Abstract
Optimizing the design of low-tungsten-content alloys represents an effective approach to address the insufficient strength and toughness of conventional tungsten alloys. This study focuses on the design and fabrication of low-tungsten-content alloys, specifically investigating the effects of Nb addition on the low-temperature sintering microstructure and mechanical properties of 50W–Ni–Fe alloy. The results demonstrate that Nb significantly lowers the liquid phase formation temperature, shifting the densification mechanism from solid phase sintering to liquid phase sintering. Nb primarily dissolves in the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase and forms nanoscale γ″-Ni3Nb precipitates. These γ″-Ni3Nb precipitates maintain coherent interfaces with the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase, exhibiting excellent interfacial bonding, which markedly enhances the hardness and modulus of the matrix phase. Through the strengthening effects of solid solution strengthening and precipitation strengthening, the tensile strength of the alloy increases to 1259 MPa while maintaining a total elongation of 23.1%. The fracture mode of the 50W-Ni-Fe-Nb alloy transitions to a mixed mechanism involving cleavage fracture of W and ductile rupture of the matrix phase.
1. Introduction
Tungsten alloys are typical two-phase composite materials, consisting of W particles and a matrix phase. The matrix phase is composed of elements such as Ni, Cu and Fe [1]. Due to their high density, high strength, high hardness, and excellent radiation absorption capability, tungsten alloys have important applications in military industry, aerospace, and other fields. With the expansion of tungsten alloy applications, there is an increasing demand for enhanced comprehensive mechanical properties, making the development of tungsten alloys with balanced strength and ductility a key research focus.
The balance of mechanical properties in tungsten alloys primarily relies on the design of the two-phase structure: the strength originates from hard and brittle W particles, while the ductility derives from the soft matrix phase. Optimizing composition and processing to achieve synergistic improvement in both strength and ductility remains a major challenge in this field.
W-Ni-Fe is a traditional high-tungsten-content alloy (>85 wt.% W). Researchers have improved the comprehensive mechanical properties of tungsten alloys by introducing minor alloy elements [2,3,4,5,6,7], optimizing the sintering process [8], deformation strengthening [9,10], adding second phase particles [11,12], and applying post-sintering treatments [13,14,15,16]. However, the intrinsic brittleness of W and the limited volume fraction of the matrix phase restrict further enhancement of ductility. In contrast, low-W-content tungsten alloys significantly improved ductility due to the increased proportion of the matrix phase. During sintering densification, restricted long-range diffusion of W atoms across the matrix phase effectively inhibits W grain coarsening, resulting in fine-grain strengthening [17]. Consequently, the development of high-performance low-W-content tungsten alloys has attracted widespread attention.
In low-W-content tungsten alloys, the dominant matrix phase (primarily Ni-based) offers opportunities for performance tuning through alloying. Studies on Ni-based alloys have demonstrated that Nb, as a potent strengthening element, enhances strength via solid solution strengthening and precipitation strengthening mechanisms [18,19,20]. Introducing Nb into low-W-content tungsten alloys may therefore enable synergistic strengthening effects to resolve the strength–ductility trade-off.
This study focuses on a 50W–Ni–Fe system with Nb additions, systematically investigating the effects of Nb on densification behavior, microstructure evolution, and mechanical properties, while elucidating the strengthening mechanisms and failure behavior of 50WNiFeNb alloys. This study aims to provide insights for designing tungsten alloys with high strength and high ductility.
2. Materials and Methods
In this experiment, the samples were prepared using high-purity reduced tungsten powder, carbonyl nickel powder, carbonyl iron powder, and reduced niobium powder, with detailed parameters listed in Table 1. Liu et al. [21] systematically investigated the influence of Nb content on the mechanical properties of Inconel 718 nickel alloys and identified an optimal amount of Nb addition. Based on their study, a 50W–35Ni–11Fe–4Nb alloy (hereafter referred to as WNiFeNb alloy) was designed in this study. For comparison, a Nb-free 50W–35Ni–15Fe alloy (hereafter referred to as WNiFe alloy) was also prepared to evaluate the effects of Nb addition on the microstructure and properties of the 50 W alloy.

Table 1.
Characterization of raw powders.
The raw powders were loaded into mixing containers under an argon atmosphere to prevent oxidation during blending. Homogenization was performed using a three-dimensional mixer (model SBH-1L) for 8 h. The pre-mixed powders were then encapsulated in rubber molds and compacted via cold isostatic pressing (CIP) at 250 MPa to form green compacts.
A conventional single-step sintering process was employed: The compacts were subjected to pressureless sintering under a vacuum atmosphere using a vacuum furnace (VVP-60, Shanghai Haoyue, Shanghai, China). The sintering process involved heating to 900 °C at 10 °C/min followed by a 30 min holding period, subsequent heating to 1200 °C, 1250 °C, 1300 °C, and 1350 °C at 5 °C/min with a 2 h holding period at each stage, and finally furnace cooling to room temperature. The vacuum level was maintained below 10−3 Pa throughout the sintering process. The dimensions of the sintered samples and the sintering process profile are shown in the Figure 1.
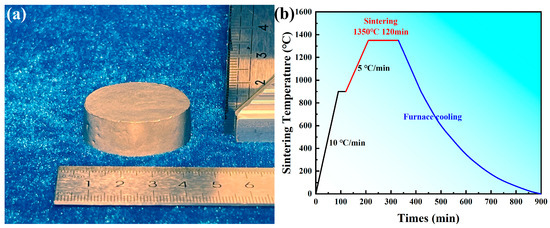
Figure 1.
(a) The dimensions of the sintered sample and (b) the sintering process profile.
The density of the tungsten alloys was measured using the Archimedes drainage method. The theoretical density of the 50 W alloy was calculated based on the theoretical densities and mass fractions of its constituent elements:
where ρ represents the theoretical density of the tungsten alloy, and Wi and ρi are the mass fraction and theoretical density of element i, respectively. The relative density is obtained by taking the ratio of the experimentally measured density to the theoretical density. Tensile strength tests of the samples were carried out using a dual-column tabletop testing system (Instron® 3369, Norwood, MA, USA). Three tensile specimens (dimensions: 26 L × 3 W × 3 H mm; gauge length: 8 mm, as shown in the Figure 2) were taken from each alloy to ensure the reliability of the tensile test data.

Figure 2.
Tensile test sample.
A field-emission scanning electron microscope (SEM, TESCAN MIRA4 LMH, Brno, Czech Republic) was used to characterize the microstructure and fracture features of the alloys. The phase composition of the alloys was characterized using X-Ray diffraction (XRD) analysis performed on a D8 ADVANCE instrument equipped with Cu Kα radiation. An electron probe micro-analyzer (EPMA, JXA-8230, Akishima, Japan) was used to characterize and analyze the chemical composition and elemental concentration variations in the matrix phase of the tungsten alloys. A focused ion beam-scanning electron microscope (FIB-SEM, TESCAN AMBER) was used to prepare transmission electron microscopy (TEM) samples, which were then observed using a spherical aberration-corrected transmission electron microscope (TEM, FEI TitanTM G2 60-300, Hillsboro, OR, USA). ImageJ software (version: 1.54h) was used to measure the grain size distribution of the alloys.
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure
Figure 1 presents the XRD patterns of WNiFe and WNiFeNb alloys sintered at different temperatures. As shown in Figure 3a,b, both WNiFe and WNiFeNb alloys exhibit nearly identical diffraction patterns at all sintering temperatures. The characteristic peaks correspond to the W phase (W(110), W(200), W(211), W(220)) and the γ-(Ni,Fe) phase (γ(111), γ(200), γ(220)), confirming the two-phase structure of the alloys. Notably, no diffraction peaks associated with elemental Nb are observed in the WNiFeNb alloy at any sintering temperature, indicating that Nb was successfully dissolved into the matrix.
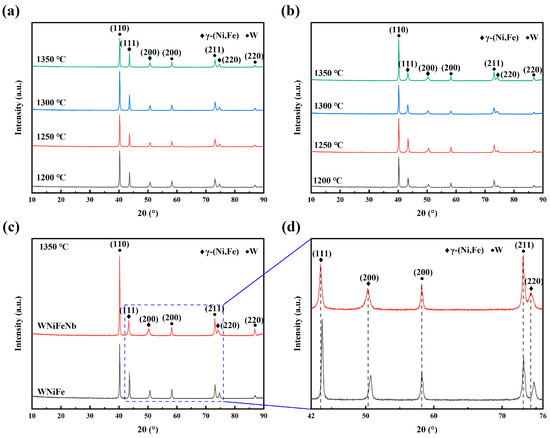
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of tungsten alloys sintered at different temperatures: (a) WNiFe alloy; (b) WNiFeNb alloy; (c) comparison of XRD results at 1350 °C; (d) enlarged view of the dashed box region in (c).
A direct comparison of the 1350 °C-sintered WNiFe and WNiFeNb alloys (Figure 3c) demonstrates that Nb addition does not alter the fundamental crystalline structure of the two phases in the tungsten alloys. The enlarged view of the dashed regions in Figure 3d reveals no significant changes in the W phase diffraction peaks. However, the γ-(Ni,Fe) phase peaks in the WNiFeNb alloy show a slight leftward shift, suggesting an expansion of the γ-phase lattice constant. This phenomenon arises from the substitutional solid solution of Nb (atomic radius: 147 pm) in the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix, where Nb atoms replace smaller Ni atoms (atomic radius: 124 pm) [22].
Figure 4 shows the SEM images of WNiFe alloys sintered at different temperatures. All microstructures exhibit white W particles embedded in a gray γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase. Notably, no significant microstructural differences are observed at all sintering temperatures. The alloys consistently display characteristic features of solid phase sintering: non-uniform distribution of W particles and the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase, irregularly shaped W particles with no apparent growth, and high W-W connectivity

Figure 4.
SEM images of the microstructure of WNiFe alloys at different sintering temperatures: (a) 1200 °C; (b) 1250 °C; (c) 1300 °C; (d) 1350 °C.
Figure 5 presents SEM images of the WNiFeNb alloy microstructure at different sintering temperatures. In addition to white W particles and a gray γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase, a small number of dark grey particles are distributed within the matrix phase. As shown in Figure 5a, pores are observed in the alloy sintered at 1200 °C, with a large number of fine W particles agglomerated together. With increasing sintering temperature (Figure 5b,c), porosity decreases and partial coarsening of W particles occurs. When the temperature further rises to 1350 °C (Figure 5d), significant W particle growth is observed, accompanied by smoother particle surfaces and more homogeneous distribution of both W particles and matrix phase. These microstructural features are characteristic of typical liquid phase sintering mechanisms.
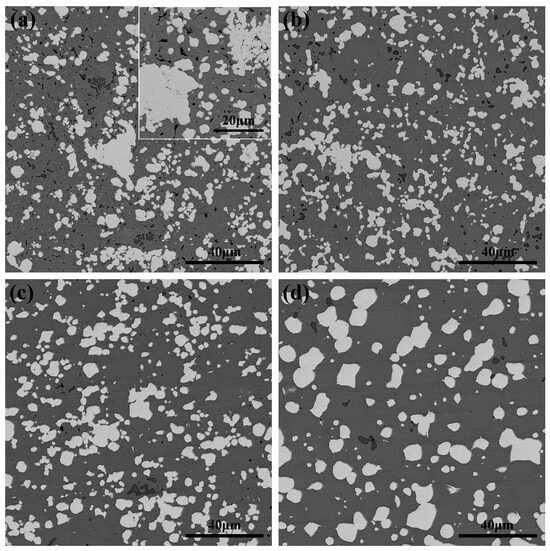
Figure 5.
SEM images of the microstructure of WNiFeNb alloys at different sintering temperatures: (a) 1200 °C; (b) 1250 °C; (c) 1300 °C; (d) 1350 °C.
To investigate the elemental distribution and identify the dark grey particles in the WNiFeNb alloy, electron probe micro-analysis (EPMA) was conducted on the alloy sintered at 1350 °C, as shown in Figure 6. Significant elemental diffusion is observed at the interface between W particles and the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase. Nb is uniformly distributed within the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase, while the dark grey particles are composed of Nb and O. A quantitative analysis was conducted on the tungsten particles (Position 1), matrix phase (Position 2) and dark grey particles (Position 3), with the results summarized in Table 2. EPMA quantitative analysis reveals that the atomic ratio of Nb to O in the dark grey particles is approximately 1:2. By referencing the Nb–O binary phase diagram, these particles are confirmed to be the NbO2 phase.

Figure 6.
EPMA analysis results of WNiFeNb alloy sintered at 1350 °C.

Table 2.
Elemental composition at the indicated position in Figure 6.
Figure 7 shows TEM images of the WNiFeNb alloy sintered at 1350 °C. As shown in Figure 7a, no significant defects are observed at the interface between W particles and the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase, indicating excellent interfacial bonding unaffected by Nb addition. Figure 7b,c confirm that the W particles exhibit a body-centered cubic (BCC) structure, while the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase adopts a face-centered cubic (FCC) structure.

Figure 7.
TEM characterization of WNiFeNb alloy sintered at 1350 °C: (a) BF image and SAED pattern; (b) W particles; (c) γ-(Ni,Fe); (d) DF image of the selected area within the white circle in (c); (e) HR-TEM and SAED of (f) γ″-Ni3Nb; (g) γ-(Ni,Fe).
The selected-area dark-field (DF) image (Figure 7d) reveals abundant nanoscale precipitates (20–50 nm) within the matrix phase. Indexing of the selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern (Figure 7c) identifies these precipitates as γ″-Ni3Nb. The orientation relationship (111)γ-(Ni,Fe)//(112)γ″-Ni3Nb confirms a coherent interface between the γ″-Ni3Nb precipitates and the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix.
3.2. Mechanical Property
Figure 8 shows the relative densities of WNiFe and WNiFeNb alloys sintered at different temperatures. As the sintering temperature increases, both alloys exhibit a progressive increase in relative density. At 1200 °C and 1250 °C, the relative density difference between the two alloys is minimal. However, at 1300 °C, the WNiFe alloy achieves a relative density of 96.0%, while the WNiFeNb alloy reaches 98.1%, demonstrating a significant densification improvement.

Figure 8.
Relative density of WNiFe and WNiFeNb alloys sintered at different temperatures.
When sintered at 1350 °C, the relative density of the WNiFe alloy remains nearly unchanged at 96.1%, showing no further enhancement compared to the 1300 °C condition. In contrast, the WNiFeNb alloy achieves a relative density of 98.7%, approaching full densification. These results clearly indicate that Nb addition markedly promotes the sintering densification of the WNiFeNb alloy.
Figure 9 presents the tensile strength and total elongation of WNiFe and WNiFeNb alloys sintered at different temperatures. As shown in Figure 9a, the tensile strength of the WNiFe alloy initially increases with rising sintering temperature, reaching a peak of 781 ± 11 MPa at 1300 °C, followed by a slight decrease to 769 ± 3 MPa at 1350 °C. Meanwhile, the total elongation of the WNiFe alloy continuously improves with temperature, reaching a maximum value of 31.0 ± 0.8% at 1350 °C.
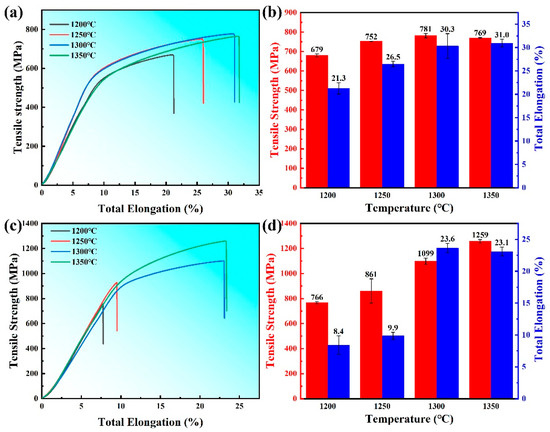
Figure 9.
Tensile test results of tungsten alloys at different sintering temperatures: (a,b) WNiFe alloys; (c,d) WNiFeNb alloys.
In contrast, the WNiFeNb alloy (Figure 9b) exhibits a consistent increase in tensile strength with sintering temperature, achieving a maximum value of 1259 ± 13 MPa at 1350 °C. This represents a remarkable 478 MPa enhancement compared to the Nb-free WNiFe alloy. The total elongation of the WNiFeNb alloy first increases to a peak of 23.6 ± 0.8% at 1300 °C, then slightly declines to 23.1 ± 0.7% at 1350 °C, showing an approximate 7% reduction relative to the WNiFe alloy.
3.3. Fracture Morphology
Figure 10 presents SEM images of the tensile fracture morphology of WNiFe alloys sintered at different temperatures. As observed in Figure 10a,b, when the sintering temperature does not exceed 1250 °C, the fracture morphologies exhibit numerous W particles retaining their original powder morphology, accompanied by extensive interconnected pores. With increasing sintering temperature, sintering necks between W particles grow larger, and porosity progressively decreases.

Figure 10.
SEM images of the tensile fracture morphology of WNiFe alloys at different sintering temperatures: (a) 1200 °C; (b) 1250 °C; (c) 1300 °C; (d) 1350 °C.
At sintering temperatures of 1300 °C and above (Figure 10c,d), the fracture morphologies no longer show significant aggregation of original W powder particles. The dominant fracture mode transitions to W-W intergranular fracture, with no W cleavage fracture features observe. Furthermore, numerous fine dimples formed by the ductile fracture of the matrix phase are observed, which is consistent with the increase in the total elongation of the alloy.
Figure 11 displays SEM images of the tensile fracture morphologies of WNiFeNb alloys sintered at different temperatures. At 1200 °C (Figure 11a), the fracture morphology exhibits extensive intergranular separation of original particles and abundant pores. When the sintering temperature increases to 1250 °C (Figure 11b), porosity remains significant, though partial coarsening of W particles is observed, accompanied by reduced aggregation of original powder particles. Additionally, pronounced W particle debonding and minor ductile tearing ridges are visible in the matrix phase.

Figure 11.
SEM images of the tensile fracture morphology of WNiFeNb alloys at different sintering temperatures: (a) 1200 °C; (b) 1250 °C; (c) 1300 °C; (d) 1350 °C.
At 1300 °C (Figure 11c), dispersed fine tearing ridges gradually coalesce into a network-like structure, while partial cleavage fracture of W particles emerges. As shown in Figure 11d, when sintered at 1350 °C, the fracture morphology demonstrates substantial W particle coarsening, with cleavage fracture becoming the dominant failure mode for W particles. Notably, interface debonding between W particles and the matrix phase nearly disappears, correlating with the significant strength enhancement of the WNiFeNb alloy.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Nb Addition on Microstructural Characteristics
According to the Ni-Fe binary phase diagram, the minimum liquidus formation temperature of the matrix phase with a Ni:Fe ratio of 7:3 is 1426 °C [17]. Consequently, within the sintering temperature range of 1200–1350 °C, the densification mechanism of the WNiFe alloy remains governed by solid phase sintering. Diffusion at contact points drives sintering neck formation and densification. The low sintering temperatures restrict diffusion rates, and the absence of a liquid phase prevents particle rearrangement, resulting in the microstructural characteristics of the WNiFe alloy: limited W particle growth, non-uniform distribution, and high W-W connectivity. At 1350 °C, the alloy achieves a relative density of only 96.1%.
The Ni-Nb binary phase diagram [23] reveals a eutectic liquid formation at 1180 °C. At 1200 °C, a minimal liquid phase forms in the WNiFeNb alloy, with microstructural features similar to those of the WNiFe alloy. As temperature increases, the liquid phase content increases, and capillary forces drive the liquid phase to infiltrate W-W interfaces, filling pores and facilitating W particle rearrangement for a more uniform distribution. Meanwhile, W dissolution and precipitation within the liquid phase contribute to localized grain growth. At 1350 °C, while significant W particle growth occurs, the increased matrix phase fraction (compared to traditional high-W alloys) restricts long-range W diffusion during dissolution/precipitation, effectively suppressing W grain growth. The resultant W particles exhibit an average grain size of 7.40 ± 0.22 μm, markedly smaller than those in conventional high-W alloys (~30 μm).
Additionally, Ni and Nb demonstrate the lowest mixing enthalpy in the matrix phase (Table 3). According to the minimum mixing enthalpy selection theory, Ni–Nb intermetallic compounds preferentially form in the alloy. Based on the Ni-Nb binary phase diagram, a eutectic reaction occurs at 1285 °C: L ↔ Ni3Nb + Ni. Ni3Nb exists in two structures: stable D0a–Ni3Nb and metastable D022-Ni3Nb [18,22]. While the alloy’s cooling process during sintering is close to equilibrium solidification, only the D022–Ni3Nb phase is observed in the sintered alloy. This occurs because Fe dissolution in the matrix phase increases its lattice constant, reducing interfacial misfit. Additionally, Fe adjusts the alloy’s electron concentration ratio to stabilize the D022 phase, thereby promoting its precipitation [24].

Table 3.
Atomic radius and enthalpy of mixtures of Ni, Fe, and Nb atoms [22].
4.2. Effect of Nb Addition on Mechanical Properties
The addition of Nb significantly enhances the tensile properties of the 50W–Ni–Fe alloy, particularly increasing the ultimate tensile strength by approximately 478 MPa, while maintaining a favorable combination of strength and ductility compared to similar alloy systems and conventional high-W-content tungsten alloys (Figure 12). The strengthening mechanisms primarily involve two factors: solid solution strengthening from Nb dissolution in the matrix phase, and precipitation strengthening by coherent γ″-Ni3Nb precipitates formed within the matrix phase.

Figure 12.
Comparison of the tensile properties of tungsten alloys in this work with those reported in the literature [10,15,16,17,25,26,27,28,29,30].
In the 50WNiFeNb alloy, the significant atomic size mismatch between Nb atoms and Ni/Fe atoms induces substantial lattice distortion when W and Nb atoms dissolve into the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase via solid solution. This dissolution alters the local atomic arrangement, creating stress fields that interact with dislocations and hinder their glide. Consequently, the hardness and modulus of the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase are enhanced. The solid solution strengthening effect can be quantitatively evaluated using the following formula [31]:
where 0 is the shear modulus of Ni (G = 79 GPa), ε is the interaction coefficient (ε = 0.33), and C is the solid solubility of W and Nb in the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase, measured via EPMA as CW = 7.06 at.% and CNb = 4.05 at.%. The calculated solid solution strengthening contribution is ΔσSS = 37.06 MPa.
The γ″-Ni3Nb phase with a D022 structure is an ordered tetragonal phase that maintains a coherent interface with the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase. The closely matched lattice parameters result in low interfacial misfit. Additionally, the small size of γ″-Ni3Nb precipitates (20–50 nm) reduces elastic interactions with dislocations while effectively inhibiting crack initiation at the γ″-Ni3Nb/γ-(Ni,Fe) interface. Furthermore, the γ″-Ni3Nb phase exhibits high antiphase boundary (APB) energy, leading to a more pronounced precipitation strengthening [32]. The precipitation strengthening contribution can be calculated using the following formula [33]:
where b is the Burgers vector of the matrix phase (b = 0.25 nm), f is the volume fraction of precipitates, λ is the average distance between Ni3Nb phase, and r is the precipitate size. The calculated precipitation strengthening contribution is ΔσOR = 462.72 MPa, demonstrating that precipitation strengthening dominates the performance enhancement induced by Nb addition.
Under the synergistic effects of Nb solid solution strengthening and nano-scale Ni3Nb precipitation, the matrix phase exhibits significantly improved hardness and modulus (as shown in Figure 13 and Table 4), providing robust support for the enhanced alloy strength.

Figure 13.
(a) Nano-indentation load-displacement curves of matrix phase; (b) the hardness and elastic modulus of matrix phase.

Table 4.
Nanoindentation measurement of hardness and elastic modulus of the matrix phase.
Coherent nano-precipitates not only generate significant precipitation strengthening effects but also induce distinctive multistage work-hardening behavior, effectively enhancing ductility by delaying local plastic instability [34]. However, the reduced ductility of the WNiFeNb alloy compared to the WNiFe alloy may be attributed to the presence of numerous NbO2 particles. As observed in the fracture morphology (Figure 11) and crack path profiles (Figure 14) of the WNiFeNb alloy, the hard and brittle NbO2 particles exhibit poor interfacial bonding with both W particles and the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix phase. These interfaces serve as preferential sites for crack initiation and propagation, thereby degrading the alloy’s plastic deformation capability.

Figure 14.
Crack path profiles of tungsten alloys after tensile test: (a) WNiFe alloy; (b) WNiFeNb alloy.
4.3. Alloy Failure Behaviour
As typical two-phase alloys, tungsten alloys exhibit a strong correlation between their mechanical properties and fracture modes. The relationship between fracture strength and fracture modes can be described by the following formula:
where fW, fW−W, fW−M, and fM are the proportions of W cleavage fracture, W-W intergranular fracture, W/matrix phase interfacial debonding, and matrix phase ductile rupture in the alloy’s fracture surface, respectively. σW, σW−W, σW−M, and σM are the cleavage strength of W particles, W-W interfacial strength, W/matrix phase interfacial strength, and matrix phase strength, respectively. Among these fracture modes, σW−W and σM are relatively low; thus, the alloy’s strength is primarily governed by σW−M and fW.
Figure 14 shows SEM images of the crack path profiles for 1350 °C-sintered WNiFe and WNiFeNb alloys after tensile testing. In the WNiFe alloy, due to the solid phase sintering mechanism, the non-uniform distribution of W particles and weak W/matrix phase interfacial bonding result in a main crack propagation path dominated by W-W intergranular fracture and W/matrix phase interfacial debonding, leading to inferior strength.
In contrast, Nb addition in the WNiFeNb alloy enhances sintering densification, resulting in a more uniform W particle distribution, reduced W–W connectivity, and strengthened W/matrix phase interfaces. Consequently, the main crack propagation path is dominated by W cleavage fracture with no significant W/matrix phase debonding observed. Furthermore, the formation of nano-scale γ″-Ni3Nb precipitates within the matrix phase due to Nb–Ni interactions significantly enhances the matrix phase’s hardness and modulus, contributing to a remarkable increase in alloy strength.
5. Conclusions
This study systematically investigated the effects of Nb addition (4 wt.%) on the microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of 50W–Ni–Fe alloys sintered at different temperatures (1200 °C, 1250 °C, 1300 °C, 1350 °C), with comparisons to Nb-free 50 W alloys. The main conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- Nb addition significantly reduces the liquid phase formation temperature, promotes sintering densification, and improves microstructural homogeneity. The 50W–35Ni–11Fe–4Nb alloy achieves an optimal relative density of 98.7% at 1350 °C.
- (2)
- Nb and Ni form a large number of γ″-Ni3Nb precipitates with sizes ranging from 20 nm to 50 nm. These precipitates maintain a coherent relationship with the γ-(Ni,Fe) matrix, exhibiting strong interfacial bonding, which significantly enhances the hardness and modulus of the matrix phase.
- (3)
- The WNiFeNb alloy achieves balanced strength and ductility primarily through precipitation strengthening, supplemented by solid solution strengthening. The alloy achieves an ultimate tensile strength of 1259 ± 13 MPa (61% improvement over the Nb-free alloy) and a total elongation of 23.1 ± 0.7%. The fracture mode transitions to a hybrid mechanism dominated by W particle cleavage fracture and matrix phase ductile rupture.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.W. and Q.C.; methodology, T.W. and Q.C.; validation, T.W. and Y.H.; investigation, T.W. and Z.M.; resources, W.L. and Y.M.; data curation, T.W. and Y.H.; writing—original draft preparation, T.W.; writing—review and editing, T.W. and Y.D.; supervision, W.L. and Y.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China, grant number 2023JJ10067.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cui, L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Pan, K.M.; Zhao, L.Z.; Ren, Y.P.; Cui, H.L. Research Progress on Strength and Toughness of Tungsten Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2024, 53, 3539–3552. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, W.S.; Lang, E.; Sprouster, D.; Olynik, N.; Pattammattel, A.; Olds, D.; Hattar, K.; Mccue, I.; Trelewicz, J.R. Alloying effects on the microstructure and properties of laser additively manufactured tungsten materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 914, 147110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R. Crystallographic texture evolution in hot-press sintered tungsten heavy alloy with the effect of niobium (Nb) addition. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 108971. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, I.; Dabhade, V.V. Transient liquid phase sintering in spark plasma sintered tungsten heavy alloys with Nb and Mo additives. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2024, 124, 106849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Dabhade, V.; Debata, M.; Panigrahi, A. The influence of Mo and Nb on liquid phase sintering and mechanical properties of W-Ni-Fe-co based tungsten heavy alloy. Mater. Charact. 2025, 224, 115034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Dabhade, V.; Debata, M.; Panigrahi, A. The role of addition of Mo and Nb on microstructure, phase and mechanical properties in tungsten heavy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Gopalan, V.; Rajan, R.A.; Jen, C.-P. Effect of Rare Earth Metals (Y, La) and Refractory Metals (Mo, Ta, Re) to Improve the Mechanical Properties of W–Ni–Fe Alloy—A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollina, R.; German, R.M. Heating rate effects on microstructural properties of liquid phase sintered tungsten heavy alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2004, 22, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalışkan, N.K.; Nuri, D.; Şakir, B. Swaging of liquid phase sintered 90W–7Ni–3Fe tungsten heavy alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2013, 36, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, J.V.; Edwards, D.J.; Henager, C.H.; Setyawan, W.; Wang, J.; Murayama, M. Characterization of ductile phase toughening mechanisms in a hot-rolled tungsten heavy alloy. Acta Mater. 2021, 204, 116523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakunt, N.S.; Gouthama; Upadhyaya, A. Effect of La2O3 addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of W–Ni–Cu tungsten heavy alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 318, 129227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Sengupta, P.; Dey, S.; Kumar, M.; Basu, S.; Debata, M. Effect of Y2O3, La2O3 and ZrO2 dispersoid addition on ultra-high temperature stability of 95W–3.5Ni–1.5Fe heavy alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 113, 106195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Prabhu, G.; Sankaranarayana, M.; Nandy, T.K. Effect of solution treatment temperature and cooling rate on the mechanical properties of tungsten heavy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 688, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Hong, X.; Ni, Y.; Cheng, C.; Wang, X.; Fan, J. Study on the mechanical properties of tungsten alloys with respect to tungsten content and post-treatment processes. Mater. Lett. 2025, 385, 138141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.E.; Wang, J.; Henager, C.H.; Setyawan, W.; Odette, G.R. The effect of hot rolling on the strength and fracture toughness of 90W–7Ni3Fe tungsten heavy metal alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 824, 141738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunčická, L.; Macháčková, A.; Lavery, N.P.; Kocich, R.; Cullen, J.C.T.; Hlaváč, L.M. Effect of thermomechanical processing via rotary swaging on properties and residual stress within tungsten heavy alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2020, 87, 105120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, L.; Du, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, M.-C.; Atrens, A. A novel dissolution-precipitation mechanism during liquid phase sintering and its strengthening effects in W–Ni–Fe alloys with low W contents. Mater. Des. 2022, 220, 110841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathon, M.; Connétable, D.; Sundman, B.; Lacaze, J. Calphad-type assessment of the Fe–Nb–Ni ternary system. Calphad 2009, 33, 136–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Chen, D.; Han, B.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wei, S.; Wei, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.T.; Kai, J.-j. Design of D022 superlattice with superior strengthening effect in high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2019, 167, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawitzki, R.; Hassan, S.; Karge, L.; Wagner, J.; Wang, D.; Von Kobylinski, J.; Krempaszky, C.; Hofmann, M.; Gilles, R.; Schmitz, G. Differentiation of γ′- and γ″- precipitates in Inconel 718 by a complementary study with small-angle neutron scattering and analytical microscopy. Acta Mater. 2019, 163, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Guo, K.; Sun, J.; Shi, H. Effect of Nb addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 718 fabricated by laser directed energy deposition. Mater. Charact. 2022, 183, 111601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and Its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesley, C.; Adefunke, F.; Peng, J.; MSIT®. Assessed Phase Diagram of the Nb–Ni System: Datasheet from MSI Eureka in Springer Materials. 2015. Available online: https://materials-springer-com-s-269.libdb.csu.edu.cn/msi/phase-diagram/docs/sm_msi_r_20_023791_01_full_LnkDia0 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Quist, W.E.; Taggart, R.; Polonis, D.H. The influence of iron and aluminum on the precipitation of metastable Ni3Nb phases in the Ni-Nb system. Metall. Trans. 1971, 2, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Han, Y.; Fan, J.; Du, Z. Fabrication of ultrafine-grain and great-performance W–Ni–Fe alloy with medium W content. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 846, 156237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, L.; Liang, Y.-J.; Zhu, Y.; Jian, R.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Xue, Y.; Wang, F.; Cai, H.; et al. A strategy to achieve high-strength WNiFe composite-like alloys with low W content by laser melting deposition. Mater. Des. 2020, 190, 108554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-B.; Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, G.-H.; Chou, K.-C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al2O3 dispersed fine-grained medium heavy alloys with a superior combination of strength and ductility. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 817, 141376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yang, C.; Gong, X.; Ding, F. Effect of Rapid Hot Extrusion on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fine-Grained Tungsten Alloy and Coarse-Grained Tungsten Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2013, 42, 372–376. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Cao, S.; Zhu, J.; Jin, Y.; Chen, B. Densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of 90W–4Ni–6Mn heavy alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2013, 37, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, Z.-B.; Liu, J.-R.; Zhang, G.-H. Effect of molybdenum addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of 90% tungsten heavy alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 106, 105868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, C.A.; Nieh, T.G.; Iwasaki, H. The effect of solid solution W additions on the mechanical properties of nanocrystalline Ni. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Liu, C.-T.; Zhang, Z.; Liaw, P.K. Nanoprecipitate-Strengthened High-Entropy Alloys. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Huang, G.; Mi, X.; Peng, L.; Xie, H.; Kang, Y. Microstructure evolution and properties of a quaternary Cu–Ni–Co–Si alloy with high strength and conductivity. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 766, 138390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Tong, Y.; Jiao, Z.B.; Wei, J.; Cai, J.X.; Han, X.D.; Chen, D.; Hu, A.; Kai, J.J.; et al. Multicomponent intermetallic nanoparticles and superb mechanical behaviors of complex alloys. Science 2018, 362, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).