Crystal Structure, Raman Spectroscopy and Optical Property Study of Mg-Doped SnO2 Compounds for Optoelectronic Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Materials
2.2. Characterization Methods of the Materials
- (i)
- Structural Characterization
- (ii)
- Optical Properties Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
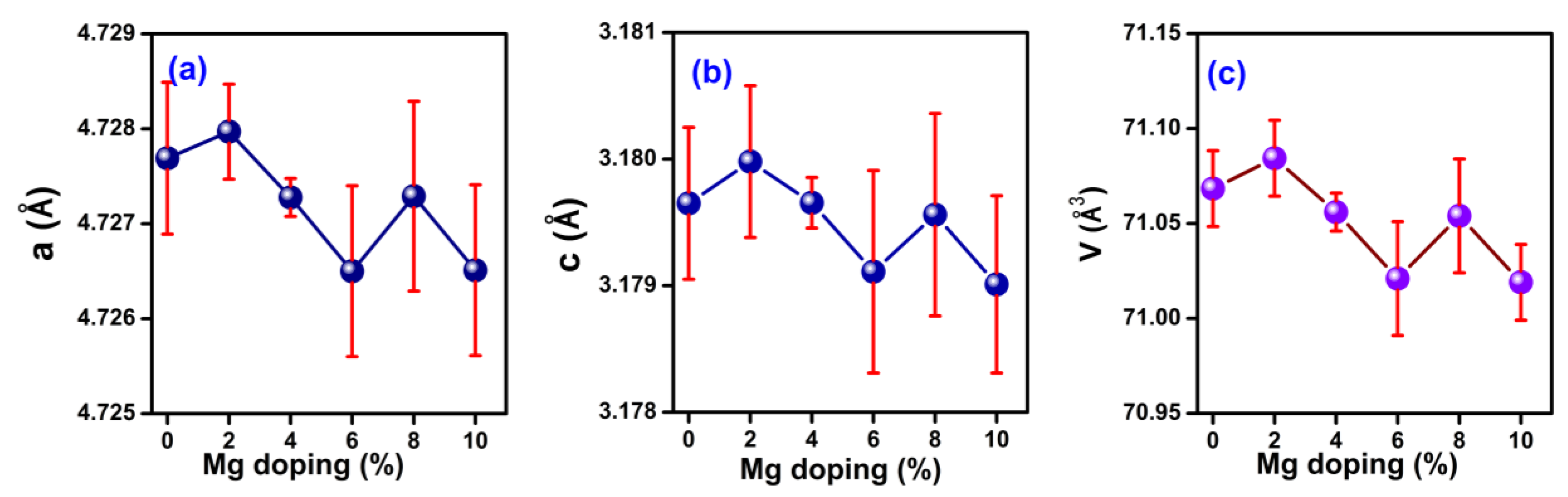
3.1. Crystal Structure
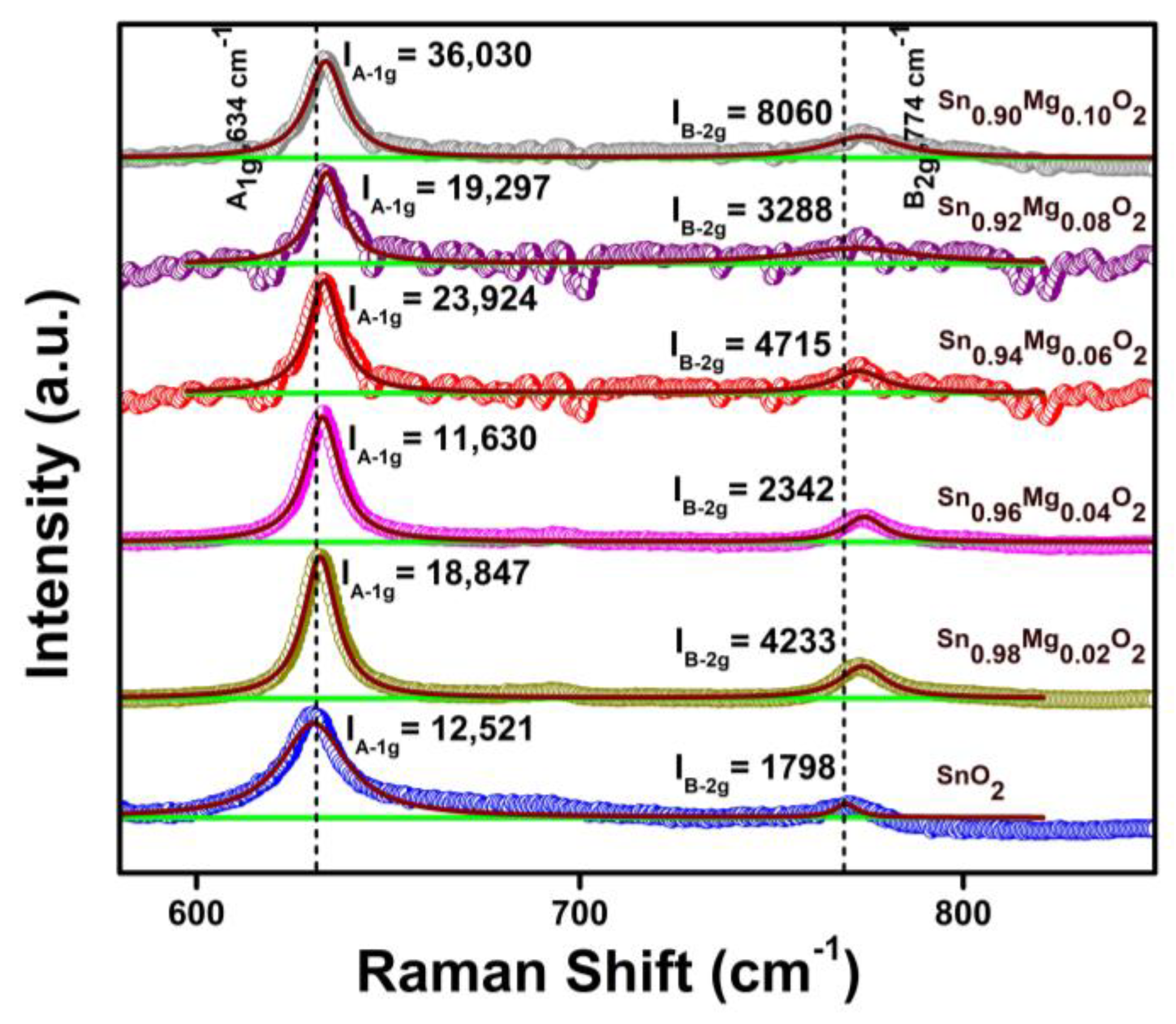
3.2. Raman Spectroscopy
3.3. Optical Property
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chouhan, L.; Srivastava, S.K. A comprehensive review on recent advancements in d0 ferromagnetic oxide materials. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 147, 106768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, H. Making nonmagnetic semiconductors ferromagnetic. Science 1998, 281, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.A.; Awschalom, D.D.; Buhrman, R.A.; Daughton, J.M.; Molnar, S.V.; Roukes, M.L.; Chtcheljanova, A.Y.; Treger, D.M. Spintronics: A spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science 2001, 294, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furdyna, J.K. Diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogale, S.B.; Choudhary, R.J.; Buban, J.P.; Lofland, S.E.; Shinde, S.R.; Kale, S.N.; Kulkarni, V.N.; Higgins, J.; Lanci, C.; Simpson, J.R.; et al. High Temperature Ferromagnetism with a Giant Magnetic Moment in Transparent Co-dopedSnO2−δ. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 077205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Lejay, P.; Barbara, B.; Boisron, O.; Pailhès, S.; Bouzerar, G. Absence of ferromagnetism in Mn-doped tetragonal zirconia. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 043929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Brahma, R.; Datta, S.; Guha, S.; Aakansha; Baro, S.S.; Narzary, B.; Basumatary, D.R.; Kar, M.; Ravi, S. Effect of (Ni-Ag) co-doping on crystal structure and magnetic Property of SnO2. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 126107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K. Magnetic Property of Mn-Doped Monoclinic ZrO2 Compounds. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2020, 33, 2501–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam-Ismail, M.; El-Hagary, M.; Shaaban, E.; Althoyaib, S. Structural and optical investigation of nanocrystalline Zn1−xNixS diluted magnetic semiconductor thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 529, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hagary, M.; Shaaban, E.; Emam-Ismail, M.; Althoyaib, S. Microstructural and optoelectronic properties of diluted magnetic semiconducting Cd1−xFexS nanocrystalline films. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 520, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selloum, D.; Henni, A.; Karar, A.; Tabchouche, A.; Harfouche, N.; Bacha, O.; Tingry, S.; Rosei, F. Effects of Fe concentration on properties of ZnO nanostructures and their application to photocurrent generation. Solid State Sci. 2019, 92, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henni, A.; Harfouche, N.; Karar, A.; Zerrouki, D.; Perrin, F.; Rosei, F. Synthesis of graphene–ZnO nanocomposites by a one-step electrochemical deposition for efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutant. Solid State Sci. 2019, 98, 106039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumura, T.; Jin, Z.; Kawasaki, M.; Shono, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Koshihara, S.; Koinuma, H. Magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 958–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietl, T. A ten-year perspective on dilute magnetic semiconductors and oxides. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Zhan, P.; Xie, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z. Room-temperature ferromagnetism in un-doped ZrO2 thin films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 445004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D.; Venkatesan, M.; Stamenov, P.; Fitzgerald, C.B.; Dorneles, L. Magnetism in hafnium dioxide. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 024450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, M.; Fitzgerald, C.B.; Coey, J.M.D. Unexpected magnetism in a dielectric oxide. Nature 2004, 430, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Gao, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Z.; Xue, D. Evidence of Vacancy-Induced Room Temperature Ferromagnetism in Amorphous and Crystalline Al2O3 Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 16814–16818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, N.H.; Sakai, J.; Poirot, N.; Brizé, V. Room-temperature ferromagnetism observed in undoped semiconducting and insulating oxide thin films. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 132404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzerar, G.; Ziman, T. Model for Vacancy-Induced d0 Ferromagnetism in Oxide Compounds, ferromagnetism in oxide compounds. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 207602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, N.H.; Song, J.-H.; Raghavender, A.T.; Asaeda, T.; Kurisu, M. Ferromagnetism in C-doped SnO2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 052505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, W. Room-temperature ferromagnetism in epitaxial Mg-doped SnO2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 182405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, V.B.; Bhat, S.V.; Umarji, A.M. Investigating thermal stability of structural defects and its effect on d0 ferromagnetism in undoped SnO2. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 244307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Iqbal, J.; Wu, Z.; He, B.; Yu, R. Structure and Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism of Zn-Doped SnO2 Nanorods Prepared by Solvothermal Method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 4790–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Lejay, P.; Hadj-Azzem, A.; Bouzerar, G. Non-magnetic Impurity Induced Magnetism in Li-Doped SnO2 Nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2013, 27, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, M.; Kumar, R.; Srivastava, S.K.; Verma, A.; Mathur, A.; Chawla, V.; Rubahn, G.-H.; Joshi, M.; Mishra, Y.K. ZnO/α-MnO2 hybrid 1D nanostructure based sensor for point-of-care monitoring of chlorinated phenol in drinking water. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narzary, R.; Dey, B.; Chouhan, L.; Kumar, S.; Ravi, S.; Srivastava, S. Optical band gap tuning, zero dielectric loss and room temperature ferromagnetism in (Ag/Mg) co-doped SnO2 compounds for spintronics applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 142, 106477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, L.; Panda, S.K.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Das, B.; Mondal, A.; Parida, B.; Brahma, R.; Manglam, M.K.; Kar, M.; Bouzerar, G.; et al. Room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, zero dielectric loss and ac-conductivity enhancement in p-type Ag-doped SnO2 compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 870, 159515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, L.; Bouzerar, G.; Srivastava, S.K. Effect of Mg-doping in tailoring d0 ferromagnetism of rutile TiO2 compounds for spintronics application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 11193–11201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Lejay, P.; Barbara, B.; Boisron, O.; Pailhès, S.; Bouzerar, G. Non-magnetic impurity induced magnetism in rutile TiO2:K compounds. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2011, 23, 442202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, L.; Narzary, R.; Dey, B.; Panda, S.K.; Manglam, M.K.; Roy, L.; Brahma, R.; Mondal, A.; Kar, M.; Ravi, S.; et al. Tailoring room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, dielectric, optical, and transport properties in Ag-doped rutile TiO2 compounds for spintronics applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 28163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narzary, R.; Dey, B.; Sen, S.; Parida, B.N.; Mondal, A.; Ravi, S.; Srivastava, S.K. Influence of Na/Mg co-doping in tuning microstructure, transport, optical and magnetic properties of TiO2 compounds for spintronics applications. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Guillén, J.; Lany, S.; Zunger, A. Atomic Control of Conductivity Versus Ferromagnetism in Wide-Gap Oxides Via Selective Doping: V, Nb, Ta in Anatase TiO2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 036601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Guan, L.; Pan, J.; Huan, C.; Wang, L.; Kuo, J. Possible room temperature ferromagnetism of Li-doped anatase TiO2: A first-principles study. Phys. Lett. A 2010, 374, 4451–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Ohno, T. First-principles study of graphene under c-HfO2(111) layers: Electronic structures and transport properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 083105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadacek, N.; Nosov, A.; Ranno, L.; Strobel, P.; Galéra, R.-M. Magnetic properties of HfO2 thin films. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 486206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Guillén, J.; Lany, S.; Barabash, S.V.; Zunger, A. Magnetism without Magnetic Ions: Percolation, Exchange, and Formation Energies of Magnetism-Promoting Intrinsic Defects in CaO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 107203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, B.; Narzary, R.; Chouhan, L.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Parida, B.N.; Mondal, A.; Ravi, S.; Srivastava, S.K. Crystal structure, optical and dielectric properties of Ag:ZnO composite-like compounds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 2855–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, B.; Narzary, R.; Panda, S.K.; Mallick, J.; Mondal, A.; Ravi, S.; Kar, M.; Srivastava, S. Room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, band-gap reduction, and high optical transparency in p-type K-doped ZnO compounds for spintronics applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 148, 106798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narzary, R.; Dey, B.; Rout, S.N.; Mondal, A.; Bouzerar, G.; Kar, M.; Ravi, S.; Srivastava, S. Influence of K/Mg co-doping in tuning room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, optical and transport properties of ZnO compounds for spintronics applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 934, 167874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Jayanthi, K.; Kotnala, R.K. Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Li-doped p-type luminescent ZnO nanorods. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 125204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Ólafsson, S.; Gíslason, H. Vacancy defect-induced d0 ferromagnetism in undoped ZnO nanostructures: Controversial origin and challenges. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 90, 45–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.-H.; Freeman, A.J.; Delley, B. Half-metallic ferromagnetism in Cu-doped ZnO: Density functional calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 033203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Yi, J.; Shen, L.; Wu, R.Q.; Yang, S.; Lin, J.Y.; Feng, Y.P.; Ding, J.; Van, L.H.; Yin, J.H. Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism in Carbon-Doped ZnO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 127201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, L.; Bouzerar, G.; Srivastava, S. d0 Ferromagnetism in Ag-doped monoclinic ZrO2 compounds. Vacuum 2020, 182, 109716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, B.; Panda, S.K.; Mallick, J.; Sen, S.; Parida, B.; Mondal, A.; Kar, M.; Srivastava, S. Observation of room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, bandgap narrowing, zero dielectric loss, dielectric enhancement in highly transparent p-type Na-doped rutile TiO2 compounds for spintronics applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 930, 167442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máca, F.; Kudrnovský, J.; Drchal, V.; Bouzerar, G. Magnetism without magnetic impurities in ZrO2 oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 212503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrere, S.; Zaban, A.; Gregg, B.A. Dye Sensitization of Nanocrystalline Tin Oxide by Perylene Derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 4490–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzill, M.; Diebold, U. The surface and materials science of tin oxide. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2005, 79, 47–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri-Mohagheghi, M.-M.; Shokooh-Saremi, M. Electrical, optical and structural properties of Li-doped SnO2transparent conducting films deposited by the spray pyrolysis technique: A carrier-type conversion study. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2004, 19, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Wu, P. Band gap widening and d0 ferromagnetism in epitaxial Li-doped SnO2 films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 314, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Lejay, P.; Barbara, B.; Pailhès, S.; Madigou, V.; Bouzerar, G. Possible room-temperature ferromagnetism in K-doped SnO2: X-ray diffraction and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy study. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 193203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieguez, A.; Romano-Rodriguez, A.; Vilà, A.; Morante, J.R. The complete Raman spectrum of nanometric SnO2 particles. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, N.; Sen, D.; Saha, S.; Ghorai, U.K.; Das, N.S.; Chattopadhyay, K.K. Enhanced Ultraviolet Emission from Mg Doped SnO2 Nanocrystals at Room Temperature and Its Modulation upon H2 Annealing. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 6454–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Xie, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Novel p-type conductivity in SnO2 thin films by Mg doping. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 714, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.M.; Hussain, S.T.; Abu Bakar, S.; Muhammad, J.; Rehman, N.U. Effect of doping on the Structural and Optical Properties of SnO2 Thin Films fabricated by Aerosol Assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition. J. Physics Conf. Ser. 2013, 439, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.A.; Wiles, D.B. Profile shape functions in Rietveld refinements. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1982, 15, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, J.R. Introduction to the Program FULLPROF: Refinement of Crystal and Magnetic Structures from Powder and Single Crystal Data, Laboratoire Leon Brillouin (CEA-CNRS); CEA/Saclay: Gif sur Yvette Cedex, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, I.; Colmenares, Y.; Pizani, P.; Leite, E.; Chiquito, A. Sb doping of VLS synthesized SnO2 nanowires probed by Raman and XPS spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 695, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Xu, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Hu, Y.; Qian, Y. Study of the Raman spectrum of nanometer SnO2. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 75, 1835–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical Properties and Electronic Structure of Amorphous Germanium. Phys. Status Solidi B 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Shah, S.M.; Hussain, H.; Khan, R.A. Effect of carrier concentration on the optical band gap of TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
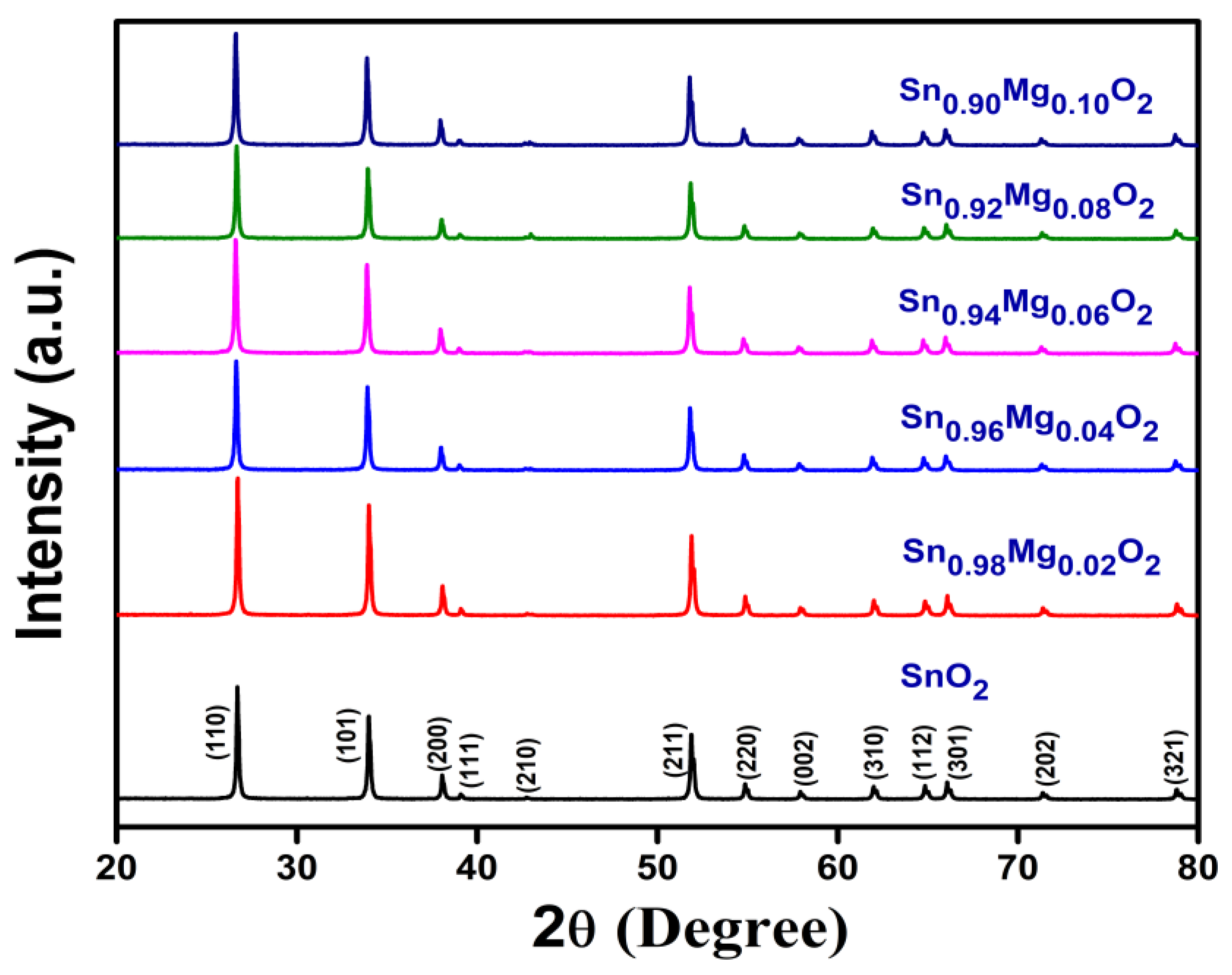
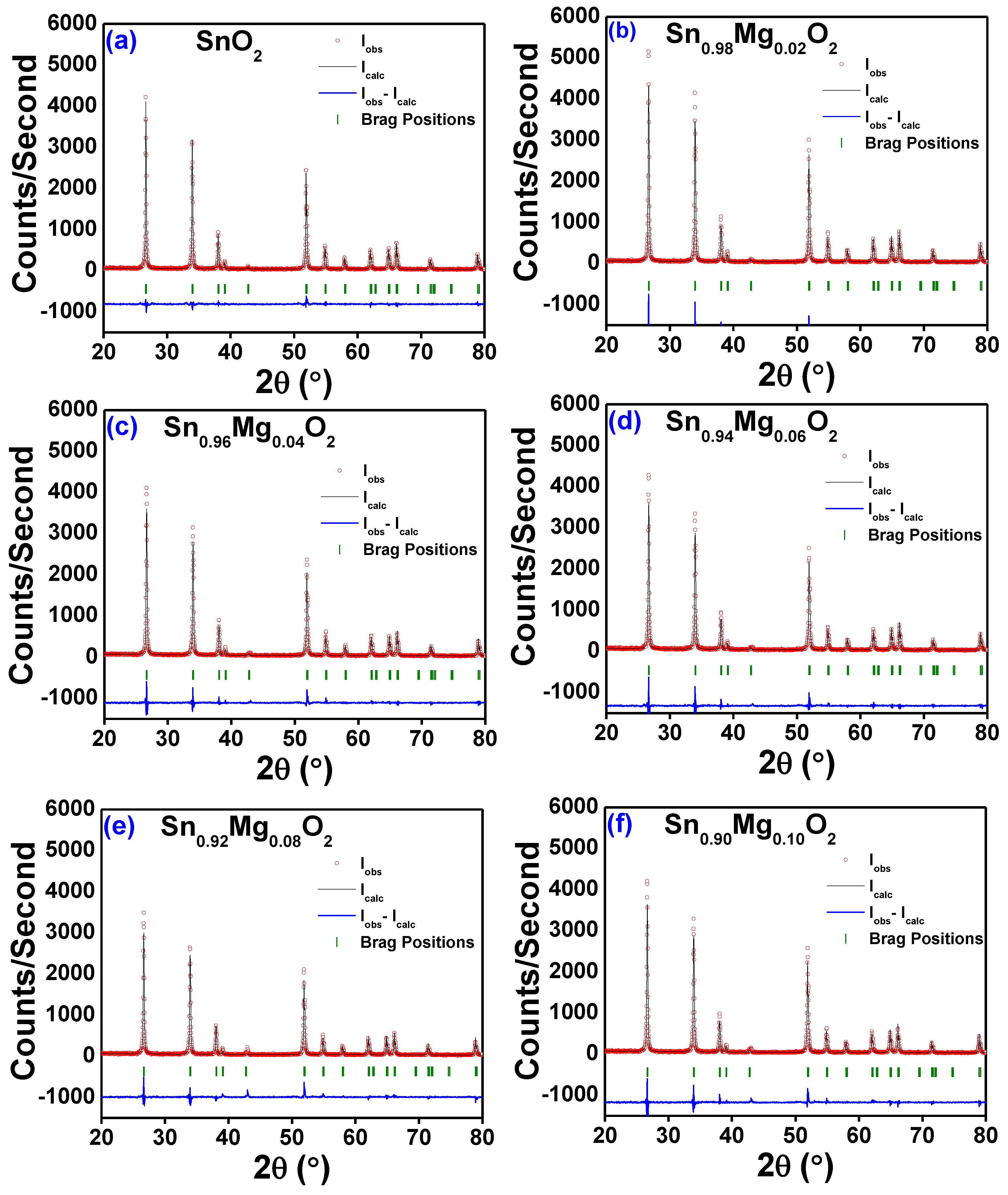




| Sample/ Parameters | x = 0.00 | x = 0.02 | x = 0.04 | x = 0.06 | x = 0.08 | x = 0.10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space Group | Tetragonal (P42/mnm) | Tetragonal (P42/mnm) | Tetragonal (P42/mnm) | Tetragonal (P42/mnm) | Tetragonal (P42/mnm) | Tetragonal (P42/mnm) |
| a (Å) | 4.7277 (0.0008) | 4.7280 (0.0005) | 4.7273 (0.0002) | 4.7265 (0.0009) | 4.7273 (0.0010) | 4.7265 (0.0009) |
| b (Å) | 4.7277 (0.0008) | 4.7280 (0.0005) | 4.7273 (0.0002) | 4.7265 (0.0009) | 4.7273 (0.0010) | 4.7265 (0.0009) |
| c (Å) | 3.1796 (0.0006) | 3.1800 (0.0006) | 3.1797 (0.0002) | 3.1791 (0.0008) | 3.1796 (0.0008) | 3.1730 (0.0007) |
| Volume (Å) | 71.07 (0.02) | 71.08 (0.02) | 71.06 (0.01) | 71.02 (0.03) | 71.05 (0.03) | 71.02 (0.02) |
| χ2 (%) | 1.33 | 2.13 | 1.94 | 2.17 | 2.29 | 2.33 |
| RBrag (%) | 3.09 | 2.89 | 2.92 | 3.16 | 6.58 | 3.89 |
| Rf (%) | 4.06 | 3.74 | 3.62 | 3.54 | 6.66 | 4.98 |
| Rp (%) | 15.60 | 13.20 | 13.60 | 14.30 | 15.20 | 14.10 |
| Rωp (%) | 17.50 | 15.00 | 15.80 | 16.20 | 18.00 | 16.50 |
| Rexp (%) | 15.20 | 10.29 | 11.39 | 11.02 | 11.90 | 10.79 |
| Crystallite Size (nm) | 79.0 | 54.9 | 53.1 | 52.0 | 56.7 | 53.4 |
| Sample/Parameters | 0% | 2% | 4% | 6% | 8% | 10% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Center (A1g) (cm−1) | 630.6 | 632.2 | 632.9 | 633.3 | 634.0 | 633.7 |
| Intensity (A1g) | 12,521.0 | 18,847.1 | 11,630.5 | 23,924.9 | 19,297.4 | 36,030.4 |
| Center (B2g) (cm−1) | 769.3 | 773.7 | 774.15 | 772.6 | 771.8 | 774.0 |
| Intensity (B2g) | 1798.6 | 4233.4 | 2342.7 | 4715.0 | 3288.8 | 8060.3 |
| FWHM (A1g) (cm−1) | 11.9 | 10.5 | 10.9 | 10.0 | 9.9 | 10.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singha, K.K.; Singh, P.P.; Narzary, R.; Mondal, A.; Gupta, M.; Sathe, V.G.; Kumar, D.; Srivastava, S.K. Crystal Structure, Raman Spectroscopy and Optical Property Study of Mg-Doped SnO2 Compounds for Optoelectronic Devices. Crystals 2023, 13, 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13060932
Singha KK, Singh PP, Narzary R, Mondal A, Gupta M, Sathe VG, Kumar D, Srivastava SK. Crystal Structure, Raman Spectroscopy and Optical Property Study of Mg-Doped SnO2 Compounds for Optoelectronic Devices. Crystals. 2023; 13(6):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13060932
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingha, K. K., P. P. Singh, R. Narzary, A. Mondal, M. Gupta, V. G. Sathe, D. Kumar, and S. K. Srivastava. 2023. "Crystal Structure, Raman Spectroscopy and Optical Property Study of Mg-Doped SnO2 Compounds for Optoelectronic Devices" Crystals 13, no. 6: 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13060932
APA StyleSingha, K. K., Singh, P. P., Narzary, R., Mondal, A., Gupta, M., Sathe, V. G., Kumar, D., & Srivastava, S. K. (2023). Crystal Structure, Raman Spectroscopy and Optical Property Study of Mg-Doped SnO2 Compounds for Optoelectronic Devices. Crystals, 13(6), 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13060932








