Morphology and Structure Characteristics of the Rare Black-Glazed Porcelains Excavated from the Jian Kiln Site of Song Dynasty
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Characterization Techniques
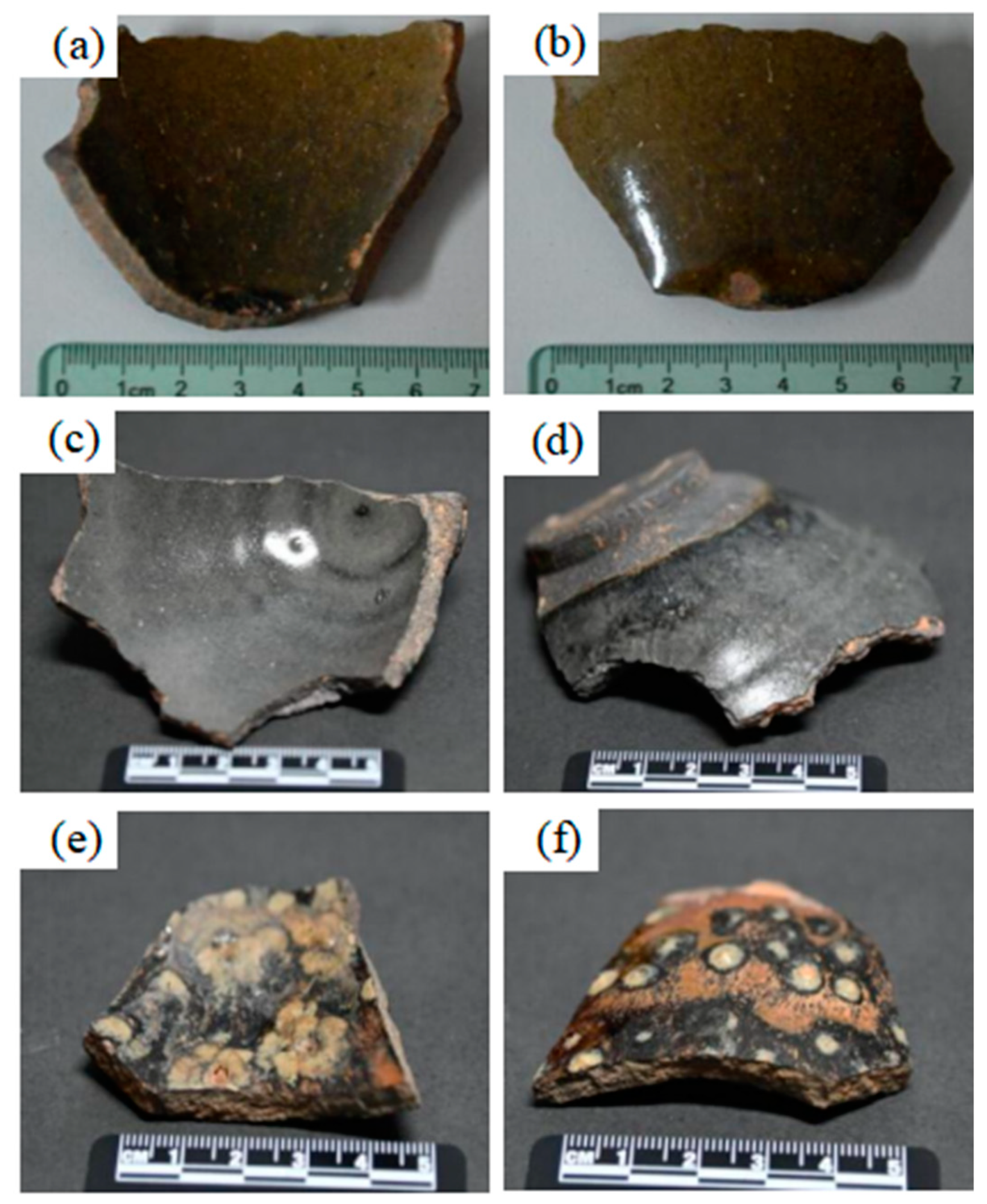
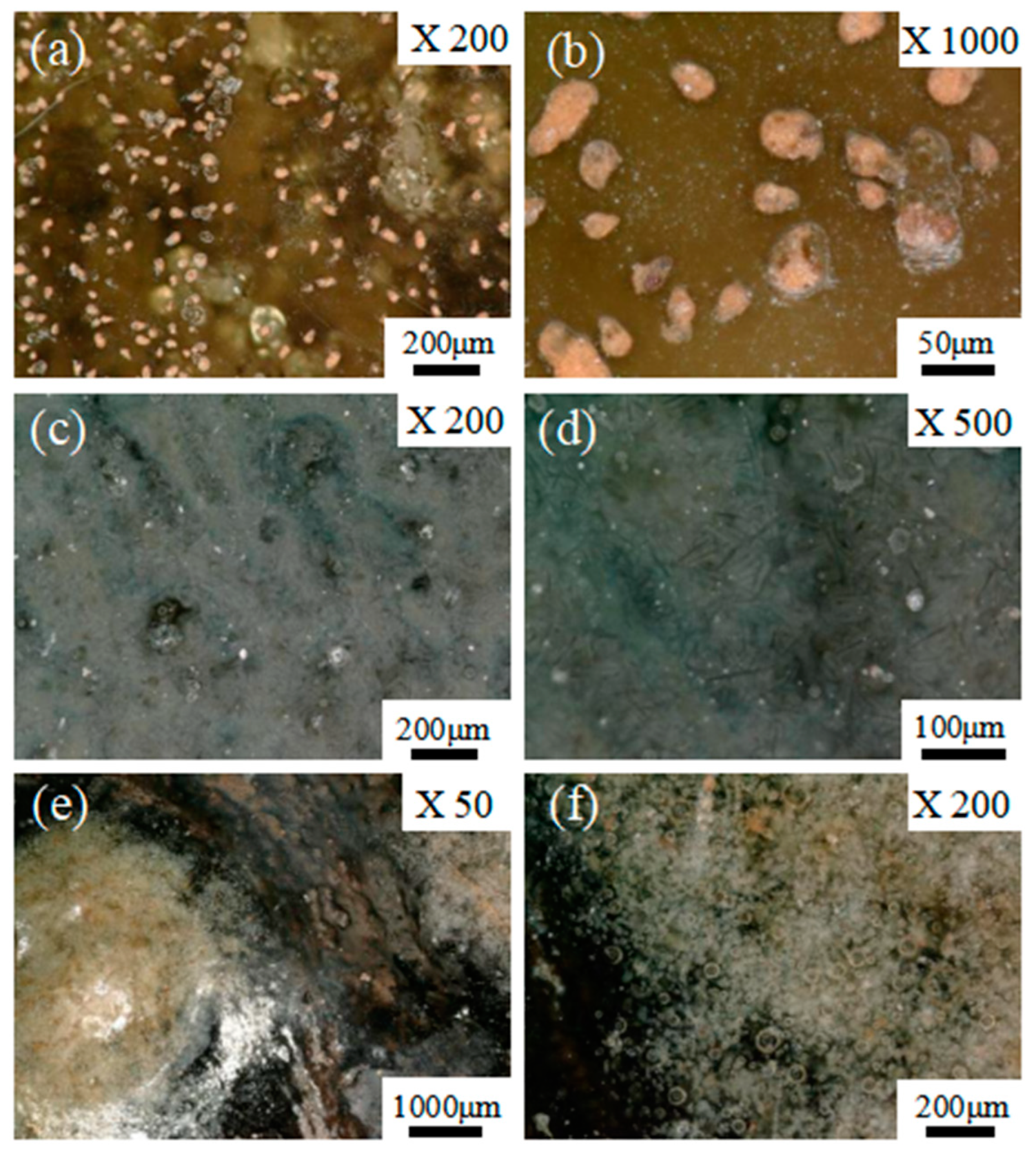
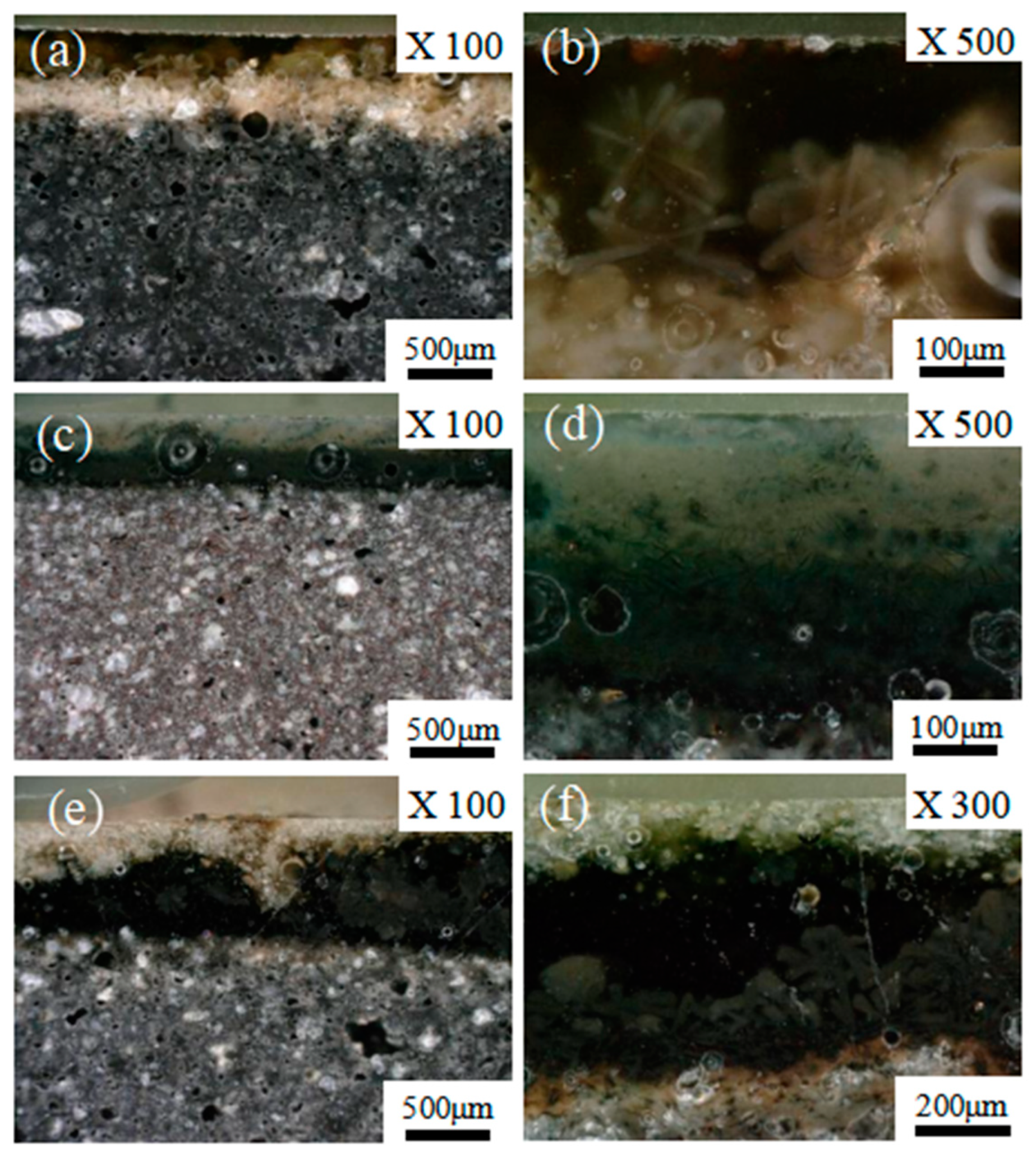
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition Analysis by XRF
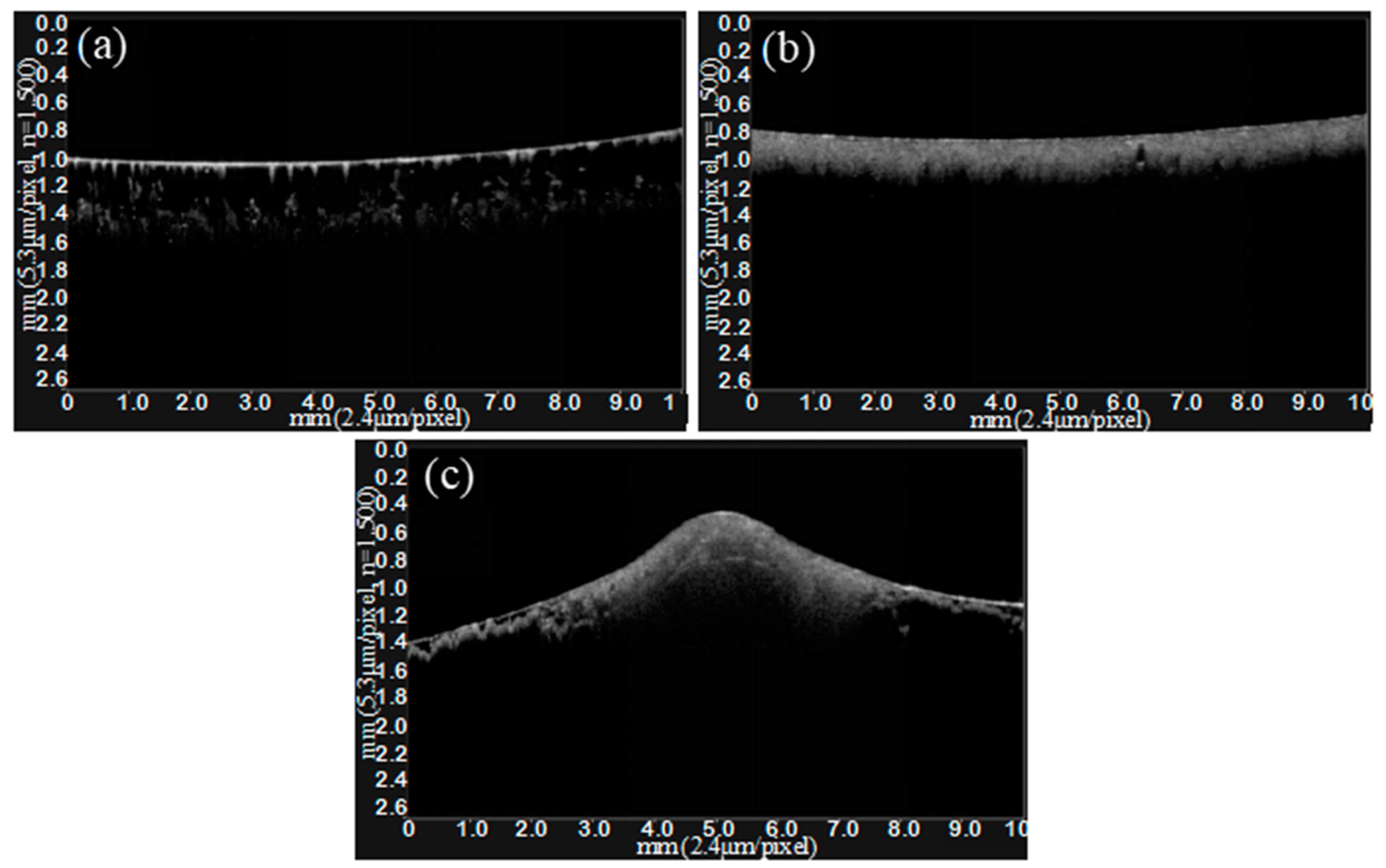
3.2. Cross-Section Structure Analysis by OCT
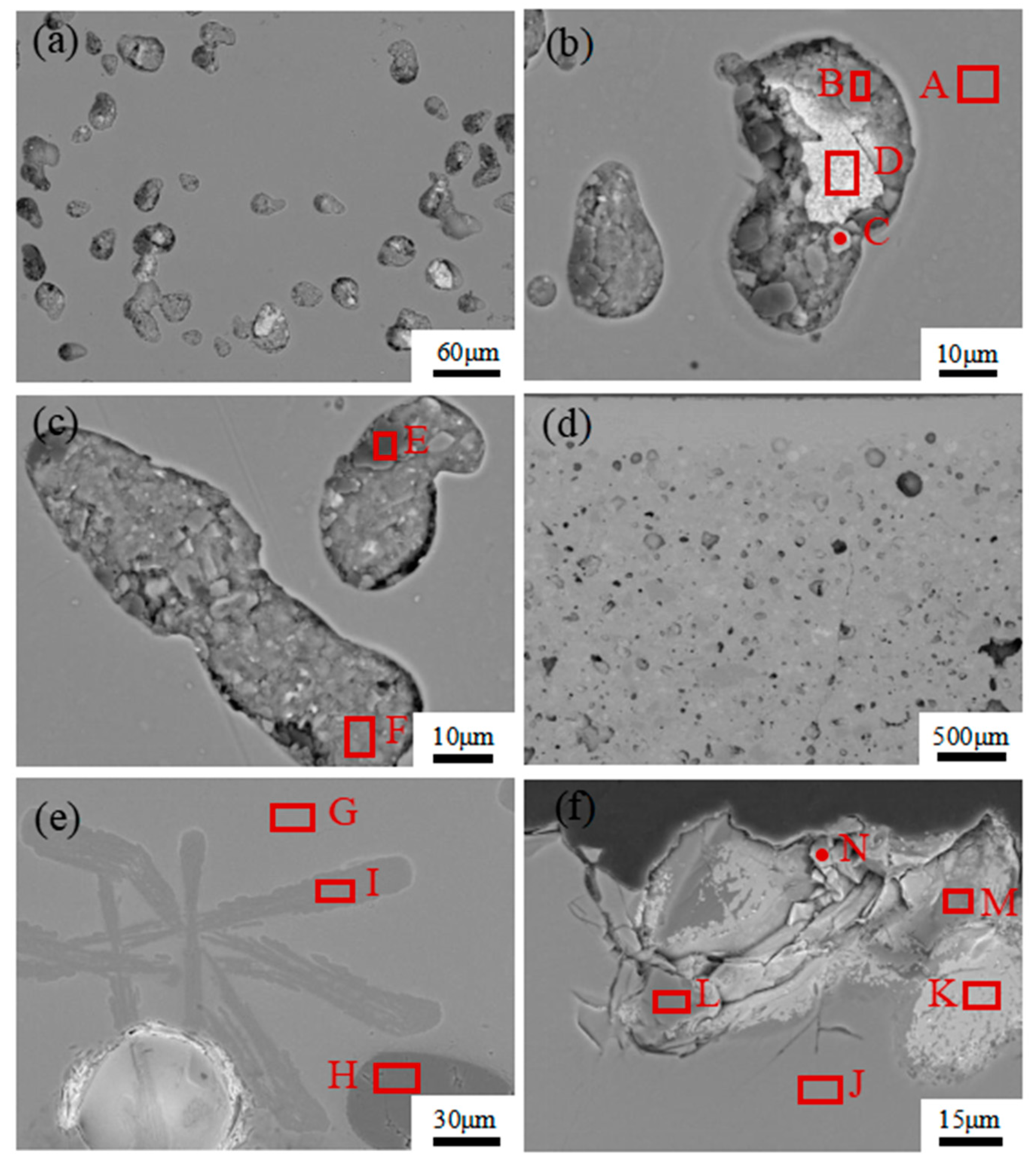
3.3. Microstructure Analysis by OM
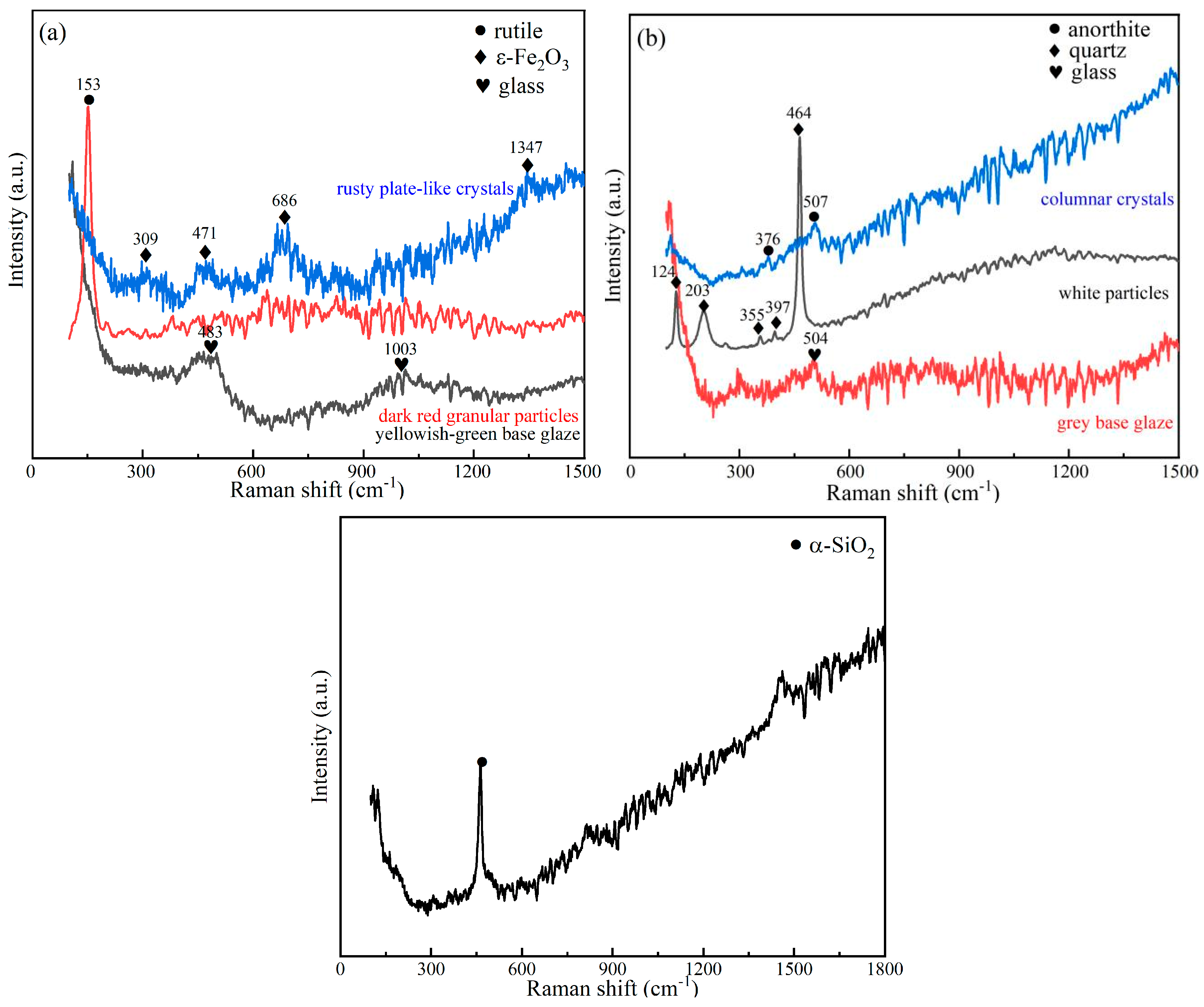
3.4. Phase Composition Analysis by RS
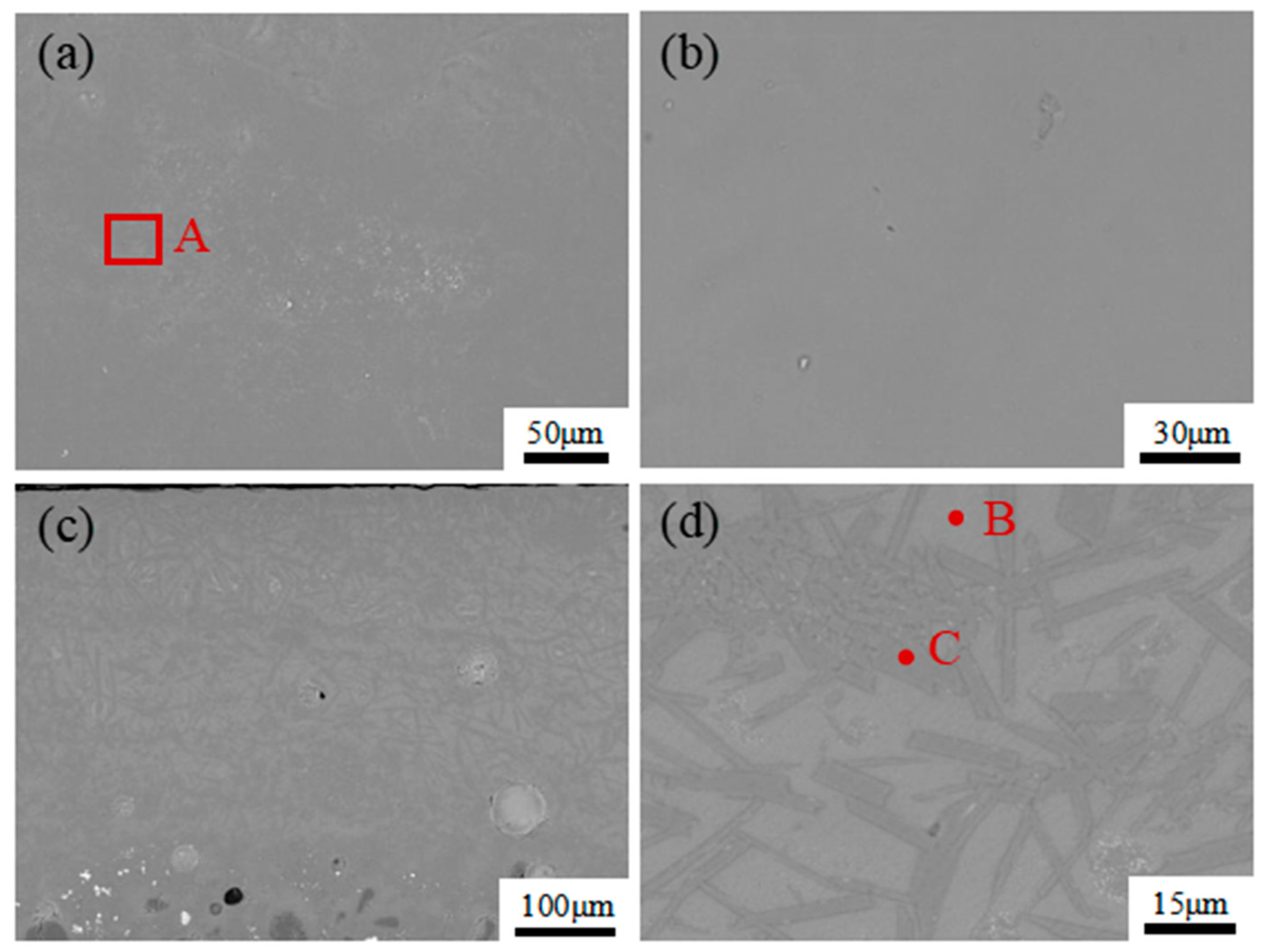
3.5. Microstructure Analysis by SEM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Huang, R. A study on Song dynasty Jian bowl. China Ceram. 1983, 2, 61–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Z. A preliminary study on ancient black glazed porcelain in China. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 1979, 7, 190–200, 283–284. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M. Black-Glazed Jian Ware and Tea Drinking in the Song Dynasty; Orientations: Hong Kong, China, 1998; pp. 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, W.; Lu, X.; Xu, C. Controllable preparation and decorative effect of iron-based crystalline glazes. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 48, 1134–1144. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Liu, S.; Yuan, Y.; Dong, J.; Li, Q. A microstructural and compositional study of ε-Fe2O3 crystals in the hare’s fur Jian Ware. Crystals 2022, 12, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, W.; Xu, C.; Lu, X. Angle dependence of Jian bowl color and its coloring mechanism. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 42, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, J.; Yu, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, L. Imitation of ancient black-glazed Jian bowls (Yohen Tenmoku): Fabrication and characterization. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 15269–15273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Kang, B.; Wei, X.; Li, G.; Jia, C.; Li, H.; Ding, Y.; Lei, Y. The microstructure of multicolor hare’s fur glaze: The correlation between mor-phological and compositional characteristics and glaze color. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N. Taking the Hare’s fur glazed bowls as an example, discussing the firing process of Jian wares. Orient. Collect. 2020, 6, 48–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Wang, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Effect of phase separation on the Jian ware blue colored glaze with iron oxide. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 16407–16413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Luo, H.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Guo, J. Studies on the microstructure of the black-glazed bowl sherds excavated from the Jian kiln site of ancient China. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejoie, C.; Sciau, P.; Li, W.; Noé, L.; Mehta, A.; Chen, K.; Luo, H.; Kunz, M.; Tamura, N.; Liu, Z. Learning from the past: Rare ε-Fe2O3 in the ancient black-glazed Jian (Tenmoku) wares. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z. Discussion on the problems related to the decoration of high-foot cup with egg white glaze pearl grains in the Yuan dynasty. China’s Ceram. 2022, 58, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Barshchevskii, B.U.; Loginov, V.M.; Neklyudova, T.L. Decorating porcelain ware with precious and semiprecious stones and colored glass. Glas. Ceram. 1995, 52, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, R.; Zhou, X. Discussion on the peculiarity of oil spot national treasure Tenmoku wares Jian of spot through the research results of the rare sherds. J. Jingdezhen Ceram. Inst. 1995, 16, 26–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X. Chemical compositions and microstructures of hare’s fur black-glazed porcelains from Jian kiln, Jizhou kiln and Yaozhou kiln sites. J. Build. Mater. 2011, 14, 329–334. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hoo, Q.; Liang, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, X.; Cao, T.; Cao, X. Millimeter-sized flower-like clusters composed of mullite and ε-Fe2O3 on the Hare’s Fur Jian Ware. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 4340–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Q.H.; Gan, F.; Zhang, P.; Lankton, J.W. Silk Road glass in Xinjiang, China: Chemical compositional analysis and interpretation using a high-resolution portable XRF spectrometer. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 2128–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Pollard, A.M.; Jiang, J.; Weng, Y. Evaluation of Quantitative XRF Analysis Applied to Determine Cobalt Sources in Chinese Blue-and-White Porcelain. Archaeometry 2020, 63, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Qiu, M.-Z.; Jing, H.-Z.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Yu, C.-L.; Zhu, J.-F.; Wang, F.; Wang, T. End-to-end ancient ceramic classification toolkit based on deep learning: A case study of black glazed wares of Jian kilns (Song Dynasty, Fujian province). Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 34516–34532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, Q.; Hu, Y. Multi-technique analysis of an ancient stratified glass eye bead by OCT, μ-XRF, and μ-Raman spectroscopy. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2020, 18, 090001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.; Guo, M.; Hu, Y.; Song, L.; Dong, J.; Li, Q. Nondestructive analysis of iron rich porcelains excavated from Qingliangsi Site in Baofeng Country, Henan Province. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 1, 172–179. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Dong, J.; Guo, M. Preliminary research in section structure characteristics of ancient glaze based on OCT technology. Chin. J. Lasers 2014, 41, 0908001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F. Science of Chinese Ancient Ceramics; Shanghai People’s Fine Arts Publishing House: Shanghai, China, 2000; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Zhao, W.; Ren, X.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Feng, S.; Feng, X.; Zhao, H. Firing process and colouring mechanism of black glaze and brown glaze porce-lains from the Yuan and Ming dynasties from the Qingliang Temple kiln in Baofeng, Henan, China. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 32817–32827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. The structural analysis and coordination discussion on iron-ion tinting principle in iron oxide Containing glass. Glass Enamel 2004, 32, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, R.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Dang, Y. The colouring mechanism of the Brown glaze porcelain of the Yaozhou Kiln in the Northern Song Dynasty. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 10589–10595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Miu, S.; Yu, P.; Wei, H.; Li, X. Development of high-temperature reducing tea dust glaze. China Ceram. Ind. 2015, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Li, W.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W.; Luo, H.; Guo, J. Unveiling the science behind the tea bowls from the Jizhou kiln. Part I. Chemical compositions and the two-layer glazing technique. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 8540–8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, W.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W.; Luo, H.; Guo, J. Unveiling the science behind the tea bowls from the Jizhou kiln. Part II. Microstructures and the coloring mechanism. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 19461–19473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franci, G.; Akkas, G.T.; Yildirim, S. Characterization of a Jian-like sherd with the optical microscope, confocal Raman, wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence, and portable XRF spectrometers. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2020, 51, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yang, J. A discussion of tea dust glaze porcelain. Palace Mus. J. 2004, 01.012, 112–117, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, L.; Qi, H. Study on microstructure and technology of black porcelain of Beijing Longquanwu kiln in Liao and Jin Dynasties. China Ceram. 1999, 35, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Wu, G. Effect of firing temperature on crystallization and color of tea dust glaze. J. Ceram. 2014, 35, 411–414. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, B.; Gu, X.; Dong, W.; Luo, T.; He, M.; Wu, P. Effect of chemical composition on microstructure and appearance of tea-dust type glaze. China Ceram. 2019, 55, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.W.; Zhang, Z.G.; Li, H.; Wu, W.; Hua, J.J.; Cheng, G.F.; Lin, C.C. Microstructure Characteristics of the Black-Glazed Shreds Excavated from the Qingliangsi Kiln. Key Eng. Mater. 2011, 492, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | P2O5 | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | MnO | Fe2O3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JZ-07 | glaze | N.D. | 1.76 | 17.85 | 63.34 | 0.06 | 2.56 | 5.17 | 0.53 | 0.65 | 8.08 |
| body | 1.07 | 1.17 | 18.35 | 64.64 | 0.06 | 2.19 | 0.11 | 0.82 | 0.08 | 11.52 | |
| JZ-16 | glaze | N.D. | 1.61 | 13.88 | 70.11 | 0.10 | 4.71 | 5.01 | 0.44 | 0.62 | 3.53 |
| body | 1.49 | 1.57 | 19.05 | 65.42 | 0.14 | 2.49 | 0.11 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 9.06 | |
| JZ-14 | glaze | N.D. | 1.81 | 18.05 | 67.86 | 0.08 | 4.39 | 4.54 | 0.28 | 0.41 | 2.59 |
| body | 1.33 | 1.49 | 19.58 | 66.96 | 0.11 | 2.20 | 0.12 | 0.59 | 0.07 | 7.53 |
| O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | K | Ca | Ti | Fe | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
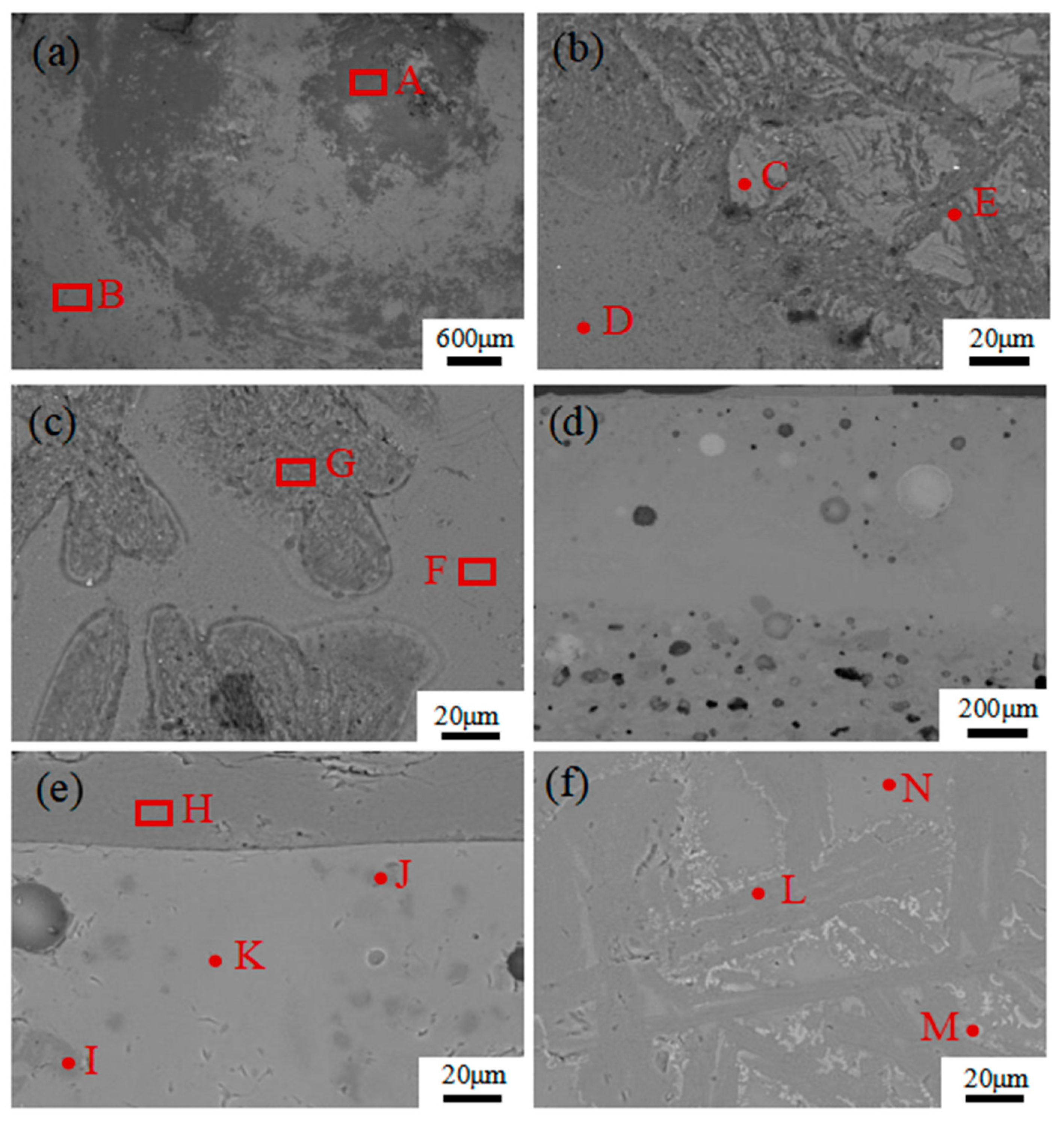
| Spots A–N, collected in Figure 6. | A | 46.68 | - | - | 8.47 | 33.54 | 3.56 | 2.28 | - | 4.40 |
| B | 56.17 | - | - | 16.99 | 22.38 | 1.29 | - | - | 1.88 | |
| C | 62.06 | - | - | 2.73 | 4.44 | - | - | 27.51 | 2.10 | |
| D | 36.63 | - | 1.72 | 2.83 | 4.60 | - | - | - | 52.49 | |
| E | 52.54 | 2.25 | - | 4.87 | 29.61 | 1.49 | 4.50 | - | 4.19 | |
| F | 57.68 | - | - | 11.92 | 21.18 | 1.22 | - | 1.69 | 5.36 | |
| G | 44.16 | - | 1.09 | 10.08 | 31.06 | 2.32 | 3.86 | - | 6.38 | |
| H | 48.63 | - | - | - | 50.18 | - | - | - | - | |
| I | 44.94 | - | - | 10.89 | 31.76 | 1.41 | 6.77 | - | 3.00 | |
| J | 45.70 | - | - | 8.47 | 34.38 | 2.75 | 3.00 | - | 4.16 | |
| K | 41.04 | - | - | 7.47 | 39.68 | 3.22 | 2.76 | - | 4.32 | |
| L | 47.76 | - | - | - | 51.04 | - | - | - | - | |
| M | 35.67 | - | - | 7.03 | 45.53 | 3.71 | 2.67 | - | 3.87 | |
| N | 52.26 | - | - | - | 46.63 | - | - | - | - | |
| Spots A–C, collected in Figure 7. | A | 45.72 | - | - | 6.90 | 38.10 | 5.70 | 1.71 | - | - |
| B | 48.73 | - | 2.28 | 6.65 | 29.36 | 2.85 | 4.87 | - | 3.91 | |
| C | 48.18 | - | - | 16.28 | 22.15 | - | 11.27 | - | 1.16 | |
| Spots A–N, collected in Figure 8. | A | 61.18 | - | - | 6.29 | 27.34 | 2.28 | 1.17 | - | 1.00 |
| B | 53.60 | - | 1.11 | 8.79 | 26.55 | 1.72 | 3.43 | - | 3.86 | |
| C | 42.56 | - | 1.30 | 7.74 | 25.53 | 3.06 | 1.50 | - | 16.83 | |
| D | 49.95 | - | 1.35 | 8.77 | 28.39 | 2.54 | 3.63 | - | 4.53 | |
| E | 51.53 | - | 1.18 | 9.55 | 26.71 | 2.69 | 1.07 | - | 6.44 | |
| F | 45.34 | - | 1.51 | 9.17 | 30.47 | 2.80 | 4.93 | - | 4.68 | |
| G | 48.65 | - | 1.31 | 4.84 | 34.09 | 3.01 | 1.15 | - | 5.56 | |
| H | 55.75 | - | - | - | 43.46 | - | - | - | - | |
| I | 52.44 | - | - | - | 46.10 | - | - | - | - | |
| J | 52.84 | - | - | 1.37 | 44.29 | - | - | - | - | |
| K | 49.54 | - | - | 8.96 | 32.37 | 3.15 | 2.93 | - | 1.79 | |
| L | 48.67 | - | - | 10.95 | 28.41 | 1.15 | 7.25 | - | 2.48 | |
| M | 47.82 | - | 2.32 | 7.85 | 30.08 | 2.48 | 2.13 | - | 5.92 | |
| N | 48.52 | - | 1.29 | 8.66 | 30.72 | 2.67 | 3.46 | - | 3.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, S.; Dong, J.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Q. Morphology and Structure Characteristics of the Rare Black-Glazed Porcelains Excavated from the Jian Kiln Site of Song Dynasty. Crystals 2023, 13, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040632
Tao S, Zhu Y, Liu S, Dong J, Yuan Y, Li Q. Morphology and Structure Characteristics of the Rare Black-Glazed Porcelains Excavated from the Jian Kiln Site of Song Dynasty. Crystals. 2023; 13(4):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040632
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Shiqian, Yuguang Zhu, Song Liu, Junqing Dong, Yimeng Yuan, and Qinghui Li. 2023. "Morphology and Structure Characteristics of the Rare Black-Glazed Porcelains Excavated from the Jian Kiln Site of Song Dynasty" Crystals 13, no. 4: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040632
APA StyleTao, S., Zhu, Y., Liu, S., Dong, J., Yuan, Y., & Li, Q. (2023). Morphology and Structure Characteristics of the Rare Black-Glazed Porcelains Excavated from the Jian Kiln Site of Song Dynasty. Crystals, 13(4), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040632






