High-Pressure Phases of Boron Pnictides BX (X = As, Sb, Bi) with Quartz Topology from First Principles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Crystal Chemistry
3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.3. Equations of State and Possible High-Pressure Phase Transitions
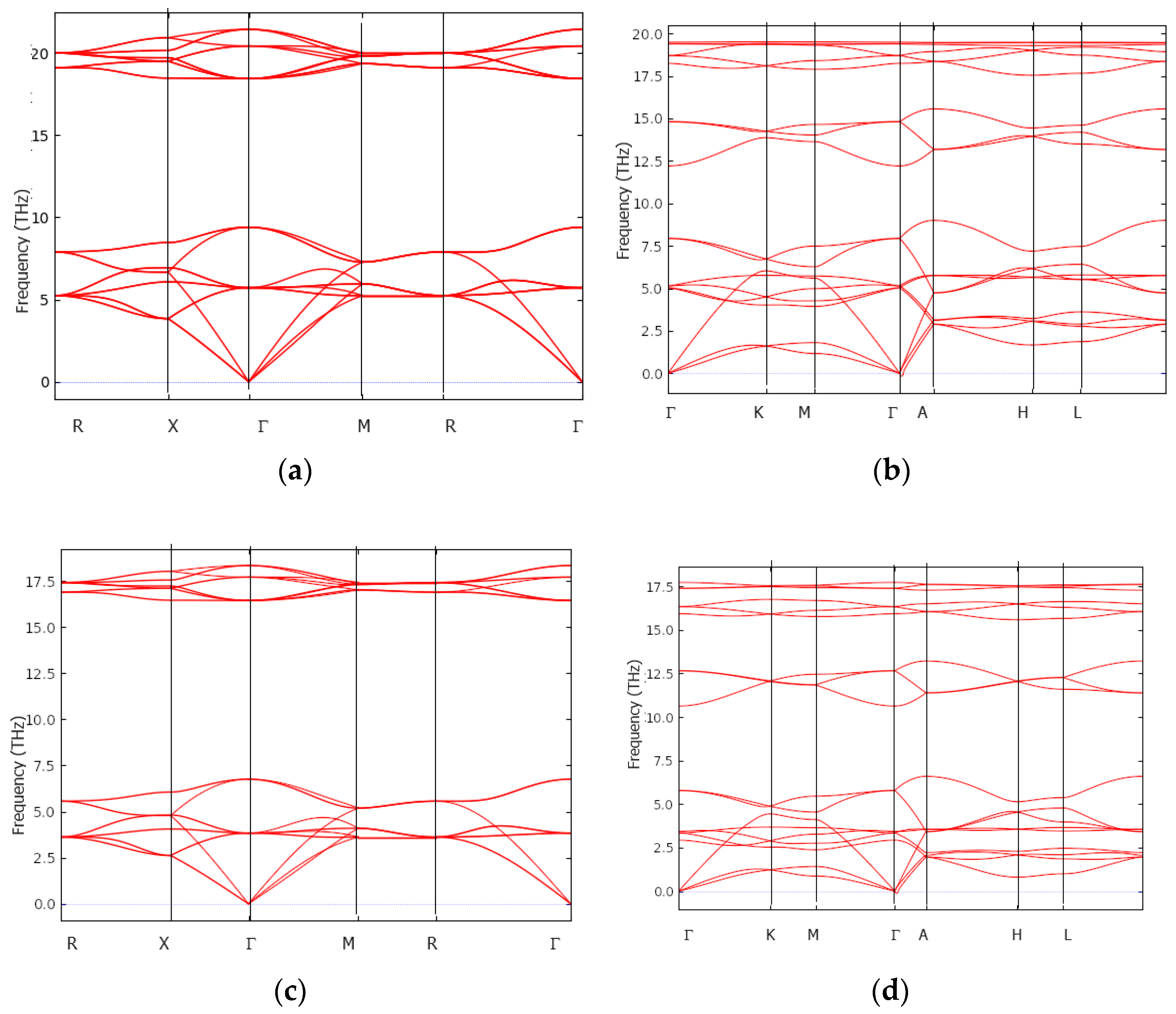
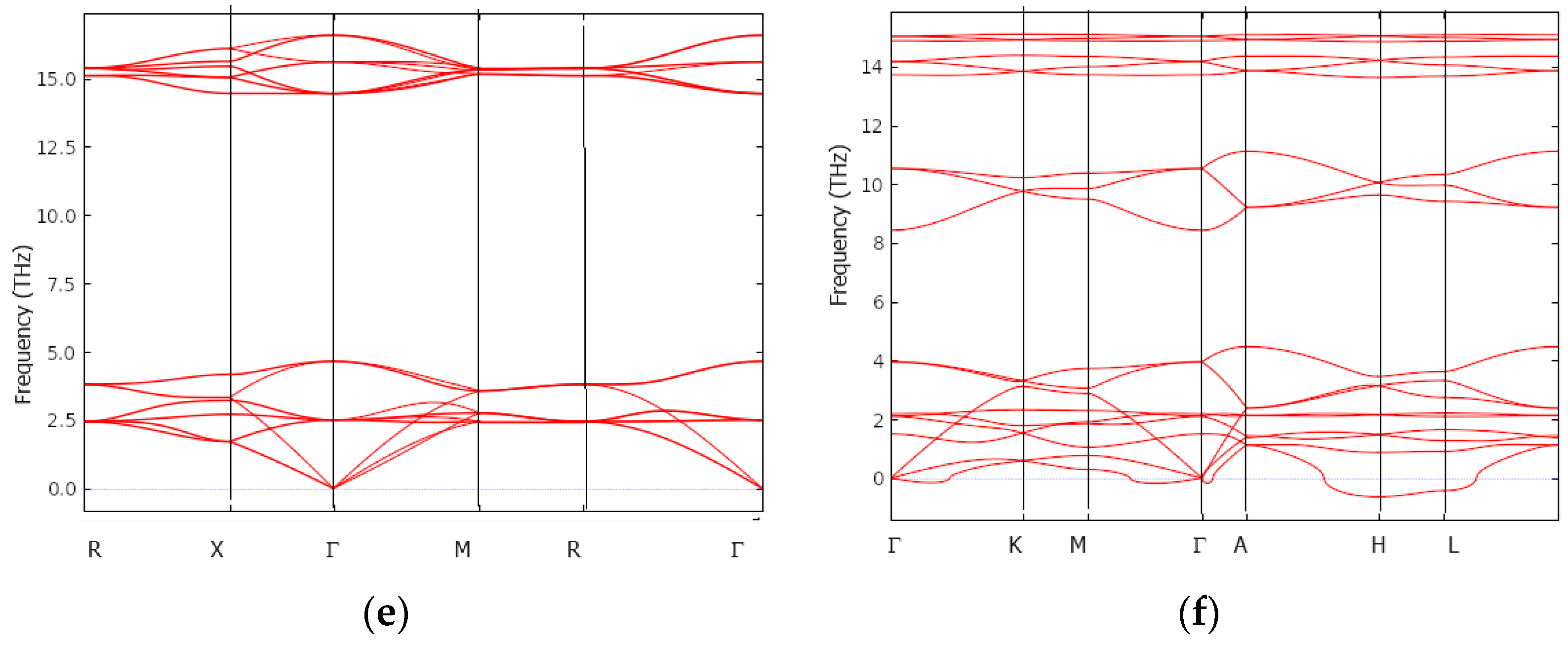
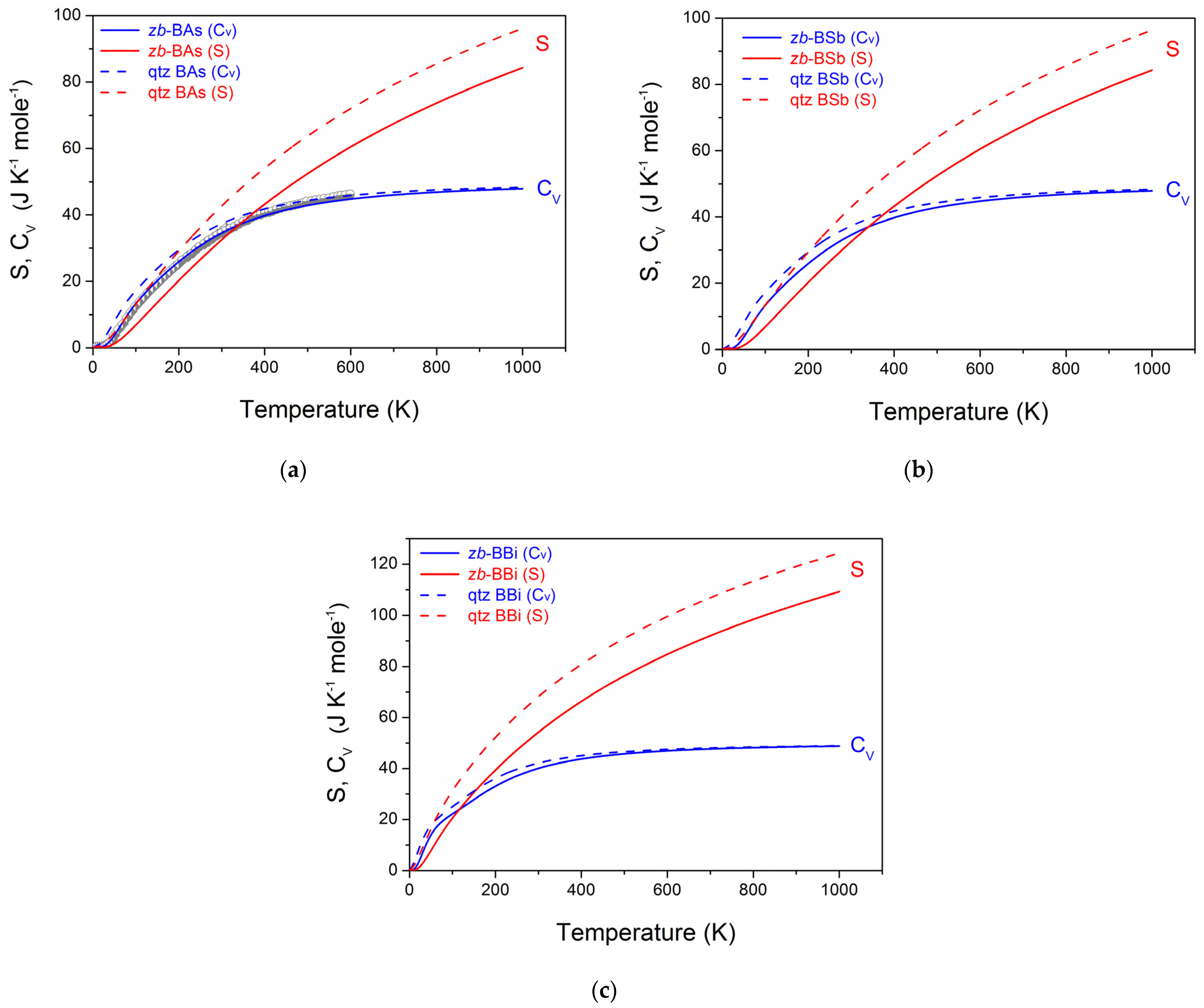
3.4. Dynamic and Thermodynamic Properties from the Phonons
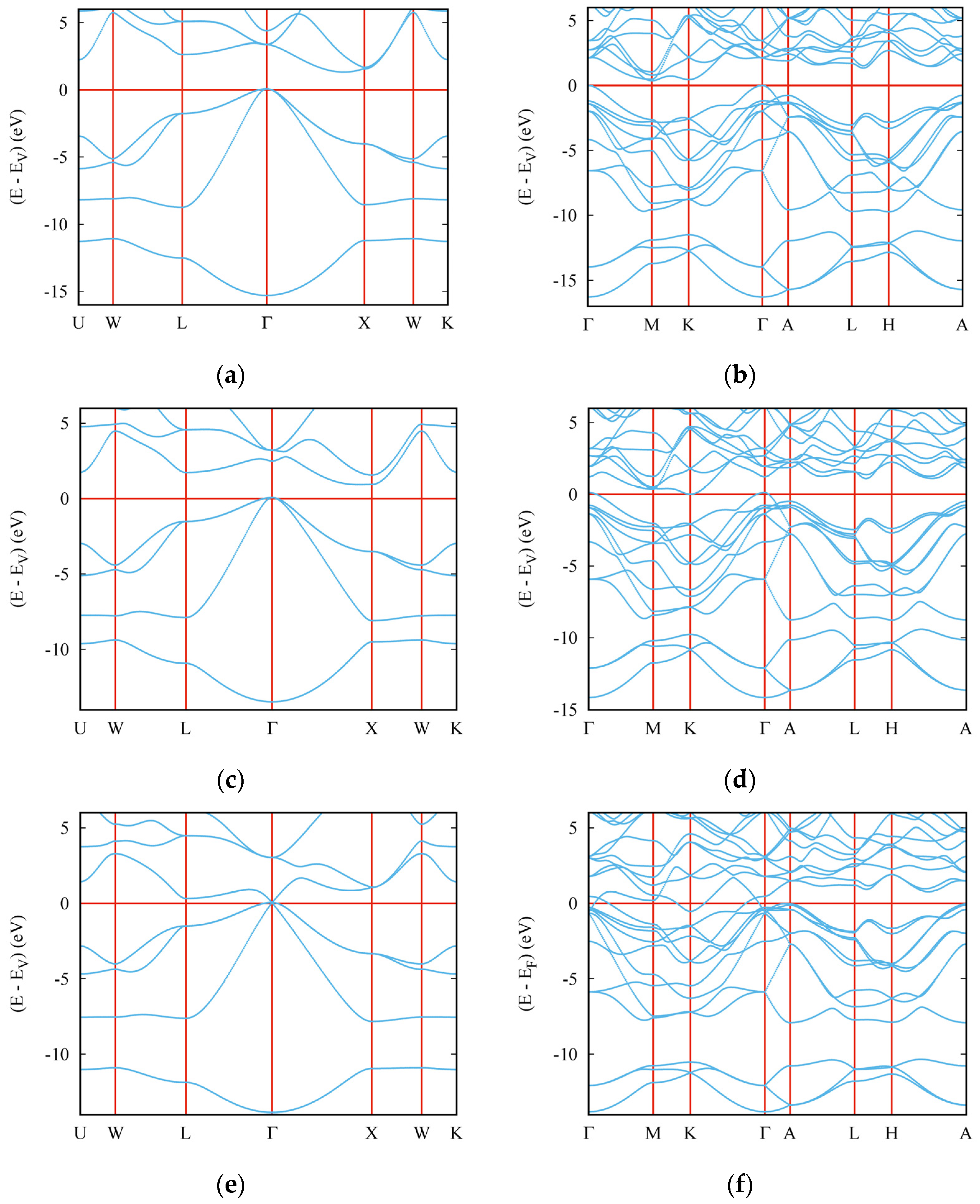
3.5. Electronic Band Structures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vurgaftman, I.; Meyer, J.R.; Ram-Mohan, L.R. Band parameters for III–V compound semiconductors and their alloys. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2001, 89, 5815–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Li, M.; Wu, H.; Nguyen, H.; Hua, Y. Basic physical properties of cubic boron arsenide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 122103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferhat, M.; Bouhafs, B.; Zaoui, A.; Aourag, H. First-principles study of structural and electronic properties of BSb. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1998, 10, 7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaoui, A.; Ferhat, M. High-pressure structural phase transition of BSb. Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 2001, 225, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustundag, M.; Aslan, M.; Yalcin, B.G. The first-principles study on physical properties and phase stability of Boron-V (BN, BP, BAs, BSb and BBi) compounds. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 81, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioud, N.; Sun, X.-W.; Daoud, S.; Song, T.; Liu, Z.-J. Structural stability and thermodynamic properties of BSb under high pressure and temperature. Mater. Res. Exp. 2018, 5, 085904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujica, A.; Rubio, A.; Munoz, A.; Needs, R.J. High-pressure phases of group-IV, III–V, and II–VI compounds. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2003, 75, 863–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentzcovitch, R.M.; Cohen, M.L.; Lam, P.K. Theoretical study of BN, BP, and BAs at high pressures. Phys. Rev. B 1987, 36, 6058–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Feng, W.; Hua, H.; Feng, Z.; Wang, Y. First-principles study of zinc-blende to rocksalt phase transition in BP and BAs. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1386–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Linghu, R.-F.; Yi, Y.; Yang, X.-D. Characterisation of the high-pressure structural transition and elastic properties in boron arsenic. Chin. Phys. B 2010, 19, 076201. [Google Scholar]
- Varshney, D.; Joshi, G.; Varshney, M.; Shriya, S. Pressure induced mechanical properties of boron based pnictides. Solid State Sci. 2010, 12, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talati, M.; Jha, P.K. Structural phase transition in boron compounds at high pressure. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2010, 24, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwan, M.; Bhardwaj, P.; Singh, S. Zinc-blende to rock-salt structural phase transition of BP and BAs under high pressure. Chem. Phys. 2013, 426, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, S.; Bioud, N.; Bouarissa, N. Structural phase transition, elastic and thermal properties of boron arsenide: Pressure-induced effects. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 31, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, R.G.; Luo, H.; Ruoff, A.L.; Trail, S.S.; DiSalvo, F.J. Pressure induced metastable amorphization of BAs: Evidence for a kinetically frustrated phase transformation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 73, 2476–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H. BSb (BoronAntimony). J. Phase Equil. 1991, 125, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. B-Bi (Boron-Bismuth). J. Phase Equil. 1991, 125, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, E.V.; Blatov, V.A.; Kochetkov, A.V.; Proserpio, D.M. Underlying nets in three-periodic coordination polymers: Topology, taxonomy and prediction from a computer-aided analysis of the Cambridge Structural Database. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2011, 13, 3947–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, S.F.; Solozhenko, V.L. Ultrahigh-density superhard hexagonal BN and SiC with quartz topology from crystal chemistry and first principles. Crystals 2023, 13, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solozhenko, V.L.; Matar, S.F. Superdense hexagonal BP and AlP with quartz topology: Crystal chemistry and DFT study. Crystals 2023, 13, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. B 1964, 136, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys. Rev. A 1965, 140, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, J. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented wave. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöchl, P.E. Projector augmented wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. The Generalized Gradient Approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceperley, D.M.; Alder, B.J. Ground state of the electron gas by a stochastic method. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Flannery, B.P.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T. Numerical Recipes, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Blöchl, P.; Jepsen, O.; Anderson, O. Improved tetrahedron method for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 16223–16233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Methfessel, M.; Paxton, A.T. High-precision sampling for Brillouin-zone integration in metals. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 40, 3616–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special k-points for Brillouin Zone integration. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillac, R.; Pullumbi, P.; Coudert, F.X. ELATE: An open-source online application for analysis and visualization of elastic tensors. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2016, 28, 275201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, W. Über die Beziehung zwischen den beiden Elasticitätsconstanten isotroper Körper. Annal. Phys. 1889, 274, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhnik, E.; Oganov, A.R. A model of hardness and fracture toughness of solids. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 125109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Niu, H.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Modeling hardness of polycrystalline materials and bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhanov, V.A.; Kurakevych, O.O.; Solozhenko, V.L. The interrelation between hardness and compressibility of substances and their structure and thermodynamic properties. J. Superhard Mater. 2008, 30, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyakhov, A.O.; Oganov, A.R. Evolutionary search for superhard materials: Methodology and applications to forms of carbon and TiO2. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 092103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togo, A.; Tanaka, I. First principles phonon calculations in materials science. Scr. Mater. 2015, 108, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, M.T. Introduction to Lattice Dynamics; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Eyert, V. Basic notions and applications of the augmented spherical wave method. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2000, 77, 1007–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseev, A.A.; Babitsyuna, A.A.; Medvedeva, Z.S. X-ray investigation of the arsenic-boron system. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 1964, 9, 633–636. [Google Scholar]
- Schowalter, M.; Rosenauer, A.; Volz, K. Parameters for temperature dependence of mean-square displacements for B-, Bi- and Tl-containing binary III-V compounds. Acta Crystallogr. A 2012, 68, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, S.F.; Solozhenko, V.L. First principles search for novel ultrahard high-density carbon allotropes: Hexagonal C6, C9 and C12. J. Superhard Mater. 2023, 45, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahat, S.; Li, S.; Wu, H.; Koirala, P.; Lv, B.; Cahill, D.G. Elastic constants of cubic boron phosphide and boron arsenide. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2021, 5, 033606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Luo, K.; Xie, C.; Liu, B.; Liang, X.; Wang, L.; Gamage, G.A.; Sun, H.; Ziyaee, H.; Sun, J.; et al. Mechanical properties of boron arsenide single crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 131903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solozhenko, V.L.; Matar, S.F. Prediction of novel ultrahard phases in the B–C–N system from first principles: Progress and problems. Materials 2023, 16, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, C.A. The mechanical properties of cubic boron nitride. Proc. Int. Conf. Sci. Hard Mater. 1986, 207–220. [Google Scholar]
- Solozhenko, V.L.; Bushlya, V. Mechanical properties of boron phosphides. J. Superhard Mater. 2019, 41, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, F. Finite strain isotherm and velocities for single-crystal and polycrystalline NaCl at high pressures and 300 K. J. Geophys. Res. 1978, 83, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murnaghan, F.D. The compressibility of media under extreme pressures. Proc. Nation. Acad. Sci. USA 1944, 30, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshchenko, V.I.; Demidenko, A.F.; Grinberg, Y.K.; Yachmenev, V.E. Specific-heats and thermodynamic functions of BP, BAs and B6As at 5-310 K. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Neorg. Mater. 1981, 17, 1965–1968. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
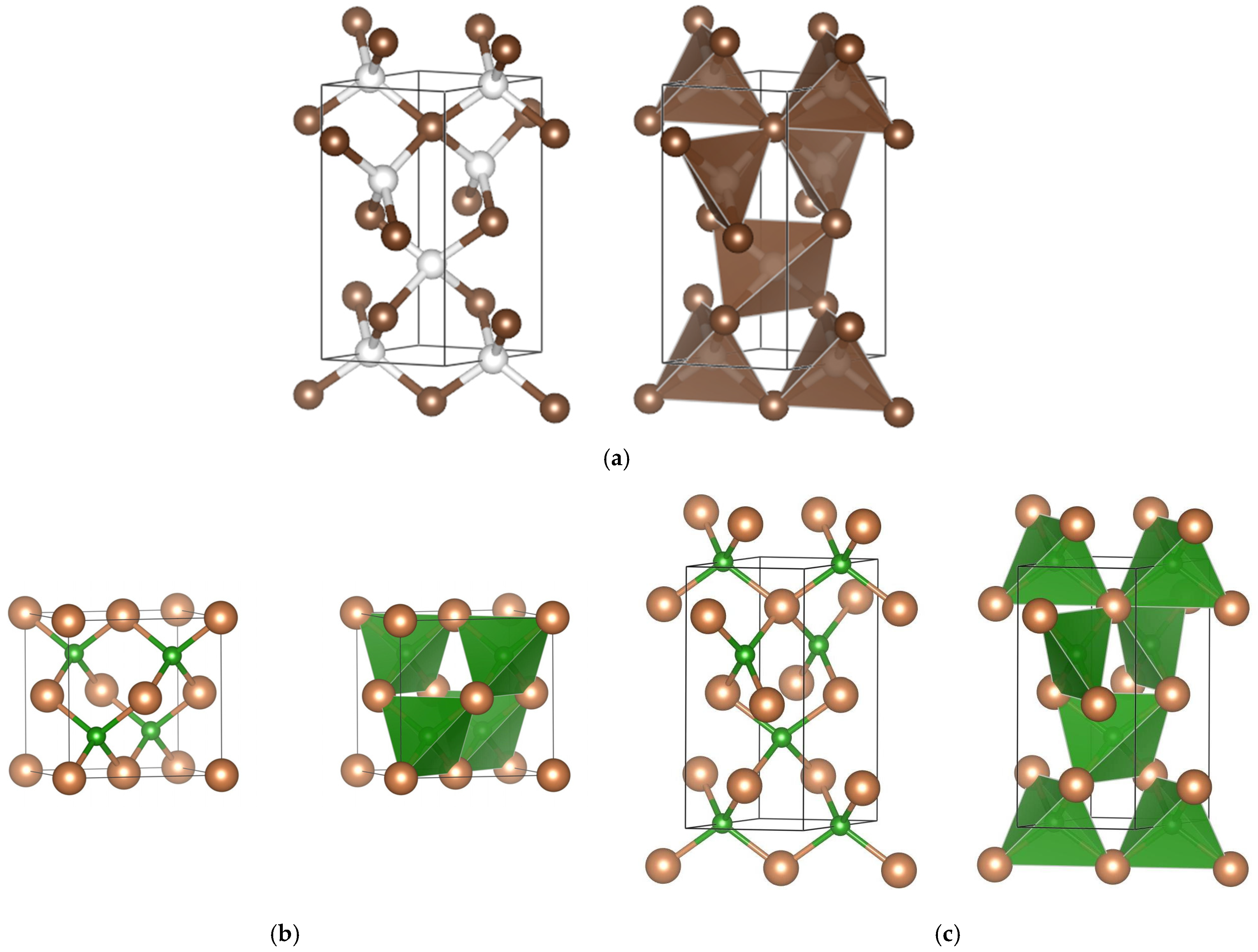

| zb-BAs (Z = 4) F-43m (No. 216) | qtz BAs (Z = 3) P6422 (No. 181) | zb-BSb (Z = 4) F-43m (No. 216) | qtz BSb (Z = 3) P6422 (No. 181) | zb-BBi (Z = 4) F-43m (No. 216) | qtz BBi (Z = 3) P6422 (No. 181) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a, Å | 4.813 (4.777 [42]) | 3.461 | 5.279 (5.267 [43]) | 3.765 | 5.536 (5.528 [43]) | 3.944 |
| c, Å | – | 7.486 | – | 8.289 | – | 8.79252 |
| Vcell, Å3 | 111.51 | 77.66 | 146.97 | 101.78 | 169.65 | 118.46 |
| V/FU, Å3 | 27.88 | 25.89 ΔV/FU = 1.99 | 36.74 | 33.93 ΔV/FU = 2.81 | 42.41 | 39.49 ΔV/FU = 2.92 |
| Shortest bond, Å | 2.08 | 2.13 | 2.29 | 2.33 | 2.40 | 2.45 |
| Angle (deg.) | 109.47 | 108.42/90.74 | 109.47 | 108.41/90.74 | 109.47 | 106.76/91.93 |
| Atomic positions | B (4c) ¼, ¼, ¼ As (4a) 0, 0, 0 | B (3c) ½, 0, 0 As (3d) ½, 0, ½ | B (4c) ¼, ¼, ¼ Sb (4a) 0, 0, 0 | B (3c) ½, 0, 0 Sb (3d) ½, 0, ½ | B (4c) ¼, ¼, ¼ Bi (4a) 0, 0, 0 | B (3c) ½, 0, 0 Bi (3d) ½, 0, ½ |
| Etotal, eV Etotal/FU, eV | −45.47 −11.37 | −31.44 −10.48 ΔE/FU = −0.89 eV | −40.14 −10.03 | −28.01 −9.34 ΔE/FU = −0.69 eV | −35.69 −8.92 | −25.06 −8.35 ΔE/FU = −0.57 eV |
| C11 | C12 | C13 | C33 | C44 | C66 | BV | GV | EV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| zb-BAs | 268 | 67 | 67 | 268 | 146 | 146 | 134 | 128 | 291 |
| qtz BAs | 323 | 38 | 57 | 307 | 143 | 160 | 140 | 146 | 324 |
| zb-BSb | 182 | 58 | 58 | 182 | 97 | 97 | 99 | 83 | 195 |
| qtz BSb | 214 | 31 | 57 | 223 | 91 | 114 | 105 | 98 | 223 |
| zb-BBi | 124 | 39 | 39 | 124 | 67 | 67 | 67 | 57 | 134 |
| qtz BBi | 135 | 49 | 39 | 152 | 43 | 72 | 75 | 57 | 137 |
| HV | B | GV | EV | ν ** | KIc‡ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T * | LO † | MO ‡ | CN § | B0 * | BV | |||||
| GPa | MPa·m½ | |||||||||
| zb-BAs #216 | 24 | 22 | 22 | 29 | 146 | 134 | 128 | 291 | 0.138 | 1.4 |
| qtz BAs #180 | 25 | 22 | 27 | 36 | 154 | 140 | 146 | 324 | 0.113 | 1.2 |
| zb-BSb #216 | 18 | 16 | 12 | 19 | 107 | 99 | 83 | 195 | 0.173 | 1.0 |
| qtz BSb #180 | 19 | 9 | 16 | 24 | 116 | 105 | 98 | 223 | 0.149 | 1.0 |
| zb-BBi #216 | 14 | 12 | 8 | 15 | 86 | 67 | 57 | 134 | 0.169 | 0.6 |
| qtz BBi #180 | 15 | 7 | 7 | 12 | 92 | 75 | 57 | 137 | 0.197 | 0.6 |
| BAs | BSb | BBi | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| zb | qtz | zb | qtz | zb | qtz | |
| B0 (GPa) | 146 * | 154 | 107 | 116 | 86 | 92 |
| E0/FU (eV) | −11.37 | −10.45 | −10.06 | −9.32 | −8.92 | −8.34 |
| V0/FU (Å3) | 27.88 † | 25.89 | 36.74 | 33.93 | 42.41 | 39.47 |
| Vtr/V0 | 0.697 | 0.724 | 0.763 | |||
| ptr (GPa) | 117 | 71 | 51 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solozhenko, V.L.; Matar, S.F. High-Pressure Phases of Boron Pnictides BX (X = As, Sb, Bi) with Quartz Topology from First Principles. Crystals 2024, 14, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14030221
Solozhenko VL, Matar SF. High-Pressure Phases of Boron Pnictides BX (X = As, Sb, Bi) with Quartz Topology from First Principles. Crystals. 2024; 14(3):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14030221
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolozhenko, Vladimir L., and Samir F. Matar. 2024. "High-Pressure Phases of Boron Pnictides BX (X = As, Sb, Bi) with Quartz Topology from First Principles" Crystals 14, no. 3: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14030221
APA StyleSolozhenko, V. L., & Matar, S. F. (2024). High-Pressure Phases of Boron Pnictides BX (X = As, Sb, Bi) with Quartz Topology from First Principles. Crystals, 14(3), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14030221






