Tuning Growth of ZnO Nano-Arrays by the Dewetting of Gel Layer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ZnO Seed Layer Preparation
2.2. ZnO Nanostructures Preparation
2.3. Measurement Methods
3. Results and Discussion
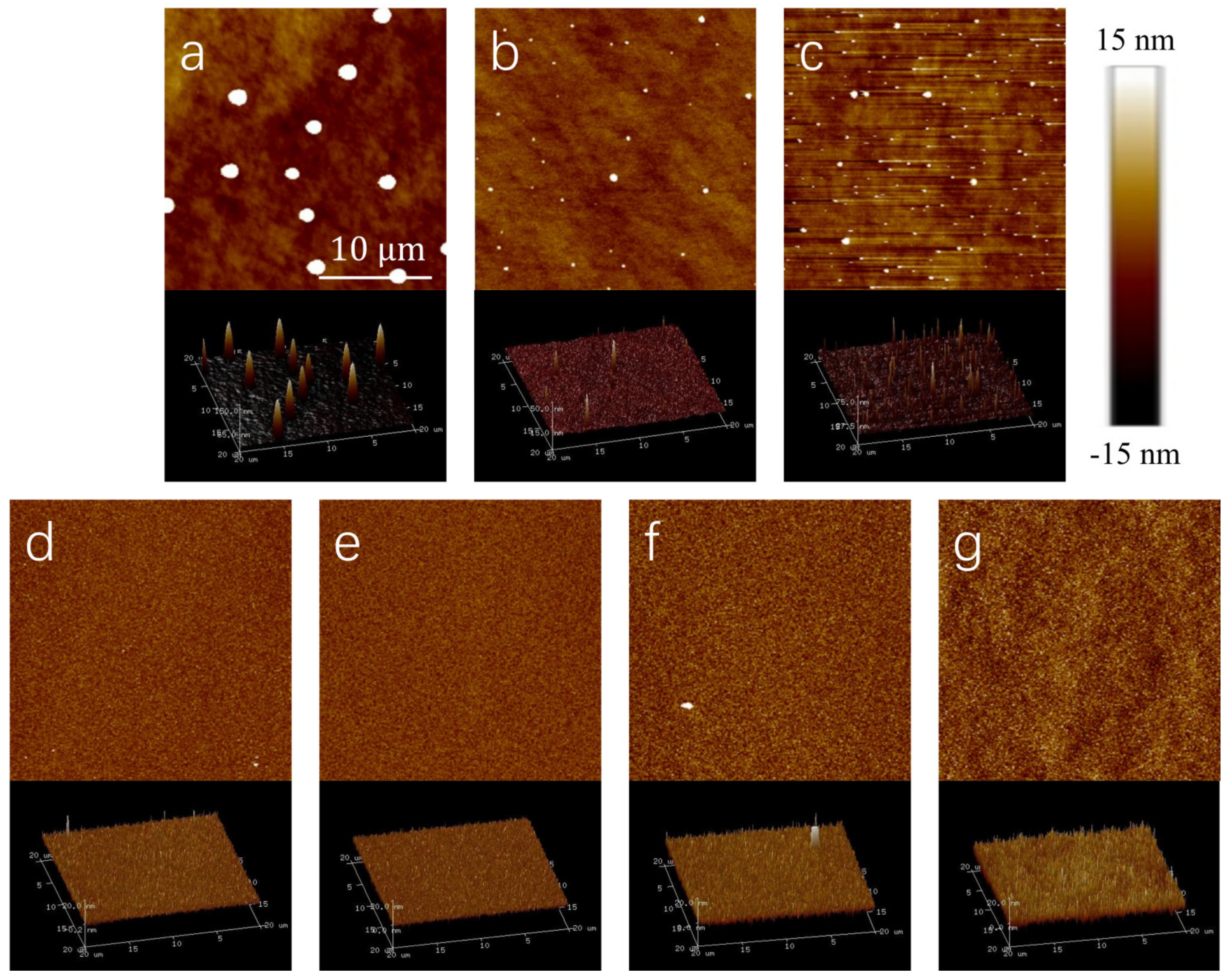
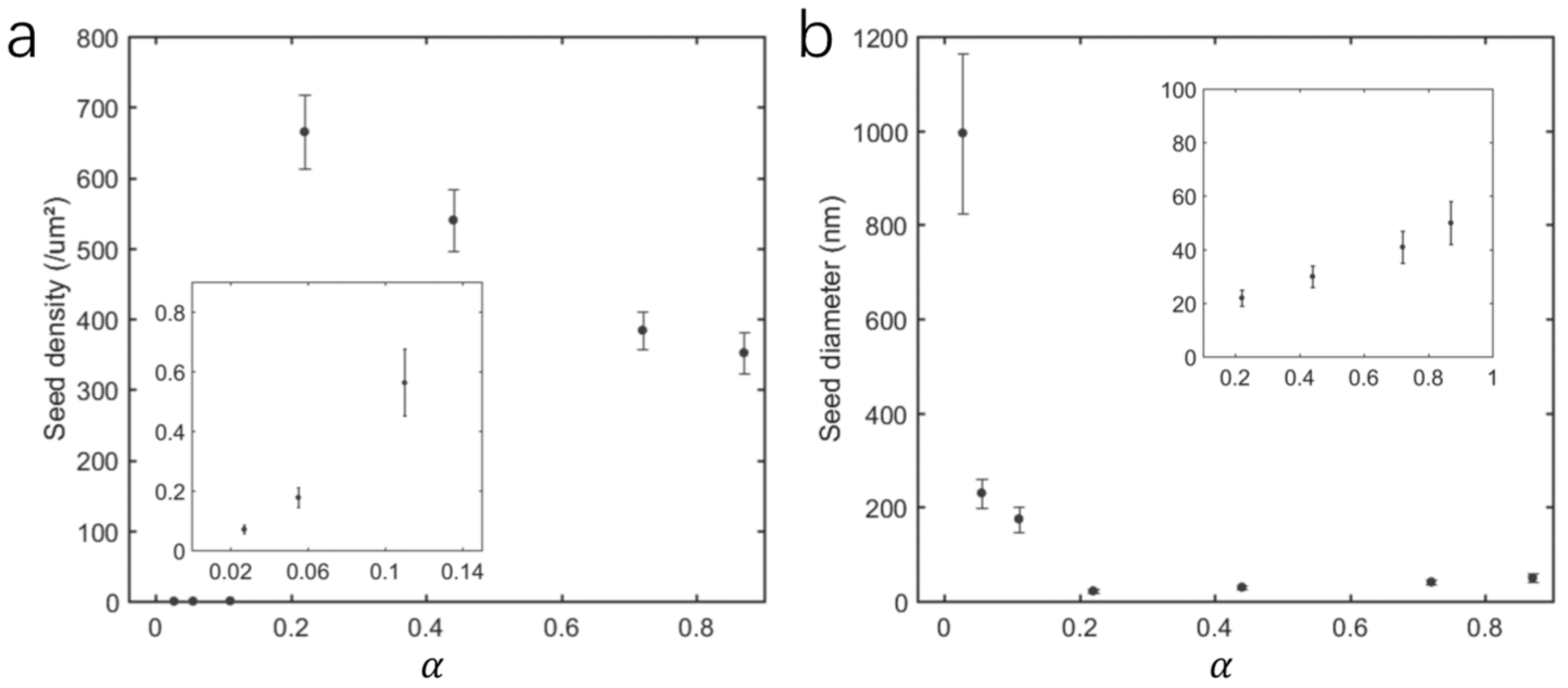
3.1. Morphology of Seed Layer
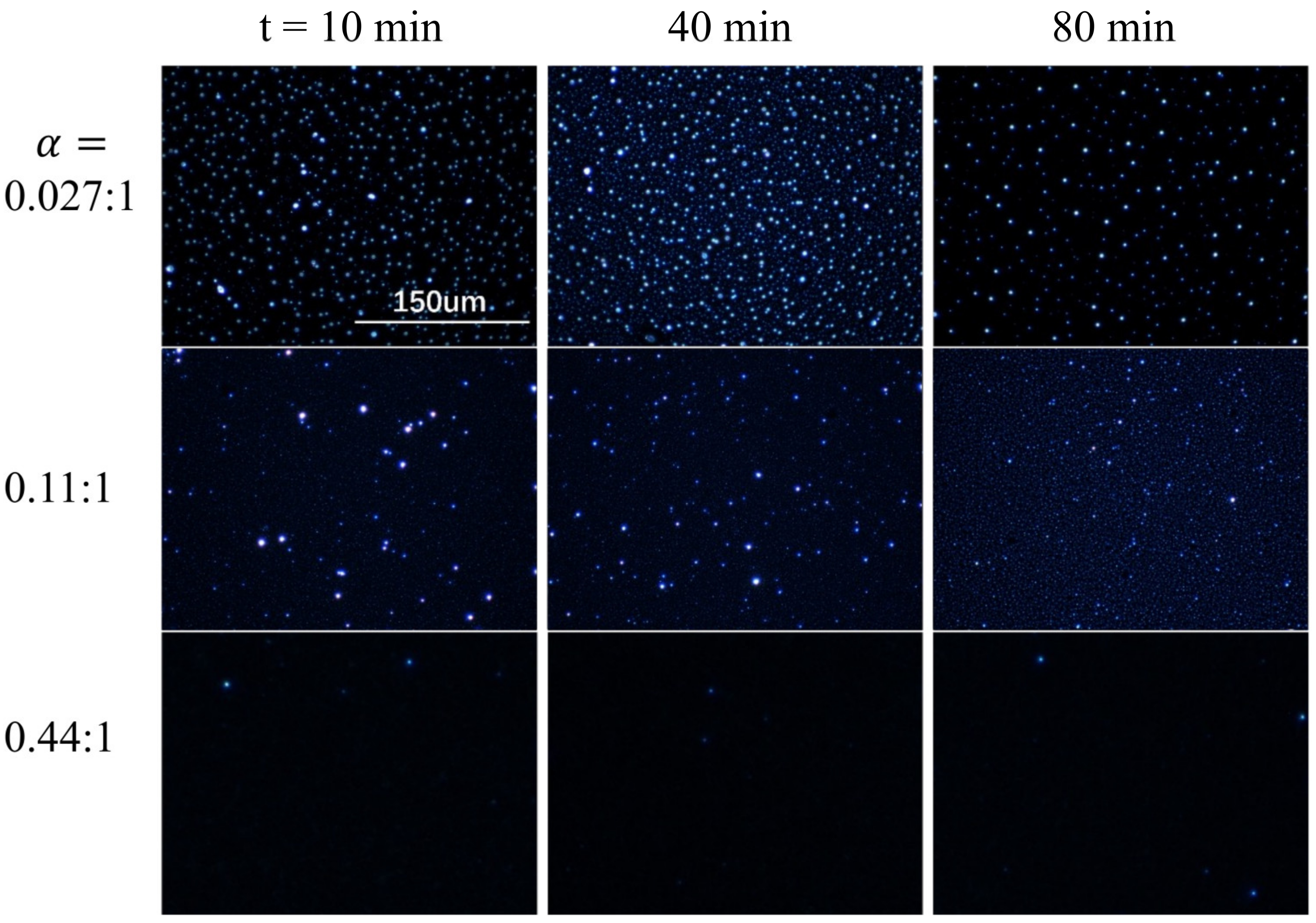
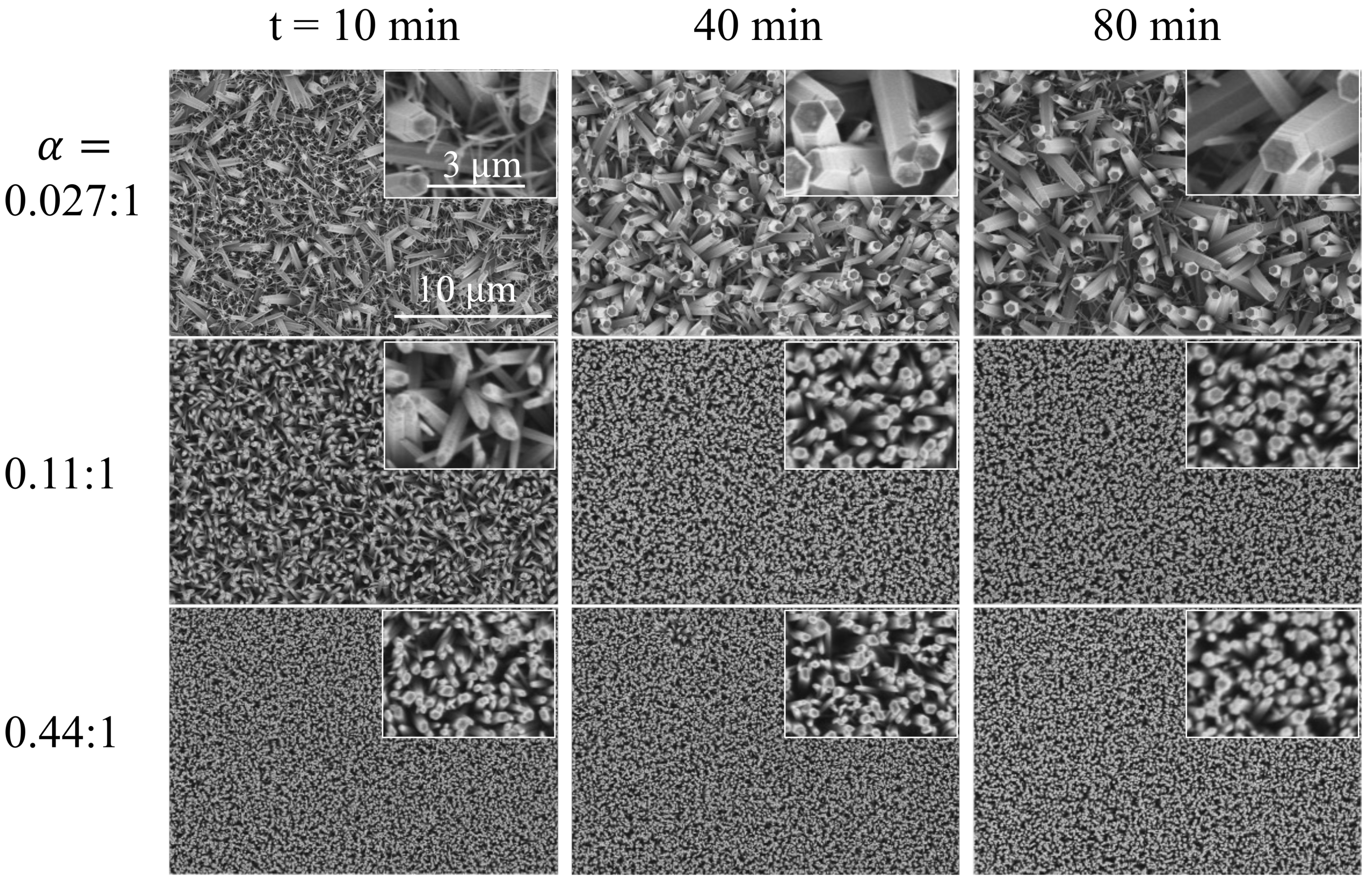
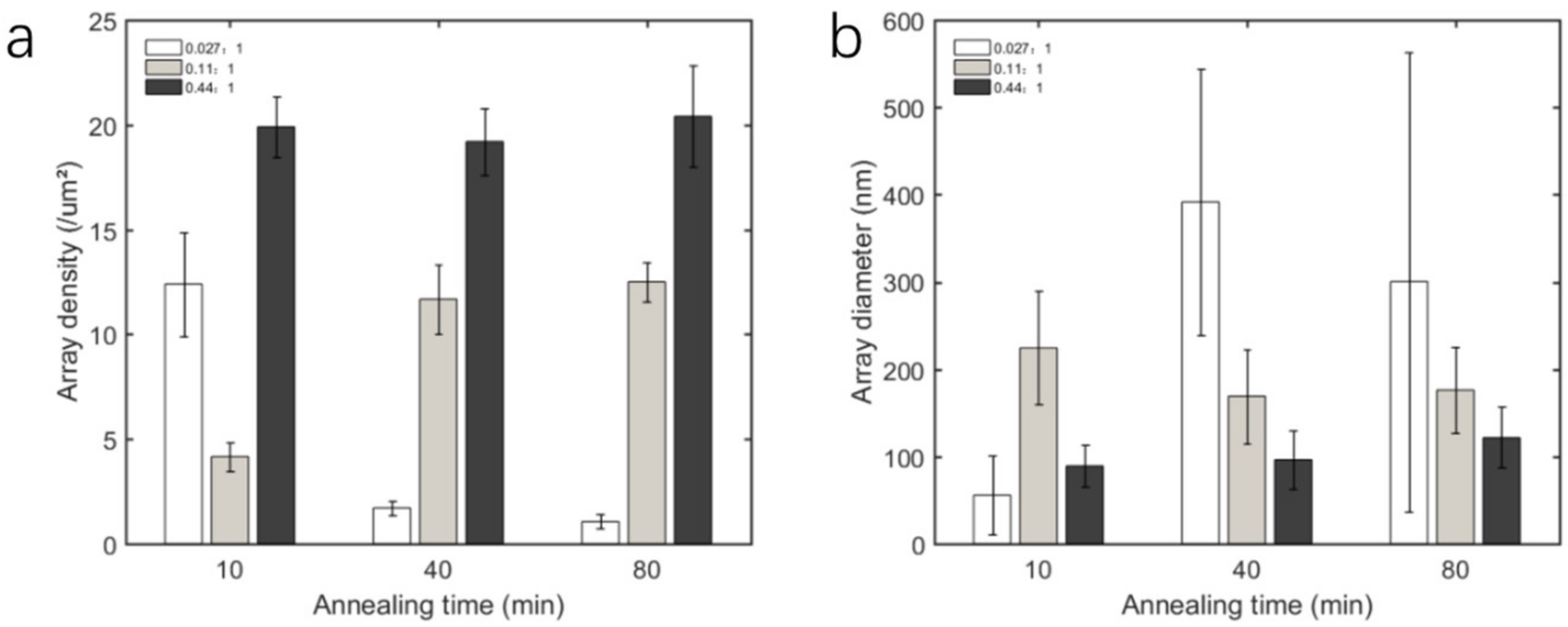
3.2. Morphology of Nanoarrays
3.3. Two Mechanisms for Seed Layer
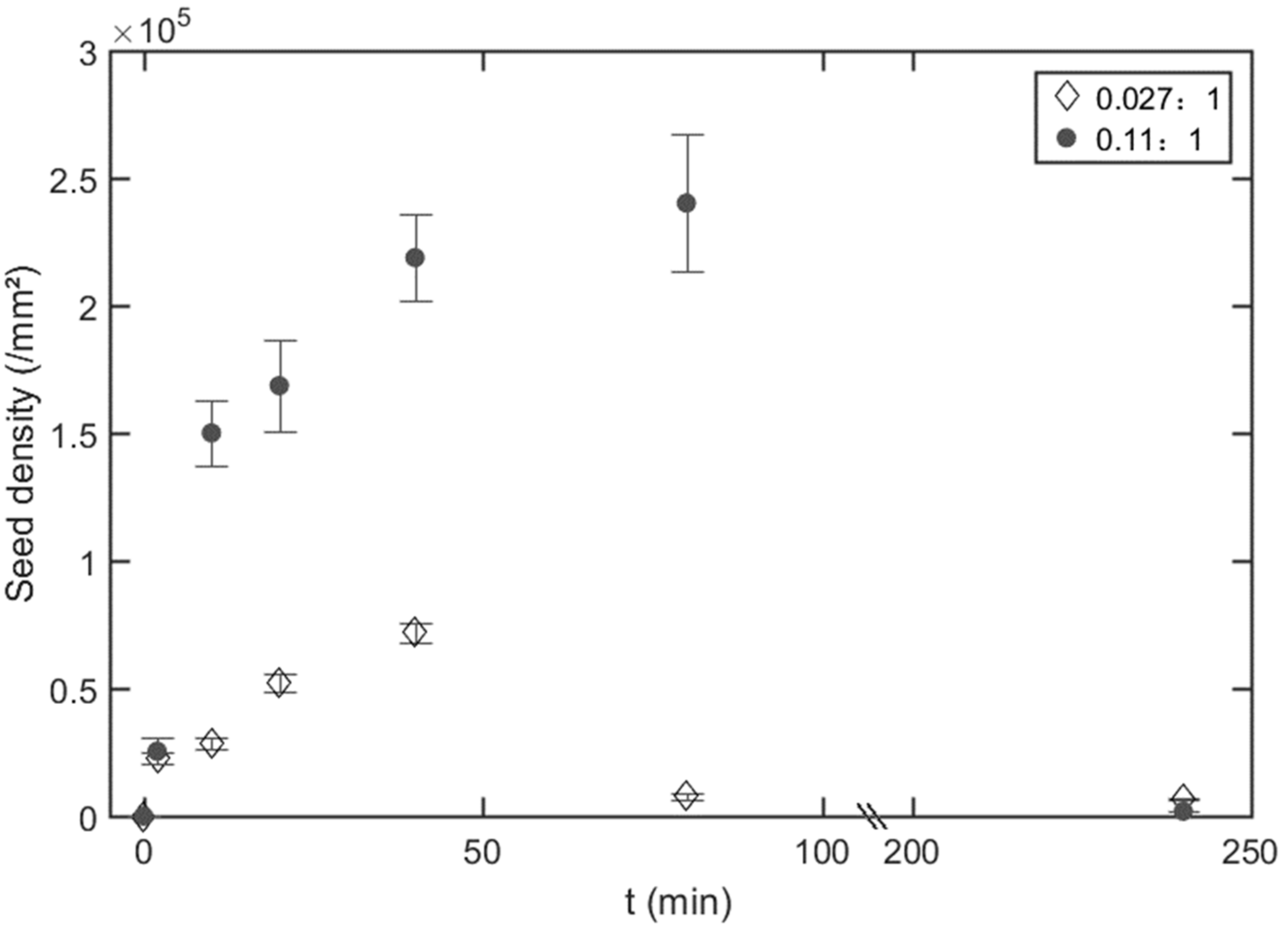
3.4. Dewetting Tunned Nanoarray Growth
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Xu, J.; Niu, J.; Yang, D. Arrays of ZnO nanowires fabricated by a simple chemical solution route. Nanotechnology 2003, 14, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greyson, E.C.; Babayan, Y.; Odom, T.W. Directed growth of ordered arrays of small-diameter ZnO nanowires. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1348–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.J.; Lee, W.; Scholz, R.; Dadgar, A.; Krost, A.; Nielsch, K.; Zacharias, M. Arrays of vertically aligned and hexagonally arranged ZnO nanowires: A new template-directed approach. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, B.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y. Solution synthesis of one-dimensional ZnO nanomaterials and their applications. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1573–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Weng, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Yeung, K.; Wang, X.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Chu, P.K. Biomedical applications of functionalized ZnO nanomaterials: From biosensors to bioimaging. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1500494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pivert, M.; Poupart, R.; Capochichi-Gnambodoe, M.; Martin, N.; Leprince-Wang, Y. Direct growth of ZnO nanowires on civil engineering materials: Smart materials for supported photodegradation. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pivert, M.; Piebourg, A.; Bastide, S.; Duc, M.; Leprince-Wang, Y. Direct One-Step Seedless Hydrothermal Growth of ZnO Nanostructures on Zinc: Primary Study for Photocatalytic Roof Development for Rainwater Purification. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Xiang, L.; Komarneni, S. Synthesis, properties and applications of ZnO nanomaterials with oxygen vacancies: A review. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 7357–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, P.; Ren, S.; Yu, Q. Fabrications and applications of ZnO nanomaterials in flexible functional devices-a review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 49, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Umar, A.; Bhasin, K.; Baskoutas, S. Chemical sensing applications of ZnO nanomaterials. Materials 2018, 11, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurišić, A.B.; Chen, X.; Leung, Y.H.; Ng, A.M.C. ZnO nanostructures: Growth, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 6526–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theerthagiri, J.; Salla, S.; Senthil, R.; Nithyadharseni, P.; Madankumar, A.; Arunachalam, P.; Maiyalagan, T.; Kim, H.-S. A review on ZnO nanostructured materials: Energy, environmental and biological applications. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 392001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Umar, A.; Kumar, G.; Nalwa, H.S. Antimicrobial properties of ZnO nanomaterials: A review. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 3940–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Ansari, A.H.; Hameedullah, M.; Ahmad, E.; Husain, F.M.; Zia, Q.; Baig, U.; Zaheer, M.R.; Alam, M.M.; Khan, A.M. Sol-gel synthesis of thorn-like ZnO nanoparticles endorsing mechanical stirring effect and their antimicrobial activities: Potential role as nano-antibiotics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Abdullah, K.; Awad, S.; Zaraket, J.; Salame, C. Synthesis of ZnO nanopowders by using sol-gel and studying their structural and electrical properties at different temperature. Energy Procedia 2017, 119, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, F.D.C.G.; López, J.L.C.; Rodríguez, A.S.L.; Gallardo, P.S.; Morales, E.R.; Hernández, G.P.; Guillen, J.C.D.; Flores, L.L.D. Sol–gel/hydrothermal synthesis of well-aligned ZnO nanorods. Boletín Soc. Española Cerámica Y Vidr. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Que, W. Preparation and characterization of sol–gel Al-doped ZnO thin films and ZnO nanowire arrays grown on Al-doped ZnO seed layer by hydrothermal method. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2010, 94, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.-H.; Hu, J.; Li, S.-S.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Shi, J.; Li, X.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Chen, Y. Improved seedless hydrothermal synthesis of dense and ultralong ZnO nanowires. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 245601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.-N.; Wu, S.-C. Synthesis of ZnO nanowires by the hydrothermal method, using sol–gel prepared ZnO seed films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2011, 22, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier-César, C.; Capochichi-Gnambodoe, M.; Leprince-Wang, Y. Growth mechanism studies of ZnO nanowire arrays via hydrothermal method. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 115, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Yan, J.; Hui, D.; Yun, J.; Zhai, C.; Zhao, W. Uniform ZnO nanowire arrays: Hydrothermal synthesis, formation mechanism and field emission performance. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 650, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, N.A.; Lewis, A.R.; Pleydell-Pearce, C.; Maffeis, T.G. Investigation of the growth parameters of hydrothermal ZnO nanowires for scale up applications. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2018, 22, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumoto, M.S.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Santilli, C.V.; Briois, V. Catalysis and temperature dependence on the formation of ZnO nanoparticles and of zinc acetate derivatives prepared by the sol−gel route. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, Y.; Yong, K. Controlled growth of well-aligned ZnO nanorod array using a novel solution method. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 19263–19269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.; Zhang, Z.; Takahashi, T. Novel micro-ring structured ZnO photoelectrode for dye-sensitized solar cell. Nano-Micro Lett. 2010, 2, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.E.; Jungjohann, K.L.; Browning, N.D.; Arslan, I. Controlled growth of nanoparticles from solution with in situ liquid transmission electron microscopy. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2809–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandin, P.; Maximova, K.A.; Gongalsky, M.B.; Sanchez-Royo, J.F.; Chirvony, V.S.; Sentis, M.; Timoshenko, V.Y.; Kabashin, A.V. Femtosecond laser fragmentation from water-dispersed microcolloids: Toward fast controllable growth of ultrapure Si-based nanomaterials for biological applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2489–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harish, V.; Ansari, M.M.; Tewari, D.; Gaur, M.; Yadav, A.B.; García-Betancourt, M.-L.; Abdel-Haleem, F.M.; Bechelany, M.; Barhoum, A. Nanoparticle and Nanostructure Synthesis and Controlled Growth Methods. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Bi, S. Nanoparticles for organic electronics applications. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, S.; Dutta, J. Effect of seeded substrates on hydrothermally grown ZnO nanorods. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2009, 50, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-L.; Rosi, N.L. Preparation of unique 1-D nanoparticle superstructures and tailoring their structural features. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6902–6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, P.; Nistor, V.; Nouneh, K.; Oyama, M.; Abd-Lefdil, M.; Díaz, R. XPS study of silver, nickel and bimetallic silver–nickel nanoparticles prepared by seed-mediated growth. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 8807–8813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Fang, Y.; Kler, R.; Canciani, G.E.; Draper, T.C.; Al-Abdullah, Z.T.; Alfadul, S.M.; Perry, C.C.; He, H.; Chen, Q. Marangoni ring-templated vertically aligned ZnO nanotube arrays with enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 149, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.M.; Mornaghini, F.C.F.; Spolenak, R. Ordered arrays of faceted gold nanoparticles obtained by dewetting and nanosphere lithography. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 485306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.P.; Blunt, M.O.; Pauliac-Vaujour, E.; Stannard, A.; Moriarty, P.; Vancea, I.; Thiele, U. Controlling pattern formation in nanoparticle assemblies via directed solvent dewetting. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 116103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-S.; Lin, C.-F. Influences of ZnO sol-gel thin film characteristics on ZnO nanowire arrays prepared at low temperature using all solution-based processing. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 014304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Yan, N.; Tian, Y.; Luo, H. Tuning Growth of ZnO Nano-Arrays by the Dewetting of Gel Layer. Crystals 2023, 13, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13010030
Li Z, Yan N, Tian Y, Luo H. Tuning Growth of ZnO Nano-Arrays by the Dewetting of Gel Layer. Crystals. 2023; 13(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ziqian, Ningzhe Yan, Yangguang Tian, and Hao Luo. 2023. "Tuning Growth of ZnO Nano-Arrays by the Dewetting of Gel Layer" Crystals 13, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13010030
APA StyleLi, Z., Yan, N., Tian, Y., & Luo, H. (2023). Tuning Growth of ZnO Nano-Arrays by the Dewetting of Gel Layer. Crystals, 13(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13010030





