Deciphering the Tanzanian Ruby–Zoisite Enigma: A Confluence of Geochemistry, Microtextures, and Mineralogy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Research in Tanzania, Longido
3. Samples and Methods
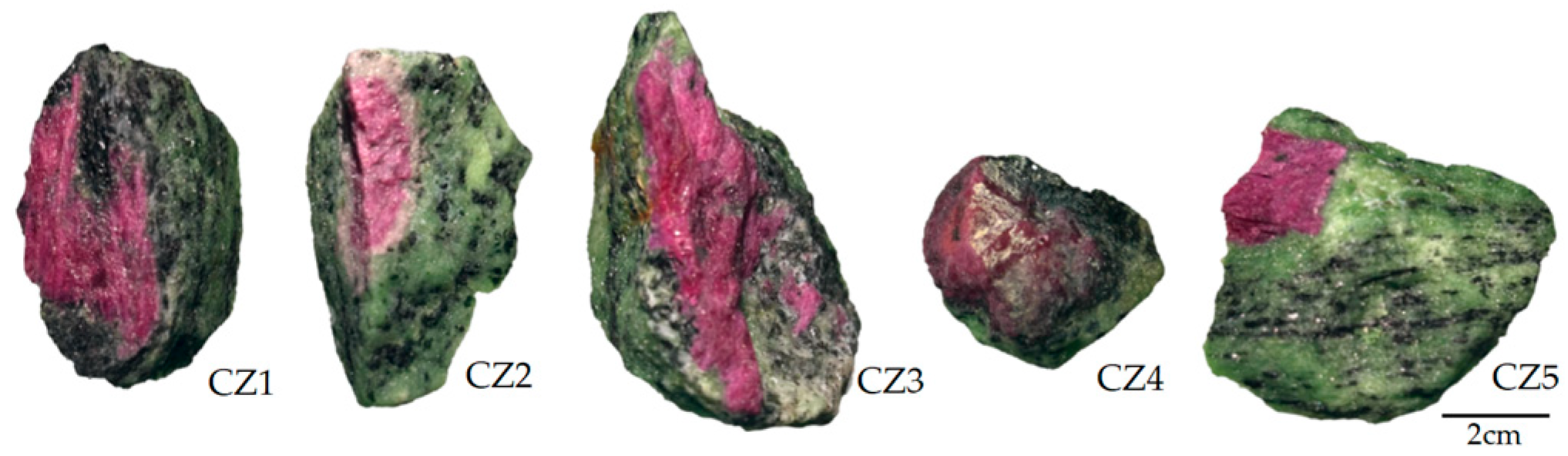
3.1. Sample Structure and Mineral Composition
3.2. Analytical Methods
4. Results
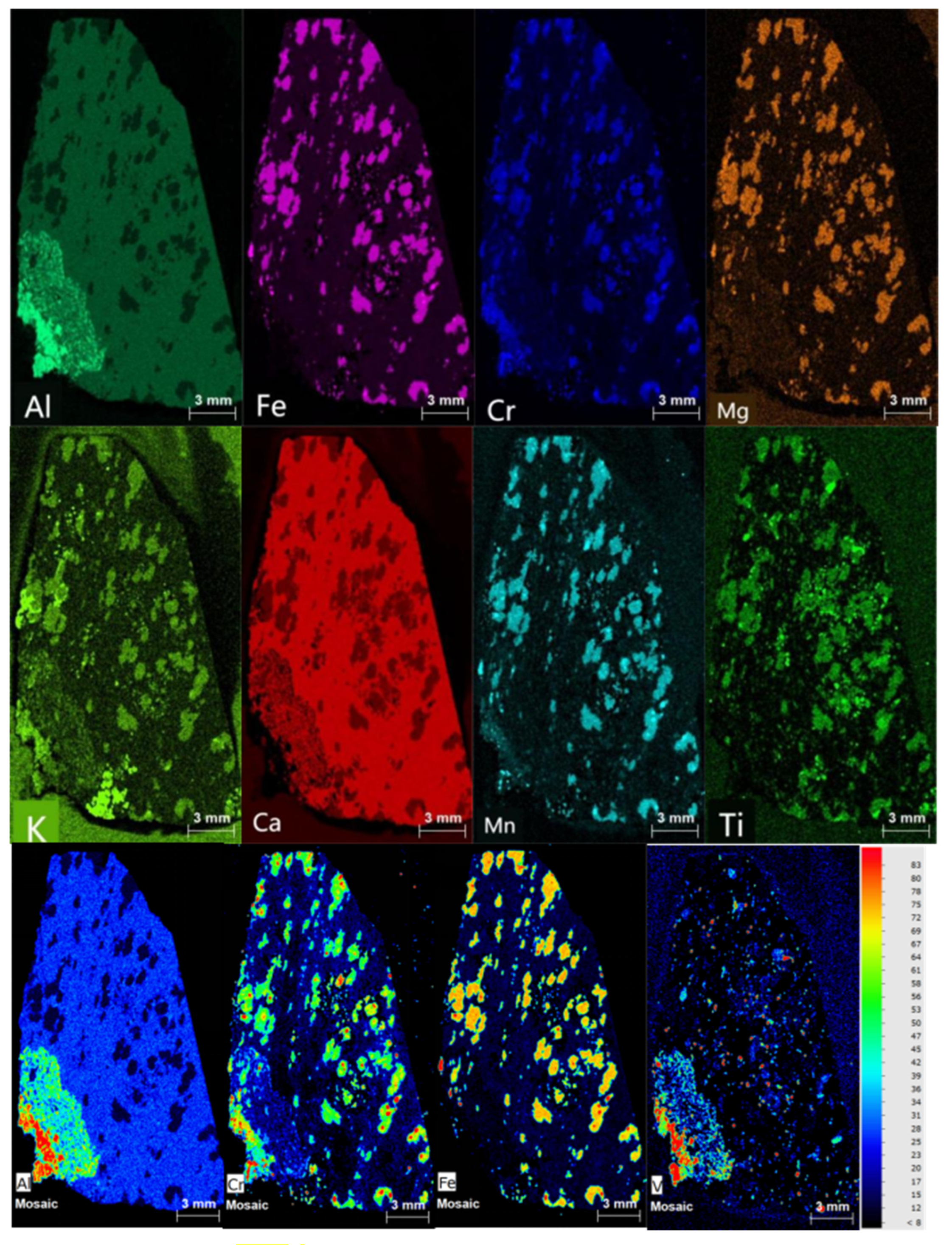
4.1. Mineralogical Composition and Genetic Implications
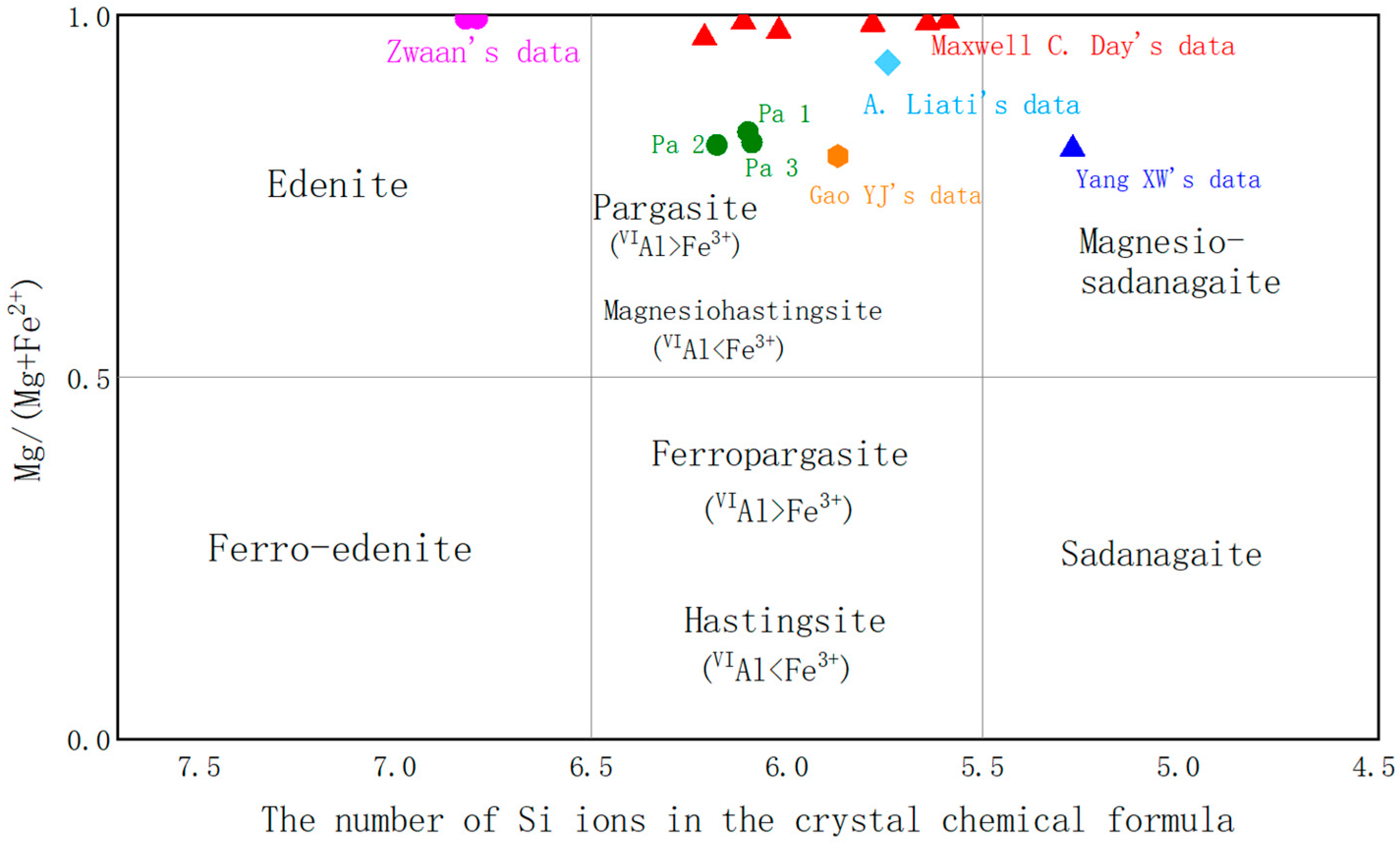
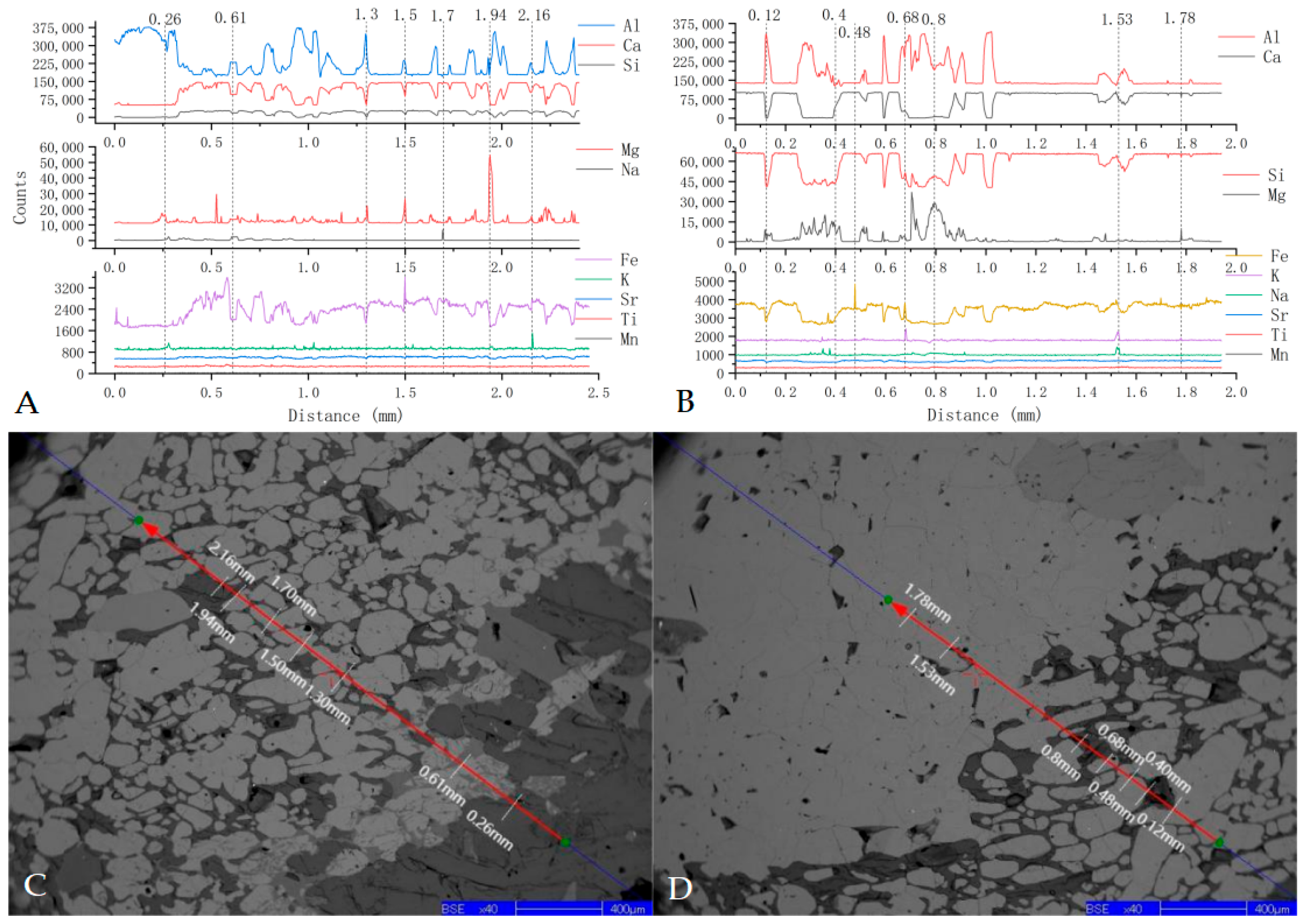
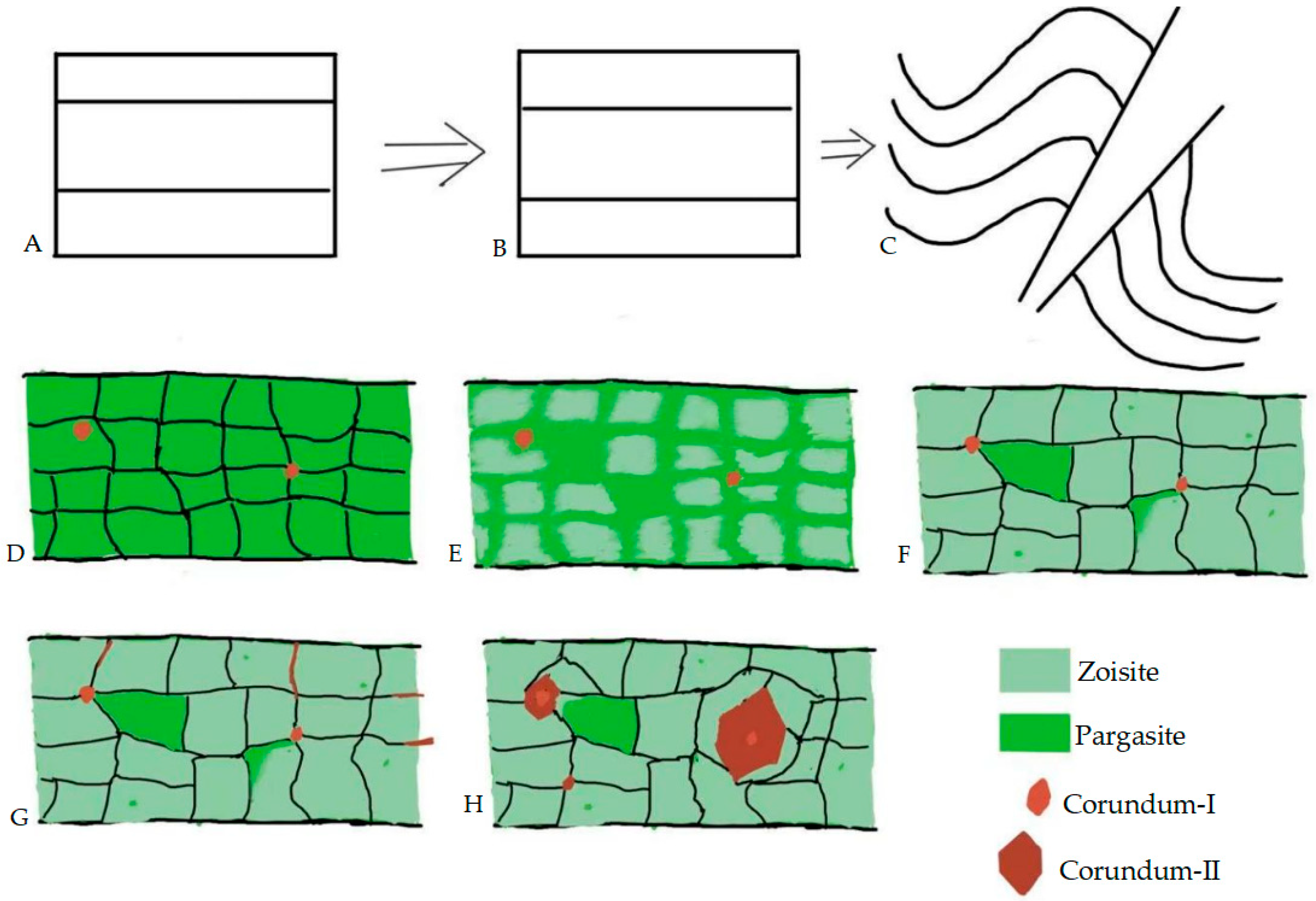
4.2. Chemical Geo-Chemical Zoisite–Corundum Paragenesis
4.3. Elemental Transport Mechanisms
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Ren, J.P.; Sun, K.; Gong, P.H.; He, F.Q. Pre-Cambrian mineralization in Tanzania. North China Geol. 2022, 45, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Hauzenberger, C.A.; Sommer, H.; Fritz, H.; Bauernhofer, A.; Kröner, A.; Hoinkes, G.; Wallbrecher, E.; Thöni, M. SHRIMP U–Pb zircon and Sm–Nd garnet ages from the granulite-facies basement of SE Kenya: Evidence for Neoproterozoic polycyclic assembly of the Mozambique Belt. J. Geol. Soc. 2007, 164, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lu, Q.; Ma, D.; Zheng, H.; Hu, R.; Shi, Z.; Qin, B. Chemical Composition and Spectroscopic Characteristics of Heat-Treated Rubies from Madagascar, Mozambique and Tanzania. Crystals 2023, 13, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.W.; Zhang, L.J.; Jia, Z.Y. Mineral composition characteristics and development prospects of Longjiduo red corundum mine in Tanzania. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2012, 2, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.W. Discussion on the Composition Characteristics and Genesis of the Longidou Ruby Mine in Tanzania. Master’s Thesis, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Gan, Y.C.; Meng, Y.L. Research on the Gemological Characteristics of Red Corundum in “Red Green Treasure”. Inf. Wkly. 2019, 18, 349–350. [Google Scholar]
- Banno, Y. Mg-rich chloritoid in a corundum-bearing zoisite rock from the Sanbagawa belt, central Shikoku, Japan. J. Mineral. Petrol. Sci. 2009, 104, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liati, A. Corundum- and zoisite-bearing marbles in the Rhodope Zone, Xanthi Area (N. Greece): Estimation of the fluid phase composition. Mineral. Petrol. 1988, 38, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.L.; Gao, B.Y.; Ma, B.L.; Susan, S. Geological characteristics of gem mines in Kenya and Tanzania. Build. Mater. Geol. 1993, 2, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.K. Eclogite in China. Chem. Miner. Geol. 2004, 4, 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.W.; Liu, X.Y.; Tang, W.L.; Wu, X.Y. The division and mineralization characteristics of the main mineralization zones in Tanzania. Geol. Explor. Discuss. Ser. 2015, 30, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kabete, J.M.; Groves, D.I.; McNaughton, N.J.; Mruma, A.H. A new tectonic and temporal framework for the Tanzanian Shield: Implications for gold metallogeny and undiscovered endowment. Ore Geol. Rev. 2012, 48, 88–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.L.; Ren, J.P.; Yuan, Y.S.; Peng, J.; Chen, J.; Bering, A.; Zuo, L.B.; Sun, H.W.; Liu, X.Y.; Sun, K.; et al. Mineral Resources and Mining Investment Environment in Tanzania. Geol. Bull. 2023, 42, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani, G.; Groat, L.A.; Fallick, A.E.; Pignatelli, I.; Pardieu, V. Ruby Deposits: A Review and Geological Classification. Minerals 2020, 10, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goff, E.; Deschamps, Y.; Guerrot, C. New geochronological data by singlezircon Pb-Pb evaporation method in north-eastern Tanzania: Regionalimplications for the Tanzanian Mozambique belt and gemstones mineralization. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Geological Congress, Oslo, Norway, 6–14 August 2008; pp. 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Curren, H.N.C.; Johnson, S.P. Tectonic evolution of the Mozambique Belt, Eastern Africa. In Proceedings of the 21st Colloquium of African Geology, Maputo, Mozambique, 3–6 July 2006; pp. 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Le Goff, E.; Deschamps, Y.; Guerrot, C. Tectonic implications of new single zircon Pb-Pb evaporation data in the Lossogonoi and Longido ruby-districts, Mozambican metamorphic Belt of north-eastern Tanzania. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2010, 342, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Xu, J.; Hu, Z.C.; Gao, S.; Gunther, D.; Gao, C.G.; Liu, Y.S. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chem. Geol. 2009, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.C.; Gao, S.; Zong, K.Q.; Chen, H.H. Accurate determinations of fifty-four major and trace elements in carbonate by LA–ICP-MS using normalization strategy of bulk components as 100%. Chem. Geol. 2011, 284, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbudak, İ.K.; Gürbüz, M.; Başıbüyük, Z.; Hatipoğlu, M.; Önal, A.Ö.; İşler, F. Mineralogical and Gemological Characteristics of Metaophiolite Hosted Corundum (Malatya-Türkiye). Sak. Univ. J. Sci. 2021, 25, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.Q.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xu, B. Gemological and Chemical Composition Characteristics of Thai Basalt Ruby. Geoscience, 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palke, A.C.; Wong, J.; Verdel, C.; Ávila, J.N. A common origin for Thai/Cambodian rubies and blue and violet sapphires from Yogo Gulch, Montana, U.S.A. Am. Mineral. 2019, 103, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokina, E.S.; Hofmeister, W.; Häger, T.; Mertz-Kraus, R.; Buhre, S.; Saul, J.M. Morphological and chemical evolution of corundum (ruby and sapphire): Crystal ontogeny reconstructed by EMPA, LA-ICP-MS, and Cr3+ Raman mapping. Am. Mineral. 2016, 101, 2716–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q. Optimization and Identification Methods for Common Gemstones; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.F.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, F.F.; Lu, Q.X.; Hu, L. Systematic mineralogical classification and nomenclature of pyroxene and clinopyroxene minerals. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2015, 1, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; He, M.; Lucas, A.C.; Sun, X.; Zhou, D.; Huang, T.; Li, K.; Fortaleché, D.; Lin, M.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Ruby from Longido, Tanzania: Mining, Color, Inclusion, and Chemical Features. Crystals 2024, 14, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, B. The Geology and Petrology of the Merelani Tanzanite Deposit, NE Tanzania. Ph.D. Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.J. Analysis and Study on Gemological Mineralogy Characteristics of Tanzanite. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Semet, M.P. A Crystal-Chemical Study of Synthetic Magnesiohastingsite. Am. Mineral. 1973, 58, 480–494. [Google Scholar]
- Emmanuel, O.; Kazimoto, E.; Mshiu, E.E. Reconnaissance assessment of the Stenian-Tonian granitoids of southern Tanzania for metal resources by using geological remote sensing and geochemical techniques. Geochemistry 2020, 80, 125533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, C.L. Contrasting Styles of Metamorphic to Metasomatic Deposits of Gemstones in Cabo Delgado, Northern Mozambique. Inżynieria Mineralna 2024, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmer, W.A.; Hauzenberger, C.A.; Fritz, H.; Sutthirat, C. Marble-hosted ruby deposits of the Morogoro Region, Tanzania. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 134, 626–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
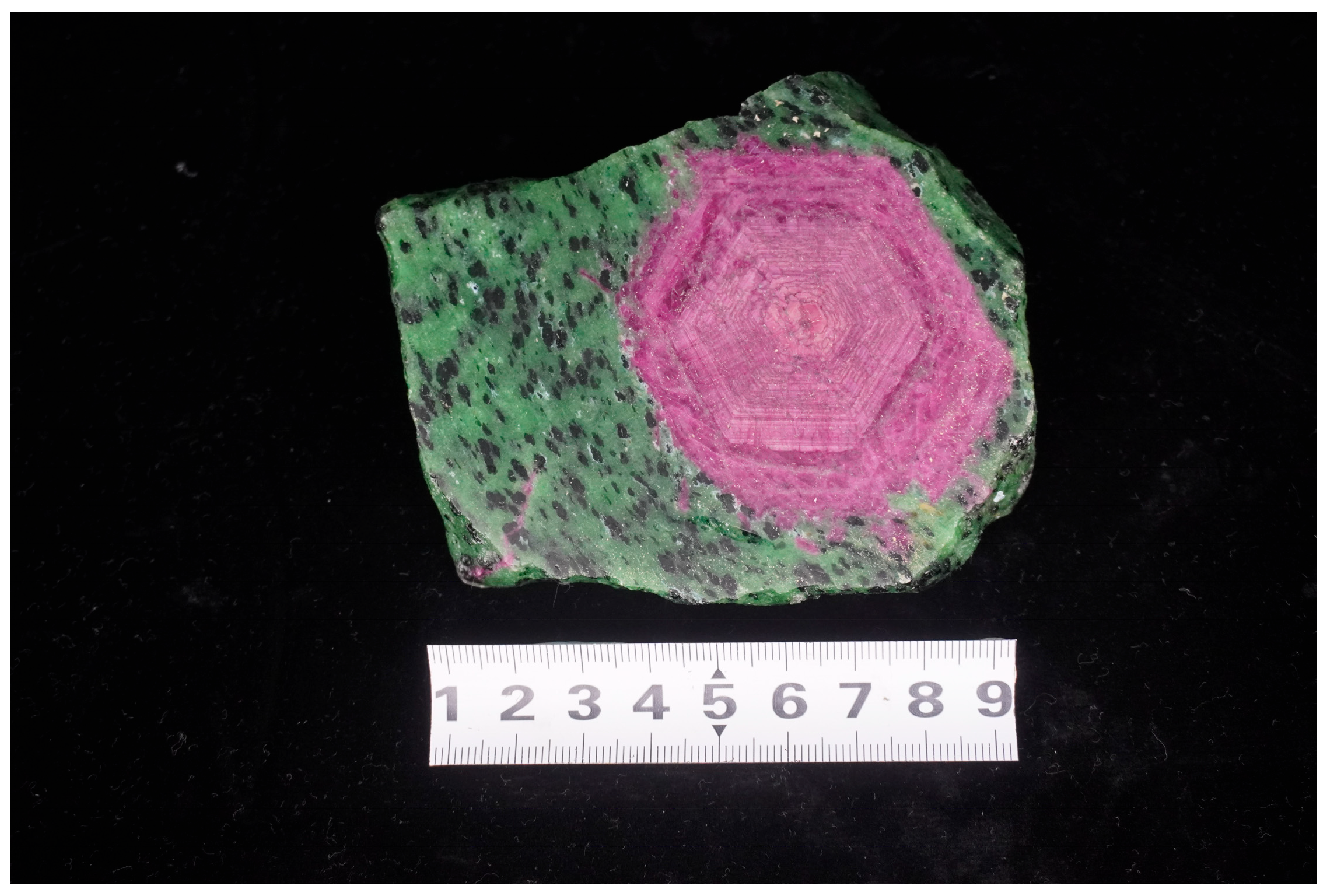



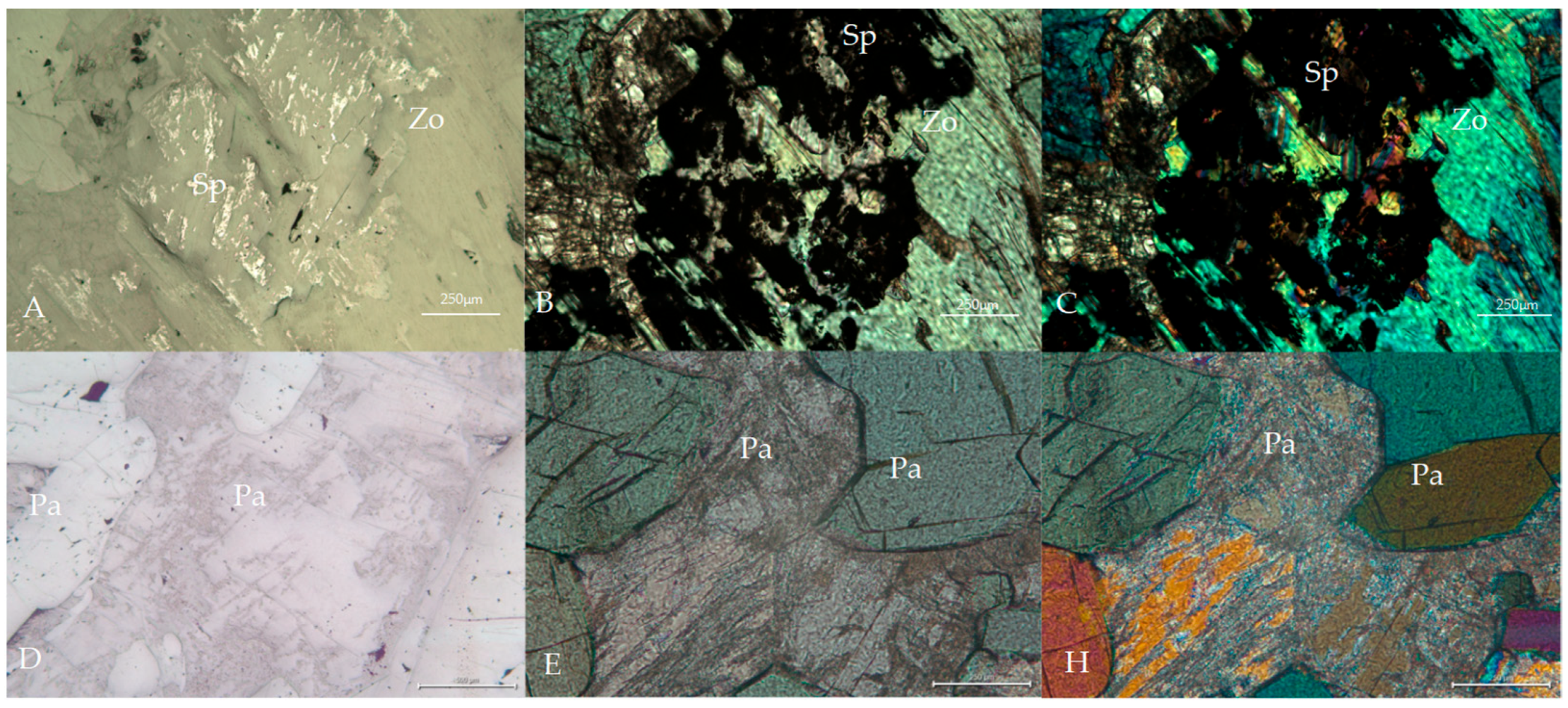
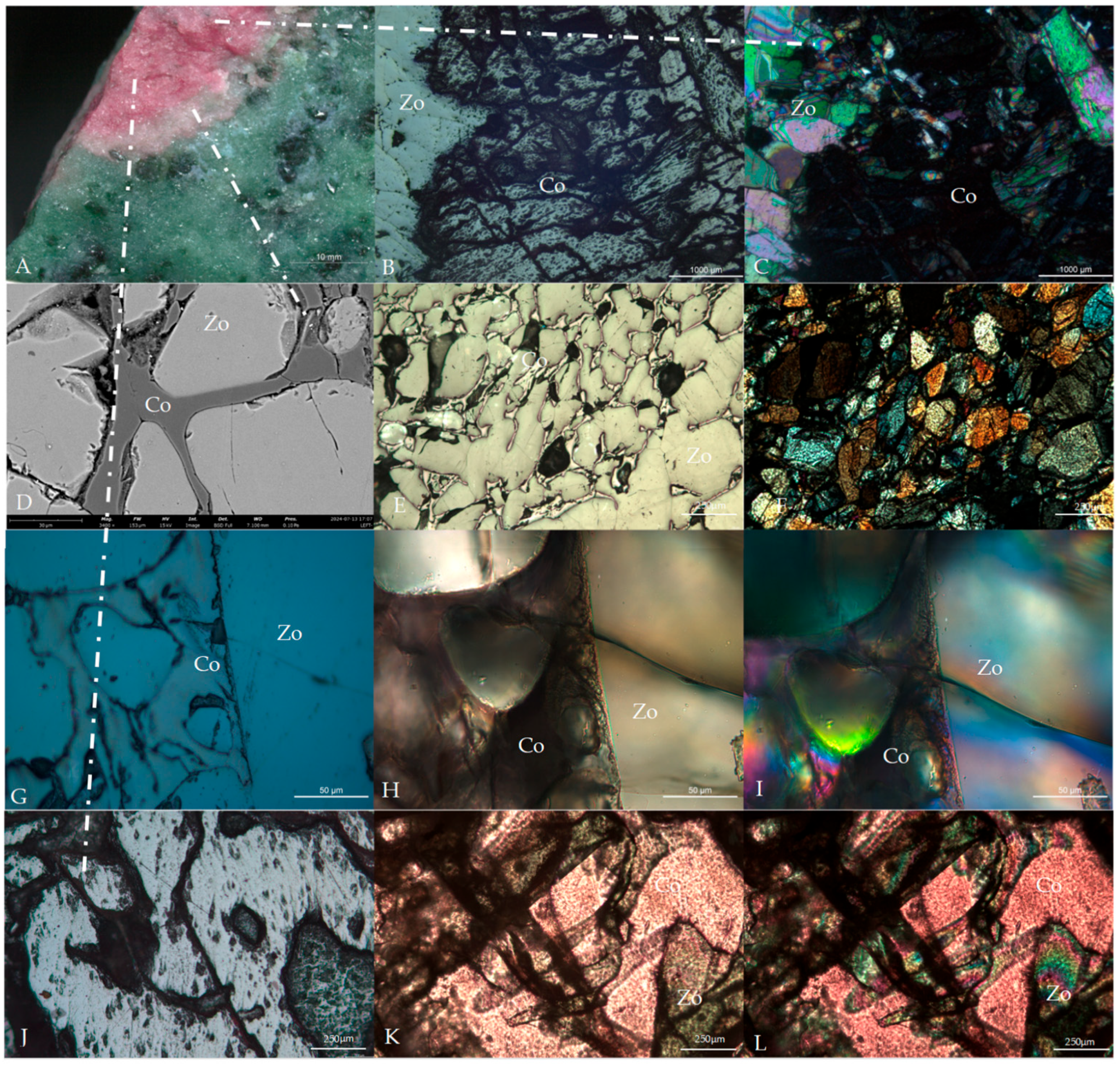
| Ore Deposit Type | Occurrence | Geological Background | Ore District | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metamorphic type | Marble-type | In calcareous crystalline granite | The interpolation of marble or the contact between marble and gneiss in metamorphic rock series in orogenic zone | Morogoro Mahenge |
| Desilicated pegmatite type | In syenite pegmatite and granite pegmatite, desilicated pegmatite cuts ultramafic rock | Desilicification aluminum-rich metasomatism | Umba | |
| Metasomatic metamorphic type | In metasomatic M-UMR | Fluid–rock interaction and metasomatism | Morogoro Mahenge | |
| M-UMR | In metamorphic amphibolite- Granulite, etc. | Metamorphism occurs in the desilicated aluminous or gneiss adjacent to ultramafic rocks | Winza | |
| In the zoisite | Longido | |||
| Sedimentary type | Songea Tunduru Winza | |||
| Mineral | Texture | Structure | Additional Notes | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zoisite | Massive, schistose | Euhedral-subhedral | Dominant phase (~75 vol.%) | Ca2Al3(SiO4)3(OH) |
| Pargasite | Disseminated, banded | Euhedral/anbhedral | ~10 vol.% | NaCa2(Mg4Al)(Si6Al2)O22(OH)2 |
| Corundum | Banded, massive | Euhedral/anhedral | ~5% vol.% | Al2O3 |
| Omphacite | - | Euhedral-subhedral | Inclusions | (Ca,Na)(Mg,Fe2+,Fe3+,Al)(Si2O6) |
| Margarite | - | Relic replacement | Inclusions | CaAl2[Si2Al2O10](OH)2 |
| Spinel | - | Euhedral | Inclusions | Fe(Al,Cr,Fe)2O4 |
| Mineral | Pre Mineralization | Main Mineralization |
|---|---|---|
| Mica 1 |  | |
| Spinel |  | |
| Pargasite |  | |
| Epidote |  | |
| Zoisite |  | |
| Corundum |  |
| Sample | Cr | Fe | Ga | Mg | Na | V | Ti | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R 1 | 1986.25 | 651.49 | 9.00 | 5.67 | - | 1.53 | 40.13 | 859.30 |
| R 2 | 2006.25 | 635.51 | 8.01 | 754.77 | - | 1.76 | 11.73 | 1174.00 |
| TR 1 | 1232.49 | 1457.95 | 9.76 | 4.31 | 3.55 | 4.26 | 16.87 | 11,419.63 |
| TR 2 | 8105.32 | 2997.50 | 29.27 | 5.08 | - | 4.77 | 93.04 | 7153.84 |
| Zo 1 | 35,696.36 | 202.074 | 66.35 | 13.36 | 6.59 | 147.18 | 84.07 | - |
| Zo 2 | 3857.40 | 15,202.09 | 17.53 | 318.43 | - | 34.37 | 76.00 | - |
| Zo 3 | 4610.19 | 16,624.67 | 17.69 | 895.00 | 81.86 | 30.12 | 75.52 | - |
| Zo 4 | 2479.21 | 13,133.19 | 16.85 | 233.06 | 8.16 | 28.32 | 82.90 | - |
| Pa 1 | 3374.18 | 39,947.05 | 9.83 | 69,128.54 | 18,442.38 | 62.49 | 764.38 | - |
| Pa 2 | 4832.46 | 37,489.07 | 79.09 | 58,315.18 | 3808.95 | 45.96 | 333.11 | - |
| Sample Number | FeO–MgO–V2O3–Cr2O3 | FeO+TiO2+Ga2O3 |
|---|---|---|
| R 1 | −0.30 | 0.27 |
| R 2 | −0.07 | 0.33 |
| TR 1 | −0.29 | 0.25 |
| TR 2 | −0.28 | 0.29 |
| Sample Number | Al2O3 | SiO2 | MgO | CaO | FeO | Cr2O3 | Na2O | K2O | NiO | ZnO | TiO2 | SrO | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red corundum matrix 1 | 98.36 | 0.03 | - | - | 0.24 | 0.54 | 0.01 | - | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.03 | - | 99.28 |
| Red corundum matrix 2 | 98.51 | 0.11 | - | - | 0.33 | 0.4 | 0.02 | - | 0.02 | 0.05 | - | - | 99.44 |
| Transitional red corundum 1 | 97.79 | 0.04 | - | - | 0.25 | 0.54 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.02 | 98.64 |
| Transitional red corundum 2 | 97.76 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.27 | 0.55 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 98.85 |
| Zoisite1 | 31.51 | 40.75 | 0.06 | 23.95 | 1.28 | 0.47 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 98.31 |
| Zoisite2 | 32.08 | 39.28 | 0.05 | 23.4 | 0.92 | 0.36 | - | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 96.34 |
| Zoisite3 | 31.59 | 39.81 | 0.06 | 23.98 | 1.29 | 0.28 | - | - | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 97.27 |
| Pargasite1 | 17.5 | 42.74 | 15.71 | 12.59 | 5.39 | 2.1 | 2.52 | 0.37 | - | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 99.18 |
| Pargasite2 | 18.06 | 43.04 | 14.78 | 12.74 | 5.76 | 1.3 | 2.47 | 0.41 | - | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 98.84 |
| Pargasite3 | 18.2 | 41.83 | 14.76 | 12.44 | 5.63 | 1.44 | 2.41 | 0.42 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 97.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; He, M.; Fei, C.; Zheng, H.; Li, X. Deciphering the Tanzanian Ruby–Zoisite Enigma: A Confluence of Geochemistry, Microtextures, and Mineralogy. Crystals 2025, 15, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110926
Yang L, He M, Fei C, Zheng H, Li X. Deciphering the Tanzanian Ruby–Zoisite Enigma: A Confluence of Geochemistry, Microtextures, and Mineralogy. Crystals. 2025; 15(11):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110926
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ling, Mingyue He, Cui Fei, Hairong Zheng, and Xinjie Li. 2025. "Deciphering the Tanzanian Ruby–Zoisite Enigma: A Confluence of Geochemistry, Microtextures, and Mineralogy" Crystals 15, no. 11: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110926
APA StyleYang, L., He, M., Fei, C., Zheng, H., & Li, X. (2025). Deciphering the Tanzanian Ruby–Zoisite Enigma: A Confluence of Geochemistry, Microtextures, and Mineralogy. Crystals, 15(11), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110926





