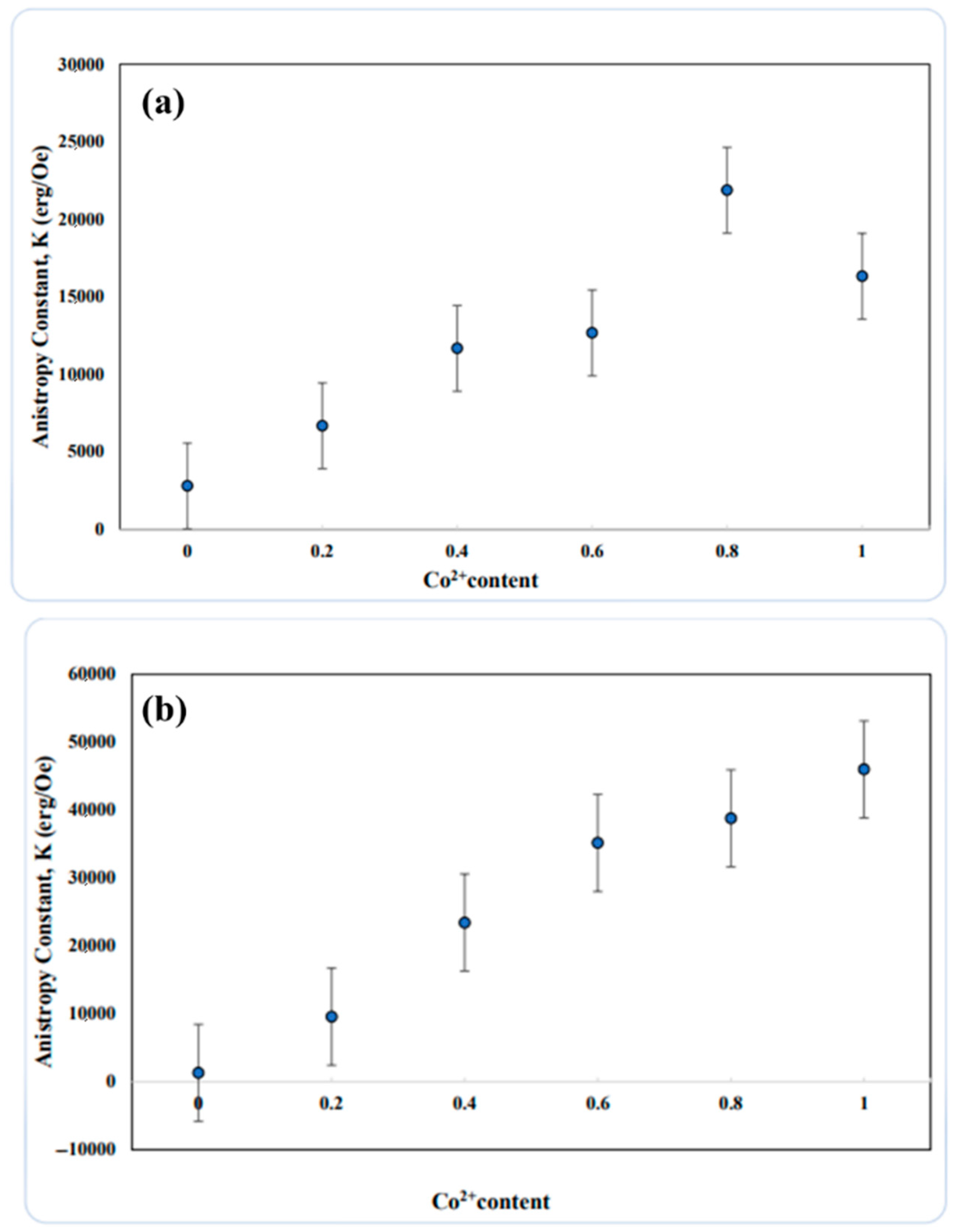
3.5. Vibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM) Analysis
4. Conclusions
- Thermal analysis (TGA) revealed that no significant weight loss occurred beyond 600 °C, indicating the formation of a stable nickel–cobalt spinel phase.
- The X-ray diffraction (XRD) profiles confirmed the spinel structure of the powders obtained. Higher synthesis temperatures resulted in sharper, more symmetric peaks that reflected better crystallinity. Moreover, the broadening of peaks decreased with an increase in temperature, consistent with increased particle sizes and an improved crystal structure. In addition, increasing cobalt concentration also increased the grain size, unit cell volume, and lattice constant.
- SEM images showed that the particle sizes ranged between 13–19 nm at 600 °C and 28–36 nm at 1000 °C, demonstrating good agreement with the XRD results.
- The purity of the material was verified using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), as no organic compounds were detected, while the presence of cations etched in octahedral and tetrahedral sites was verified. Furthermore, it can be seen from the FTIR results that the v1 band shifted to lower wave numbers with an increase in temperature and Co substitution. Shifts to lower wave numbers are explained by the inverse relationship between atomic mass and wave number in FTIR spectra.
- Vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM) analysis demonstrated that coercivity increased almost linearly with higher cobalt concentrations at both synthesis temperatures. The inherently higher anisotropic nature of cobalt ions compared to nickel ions resulted in an increase in coercivity with cobalt doping. This increase in coercivity can be attributed to the enhancement of the anisotropic field, which subsequently raises domain wall energy.
- Saturation and remanent magnetization were shown to have random tendencies. This might be attributed to the presence of the low remanent magnetization of soft nickel ferrites. The observed random increasing trend in saturation magnetization and remanent magnetization may be due to the replacement of cobalt cations for iron cations in tetrahedral sites, which reduced MA and ultimately led to a greater overall magnetic moment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, P.; Wu, Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, R.; Zeng, Z.; Li, L.; Su, C.; Wang, S. Enhanced iodine capture by nano-copper particles modified benzimidazole-based molded porous carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 708, 163754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Liao, L.; Liang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, W.; Chen, M.; Fang, B.; Wu, D.; Jin, H.; et al. Fast Removing Ligands from Platinum-Based Nanocatalysts by a Square-Wave Potential Strategy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, e202509746. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhao, S.; Hartmann, D.M.F.; Yang, W.; Lin, X.; Zhao, W.; Lavrijsen, R. Modulation of the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction in Pt/Co/Pt with electric field induced strain. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2025, 126, 162401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Levei, E.A.; Cadar, O.; Mesaros, A.; Borodi, G. Sol-gel synthesis of CoFe2O4:SiO2 nanocomposites—Insights into the thermal decomposition process of precursors. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 125, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Z.; Qi, M. Development of multifunctional cobalt ferrite/graphene oxide nanocomposites for magnetic resonance imaging and controlled drug delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 289, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.N.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Nazir, M.S.; Imran, M.; Ali, A.; Sattar, A.; Murtaza, G. Evaluation of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of CuZnNi (Cu Zn0.5−Ni0.5Fe2O4) nanocrystalline ferrites for core, switching and MLCI’s applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 421, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawale, A.B.; Kanhe, N.S.; Raut, S.A.; Bhoraskar, S.V.; Das, A.K.; Mathe, V.L. Investigation of structural, optical and magnetic properties of thermal plasma synthesized Ni-Co spinel ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 6637–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Huang, Y.; Qing, Y.; Misra, R.D.K. Effects of Y and Hf addition on soft magnetic property and ductility improvement of Fe–6.9 wt% Si alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 37, 1362–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Ge, X.; Li, S.; Tian, Z.; Cui, S.; Guo, G.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, S.; et al. Facile preparation of a 3D rGO/g-C3N4 nanocomposite loaded with Ag NPs for photocatalytic degradation. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 17089–17101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, I.H.; Amin, F.; Abbasi, A.Z.; Anis-ur-Rehman, M.; Maqsood, A. Physical and magnetic characterization of co-precipitated nanosize Co–Ni ferrites. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, K.; Moskowitz, B.; Casciari, R. Advances in ferrofluid technology. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1995, 149, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeela, N.; Maaz, K.; Khan, U.; Karim, S.; Nisar, A.; Ahmad, M.; Ali, G.; Han, X.F.; Duan, J.L.; Liu, J. Influence of manganese substitution on structural and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 639, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshisundaram, A.; Gunasekaran, N.; Srinivasan, V. Distribution of Metal Ions in Transition Metal Manganites AMn2O4 (A: Co, Ni, Cu, or Zn); De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Mozaffari, M.; Amighian, J.; Darsheshdar, E. Magnetic and structural studies of nickel-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles, synthesized by the sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 350, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambale, R.C.; Shaikh, P.A.; Kamble, S.S.; Kolekar, Y.D. Effect of cobalt substitution on structural, magnetic and electric properties of nickel ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 478, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkian, S.; Ghasemi, A.; Razavi, R.S. Cation distribution and magnetic analysis of wideband microwave absorptive CoxNi1−xFe2O4 ferrites. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 6987–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.I.; Astudillo, S.; Hernandez, J.H.M.; Saavedra, M.; Zapata, P.A.; Valencia-Llano, C.H.; Chaur, M.N.; Grande-Tovar, C.D. Synthesis, Characterization, and Optimization Studies of Polycaprolactone/Polylactic Acid/Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle/Orange Essential Oil Membranes for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2022, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ati, A.A.; Othaman, Z.; Samavati, A. Influence of cobalt on structural and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1052, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, S.; Selvan, R.K.; Berchmans, L.J.; Angappan, S.; Subramanian, K.; Augustin, C.O. Combustion synthesis and characterization of Sn4+ substituted nanocrystalline NiFe2O4. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2005, 119, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinosha, P.A.; Manikandan, A.; Ragu, R.; Dinesh, A.; Thanrasu, K.; Slimani, Y.; Baykal, A.; Xavier, B. Impact of nickel substitution on structure, magneto-optical, electrical and acoustical properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 857, 157517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.F.; Naresh, U.; Ramprasad, T.; Kumar, R.J. Structural, Morphological, and Magnetic Properties of Cobalt-Doped Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2021, 34, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandekar, K.V.; Yadav, S.P.; Chinke, S.; Shkir, M. Impact of Co-doped NiFe2O4 (CoxNi1−xFe2O4) nanostructures prepared by co-precipitation route on the structural, morphological, surface, and magnetic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 966, 171556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.S.; Raguram, T.; Rajni, K.S. Synthesis and Characterization of Nickel-Substituted Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles Using Sol–Gel Auto-combustion Method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2019, 32, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumalatha, M.; Reddy, S.S.K.; Reddy, M.S.; Sripada, S.; Reddy, P.V.; Ch, G.R.; Reddy, P.Y.; Reddy, V.R. Effect of indium substitution on structural and hyperfine parameters of CoFe2O4. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2220, 110038. [Google Scholar]
- Debnath, S.; Das, A.; Das, R. Effect of cobalt doping on structural parameters, cation distribution and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite nanocrystals. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 16467–16482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, M.N.; Butt, M.S.; Gul, I.H.; Saleem, M.; Irfan, M.; Baluch, A.H.; Akram, M.A.; Raza, M.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Cobalt-Doped Ferrites for Biomedical Applications. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 3755–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, V.; Feldbach, E.; Kärner, T.; Maaroos, A.; Mironova-Ulmane, N.; Popov, A.I.; Shablonin, E.; Vasil’chenko, E.; Lushchik, A. Fast-neutron-induced and as-grown structural defects in magnesium aluminate spinel crystals with different stoichiometry. Opt. Mater. 2019, 91, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarchuk, T. Studying the Defects in Spinel Compounds: Discovery, Formation Mechanisms, Classification, and Influence on Catalytic Properties. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, K.; Aadil, M.; Hassan, W.; Choudhry, Q.; Gul, S.; Rais, A.; Fattah, A.A.; Mahmoud, K.H.; Ansari, M.Z.; Mohd, Z. Cobalt and holmium co-doped nickel ferrite nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic application studies. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 2023, 237, 1325–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, E.R.; Srinivas, C.; Deepty, M.; Pradeep, I.; Mehar, M.V.K.; Prajapat, C.L.; Rao, T.V.C.; Mohan, N.K.; Sastry, D.L. Synergistic effect of heat treatment on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 20968–20977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, K.; Zabihi, R. Preparation and magnetic properties of nano size nickel ferrite particles using hydrothermal method. Chem. Cent. J. 2012, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, F.; Dildar, S.; Ata, S.; Bibi, I.; Mohsin, I.U.; Ali, A.; Almoneef, M.M.; Iqbal, M.; Irshad, S.; Nazir, A.; et al. Cobalt doping of nickel ferrites via sol gel approach: Effect of doping on the structural and dielectric properties. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 2021, 235, 1811–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milutinović, A.; Lazarević, Z.Ž.; Šuljagić, M.; Andjelković, L. Synthesis-Dependent Structural and Magnetic Properties of Monodomain Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles. Metals 2024, 14, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sertkol, M.; Köseoǧlu, Y.; Baykal, A.; Kavas, H.; Toprak, M.S. Synthesis and magnetic characterization of Zn0.7Ni0.3Fe2O4 nanoparticles via microwave-assisted combustion route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, T.; Fan, L.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, H. Static magnetic, complex dielectric and complex permeability properties of aluminum substituted hexagonal barium ferrites based on doping concentration. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2021, 129, 21037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šuljagić, M.; Vulić, P.; Jeremić, D.; Pavlović, V.; Filipović, S.; Kilanski, L.; Lewinska, S.; Slawska-Waniewska, A.; Milenković, M.R.; Nikolić, A.S.; et al. The influence of the starch coating on the magnetic properties of nanosized cobalt ferrites obtained by different synthetic methods. Mater. Res. Bull. 2021, 134, 111117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, I.; Hossain, M.D.; Sikder, M.S.; Khan, M.N.I.; Rahman, M.R. Enhancement of coercivity, permeability, and dielectric properties of Co0.2Zn0.3Ni0.5Eu Fe2–O4 ferrites for memory and high frequency devices. J. Rare Earths 2024, 42, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, A.R.; Arrasyid, E.N.; Dedi, D.; Nugroho, A.A. The Distorted Octahedral and Magnetocrystalline Anisotropy of FeMnO3 by Stoner-Wohlfarth Model. Mater. Sci. Forum 2023, 1080, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerina, M.; Angotzi, M.S.; Mameli, V.; Gajdošová, V.; Rainer, D.N.; Dopita, M.; Steinke, N.-J.; Aurélio, D.; Vejpravová, J.; Zákutná, D. Size dependence of the surface spin disorder and surface anisotropy constant in ferrite nanoparticles. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 4563–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, G.; Fu, Q.; Zhou, D. Particles size effects of single domain CoFe2O4 on suspensions stability. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, K.; Kim, G.H. Single domain limit for NixCo1−xFe2O4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) nanoparticles synthesized by coprecipitation route. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, W.; Zeeshan, T.; Waseem, S.; Ali, M.D.; Kayani, Z.; Aftab, Z.-E.-H.; Mehtab, S.M.T.; Ezzine, S. Impact of silver substitution on the structural, magnetic, optical, and antibacterial properties of cobalt ferrite. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, F.; Shahin, A.; Ata, S.; Bibi, I.; Malik, A.; Ali, A.; Laref, A.; Iqbal, M.; Nazir, A. The effect of temperature on the structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrites synthesized via hydrothermal method. Z. Fur Phys. Chem. 2021, 235, 1279–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brik, M.G.; Ma, C.G.; Yamamoto, T.; Piasecki, M.; Popov, A.I. First-Principles Methods as a Powerful Tool for Fundamental and Applied Research in the Field of Optical Materials. In Phosphor Handbook: Experimental Methods for Phosphor Evaluation and Characterization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; Chong, K.; Su, Y.; Du, L.; Zhang, G. Connecting the macroscopic and mesoscopic properties of sintered silver nanoparticles by crystal plasticity finite element method. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2023, 281, 109137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, B.; He, Q.; Cao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Su, K.; Yan, H.; Sun, P.; Li, R.; et al. Ultra-Bandwidth Microwave Absorption and Low Angle Sensitivity in Dual-Network Aerogels with Dual-Scale Pores. Small 2025, 2412744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| No. | Molar Ratio of Co:Ni:Fe | Nominal Composition |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0:1.0:2.0 | NiFe2O4 |
| 2 | 0.2:0.8:2.0 | Co0.2Ni0.8Fe2O4 |
| 3 | 0.4:0.6:2.0 | Co0.4Ni0.6Fe2O4 |
| 4 | 0.6:0.4:2.0 | Co0.6Ni0.4Fe2O4 |
| 5 | 0.8:0.2:2.0 | Co0.8Ni0.2Fe2O4 |
| 6 | 1.0:0.0:2.0 | CoFe2O4 |
| Sample | (emu/g) | (emu/g) | (Oe) | Mr/MS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiFe2O4 | 33.65 | 6.30 | 81.2 | 0.18 |
| Co0.2Ni0.8Fe2O4 | 43.0 | 10.49 | 152.0 | 0.24 |
| Co0.4Ni0.6Fe2O4 | 57.88 | 13.44 | 197.55 | 0.23 |
| Co0.6Ni0.4Fe2O4 | 68.60 | 11.90 | 180.91 | 0.17 |
| Co0.8Ni0.2Fe2O4 | 62.43 | 16.04 | 343.22 | 0.25 |
| CoFe2O4 | 61.17 | 15.70 | 275.182 | 0.25 |
| Sample | (emu/g) | (emu/g) | (Oe) | Mr/MS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiFe2O4 | 22.37 | 1.62 | 58.12 | 0.07 |
| Co0.2Ni0.8Fe2O4 | 32.58 | 7.71 | 288.46 | 0.23 |
| Co0.4Ni0.6Fe2O4 | 48.77 | 19.28 | 471.40 | 0.39 |
| Co0.6Ni0.4Fe2O4 | 53.11 | 20.15 | 649.27 | 0.37 |
| Co0.8Ni0.2Fe2O4 | 59.49 | 21.06 | 639.27 | 0.35 |
| CoFe2O4 | 52.88 | 19.97 | 852.70 | 0.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vahedrouz, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Bahrami, A.; Heidari Laybidi, F. Magnetic Behavior of Co2+-Doped NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles with Single-Phase Spinel Structure. Crystals 2025, 15, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070624
Vahedrouz F, Alizadeh M, Bahrami A, Heidari Laybidi F. Magnetic Behavior of Co2+-Doped NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles with Single-Phase Spinel Structure. Crystals. 2025; 15(7):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070624
Chicago/Turabian StyleVahedrouz, Fatemeh, Mehdi Alizadeh, Abbas Bahrami, and Farnaz Heidari Laybidi. 2025. "Magnetic Behavior of Co2+-Doped NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles with Single-Phase Spinel Structure" Crystals 15, no. 7: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070624
APA StyleVahedrouz, F., Alizadeh, M., Bahrami, A., & Heidari Laybidi, F. (2025). Magnetic Behavior of Co2+-Doped NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles with Single-Phase Spinel Structure. Crystals, 15(7), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070624








