Highly Collimated Monochromatic X-rays Generated by Collision of High-Energy Electrons with Tightly Focused Linearly Polarized Laser Pulse
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory and Formula
3. Numerical Results
3.1. Radiation Energy Angular Distribution
3.2. Maximum Radiation Energy
3.3. The Harmonic Spectrum
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoshitaka, T.; Masahiro, K. Generation of Optical Vortices by Nonlinear Inverse Thomson Scattering at Arbitrary Angle Interactions. Astrophys. J. 2018, 860, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Vais, O.E.; Bochkarev, S.G.; Bychenkov, V.Y. Nonlinear Thomson scattering of a relativistically strong tightly focused ultrashort laser pulse. Plasma Phys. Rep. 2016, 42, 818–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, D.; Malaca, B.; Piazza, A.D.; Formanek, M.; Palastro, J.P. Nonlinear thomson scattering with ponderomotive control. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 105, 065201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borovskiy, A.V.; Galkin, A.L. Saturation of electron emission with increasing ultrarelativistic intensity of the Gaussian laser pulse. Laser Phys. Lett. 2021, 18, 066002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, V.; Bacci, A.; Curatolo, C.; Drebot, I.; Giribono, A.; Maroli, C. Polarization of x-gamma radiation produced by a thomson and compton inverse scattering. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top.—Accel. Beams 2015, 18, 110701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmykov, S.Y.; Davoine, X.; Ghebregziabher, I.; Shadwick, B.A. Customizable electron beams from optically controlled laser plasma acceleration for γ-ray sources based on inverse Thomson scattering. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 2016, 829, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Pan, W. High Energy Photon Source. High Power Laser Part. Beams 2022, 34, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y. High Energy Photon Source. Mod. Phys. 2022, 34, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Long, F.; Gao, Y.; Wei, P.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, S.; Du, Y. Development of corrector magnet power supply for high energy photon source. Radiat. Detect. Technol. Methods 2022, 6, 470–478. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Lu, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, W.; et al. Mechanical design of a cryogenic Delta–Knot undulator for high energy photon source. Radiat. Detect. Technol. Methods 2021, 5, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y. High Energy Photon Source (HEPS): A High-performance Light Source for Biological Sciences. C.; The Biophysical Society of China, Institute of Biophysics, CAS: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, H.; Huang, Y.; Sun, S.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S.; Chen, W.; et al. A new practical design of a merged APPLE-Knot undulator for High Energy Photon Source. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 2022, 1034, 166816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Sui, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Yue, J.; Cao, J. Beam Position Monitor Characterization for the High Energy Photon Source Synchrotron. Symmetry 2023, 15, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Du, Y.; Huang, W.; Tang, C. Linearly polarized X-ray fluorescence computed tomography based on a Thomson scattering light source: A Monte Carlo study. Synchrotron Radiat. 2020, 27, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suortti, P.; Thomlinson, W. Medical applications of synchrotron radiation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2003, 48, R1–R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taira, Y.; Hayakawa, T.; Katoh, M. Gamma-ray vortices from nonlinear inverse Thomson scattering of circularly polarized light. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Chung, S.; Park, S.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, D. Effects of high-order fields of a tightly focused laser pulse on relativistic nonlinear Thomson scattered radiation by a relativistic electron. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2010, 89, 64006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Yu, T.; Chen, M.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhuo, H. Generation of bright attosecond x-ray pulse trains via Thomson scattering from laser-plasma accelerators. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 32098–32106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, F.; Zhu, B.; Han, D.; Xin, J.-T.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Cao, L.-F.; Gu, Y.-Q.; Zhang, B.-H. Numerical simulation for all-optical Thomson scattering X-ray source. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelsky, I.; Ben-Zvi, I.; Hirose, T.; Kashiwagi, S.; Yakimenko, V.; Kusche, K.; Siddons, P.; Skaritka, J.; Kumita, T.; Tsunemi, A.; et al. Demonstration of 8 × 1018 photons/second peaked at 1.8 å in a relativistic Thomson scattering experiment. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top. Beams 2000, 3, 090702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Salamin, Y.I.; Dou, Z.-K.; Xu, Z.-F.; Li, J.-X. Vortex γ rays from scattering laser bullets off ultrarelativistic electrons. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, I.; Aoki, T.; Dobashi, K.; Fukuda, M.; Higurashi, A.; Hirose, T.; Iimura, T.; Kurihara, Y.; Okugi, T.; Omori, T.; et al. Production of high brightness γ rays through backscattering of laser photons on high-energy electrons. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top. Beams 2003, 6, 091001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, C.; Long, Z.; Tian, Y. Modulation of high-energy γ -rays by collision of an ultra-high-energy electron with a tightly focused circularly polarized laser pulse. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 6038–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Long, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Tian, Y. Collimation and monochromaticity of γ-rays generated by high-energy electron colliding with tightly focused circularly polarized laser with varied intensities. Laser Phys. Lett. 2022, 19, 065301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Investigators at National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (NIAIST) Discuss Findings in Applied Materials (Ammonia-free Epitaxy of Single-crystal Inn Using a Plasmaintegrated Gas-injection Module). Electronics Newsweekly. 2022.
- Salamin, Y.I.; Keitel, C.H. Electron Acceleration by a Tightly Focused Laser Beam. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, M.; Golshani, M.; Sohaily, S.; Bahrampour, A. Electron acceleration by linearly polarized twisted laser pulse with narrow divergence. Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 033118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhyani, M.; Jahangiri, F.; Niknam, A.R.; Massudi, R. Optimizing chirped laser pulse parameters for electron acceleration in vacuum. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 183106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.-M.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Lin, Q.; Luo, J.-L. Electron acceleration by sub cycle pulsed focused vector beams. JOSA B 2016, 33, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, P.; Lu, P.; Cao, W.; Wang, X. Attosecond and zeptosecond x-ray pulses via nonlinear Thomson backscattering. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2005, 72, 066501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobzak, S.; Weidenmüller, H.A.; Pálffy, A. Laser-nucleus interactions in the sudden regime. Phys. Rev. C 2021, 103, 044616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, D.J.; Mcneil BW, J.; Thompson, N.R. Towards Zeptosecond-Scale Pulses from X-ray Free-Electron Lasers. Phys. Procedia 2013, 52, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

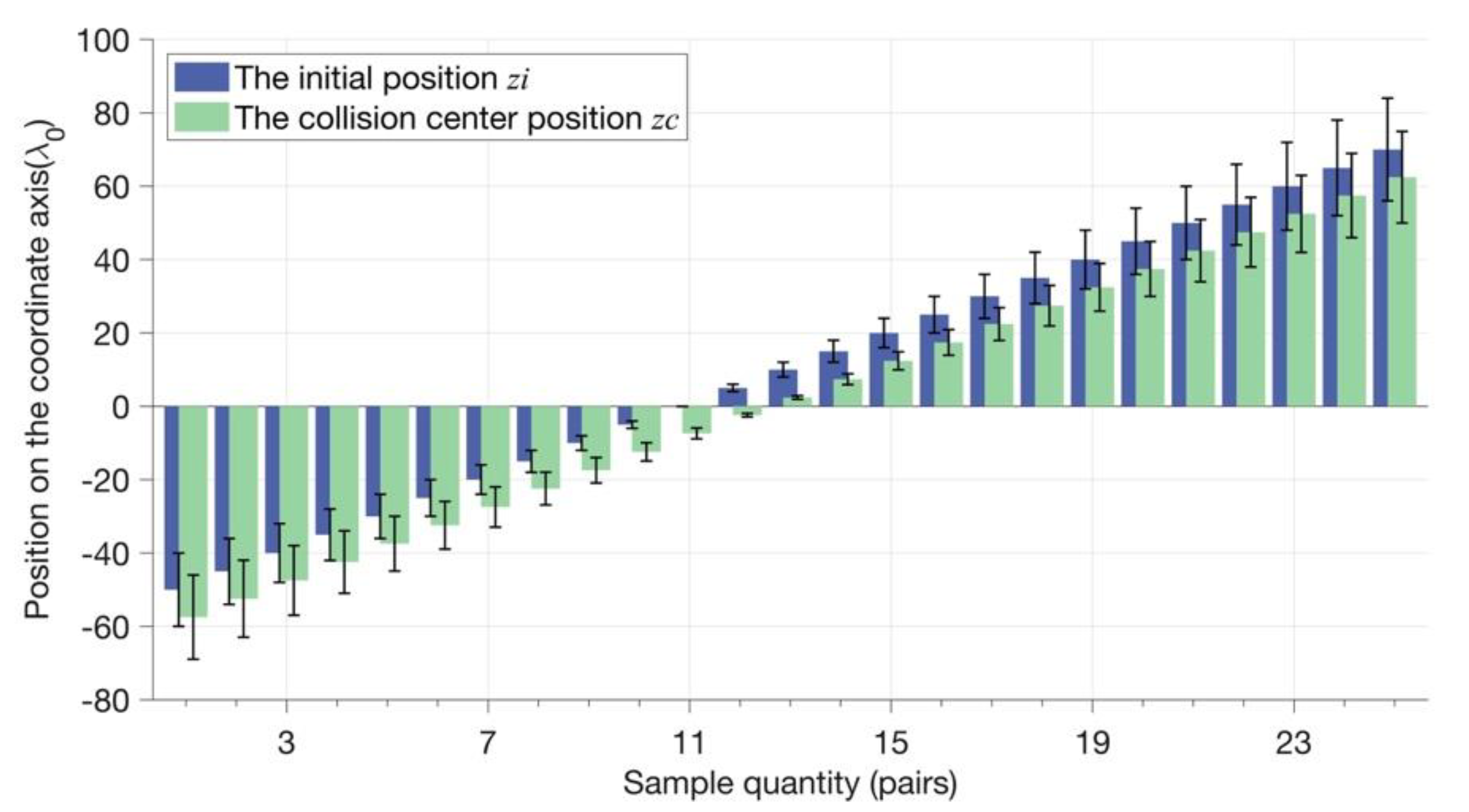


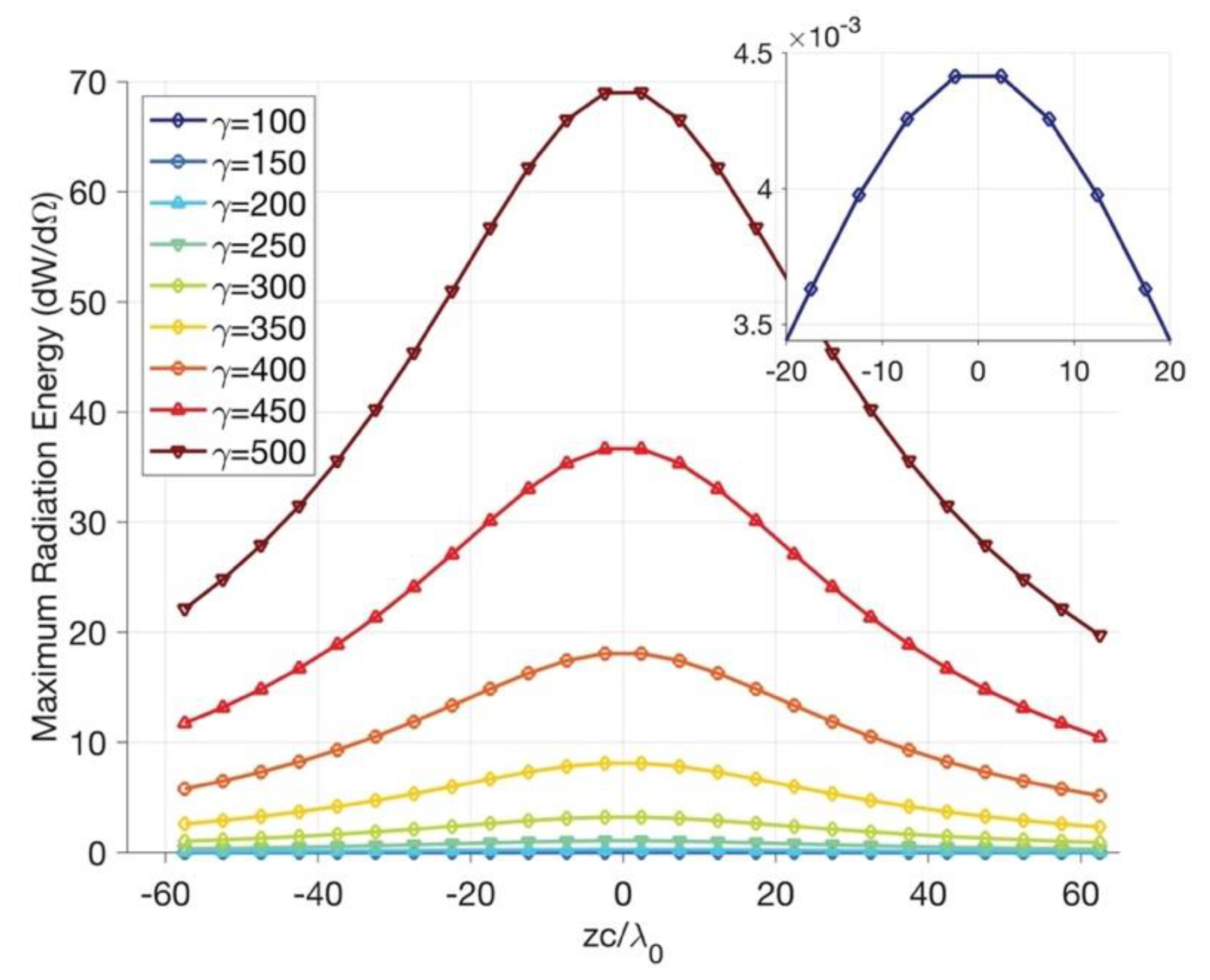
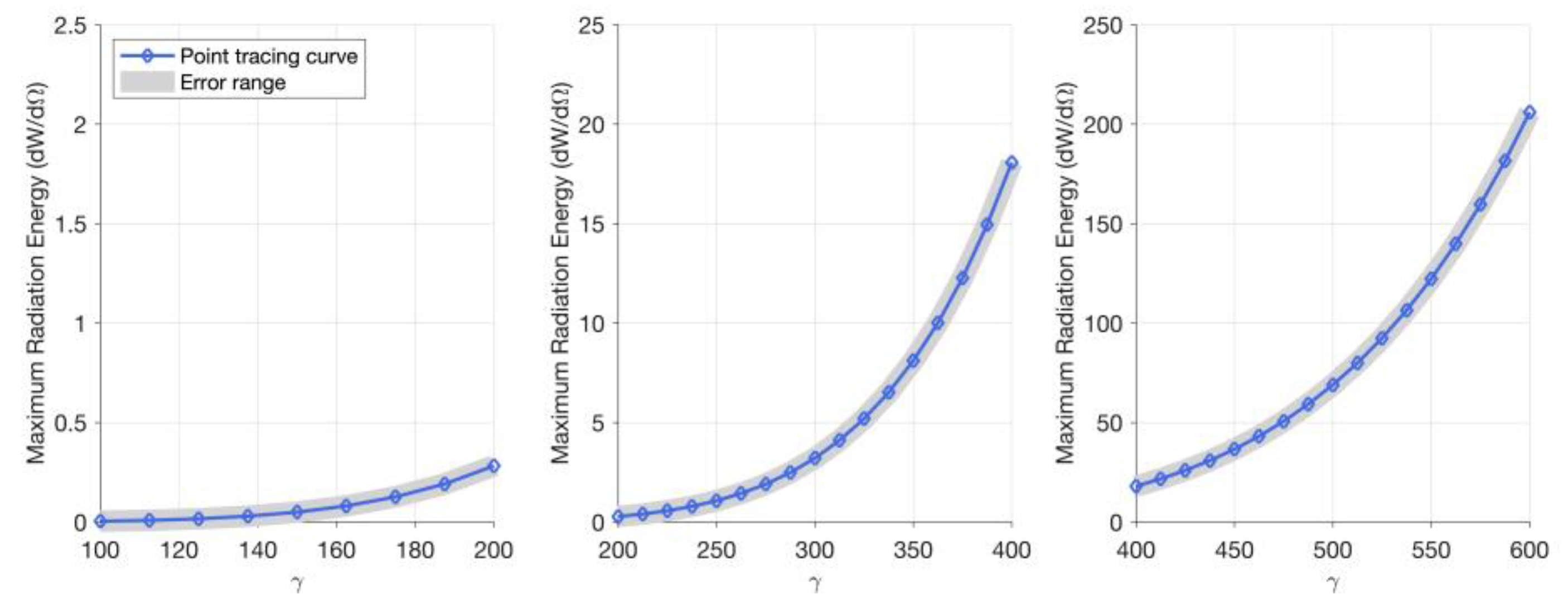
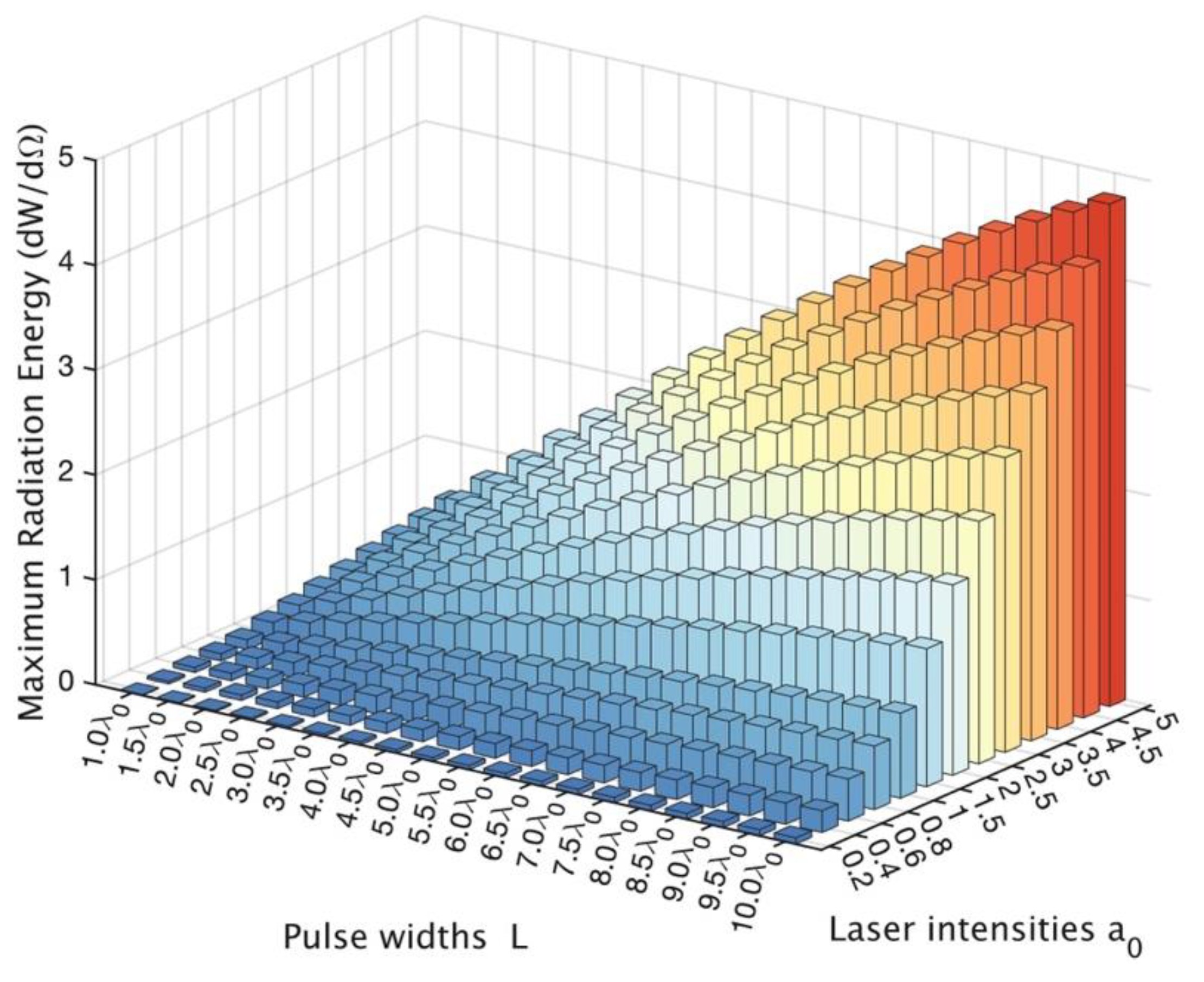
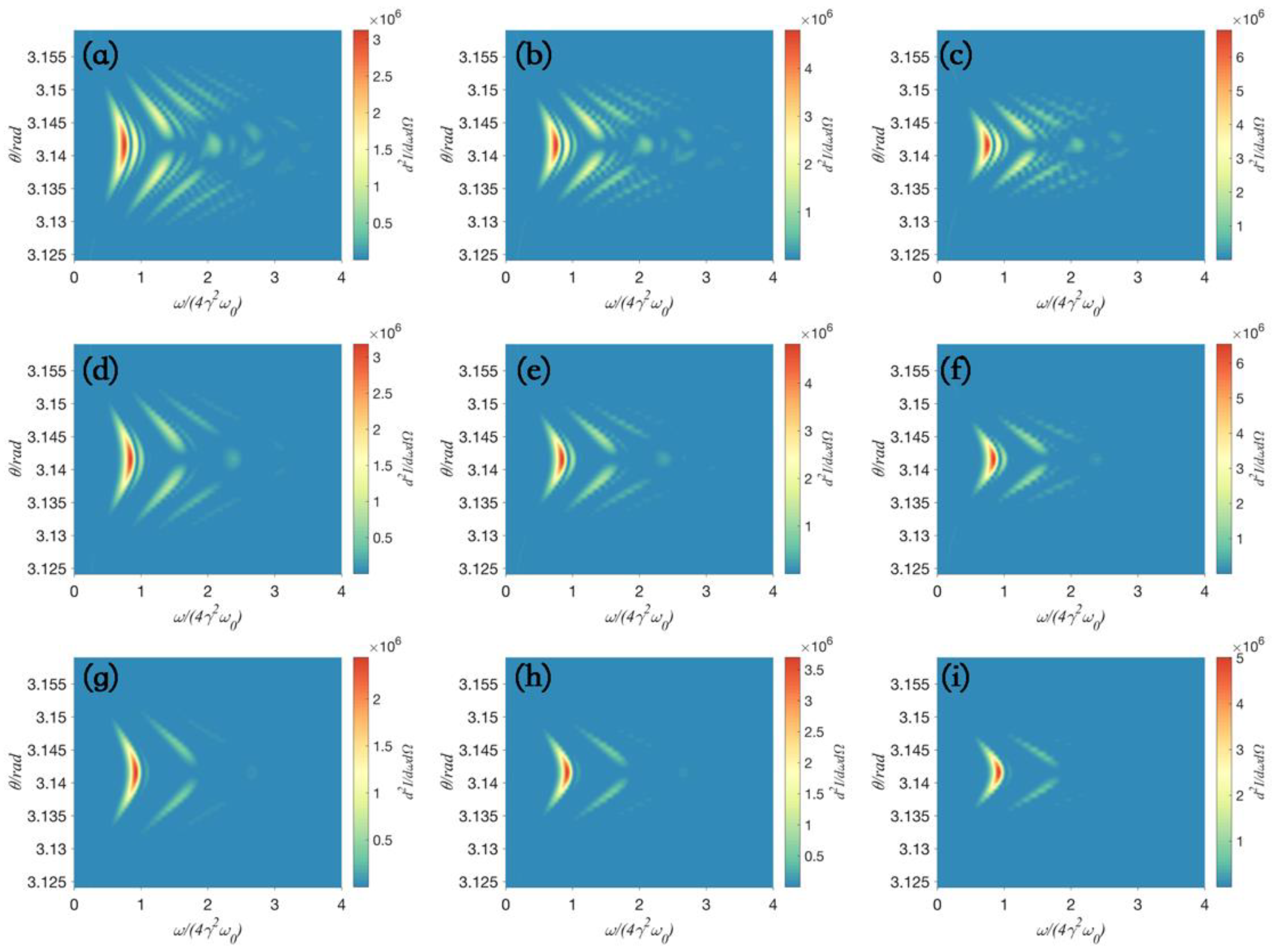
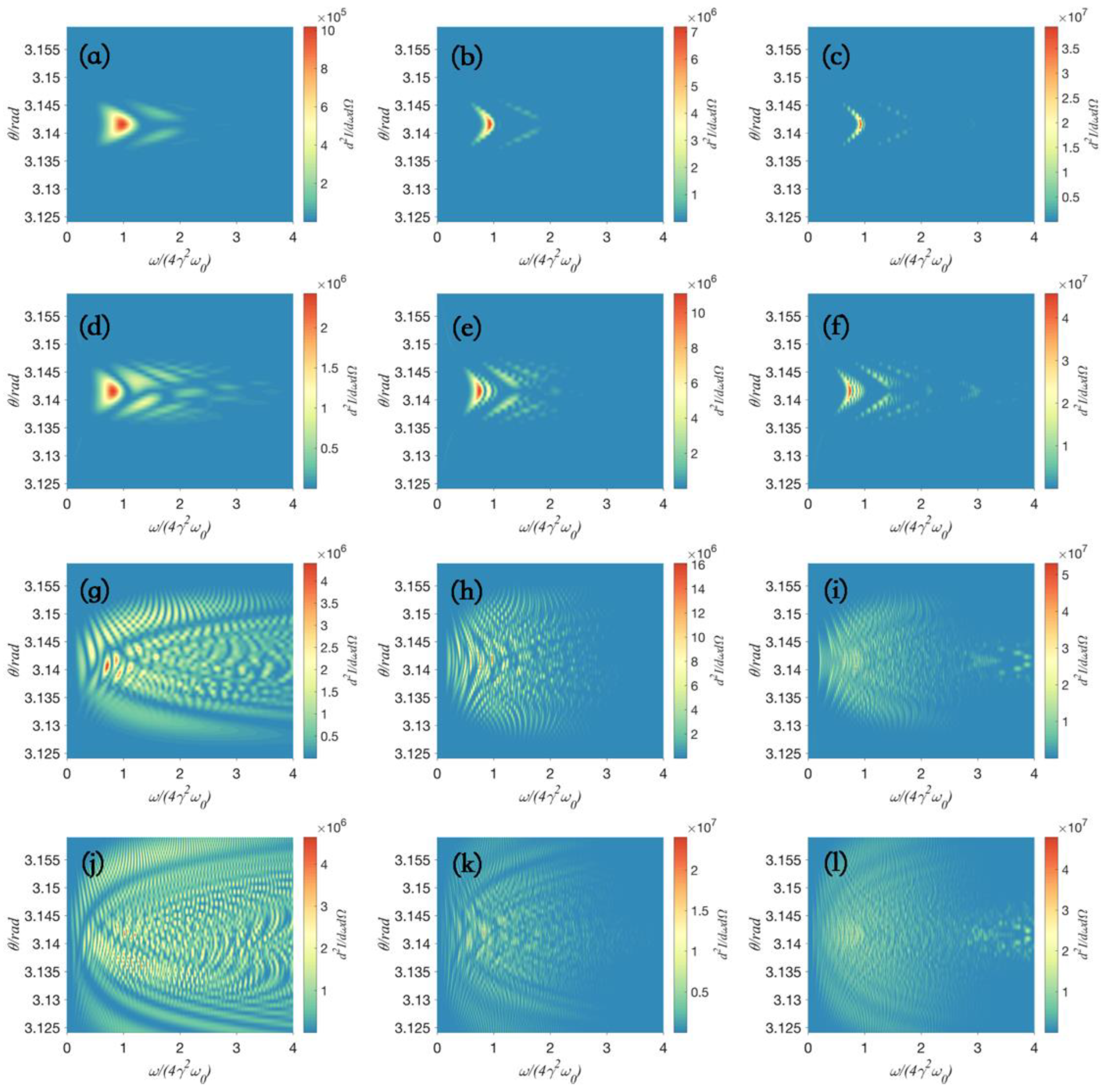
| Label on Figure 3 | (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | (e) | (f) | (g) | (h) | (i) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0308 | 0.0256 | 0.0216 | 0.0307 | 0.0252 | 0.0210 | 0.0306 | 0.0244 | 0.0204 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Tian, Y. Highly Collimated Monochromatic X-rays Generated by Collision of High-Energy Electrons with Tightly Focused Linearly Polarized Laser Pulse. Crystals 2024, 14, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14010013
Zeng M, Zhang Y, Chang Y, Tian Y. Highly Collimated Monochromatic X-rays Generated by Collision of High-Energy Electrons with Tightly Focused Linearly Polarized Laser Pulse. Crystals. 2024; 14(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Mingjing, Yangyi Zhang, Yifan Chang, and Youwei Tian. 2024. "Highly Collimated Monochromatic X-rays Generated by Collision of High-Energy Electrons with Tightly Focused Linearly Polarized Laser Pulse" Crystals 14, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14010013
APA StyleZeng, M., Zhang, Y., Chang, Y., & Tian, Y. (2024). Highly Collimated Monochromatic X-rays Generated by Collision of High-Energy Electrons with Tightly Focused Linearly Polarized Laser Pulse. Crystals, 14(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14010013






