Abstract
The casting table with lubricating oil and wiper is applied simultaneously to produce super-high-strength 7055 aluminum alloy (Al7055) ingots, and 30 T Al7055 ingots with a diameter of 582 mm were cast successfully. In this study, the microstructure and macrosegregation of the ingots were investigated using an optical microscope (OM). The research results show that the hydrogen content in the liquid metal can be decreased from 0.198 mL/100 g Al to 0.103 mL/100 g Al when three rotors are used in the degassing tank. Compared with the conventional hot-top casting table, the surface quality can be improved by using the casting table with oil lubrication. The temperature gradient between the ingot center and edge can be decreased by using the wiper during the casting process from 320 °C to 150 °C, the cracking tendency caused by the ingot temperature gradient can be decreased, the segregation layer thickness is decreased by about 87%, and the ingot can be homogenized at a high temperature by using the heat of the feed itself.
1. Introduction
With the development of the aviation industry, 7xxx super-high-strength aluminum alloys, such as Al7055, with low density, high strength, good fracture toughness, and stress corrosion resistance were developed in 1990–2000. It is an ideal light structure material for the aerospace industry [1,2,3]. However, it is difficult for some aluminum plants to produce high-quality ingots. The quality of ingots is determined by the macro- and micro-structure, macro- and micro-segregation, macro- and micro-defects, and so on [4,5]. Coarse grains, hot cracking and negative segregation are the primary defects in large-size aluminum Al alloy ingots processed by DC casting. The microstructure’s inhomogeneity and the downstream products’ poor performance can also bring about. At present, an effective and advanced low-frequency electromagnetic casting (LFEC) process developed by Cui [6] has attracted much attention in the field of aluminum alloy casting [7,8]. Moreover, the factors during the solidification and cooling procedure are more critical for the ingots to obtain high quality, such as adding grain refiners and applying magnetic fields [9,10,11]. Usually, the addition of grain refiners, such as Al-Ti-B, Al-Ti-C, or Al-V-B alloys, is used to refine grains [12,13,14]. The flow of melt in the sump is modified and the heat transfer is intensified by electromagnetic stirring. The relative movement of the liquid and solid phases changes significantly. With the application of large-bearing parts in aviation, the need for a large-scale extrusion plate of 7xxx aluminum alloy is increasing rapidly. It is known that the quality of the ingots is essential for the performance of the extrusion plate, and melting and casting play a decisive role in ingot quality. The content of Zn and Cu in Al7055 is increased in the existing high-strength aluminum alloys used in aerospace, based on a 7050 aluminum alloy, and the mass percent of (Mg + Zn + Cu) is as high as 12.8%, and the intensity is the highest in wrought aluminum alloys [15,16]. For Al7055, the ratio of w(Zn)/w(Mg) and w(Cu)/w(Mg) is high. Hence, Al7055 has high strength, good fracture toughness, strong fatigue crack growth resistance, and all-around performance [17,18]. Fe and Si are harmful impurity elements in 7xxx super-high-strength aluminum alloy, which can form crystalline phases such as Cu2FeAl7, FeAl3, Mg2Si, etc. With other elements, the crystalline phases mentioned above mainly exist in coarse compounds and brittle phases. These crystalline phases are not coherent with the matrix, and the fracture toughness of the 7xxx aluminum alloy is decreased [19,20]. The ratio of Fe and Si is essential for the ingot crack tendency of the 7xxx series of super-high-strength aluminum alloy, which can change the number and distribution of eutectic or peritectic constituents. When Fe/Si ratio is more significant, it is more likely to generate the Al2Fe2Si phase, improve the plasticity, and decrease the ingot crack tendency in the following DC casting process [21,22]. For the Al7055 used in the present investigation, the values of 501.1 °C and 624.3 °C are the solidus and liquidus temperatures, respectively [23]. The solidification range of Al7055 is vast, the thermal conductivity is low, and the content of alloy composition is high. The cooling effect and shrinkage rate differ in different areas, so the ingot crack tendency increases. Microstructure inhomogeneity and negative segregation have several challenges for large-size alloy ingots that directly affect the downstream processing and final performance of products [24], as for the large-scale Al7055 ingot. The ingot crack tendency is severe during the DC casting process [25,26]. For large ingot formats and high strength alloys, the wiper is placed below the open mold during casting in order to eject the falling water from the ingot surface. Cooling intensity and thus internal stresses are significantly reduced, the stress relief treatment right after casting can be suppressed, the uniformity of ingot temperature distribution can be improved, and the ingot crack tendency can be reduced [27,28]. However, the large difference in the cooling rate causes inhomogeneous microstructures and macrosegregations in the DC casting process. Also, Drezet et al. validated the case of using a wiper during the start-up phase of casting [29]. Although excellent metallurgical bonding was formed in these studies, the effect of lubricating oil and wiper on super-high-strength 7055 aluminum alloy ingots has not been studied, thus it is particularly critical to control the casting table with lubricating oil and wiper, which will refine grains and reduce the negative centerline segregation.
In this paper, an electromagnetic field and grain refiners were used to control the physical areas during solidification and the cooling procedure. Therefore, the casting table with lubricating oil and wiper is applied simultaneously to produce super-high-strength Al7055 ingots. The microstructure and macrosegregation of the ingot were systematically investigated, and the corresponding mechanism was also discussed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
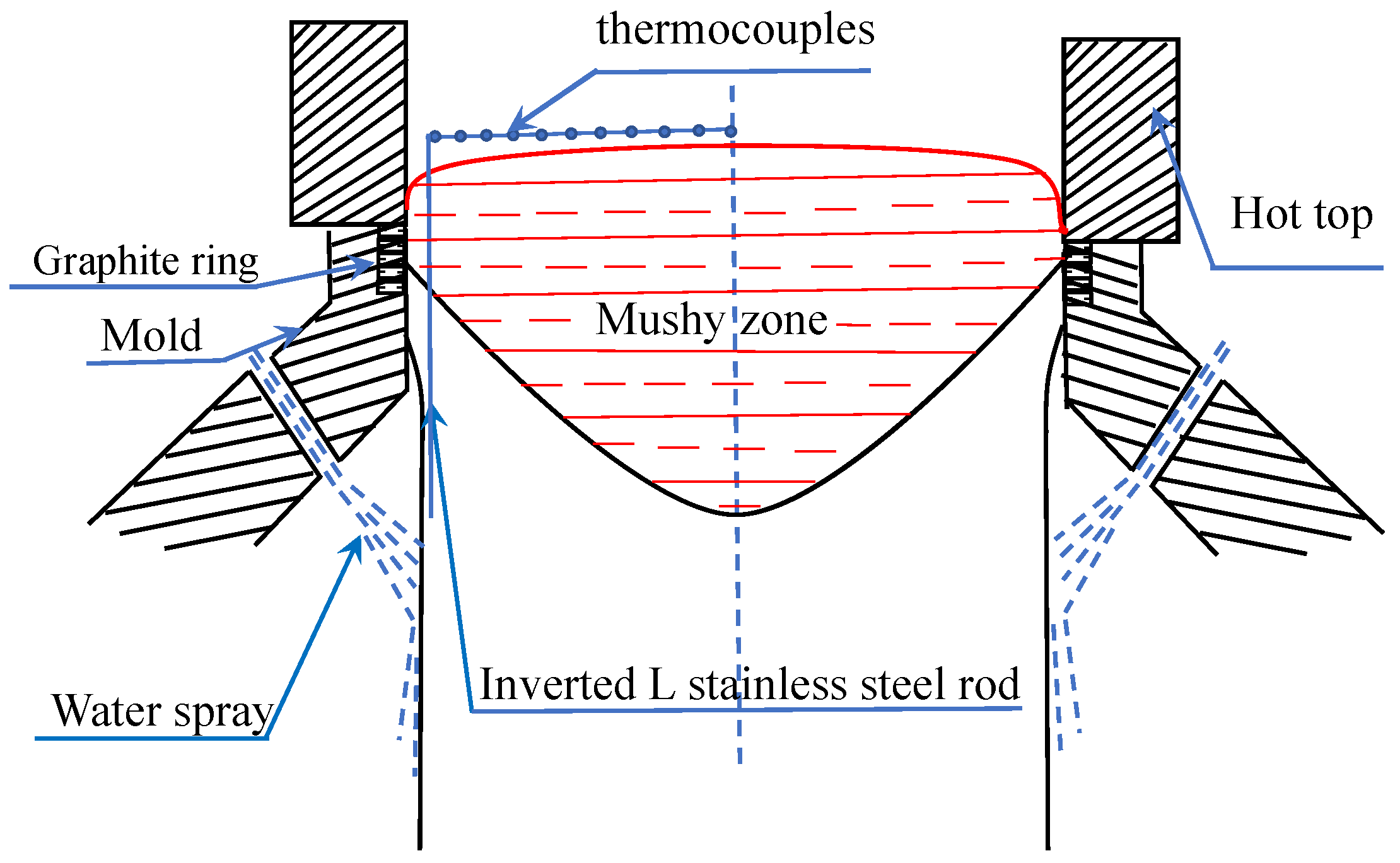
The 7075 aluminum alloy with a diameter of 582 mm was cast successfully in the Liaoning Zhongwang Group casting plant at Liaoyang, China. The content of Fe is less than 0.07 wt.%, Si is less than 0.03 wt.%, and the ratio of Fe and Si is about 2. The liquid metal temperature range in the melting furnace is 730~740 °C, 0.015 wt.% Ti was added to refine the solidification structure and reduce hot tearing risks during the melting process. In the present study, the electromagnetic stirring was put under the furnace to stir the liquid metal, and the alloy component and temperature distribution were improved. The crucible, distribution launder and other tools were sprayed with BN coating material to avoid agencies connecting with the liquid aluminum directly, which can help control the content of Fe. As Al7055 contains zirconium, which can cause a poisoning effect [30]. In the case of zirconium, the poisoning effect is due to the coating of TiB2 particles by the layer of ZrB2, which can prevent TiB2 from behaving as nucleation particles. Al-3Ti-0.15C grain refiner was used to replace the Al-5Ti-1B in this study. For casting large-scale Al7055 ingots, casting velocity is slow. Al-3Ti-0.15C grain refiner is added into the liquid metal behind the ceramic foam filter box and the 0.015 wt.% Ti is added online. The degassing system with rotors was used to treat liquid metal, and the crack tendency caused by oxide inclusion can be reduced. The casting velocity is 15 mm/min, and the cooling water flow rate is 600 L/min during the start-up stage. The casting velocity is 25 mm/min, and the cooling water flow rate is 1300 L/min during the steady phase. The wiper was used to remove the cooling water from the outer surface of the ingot, and the distance between the bottom of the graphite ring and wiper is 230 mm. K-type thermocouples were used to measure the temperature distribution in the sump and the temperatures were recorded by a HIOKI LR8402-21 multiple-path temperature measurement instrument. Eleven thermocouples fastened on stainless steel frames were put in the liquid pool along the inner wall of the hot top during the steady state. As shown in Figure 1, the eleven thermocouples moved down with the casting speed (starting from the liquid part). They were eventually frozen into solid metal, and the temperature profile in the liquid and solid parts of the ingot could be obtained. Following the experiment, the ingot was homogenized at 475 °C for 48 h.
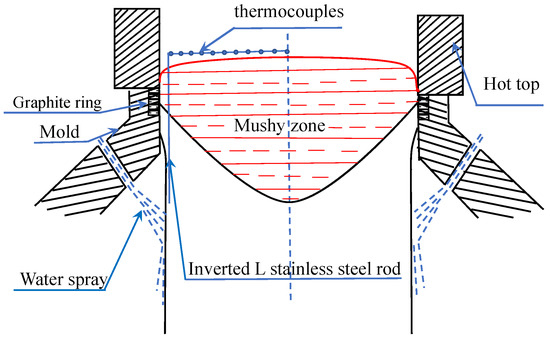
Figure 1.
Schematic of the mold and the temperature measurement.
2.2. Characterizations and Testing
The microstructures were investigated with the LeitzMM-6 optical microscopy (OM). The OM samples taken from the ingot were mechanically polished by a lathe, etched in a 12 wt.% NaOH water solution, and pickled in 20 vol.% HNO3 water solution to observe the macrostructure of the ingots. The hydrogen concentration in liquid metal was measured using an ALSCAN hydrogen tester, and the effect of the rotor number for hydrogen content was studied according to GB/T15460-2003 (the allowable measurement error was 0.025 mL/g). The ingot was sectioned, and a SPECTROLAB S direct reading spectrometer analyzed the chemical compositions in different positions. The same sample was agitated 10 times continuously, and the chemical composition of the alloys was used in this experiment, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of Al7055 ingot produced with oil-lubrication and wiper hot-top casting process (wt.%).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of Graphite Rotor on Hydrogen Content in the Liquid Metal
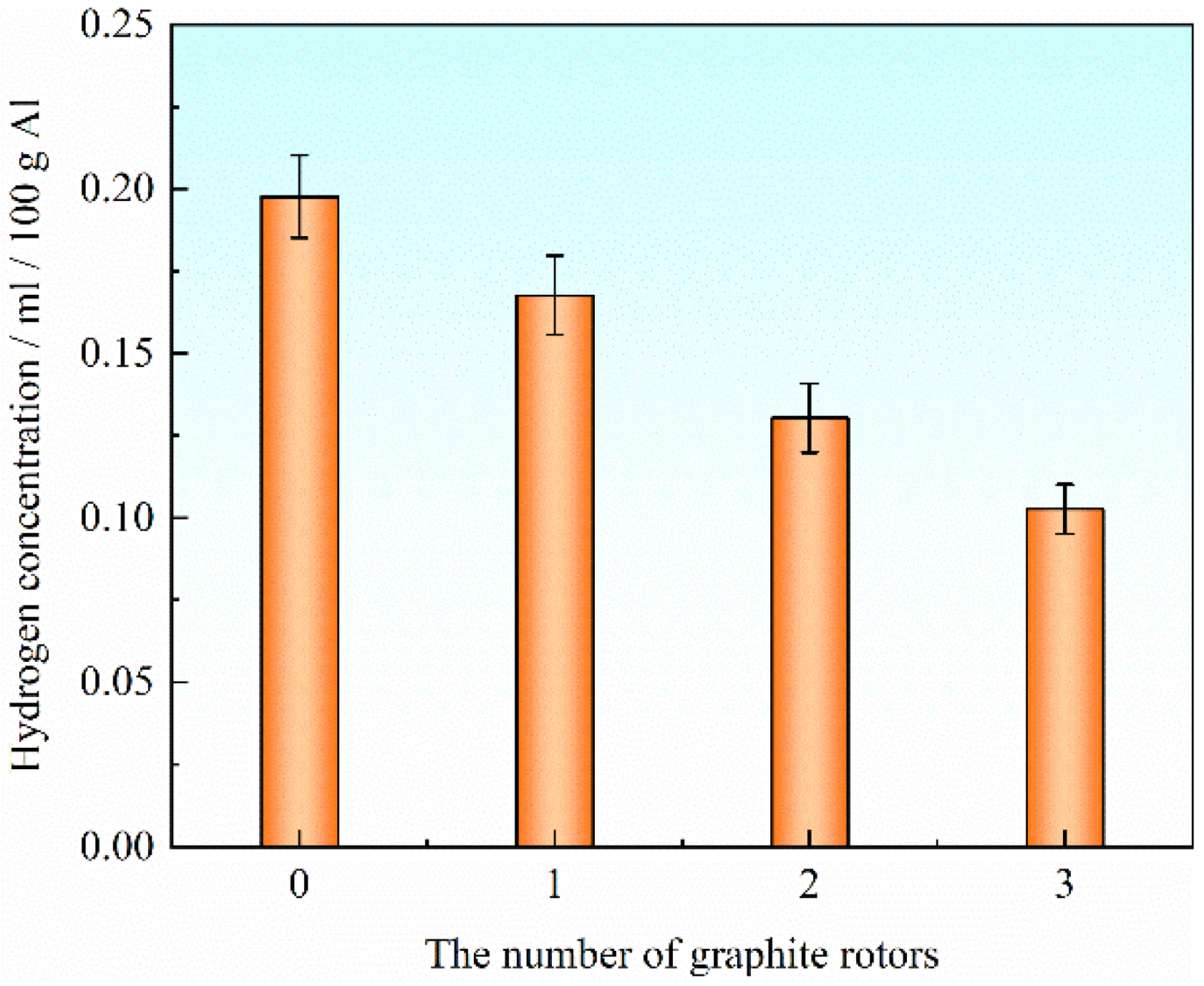
The hydrogen content in the liquid metal is essential for the metallurgical quality and performance of the ingot. The hydrogen concentration of liquid metal in the holding furnace measured by an ALSCAN hydrogen tester was 0.198 mL/100 g Al. Figure 2 shows the relationship between the hydrogen content of aluminum melt and the number of graphite rotors. We can see that the 0.167 mL/100 g Al and 0.130 mL/100 g Al are the hydrogen content degassed by one and two graphite rotors, respectively. When three graphite rotors treat the liquid metal, the hydrogen content can decrease to 0.103 mL/100 g Al, which is low enough to obtain high metallurgical quality and good performance of the ingot. So, in this work, three graphite rotors were used to degas the liquid metal.
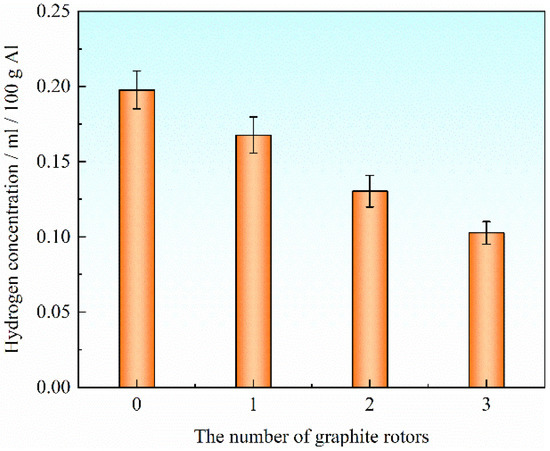
Figure 2.
The relationship between hydrogen content and the number of graphite rotors.
3.2. Chemical Composition Analysis and Segregation of Homogenized Al7055 Ingot
The ingots were homogenized at 475 °C for 48 h and then sectioned along the cross-section. We analyzed the chemical composition distribution for Cu, Mg, Zn, and Zr elements, which are the main chemical elements for Al7055. Table 2 shows the composition distribution along the ingot edge to the center, which means that all these chemical elements are distributed uniformly along this sample cross-section. This result meets the extrusion process requirement.

Table 2.
Composition analysis of homogenized Al7055 ingot (wt.%).
3.3. The Effect of Oil-Lubrication on the Ingot Segregation Layer
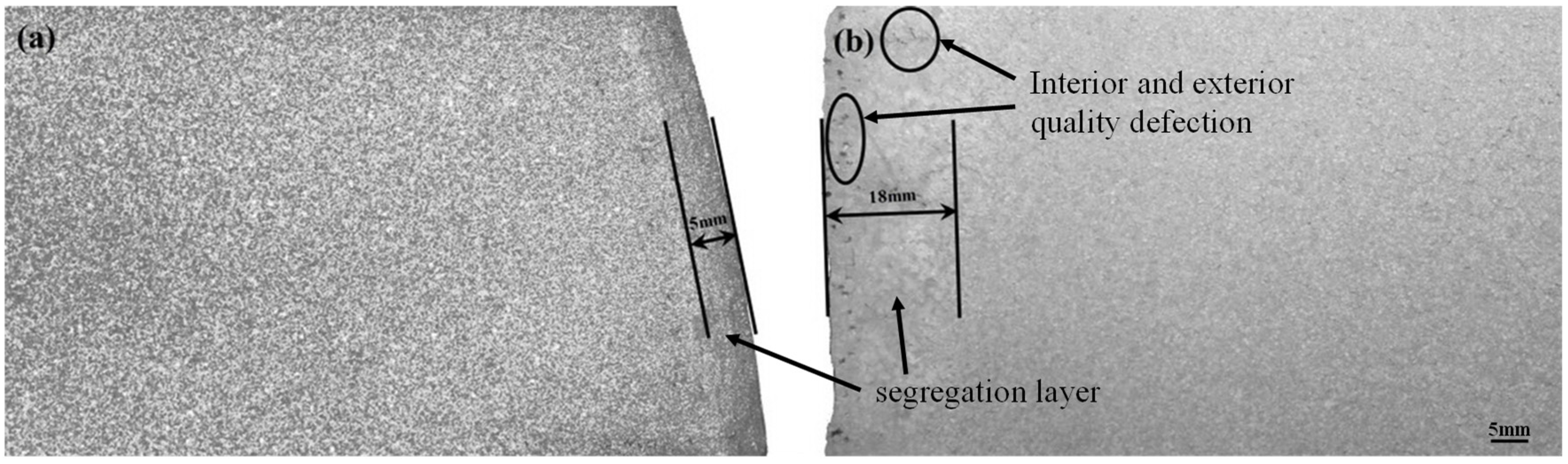
Figure 3 shows the macrostructure close to the ingot surface. These two ingots are cast individually by the oil-lubrication hot-top casting process and the normal hot-top casting process. Figure 3a shows the ingot segregation layer to be about 5 mm cast by an oil-lubrication hot-top casting process. After acid etching, we could see a homogeneous macrostructure on the edge of this ingot. On the other hand, Figure 3b shows the ingot segregation layer to be about 18 mm, which is the ingot cast by a normal hot-top casting process, and the ingot edge is not smooth. After acid etching, we could see an inhomogeneous macrostructure on the edge of this ingot. We can conclude that an ingot cast by the oil-lubrication hot-top casting process can improve the ingot surface.
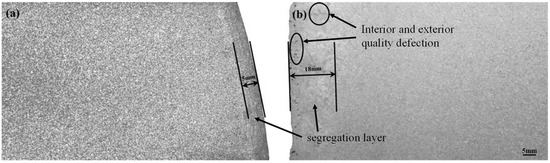
Figure 3.
Macrostructure closes the ingot surface (a) oil-lubrication hot-top casting process; (b) normal hot-top casting process.
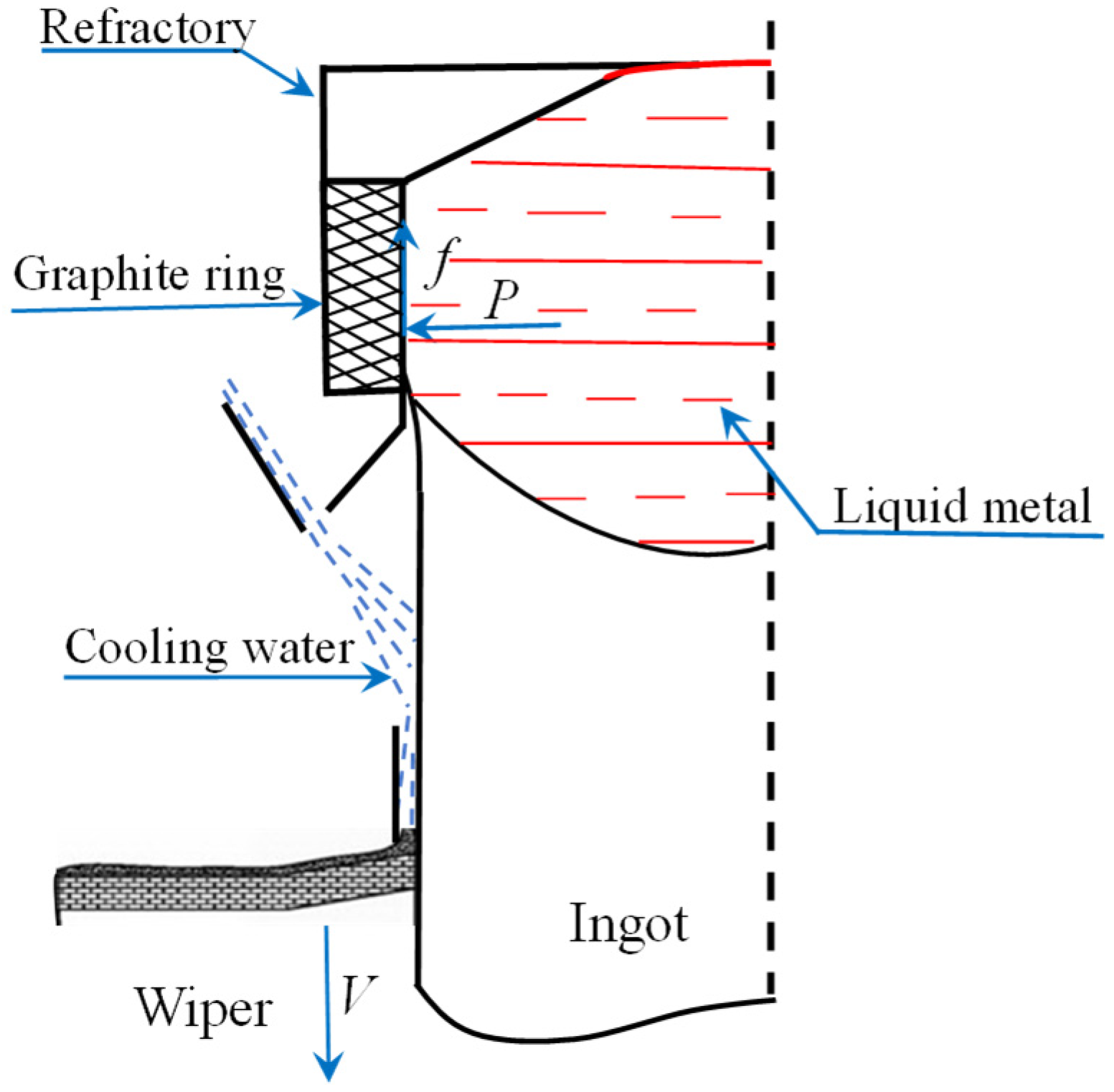
During the traditional semi-continuous casting process, hot metal cooled down at the graphite ring position. Liquid metal started to solidify under the cooling effect of the graphite ring. The solidified shell suffered metal static pressure P from the liquid metal in the thimble. So, the friction force f generates between the solidified shell and the graphite ring, and this friction force is opposite to the casting velocity V. Figure 4 shows the schematic of force analysis near the graphite ring. The metal close to the graphite ring has yet to solidify fully, which can easily form hydrogen or oil holes in the ingot or zip defect on the ingot surface. The defects of both the interior and exterior quality of the ingots are labeled in Figure 3b with a black circle. Furthermore, this friction force can create a thicker segregation layer, even up to approximately 18 mm, as shown in Figure 3b. However, the oil-lubrication hot-top casting uses a graphite ring with a multi-pore that can force the lubrication oil through the oil channel and then to the inner surface of the graphite ring. Oil lubrication can provide an excellent lubricating effect between the graphite ring and the solidified shell. The friction force f between the graphite ring and hardened body decreased significantly, which helped improve the quality of the ingot surface, and reduced the subcutaneous segregation thickness (to only approximately 5 mm, as shown in Figure 3a).
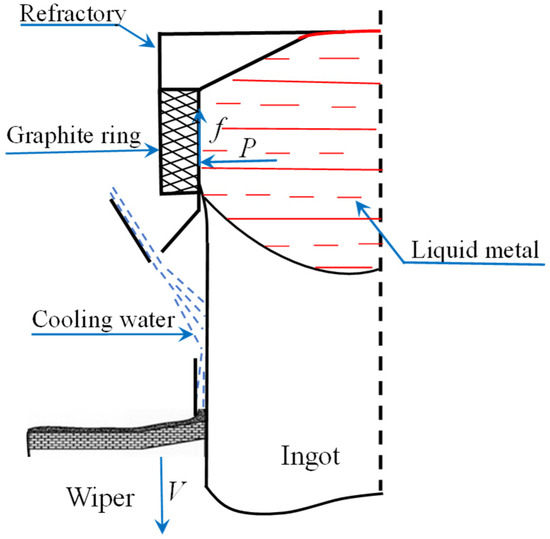
Figure 4.
Schematic of force analysis near the graphite ring.
3.4. The Effect of Wiper on Ingot Crack Defect
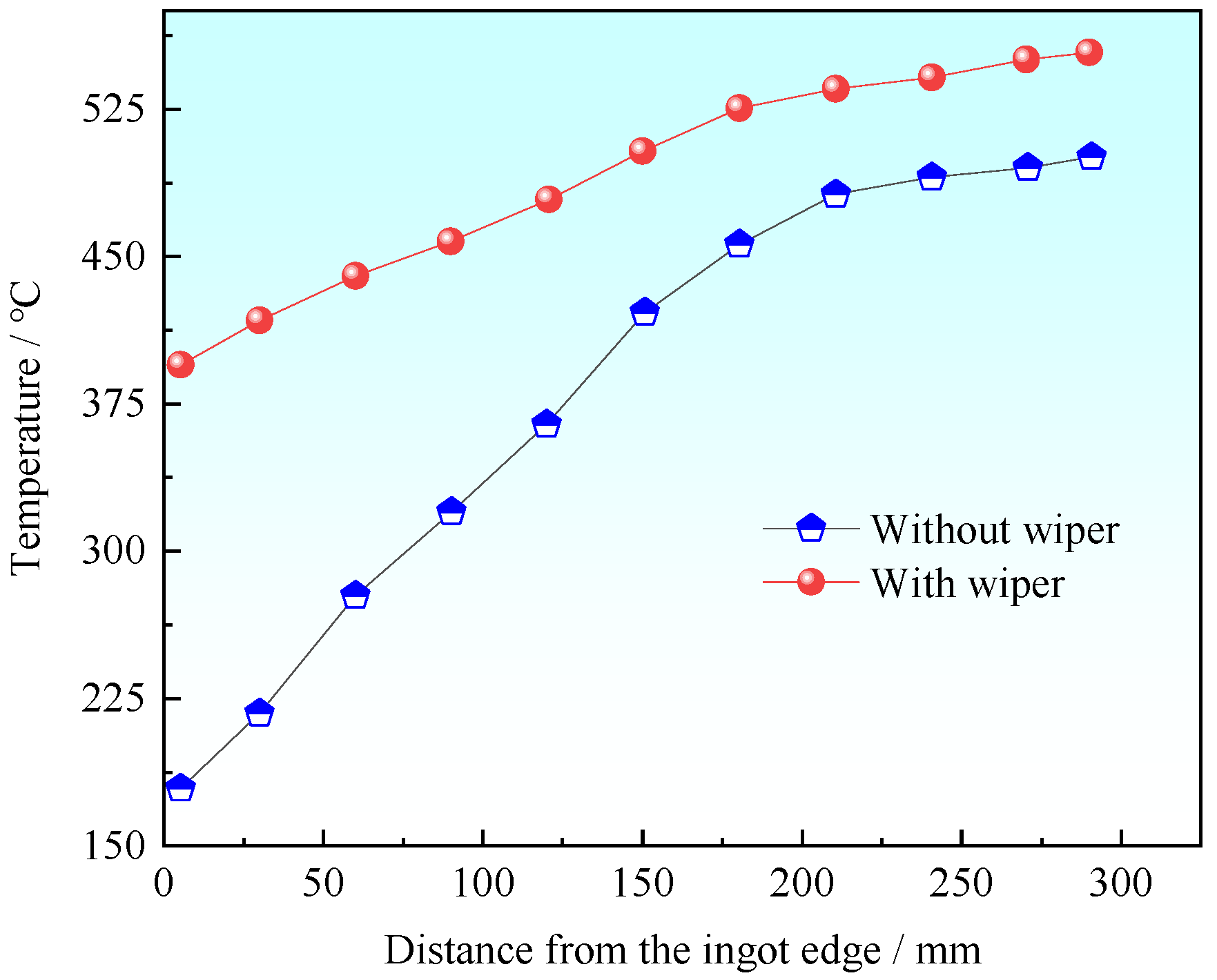
Figure 5 shows the temperature distribution along the ingot edge to the center at the position of 290 mm away from the bottom of the mold. When the wiper was not used during the casting process, the ingot surface was primarily cooled by the graphite ring and then cooled down directly by secondary cooling water. In this case, the temperature at the center of the ingot is approximately 500 °C, whereas at the edge of the ingot it is approximately 180 °C, which means the temperature difference between the ingot center and edge is approximately 320 °C. When the wiper was used during the casting process, the temperature of the center of the ingot was around 550 °C. The temperature at the edge of the ingot was slightly lower than at the center, which was approximately 400 °C at the position of 290 mm away from the bottom of the mold. The temperature difference was 150 °C between the ingot center and edge when casting with the wiper.
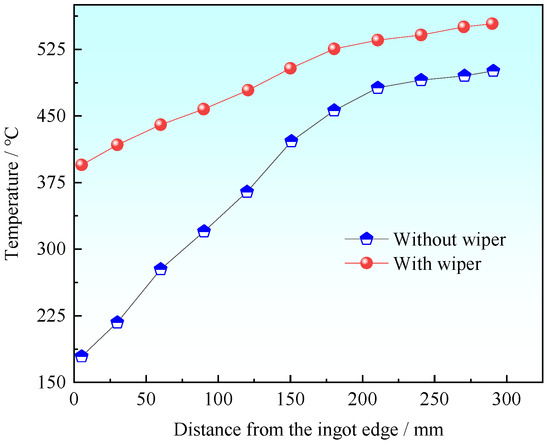
Figure 5.
Temperature distribution from ingot edge to center.
During the casting process with the wiper, secondary cooling water flows to the wiper along the ingot casting velocity direction. The wiper prevents secondary cooling water from flowing along the ingot surface. Hence, the secondary cooling water bypasses the ingot surface and flows into the casting pit along the wiper directive flow piping system. With the wiper wiping off the cooling water, the ingot surface is no longer cooled by secondary cooling water. The ingot core with the high temperature then starts to transfer heat to the ingot edge, which makes the temperature of the ingot edge increase. For 7055 super-high-strength aluminum alloy, the shrinkage coefficient changes with the temperature, which means that the ingot shrinkage is different from ingot edge to ingot center, and the internal stress forms. Applying stirring or adding grain refiners cannot effectively decrease the temperature difference between the central and periphery parts of the melt during solidification. This is because the heat is removed mainly through outside cooling, including mold cooling and water spraying cooling [31]. As mentioned above, the temperature difference (320 °C) without the wiper is twice the temperature difference (150 °C) with the wiper. The wiper is therefore very helpful in decreasing internal stress and reducing the tendency of ingot to crack.
3.5. The Effect of Wiper on Microstructure of Homogenization Al7055 Ingot
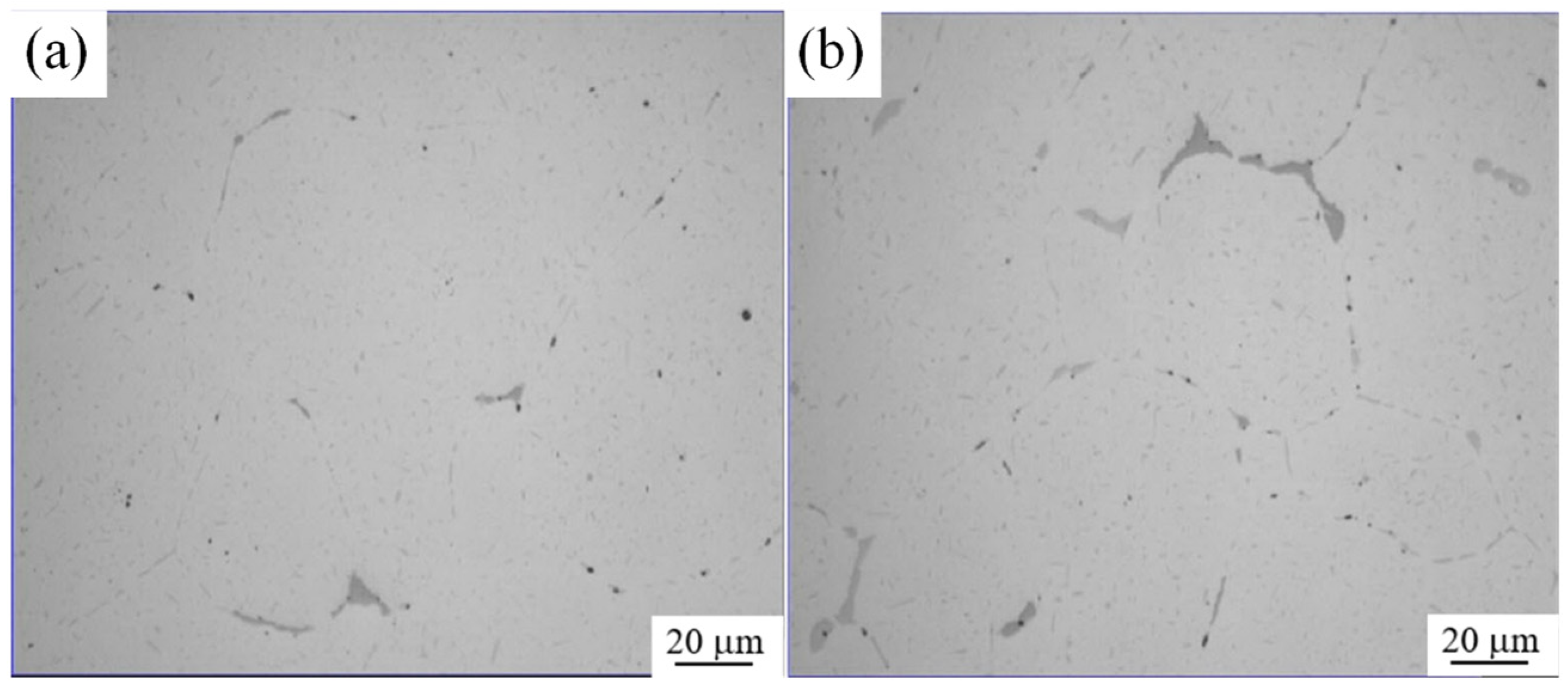
Figure 6 shows the microstructures of Al7055 ingots cast with wiper and without wiper, respectively. Both ingots were homogenized at 475 °C for 36 h. Figure 6a shows most alloy phases at the grain boundaries have dissolved in the base phase. Figure 6b shows residual alloy phases at the grain boundaries where the ingot cast without a wiper is much more than that of the ingot cast with a wiper. When the secondary cooling water on the ingot surface is wiped off during the casting process with the wiper, the heat of the ingot core can transfer to the ingot surface, which can cause the ingot temperature to be approximately 400~500 °C, as shown in Figure 5. The ingot can be homogenized at this temperature, and when the heat is dissipated, this is equivalent to homogenizing the alloy, making the homogenization more complete. So, the residual alloy phases (such as Fe-containing particles, undisclosable but with some alpha to beta transition) at the grain boundaries of Al7055 ingots cast with a wiper can be reduced.
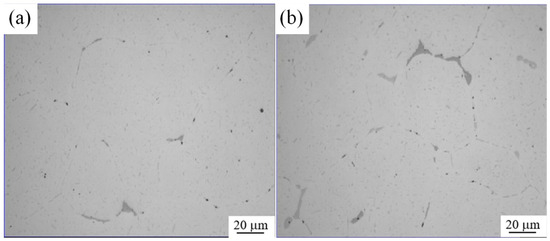
Figure 6.
Microstructure of ingot after homogenization (a) With wiper; (b) No wiper.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the effects of oil lubrication and wiper on the melting and casting of Al7055 ingots with several microstructures and macrosegregation were studied, and the temperature distribution of the casting process was measured. The conclusion can be summarized as follows:
- (1)
- Running three runners simultaneously during the casting process reduces the hydrogen content in the metal solution from 0.198 mL/100 g of aluminum before the degasser to 0.103 mL /100 g of aluminum after the degasser.
- (2)
- Ingots cast using the oil-lubrication hot-top casting process can improve the ingot surface. The segregation layer thickness is around 18 mm in the normal hot-top casting process. Compared to the normal hot-top casting process, the segregation thickness can be decreased to 5 mm using the oil-lubrication hot-top casting process, which greatly improves the surface quality of the ingot.
- (3)
- The wiper is very helpful for decreasing internal stress and the tendency of ingot to crack. Compared with casting without the wiper, the temperature difference between the ingot center and edge can be decreased from 320 °C to 150 °C with the wiper during the casting process, which can reduce the tendency of the ingots to crack, and this advantage can reach homogenizing effect and reduced micro-segregation during casting.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C. and X.W.; methodology, X.W.; validation, X.W.; formal analysis, X.W.; investigation, Y.X.; resources, J.C. and X.W.; data curation, X.W.; writing original draft preparation, X.W.; writing-review and editing, L.Y., Y.X., C.C. and Z.S.; visualization, X.W.; supervision, X.W.; project administration, J.C.; funding acquisition, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to thank the Fundamental Research Funds for the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52271094, U1708251), the Key Research and Development Program of Liaoning, China (2020JH2/10700003) and the National Key R&D Program (2022YFB3504401). The authors are also grateful to Umeda Takateru for his help in the past.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Staley, J.T.; Lege, D.J. Advance in aluminum alloy products for structural applications in transportation. J. Phys. IV 1993, 3, 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Yin, Z.M.; Shen, K.; Li, J.; Huang, J.W. Single-aging characteristics of 7055 aluminum alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 2007, 17, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yin, Z.M. Research Status and Development Trend of Ultra-High Strength Aluminum Alloys. Chin. J. Rare Metals 2006, 30, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.T.; Cui, J.Z.; Nagaumi, H. Study on electromagnet-air knife dc casting process of large-size AA 7055 aluminum alloys. ICAA13 Pittsburgh 2012, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.W.; Wang, S.C.; Shu, D. Grain size prediction and investigation of 7055 aluminum alloy inoculated by Al-5Ti-1B master alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 821, 153504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.Z.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Le, Q.C. DC casting of light alloys under magnetic fields. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. Chin. 2010, 20, 2046–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Cui, J.Z. Effect of low-frequency electromagnetic casting on micro-structure and macro-segregation of 5A90 alloy ingots. Materials 2020, 13, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaburova, N.; Krymsky, V.; Moghaddam, A.O. Theory and practice of using pulsed electromagnetic processing of metal melts. Materials 2022, 15, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Cui, J.Z. Effects of low-frequency electromagnetic field on microstructures and macro segregation of continuous casting 7075 aluminum alloy. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 1502–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.B.; Cui, J.Z. Effect of low frequency electromagnetic field on casting crack during DC casting superhigh strength aluminum alloy ingots. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 406, 286–292. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Cui, J.Z. Effect of low-frequency electromagnetic casting on the castability, microstructure, and tensile properties of direct-chill cast Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 2487–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.X.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Luo, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, Q.L.; Li, Q. Enhanced grain refinement of Al-Si alloys by novel Al-V-B refiners. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 94, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, T.; Zhou, X.R.; Thompson, G.E.; Pennycook, T.; Hashimoto, T. Grain refining mechanism in the Al/Al-Ti-B system. Acta Mater. 2015, 84, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezer, B.T.; Toptan, F.; Daglilar, S.; Kerti, I. Production of Al-Ti-C grain refiners with the addition of elemental carbon. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, S30–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivatsan, T.S.; Sriram, S.; Veeraraghavan, D.; Vasudevan, V.K. Microstructure tensile deformation and fracture behavior of aluminum alloy 7055. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 2883–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukasak, D.A.; Hart, M.R. Strong aluminum alloy shaves airframe weight. Adv. Mater. Process. 1991, 10, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kaibyshev, R.; Sakai, T.; Musin, F.; Nikulin, I.; Miura, H. Superplastic behavior of a 7055 aluminum alloy. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, M.; Mishra, R.S.; Sankaran, K.K. Structure property correations in Al 7050 and Al 7055 high-strength aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 478, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiekau, E.C.; Feribebr, U.T. Possibilities for calculation heat treatment diagram of for industrial AlZnMg(Cu) alloys. Aluminium 1999, 75, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Poganitsch, R.; Zhang, Y.Q. Intermetallic compound in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu high strength aluminum alloy. Light Alloy. Fabr. Technol. 1984, 9, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- You, C.P.; Thompson, A.W.; Bernstein, I.M. Ductile fracture processes in 7075 aluminum alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1995, 26, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.K.; Cui, J.Z. Effect of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu series alloy structures on the properties. Light Alloy Fabr. Technol. 2008, 36, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Shao, G.J.; Hu, S.C. Simulation of 7055 aluminum alloy regional water in the semi-continuous casting process. J. Hunan City Univ. 2010, 23, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Zhao, Z.H.; Zhu, Q.F.; Wang, G.S.; Zuo, Y.B.; Li, Q.Q.; Qin, G.W. Hot-top direct chill casting assisted by a twin-cooling field: Improving the ingot quality of a large-size 2024 al alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 112, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalpoor, M.; Eskin, D.G.; Katgerman, L. Cold-cracking assessment in AA7050 billets during direct-chill casting by thermomechanical simulation of residual thermal stresses and application of fracture mechanics. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2009, 40, 3304–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalpoor, M.; Eskin, D.G.; Katgerman, L. Cold cracking development in AA7050 direct chill-cast billets under various casting conditions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elliott, H.; Simons, F.A. The Dow Chemical Co. Apparatus for Removal of Coolant from Metal Surface. U.S. Patent 3,758,913, 18 September 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Zinniger, T.C. Kaiser Aluminum & Chemical Corp. Direct Chill Casting Method with Coolant Removal. U.S. Patent 4,237,961, 9 December 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Drezet, J.M.; Pirling, T. Influence of a wiper on residual stresses in AA7050 rolling plate ingots. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bunn, A.M.; Schumacher, P.; Kearns, M.A.; Boothroyd, C.B.; Greer, A.L. Grain refinement by Al-Ti-B alloys in aluminum melts a study of the mechanisms of poisoning by zirconium. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1999, 15, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wang, G.S.; Zhao, Z.H.; Zhu, Q.F.; Wang, S.L. Effect of 2024 al alloy insert on the grain refinement of a 2024 al alloy prepared via insert mold casting. Metals 2019, 9, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).