Indentation Size Effect in Electrodeposited Nickel with Different Grain Size and Crystal Orientation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
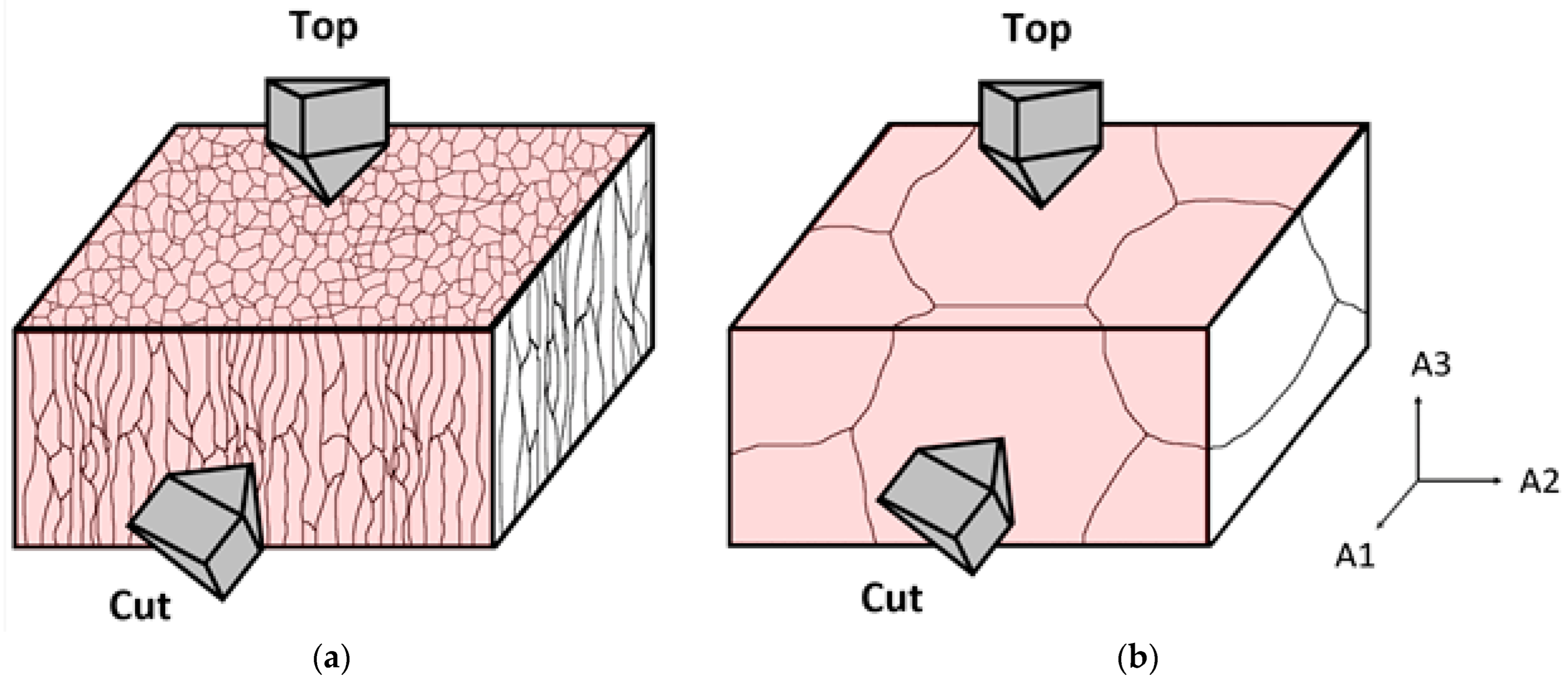
2. Material and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
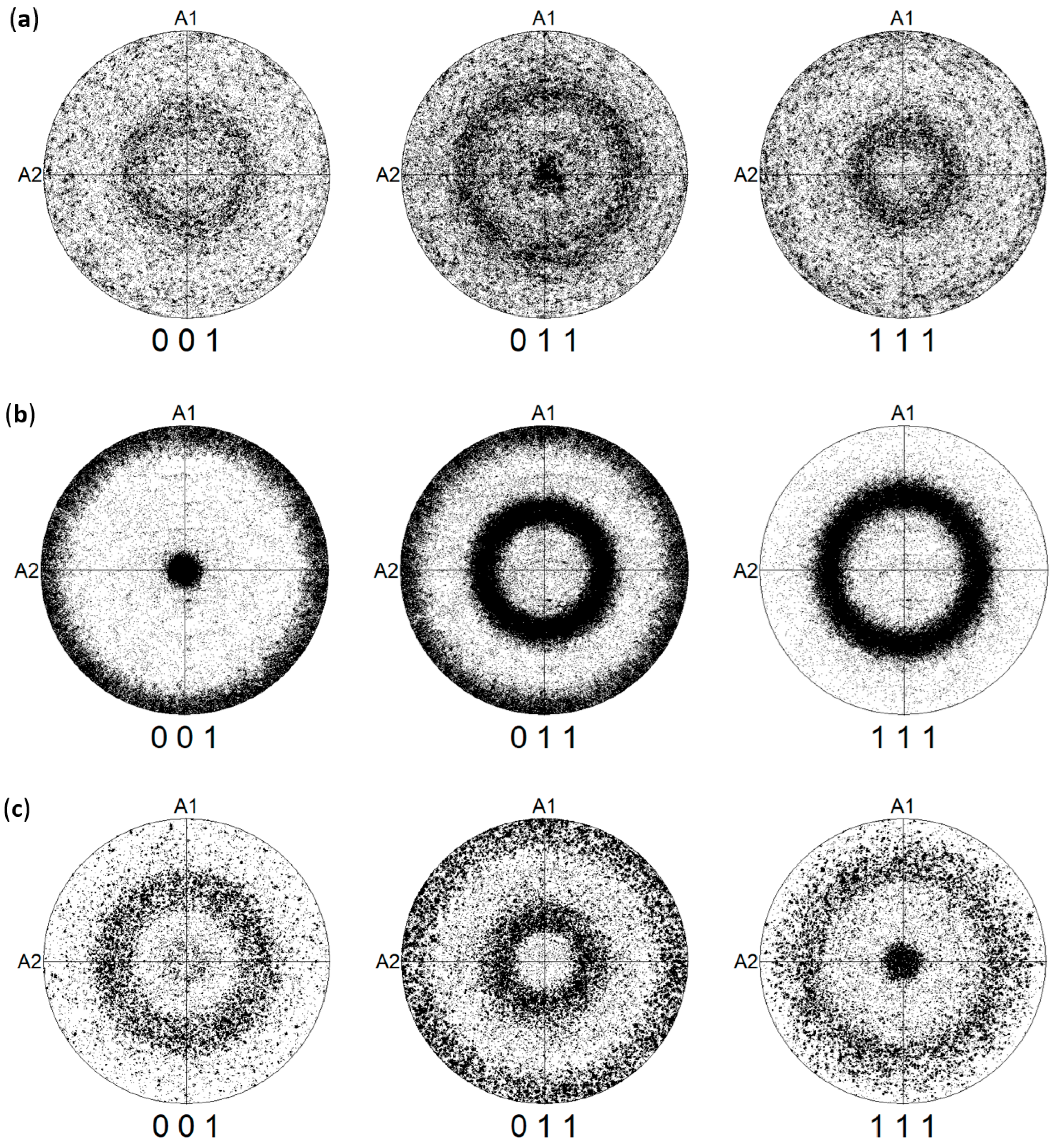
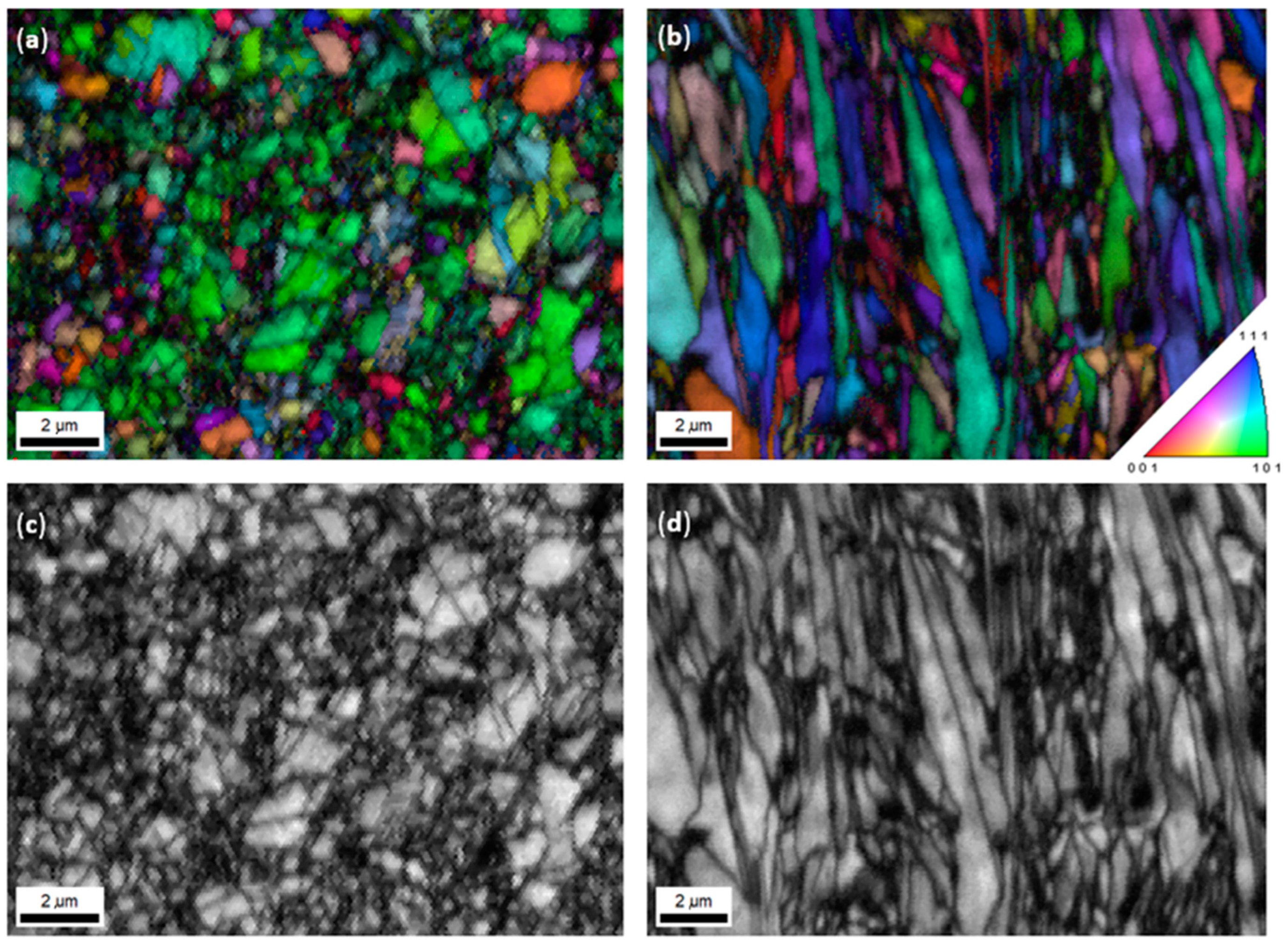
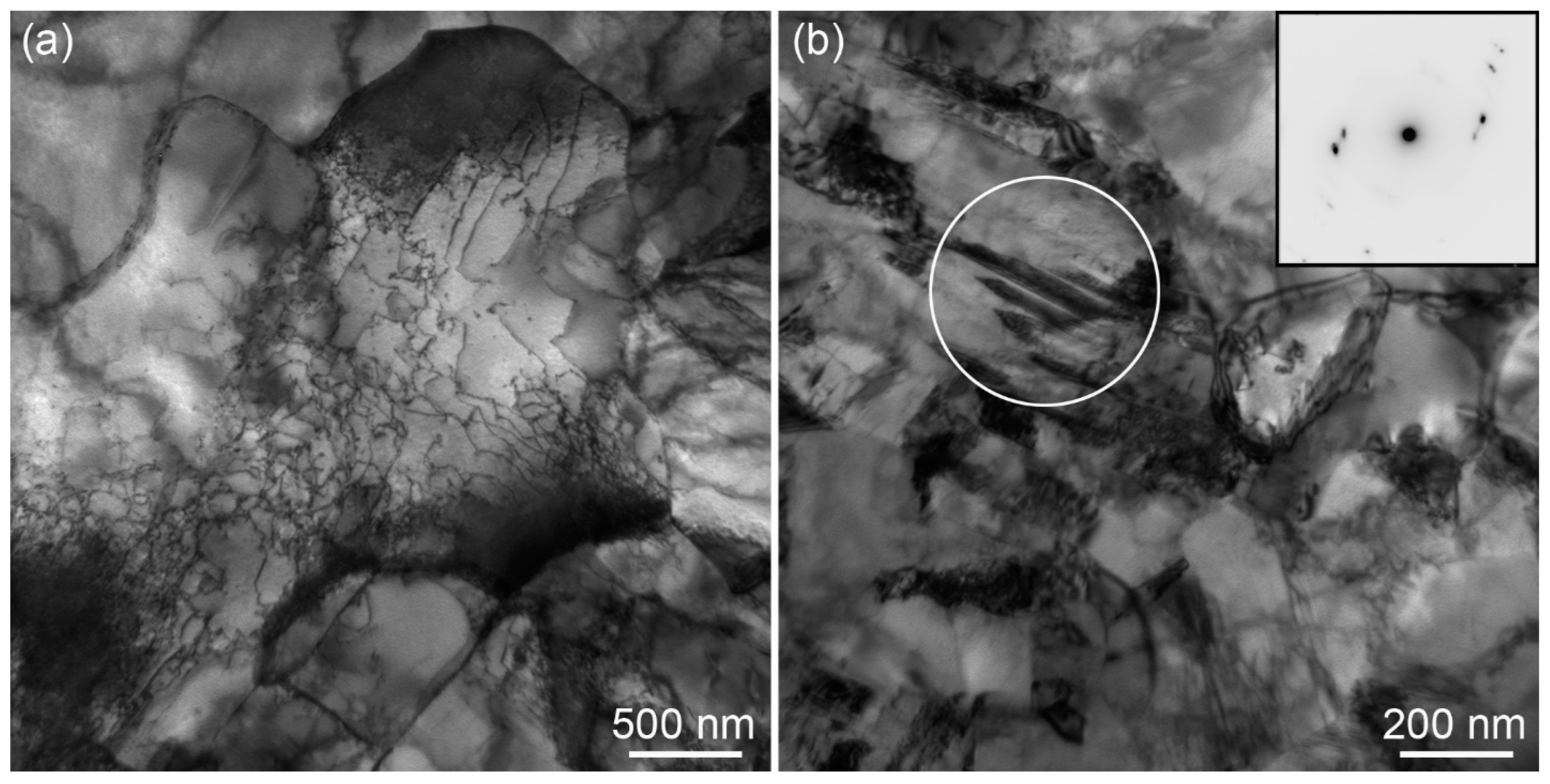
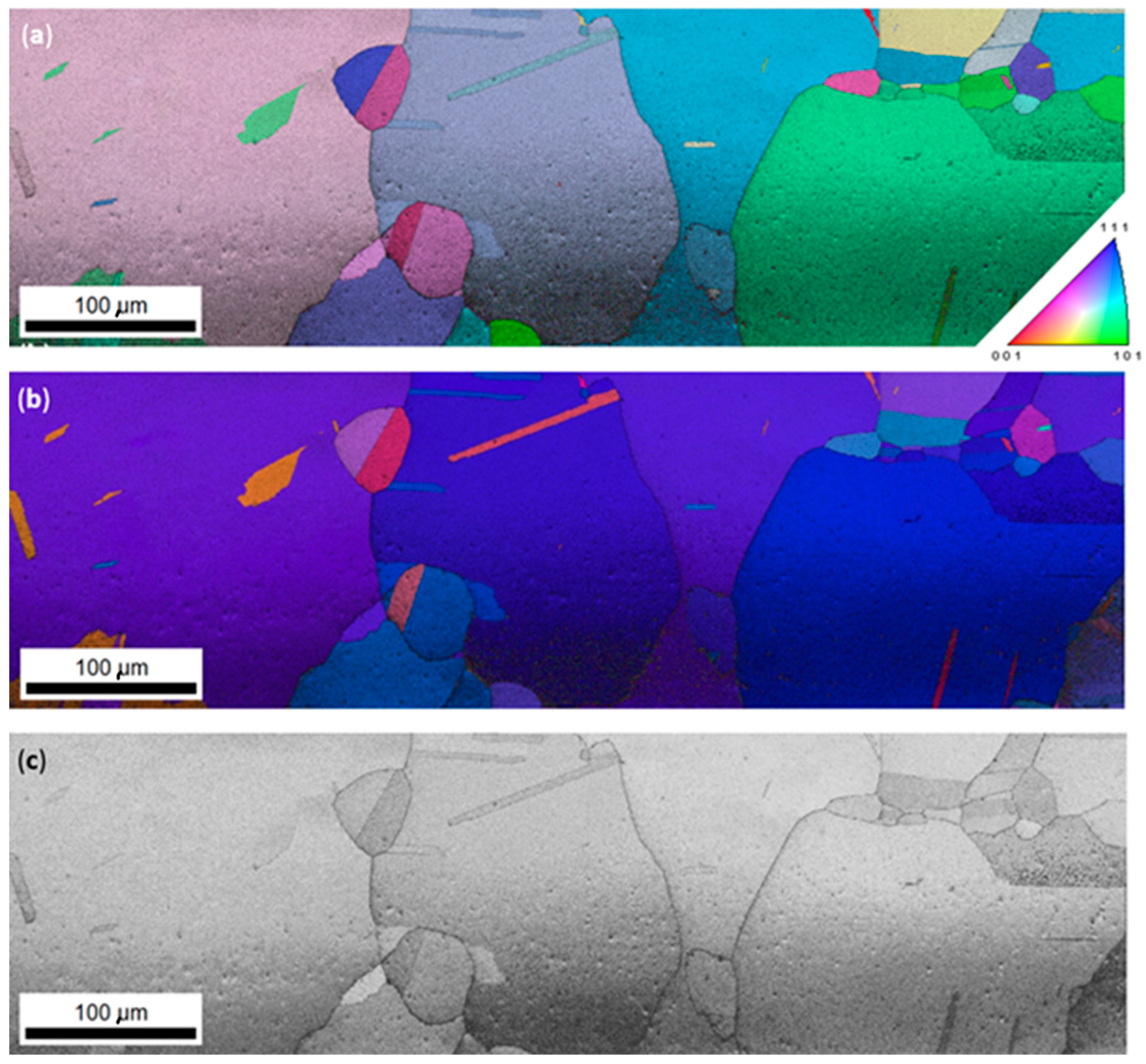
3.1. Microstructure
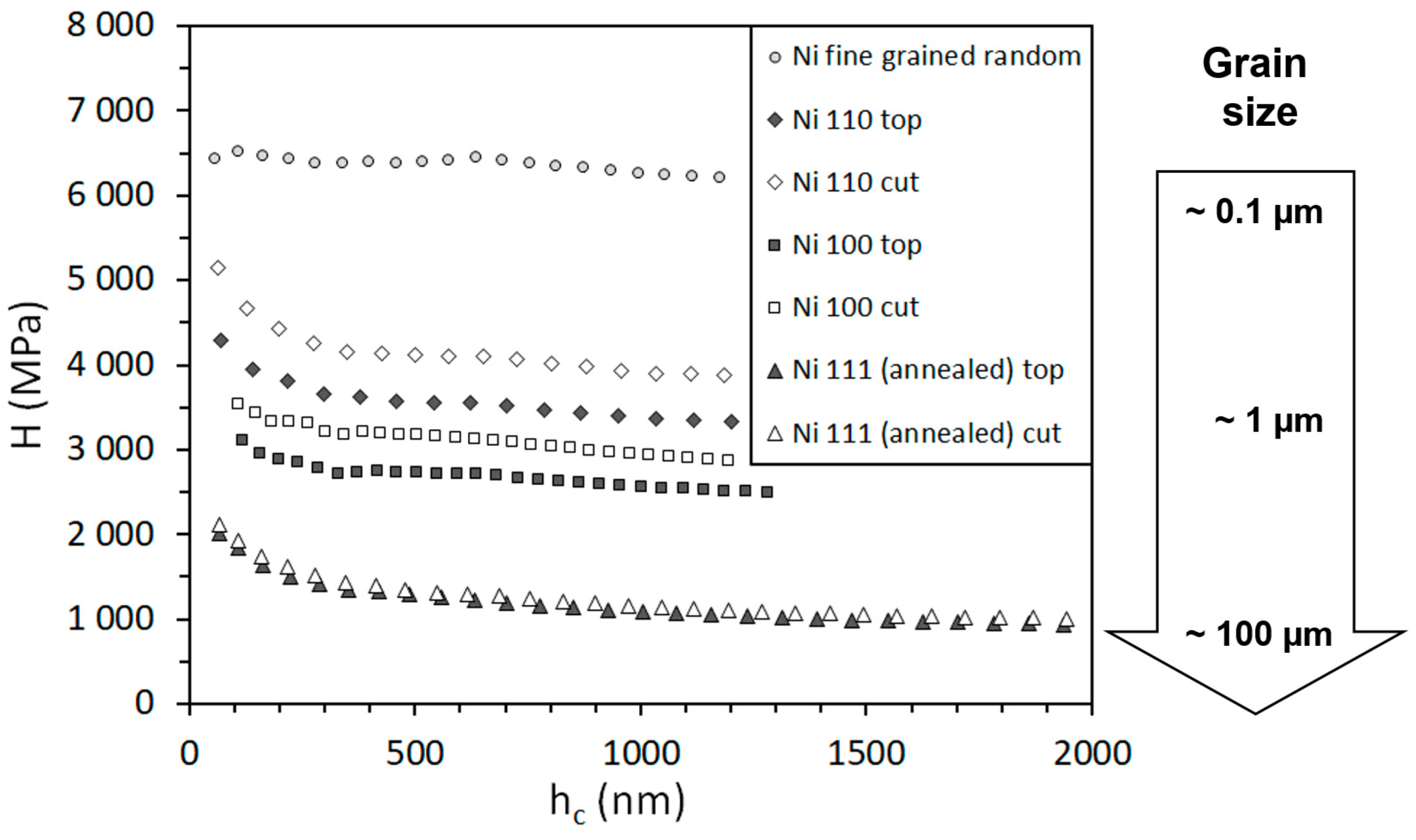
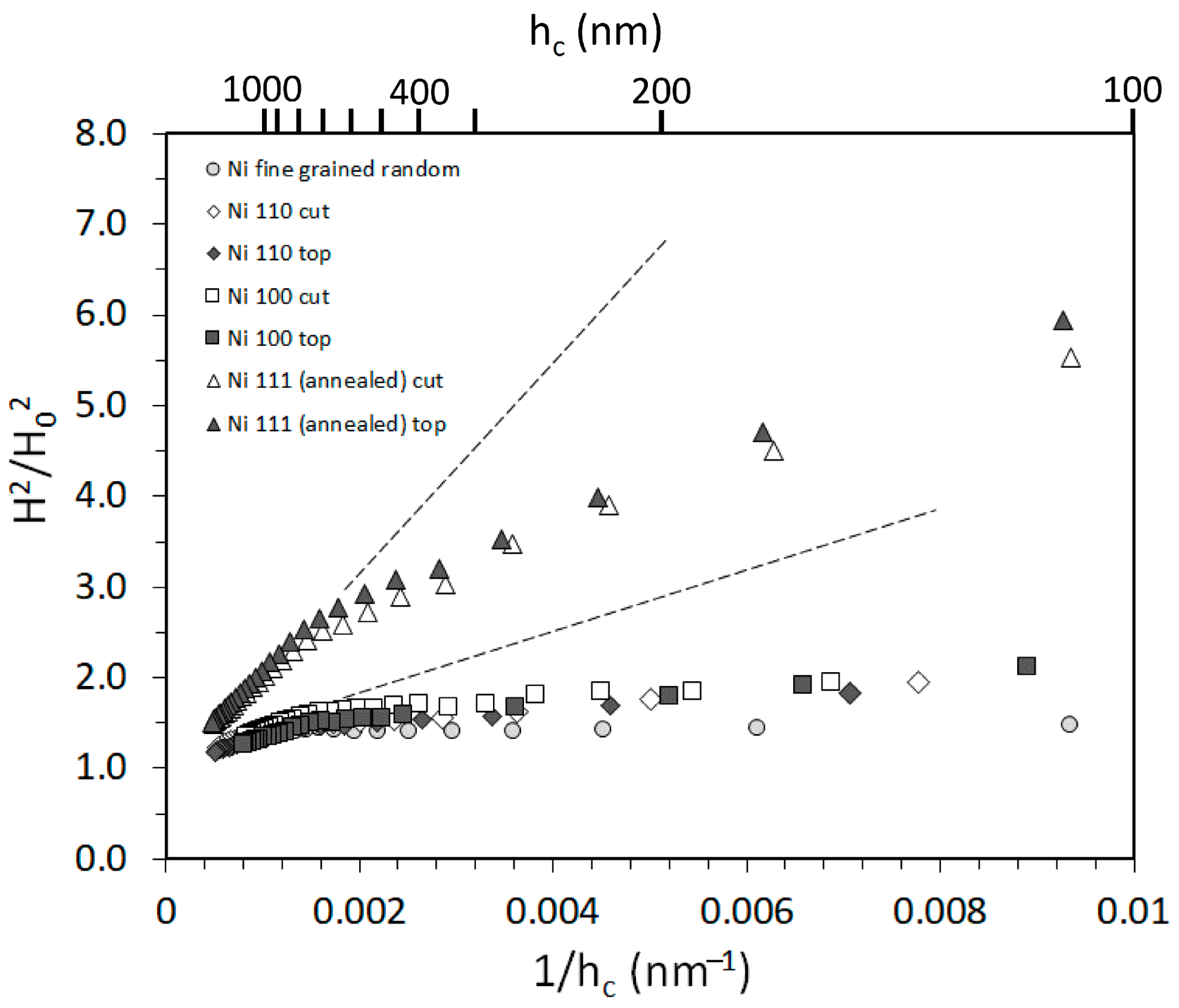
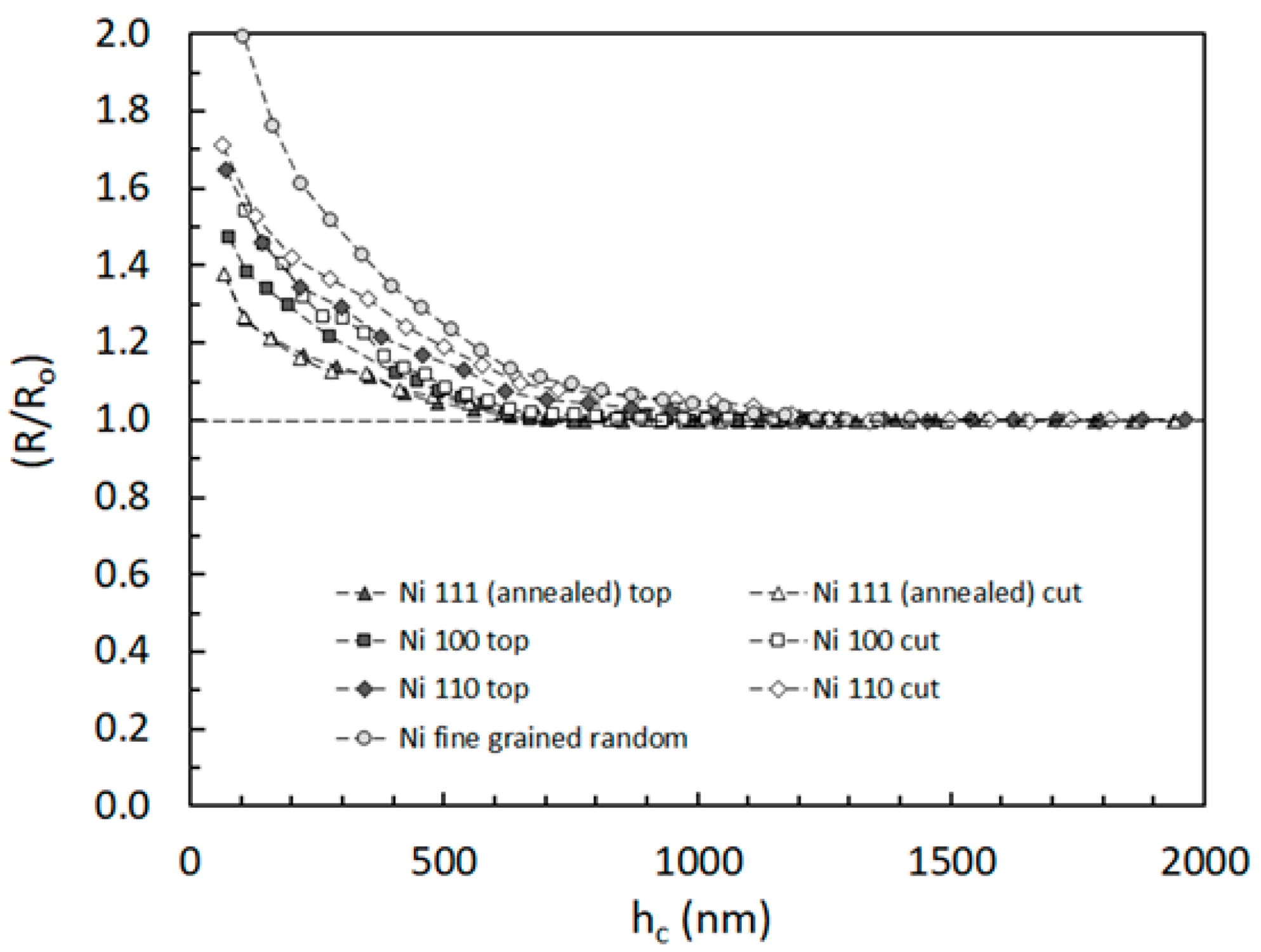
3.2. Nanoindentation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manika, I.; Maniks, J. Size effects in micro- and nanoscale indentation. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharr, G.M.; Herbert, E.G.; Gao, Y. The indentation size effect: A critical examination of experimental observations and mechanistic interpretations. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2010, 40, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nix, W.D.; Gao, H. Indentation size effects in crystalline materials: A law for strain gradient plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1998, 46, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, K.; Backes, B.; Göken, M. Indentation size effect in metallic materials: Correcting for the size of the plastic zone. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hwang, K.C.; Nix, W.D.; Pharr, G.M.; Feng, G. A model of size effects in nano-indentation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2006, 54, 1668–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swadener, J.G.; George, E.P.; Pharr, G.M. The correlation of the indentation size effect measured with indenters of various shapes. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2002, 50, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rester, M.; Motz, C.; Pippan, R. Where are the geometrically necessary dislocations accommodating small imprints? J. Mater. Res. 2009, 24, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, K.; Backes, B.; Franke, O.; Göken, M. Indentation size effect in metallic materials: Modeling strength from pop-in to macroscopic hardness using geometrically necessary dislocations. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 2547–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Nix, W.D. Indentation size effect in MgO. Scr. Mater. 2004, 51, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haušild, P. On the breakdown of the Nix-Gao model for indentation size effect. Philos. Mag. 2021, 101, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randle, V.; Rios, P.R.; Hu, Y. Grain growth and twinning in nickel. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reca, N.W.; Pampillo, C.A. Grain boundary diffusivity via bulk diffusion measurements during grain growth. Scr. Metall. 1975, 9, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čech, J.; Haušild, P.; Materna, A.; Kovářík, O. Examination of Berkovich indenter tip bluntness. Mater. Des. 2016, 109, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicot, D.; N’Jock, M.Y.; Puchi-Cabrera, E.S.; Iost, A.; Staia, M.H.; Louis, G.; Bouscarrat, G.; Aumaitre, R. A contact area function for Berkovich nanoindentation: Application to hardness determination of a TiHfCN thin film. Thin Solid Film. 2014, 558, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amblard, J.; Froment, M.; Maurin, G.; Spyrellis, N.; Trevisan-Souteyrand, E. Nickel electrocrystallization-from nucleation to textures. Electrochim. Acta 1983, 28, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.B.; Holmes, S.M. The stacking-fault energy of nickel. Philos. Mag. A 1977, 35, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Voort, G.F. Metallography: Principles and Practice; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1984; ISBN 0070669708. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, J.; Jiang, B.; Dong, Y.; Yang, L.; Drummer, D.; Zhang, L. Tuning residual stress in electrodeposited nickel films via pulse current. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 40, 103038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinville, J.C.; Tromas, C.; Villechaise, P.; Templier, C. Anisotropy changes in hardness and indentation modulus induced by plasma nitriding of 316L polycrystalline stainless steel. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haušild, P.; Materna, A.; Nohava, J. Characterization of anisotropy in hardness and indentation modulus by nanoindentation. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2014, 3, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Vehoff, H. Dependence of nanohardness upon indentation size and grain size—A local examination of the interaction between dislocations and grain boundaries. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.B.; Lee, H.K.; Park, H.C. Effect of grain size on the indentation hardness for polycrystalline materials by the modified strain gradient theory. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 2719–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Greer, J.R. Size-induced weakening and grain boundary-assisted deformation in 60 nm grained Ni nanopillars. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.K.; Chen, Z.; Lu, W.J.; Xiao, L. Continuous multi-cycle nanoindentation behavior of a gradient nanostructured metastable β titanium alloy fabricated by rotationally accelerated shot peening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 799, 140370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Legros, M.; Minor, A.M. In situ TEM nanomechanics. MRS Bull. 2015, 40, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| J (A cm−2) | D (nm) | H0 (MPa) | h0 (nm) | h1 (nm) | n | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni 111 (annealed) top | 0.1 | ~105 | 752 | 1077 | 37 | 0.68 |
| Ni 111 (annealed) cut | 0.1 | 818 | 990 | 37 | 0.68 | |
| Ni 100 top | 0.1 | ~103 | 2205 | 356 | 85 | 0.78 |
| Ni 100 cut | 0.1 | 2461 | 427 | 145 | 0.73 | |
| Ni 110 top | 0.01 | ~500 | 2922 | 368 | 128 | 0.80 |
| Ni 110 cut | 0.01 | 3343 | 436 | 110 | 0.75 | |
| Ni fine grained random | 0.01 | ~100 | 5363 | 408 | 2260 | 1.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haušild, P.; Čech, J.; Karlík, M.; Legros, M.; Nohava, J.; Merle, B. Indentation Size Effect in Electrodeposited Nickel with Different Grain Size and Crystal Orientation. Crystals 2023, 13, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13091385
Haušild P, Čech J, Karlík M, Legros M, Nohava J, Merle B. Indentation Size Effect in Electrodeposited Nickel with Different Grain Size and Crystal Orientation. Crystals. 2023; 13(9):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13091385
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaušild, Petr, Jaroslav Čech, Miroslav Karlík, Marc Legros, Jiří Nohava, and Benoit Merle. 2023. "Indentation Size Effect in Electrodeposited Nickel with Different Grain Size and Crystal Orientation" Crystals 13, no. 9: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13091385
APA StyleHaušild, P., Čech, J., Karlík, M., Legros, M., Nohava, J., & Merle, B. (2023). Indentation Size Effect in Electrodeposited Nickel with Different Grain Size and Crystal Orientation. Crystals, 13(9), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13091385






