The Influence of the Addition of Ca, Zn, and Zr on the Corrosion Properties of As-Homogenized Mg-3Sn Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Microstructure Analysis
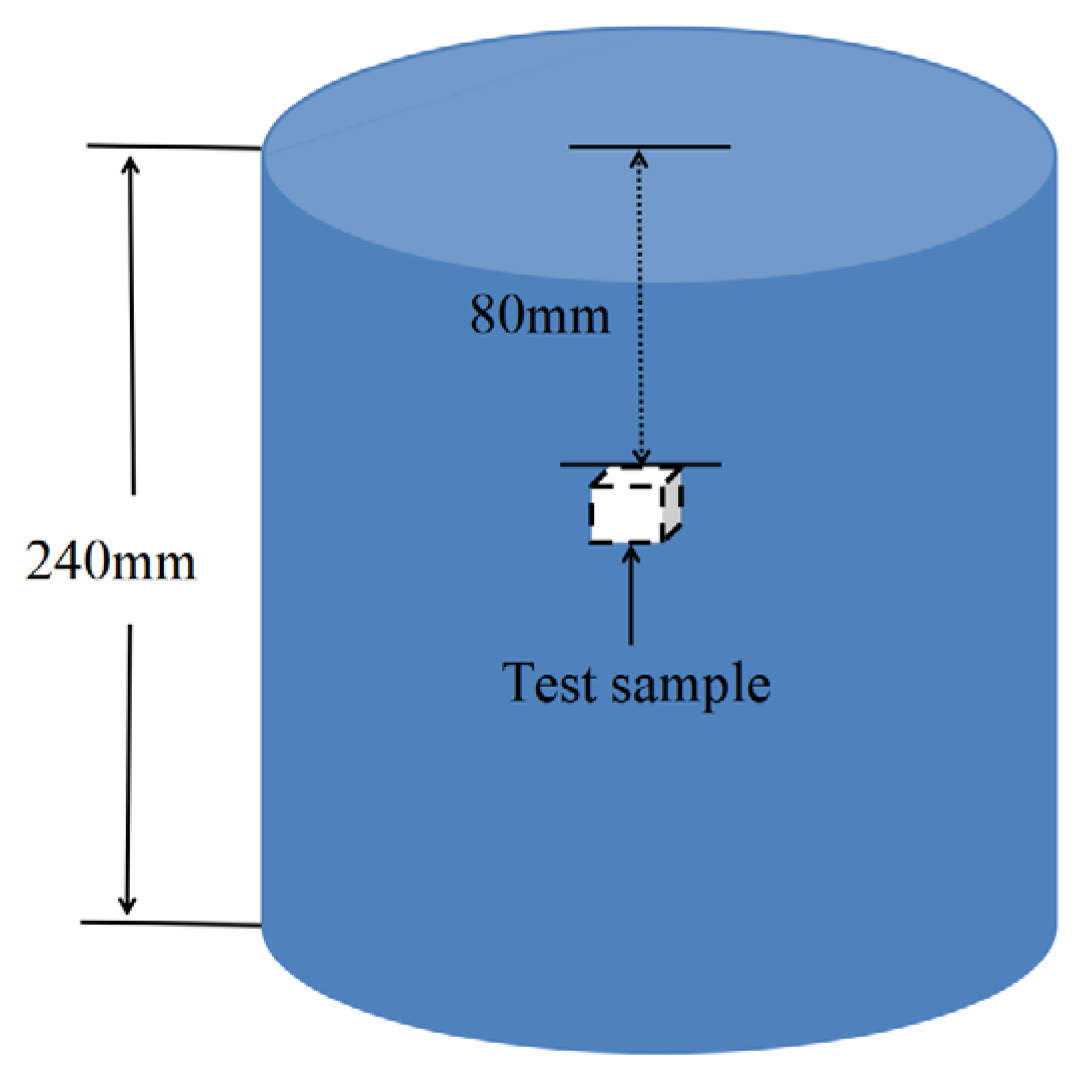
2.3. Corrosion Performance Test
3. Results
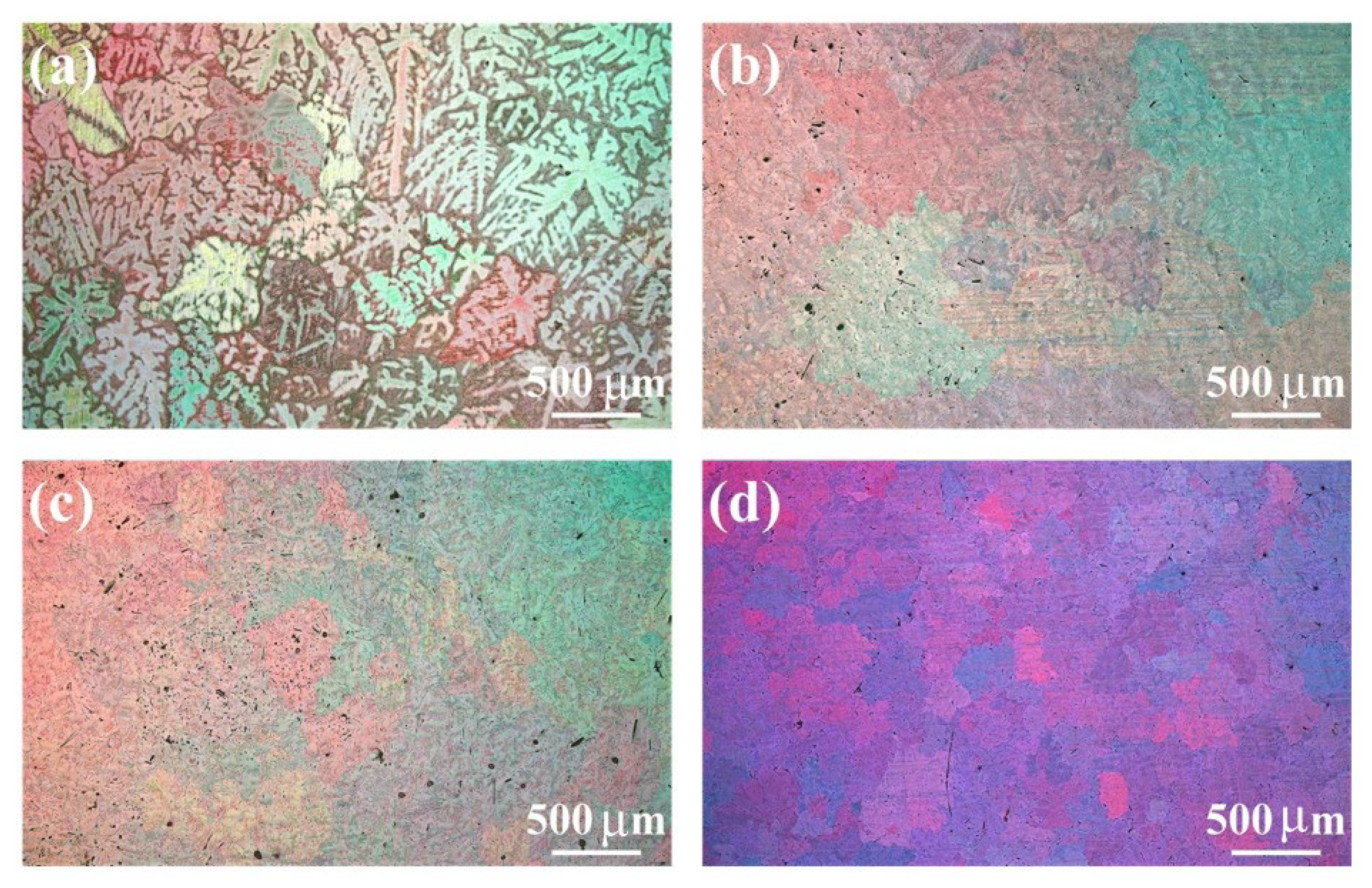
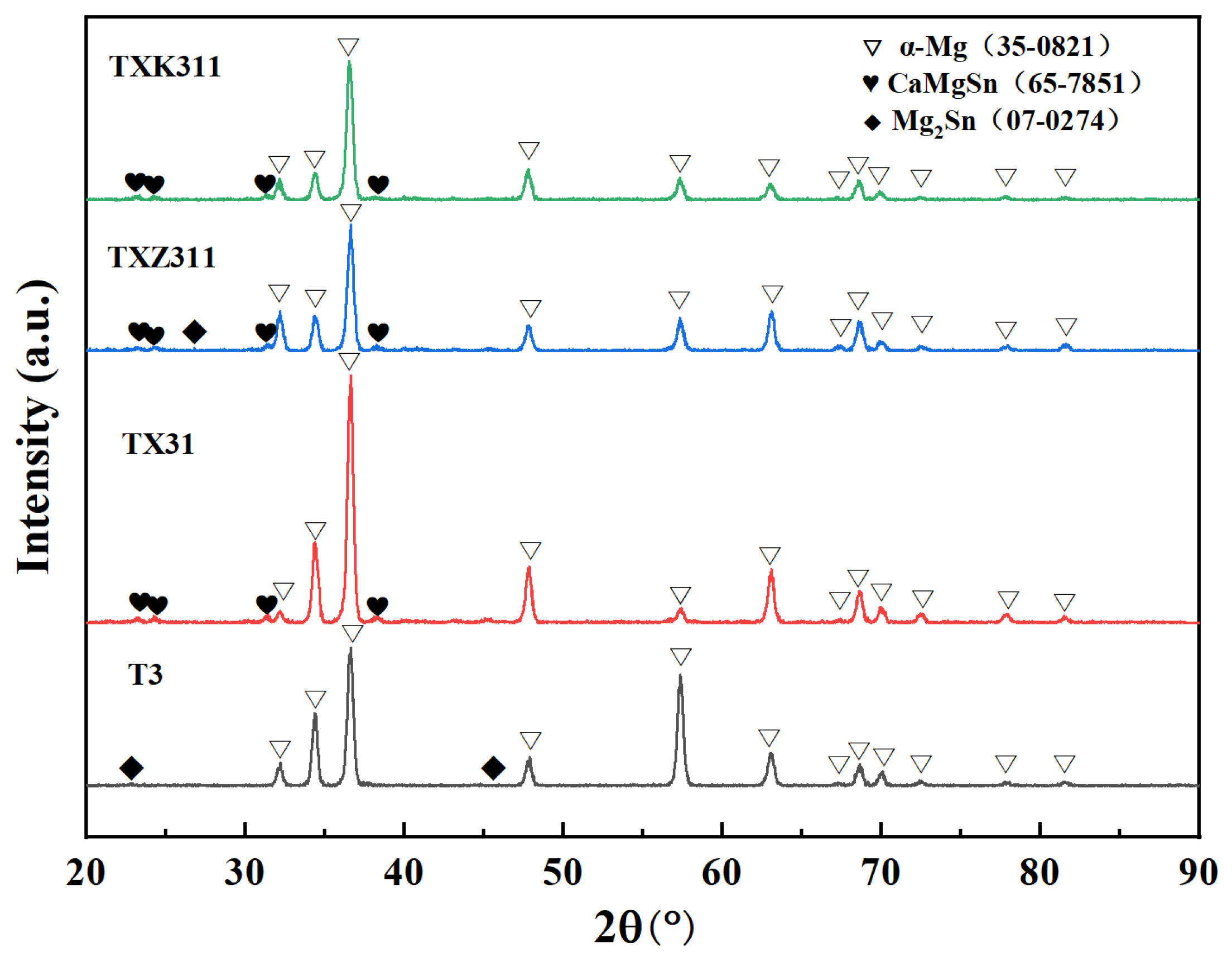
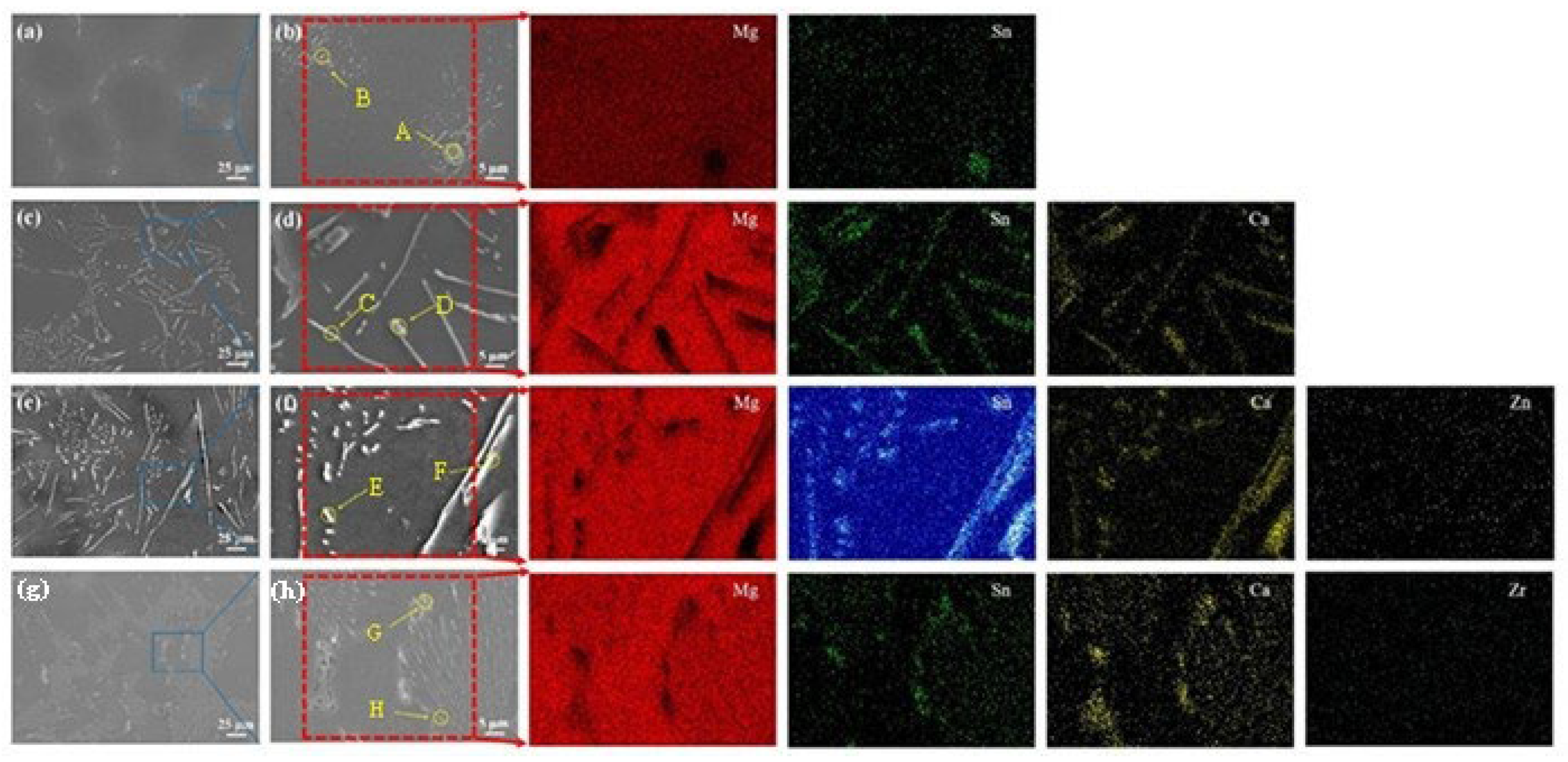
3.1. Microstructure Characterization
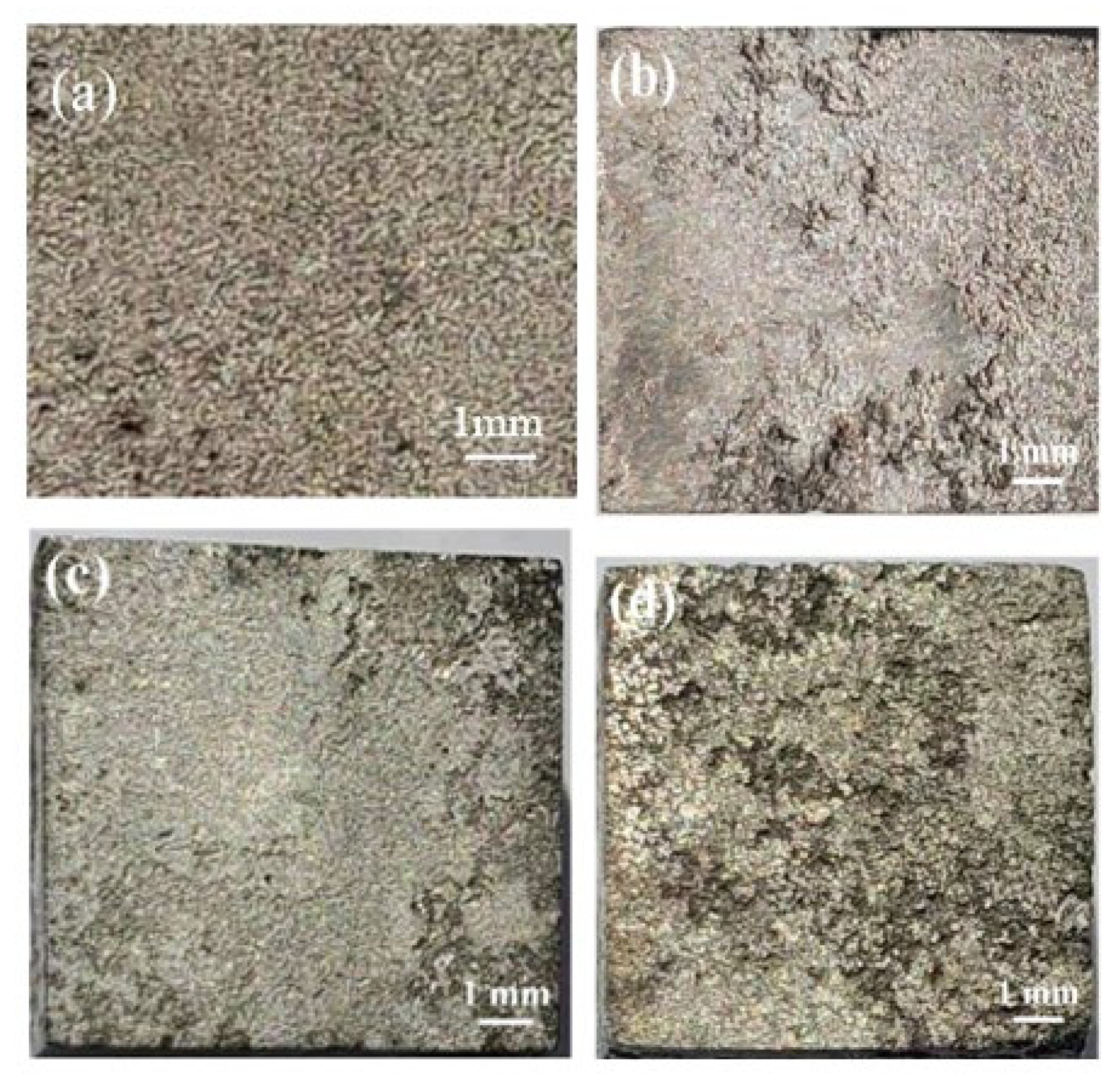
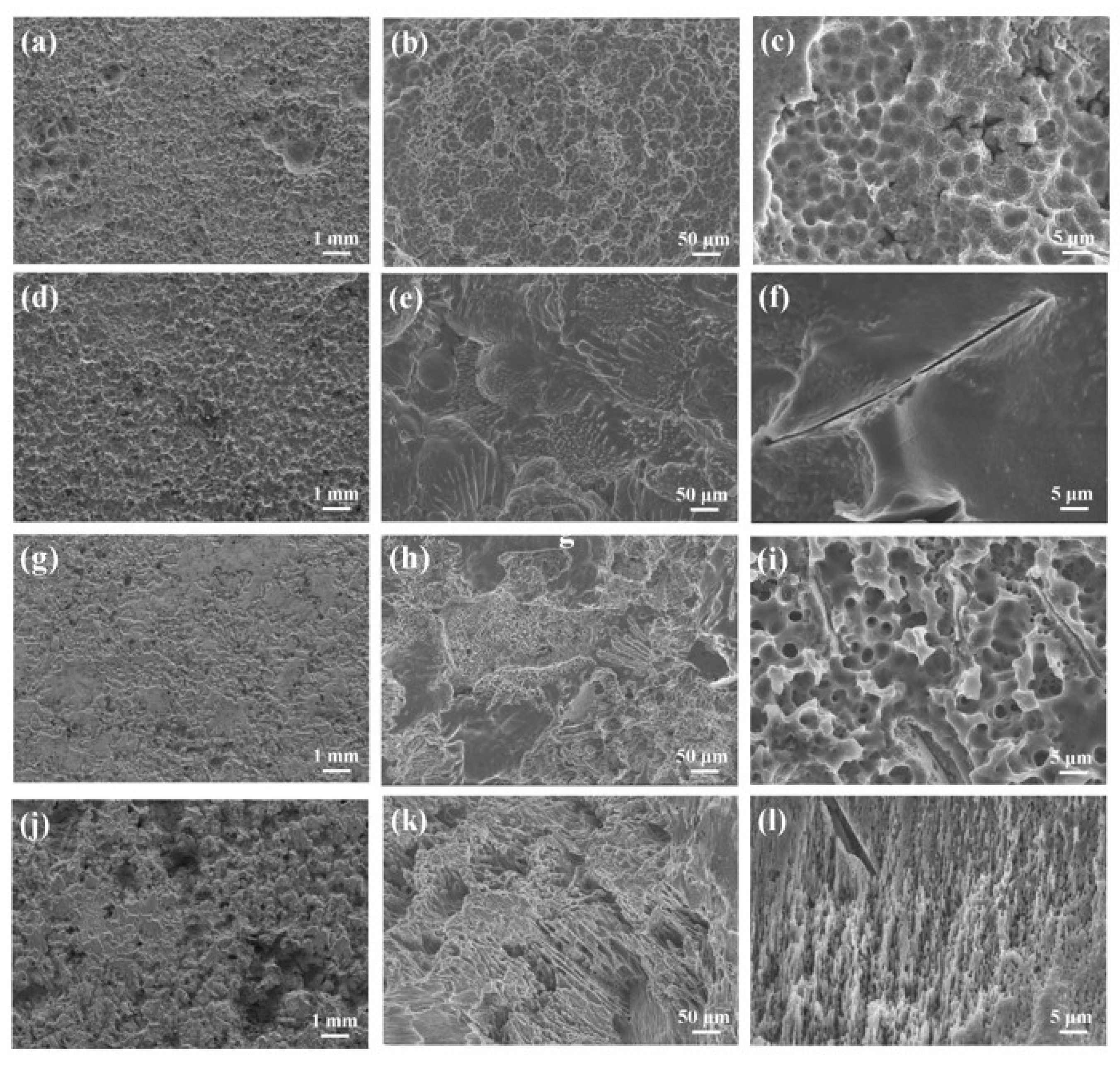
3.2. Immersion Test
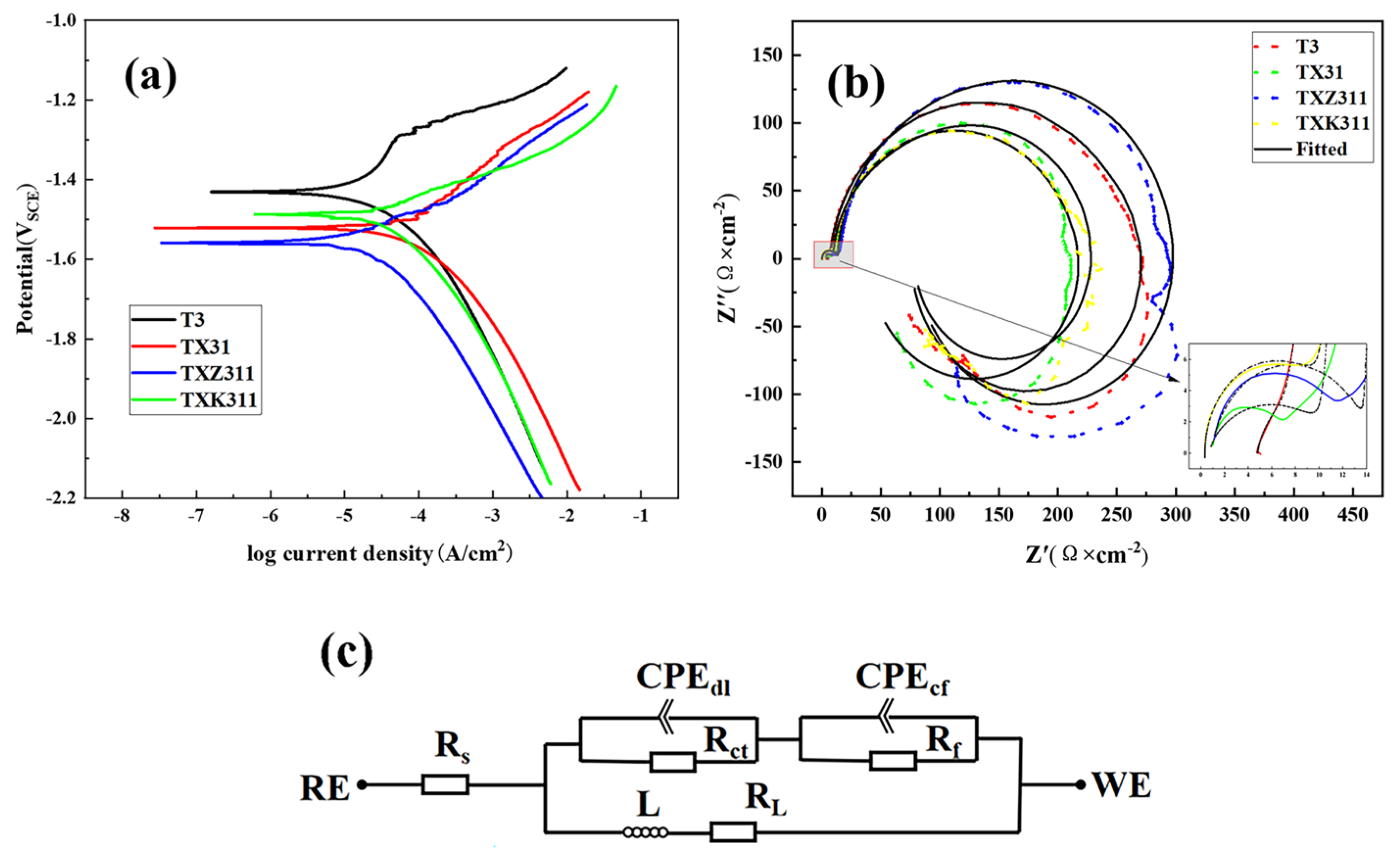
3.3. Electrochemical Behavior
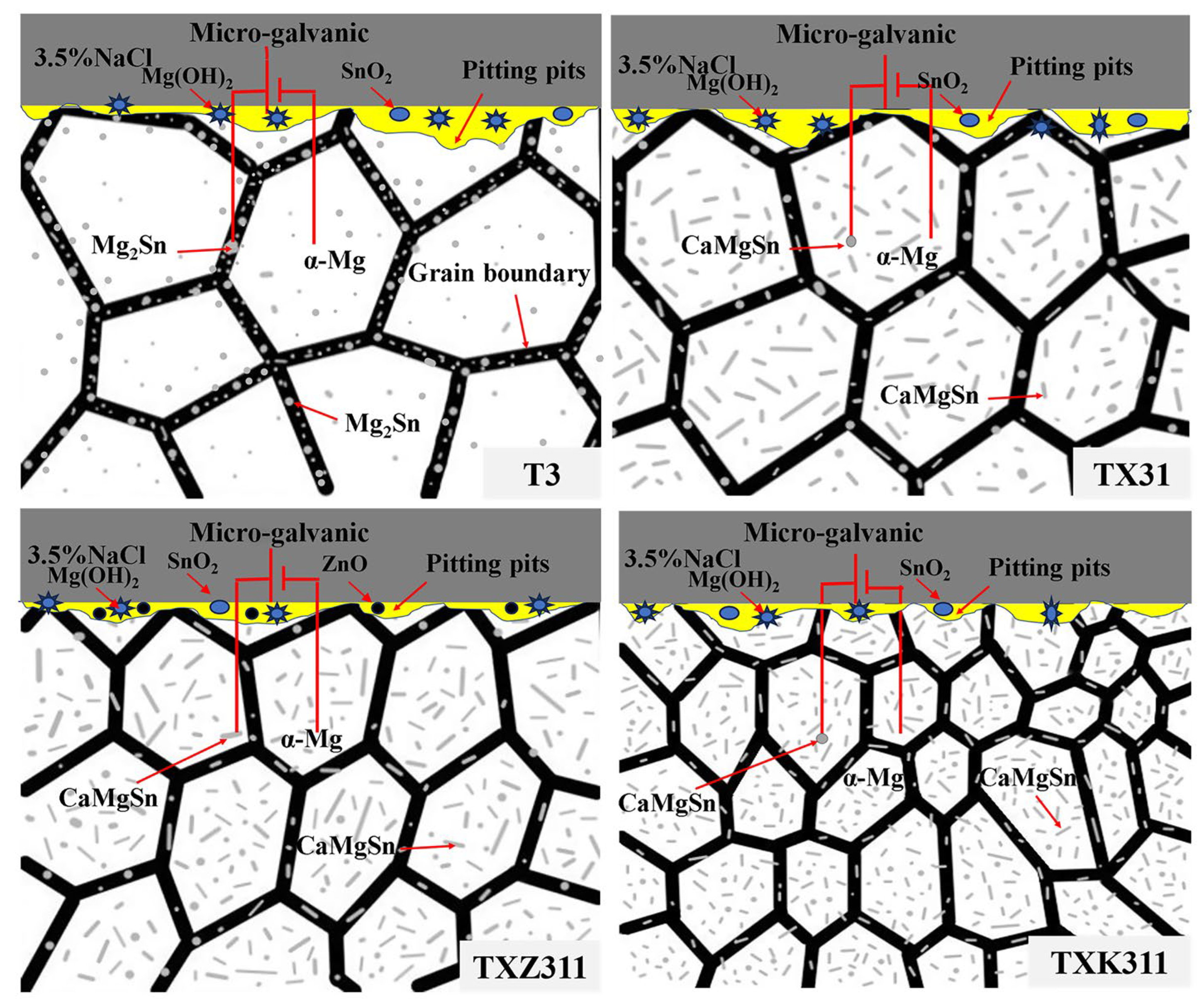
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- In the as-homogenized Mg-3Sn alloy, the addition of Ca inhibits the precipitation of Mg2Sn and the formation of the intermetallic compound CaMgSn. The Zn and Zr elements can refine the grain size and the average size of the CaMgSn phase in TXZ311 alloys and increase the area fraction of the second phase.
- The corrosion of the T3 alloy is mainly electrochemical galvanic corrosion. The addition of Ca changes the type of the second phase (from Mg2Sn to CaMgSn) but does not alter the fundamental corrosion mechanism. The Zn and Zr elements change the corrosion rate of the Mg alloys by altering the polarization resistance of the alloys, while the corrosion mechanism does not change.
- The hydrogen evolution test, electrochemical test, and corrosion morphology show that the as-homogenized TXZ311 alloy has the best corrosion resistance. The addition of the Zn element can refine the alloy, improve the corrosion resistance of the alloy, and form a dense passivation film on the surface during the corrosion process of the alloy, reducing the corrosion rate.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, J.; She, J.; Chen, D.; Pan, F. Latest research advances on magnesium and magnesium alloys worldwide. J. Magnes. Alloys 2020, 8, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, G.S. Summary of “Magnesium vision 2020: A North American automotive strategic vision for magnesium”. In Essential Readings in Magnesium Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, V.V.; Ramasamy, P.; Kovukkal, M.D.; Myilsamy, G. Research and development in magnesium alloys for industrial and biomedical applications: A review. Met. Mater. Int. 2020, 26, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubásek, J.; Minárik, P.; Hosová, K.; Šašek, S.; Knapek, M.; Veselý, J.; Stráská, J.; Dvorský, D.; Čavojský, M.; Vojtěch, D. Novel magnesium alloy containing Y, Gd and Ca with enhanced ignition temperature and mechanical properties for aviation applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 877, 160089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoubrou, I.; Nami, B.; Miresmaeili, S.M.; Yazdani, M. Evolution of Microstructure, Texture and Mechanical Properties of ECAP-Processed ZK60 Magnesium Alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 2024, 31, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, X.; Shao, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhichao, H.; Huan, L. Effect of Hot Rolling on the Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of a Mg-5Sn Alloy. Materials 2022, 15, 5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Yu, B.; Fu, L. Effect of Zn and Cu Addition on Mechanical Properties of As-Extruded Mg-3Sn-1Ca Alloy. Materials 2022, 15, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Shi, O.L.; Jiang, B.; Quan, G.F.; Pan, S. Improved formability with theoretical critical shear strength transforming in Mg alloys with Sn addition. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 764, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, H.; Turen, Y.; Ahlatci, H.; Yavuz, S.; Abdullah, C. Influence of Sn addition on microstructure and corrosion resistance of AS21 magnesium alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Dietzel, W.; Kainer, K.U.; Blawert, C.; Wei, K. Review of studies on corrosion of magnesium alloys. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2006, 16, s763–s771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.Y.; Kang, J.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, B.; Park, S.S.; Yim, C.D.; You, B.S. Influences of metallurgical factors on the corrosion behaviour of extruded binary Mg-Sn alloys. Corros. Sci. 2014, 82, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shan, D.; Song, Y.; Chen, R.; Han, E. Influences of the quantity of Mg2Sn phase on the corrosion behavior of Mg-7Sn magnesium alloy. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 2582–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Cui, L.; Ke, W. Biomedical magnesium alloys: Composition, microstructure and corrosion. Acta Met. Sin. 2018, 54, 1215–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Kamde, M.A.; Mahton, Y.; Singh, Y.; Sahoo, S.K.; Ganguly, S.; Prakash, N.S.; Roy, M.; Mishra, V.; Sarkar, S.; Saha, P. Correlation of Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of squeeze-cast Mg-4.0-4.0Zn-0.5Zr-0.2Ca (wt%) Alloys Constituting W and LPSO Secondary Phases. Met. Mater. Int. 2024, 30, 3379–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, A.; Ohno, M.; Leil, T.A. Phase equilibria, thermodynamics and solidification microstructures of Mg-Sn-Ca alloys, Part 2: Prediction of phase formation in Mg-rich Mg-Sn-Ca cast alloys. Intermetallics 2008, 16, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Rao, K.P.; Prasad, Y.; Hort, N.; Kainer, K.U. Microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast Mg-Sn-Ca alloys and effect of alloying elements. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 3604–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, S.; Chen, Y. Effects of Sn, Ca additions on thermal conductivity of Mg matrix alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, N.; Angrisani, N.; Reifenrath, J.; Lucas, A.; Thorey, F.; Bormann, D.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. Biomechanical testing and degradation analysis of MgCa0.8 alloy screws: A comparative in vivo study in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Peng, J.; Nyberg, E.A.; Pan, F. Effect of Ca addition on the corrosion behavior of Mg-Al-Mn alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 369, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Liu, K.; Ma, K.; Zhao, H.W.; Li, S.B. Effects of trace Ca/Sn addition on corrosion behaviors of biodegradable Mg-4Zn-0.2 Mn alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2018, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, L.; Huang, G.; Liu, K.; Jiang, B.; Wang, G.G.; Xia, D.; Atrens, A.; Pan, F. Influence of microalloying with Ca and Ce on the corrosion behavior of extruded Mg-3Al-1Zn. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, C445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J. The role of Ca on the microstructure and corrosion behavior of Mg-8Sn-1Al-1Zn-Ca alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 590, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; He, X.; Yan, X. Corrosion behavior of Mg-Ca-Zn alloys with high Zn content. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 152, 109952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercetin, A.; Özgün, Ö.; Aslantas, K.; Aykutoğlu, G. The microstructure, degradation behavior and cytotoxicity effect of Mg-Sn-Zn alloys in vitro tests. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yim, C.D.; You, B.S. Effects of solute Zn on corrosion film of Mg-Sn-Zn alloy formed in NaCl solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, C839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.Y.; Kang, J.Y.; Yim, C.D.; Lee, Y.L. Role of hydrogen evolution rate in determining the corrosion rate of extruded Mg-5Sn-(1-4 wt%) Zn alloys. Corros. Sci. 2014, 89, 275–285. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, S.; Wei, M.; Liming, P.; Yujuan, W.; Xintian, L. Research progress on solidification structure of alloys by synchrotron X-ray radiography: A review. J. Magnes. Alloys 2020, 8, 396–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Guo, E.; Wang, X.; Kang, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T. Influence of Alloyed Ga on the Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of As-Cast Mg-5Sn Alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Research progress in effect of alloying on electrochemical corrosion rates of Mg alloys. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2021, 50, 361–372. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.W.; Fu, P.H.; Guo, X.W.; Suhong, Z.; Chunquan, C.; Wenjiang, D. The effects of heat treatment and zirconium on the corrosion behaviour of Mg-3Nd-0.2 Zn-0.4 Zr (wt.%) alloy. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 2612–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Xiao, W.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Lyu, S.; Zheng, R.; Ma, C. Improving Tensile Properties of Mg-Sn-Zn Magnesium Alloy Sheets Using Pretension and Ageing Treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 1494–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Pan, F.; Pan, H. Microstructure, mechanical and bio-corrosion properties of as-extruded Mg-Sn-Ca alloys. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zou, J.; Huang, Z. Effect of rolling temperature on corrosion resistance of AZ61 magnesium alloy. Nonferr. Met. Sci. Eng. 2023, 14, 473–480. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Bing, Y.; Li, F.; Qizhi, L. The effect of Zn on the corrosion resistance of extruded Mg-3Sn-1Ca alloy. Surf. Technol. 2023, 52, 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, B.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Chao, L.; Wei, L.; Zhicheng, N.; Anmin, L. The influence of the second phase on the corrosion behavior of Mg Zn Zr alloy. Mater. Prot. 2021, 54, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Guo, S.; Zeng, L. Effects of second phases on microstructure, microhardness, and corrosion behavior of Mg-3Sn—(1Ca) alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Alloy | Measured Composition (wt.%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Sn | Ca | Zn | Zr | |
| Mg-3Sn(T3) | Bal. | 2.97 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mg-3Sn-1Ca(TX31) | Bal. | 3.14 | 1.02 | 0 | 0 |
| Mg-3Sn-1Ca-1Zn(TXZ311) | Bal. | 3.14 | 1.02 | 1.09 | 0 |
| Mg-3Sn-1Ca-1Zr(TXK311) | Bal. | 3.08 | 1.03 | 0 | 0.6 |
| Alloy | Grain Size (μm) | Second-Phase Size Distribution (μm) | Area Fraction of Second Phase (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg2Sn | CaMgSn | |||
| T3 | 406.5 ± 6.6 | 1.5~11.5 | - | 2.4 ± 0.6 |
| TX31 | 698.7 ± 7.2 | - | 1.6~31.2 | 7.4 ± 1.5 |
| TXZ311 | 364.8 ± 5.1 | - | 1.4~35.1 | 7.9 ± 2.1 |
| TXK311 | 260.4 ± 3.4 | - | 0.8~22.7 | 13.1 ± 2.2 |
| Point | Chemical Composition (at.%) | Phase Types | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Sn | Ca | Zn | Zr | ||
| A | 79.54 | 20.46 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Mg2Sn |
| B | 75.74 | 24.26 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Mg2Sn |
| C | 66.50 | 17.89 | 14.58 | 0 | 0 | CaMgSn |
| D | 57.19 | 19.82 | 22.98 | 0 | 0 | CaMgSn |
| E | 87.07 | 7.03 | 4.65 | 1.26 | 0 | CaMgSn |
| F | 83.51 | 8.34 | 7.20 | 0.94 | 0 | CaMgSn |
| G | 75.55 | 12.99 | 11.26 | 0 | 0.19 | CaMgSn |
| H | 72.90 | 15.35 | 11.33 | 0 | 0.04 | CaMgSn |
| Alloy | Ecorr/V | Icorr/A·cm−2 | Rs | CPEt | Rct | CPEf | Rf | Rl | L | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ω·cm2 | Y1 | n1 | Ω·cm2 | Y2 | n2 | Ω·cm2 | Ω·cm2 | H·cm−2 | |||
| T3 | −1.43 | 5.78 × 10−5 | 1.37 | 4.7 × 10−4 | 0.71 | 7.94 | 8.9 × 10−5 | 0.93 | 126.6 | 48.84 | 337.7 |
| TX31 | −1.52 | 6.69 × 10−5 | 0.76 | 2.8 × 10−6 | 0.85 | 8.01 | 8.3 × 10−5 | 0.90 | 212.1 | 36.19 | 1117 |
| TXZ311 | −1.56 | 3.81 × 10−5 | 0.94 | 4.88 × 10−7 | 0.92 | 11.89 | 3.9 × 10−5 | 0.92 | 291.2 | 93.65 | 1322 |
| TXK311 | −1.49 | 4.67 × 10−5 | 0.39 | 2.72 × 10−6 | 0.90 | 8.73 | 7.1 × 10−5 | 0.92 | 221 | 68.44 | 354.6 |
| Alloy | T3 | TX31 | TXZ311 | TXK311 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion rate (PW/mm·y−1) | 5.34 | 7.55 | 3.94 | 6.42 |
| Corrosion rate (PH/mm·y−1) | 3.94 | 6.14 | 2.82 | 4.96 |
| Corrosion rate (Pi/mm·y−1) | 1.31 | 1.52 | 0.87 | 1.07 |
| Alloy | Ecorr/V | Icorr/A·cm−2 | Status | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T3 | −1.43 | 5.78 × 10−5 | as-homogenized | This work |
| TX31 | −1.52 | 6.69 × 10−5 | as-homogenized | This work |
| TXZ311 | −1.56 | 3.81 × 10−5 | as-homogenized | This work |
| TXK311 | −1.49 | 4.67 × 10−5 | as-homogenized | This work |
| Mg-2Al-0.2Si-0.5Sn | −1.58 | 6.73 × 10−5 | cast | [9] |
| Mg-7Sn | −1.58 | 2.88 × 10−5 | cast | [12] |
| Mg-5Al-0.4Mn-1Ca | −1.58 | 4.65 × 10−5 | cast | [19] |
| Mg-1Sn-0.5Ca | −1.47 | 5.95 × 10−6 | as-extruded | [32] |
| Mg-2Sn-0.5Ca | −1.45 | 6.73 × 10−6 | as-extruded | [32] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, Z.; Yu, Y.; Mao, Z.; Du, S.; Chen, Q.; Niu, X. The Influence of the Addition of Ca, Zn, and Zr on the Corrosion Properties of As-Homogenized Mg-3Sn Alloys. Crystals 2025, 15, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15060537
Jia Z, Yu Y, Mao Z, Du S, Chen Q, Niu X. The Influence of the Addition of Ca, Zn, and Zr on the Corrosion Properties of As-Homogenized Mg-3Sn Alloys. Crystals. 2025; 15(6):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15060537
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Zheng, Yongzhi Yu, Zhiwen Mao, Sichao Du, Qiuli Chen, and Xiaowei Niu. 2025. "The Influence of the Addition of Ca, Zn, and Zr on the Corrosion Properties of As-Homogenized Mg-3Sn Alloys" Crystals 15, no. 6: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15060537
APA StyleJia, Z., Yu, Y., Mao, Z., Du, S., Chen, Q., & Niu, X. (2025). The Influence of the Addition of Ca, Zn, and Zr on the Corrosion Properties of As-Homogenized Mg-3Sn Alloys. Crystals, 15(6), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15060537





