Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Rhazya stricta Decne Extracts and Their Anti-Microbial and Anti-Oxidant Activities
(This article belongs to the Section Inorganic Crystalline Materials)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Collection of Plant Materials and Preparation of Aqueous and Methanolic Extract
2.2. Phytochemical Screening
2.3. Synthesis of Ag NPs
2.4. Instrumentation
2.5. Biological Assays
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phytochemical Analysis
3.2. Characterizations of Ag NPs
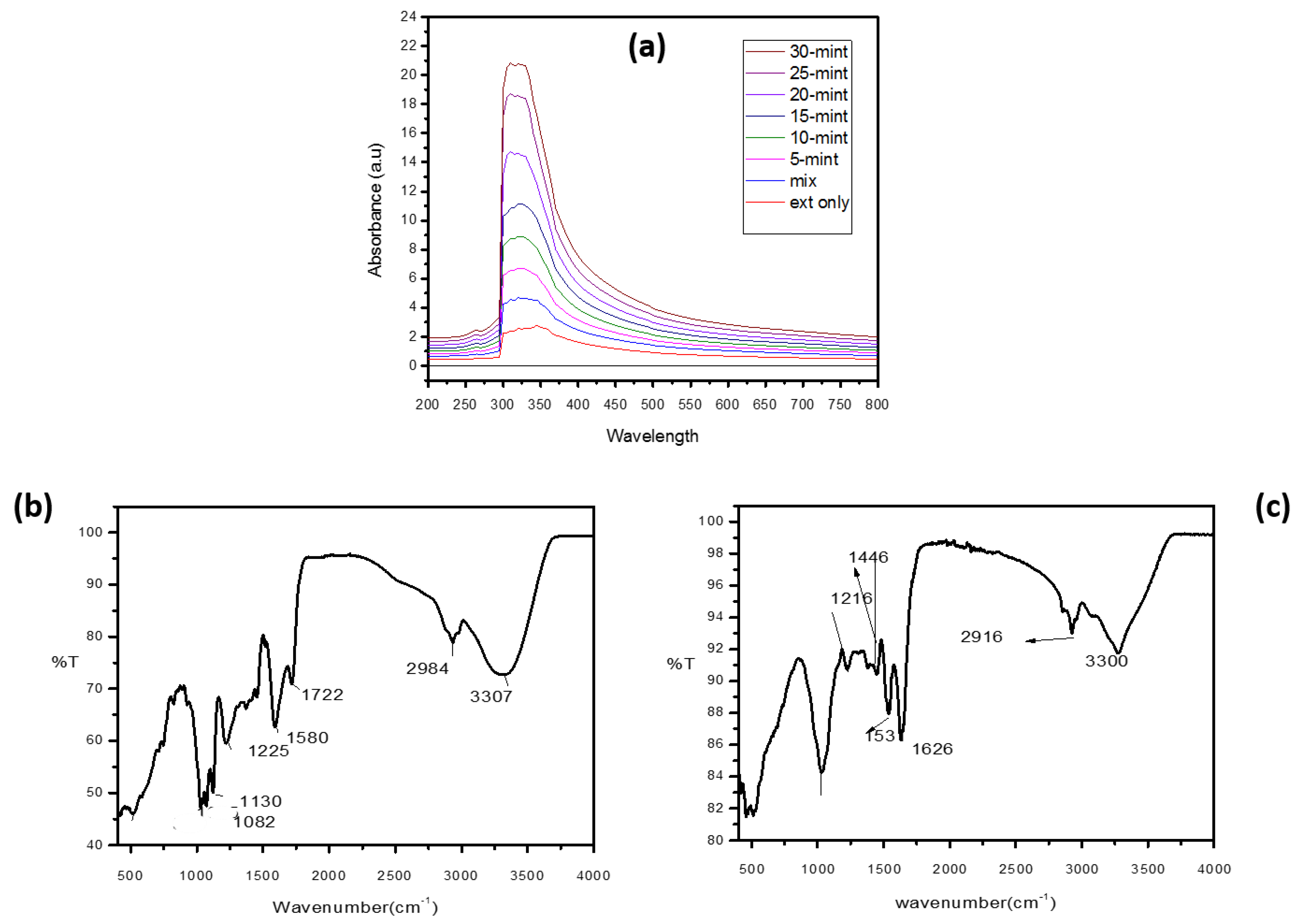
3.2.1. UV–Visible Spectroscopy
3.2.2. FTIR
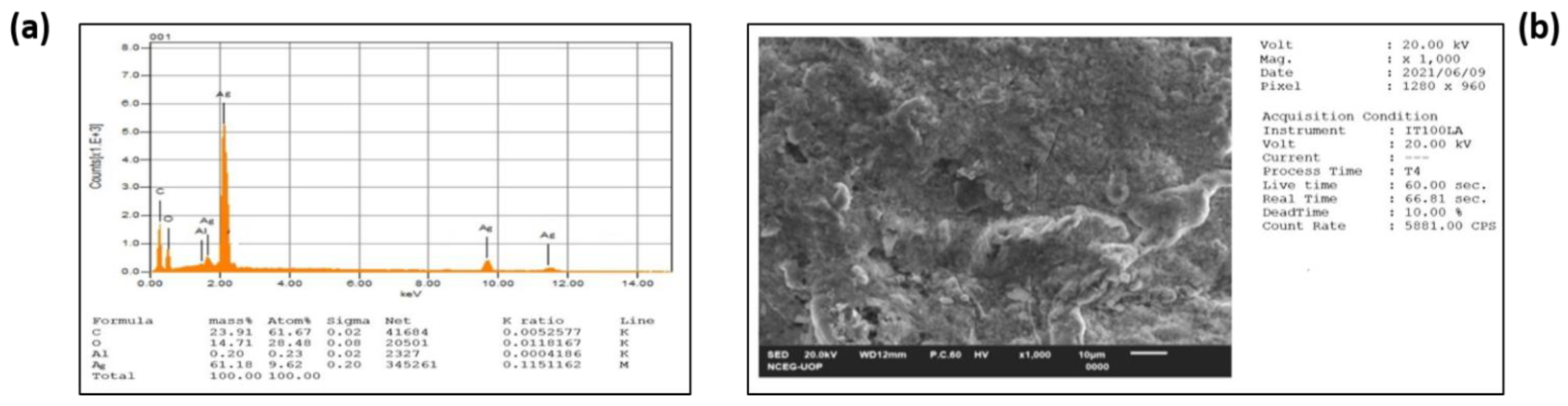
3.2.3. EDX
3.2.4. FESEM
3.3. Biological Assays
3.3.1. Anti-Bacterial Activities
3.3.2. Anti-Fungal Activities
3.3.3. Anti-Oxidant Activities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, Z.; Shah, S.A.; Khattak, I.; Ullah, H.; Khan, A.A.; Shah, R.A.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B. Melia Azedarach impregnated Co and Ni zero-valent metal nanoparticles for organic pollutants degradation: Validation of experiments through statistical analysis. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 16938–16950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.P.; Lahtinen, M.; Sillanpää, M. Green synthesis and characterizations of silver and gold nanoparticles using leaf extract of Rosa rugosa. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 364, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlJohny, B.O.; Ahmad, Z.; Shah, S.A.; Anwar, Y.; Khan, S.A. Cellulose acetate composite films fabricated with zero-valent iron nanoparticles and its use in the degradation of persistent organic pollutants. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Shahida, B.; Khan, S.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Saeeduddin; Sheikh, Z.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Alraddadi, H.M.; Fagieh, T.M.; Khan, S.B. Anchoring Zero-Valent Cu and Ni Nanoparticles on Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Polystyrene–Block Polyisoprene–Block Polystyrene Composite Films for Nitrophenol Reduction and Dyes Degradation. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 31, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Rashid, R.; Murtaza, G.; Zahra, A. Gold Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications in Drug Delivery. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Prajapati, P. Nanotechnology in medicine: Leads from Ayurveda. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2016, 8, 80–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.; Khan, N.; Khan, S.A.; Saeeduddin; Ahmad, Z.; Khan, M.A.; Iqbal, M.; Hemeg, H.A.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, S.B. Enhanced catalytic reduction/degradation of organic pollutants and antimicrobial activity with metallic nanoparticles immobilized on copolymer modified with NaY zeolite films. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 359, 119246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Rauf, A.; Zeb, H.; Ur-Rehman, M.; Hemeg, H.A. An Overview of Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles: From Synthetic Strategies, Characterization to Antibacterial and Anticancer Applications. Crystals 2022, 12, 1809. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Khan, S.A.; Al-Ghamdi, Y.O.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, N.; Rehman, M.U.; Jabli, M.; Khan, S.B. Biomass impregnated zero-valent Ag and Cu supported-catalyst: Evaluation in the reduction of nitrophenol and discoloration of dyes in aqueous medium. J. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 938, 121756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, G. History, Economic and Agro-Ecological Importance; FAO Plant Production and Protection Paper (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- MubarakAli, D.; Thajuddin, N.; Jeganathan, K.; Gunasekaran, M. Plant extract mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity against clinically isolated pathogens. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, A.; Jain, N.K. Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, I.; Singh, N.B.; Singh, A.; Singh, H.; Singh, S.C. Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its potential application. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Mañas, M.; Pleixats, R. Formation of Carbon−Carbon Bonds under Catalysis by Transition-Metal Nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Murray, C.B.; Weller, D.; Folks, L.; Moser, A. Monodisperse FePt Nanoparticles and Ferromagnetic FePt Nanocrystal Superlattices. Science 2000, 287, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.S.H.M.; Anwar, Y.; Khan, S.A. Vigna radiata Impregnated Zero-Valent CuAg NPs: Applications in Nitrophenols Reduction, Dyes Discoloration and Antibacterial Activity. J. Clust. Sci. 2021, 33, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Ghani, U.; Khan, S.A.; Tirth, V.; Algahtani, A.; Alhodaib, A.; Ali, A.; Sultana, F.; Mushtaq, M.; Zaman, A. Sequestration of Anionic and Cationic Dyes through Thermally Activated Slate and Their Kinetics and Thermodynamic Characteristics. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 12212–12221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, W.U.; Khattak, M.T.N.; Saeed, A.; Shaheen, K.; Shah, Z.; Hussain, S.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Alraddadi, H.M.; Fagieh, T.M.; Akhtar, K.; et al. Co3O4/NiO nanocomposite as a thermocatalytic and photocatalytic material for the degradation of malachite green dye. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Ikram, S. A review on biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using plant extracts and microbes: A prospect towards green chemistry. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 166, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariq, A.; Khan, T.; Yasmin, A. Microbial synthesis of nanoparticles and their potential applications in biomedicine. J. Appl. Biomed. 2017, 15, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Rauf, A.; Hemeg, H.A.; Qureshi, M.N.; Sharma, R.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Khan, I.; Alam, A.; Rahman, M. Green Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles Using Opuntia dillenii Aqueous Extracts: Characterization and Their Antimicrobial Assessment. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Khan, I.; Rauf, A.; Qureshi, M.N.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; Khan, S.A.; Khalil, A.A.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Muhammad, N. Synthesis, characterization, biological activities, and catalytic applications of alcoholic extract of saffron (Crocus sativus) flower stigma-based gold nanoparticles. Green Process. Synth. 2021, 10, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahattab, O.; Khan, I.; Bawazeer, S.; Rauf, A.; Qureshi, M.N.; Al-Awthan, Y.S.; Muhammad, N.; Khan, A.; Akram, M.; Islam, M.N.; et al. Synthesis and biological activities of alcohol extract of black cumin seeds (Bunium persicum)-based gold nanoparticles and their catalytic applications. Green Process. Synth. 2021, 10, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Bawazeer, S.; Bakht, J.; Rauf, A.; Shah, M.R.; Khalil, A.A.; El-Esawi, M.A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Valeriana jatamansi shoots extract and its antimicrobial activity. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Bawazeer, S.; Rauf, A.; Qureshi, M.N.; Muhammad, N.; Al-Awthan, Y.S.; Bahattab, O.; Maalik, A.; Rengasamy, K.R.R. Synthesis, biological investigation and catalytic application using the alcoholic extract of Black Cumin (Bunium persicum) seeds-based silver nanoparticles. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2021, 12, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Almarhoon, Z.M.; Bakht, J.; Mabkhot, Y.N.; Rauf, A.; Shad, A.A. Single-Step Acer pentapomicum-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Potential Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uz-Zaman, K.; Bakht, J.; Malikovna, B.K.; Elsharkawy, E.R.; Khalil, A.A.; Bawazeer, S.; Rauf, A. Trillium govanianum Wall. Ex. Royle rhizomes extract-medicated silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activity. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Alqarawi, A.A.; Bashir, A.K.; Tanira, M.O. Antioxidant action of extract of the traditional medicinal plant Rhazya stricta Decne. in rats. Phytother. Res. 2000, 14, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhgari, A. Alkaloids of In Vitro Cultures of Rhazya stricta. 2015, Volume 93. Available online: https://www.vttresearch.com/sites/default/files/pdf/science/2015/S93.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Akhgari, A.; Laakso, I.; Seppänen-Laakso, T.; Yrjönen, T.; Vuorela, H.; Oksman-Caldentey, K.-M.; Rischer, H. Determination of terpenoid indole alkaloids in hairy roots of Rhazya stricta (Apocynaceae) by GC-MS. Phytochem. Anal. 2015, 26, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabih, A.B.; Ayman, I.E.; Osama, A.A.; Mohammed, H.M. Potential anticancer activity of the medicinal herb, Rhazya stricta, against human breast cancer. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 8960–8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laloi, C.; Apel, K.; Danon, A. Reactive oxygen signalling: The latest news. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Qureshi, M.M.; Zaman, K.; Malik, S.; Ali, S.S. The alkaloids of Rhazya stricta and R. orientalis-a review. Fitoterapia 1989, 60, 291–322. [Google Scholar]
- Baeshen, N.; Lari, S.A.; Doghaither, H.A.; Ramadan, H.A.I. Effect of Rhazya stricta extract on rat adiponectin gene and insulin resistance. J. Am. Sci. 2010, 6, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Baeshen, N.A.; Sabir, J.S.M.; Abo-Aba, S.E.M.; Qari, S.H. Evaluation of the cytogenetic status and DNA integrity of human lymphocytes after exposure to an aqueous extract of Rhazya stricta leaves in vitro. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2009, 5, 986–994. [Google Scholar]
- Albeshri, A.; Baeshen, N.A.; Bouback, T.A.; Aljaddawi, A.A. A review of Rhazya stricta decne phytochemistry, bioactivities, pharmacological activities, toxicity, and folkloric medicinal uses. Plants 2021, 10, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S. Indigenous knowledge of folk herbal medicines by the women of district Chakwal, Pakistan. Ethnobot. Leafl. 2006, 2006, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Jadoun, S.; Arif, R.; Jangid, N.K.; Meena, R.K. Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 19, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, P.; Fu, J.; Wallen, S.L. Completely “green” synthesis and stabilization of metal nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13940–13941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balunas, M.J.; Kinghorn, A.D. Drug discovery from medicinal plants. Life Sci. 2005, 78, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Shah, S.A.; Gul, Z.; Khan, S.A. Phytochemical Analysis and Antibacterial Activity of Nicotiana tabacum and Nicotiana rustica. RADS J. Biol. Res. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrami-Teimoori, B.; Nikparast, Y.; Hojatianfar, M.; Akhlaghi, M.; Ghorbani, R.; Pourianfar, H.R. Characterisation and antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles biologically synthesised by Amaranthus retroflexus leaf extract. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2017, 12, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, A.; Qureshi, M.; Jabeen, S.; Ahmad, R.; Alabdalall, A.H.; Aljafary, M.A.; Al-Suhaimi, E. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles using Rhazya stricta. Peerj 2018, 6, e6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, R.; Malik, F.; Shamas, S.; Ahmed, T.; Kausar, M.; Rubnawaz, S.; Ashfaq, M.; Hussain, S.; Green, B.D.; Mirza, B. Pharmacological evaluation of Rhazya stricta root extract. Bol. Lat. Caribe Plant Med. Aromat 2020, 19, 188–206. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, A.T.; Alshehri, M.A.; Alanazi, N.A.; Panneerselvam, C.; Trivedi, S.; Maggi, F.; Sut, S.; Dall’Acqua, S. Phytochemical analysis of Rhazya stricta extract and its use in fabrication of silver nanoparticles effective against mosquito vectors and microbial pathogens. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollick, M.M.R.; Bhowmick, B.; Maity, D.; Mondal, D.; Bain, M.K.; Bankura, K.; Sarkar, J.; Rana, D.; Acharya, K.; Chattopadhyay, D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Paederia foetida L. leaf extract and assessment of their antimicrobial activities. Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. 2012, 4, 230–239. [Google Scholar]
- Hadacek, F.; Greger, H. Testing of antifungal natural products: Methodologies, comparability of results and assay choice. Phytochem. Anal. Int. J. Plant Chem. Biochem. Tech. 2000, 11, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondet, V.; Brand-Williams, W.; Berset, C. Kinetics and Mechanisms of Antioxidant Activity using the DPPH. Free Radical Method. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 30, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawidowicz, A.L.; Wianowska, D.; Olszowy, M. On practical problems in estimation of antioxidant activity of compounds by DPPH method (Problems in estimation of antioxidant activity). Food Chem. 2012, 131, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Phytochemicals | Methanol Extract | Aqueous Extract |
|---|---|---|
| Phlobatanins | − | + |
| Tannins | + | − |
| Flavonoids | + | + |
| Saponins | + | + |
| Glycosides | + | + |
| Steroids | + | + |
| Terpenoids | + | + |
| Caumarine | + | − |
| Betacyanins | + | − |
| Anthocyanins | − | − |
| Sample | Zone of Inhibition (n = 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | S. typhi | |
| Cefixime | 19 ± 0.5 mm | 24 ± 0.76 mm | 19 ± 0.3 mm |
| DMSO | NA | NA | NA |
| R. stricta plant extract | 9.8 ± 0.6 mm | 16± 0.45 mm | 11.6 ± 0.3 mm |
| AgNPs | 20 ± 0.73 mm | 22 ± 0.37 mm | 18 ± 0.5 mm |
| Sample | Zone of Inhibition (n = 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichophyton longifusis | Candida albican | Fusarium solani | |
| Amphotericin B | 26 ± 0.5 mm | 31 ± 0.76 mm | 32 ± 0.3 mm |
| DMSO | NA | NA | NA |
| R. stricta plant extract | 21 ± 0.6 mm | 20 ± 0.45 mm | 16 ± 0.3 mm |
| AgNPs | 31 ± 0.23 mm | 29 ± 0.37 mm | 26 ± 0.5 mm |
| S. No. | Sample Name | Solvent | Percent DPPH Scavenging Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | R. stricta plant extract | Methanol | 43.12% ± 2.1 |
| 2 | AgNPs | Methanol | 75.16% ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, H.; Rauf, A.; Khan, S.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Alshammari, A.; Alharbi, M.; Alam, A.; Suleria, H.A.R. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Rhazya stricta Decne Extracts and Their Anti-Microbial and Anti-Oxidant Activities. Crystals 2023, 13, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030398
Rahman H, Rauf A, Khan SA, Ahmad Z, Alshammari A, Alharbi M, Alam A, Suleria HAR. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Rhazya stricta Decne Extracts and Their Anti-Microbial and Anti-Oxidant Activities. Crystals. 2023; 13(3):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030398
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Haji, Abdur Rauf, Shahid Ali Khan, Zubair Ahmad, Abdulrahman Alshammari, Metab Alharbi, Amir Alam, and Hafiz Ansar Rasul Suleria. 2023. "Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Rhazya stricta Decne Extracts and Their Anti-Microbial and Anti-Oxidant Activities" Crystals 13, no. 3: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030398
APA StyleRahman, H., Rauf, A., Khan, S. A., Ahmad, Z., Alshammari, A., Alharbi, M., Alam, A., & Suleria, H. A. R. (2023). Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Rhazya stricta Decne Extracts and Their Anti-Microbial and Anti-Oxidant Activities. Crystals, 13(3), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030398









