Biochemical and Structural Characterization of Glyoxylate Reductase/Hydroxypyruvate Reductase from Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cloning
2.2. Protein Expression and Purification
2.3. Size-Exclusion Chromatography Combined with Multi-Angle Light Scattering
2.4. Protein Crystallization, Data Collection, and Structure Determination
2.5. Activity Assay and Kinetic Analysis
2.6. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy and Thermal Denaturation
3. Results and Discussion
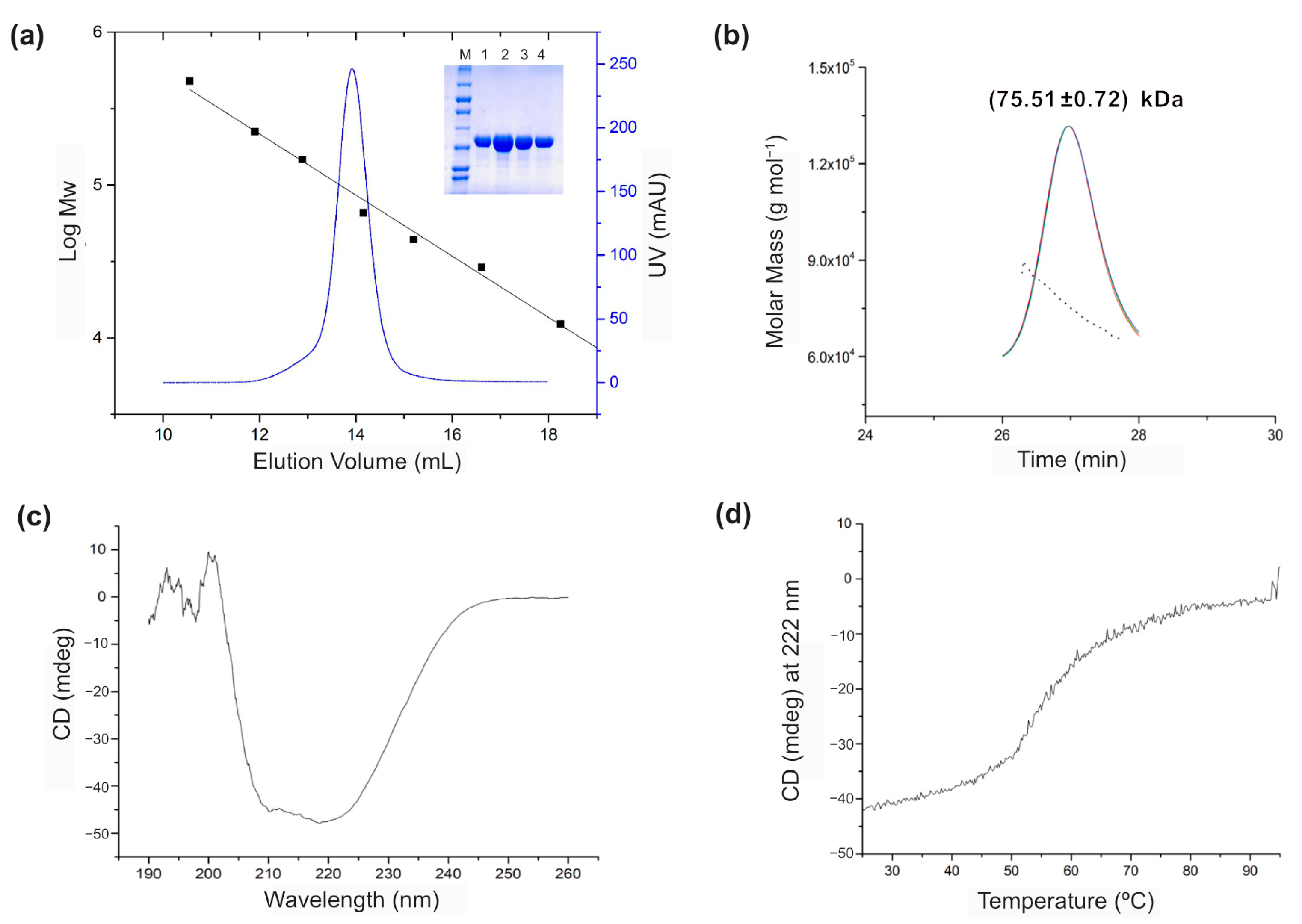
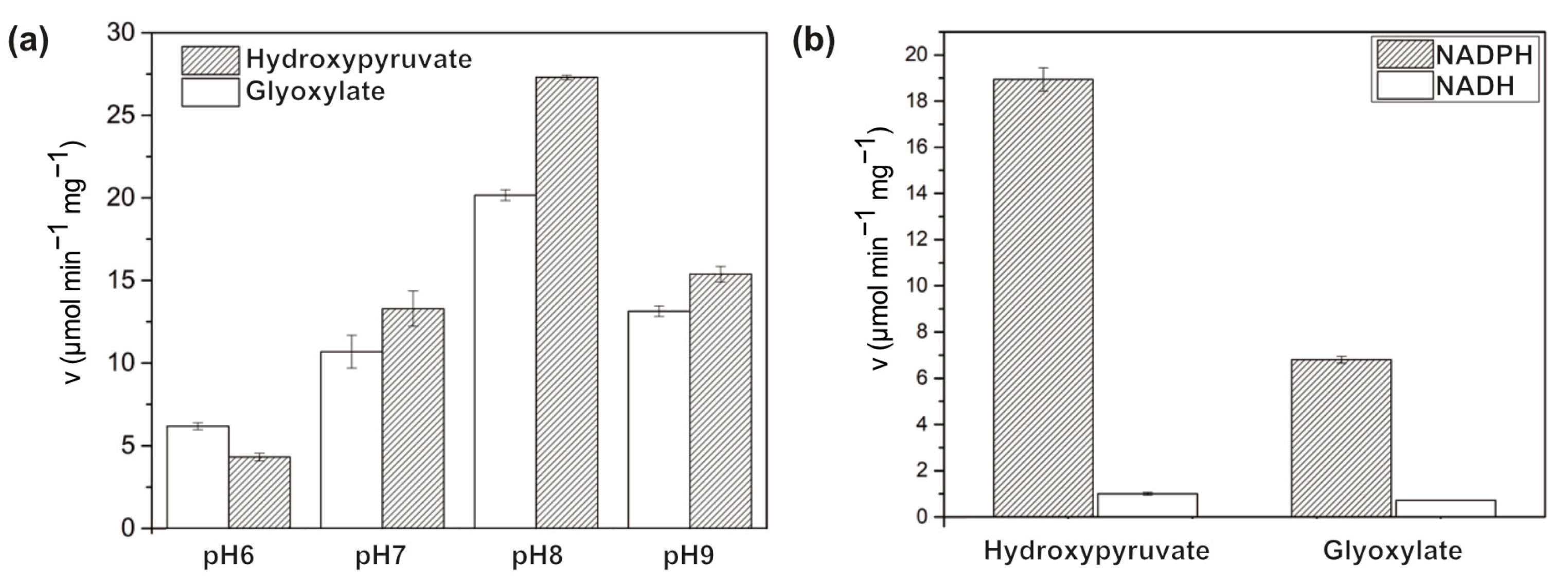
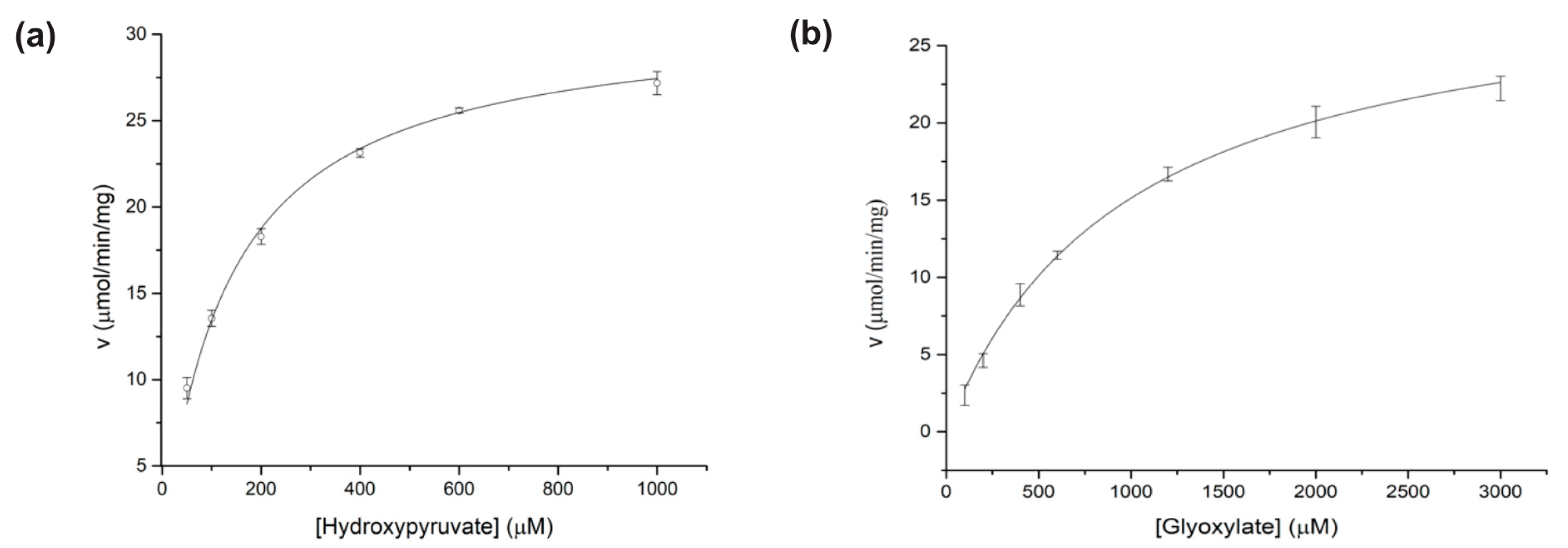
3.1. Biochemical Characterizations of BsGRHPR
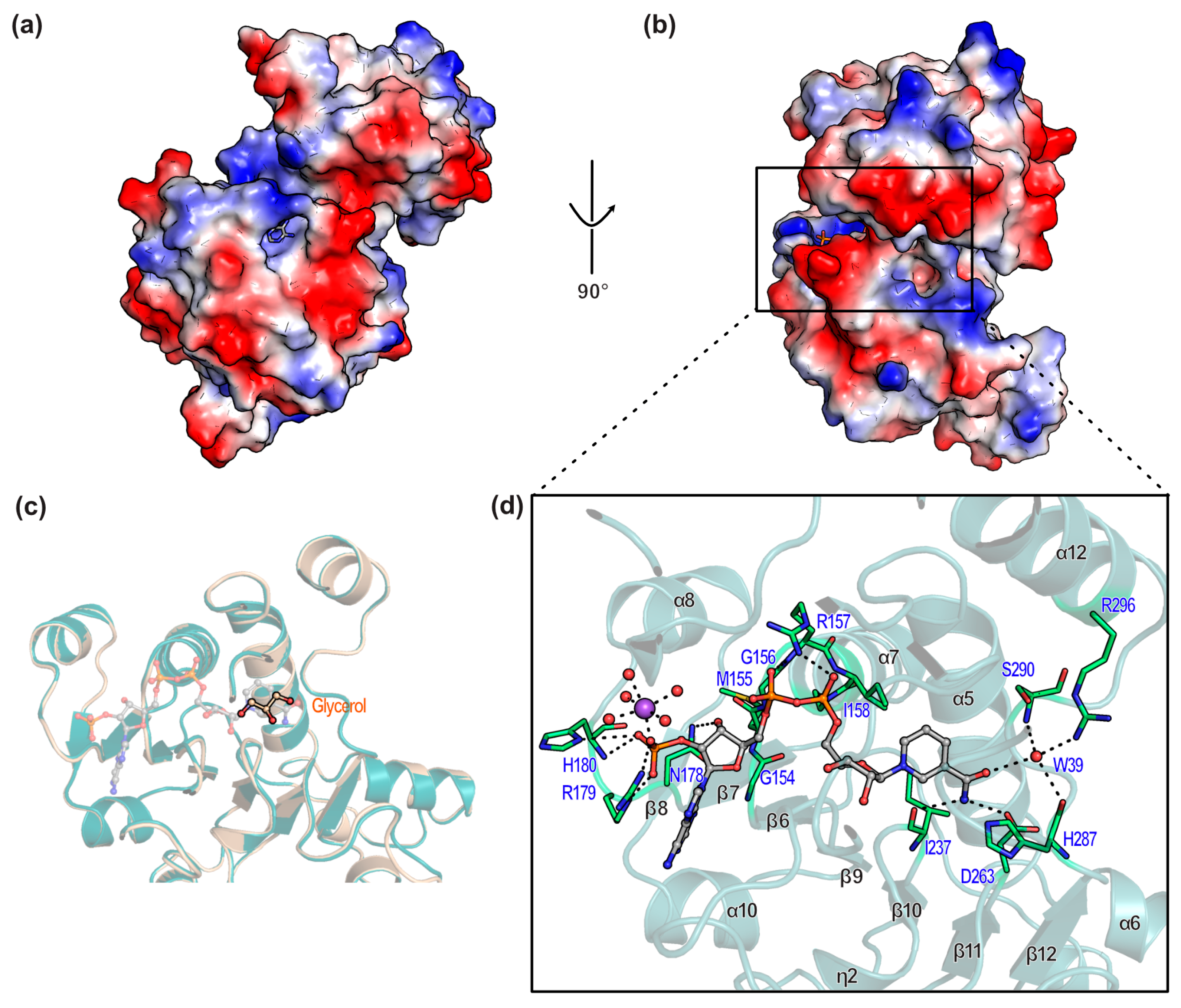
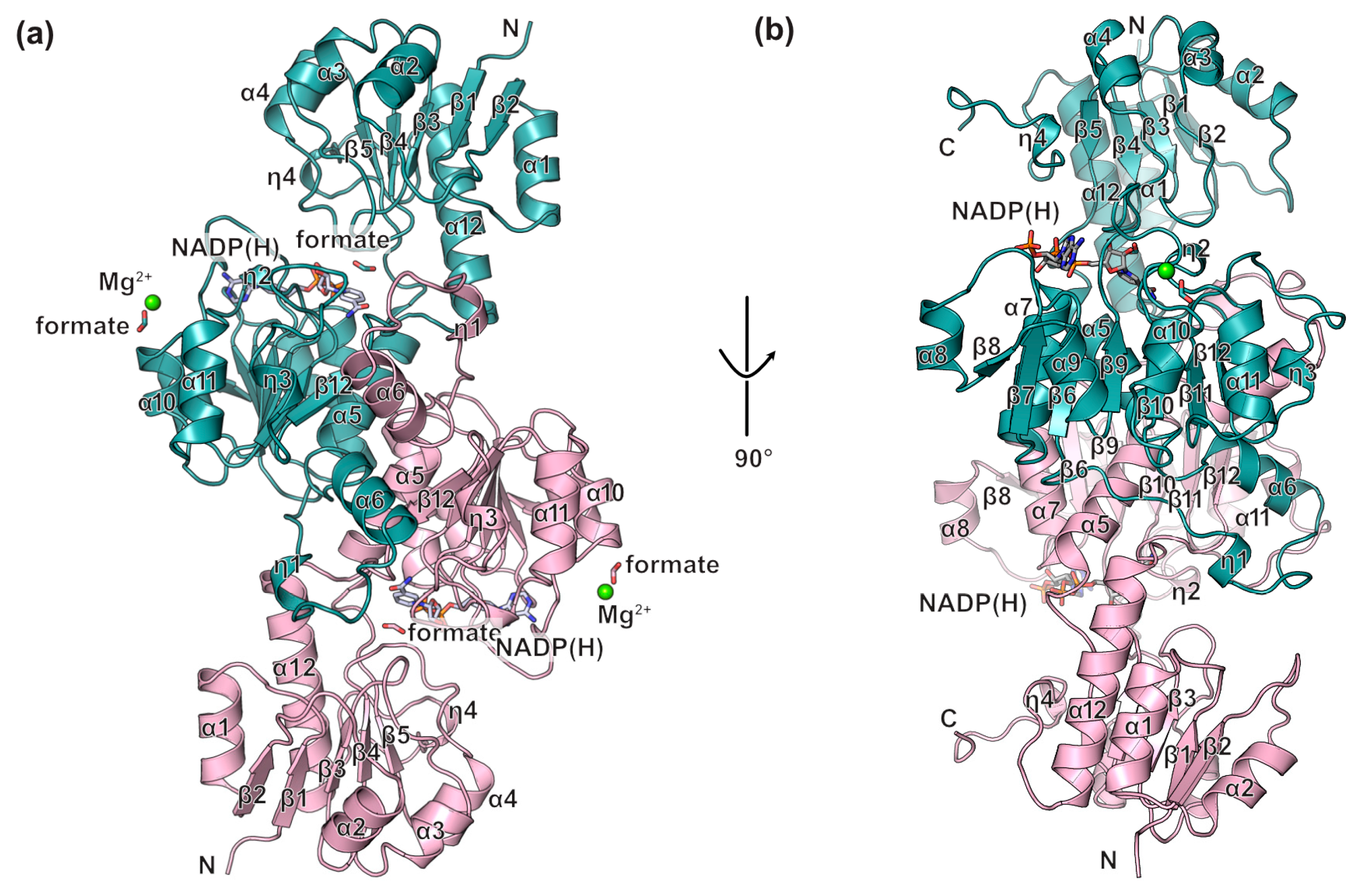
3.2. Overall Structure of BsGRHPR Complex with Both Formate and Cofactor
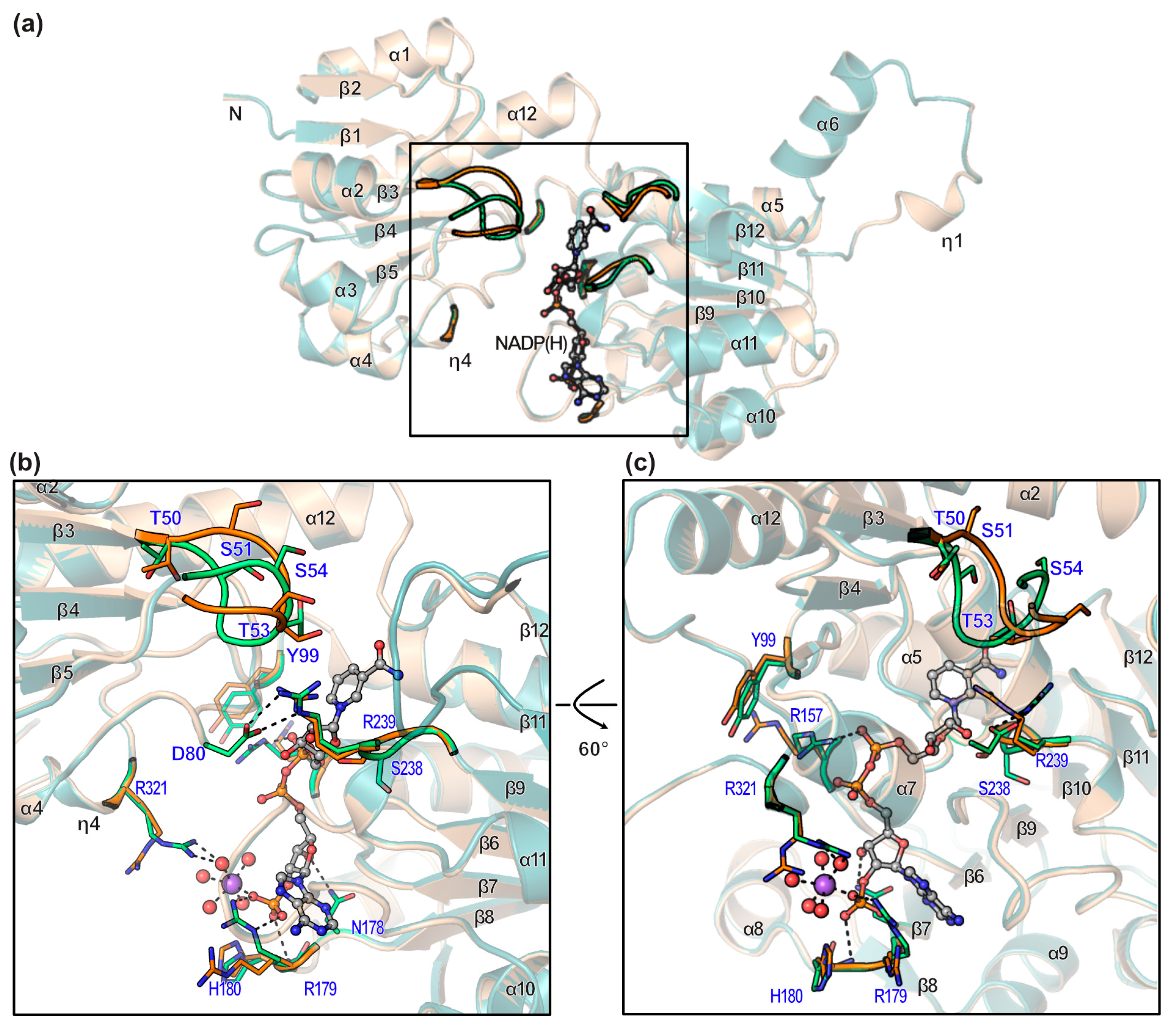
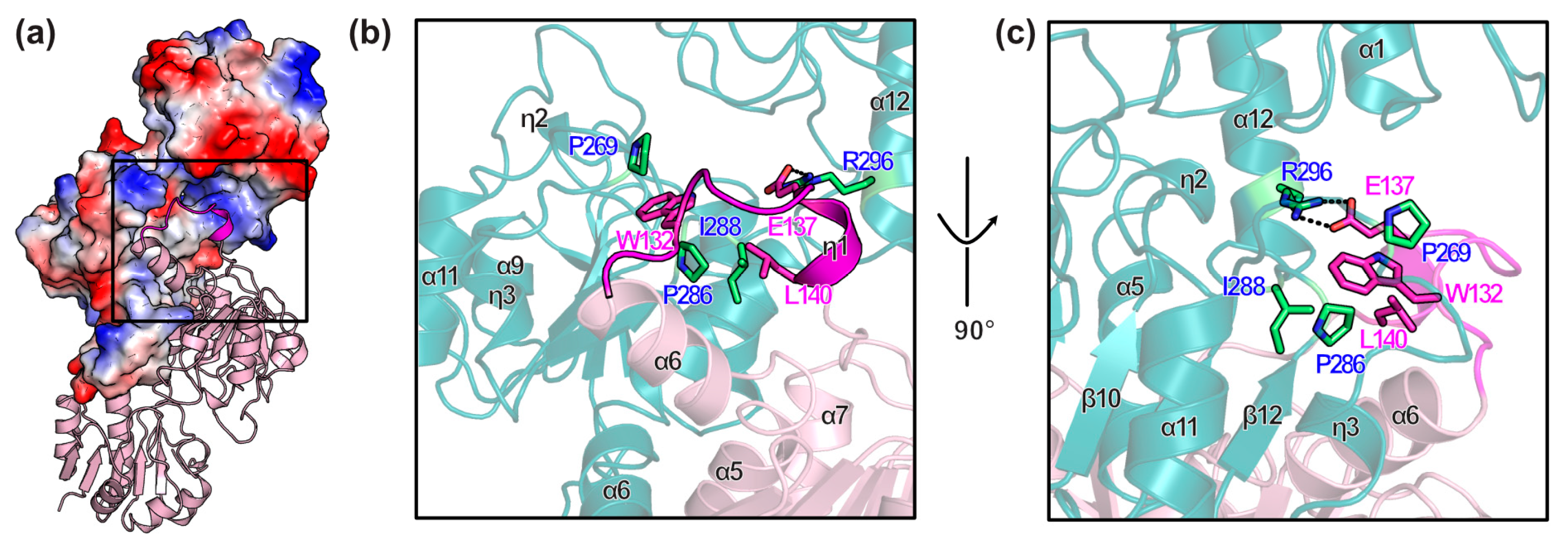
3.3. Conformational Changes on Binding of Cofactor
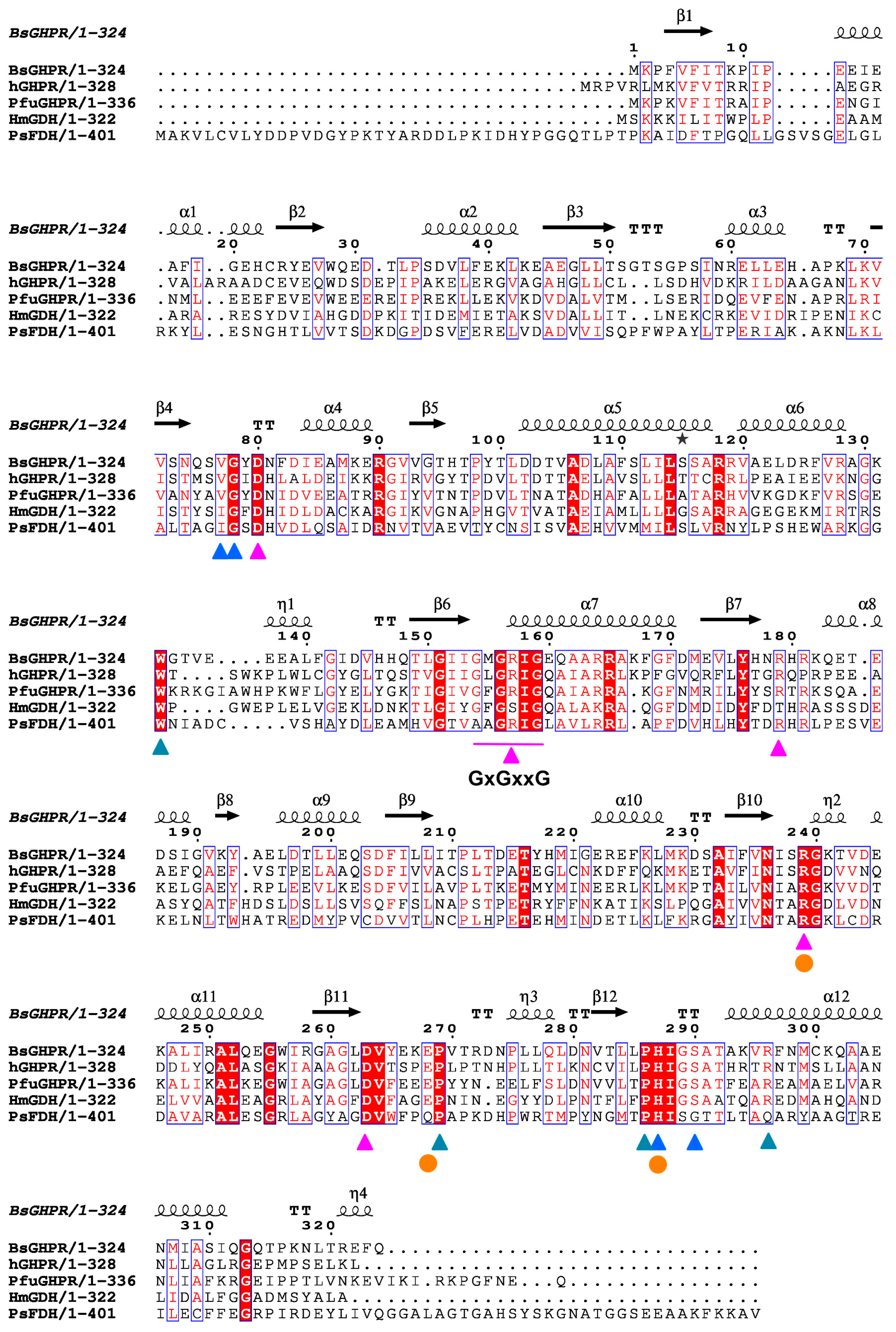
3.4. Cofactor Specificity
3.5. Substrate Binding Site
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wanders, R.J.A.; Groothoff, J.W.; Deesker, L.J.; Salido, E.; Garrelfs, S.F. Human glyoxylate metabolism revisited: New insights pointing to multi-organ involvement with implications for siRNA-based therapies in primary hyperoxaluria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2025, 48, e12817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuyan, R.; Maggio, T.; Thomas, C.; Sambharia, M.; Gehrs, K.; Boyce, T. Late-onset retinal oxalosis in primary hyperoxaluria type 2. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2024, 36, 102156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutner, J.; Shabalin, I.G.; Matelska, D.; Handing, K.B.; Gasiorowska, O.; Sroka, P.; Gorna, M.W.; Ginalski, K.; Wozniak, K.; Minor, W. Structural, Biochemical, and Evolutionary Characterizations of Glyoxylate/Hydroxypyruvate Reductases Show Their Division into Two Distinct Subfamilies. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, J.D.; Yoshida, T.; Brick, P. Crystal structure of a NAD-dependent D-glycerate dehydrogenase at 2.4 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 236, 1123–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumsby, G.; Cregeen, D.P. Identification and expression of a cDNA for human hydroxypyruvate/glyoxylate reductase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1446, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, W.L.; Clark, S.M.; Hoover, G.J.; Shelp, B.J. Role of plant glyoxylate reductases during stress: A hypothesis. Biochem. J. 2009, 423, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, M.P.; Conners, R.; Rumsby, G.; Brady, R.L. Structural basis of substrate specificity in human glyoxylate reductase/hydroxypyruvate reductase. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 360, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassalle, L.; Engilberge, S.; Madern, D.; Vauclare, P.; Franzetti, B.; Girard, E. New insights into the mechanism of substrates trafficking in Glyoxylate/Hydroxypyruvate reductases. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, S.; Arai, R.; Kinoshita, Y.; Uchikubo-Kamo, T.; Wakamatsu, T.; Akasaka, R.; Masui, R.; Terada, T.; Kuramitsu, S.; Shirouzu, M.; et al. Structure of archaeal glyoxylate reductase from Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 complexed with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2007, 63, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, T.; Nunoura-Kominato, N.; Kudome, T.; Sakuraba, H. A novel hyperthermophilic archaeal glyoxylate reductase from Thermococcus litoralis. Characterization, gene cloning, nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 4740–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otwinowski, Z.; Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzym. 1997, 276, 307–326. [Google Scholar]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkoczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Davis, I.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.W.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; et al. PHENIX: A comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krissinel, E.; Henrick, K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holton, S.J.; Anandhakrishnan, M.; Geerlof, A.; Wilmanns, M. Structural characterization of a D-isomer specific 2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus. J. Struct. Biol. 2013, 181, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumsab, J.; Tobe, R.; Kurihara, T.; Hirose, Y.; Omori, T.; Mihara, H. Characterization of a novel class of glyoxylate reductase belonging to the beta-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase family in Acetobacter aceti. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2020, 84, 2303–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| BsGRHPR + Formate | BsGRHPR + Formate, NADPH | |
|---|---|---|
| PDB ID | 9M0T | 9M0V |
| Data collection | ||
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.979 | 0.979 |
| Space group | C2 | C2 |
| Total reflections | 648,293 (26,705) | 336,953 (16,325) |
| Unique reflections | 95,288 (4,200) | 50,733 (2502) |
| Cell dimensions | ||
| a, b, c (Å) | 93.1, 59.6, 59.9 | 93.2, 59.2, 59.7 |
| β (°) | 99.8 | 99.8 |
| Resolution (Å) | 29.8–1.2 (1.22–1.20) | 49.8–1.5 (1.53–1.50) |
| Rpim 1 | 0.022 (0.422) | 0.038 (0.478) |
| CC1/2 | 0.999 (0.715) | 0.999 (0.648) |
| I/σ I | 16.2 (1.8) | 12.5 (1.7) |
| Completeness (%) | 94.7 (85.0) | 98.8 (98.8) |
| Multiplicity | 6.8 (6.4) | 6.6 (6.5) |
| Refinement | ||
| Resolution (Å) | 29.5–1.2 (1.23–1.20) | 49.8–1.5 (1.54–1.50) |
| No. reflections | 95,255 | 50,703 |
| Rwork/Rfree 2 | 0.165/0.184 | 0.162/0.200 |
| No. atoms | ||
| Protein | 2668 | 2658 |
| Ligand/ion | 16 | 59 |
| Water | 421 | 342 |
| B-factors | ||
| Protein | 17.93 | 21.3 |
| Ligand | 17.65 | 16.1 |
| Water | 28.7 | 3.1 |
| R.m.s. deviations | ||
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.005 | 0.007 |
| Bond angles (°) | 0.87 | 0.91 |
| Ramachandran plot (%) | ||
| Favored | 97.86 | 96.94 |
| Allowed | 2.14 | 3.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.Q.; Duong, T.H.; Yang, J.K.; Kang, W. Biochemical and Structural Characterization of Glyoxylate Reductase/Hydroxypyruvate Reductase from Bacillus subtilis. Crystals 2025, 15, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040298
Nguyen TQ, Duong TH, Yang JK, Kang W. Biochemical and Structural Characterization of Glyoxylate Reductase/Hydroxypyruvate Reductase from Bacillus subtilis. Crystals. 2025; 15(4):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040298
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thang Quyet, Thai Huu Duong, Jin Kuk Yang, and Wonchull Kang. 2025. "Biochemical and Structural Characterization of Glyoxylate Reductase/Hydroxypyruvate Reductase from Bacillus subtilis" Crystals 15, no. 4: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040298
APA StyleNguyen, T. Q., Duong, T. H., Yang, J. K., & Kang, W. (2025). Biochemical and Structural Characterization of Glyoxylate Reductase/Hydroxypyruvate Reductase from Bacillus subtilis. Crystals, 15(4), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040298







