Abstract
Three lightweight aluminum-based complex concentrated alloys with chemical compositions that have not been previously studied were manufactured and studied: Al52Mg9.6Zn16Cu15.5Si6.9 w.t.% or Al63Mg13Zn8Cu8Si8 a.t.% (alloy A), Al44Mg18Zn19Cu19 w.t.% or Al55Mg25Zn10Cu10 a.t.% (alloy B), and Al47Mg21.4Zn12Cu9.7Si9.7 w.t.% or Al52.7Mg26.6Zn5.6Cu4.6Si10.4 a.t.% (alloy AM), with low densities of 3.15 g/cm3, 3.18 g/cm3 and 2.73 g/cm3, respectively. During alloy design, the CALPHAD method was used to calculate a variety of phase diagrams for the various chemical compositions and to predict possible phases that may form in the alloy. The CALPHAD methodology results showed good agreement with the experimental results. The potential of the designed alloys to be used in some industrial applications was examined by manufacturing them using standard industrial techniques, something that is a rarity in this field. The alloys were produced using an induction furnace and pour mold casting process, while industrial-grade raw materials were utilized. Heat treatments with different soaking times were performed in order to evaluate the possibility of improving the mechanical properties of the alloys. Alloys A and AM were characterized by a multiphase microstructure with a dendritic FCC-Al matrix phase and various secondary phases (Q-AlCuMgSi, Al2Cu and Mg2Si), while alloy B consisted of a parent phase T-Mg32(Al,Zn)49 and the secondary phases α-Al and Mg2Si. The microstructure of the cast alloys did not appear to be affected by the heat treatments compared to the corresponding as-cast specimens. However, alterations were observed in terms of the elemental composition of the phases in alloy A. In order to investigate and evaluate the mechanical properties of the as-cast and heat-treated alloys, hardness testing along with electrical conductivity measurements were conducted at room temperature. Among the as-cast samples, alloy AM had the highest hardness (246 HV4), while among the heat-treated ones, alloy A showed the highest value (256 HV4). The electrical conductivity of all the alloys increased after the heat treatment, with the highest increase occurring during the first 4 h of the heat treatment.
1. Introduction
In the automotive industry, reducing the vehicle’s weight is the primary goal in order to lower fuel consumption and CO2 emissions. Aluminum, with its low specific weight and excellent mechanical properties, plays a key role in achieving this objective [1]. An average car (1300–1400 kg) contains approximately 180 kg of aluminum, of which, 65% (117 kg) is cast aluminum—about 10% of the vehicle’s total weight [2,3]. Notably, reducing a vehicle’s weight by 1 kg can prevent 20 kg of CO2 emissions over its lifecycle [4].
The key cast aluminum components include cylinder heads, engine blocks, pistons, brake calipers, rims, and crankcases. Pistons, subjected to high mechanical and thermal loads, require alloys with high strength, hardness, and thermal stability [5]. Cylinder heads and engine blocks prioritize strength, thermal conductivity, and recyclability, with recycled aluminum gaining importance over primary aluminum as a raw material [5]. Common alloys such as AlCu4MgSi (A206), AlSi10Mg (A360), and AlSi9Cu3 (A380) are widely used, though the adoption of cast aluminum in automotive applications is expected to decline [2]. Therefore, continuous research is being carried out to develop novel low-density alloys, which will have the required properties at a reasonable cost in order to replace Al cast components.
Aluminum alloys are essential in internal combustion engine (ICE) applications, where they must exhibit high strength, fatigue resistance, and thermal stability [6]. While traditional Al-Si alloys have dominated due to their casting properties and mechanical performance [6], sustainability goals have prompted exploration of complex concentrated alloys (CCAs). These CCAs can incorporate recycled aluminum scrap with a high alloying element content, transforming post-consumer waste into valuable raw materials. This approach conserves natural resources, while reducing energy consumption and the carbon footprint of aluminum production. The innovative use of “dirty” alloys, as highlighted by Raabe et al., enables the development of advanced aluminum alloys that meet stringent mechanical requirements while promoting a circular economy by leveraging sustainable raw materials [7].
In this direction, along with the CCAs, the Lightweight High-Entropy Alloys (LWHEAs) could offer an alternative. In general, High-Entropy Alloys (HEAs) constitute a relatively new field of research that is trying to subvert and revitalize the materials science sector’s way of thinking about alloying design strategies. Lightweight High Entropy Alloys (LWHEAs) are defined as alloys with a density less than or equal to that of commercial titanium alloys (4.51 g/cm3) [8]. In other publications, alloys with a density lower than the density of an alloy used for a particular application are considered LWHEAs [9].
By definition, HEAs or equiatomic multicomponent alloys are composed of at least five metallic elements in equimolar or near-equimolar ratios [10]. Yeh et al. proposed a classification of the alloys based on their configurational entropy (ΔSconf). The alloys were classified as HEAs if their ΔSconf in a random state is greater than 1.5 R (R being the gas constant); as Medium-Entropy Alloys (MEAs) when the value of their ΔSconf is in the range of 1R-1.5 R; and finally, traditional alloys are classified as Low-Entropy Alloys, with a ΔSconf less than 1R. The concept of HEAs was initially based on the theory that an increase in the number of alloying elements would result in an increase in the ΔSconf of such systems and it would promote solid-solution (SS) structures, such as FCC and BCC structures [10]. However, now that this field is more scientifically mature, this effect is not considered to be as great as was initially believed [11], since the addition of more components has been proven to lead to the formation of second phases [12]. Therefore, since the limitation of single-phase SS microstructures was surpassed, the term CCAs [8] was introduced, which enables a greater degree of freedom in the design and development of novel compositions with a more complex microstructure, which could provide broader potential comparing to HEAs. Multiphase HEAs, known as CCAs [13], are now mainly composed of two or more phases, sharing similar core effects with HEAs and are a unique subject of research [14]. High-Entropy Aluminum Alloys (HEAls), a promising derivative of HEAs, were recently introduced by Asadikiya et al. as a novel category of aluminum alloys [15]. Although, their entropy is lower than that of traditional HEAs, HEAls still take advantage of it to achieve enhanced properties [16]. The formation of intermetallics (ICs) in HEAls is inevitable due to the high negative enthalpy of mixing (ΔHmix) between Al and most of the commonly employed alloying elements [4]. As a result, HEAls generally feature multiphase microstructures with α-Al solid-solution phases reinforced by multicomponent ICs. Mundrha et al. proposed this novel approach as robust design direction to create high-performance Al alloys strengthened with multicomponent ICs [9].
HEAs, MEAs, and CCAs are usually manufactured using expensive high-purity raw materials and vacuum arc melting and vacuum induction melting techniques, in an Ar or N2 protective atmosphere, and cast in water-cooled copper molds [15]. However, in order to scale up the production of these alloys, a more industrially applicable approach is necessary [9,16]. In the industry, instead of high-purity raw materials, industrial-grade raw materials are used, making the large-scale production of metals sustainable [14,17]. Thus, the concept of a circular economy is capitalized on and added value is created for lower-purity materials [18,19,20]. The aim of the current project was to design alloys using standard industrial techniques and economically viable raw materials.
Barnett et al. introduced a scrap-tolerant alloying concept based on HEAs, highlighting compositional flexibility as a pathway to create value from waste alloys [18]. HEAls are promising for high-wear, high-temperature applications, and as candidate materials for circular product design. Their multicomponent, multiphase compositions also render them suitable for manufacturing using recycled scrap materials.
There have been several studies of promising Lightweight HEAs (LWHEAs) using Al as the principal element. Lei Shao et al. developed a series of low-density alloys with Al and Mg as the main components, accounting for 90 at.% of the alloy, with the remaining components consisting of Cu, Zn, and Si [21]. These alloys were prepared using pure raw materials in an Ar protective atmosphere and they presented densities ranging from 2.64 to 2.75 g/cm3 and compression strengths of up to 814 MPa. Their microstructure consisted of various large intermetallic phases such as Mg2Si and Mg32(AlZn)49 within an aluminum matrix. Using the same components, Sanchez et al, through Thermocalc software (TCAL5 database), designed two systems, Al65Cu5Mg5Si15Zn5X5 and Al70Cr5Cu5Mg5Si10Zn5X5, where the elements Fe, Ni, Cr, Mn, and Zr were introduced in place of X. The best results were from the Al70Cr5Cu5Mg5Si10Zn5 at.% alloy, which consisted of Al2Cu, Mg2Si, and Al13Cr4Si4 intermetallic phases in an aluminum matrix with compressive strength of 490 MPa, plastic deformation of 6%, and microhardness of 200HV0.1. The rest of the alloys demonstrated slightly higher strengths and hardnesses, but the majority exhibited embrittlement behaviors [13]. Following his original research, Sanchez designed a number of LWHEAs by testing various combinations of compositions with the primary elements Al, Mg, Cu, Zn, and Si and additional elements Ca, Ti, Sn, Mn, Ni, and Fe [8,22,23]. The results of his work revealed that with the HEA design strategy, hardness values ranging from 437 HV to 916 HV with densities in the range of 3.15–5.10 g/cm3 could be achieved. In further continuation of this design strategy, Sanchez et al. designed two scrap-tolerant LWHEAs, Al65Cu10Mg10Si10Zn5 and Al80Cu5Mg5Si5Zn5 at.%, with high compressive strengths of 696 and 722 MPa, respectively, due to the formation of ICs [24]. In an attempt to produce alloys with even lower densities, Tun et al. used Li in the composition of their alloys. As a result, they successfully manufactured Al70Li10Mg10Cu5Zn5 and Al75Li10Mg5Cu5Zn5 a.t% systems, with densities of 2.76 g/cm3 and 2.7 g/cm3, respectively. The alloys were prepared using disintegrated melt deposition and ultra-pure raw materials in a protective Ar atmosphere [25] [21]. In fact, the latter alloy, which presented the highest compressive strength (533 MPa), was also examined for its anti-corrosion behavior, with encouraging results [26]. However, Li is a scarce and expensive raw material. More generally, the density found in the LWHEA literature varies between 2.67 g/cm3 and 5.20 g/cm3 [12]. The largest high-entropy alloy reported in the literature is approximately 10 kg with a density of 3.08 g/cm3 and it is the only Al-based CCA, which was prepared by electromagnetic stirring casting. Using this method, a microhardness of 177 HV and compressive strength of 554 MPa were achieved. The most important finding of this work, however, was that the electromagnetic frequency influenced the morphology and distribution of the Mg2Si phase, whose average particle size decreased from 40.0 to 17.7 mm. The research on the Al-Mg-Zn-Cu-Si system is limited to few alloys [27]. Recently, Chaskis et al. designed an Al58Mg18Zn12Cu5Si7 at.% (Al47.4Mg13Zn23Cu9Si6 wt.%) alloy, which displayed a multiphase microstructure consisting of an Al matrix reinforced with various secondary phases, such as Mg2Si and MgZn2. In terms of mechanical properties, the developed alloy exhibited a high hardness value of 249 Vickers and compressive strength of 588 MPa. In this work, it was proven that, if the Mg2Si phase is present in large amounts, it leads to embrittlement of the alloy [28,29]. Nonetheless, the importance of controlling Mg2Si- and Mg-bearing eutectic phases was underlined, since plasticity can be compromised [30]. Therefore, a way to reduce the size and the percentage of this phase is deemed important.
However, most studies on these alloys have focused solely on hardness and compressive strength, with limited investigation into other mechanical properties. Additionally, alloy designs often lack application-specific targets, complicating the assessment of their potential to replace existing commercial materials. Moreover, the reliance on protective atmospheres and high-purity raw materials in HEA production significantly increases costs.
The motor contributes slightly to the overall vehicle weight, but sustainability demands innovative solutions to repurpose cast aluminum alloys from machine parts and utilize them as raw materials. These alloys, with their high alloying content, are unsuitable for malleable products and require alternatives for use in next-generation internal combustion engines (ICEs) or other cast aluminum components. For example, Tesla utilizes two die-cast aluminum parts for the chassis of its models, highlighting opportunities for aluminum-based CCAs in a circular product design approach.
To evaluate their industrial potential, the alloys in this study were manufactured in a standard induction furnace without a protective atmosphere, using industrial purity raw materials from the Greek metallurgical industry. Developed for cast aluminum automotive components, the alloys were compared with 3xx and 7xx series casting alloys since they combine elements from these groupings. This research aimed to develop lightweight aluminum-based alloys in the Al-Mg-Cu-Zn-Si and Al-Mg-Cu-Zn systems using an industry-relevant approach.
In this work, the term HEAs is used for single-phase alloys with a ΔSconf greater than 1.5 R. The term CCAs is used for multiphase alloys with a ΔSconf greater than 1.5 R. Finally, MEAs have a ΔSconf that lies between 1 R and 1.5 R. Since MEAs can also be multiphase alloys, in order to better describe the manufactured alloys under investigation, the term CCAs was adopted. The developed alloys could offer a lightweight alternative to some other aluminum alloys, while promoting a sustainable alloy design approach utilizing raw materials commonly used in industry practices. Moreover, the compositional design focuses on controlling the size and the percentage of specific phases found in earlier studies. This work provides valuable information for researchers aiming to design and produce industry-like aluminum-based CCAs with an industrially relevant approach.
2. Materials and Methods
In this work, the Al-Mg-Cu-Zn-Si and Al-Mg-Cu-Zn systems were selected for study. Aluminum was chosen to be the main component of the alloy due to its low specific weight, combined with its excellent mechanical properties and recyclability [1]. The remaining components were selected based on certain criteria, such as
- Widely available components in the Greek metallurgical industry.
- Does not significantly increase the specific weight of the alloy.
- Provides positive properties to the alloy for its final application.
The components Mg, Zn, Cu, and Si satisfy most of the requirements and were therefore considered the most suitable. The design of the first system was based on the restriction of the Mg2Si phase in a controlled quantity. Although this phase is known to enhance the hardness of commercial aluminum alloys [31], when present in large amounts, it has been proven to lead to embrittlement of the alloy [28,29] due to its high hardness in contrast to the neighboring phases. It is also known that Al-Cu alloys exhibit deteriorated casting properties, which significantly limits the production of these alloys. Additionally, they do not respond to aging heat treatments, preventing the achievement of higher levels of strengthening [30]. Thus, the chemical composition of the first alloy (alloy A—Al63Mg13Zn8Cu8Si8 a.t.%) was chosen with the aim of having a very low percentage of the Mg2Si phase according to the Thermocalc software’s calculations (TCAL7 database). The design of the second system (alloy B—Al55Mg25Zn10Cu10 a.t.%) was based on the complete absence of the Μg2Si phase, so that the properties of an Al-based HEA without its presence could be examined. Finally, the purpose of the third alloy (alloy AM—Al52.7Mg26.6Zn5.6Cu4.6Si10.4 a.t.%) design was to test the limits of adding Mg to an HΕA without ignition occurring in the melt pool.
For the purpose of designing HEAs and CCAs, some thermo-physical parameters, based on Hume–Rothery rules and thermodynamic parameters, were taken into account [32]. These criteria consist of parameters such as the enthalpy of mixing in the liquid phase (ΔHmix), atomic size difference (r), Pauling electronegativity difference (Δχ), and Ω parameter. In the current study, the artificial neural network software pyMPEALab Toolkit (Upadesh Subedi et al.) was used for the thermodynamic calculations, as a means of calculating the thermo-physical parameters of the chosen alloys [33].
Thermocalc® software (Version 2022a, Thermo-Calc Software AB, Stockholm, Sweden) in conjunction with the TCAL7 [34] thermodynamic database was used to calculate a variety of phase diagrams for various chemical compositions with the selected components during the alloy development process. ThermoCalc® software utilizes the CALPHAD (CALculation of PHAse Diagrams) method which has been extensively used in the prediction of the thermodynamic equilibrium of multicomponent systems. In the CALPHAD method, the thermodynamic equilibrium is predicted by minimizing the total ΔG for a certain temperature, pressure, and chemical composition. The TCAL7 database is commonly used for commercial Al alloys and according to previous works, the use of this database for Al-based HEAs shows good agreement with experimental results [8,29]. This tool shows the equilibrium phases as a function of temperature in order to provide an approximate idea of the type of phases that would form in the selected alloy [35].
The experimental alloys were melted in an electrical resistance Ν 41/H Nabertherm furnace under atmospheric conditions and casted into conventional cast iron ingot molds. The raw materials used to produce the alloys consisted of master alloys of industrial purity (such as Al65Cu35, Al50Si50, and Al95Mg5, supporting the approach of scrap-based alloy design), sheets of pure zinc, and tablets of cast bars of pure magnesium. These master alloys are commercially available and their physical characteristics are listed in Table 1. To prevent the oxidation of the elements, casting flux was used to protect the melt pool surface and prior to casting the molten metal, it was skimmed (after each of the alloying additions, the melt was thoroughly stirred with a graphite rod to ensure a homogenous melt without disturbing the metal/flux interface). The ingot was manufactured using a typical furnace pour mold casting method similar to industry practices.

Table 1.
Physical information about the utilized alloying elements and master alloys [29,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45].
For alloys A and AM, master alloys Al65Cu35, Al50Si50 and Al95.5Mg4.5 were added to a steel mold, which was placed in the furnace at 1100 °C. After melting, a bath base at 800 °C was guaranteed. Subsequently, Mg and Zn were added to the molten pool and soaked for 1 h. The reason the direct addition of magnesium and zinc was avoided is because they have a boiling point lower than the initial bath temperature and they would volatilize (see Table 1). Finally, the melt was cooled down to 700 °C and manually poured into a steel mold (pouring temperature of melting: +50 °C superheat).
For alloy B, master alloys Al65Cu35 and Al95.5Mg4.5 were added to the mold together with the pieces of pure magnesium and Zn sheets and placed in the furnace at 700 °C. After melting, the melt was manually poured into a steel mold. For all 3 alloys, before casting, the melt was stirred for at least for 15 min in order to achieve a fully homogenous bath.
Ingots with dimensions of 35 mm × 35 mm × 40 mm were obtained for each alloy, as shown below (Figure 1). Following this, the microstructures of the as-cast and heat-treated alloys at room temperature were studied to evaluate the suitability and behavior of the developed CCAs. The alloys’ density was determined experimentally using the Archimedes Principle [46].
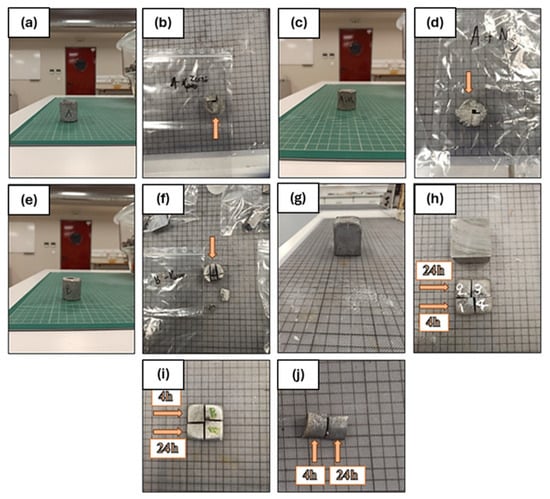
Figure 1.
Specimens before and after sectioning (1 box is equal to 1cm): (a,b) as-cast sample A, (c,d) as-cast sample B, (e,f) as-cast sample AM, (g,h) heat-treated sample A, (i) heat-treated sample B, and (j) heat-treated sample AM.
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) equipment used to characterize the crystal structures of the alloys was a Phillips Xpert diffractometer with a long fine focus copper anode X-ray source and the diffraction diagrams were measured at a diffraction angle of 2θ, in the range from 10° to 110°, with a step size of 0.02°/sec.
Samples were sectioned from the center of the ingot, parallel to the casting direction. Metallographic preparation of the samples was conducted with the appropriate techniques and microscopic observation was performed on as-polished condition, without prior etching using a Nikon Epiphot 300 inverted metallographic microscope.
Specimens AH4, BH4, and AMH4 underwent a solid-solution heat treatment at 400 °C for 4 h, followed by water cooling, while AH24, BH24, and AMH24 were subjected to a heat treatment at 400 °C for 24 h, followed again by water cooling, with the purpose of examining the effect of soaking time. For the heat treatment of the samples, an N 60/85HA Nabertherm furnace was used.
The different regions, the average overall chemical composition of each sample and of the phases in it were investigated using a JEOL JSM-IT800 scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS).
A Vickers hardness Duramin-40 M1 model (Struers, Copenhagen, Denmark) measurer was employed on the polished sample surface using a 4 kg load, which was applied for 10 s. At least 10 random individual measurements were made for each test. At least five specimens were recorded to ensure repeatability. To measure the electrical conductivity, a SIGMATEST D-2.068 (FOERSTER Instruments Inc., Pittsburgh, PA, USA) device was utilized and at least 5 random individual measurements were made for each specimen.
3. Results
3.1. Thermo-Physical Parameters for Phase Formation in HEAs/CCAs
After the preliminary study of the thermo-physical parameters for phase formation in the HEAs and of various equilibrium phase diagrams for the different chemical compositions, the systems that were finally selected were the following: Al52Mg9.6Zn16Cu15.5Si6.9 w.t.% or Al63Mg13Zn8Cu8Si8 a.t.% (alloy A), Al44Mg18Zn19Cu19 w.t.% or Al55Mg25Zn10Cu10 a.t.% (alloy B), and Al47Mg21.4Zn12Cu9.7Si9.7 w.t.% or Al52.7Mg26.6Zn5.6Cu4.6Si10.4 a.t.% (alloy AM) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Chemical compositions of alloys in wt.% and at.% in this work.
In Table 3, the calculated thermo-physical parameters of the defined systems are summarized. The ΔHmix of this system was in the range of −8 to −1 kJ/mole, which is outside the limits required for the formation of SS structures [23]. Additional criteria related to the formation of SS structures in alloys containing low-density elements are δ values below 4.5%, a Δχ equal or below 0.175, and an Ω higher than 10 [23,47]. It is expected that multiphase alloys were obtained regardless of the ΔSmix value, since the ΔHmix i–j between Al and other elements is highly negative [12]. Thus, based the alloy design approach of other studies [13,23,29,48,49,50], the parameters were kept as close as possible to the threshold parameters for SS formation, in order to restrain the formation of excessive amounts of ICs. Following the standard classification of HEAs, all three alloys were categorized as Medium-Entropy Alloys. Nonetheless, maximizing the ΔSmix was not necessary in the developed alloys. In contrast to the main goal of classic HEA design approaches, which is to promote the formation of SS phases, in this study, the formation of multiphase microstructures was promoted to enhance the mechanical properties of the aluminum alloys. To obtain a microstructure composed of a mix of SS structures and ICs, the ΔHmix was kept between −8 kJ/mol and −4 kJ/mol, avoiding excessively high negative values. A decrease in the Al content and absence of Si increased the value of ΔHmix, whereas increases in the Mg and Si contents further decreased the value of ΔHmix. The increased δ in all three alloys highlights the tendency to form intermetallics. On the other hand, in alloy A, the Δχ value indicates that SS structures can be formed, but it is well known that satisfying only one parameter does not promote the formation of SS structures [51,52]. The calculated Ω parameters (ratio between the ΔHmix and the ΔSmix in the liquid state of the alloy) were very far away from the literature’s proposed value of Ω > ~10 for the formation of SS structures in low-density multiprincipal-component alloys [48]. A higher Ω is related to a lower tendency to form complex phases in Al-based multicomponent alloys [53]. In contrast, the Ω value in all three alloys indicated a tendency of promoting intermetallics according to the threshold value proposed for traditional HEAs [12]. Lastly, the Δχ was within the recommended values (under 0.175) for forming SS structures in HEAs for alloys A and B and above that limit for alloy AM [12]. Therefore, mixed microstructures consisting of SS structures and ICs were expected to form based on the known thermo-physical parameters. This was found to be consistent with the CALPHAD calculations for these alloys. The theoretical density of the alloys was calculated using the rule of mixtures.

Table 3.
Thermo-physical parameters and the theoretical density of the developed alloys.
In these systems, a microstructure consisting mainly of an Al-based face-centered cubic (FCC) matrix phase along with other intermetallic compounds was expected to be stable at room temperature.
3.2. CALPHAD Methodology and Equilibrium Phase Diagrams
The equilibrium phase diagrams of the developed alloys are shown in Figure 2. Alloy A was expected to be composed of a mixture of five different phases at equilibrium, namely Al2Cu, α (Al-FCC), C14_Laves (MgZn2), Q (Al4Cu2Mg8Si7), and V (AlCuMgZn), while alloy B was expected to be composed of just three phases, namely α (Al), C14_Laves (MgZn2), and και T (Al2Mg3Zn3 or Mg32(Al,Zn)49). As for alloy AM, it was expected to consist of Al2Cu, α (Al-FCC), C14_Laves (MgZn2), Mg2Si, and T (Mg32(Al,Zn)49).
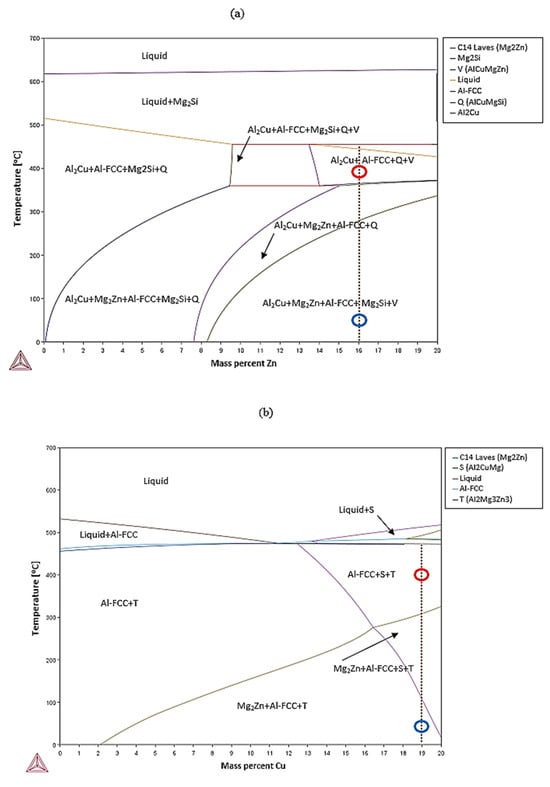
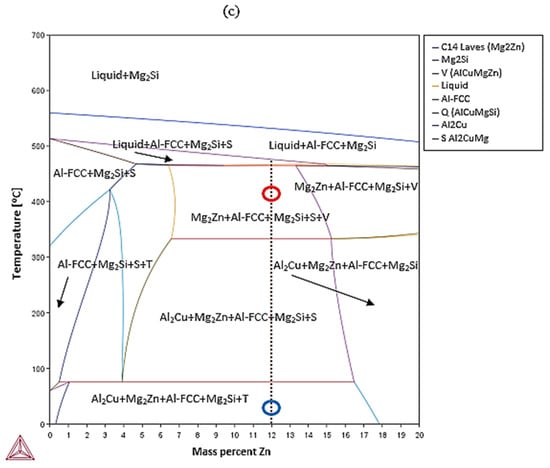
Figure 2.
Al-Zn isopleth pseudo-binary phase diagram for (a) alloy A and (c) alloy AM and Al-Cu isopleth pseudo-binary phase diagram for (b) alloy B. The arrows represent the areas of thermodynamic stability for the various phases. The red circle represents the heat-treatment temperature and the blue circle the room temperature.
A brief description of the aforementioned phases is provided below. The θ (Al2Cu) phase is widely known to enhance the strength of Al-Cu alloys after aging [54] and to form during solidification as well along the grain boundaries in the form of veins or skeletal shapes and after metallic mold casting, they can only be revealed after detailed and meticulous microanalysis [30]. Precipitation of the Q-Al4Cu2Mg8Si7 phase (also known as the Al5Cu2Mg8Si6 or Al3Cu2Mg9Si7 phase) in Al-Cu-Mg-Si quaternary alloys has been demonstrated to improve creep resistance and tensile strength, both at room temperature and at higher temperatures [55]. It was reported that the addition of copper, even with impurities, will promote the formation of the Q phase, which appears as inclusions with sharp and irregularly shaped edges [30]. The C_14 Laves (MgZn2) phase is the most commonly encountered intermetallic phase in all HEAs [56]. It plays an important role in the excellent mechanical properties of the precipitation-hardenable 7xxx series [57]. The Mg2Si phase, as mentioned previously, is a desirable phase in various Al-based alloys to improve the mechanical properties through the formation of intermetallic compounds. It is usually found in plate shapes [58], as octahedron [59] or truncated octahedron blocks [60], and as nano-particles [57]. Finally, the S (Al2CuMg) and T (Mg32(Al,Zn)49 or Al2Mg3Zn3) phases in the 7XXX series are responsible for the increased hardness after aging [61]. The S (Al2CuMg) phase has been reported to provide a strong increase in the hardness of mold-casted alloys [30].
In Table 4, the volume fraction of the formed phases was estimated for the thermodynamic equilibrium conditions.

Table 4.
Volume fraction of phases in the developed alloys at room temperature.
3.3. Microstructural Characterization
3.3.1. Microstructural Characterization of As-Cast Alloys
By studying the as-cast sample A, its dendritic morphology and intense porosity was distinguished (Figure 3), which was more obvious in the upper part of the ingot (part that was in contact with the atmospheric air). Nevertheless, the existence of minor shrinkage porosity did not influence the outcome of the present study, since it can be easily addressed at the industrial scale.
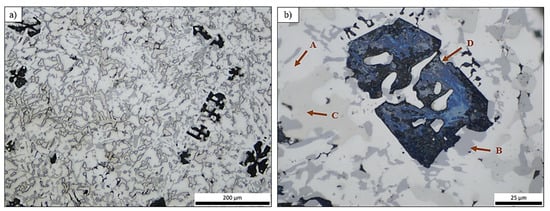
Figure 3.
Optical micrographs of specimen A at (a) center of the middle part of the ingot and (b) edge of the middle part of the ingot. A, B, C, D.
The microstructure of the alloy revealed four distinct phases: a white-colored dendritic phase, which is probably the aluminum base phase (A), a dark grey phase (B), a light grey phase (C), and large dark intermetallic phases (D).
The microstructure of alloy B revealed a dendritic morphology and shrinkage porosity, mainly in the upper part of the cast (Figure 4). At low magnification, it was easy to distinguish two phases: a polygonal phase (A) and a eutectic structure. The eutectic structure consisted of a light-colored dendritic phase (B) and phase (A). The thickness of the B phase was greater than that of A, but the B phase was present in a smaller volume fraction in the microstructure. At higher magnification, a dark angular phase (C) and gray dendritic phase were evident.
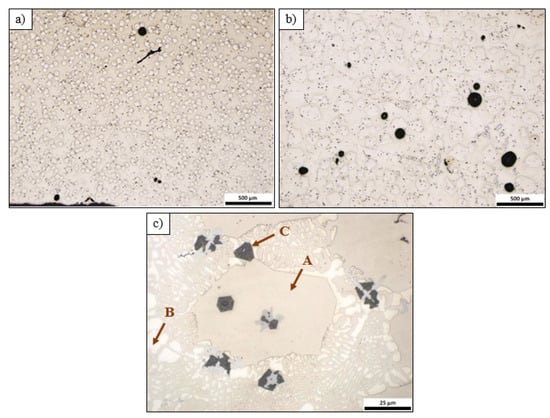
Figure 4.
Optical micrographs of specimen B at (a) edge of the bottom of the ingot and (b,c) center of the bottom of the ingot.
An interesting observation was that the A phases appeared to be larger in the center of the ingot than at the edge. Τhis phenomenon can be attributed to temperature gradients and the cooling rate. At the edge of the mold, the cooling rate is faster than in the center; thus, there is limited time for the phases to grow.
Similar to all the previous castings, alloy AM was characterized by a noticeable dendritic morphology and porosity (greater in the upper part of the ingot) (Figure 5). The microstructure of this alloy revealed three distinct phases: a white-colored dendritic phase, which is probably the aluminum base phase (A); a large dark angular phase (B); and a eutectic structure. At higher magnification, it can be seen that the eutectic structure consisted of small dendrites of phase (A) and a small ecru phase, designated as (C). It is worth mentioning that the dark phases (B) were slightly larger in the center of the ingot than at the edge.
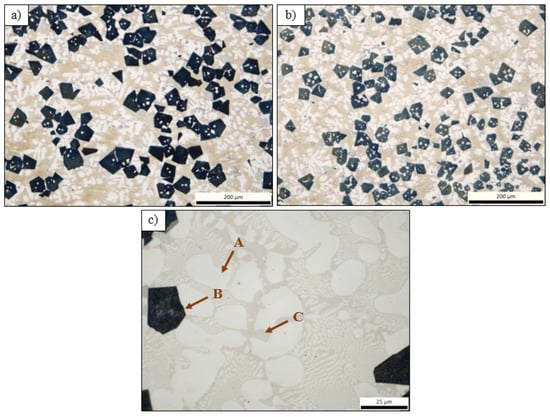
Figure 5.
Optical micrographs of specimen AM from (a) center of the upper part of the ingot and (b,c) edge of the upper part of the ingot.
In all the heat-treated samples (A4, A24, B4, B24, AM4 and AM24), no substantial structure alteration was perceived compared to the corresponding as-cast specimens. Hence, the same main phases as the as-cast samples were identified.
The overall composition of the alloys was estimated using scanning electron microscopy (S.E.M.) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry (E.D.S.) on large areas. At least three random measurements were made, and the overall values are presented in Table 5. The obtained results showed good approximations to the target compositions of the alloys (Table 2). Any deviations could be attributed to (i) partial oxidation of the components during the melting due to the absence of a protective atmosphere and (ii) E.D.S. analyses only providing semi-quantitative information. Therefore, the manufacturing process that was followed, in order to achieve the target compositions, was considered successful.

Table 5.
Indicative chemical composition in wt.% and at.% of the manufactured alloys obtained by EDS.
Table 6 summarizes the phases in alloy A and their chemical compositions, as measured by the EDS analyses. For alloy A, the EDS analysis at spot 1 indicated that this phase is a primary Mg2Si intermetallic compound. Based on the analysis of spot 2, the light white phase in Figure 6 is an Al2Cu phase. Both phases were in good agreement with the Thermocalc predictions at room temperature (RT). The analysis of spot 3 verified the formation of an Al-rich solid-solution matrix with a small amount of Zn. It is interesting to note that there was very good agreement between the composition of this phase and the Al-FCC phase predicted by Thermocalc near the solidus temperature of the alloy, although the composition of the Al-FCC phase at room temperature was significantly different from the one predicted by the EDS analysis. The composition was predicted by Thermocalc under thermodynamic equilibrium conditions, whereas in reality, the cooling rates were faster. This phenomenon needs further investigation and it is worth studying whether it appears in the remaining phases. The analysis of spot 4 showed that this phase consisted of all the components in similar quantities. The composition of this phase was consistent with what Thermocalc predicted as the Q-Al4Cu2Mg8Si7 phase at room temperature and near the solidus temperature. Finally, the analysis performed on spot 5 detected a high content of Fe (11 w.t.%). As can be seen, the main impurity was Fe, which is commonly found in secondary aluminum alloys [62]. The presence of Fe was probably due to impurities, which were included in the industrial purity raw materials. This phase was not predicted during the alloy design and it an AlFeSi-type phase, which is well known in 3xx series alloys with a low Mg content such as Al5FeSi [30]. It is known that all industrial aluminum alloys contain iron-bearing constituents. Such iron-bearing phases tend to not undergo significant changes during heat treatments prior to quenching [30].

Table 6.
Elemental composition of the manufactured alloy in sample A obtained by EDS.
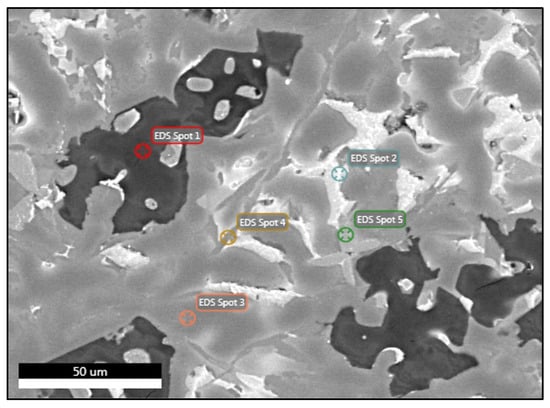
Figure 6.
FESEM backscatter electron microstructure with EDS analysis of selected phases in specimen A.
Qualitative elemental mapping was conducted using EDS to identify the distribution of elements in the observed regions (Figure 7). For a better understanding of the maps, oxygen was ignored due to its insignificant amount in the composition of the alloys. The microstructure showed a matrix composed of an Al-rich area. This region corresponded to the phase predicted by Thermocalc as Al-FCC. The elements Mg and Si were located in the same areas and in places where the Mg2Si phases were found. Si, however, appeared to be found in small amounts in other areas of the cast, possibly in phase C. Finally, Cu appeared to be located in places where the light gray phase B appeared in the OM, which was designated as Al2Cu, while Zn was dispersed throughout the ingot.
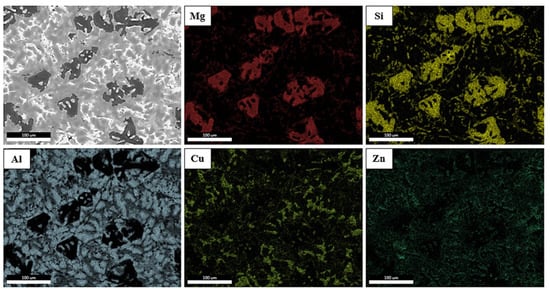
Figure 7.
EDS map of specimen A.
Regarding alloy B, the EDS analysis at area 1 showed that this phase consisted of all the components that constitute the alloy in relatively equal amounts (Figure 8). Table 7 summarizes the phases in alloy B and their chemical compositions, as measured by the EDS analyses. The composition of this phase was highly consistent with that of the phase calculated by Thermocalc near the solidus temperature and reported as the T-Mg32(Al,Zn)49 phase. However, the composition calculated by the software at room temperature deviated significantly from the point analysis results. This phenomenon was also observed in the Al-FCC phase of alloy A. The analysis of spot 1 found that it was enriched in Mg and Si. For alloy B, silicon was not included in the alloy design and it may have derived from the industrial-grade raw materials. It appears that its minimal presence in the melt led to the formation of several Mg2Si phases, much smaller in size than those in alloy A. As for spot 2, it corresponded to an Al-rich phase. This phase is the Al-FCC phase since the Al-FCC composition predicted by Thermocalc near the solidus temperature was predominantly in agreement with that of the spot analysis. In the OM, this phase was visualized as a white color and was designated as phase B (Figure 4). The analysis carried out in the neighboring phase of α (Al-FCC) in the eutectic area showed a composition close to that of the Q-Al4Cu2Mg8Si7 phase. However, due to the relatively small lamellae of the eutectic phase, which were less than 0.5 μm, the measured phase was probably influenced by the neighboring phase so the displayed percentages may deviate from the actual values. Neither the C14 Laves (MgZn2) phase that was predicted at room temperature or the S phase near the solidus temperature were observed.
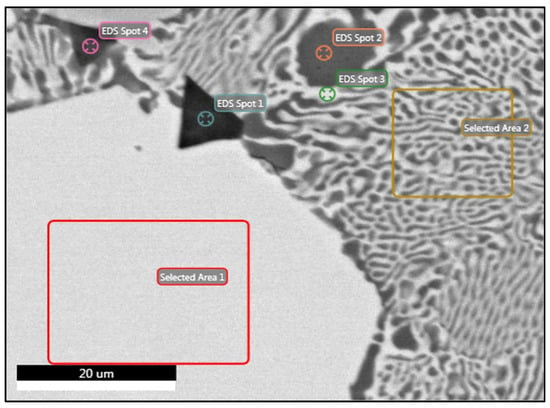
Figure 8.
FESEM backscatter electron microstructure with EDS analysis of selected phases in specimen B.

Table 7.
Elemental composition of the manufactured alloy in sample B obtained by EDS.
Qualitative elemental mapping was conducted using EDS to identify the distribution of elements in the observed regions (Figure 9). It can be seen that Al was mainly distributed in the B phases, identified as α (Al-FCC) in the EDS analysis, and there was a stronger enrichment in the T phase’s grain boundaries. Mg seemed to be more concentrated in the places where there was a presence of Si, which was probably trapped in the melt from the industrial purity raw materials and lead to the formation of Mg2Si phases. As for Cu and Zn, there seems to be a greater concentration of them in the T phase, but in general, they were distributed throughout the cast.
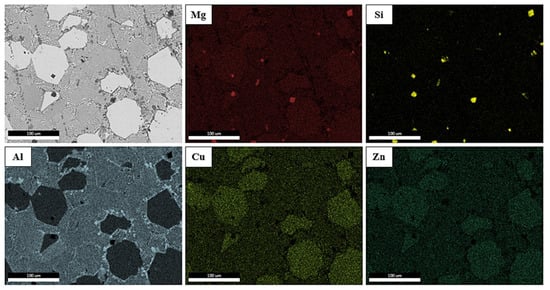
Figure 9.
EDS map of specimen B.
For alloy AM, Table 8 summarizes the phases and their chemical compositions, as measured by the EDS analyses. The analysis at spot 1 (EDS Spot 1) proved that the dark angular phases were Mg2Si phases, as they were overwhelmingly composed of Mg and Si as shown in Figure 10. This confirmed that this was an Mg2Si phase. An expected alteration resulting from the further addition of Mg to the composition of alloy A was the formation of more Mg2Si phases, which were much bigger and angular than those in alloy A. The results from the analysis at spot 2 revealed that the dendrites of phase A were an Al-FCC phase since its composition was in close agreement with that predicted by Thermocalc as an Al-FCC phase near the solidus temperature of the alloy. The analysis at spot 3 indicated that this phase, located in the grain boundaries of the Al-FCC dendrites, showed very high percentages of Al and Cu and a small percentage of Zn. This composition is consistent with the phase predicted by Thermocalc at room temperature as Al2Cu, though it was not detected during the OM observations. Finally, the EDS analysis in the eutectic area (Selected Area 1) where phases A (FCC) and B alternated showed a high percentage of Al and a significant proportion of Cu, Zn, and Mg. The identification of the B phase was difficult due to its very small size (less than 0.5 μm) and therefore the analysis was probably influenced by the neighboring Al-FCC phase. It is not clear whether the phase identified as Al2Cu, based on the analysis of spot 3, corresponded to the B phases alternating with the Al-FCC phases. However, it can be assumed that it was a phase of the T-Mg32(Al,Zn)49 or Q-Al4Cu2Mg8Si7 form, in which all the components that constitute the alloy were present.

Table 8.
Elemental composition of the manufactured alloy in sample AM obtained by EDS.
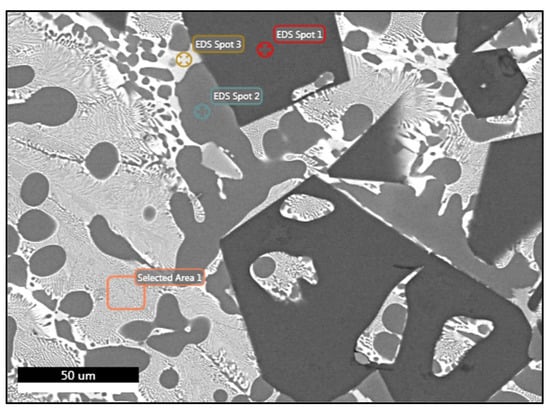
Figure 10.
FESEM backscatter electron microstructure with EDS analysis of selected phases in specimen AM.
By studying the qualitative elemental map from the EDS analysis in Figure 11, it can be seen that Al was mainly found in the large dendrites of the A phase, identified as Al-FCC, and to a lesser extent in the smaller dendrites throughout the cast. The elements Mg and Si were located in the same areas where the presence of Mg2Si phases was evident. Zn and Cu appeared to be uniformly distributed throughout the ingot, in places far from the Mg2Si and Al-FCC phases.
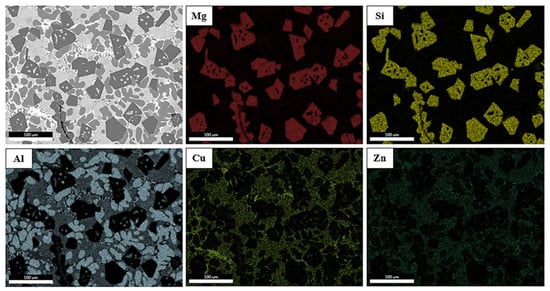
Figure 11.
EDS map of specimen AM.
3.3.2. Microstructural Characterization of Heat-Treated Alloys
Despite the fact that no morphological changes were observed after the heat treatments in alloy A, there were changes in the compositions of its phases, according to the spot analyses which are summarized in Table 9. In particular, the Al-FCC phase displayed a significant decrease in Al (10%), while it was significantly enriched in Zn (13%) as shown in Figure 12. Comparing the spot analysis of the Q phase in the as-cast and the heat-treated samples, a major reduction in Zn (by 11%) was observed. Therefore, it can be assumed that this is where the enrichment of Zn in the Al-FCC phase was derived from. There was also a small drop in the percentages of Al and Cu (2% and 3%, respectively), while significant increases in Mg and Si (8% each) were observed. Mg and Si probably diffused into the Q phase from the interface of the Mg2Si phases or from the Mg2Si into the matrix phase and then to the Q phase, as observed by the small reduction (2%) in these percentages (EDS Spot 1). Nonetheless, distortions in the analysis from the neighboring phases should always be taken into consideration. As for the Al2Cu phase (EDS Spot 3), its composition remained stable after the heat treatment. Regarding the remaining heat-treated samples (B4, B24, AM4, and AM24), no alterations in the compositions of their phases were noted in comparison with the corresponding as-cast specimens.

Table 9.
Elemental composition of the manufactured alloy in heat-treated sample A4 obtained by EDS.
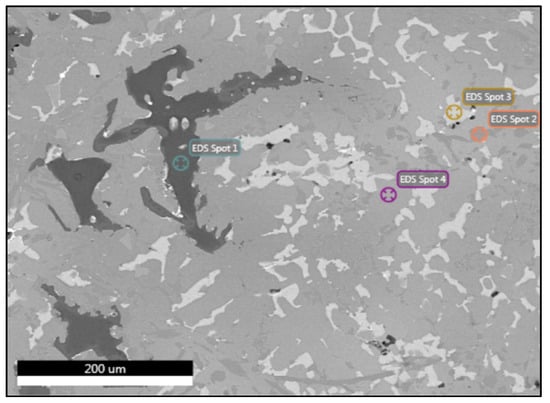
Figure 12.
FESEM backscatter electron microstructure with EDS analysis of selected phases in heat-treated specimen A4.
3.4. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
In addition, diffraction analysis was used to evaluate the produced alloys in order to verify the phases that were identified. In Figure 13, the XRD analysis results for samples A, B, and AM are presented.
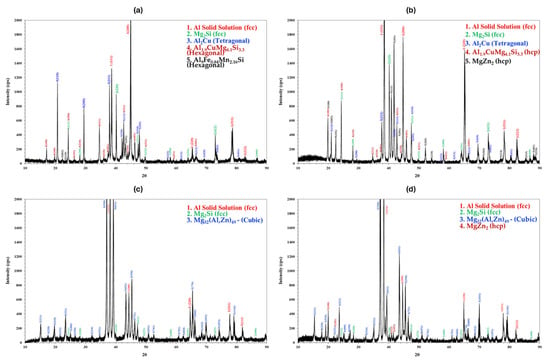
Figure 13.
X-ray diffraction patterns of (a) specimen A, (b) specimen AM, (c) specimen B, and (d) heat-treated specimen B4.
In alloy A, the parent Al-base phase with an FCC structure can be observed. Moreover, the intermetallic phases of Mg2Si (FCC), Al2Cu (Tetragonal), and Al1.9CuMg4.1Si3.3 (Hexagonal), which is the stoichiometric equivalent of the Al4Cu2Mg8Si7–Q phase, were noted. The Al9Fe0.84Mn2.16Si (Hexagonal) is the phase that appeared due to the impurities included in the industrial purity raw materials. As for alloy B, the primary Mg32(Al,Zn)49—T phase (Bergman Cubic) was recognized. Additionally, the Al-base phase (FCC) and Mg2Si phase (FCC) were observed. For alloy AM, the XRD analysis identified the Al-base matrix phase (FCC), along with various intermetallic phases, such as Mg2Si (FCC), Al2Cu (Tetragonal), Al1.9CuMg4.1Si3.3—Q (Hexagonal) and MgZn2 (Hexagonal) phases. Thanks to the XRD analysis, it was obvious that the eutectic lamellae that were not identified in the EDS analysis was the Q phase. Thus, the XRD analysis confirmed the results from the EDS analyses and all the phases were accurately identified.
Regarding the heat-treated samples, only alloy B showed alterations. It was interesting to note that, in the case of the heat-treated B4 alloy, the XRD analysis identified a MgZn2 phase. This could mean that this phase precipitated following the thermal treatment at the nanometer scale. It would be intriguing to use TEM to verify this hypothesis.
3.5. Mechanical and Physical Properties
The hardness of the as-cast and heat-treated alloys at room temperature is shown in Figure 14. Additionally, a hardness/density ratio diagram is presented, with the purpose of evaluating their performance in relation to that of commercial aluminum alloys (Figure 15).
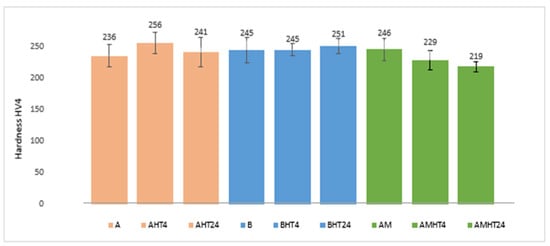
Figure 14.
Hardness values of as-cast and heat-treated samples of manufactured alloys.
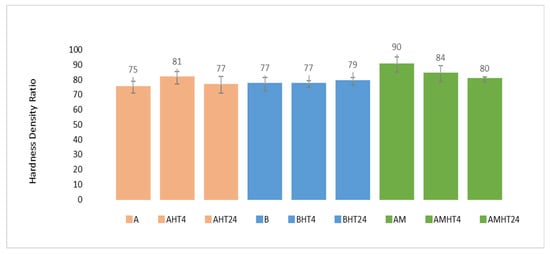
Figure 15.
Hardness/density ratio values of as-cast and heat-treated samples of manufactured alloys.
The hardness of the as-cast and heat-treated alloys was measured at room temperature and the results are shown in Table 10. In addition, the hardness to density ratio is depicted as well.

Table 10.
Average hardness values of as-cast and heat-treated samples of manufactured alloys.
According to hardness measurements, alloy AM had the highest hardness (246 HV4) among the as-cast samples, while from the heat-treated ones, alloy A showed the highest value (256 HV4). In alloy A, the hardness increased by 8.5% in the first 4 h of the heat treatment, followed by a 6% decrease. In alloy B, the hardness remained constant in the first 4 h of the heat treatment, followed by a small increase (2.5%), while in alloy AM, a reduction of 7% in hardness was observed after 4 h of soaking, followed by a reduction of 4% after 24 h of soaking in the furnace. However, comparing the hardness to density ratios, alloy AM showed the highest value both in the as-cast and heat-treated samples. The increase in hardness after the heat treatment for alloys A and B indicates that the most prominent strengthening mechanism was precipitation hardening due to the natural aging effect, while in the case of alloy AM, the decrease in hardness indicates that the main strengthening mechanism was probably solid-solution hardening.
Furthermore, electrical conductivity measurements were conducted in order to estimate the amount of alloying elements that were trapped in the solid solution and diffused/precipitated during the heat treatment stage, as shown in Figure 16. It is evident that after the heat treatment, the electrical conductivity of all the alloys increased, with the highest percentage increase occurring in the first 4 h of the heat treatment. Alloy A presented the highest conductivity values in both conditions (as-cast and heat-treated). Alloy B showed the lowest values, although after a 4 h heat treatment, it demonstrated the largest percentage increase (36%) compared to alloys A and AM, with percentage increases of 7% and 13%, respectively. The fact that the electrical conductivity increased in all three alloys after the heat treatment indicates that the alloying elements diffused from the solid solution, which were trapped during casting and solidification due to the limited time for diffusion, as described as the sluggish diffusion principle that defines HEAs. More importantly, since the greatest percentage increase in conductivity occurred in the first 4 h of the heat treatment, it demonstrates that for sufficient precipitation of the components trapped in the solid solution, 4 h of heat treatment is adequate.
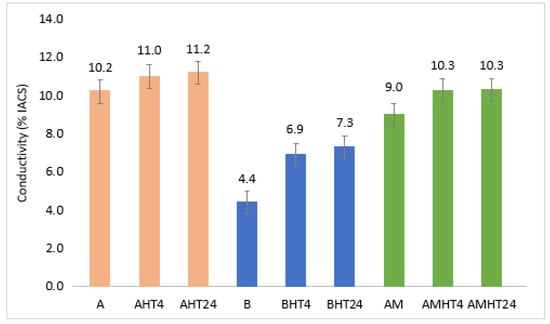
Figure 16.
Conductivity measurements of as-cast and heat-treated specimens.
4. Discussion
4.1. Better Understanding of Al-Based CCA Phase Diagrams Calculated by Thermocalc
The order in which the phases solidified in each of the manufactured alloys will be mentioned bellow, since these were the phases that appeared in the final microstructure at RT.
Based on the phase diagram corresponding to alloy A, when reducing the temperature in the melt, the first phase formed was Mg2Si at about 610 °C. As the temperature decreased to 480 °C, the Al-FCC, Q (Al4Cu2Mg8Si7), Al2Cu, and V (AlCuMgZn) phases began to nucleate until the melt completely solidified at 380 °C. The only phase that was not present in the final microstructure of the alloy was the V phase.
For alloy B, by studying its phase diagram, it was clear that the first phases formed were T (Mg32(Al,Zn)49) and S (Al2CuMg) at about 520 °C. At 480 °C, the eutectic reaction of L = Al-FCC + T (Mg32(Al,Zn)49) was taking place until the melt completely solidified. It should be noted that the S phase was not observed in the final microstructure.
Finally, in alloy AM, at around 700 °C, Mg2Si started forming. As the temperature decreased to 550 °C, Al-FCC (pro-eutectic) began to nucleate, while below 40 °C, the eutectic reaction L = Al-FCC + Q (Al4Cu2Mg8Si7) started taking place until the melt completely solidified. The solidification process was completed before the C14 Laves (MgZn2) and V (AlCuMgZn) phases started to nucleate, since they were not observed in the final microstructure.
This new knowledge and better interpretation of the Al-based CCA phase diagrams will help future research to be more accurate in predicting the final microstructure and consequently will considerably improve CALPHAD alloy design strategies.
4.2. Alloy Design Outcome
The design strategy for alloy A was based on the restriction of the Mg2Si phase to a controlled quantity. Nevertheless, this phase formed to a large extent. Thanks to a better understanding of the phase diagrams due to this research, it was concluded that it is challenging to limit this phase to a controlled quantity, since, according to the phase diagrams (Figure 2), the Mg2Si phase was the first to form and it was found that it remained stable until room temperature was reached.
Therefore, one approach to reduce the percentage of this phase, as demonstrated in the case of alloy B, is to minimize the percentage of Si. However, it was found that even the minimum amount of Si led to a few small-sized Mg2Si phases with a particularly angular morphology, the edges of which may generate crack initiation points and thus make the material brittle [29]. Such an approach did not result in the expected improvement in mechanical properties and brittleness. Another intriguing design direction would be to add an appropriate modifier to the melt in order to convert the angular morphology of the brittle Mg2Si phases into a more spherical one [28]. Lastly, the addition of industrial grain refining, e.g., Ti-B, could be considered as an alternative to controlling the brittle Mg2Si phases. As for alloy AM, it was successfully designed with a major Mg addition, without ignition occurring in the melt pool, and thus a lightweight HEA with a very low density of 2.73 g/cm3 was produced. Nonetheless, Mg2Si is an intermetallic compound, which results in high-hardness alloys and since it has a high melting point, its formation has potential in automotive components where thermal loads are a challenge.
It is important to highlight that the presence of impurities is very likely to lead to the appearance of unexpected phases, which are not predicted by Thermocalc. Therefore, any research intended to produce industry-like Al-based CCAs with a more industrially applicable approach should expect that the utilization of industrial-grade raw materials will create unanticipated phases, which must be taken into account during the alloying design.
For thermal stability, composition design should incorporate an element that will provide coherent precipitates that do not dissolve or coarsen at the operating temperature, e.g., something like Al₃X where X = Sc, Zr, Ti, V, etc.
It is evident that the proposed alloys showed high hardness–density ratios, specifically when compared to other cast aluminum alloys, as shown in Figure 17. These results are very promising, since the newly manufactured alloys have been shown to be an appealing alternative for applications where commercial cast aluminum alloys are used, since the hardness-to-density ratios are higher. Furthermore, this new system can be directly compared with some major LWHEAs from the literature. From an economic point of view, taking into consideration production and cost limitations, all three alloys offer a friendly alternative since they were manufactured with industrial purity raw materials using a common furnace. Although there is still a lot of room for exploration in the field of CCAs, the microstructures and the superior strength-to-density ratios of the investigated alloys in combination with the manufacturing method that focuses on industrial practices can broaden the horizon for various applications in the structural, automotive and energy industries. The assessment of particular properties based on the exact needs can confirm the suitability of alloys for each specific application.
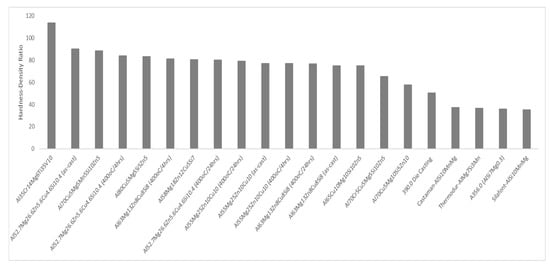
Figure 17.
Comparative diagram of compressive strength hardnesses and density ratios from current study and of various alloys found in commercial applications and in the literature [13,24,29,63,64,65].
5. Conclusions
In this work, three new lightweight aluminum-based CCAs were successfully produced using an industrially relevant approach: Al52Mg9.6Zn16Cu15.5Si6.9 w.t.% or Al63Mg13Zn8Cu8Si8 a.t.% (alloy A), Al44Mg18Zn19Cu19 w.t.% or Al55Mg25Zn10Cu10 a.t.% (alloy B), and Al47Mg21.4Zn12Cu9.7Si9.7 w.t.% or Al52.7Mg26.6Zn5.6Cu4.6Si10.4 a.t.% (alloy AM), with low densities of 3.15 g/cm3, 3.18 g/cm3, and 2.73 g/cm3, respectively. They were manufactured using industrial-grade raw materials, a standard furnace, and a pour mold casting process.
- The Thermocalc software predictions showed good agreement with the experimental results as it successfully predicted the majority of phases that appeared in the alloys. Therefore, Thermocalc can be a useful tool to guide alloy design.
- During the alloy design process, the presence of impurities in industrial-grade raw materials should be taken into consideration since it could lead to the formation of unforeseen phases, though such phases do not undermine the alloy’s properties.
- Alloy AM had the highest hardness (246 HV4) from among the as-cast samples, while from the heat-treated ones, alloy A showed the highest value (256 HV4). By comparing the hardness/density ratios of the alloys of this work with other alloys in the HEA literature and commercial cast Al alloys that are used for automotive pistons, it was evident that they could offer alternatives with a high hardness strength for automotive Al cast pistons.
- Heat treatment was found to induce alterations in the elemental composition of the constitutional phases along with changes in hardness. It was found that natural aging can be used in these alloys to improve their hardness. Alloy A underwent an 8% increase in hardness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C., E.G. and S.P.; methodology, S.C., C.T. and E.G.; software, S.C., C.T., M.B. and F.T.; resources, E.G., M.B. and F.T.; writing—original draft preparation, S.C., C.T., M.B. and F.T.; writing—review and editing, S.C., C.T., E.G., M.B., F.T. and S.P.; visualization, S.C.; supervision, S.C. and S.P.; project administration, S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the Hellenic Research Centre for Metals ELKEME S.A. for supporting this research. We thank E. Stachouli for contributing to the metallography and electron microscopy analyses and A. Flampouri for the design and realization of the casting trials on behalf of ELKEME S.A., V. Loukadakis on behalf of National Technical University of Athens.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Spyridon Chaskis was employed by the company ELVALHALCOR S.A. and authors Dr. Evangelos Gavalas, Dr. Marianthi Bouzouni, Fotis Tsiolis were employed by the company ELKEME S.A. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Poznak, A.; Freiberg, D.; Sanders, P. Automotive Wrought Aluminium Alloys. In Fundamentals of Aluminium Metallurgy; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 333–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducker Frontier. Aluminum Content In European Passenger Cars. Available online: www.duckerfrontier.com (accessed on 2 May 2022).
- European Aluminum. Aluminium Content in Cars Up 20% in the Last Three Years | EURACTIV PR. Available online: https://pr.euractiv.com/pr/aluminium-content-cars-20-last-three-years-195339 (accessed on 2 May 2022).
- Gondhaleka, A.A. Design and Development of Light Weight High Entropy Alloys. Master’s Thesis, JÖNKÖPING University, Jönköping, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aluminium Automotive Manual—European Aluminium. Available online: https://european-aluminium.eu/blog/aluminium-automotive-manual/ (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Koos, R. Correlation Between 3D Microstructure and Thermo-Mechanical Behavior of Near Eutectic Piston Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Wien, Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, D.; Ponge, D.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Roscher, M.; Paolantonio, M.; Liu, C.; Antrekowitsch, H.; Kozeschnik, E.; Seidmann, D.; Gault, B.; et al. Making sustainable aluminum by recycling scrap: The science of “dirty” alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 128, 100947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.; Vicario, I.; Albizuri, J.; Guraya, T.; Garcia, J.C. Phase prediction, microstructure and high hardness of novel light-weight high entropy alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 8, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulik, O.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, S.; Dewangan, S.K.; Kumar, V. Structure and properties of lightweight high entropy alloys: A brief review. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 052001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.J.; Jones, N.G. High-entropy alloys: A critical assessment of their founding principles and future prospects. Int. Mater. Rev. 2016, 61, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.; Vicario, I.; Albizuri, J.; Guraya, T.; Acuña, E.M. Design, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cast Medium Entropy Aluminium Alloys. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.S.; Odbadrakh, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Mu, S.; Körmann, F.; Sun, C.-J.; Ahn, H.S.; Yoon, K.N.; Ma, D.; Tasan, C.C.; et al. Element-resolved local lattice distortion in complex concentrated alloys: An observable signature of electronic effects. Acta Mater. 2021, 216, 117135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.C.; Liaw, P.K.; Yeh, J.W.; Zhang, Y. High-Entropy Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, M. An Insight into Evolution of Light Weight High Entropy Alloys: A Review. Metals 2016, 6, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H. Three Strategies for the Design of Advanced High-Entropy Alloys. Entropy 2016, 18, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.; Senadeera, M.; Fabijanic, D.; Shamlaye, K.; Joseph, J.; Kada, S.; Rana, S.; Gupta, S.; Venkatesh, S. A scrap-tolerant alloying concept based on high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2020, 200, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrica, D.; Badea, I.C.; Serban, B.A.; Olaru, M.T.; Vonica, D.; Burada, M.; Piticescu, R.-R.; Popov, V.V. Complex Concentrated Alloys for Substitution of Critical Raw Materials in Applications for Extreme Conditions. Materials 2021, 14, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaskis, S.; Bouzouni, M.; Gavalas, E.; Loukadakis, V.; Papaefthymiou, S. Development of Complex Concentrated Alloys (CCAs) Utilizing Scrap to Preserve Critical Raw Materials. Mater. Proc. 2022, 5, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. A Low-Cost Lightweight Entropic Alloy with High Strength. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 6648–6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.; Vicario, I.; Albizuri, J.; Guraya, T.; Koval, N.E.; Garcia, J.C. Compound Formation and Microstructure of As-Cast High Entropy Aluminums. Metals 2018, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.; Pascual, A.; Vicario, I.; Albizuri, J.; Guraya, T.; Galarraga, H. Microstructure and Phase Formation of Novel Al80Mg5Sn5Zn5X5 Light-Weight Complex Concentrated Aluminum Alloys. Metals 2021, 11, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.; Galarraga, H.; Del Molino, E.; Albizuri, J.; Guraya, T.; Hudson, S.W. Microstructure and mechanical properties of two novel scrap tolerant Al65Cu10Mg10Si10Zn5 and Al80Cu5Mg5Si5Zn5 high entropy aluminum alloys. Intermetallics 2023, 162, 108023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, K.; Murugan, P.; Srivatsan, T.; Gupta, M. Synthesis and Characterization of aluminium based multicomponent alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, P.; Tun, K.S.; Gupta, M.; Mourad, A.I.; Vincent, S. Electrochemical characterization of a novel multicomponent Al75Mg5Li10Zn5Cu5 low entropy alloy in different pH environments. Mater. Corros. 2022, 73, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.-G. Lightweight Al-based entropy alloys: Overview and future trend. Sci. China Mater. 2023, 67, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Xiang, S.; Lv, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, W. Modification of Mg2Si Phase Morphology in Mg-4Si Alloy by Sb and Nd Additions. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 3678–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaskis, S.; Stachouli, E.; Gavalas, E.; Bouzouni, M.; Papaefthymiou, S. Microstructure, Phase Formation and Heat-Treating of Novel Cast Al-Mg-Zn-Cu-Si Lightweight Complex Concentrated Aluminum Based Alloy. Materials 2022, 15, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolotorevsky, V.S.; Belov, N.A.; Glazoff, M.V. Casting Aluminum Alloys; Elsevier: Amsterdam, NX, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, H.; Dong, X.; Ji, S. The effects of varying Mg and Si levels on the microstructural inhomogeneity and eutectic Mg2Si morphology in die-cast Al–Mg–Si alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 54, 5773–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivatsan, T.S.; Gupta, M. (Eds.) High Entropy Alloys: Innovations, Advances, and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Subedi, U.; Kunwar, A.; Coutinho, Y.A.; Gyanwali, K. pyMPEALab Toolkit for Accelerating Phase Design in Multi-principal Element Alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 28, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo-Calc Software. TCS Al-Based Alloy Database (TCAL7); Thermo-Calc Software, Inc.: McMurray, PA, USA, 2020; Available online: www.thermocalc.com (accessed on 14 June 2022).
- Computational Materials Engineering—Thermo-Calc Software. Available online: https://thermocalc.com/ (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Kuryntsev, S. A Review: Laser Welding of Dissimilar Materials (Al/Fe, Al/Ti, Al/Cu)—Methods and Techniques, Microstructure and Properties. Materials 2021, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electronegativity | Periodic Table of Elements—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ptable/electronegativity/ (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- WebElements Periodic Table ‘Magnesium’ Electronegativity. Available online: https://www.webelements.com/magnesium/electronegativity.html (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Magnesium—Crystal Structure. Available online: https://www.periodic-table.org/magnesium-crystal-structure/?utm_content=cmp-true (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Magnesium—Atomic Radius—Mg. Available online: https://www.periodic-table.org/magnesium-atomic-radius/ (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Lattice Constants for All the Elements in the Periodic Table. Available online: https://periodictable.com/Properties/A/LatticeConstants.html (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Zinc—Periodic Table and Atomic Properties. Available online: https://material-properties.org/zinc-periodic-table-atomic-number-mass-radius-density/ (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Zinc (Zn). Available online: https://periodictable.chemicalaid.com/element.php/Zn?lang=en (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Silicon—Atomic Radius—Si. Available online: https://www.periodic-table.org/silicon-atomic-radius/ (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Silicon—Crystal Structure. Available online: https://www.periodic-table.org/Silicon-crystal-structure/ (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Biran, A.; López-Pulido, R. Basic Ship Hydrostatics. Sh. Hydrostatics Stab. 2014, 23–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, H.; Tajally, M.; Habibolahzadeh, A. Calculations to introduce some light high entropy alloys based on phase formation rules. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 912, 165222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, S.Y.; Cotton, J.D.; Zhang, Y. Phase Stability of Low-Density, Multiprincipal Component Alloys Containing Aluminum, Magnesium, and Lithium. JOM 2014, 66, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrica, D.; Badea, I.C.; Olaru, M.T.; Serban, B.A.; Vonica, D.; Burada, M.; Geanta, V.; Rotariu, A.N.; Stoiciu, F.; Badilita, V.; et al. Modeling and Experimental Results of Selected Lightweight Complex Concentrated Alloys, before and after Heat Treatment. Materials 2020, 13, 4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, H.; Zengin, H. Microstructure, Mechanical and Wear Properties of Low-Density Cast Medium and High Entropy Aluminium Alloys. Int. J. Met. 2022, 16, 1976–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Yeh, J.-W. High-Entropy Alloys: A Critical Review. Mater. Res. Let. 2014, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, C.; Gao, P.; Zhang, F.; Ouyang, L.; Widom, M.; Hawk, J. Thermodynamics of concentrated solid solution alloys. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 21, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.-G. Development of lightweight Al-based entropy alloys for elevated temperature applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 938, 168619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Chen, P.; Li, X.; Liu, Z. Microstructural evolution of Al2Cu phase and mechanical properties of the large-scale Al alloy components under different consecutive manufacturing processes. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 808, 151634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Bobel, A.; Baik, S.-I.; Walker, M.; Voorhees, P.; Olson, G. Enhanced Coarsening Resistance of Q-phase in Aluminum alloys by the addition of Slow Diffusing Solutes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 735, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Tsai, R.-C.; Chang, T.; Huang, W.-F. Intermetallic Phases in High-Entropy Alloys: Statistical Analysis of their Prevalence and Structural Inheritance. Metals 2019, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lervik, A.; Marioara, C.; Kadanik, M.; Walmsley, J.; Milkereit, B.; Holmestad, R. Precipitation in an extruded AA7003 aluminium alloy: Observations of 6xxx-type hardening phases. Mater. Des. 2019, 186, 108204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Jia, Z.; Nie, J.-F.; Weng, Y.; Cao, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, X.; Liu, Q. The structural and compositional evolution of precipitates in Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 145, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Samuel, F.; Al Kahtani, S. Microstructure, tensile properties and fracture behavior of high temperature Al–Si–Mg–Cu cast alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 577, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Morphological evolution and growth mechanism of primary Mg2Si phase in Al–Mg2Si alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, C.; Mukhopadhyay, A. On the nature of T(Al2Mg3Zn3) and S(Al2CuMg) phases present in as-cast and annealed 7055 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 391, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Damoah, L.N.W.; Robertson, D.G. Removal of Iron From Aluminum: A Review. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. Rev. 2012, 33, 99–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wen, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effects of electromagnetic frequency on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al70Zn10Mg10Cu5Si5 medium entropy alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 3105–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Yebaji, S.; Nadakuduru, V.N.; Shanmugasundaram, T. Development of a novel light weight Al35Cr14Mg6Ti35V10 high entropy alloy using mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 820, 153367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluminum Alloys Wrought and Cast Property Data. Available online: https://www.matweb.com/reference/aluminum.aspx (accessed on 7 January 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).