Abstract
In this work, Al(OH)3 nanosheets are synthesized in situ on the surface of an Al-20Si alloy via the water bath method, and Al–20Si@Al2O3 composites are then obtained after calcination. The growth mechanism of the Al(OH)3 nanosheets is revealed, and a pathway is demonstrated to obtain Al–20Si@Al2O3 nanosheets with the desired structure and thickness. Furthermore, the influence of different Al–20Si@Al2O3 contents on the primary silicon phase in the Al–20Si alloy is investigated, and the mechanism of such an influence is theoretically analyzed. The mechanical properties of the modified Al–20Si alloy are tested, and the effects of the morphology and particle size of the silicon phase on the alloy properties are studied. The results show that Al–20Si@Al2O3 synthesized in situ by water bath has good dispersion in the melt. There is a lot of γ-Al2O3 dispersed in the matrix of the alloy, and the primary silicon of the Al-20Si alloy is obviously refined. By increasing the content of the modifier, the average size of primary silicon decreases first and then increases. When 15 wt% of the modifier is added, the refinement effect of primary silicon reaches its peak, and the size of primary silicon is reduced from unmodified 86.4 μm to 28.5 μm. The hardness and tensile strength of 75.2 HB and 120.3 MPa are increased to 107.2 HB and 185.9 Mpa by 42% and 55%, respectively. Compared with adding γ-Al2O3 directly, this experiment provides a simple method to synthesize the modifier, and γ-Al2O3 can be dispersed evenly in the aluminium-silicon alloy melt more easily by in-situ generation, without ultrasonic treatment or other ways. During mass production, the cost can be better controlled and good results can be achieved at the same time.
1. Introduction
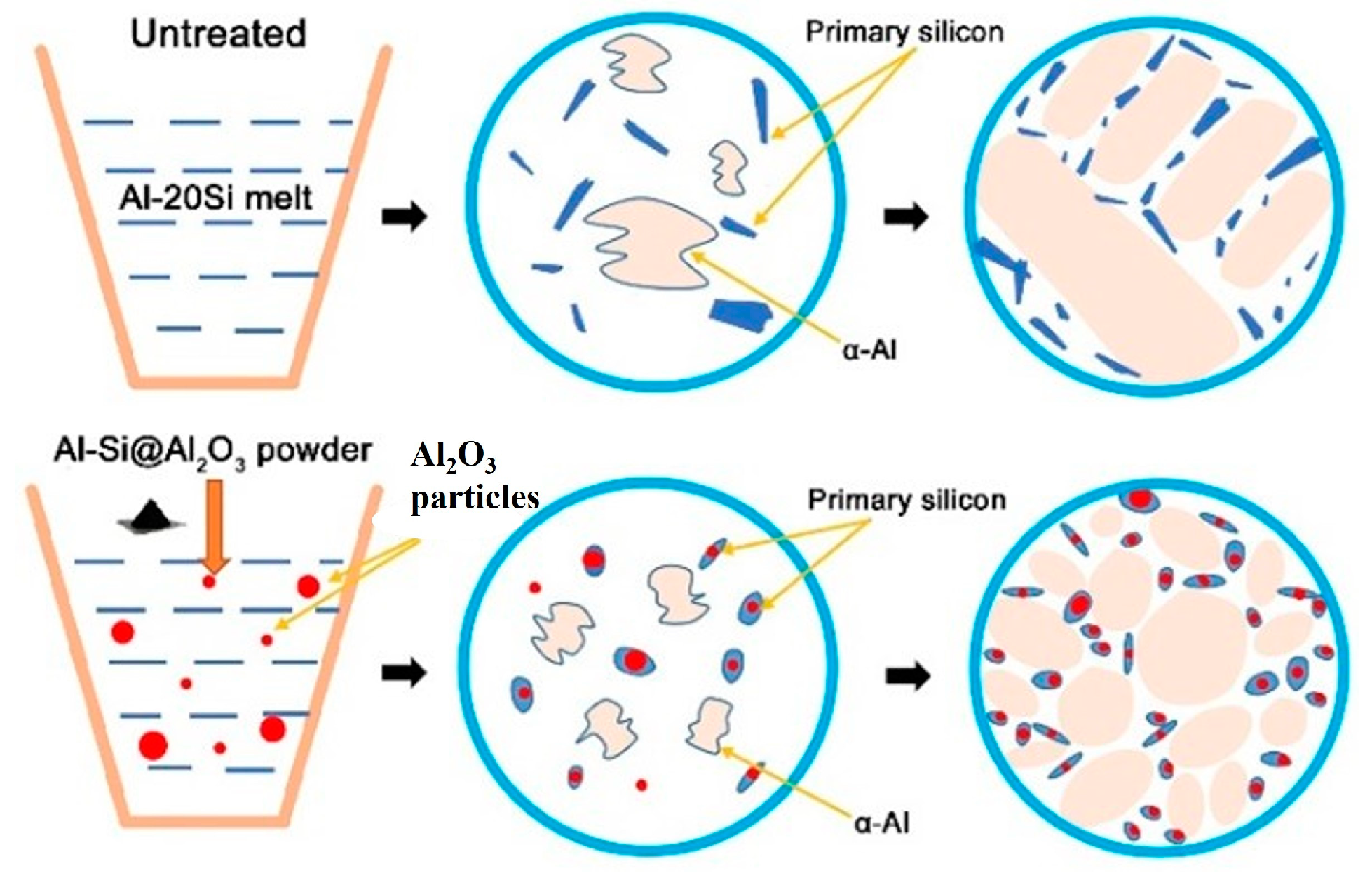
Hypereutectic Al–Si alloy has been widely used in automobile manufacturing, aerospace, shipbuilding, marine, chemistry, and chemical industry due to its advantages of low density, high specific strength, good casting performance, excellent wear resistance, low thermal expansion coefficient, continuous adjustment, etc. [1,2,3,4,5,6]. In traditional casting, when the rate of cooling is slow and the Al–Si alloy is not changed, a lot of plate- or needle-shaped eutectic Si forms, and stress is concentrated at the tip and edges of the Si phase. This stress results in the fragmentation of the alloy substrate and deterioration of the tissue, which significantly degrades the mechanical properties of the alloy [7], especially its plasticity and resistance to wear. These are the main reasons behind the limited industrial use of Al–Si alloys. Over the past few decades, several strategies have been developed to achieve primary Si refinement [8], which can be roughly divided into two main routes. One is to use physical methods, such as rapid solidification treatment [9], ultrasonic melt treatment [10], and electromagnetic stirring [11], to control the nucleation and growth of the Si phase during solidification. However, these methods usually have some shortcomings, such as high cost, low efficiency, and complicated equipment, which limit their application in large-scale industrial production. The other is to refine primary silicon by adding trace elements, including P [12], Sr [13], Na [14], Ce [15], Er [16], Y [17], Eu [18], etc. Compared with the above technologies, modification treatment can simply and efficiently refine the size and morphology of the silicon phase in the Al–Si alloy and make it more evenly dispersed in the matrix, thus improving its comprehensive properties. Additionally, it is convenient to combine with other methods. It is the most widely used refinement method in industrial production at present.
Among them, phosphorus is considered the most effective refiner and improver of primary Si in the industry [19]. Adding a small amount of P to the hypereutectic Al–Si alloy can refine coarse primary silicon into fine particles. However, in industrial production, P is usually added to alloy melt in the form of phosphorus salt. In this case, adding alloy melt will lead to a large number of toxic gases, which will seriously pollute the environment. Sr, as an effective modifier, can refine eutectic silicon into a hypereutectic Al–Si alloy. However, strontium is easy to oxidize, which makes Al–Si alloy absorb oxygen, resulting in many pores in the cast alloy that reduce the mechanical properties of the material [20]. Furthermore, rare-earth elements, such as Ce, Er, and Y, can be simultaneously used to refine the primary Si phase in the hypereutectic Al–20Si alloy. However, their high cost, complex processing, and poor chemical activity limit their application in the industry. In addition to rare-earth elements, γ-Al2O3 particles can also refine the primary Si phase in the Al–20Si alloy. Choi et al. [21] found that the primary Si phase can be significantly refined through the addition of γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles to the Al–20Si alloy under the action of ultrasounds. However, under normal conditions, ceramic particles may aggregate due to van der Waals forces, resulting in an unstable thinning effect that adversely affects the mechanical properties of the alloy, especially when nanoparticles are added [22]. Therefore, it is of great practical significance to develop a simple, economical, and effective one-step method for simultaneously refining and modifying Si phases using dispersed γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles. In this study, Al-20Si@Al2O3 synthesized by the hydrothermal method was added to the Al-20Si alloy melt as a modifier, and γ-Al2O3 was generated in situ. The dispersibility was obviously better than that of direct addition, so the refining effect was better.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Preparation of Al-20Si@Al2O3
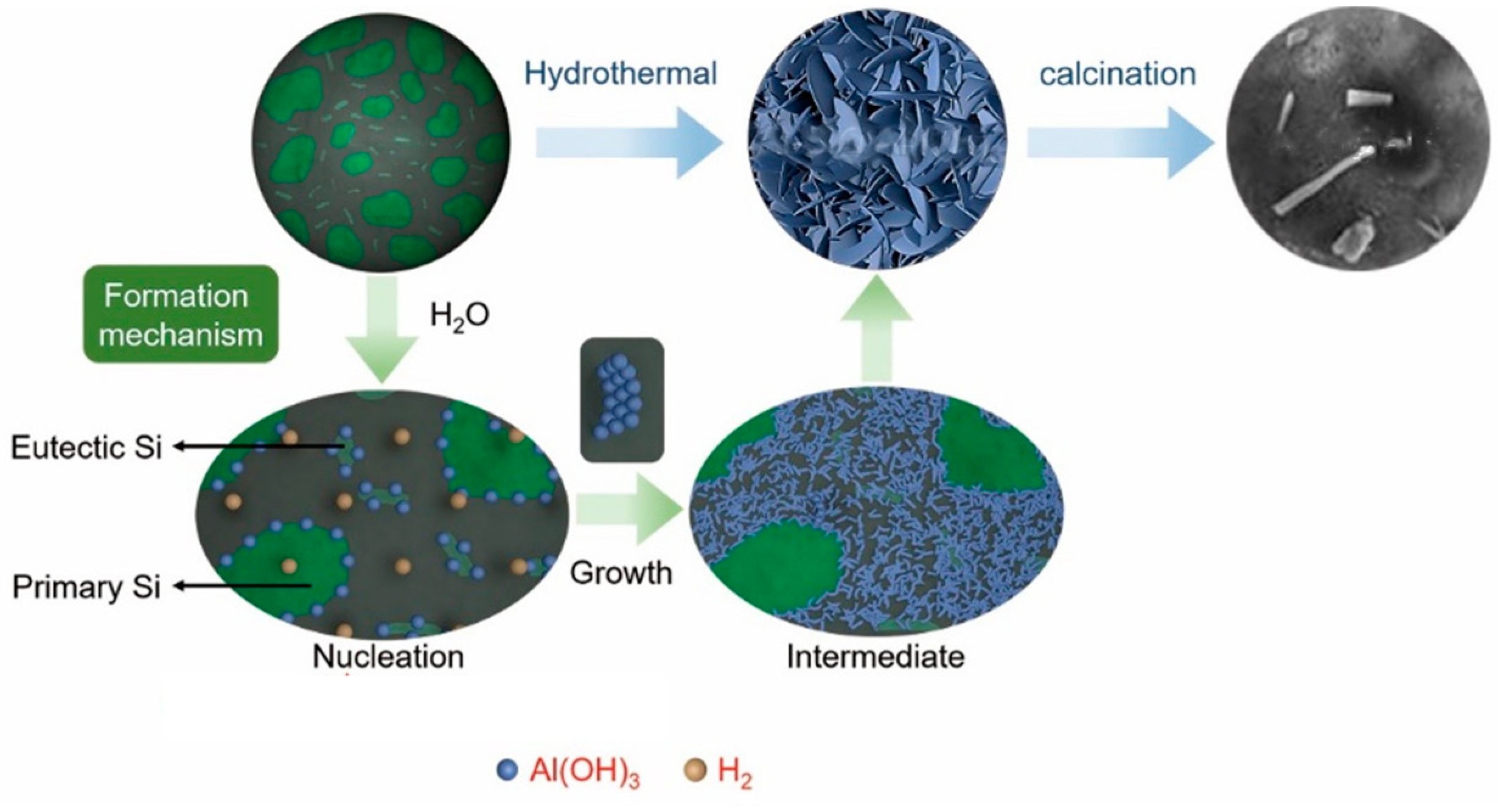
Figure 1 shows the preparation of Al-20Si@Al2O3. Al-20Si powder with a particle size of 38 μm was selected for this experiment. The Al–20Si powder was treated using deionized water at 80 °C for 3 h via the hydrothermal method. The thickness of Al(OH)3 on the surface of Al-20Si powder increased with time. After 3 h, the surface of the Al-20Si powder was basically covered with Al(OH)3. When the time continued to increase, a large number of impurities appeared around the core-shell structure, which adversely affected the subsequent experiments. It was then centrifugated, washed with absolute alcohol three times, and dried at 50 °C for 12 h. This process resulted in Al–20Si@Al(OH)3. Al-20Si@Al2O3 was obtained through the calcination of Al–20Si@Al(OH)3 at 500 ℃ for 2 h. The morphology of the as-prepared core–shell composites was observed via scanning electron microscopy (SEM). X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was carried out using a X-ray diffractometer (Japan) at a scan rate of 10°/min.
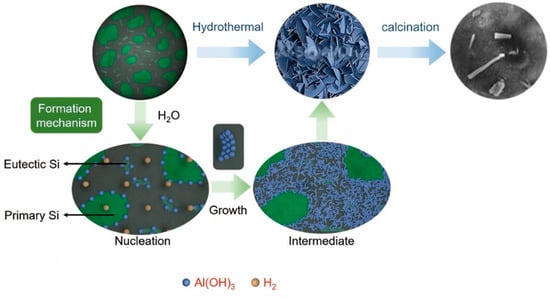
Figure 1.
Preparation flow chart of Al–20Si@Al2O3.
2.2. Experiments on the Modification of Al-20Si
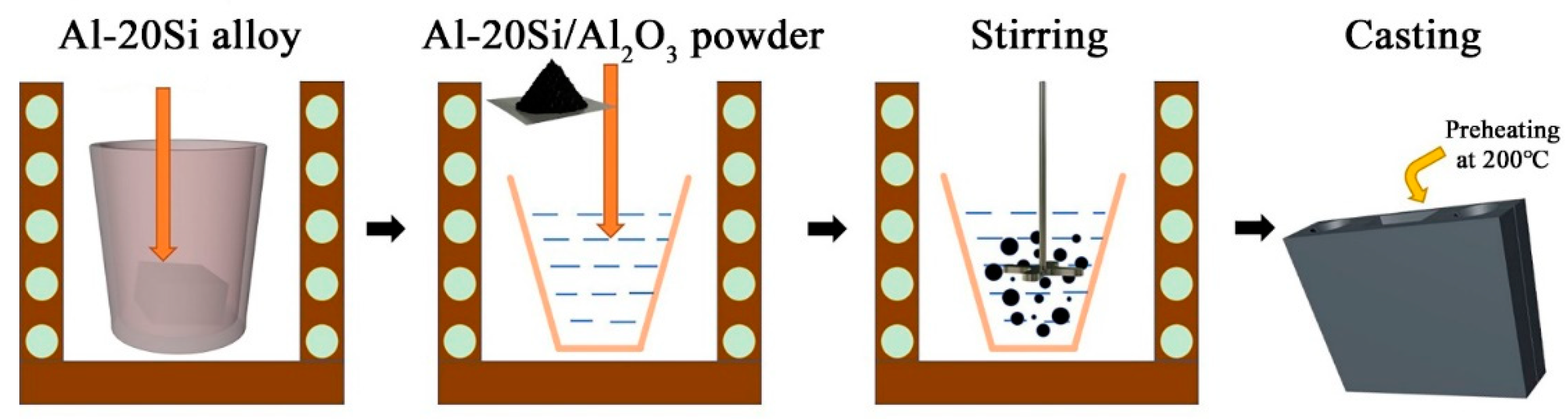
Before adding modifier to Al-20Si alloy, the alloy shall be pretreated. First, weigh about 300 g of hypereutectic Al-20Si alloy and wash the impurities on the alloy surface with deionized water. Because the alloy is placed in the air for a long time, the aluminium in the hypereutectic Al-20Si alloy will react with the oxygen in the air to form a dense layer of aluminium oxide film on the surface of the alloy. Therefore, the surface of the alloy is usually polished with sandpaper. After polishing, the surface of the alloy is washed clean with deionized water. Finally, put the washed hypereutectic Al–Si alloy into a graphite crucible and then put it together in a box-type resistance furnace. Set the temperature of the box-type resistance furnace to 200 °C and keep it there for 12 h so that the moisture in the alloy can be fully dried to prevent a thermal explosion.
Since the temperature of the alloy during modification is near the liquidus temperature, the Si phase in the alloy melt is not completely melted, so it is necessary to overheat the hypereutectic Al-20Si alloy. First, put the dried hypereutectic Al-20Si alloy into a graphite crucible and put it into a well-type heating resistance furnace. Set the temperature of the heating resistance furnace to 900 °C. Some researchers [23] found that when a hypereutectic Al-20Si alloy is heated to 900 °C, there will be no solid Si phase in the alloy melt and the Si phase will be evenly distributed in the alloy melt. This means that the Si phase can be dispersed in the matrix after the modification treatment, which makes the modification effect better.
The main purpose of alloy refining is to remove the gas and impurities in the alloy that formed during melting. After the hypereutectic Al–Si alloy is overheated, the temperature of the well heating resistance furnace is reduced from 900 °C to 700–750 °C, and the alloy quality is refined with about 0.5 wt% refining agent. The main component of the refining agent is hexachloroethane, which will decompose at high temperatures and react with the gas in the alloy to draw the impurities and gas out of the melting alloy. The refining agent is wrapped in aluminium foil and added to the alloy melt. A ladle was used to press the refining agent into the bottom of the alloy melt. Stir for 2 min to better disperse the refining agent in the alloy melt, and stand for 10 min. Finally, the impurities on the surface of the alloy melt are skimmed off to obtain a relatively pure hypereutectic Al-20Si alloy melt.
The modification temperature will directly affect the reaction between the modifier and the alloy, thus affecting the internal structure of the melt. If the modification temperature cannot reach the reaction temperature of the two, the modification cannot be played. If the temperature is too high, the modification will be weakened. According to a large number of previous comparative tests, the modification temperature of the modifier and Al-20Si alloy is about 900 °C, and the modification effect is best when the holding time is 15 min. After Al-20Si was overheated and refined, reduce the temperature of the well-resistance furnace to 730 °C.
Therefore, the overall modification process is as follows: Firstly, the Al–20Si alloy in the graphite crucible was heated to 900 °C, and this temperature was maintained for 15 min. After the temperature was reduced to 730 °C, add a refining agent to obtain a pure Al-20Si alloy melt. Different Al-20Si@Al2O3 powder amounts (5, 10, 15, and 20 wt%) were then added to the Al–20Si alloy at a temperature of 730 °C, stirred for 2 min, and maintained for 10 min to modify the alloy. Finally, the scum was skimmed and poured into the metal mold (which had been preheated at 200 °C for 2 h) for casting, as shown in Figure 2. The metallographic samples were sectioned, mechanically polished, and then etched for SEM observations. The morphology and particle size of the primary Si phase in the Al–20Si alloy before and after modification were analyzed via high-resolution TEM (HRTEM) and element-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The mechanical properties of the alloy were tested at ambient temperature using a tensile testing machine. The hardness changes of Al-20Si before and after modification were tested by the Brinell hardness tester. These tests were carried out three times for each sample, and the three readings were averaged to obtain the final results.
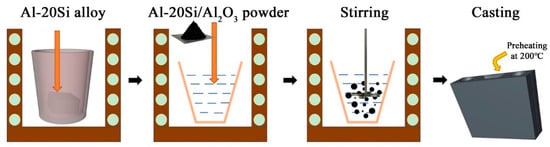
Figure 2.
Preparation of Al–20Si alloy modified with Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder.
3. Results
3.1. Qualitative Analysis of Al-20Si@Al2O3
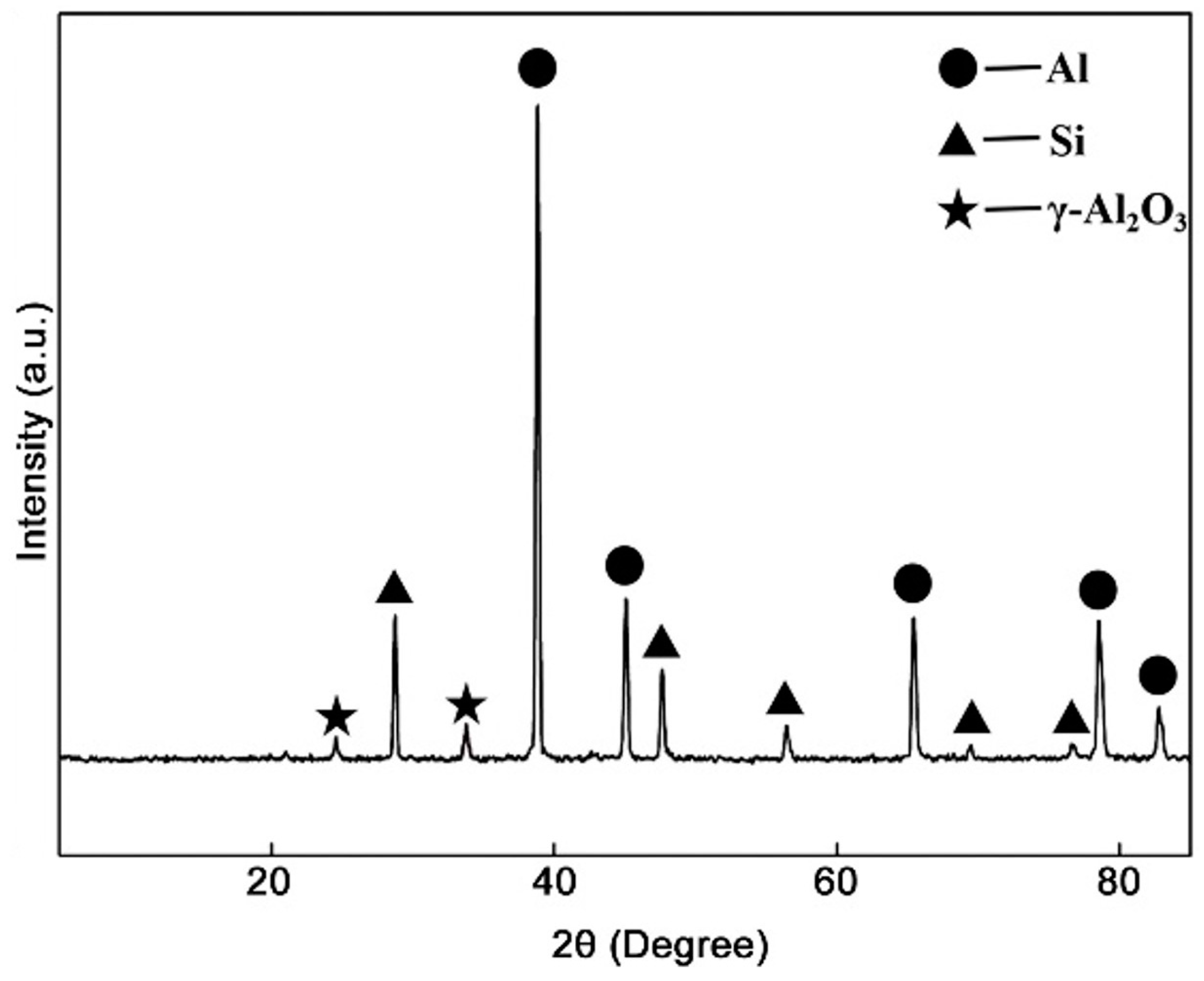
Figure 3 shows the XRD patterns of Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder. The Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder is composed of α-Al, Si, and γ-Al2O3 phases as shown in Figure 3. Theoretically, the formation of γ-Al2O3 phase can be described by the reactions below:
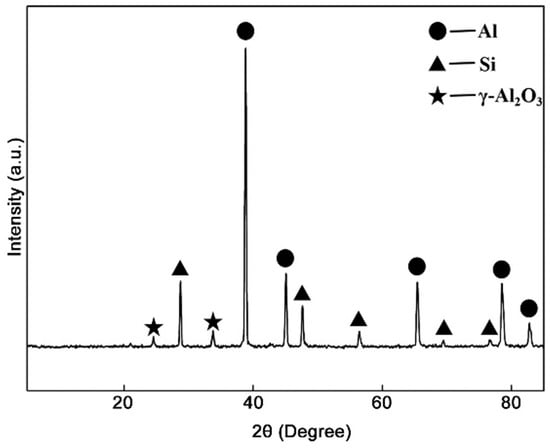
Figure 3.
XRD pattern of Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder.
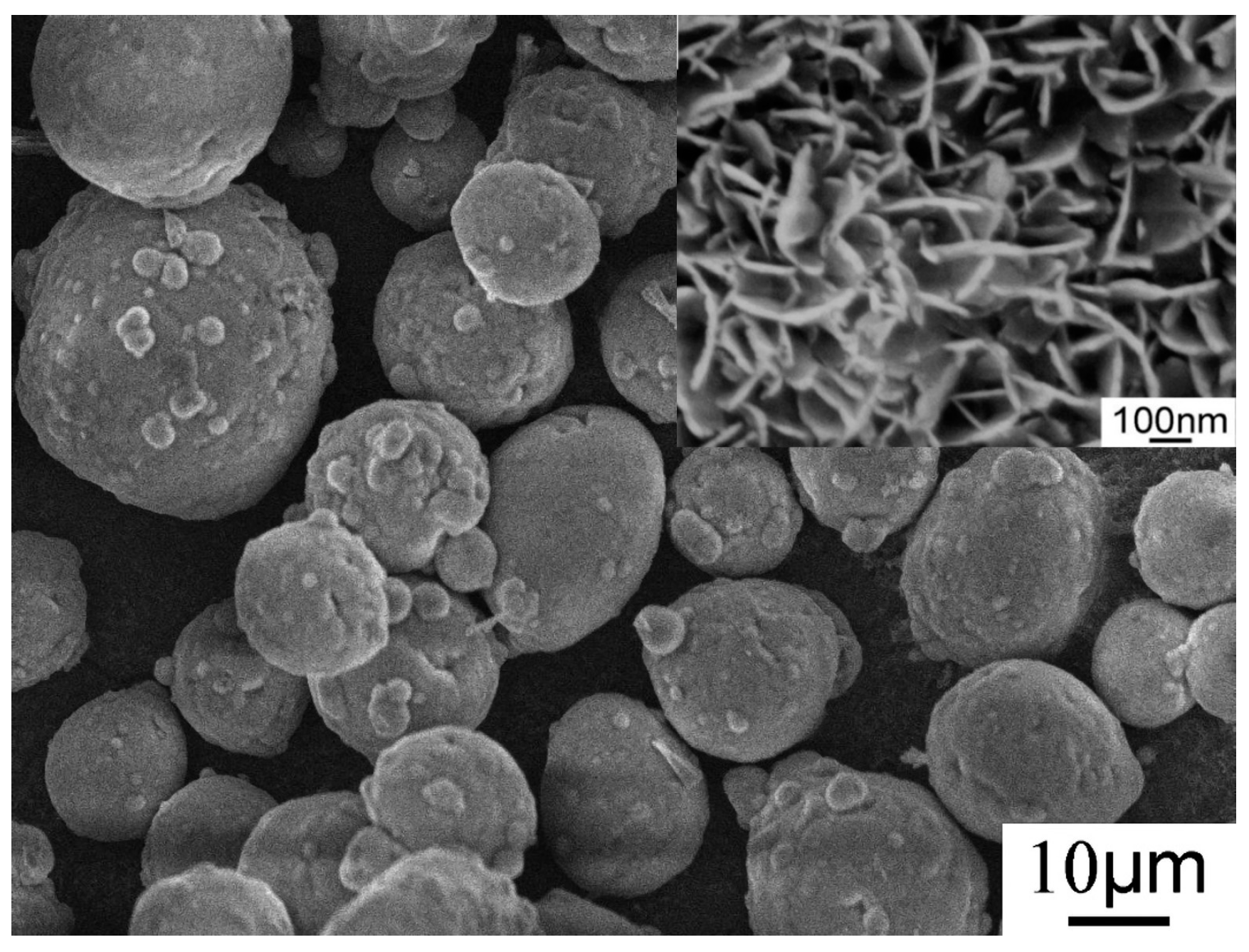
The Al–20Si@Al(OH)3 powder was investigated via SEM, and the corresponding SEM images are shown in Figure 4. It can be seen that the surface of Al-20Si powder is basically covered with Al(OH)3 nanosheets. It is found that too much hydrothermal time will make Al-20Si@Al(OH)3 nanosheets grow abnormally, and more impurities will appear around the core-shell structure. This is not conducive to the preparation of Al-20Si@Al2O3 powder and the modification effect. It is found that the particle size of Al-20Si powder has little effect on the morphology and thickness of the nano-flakes on the surface of Al-20Si@Al(OH)3.
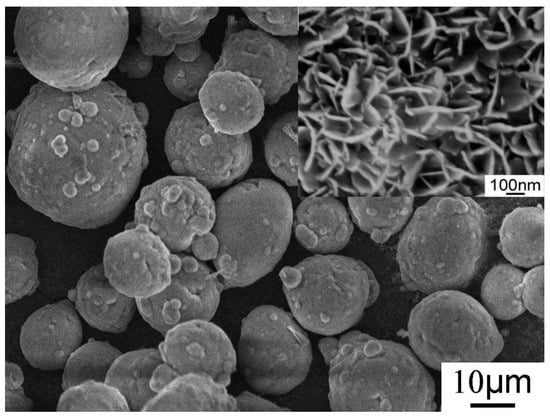
Figure 4.
SEM image of Al-20Si@Al(OH)3.
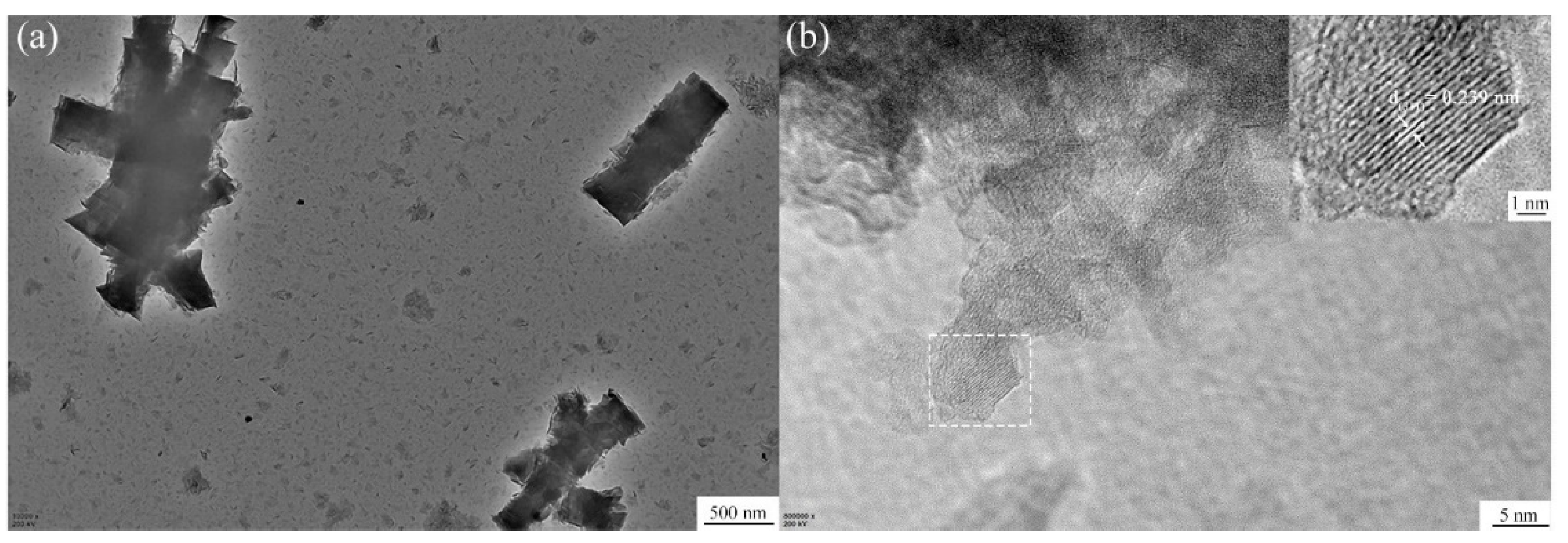
The Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder was investigated via TEM, and the corresponding TEM images are shown in Figure 5. These images, combined with the XRD pattern, reveal the presence of a γ-Al2O3 nanosheet on the surface of the Al–20Si powder. The crystal plane spacing was calculated to be d = 0.239 nm, which is consistent with the (311) crystal plane spacing of γ-Al2O3. Overall, the nanosheets are predominantly concentrated at the interface between the Si phase and the Al matrix, indicating that Al2O3 nucleation occurs mainly at this interface. With increasing reaction time, the nanosheets cover completely the surface of the Al–Si particles. This will facilitate the dispersion of nano-Al2O3 in the alloy melt.
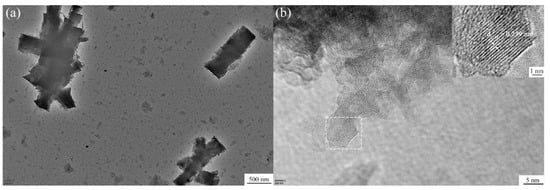
Figure 5.
(a) TEM and (b)HRTEM images of Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder.
3.2. Quantitative Analysis of Al-20Si@Al2O3
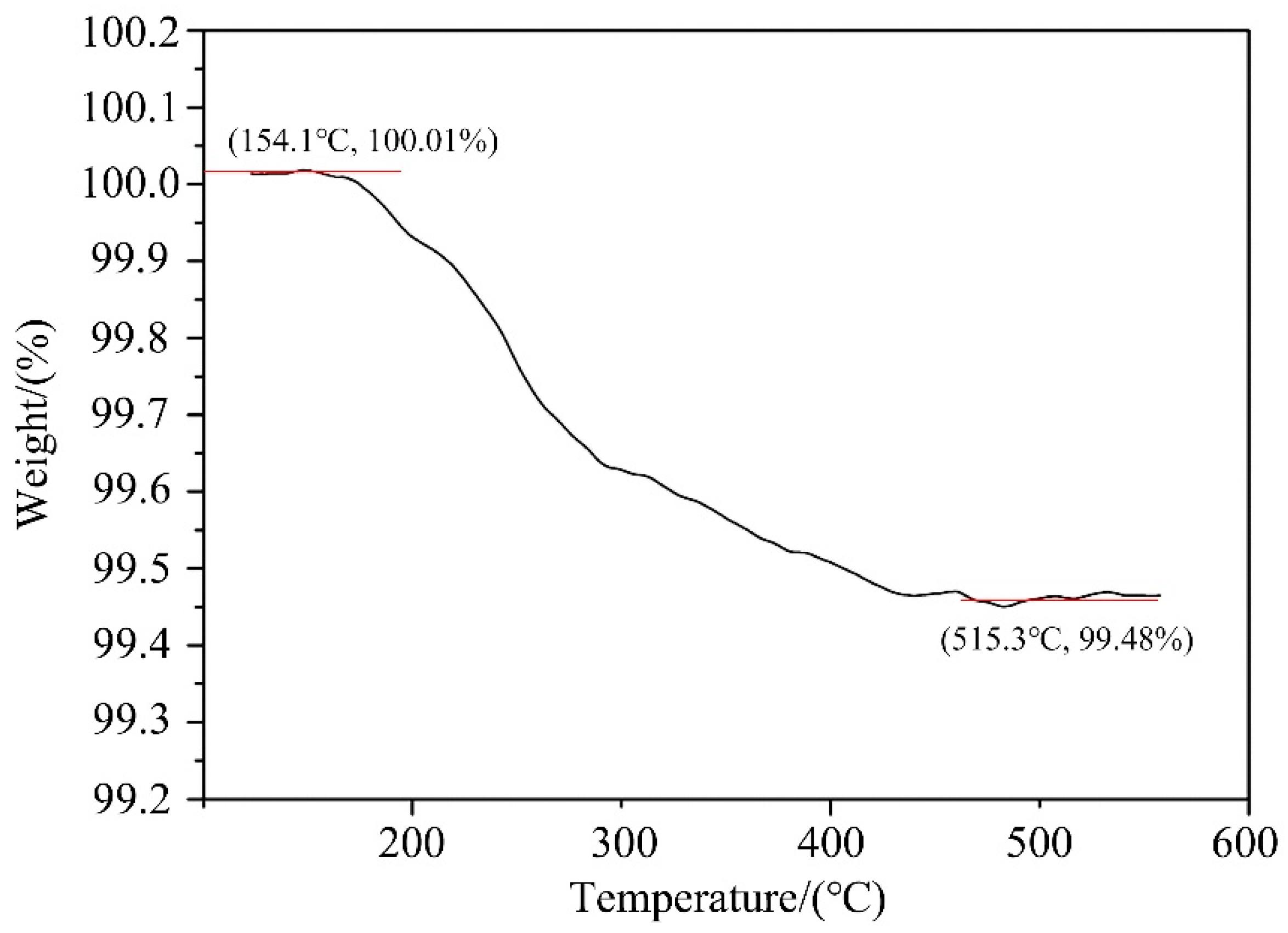
A thermogravimetric analyzer (TG209F3) made by a German company was used to test the prepared Al-20Si@Al(OH)3 powder. The heating rate is 10 °C/min. According to chemical formula (2) and thermogravimetric analysis, when Al–20Si@Al(OH)3 powder is calcined, Al(OH)3 on the surface of Al–20Si particles reacts AT 154.1 °C to generate Al2O3, and when the reaction temperature reaches 515.3 °C, the reaction has ended, as shown in Figure 6. At this time, the weight ratio of the powder is reduced from 100.01 to 99.48%, and the reduced weight is the water vapor generated via the reaction, which is about 0.53% of the overall weight of the powder. According to formula (2), the Al2O3 generated by the reaction is about 1.02% of the overall weight of the powder.
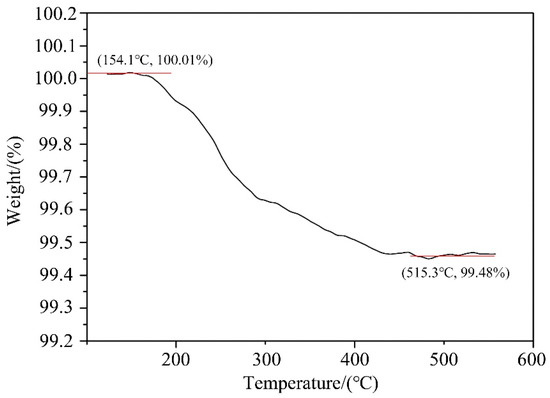
Figure 6.
Thermogravimetric analysis of Al–20Si@Al2O3.
3.3. Effect of Al-20Si@Al2O3 on Primary Silicon and Properties of Al-20Si Alloy
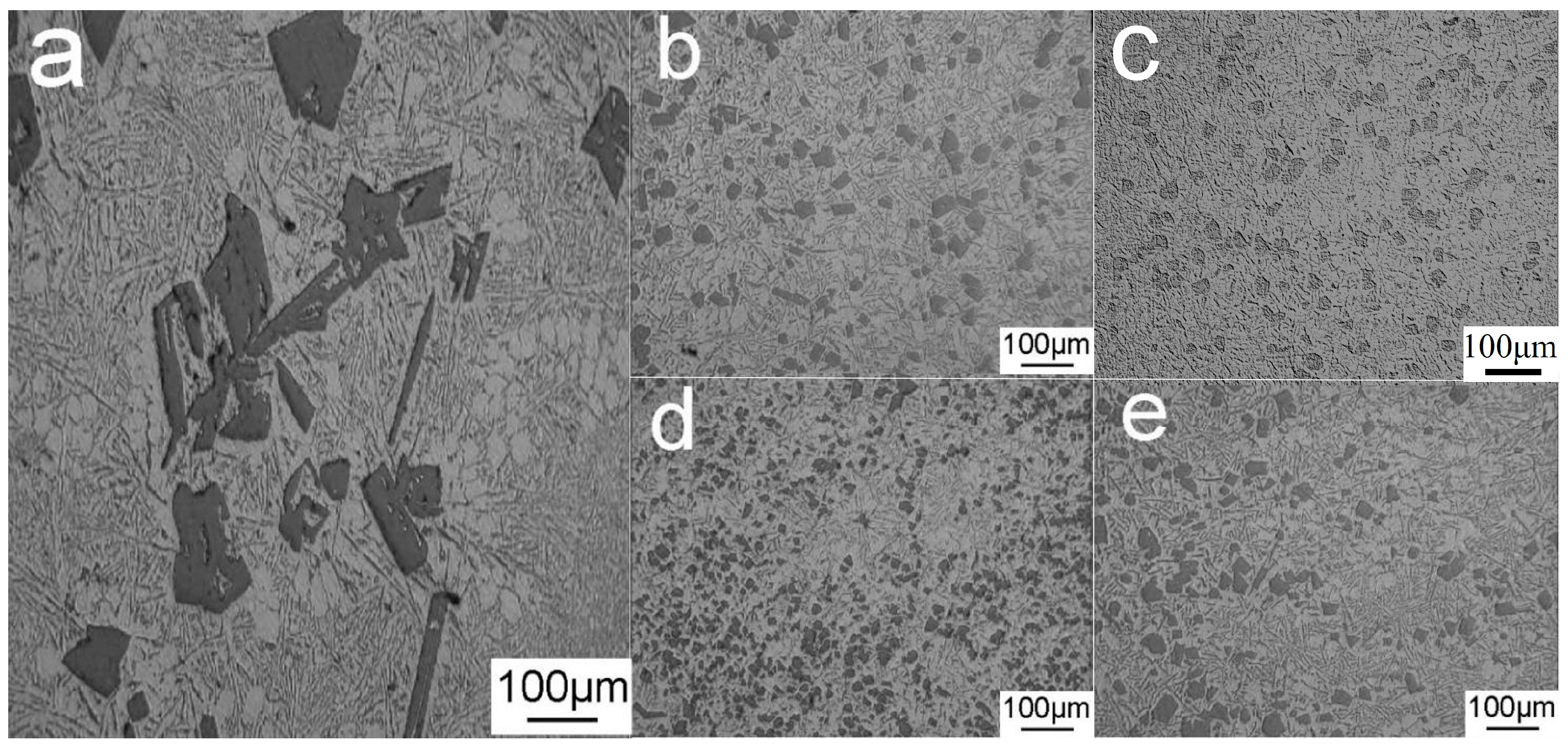
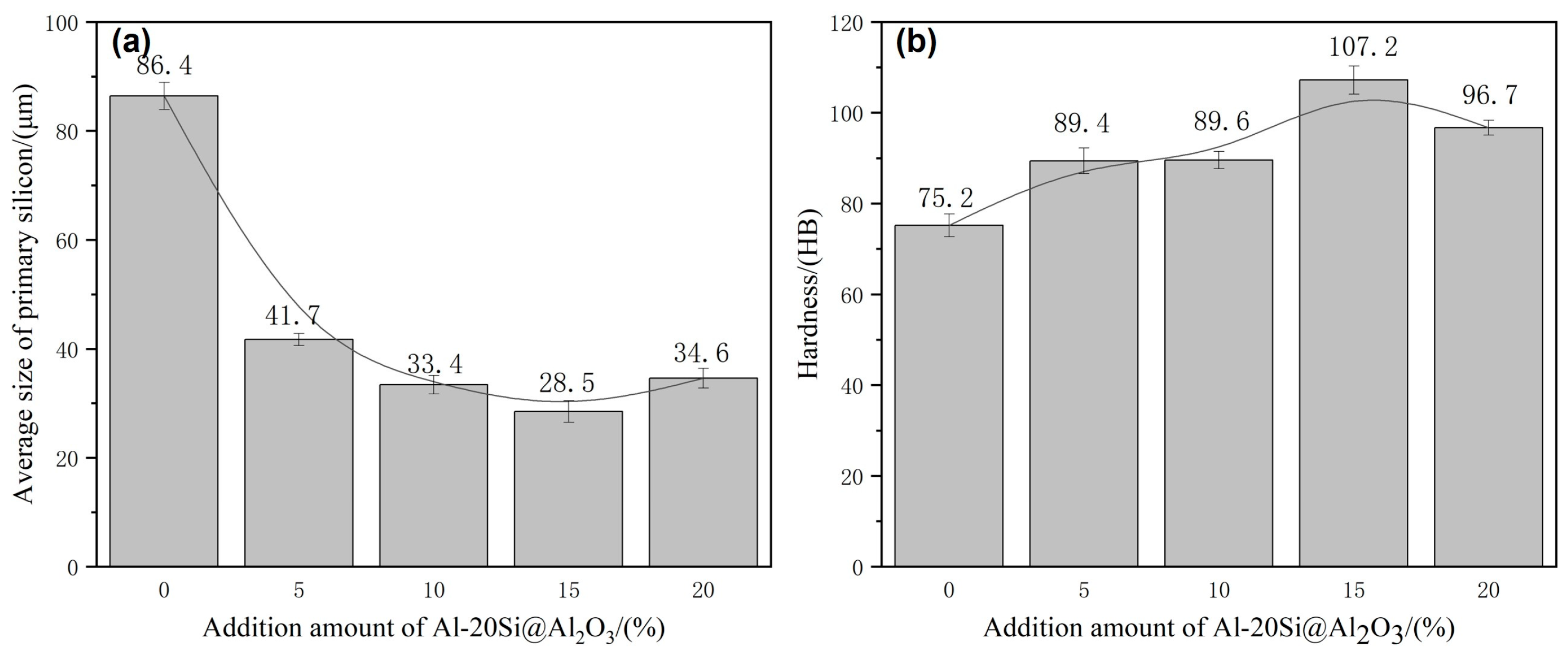
The typical strip shape of the primary Si phase in the Al–20Si alloy before modification is shown in Figure 7a. The average particle size of the primary Si phase and Brinell hardness of the Al–20Si alloy are 86.4 μm and 75.2 HB, respectively, as shown in Figure 8. Figure 7b–e shows the microstructure of the Al–20Si alloy with 5, 10, 15, and 20 wt% Al–20Si@Al2O3 powders. When the content of the added Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder is 5 wt%, the primary Si phase is clearly refined, the sharp shape tends to be regular, and the average particle size of the primary Si phase is 41.7 μm. Since the primary Si phase in the alloy is clearly refined and Al2O3 can be used as a reinforcing phase to make the Al–20Si alloy stronger, the Al–20Si alloy has a hardness of 89.4 HB in this case. When the Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder content is increased to 10 wt%, a proportion of the primary Si phase is further refined, and the average particle size and hardness of the primary Si phase are 33.4 μm and 89.6 HB, respectively. When the Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder content is increased to 15 wt%, the refining effect is the strongest, and the average particle size of the primary Si phase reaches the minimum value of 28.5 μm. Furthermore, the hardness of the Al–20Si alloy reaches a maximum value of 107.2 HB. Compared with the unmodified Al–20Si alloy, the hardness is increased by 42%. As the Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder content is further increased to 20 wt%, the primary Si phase is not further refined; the average particle size increases to 34.6 μm and the hardness also decreases to 96.7 HB. Thus, we can conclude that an appropriate amount of the Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder can refine the irregular flakes of the primary Si phase into a small and regular Si phase, which can greatly improve the mechanical properties of the alloy. Therefore, the best alloy properties in this study were obtained with a 15 wt% addition of the Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder.
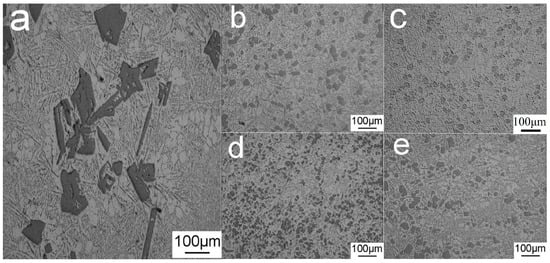
Figure 7.
Metallographic diagram of Al–20Si alloy with different Al–20Si@Al2O3 addition amounts: (a) non-modified, (b) 5 wt%, (c) 10 wt%, (d) 15 wt%, (e) 20 wt%.
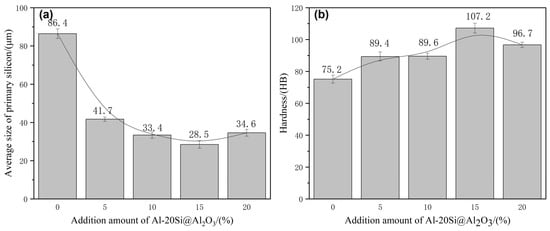
Figure 8.
Average size of primary silicon and hardness of Al–20Si alloys modified with different amounts of Al-Si@Al2O3 powder: (a) average size of primary silicon; (b) HB hardness.
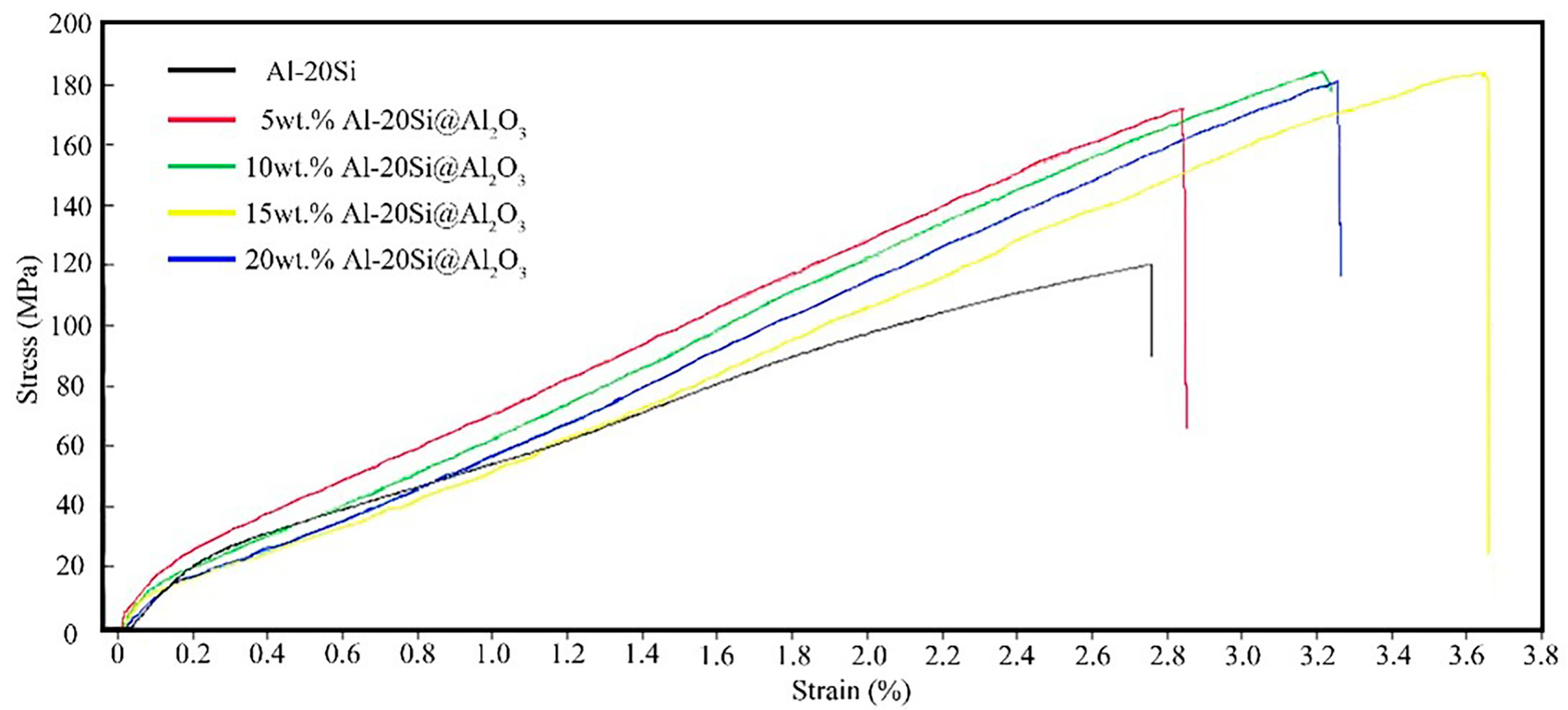
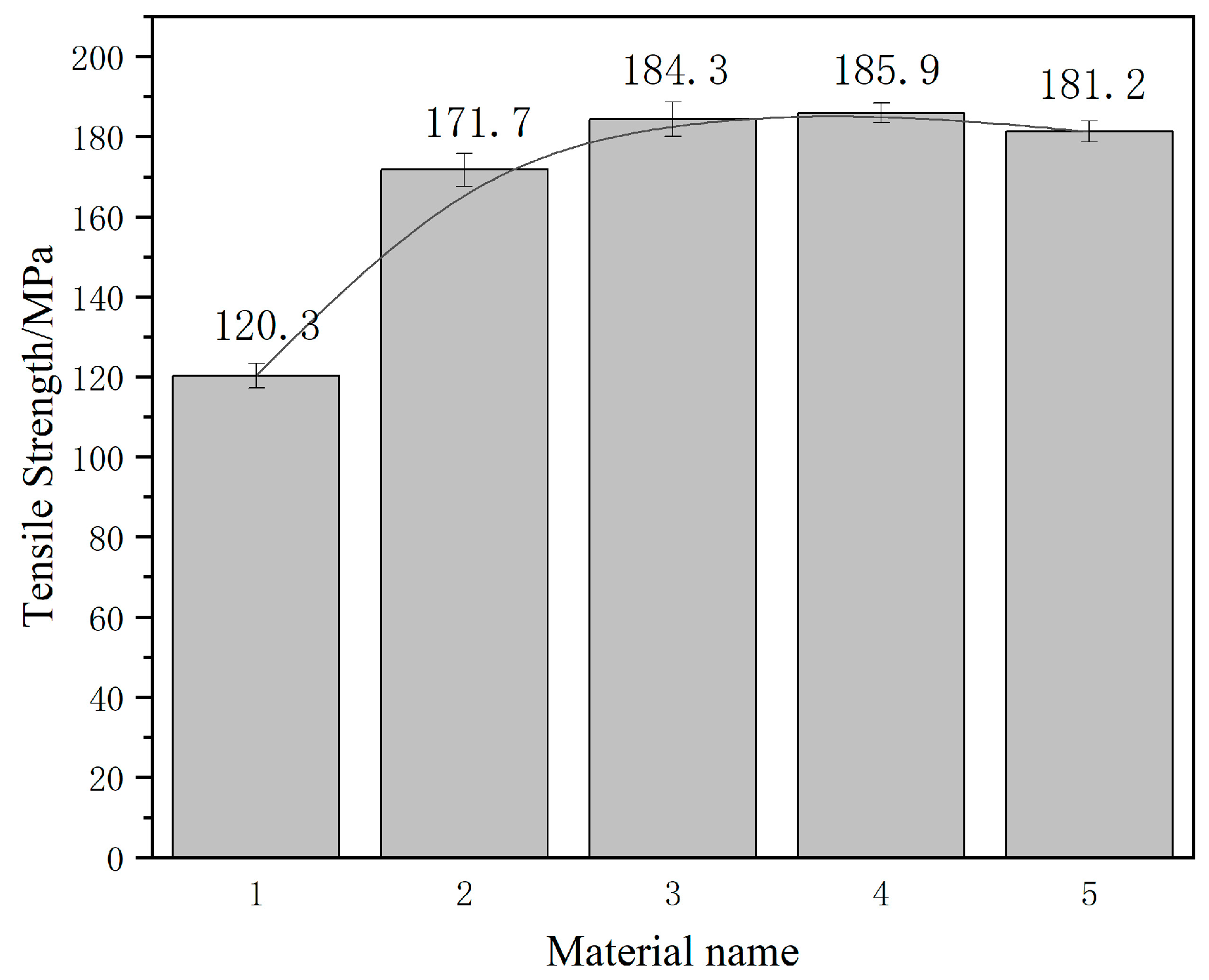
The modified Al–20Si alloy has a higher tensile strength than the unmodified alloy because the fine grains have become stronger. A universal tensile tester is used in this experiment; the tensile speed is 5 mm/min. The tensile strength of the unmodified Al–20Si alloy is 120.3 MPa, as shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10. The tensile strength of the modified Al–20Si alloy first increases with increasing Al–20Si@Al2O3 content and then decreases. When the Al–20Si@Al2O3 content is 5 wt%, the tensile strength of the Al-20Si alloy is obviously improved, reaching 171.7 MPa. The addition of Al-20Si@Al2O3 powder was increased to 10 wt%, and the tensile strength continued to increase to 184.3 MPa. When the Al–20Si@Al2O3 content is 15 wt%, the tensile strength reaches its maximum value, which is 185.9 MPa. Compared with the unmodified sample, the tensile strength is increased by 55%. If the addition of Al-20Si@Al2O3 powder is increased to 20%, the tensile strength will begin to decrease. According to the strengthening theory, adding Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder can modify the primary Si phase, and Al2O3 itself can be used as a reinforcing phase to strengthen the alloy, which can significantly improve the mechanical properties of the Al–20Si alloy.
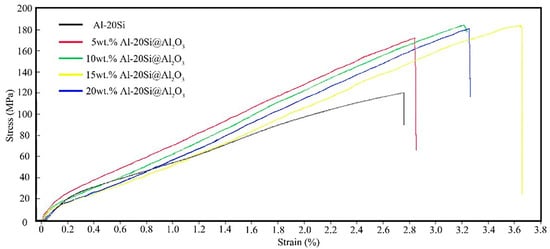
Figure 9.
Tensile strength curves of Al–20Si with different additions.
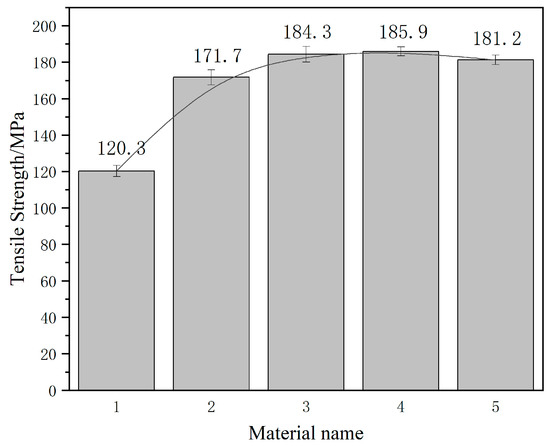
Figure 10.
Tensile strength of Al–20Si with different additions.
3.4. Characterization of Microstructure of Modified Al-20Si Alloy
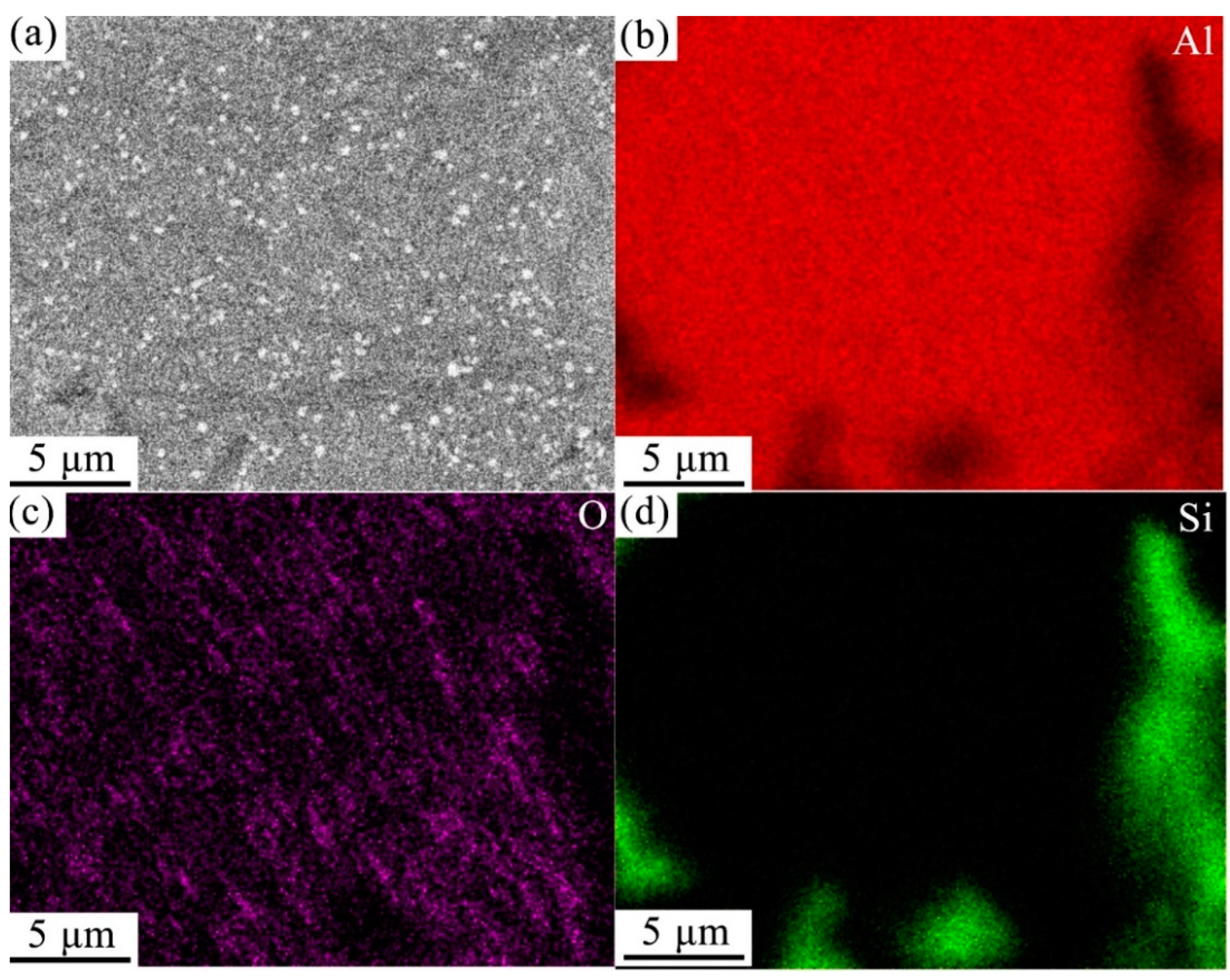
Figure 11 shows the SEM and EDS image of Al-20Si alloy.
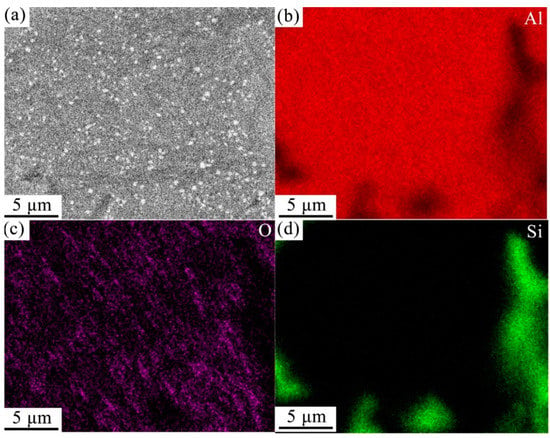
Figure 11.
SEM image (a) and EDS images (b–d) of modified Al–20Si alloy.
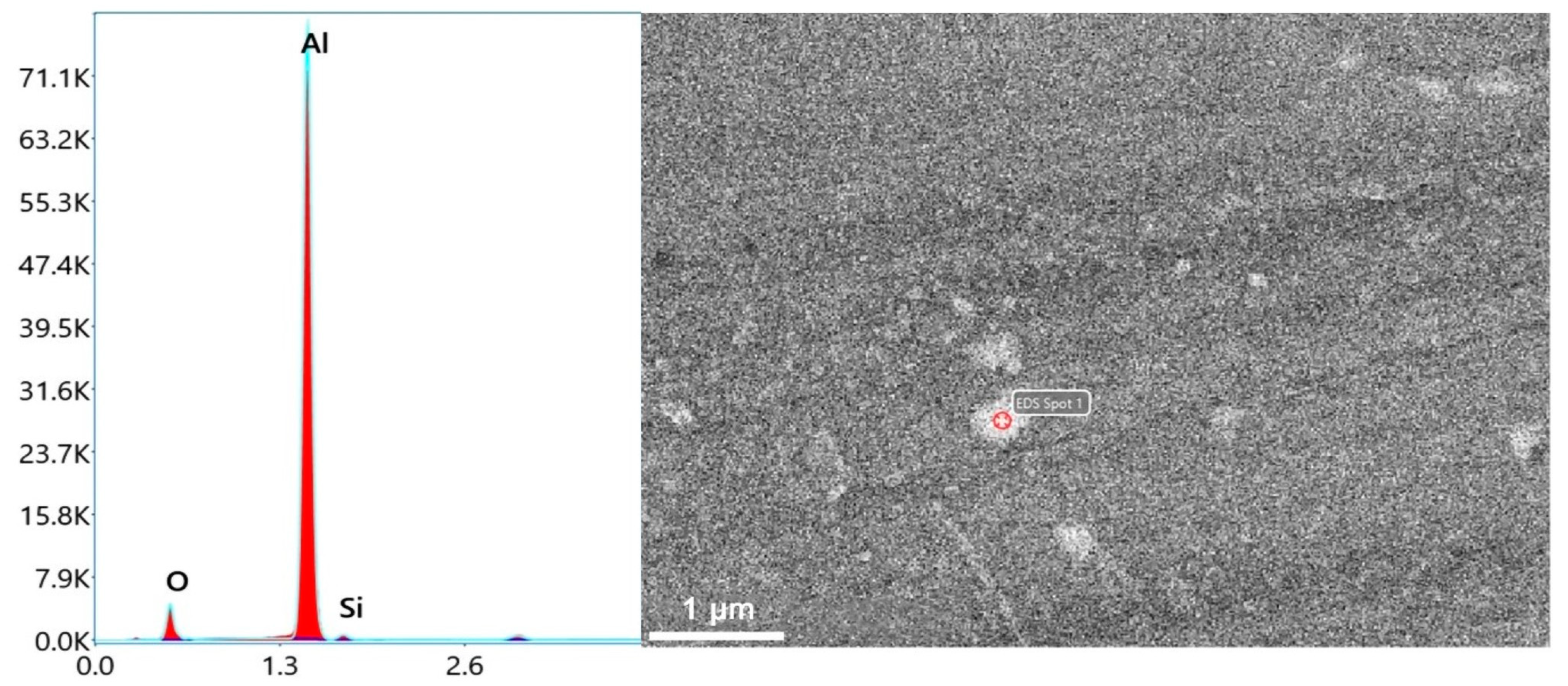
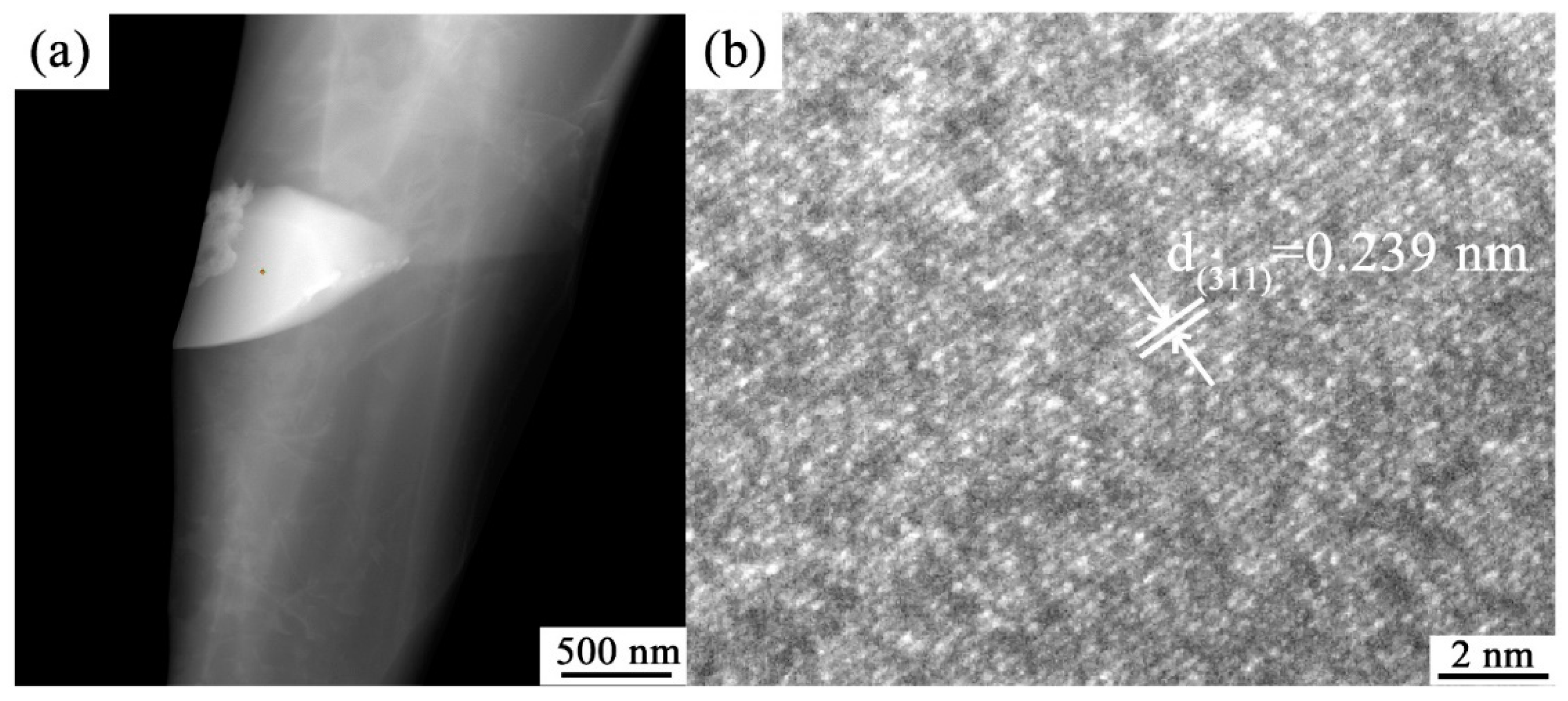
The SEM and EDS image displayed in Figure 11. Figure 11a shows that many bright white spots are evenly distributed in the matrix of the Al–20Si alloy. From Figure 11b–d, it can be seen that these bright white spots are composed of Al and O elements. The TEM image shown in Figure 12 also reveals that numerous bright white spots are present in the Al–20Si alloy matrix. The crystal plane spacing calculated from Figure 12b is 0.239 nm, which is consistent with the (311) crystal plane spacing of γ-Al2O3. From Figure 13, it can be seen that the white spots on the surface of the Al–Si powder are composed of γ-Al2O3. The lattice mismatch between Si and γ-Al2O3 is around 3%, and the γ-Al2O3 particles can provide heterogeneous nucleation sites for primary Si phases. As the in situ synthesized γ-Al2O3 particles usually possess a favorable wettability with the matrix, the primary Si phases can easily adhere to the γ-Al2O3 substrate for nucleation and growth, which improves the nucleation efficiency of γ-Al2O3. This is also the main reason why the primary silicon in the Al-20Si alloy is obviously refined.
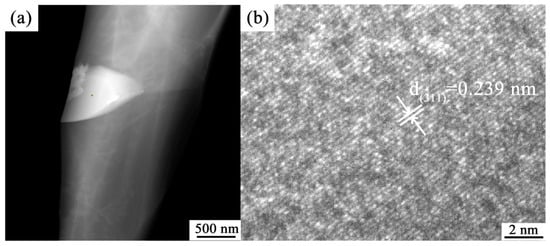
Figure 12.
(a) TEM and (b) HRTEM images of modified Al–20Si alloy.

Figure 13.
EDS spectra of modified Al–20Si alloy.
3.5. Strengthening Mechanism of Al-20Si@Al2O3
The refining mechanism of the Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder is shown in Figure 14. In this experiment, γ-Al2O3 was produced in situ by adding modifiers to the alloy melt, so its wettability and dispersibility in the melt were good. According to the corresponding γ-Al2O3 (JCPDS no. 50-0741) and primary Si (JCPDS no. 65-1060) in Figure 3 XRD analysis, γ-Al2O3 has a cubic structure with a = 7.9 nm, and primary Si has a cubic structure with a = 5.4 nm. This suggests that γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles could serve as a good heterogeneous nucleation agent for primary Si, as , which has a small lattice mismatch of about 3% between primary Si and γ-Al2O3. Thus, γ-Al2O3 serves as the core of the primary Si nucleation sites and plays an important role in refining the primary Si phase [24]. At the same time, γ-Al2O3 in Al-20Si alloy melt will be pushed to the solid-liquid interface of the melt. This will increase the undercooling degree of the alloy melt, accelerate the nucleation rate of primary silicon in the melt, and improve the nucleation rate of primary silicon [25]. The silicon phase grows fastest in the <112> direction and slowest in the <111> direction, so the silicon phase grows anisotropically and finally grows into a sheet. After γ-Al2O3 is added to the alloy melt, it will be adsorbed at the concave corner of the twin growth of the silicon phase, which will hinder the TPRE growth mechanism of the silicon phase and make the growth of the silicon phase change from anisotropic to isotropic, thus changing its morphology and size.
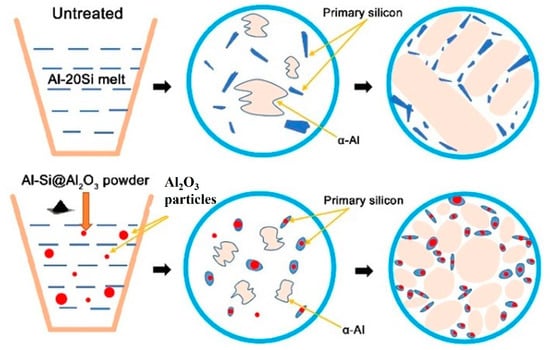
Figure 14.
The refining mechanism of Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder.
The strengthening mechanism of the Al–20Si alloy prepared in this work is mainly the second-phase strengthening mechanism. Due to the small Al2O3 content in the alloy, the primary Si phase is mainly used to analyze the Orowan strengthening grain. Orowan strengthening, which is due to the second phase, can be quantified as follows [26,27,28]:
where ΔσOrowan is the contribution of the second phase’s refinement to the yield strength. M, G, and b are the Taylor factor (approximately equal to 3 [29]), shear modulus (26.2 GPa), and the Burgers vector of the base alloy (0.286 nm), respectively. v and f are Poisson’s ratio (1/3) and the volume fraction of the second phase, respectively. a is defined as d/t, where d and t are the diameter and thickness of the precipitation, respectively. With the decrease in the average size of primary silicon grains in the alloy, the grain refinement strength increases. When the addition amount is 15 wt%, the grain refinement strength of the alloy reaches its maximum. Meanwhile, the distribution of the second phase becomes dense and dispersed, which hinders dislocations more efficiently after the manipulation by nanocrystals. Therefore, the room temperature tensile properties and hardness are distinctly enhanced.
4. Conclusions
The preparation method of Al–20Si@Al2O3 and its effect on primary silicon and the mechanical properties of the Al–20Si alloy were studied. The main conclusions are as follows:
- A layer of Al(OH)3 nanosheets can be formed on Al–20Si particles by the water bath method. After calcination, Al(OH)3 is transformed into γ-Al2O3.
- After the prepared Al–20Si@Al2O3 powder is added to the Al–20Si alloy for modification, the primary silicon in the alloy is significantly refined. The average particle size of the primary Si phase first decreases and then increases with increasing Al–20Si@Al2O3 content. When the content of Al–20Si@Al2O3 is 15%, the refinement of the primary Si phase is the best, and the particle size of the primary Si phase decreases from 86.4 μm (for the unmodified alloy) to 28.5 μm. This is due to the in-situ generation of γ-Al2O3 by adding modifiers and its uniform dispersion in the alloy melt.
- With the addition of Al-20Si@Al2O3 powder with different contents, the average size of primary silicon in Al-20Si alloy decreases obviously, and γ-Al2O3 can also be used as particles to further enhance the properties of Al-20Si alloy. When the content of Al–20Si@Al2O3 is 15%, the hardness and tensile strength are 107.2 HB and 185.9 MPa, respectively. At this time, the hardness and ultimate tensile strength of Al-20Si alloy increase the most. Compared with the unmodified sample, the hardness and tensile strength are increased by 42% and 55%, respectively. This is also consistent with the grain size change law of Al-20Si alloy.
Author Contributions
K.Y. wrote the initial drafts of the work. All the authors contributed to the discussion. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Science and Technology Project of State Grid Corporation of China (SGZJ0000KXJS1900221) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51672145).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Ammar, H.R.; Samuel, A.M.; Samuel, F.H. Porosity and the fatigue behavior of hypoeutectic and hypereutectic aluminum–silicon casting alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2008, 30, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Guan, G.; Zhou, R.; Li, Z.; Zhou, R. Refinement of primary Si in hypereutectic Al–Si alloy by electromagnetic stirring. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 189, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitake, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Sasaguri, N.; Era, H. Refinement of Primary Si Grains of Al–21%Si Alloy Using Vibration Mold. Mater. Trans. 2020, 61, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghayeghi, R.Z.; Timelli, E.J.G. Enhanced refinement and modification via self-inoculation of Si phase in a hypereutectic aluminium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Elmadagli, M.; Gertsman, V.Y.; Lo, J.; Alpas, A. FIB and TEM characterization of subsurfaces of an Al–Si alloy (A390) subjected to sliding wear. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 421, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Gautam, G.; Kumar, N.; Mohan, A.; Mohan, S. Effect of Primary Silicon Refinement on Mechanical and Wear Properties of a Hypereutectic Al-Si Alloy. Silicon 2018, 10, 2227–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, D.K.; Arjun, T.S.; Thakur, P.; Vaidya, H.; Singh, K. Sliding wear and friction behaviour of Al–18% Si–0.5% Mg alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 152, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghayeghi, R.; Timelli, G. An investigation on primary Si refinement by Sr and Sb additions in a hypereutectic Al-Si alloy. Mater. Lett. 2020, 283, 128779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, Z.; Kilicaslan, M.F.; Yilmaz, F. Formation of novel flower-like silicon phases and evaluation of mechanical properties of hypereutectic melt-spun Al–20Si–5Fe alloys with addition of V. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 607, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, C.J.; Easton, M.A.; Qiu, D.; Wang, G.; StJohn, D.H.; Qian, M. Effect of ultrasonic melt treatment on intermetallic phase formation in a manganese-modified Al-17Si-2Fe alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 271, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Q.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, J.; Guo, R.; Le, Q. The relationship between the thermoelectric power and resultant solidification microstructures of Al-Si melt under electromagnetic field. Mater. Ch em. Phys. 2019, 231, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.F.; Dai, H.S. Re-formation of AlP compound in Al–Si melt. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 480, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srirangam, P. Probing the local atomic structure of Sr-modified Al–Si alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 65, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrirero, J.; Li, J.H.; Engstler, M.; Ghafoor, N.; Schumacher, P.; Oden, M.; Muecklich, F. Cluster formation at the Si/liquid interface in Sr and Na modified Al–Si alloys. Scr. Mater. 2016, 117, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xia, T.; Lan, Y.F. Effect of rare earth cerium addition on the microstructure and tensile properties of hypereutectic Al–20%Si alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 562, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xia, T.D.; Lan, Y.F.; Li, P.F.; Fan, L. Effects of rare earth Er addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of hypereutectic Al–20% Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 588, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Li, B.Q.; Li, J.B.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Xia, T.D. Effect of yttrium addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of hypereutectic Al-20Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 722, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Ji, Z.W.; Zhao, J.J.; He, J.; Jiang, H.X. Factors affecting eutectic Si modification in Al-Si hypoeutectic alloy with the addition of Na, Sr, Eu and Yb. Mater. Lett. 2021, 308, 131206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hage, F.S.; Liu, X.; Ramasse, Q.; Schumacher, P. Revealing heterogeneous nucleation of primary Si and eutectic Si by AlP in hypereutectic Al-Si alloys. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timpel, M.; Wanderka, N.; Schlesiger, R.; Yamamoto, T.; Banhart, J. The role of strontium in modifying aluminium–silicon alloys. Acta. Mater. 2012, 60, 3920–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Konishi, H.; Li, X.C. Al203 nanoparticles induced simultaneous refinement and modification of primary and eutectic Si particles in hypereutectic Al–20Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 541, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Fernández, R.; Springer, H.; Szczepaniak, A.; Zhang, H.; Raabe, D. In-situ metal matrix composite steels: Effect of alloying and annealing on morphology, structure and mechanical properties of TiB2 particle containing high modulus steels. Acta. Mater. 2016, 107, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Liu, X.; Dai, H.; Liu, X. Al-Si-P master alloy and its modification and refinement performance on Al-Si alloys. Rare Met. 2009, 28, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuemmel, M.; Grosso, D.; Boissière, C.; Smarsly, B.; Brezesinski, T.; Albouy, P.A.; Amenitsch, H.; Sanchez, C. Thermally Stable Nanocrystalline γ-Alumina Layers with Highly Ordered 3D Mesoporosity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4589–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhu, C.C.; Wu, Z.; Gao, W.L. Effect of Sb Addition on the Al–Si Eutectic of Hypoeutectic Al–Si Casting Alloys under Different Cooling Rates. Mater. Trans. 2020, 61, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Qiu, F.; Dong, B.X.; Gao, X.; Shu, S.L.; Yang, H.Y.; Jiang, Q.C. Processing, multiscale microstructure refinement and mechanical property enhancement of hypoeutectic Al–Si alloys via in situ bimodal-sized TiB2 particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 777, 139081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Qiu, F.; Dong, B.X.; Geng, R.; Lv, M.M.; Zhao, Q.L.; Jiang, Q.C. Fabrication, microstructure refinement and strengthening mechanisms of nanosized SiCP/Al composites assisted ultrasonic vibration. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 735, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yang, F.; Yang, H.; Sui, R.; Wang, J. Wetting of graphite by molten Cu–xSn–yCr ternary alloys at 1373 K. Carbon 2020, 159, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Shi, M.J.; Chen, J.H.; Wang, S.B.; Liu, C.H.; Wu, C.L. A facile electron microscopy method for measuring precipitate volume fractions in AlCuMg alloys. Mater. Charact. 2012, 69, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).