Effect of Solvent Composition on Solubility, Thermodynamics, Metastable Zone Width (MSZW) and Crystal Habit of L-Ascorbic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Binary Solvent Systems
2.3. Apparatus and Methodology
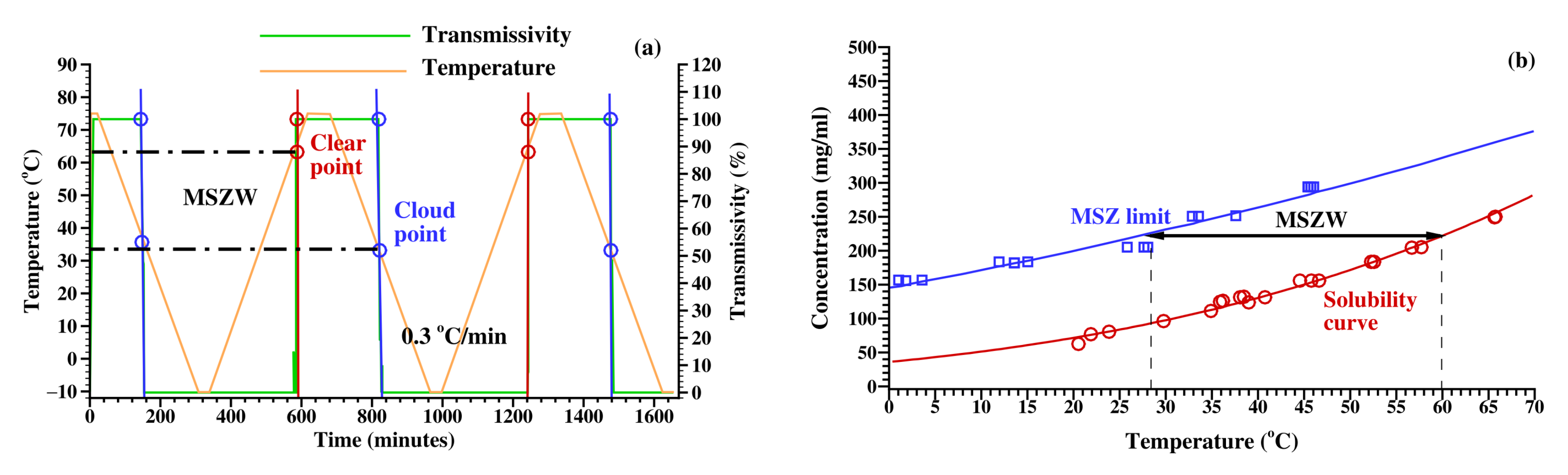
2.3.1. Measurement of Solubility and MSZ Limit
2.3.2. Cooling Crystallization Experiment
3. Solubility Prediction: Jouyban-Acree Model
4. Results and Discussion
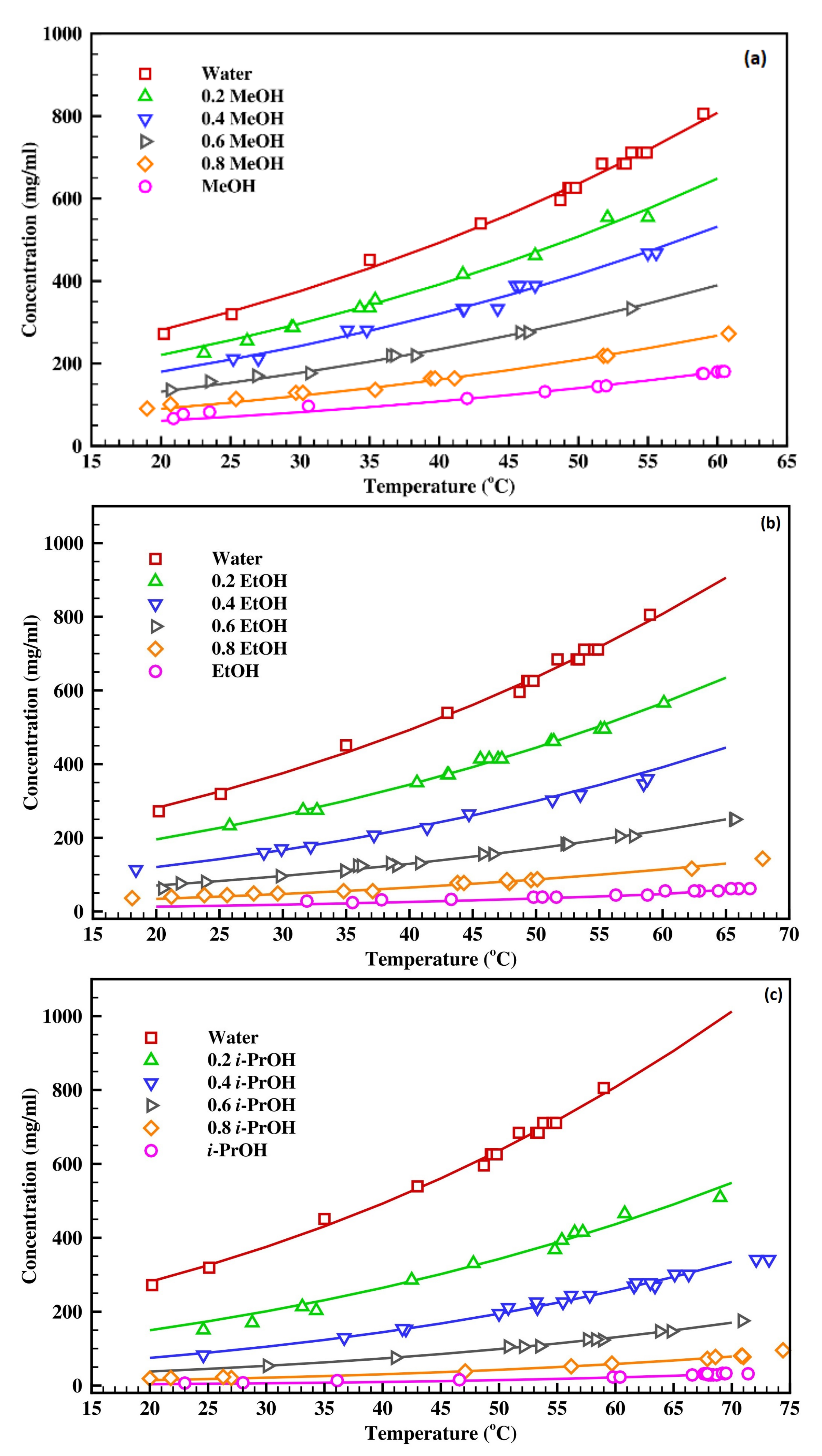
4.1. Effect of Solvent Composition on Solubility
4.2. Estimation of Solubility in Binary Solvent Systems
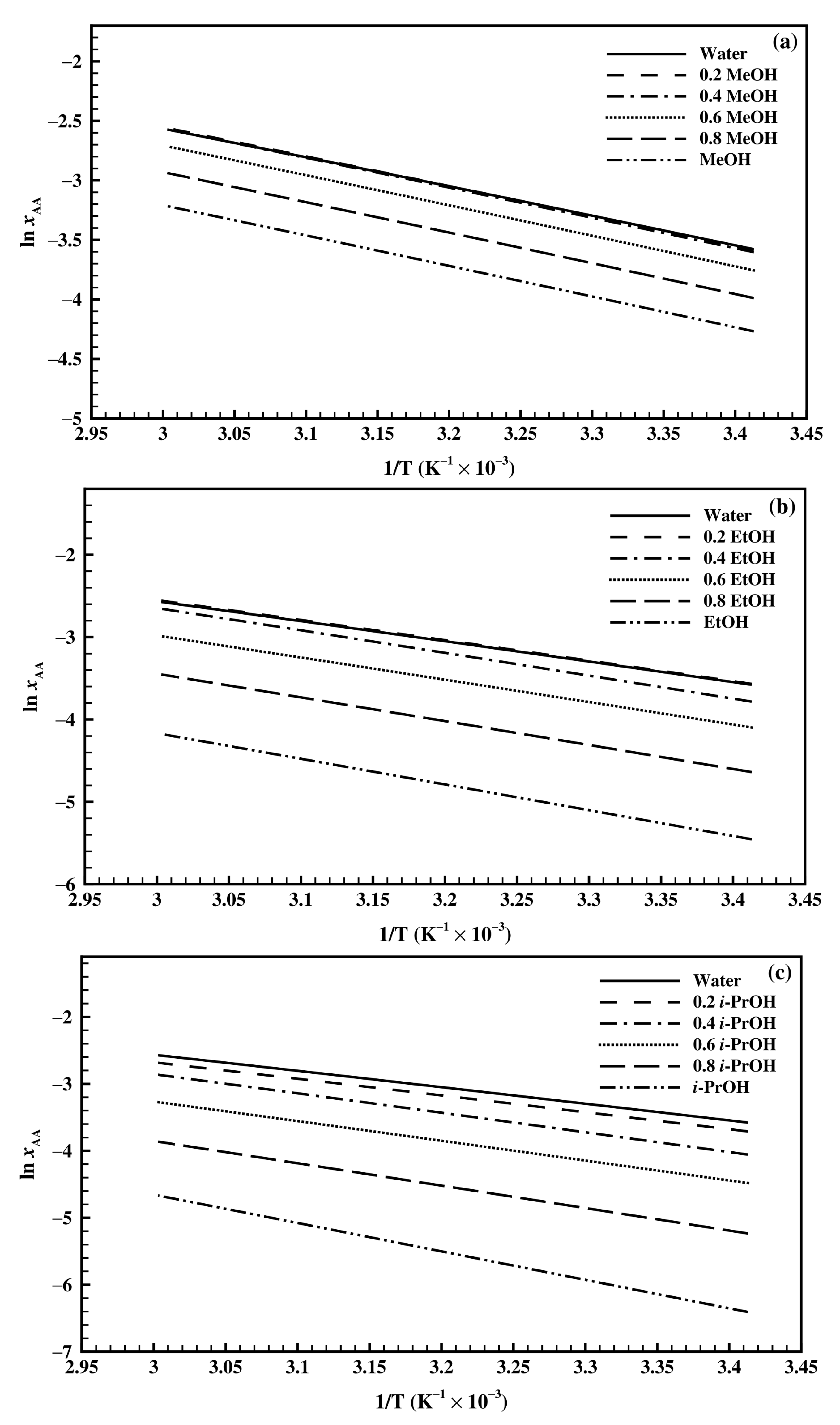
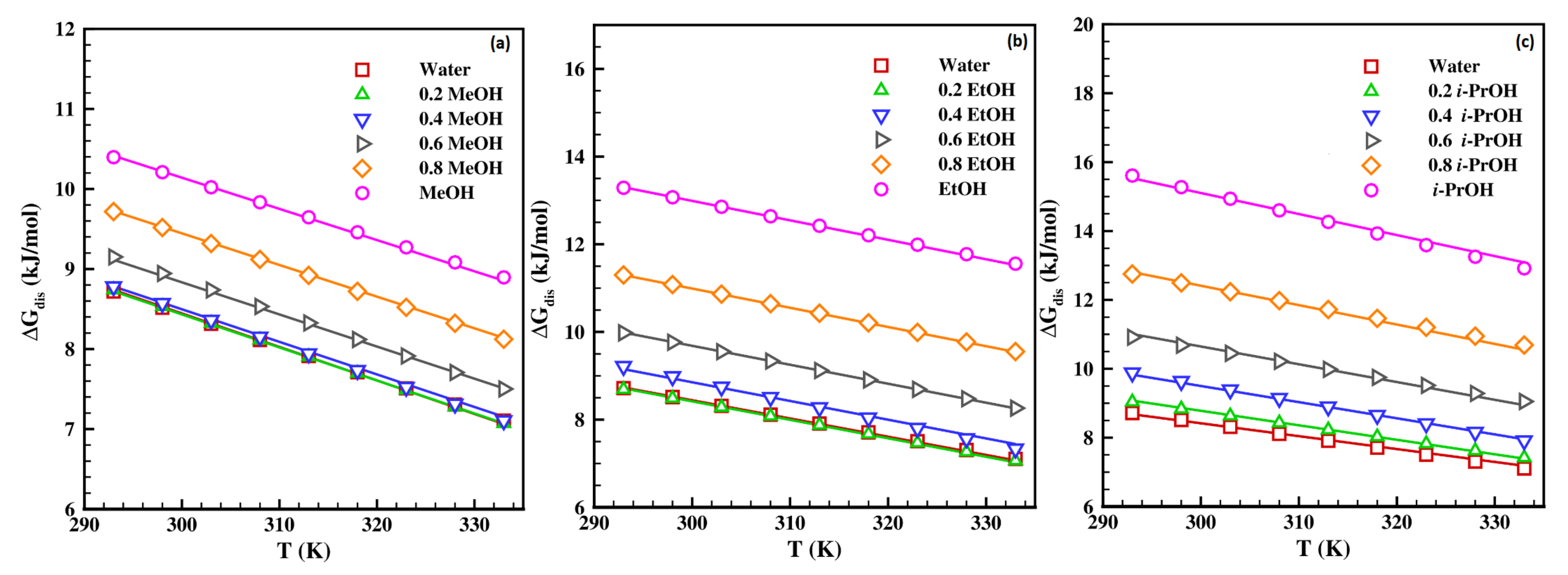
4.3. Analysis of Thermodynamic Properties
4.3.1. Estimation of Thermodynamic Properties Using Van’t Hoff Model
4.3.2. Estimation of Thermodynamic Properties Using Jouyban-Acree Model
4.4. Effect of Solvent Composition on MSZW
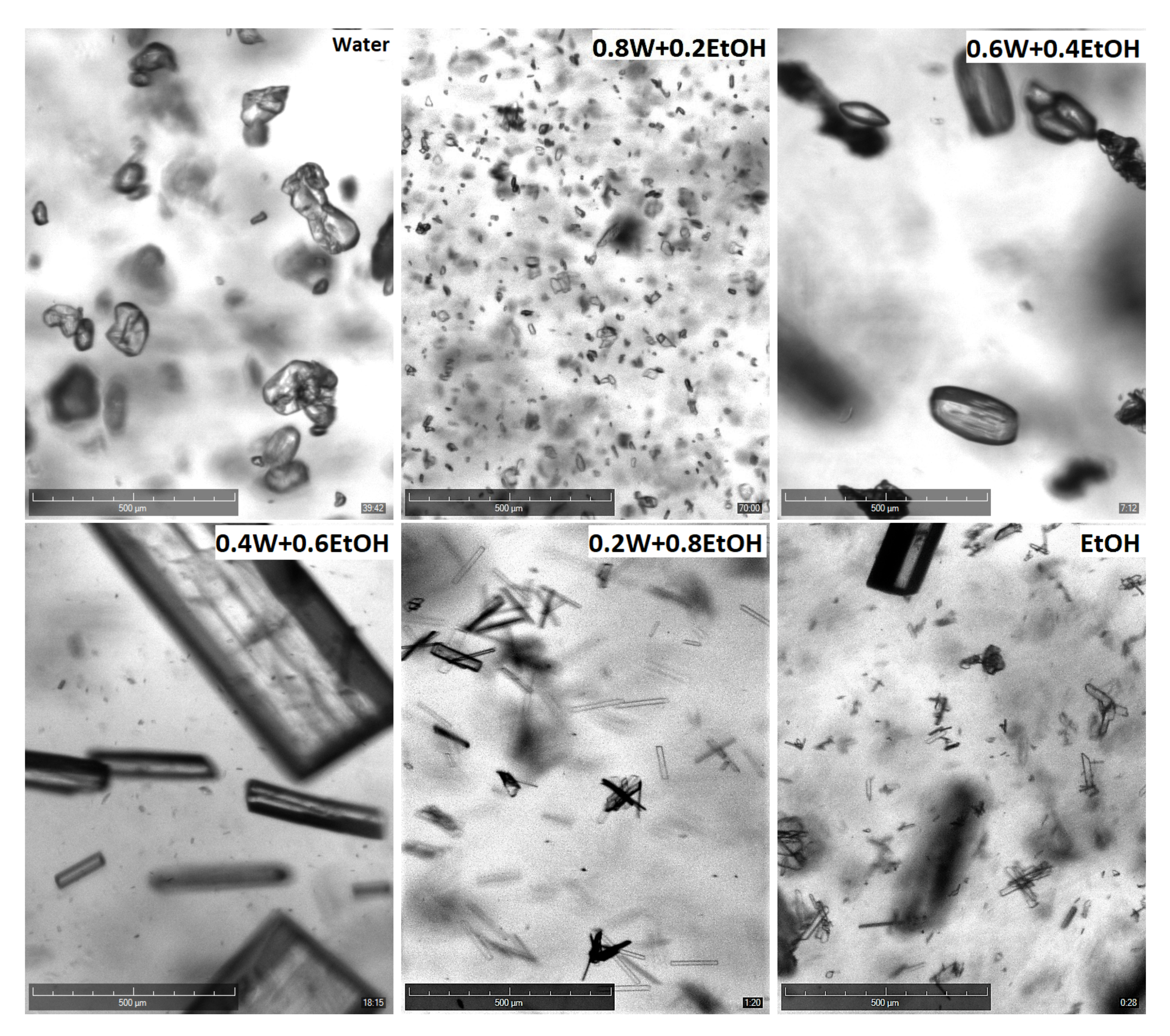
4.5. Effect of Solvent Composition on Crystal Habit
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| Exp. | Experimental |
| i-PrOH | Iso-propanol |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| MPD | Mean percentage deviation |
| MSZW | Metastable zone width |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| W | Water |
References
- Grosso, G.; Bei, R.; Mistretta, A.; Marventano, S.; Calabrese, G.; Masuelli, L.; Giganti, M.G.; Modesti, A.; Galvano, F.; Gazzolo, D.; et al. Effects of vitamin C on health: A review of evidence. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2013, 18, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sorice, A.; Guerriero, E.; Capone, F.; Colonna, G.; Castello, G.; Costantini, S. Ascorbic acid: Its role in immune system and chronic inflammation diseases. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichstein, T.; Grussner, A. Productive synthesis of l-ascorbic acid, vitamin C. Helv. Chim. Acta 1934, 17, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucker, R.B.; Zempleni, J.; Suttie, J.W.; McCormick, D.B. Handbook of Vitamins; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Karunanithi, A.T.; Achenie, L.E. Solvent design for crystallization of pharmaceutical products. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 23, pp. 115–147. [Google Scholar]
- Sheraz, M.; Khan, M.F.; Ahmed, S.; Kazi, S.H.; Ahmad, I. Stability and stabilization of ascorbic acid. Househ. Pers. Care Today 2015, 10, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.P.; Chen, F. Degradation of ascorbic acid in aqueous solution. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 5078–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro Neto, A.C.; Pires, R.F.; Malagoni, R.A.; Franco Jr, M.R. Solubility of vitamin C in water, ethanol, propan-1-ol, water+ ethanol, and water+ propan-1-ol at (298.15 and 308.15) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 1718–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Farajtabar, A.; Hongkun, Z. Preferential solvation of vitamin C in binary solvent mixtures formed by methanol, ethanol, n-propanol, isopropanol and water. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, A.C.; Robazza, W.S.; Bianchi, A.D.; Matiello, J.A.; Paludo, A.R.; Thomas, R. Solubility and thermodynamics of vitamin C in binary liquid mixtures involving water, methanol, ethanol and isopropanol at different temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2018, 121, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Adam, F.; Bakar, M.A.; Mudalip, S.A. Evaluation of solvents’ effect on solubility, intermolecular interaction energies and habit of ascorbic acid crystals. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2019, 23, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbowska, B.; Matynia, A.; Piotrowski, K.; Koralewska, J. Solubility and nucleation in l (+)-ascorbic acid–methanol–ethanol–water system. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2007, 46, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemdili, L.; Guedjali, R.; Habchi, S.; Mameri, F.; Koutchoukali, O.; Dehane, A.; Merouani, S. Ascorbic Acid Solubility and Thermodynamic Characteristics in Several Neat Solvents with Temperatures Ranging from 293 to 313 K. Int. J. Thermophys. 2022, 43, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, W.; Ulrich, J. Effect of the addition of alcoholic miscible co-solvents on the properties of ascorbic acid in its supersaturated aqueous solution. Cryst. Res. Technol. J. Exp. Ind. Crystallogr. 2006, 41, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, W. Effect of solvent composition on crystallization process of ascorbic acid. Chem. Eng. Technol. Ind. Chem. Plant Equip. Process. Eng. Biotechnol. 2006, 29, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbowska, B.; Piotrowski, K.; Koralewska, J.; Matynia, A. Growth Kinetics of Vitamin C Crystals in a Batch L (+)-Ascorbic Acid–Methanol–Ethanol–Water System: Size Independent Growth Model Approach. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2008, 22, 327–337. [Google Scholar]
- Arslantaş, A.; Ermler, W.C.; Yazici, R.; Kalyon, D.M. Crystal habit modification of vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid) due to solvent effects. Turk. J. Chem. 2004, 28, 255–270. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, K.; Vanitha Devi, K. Characterization of L-ascorbic acid single crystals grown from solution with different solvents. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2010, 45, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Adam, F.; Bakar, M.A. Thermal Characteristic Evaluation of Different Ascorbic Acid Crystal Habits. J. Chem. Eng. Ind. Biotechnol. 2018, 3, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiatt, A.N.; Taylor, L.S.; Mauer, L.J. Influence of simultaneous variations in temperature and relative humidity on chemical stability of two vitamin C forms and implications for shelf life models. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3532–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crystal16, Operating Parameters. Available online: https://www.crystallizationsystems.com/crystal16/operating-parameters-crystal16/winnt/kernel.htm (accessed on 7 October 2022).
- Turner, T.; Corzo, D.; Toroz, D.; Curtis, A.; Dos Santos, M.; Hammond, R.; Lai, X.; Roberts, K. The influence of solution environment on the nucleation kinetics and crystallisability of para-aminobenzoic acid. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 27507–27520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maosoongnern, S.; Flood, A.E. Validation of models predicting nucleation rates from induction times and metastable zone widths. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 2066–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Spix, L.; De Reus, S.C.; Meekes, H.; Kramer, H.J.; Vlieg, E.; Ter Horst, J.H. Deracemization of a racemic compound via its conglomerate-forming salt using temperature cycling. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 5563–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, D.E.; Oberacher, H.; Arnhard, K.; Orlova, M.; Griesser, U.J. 4-Aminoquinaldine monohydrate polymorphism: Prediction and impurity aided discovery of a difficult to access stable form. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 4053–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Black, S.; Dang, L.; Liu, C.; Wei, H. On the measurement of solubility. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2013, 17, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Leon, C.; Mack, C.; Roy, S.; ter Horst, J.H. Solubility Analysis of 18 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients and Intermediates in the non–Polar Solvents Dioxane, Toluene and Cyclopentyl Methyl Ether. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 367, 120365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crystalline, Operating Parameters. Available online: https://www.crystallizationsystems.com/crystalline/operating-parameters-crystalline/winnt/kernel.htm (accessed on 7 October 2022).
- Klapwijk, A.R.; Simone, E.; Nagy, Z.K.; Wilson, C.C. Tuning crystal morphology of succinic acid using a polymer additive. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 4349–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kort, A.K.; Lorenz, H.; Seidel-Morgenstern, A. Physical–Chemical Properties of the Chiral Fungicide Fenamidone and Strategies for Enantioselective Crystallization. Chirality 2016, 28, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornachary, S.K.; Han, G.; Kwek, J.W.; Chow, P.S.; Tan, R.B. Crystallizing micronized particles of a poorly water-soluble active pharmaceutical ingredient: Nucleation enhancement by polymeric additives. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyban, A.; Chan, H.K.; Chew, N.Y.K.; Khoubnasabjafari, M.; Acree Jr, W.E. Solubility prediction of paracetamol in binary and ternary solvent mixtures using Jouyban–Acree model. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jouyban, A.; Nozohouri, S.; Martinez, F. Solubility of celecoxib in {2-propanol (1)+ water (2)} mixtures at various temperatures: Experimental data and thermodynamic analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 254, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Han, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, J. Measurement and correlation for solubility of levofloxacin in six solvents at temperatures from 288.15 to 328.15 K. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2012, 335, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wei, L.; Si, T.; Guo, H.; Yang, C. Solution thermodynamics of creatine monohydrate in binary (water+ ethanol) solvent systems at T=(278.15 to 328.15) K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 92, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, C.; Xue, J.; Li, P.; Yu, J. Determination of metastable zone width of potassium sulfate in aqueous solution by ultrasonic sensor and FBRM. J. Cryst. Growth 2017, 469, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apelblat, A.; Manzurola, E. Solubility of ascorbic, 2-furancarboxylic, glutaric, pimelic, salicylic, and o-phthalic acids in water from 279.15 to 342.15 K, and apparent molar volumes of ascorbic, glutaric, and pimelic acids in water at 298.15 K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 1989, 21, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalmashi, A.; Eliassi, A. Solubility of L-(+)-ascorbic acid in water, ethanol, methanol, propan-2-ol, acetone, acetonitrile, ethyl acetate, and tetrahydrofuran from (293 to 323) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2008, 53, 1332–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi-Azarbayjani, A.; Abbasi, M.; Vaez-Gharamaleki, J.; Jouyban, A. Measurement and correlation of deferiprone solubility: Investigation of solubility parameter and application of van’t Hoff equation and Jouyban–Acree model. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ángeles Peña, M.; Sánchez, A.B.; Escalera, B.; Jouyban, A.; Martinez, F. Thermodynamic Analysis for the Solubility of Allopurinol in Aqueous and Non-aqueous Mixtures at Various Temperatures. Int. J. Thermophys. 2022, 43, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashchiev, D.; Verdoes, D.D.; van Rosmalen, G.M. Review: Nucleation in solutions revisited. Cryst. 2003, 38, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslantas, A.; Ermler, W.C.; Yazici, R.; Kalyon, D.M. Study of polymorph prediction for L-ascorbic acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2005, 6, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Solubility Curve | MSZ Limit | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | A | B | |||
| Water/Methanol | ||||||
| 0 | 14.44 | −2577.80 | 0.962 | 9.42 | −864.55 | 0.919 |
| 0.2 | 14.38 | −2631.41 | 0.987 | 10.10 | −1115.91 | 0.948 |
| 0.4 | 14.21 | −2643.19 | 0.979 | 9.69 | −1058.67 | 0.975 |
| 0.6 | 13.92 | −2649.26 | 0.993 | 9.74 | −1149.05 | 0.904 |
| 0.8 | 13.55 | −2649.66 | 0.995 | 9.04 | −1041.11 | 0.904 |
| 1 | 13.09 | −2630.46 | 0.999 | 5.76 | −168.97 | 0.883 |
| Water/Ethanol | ||||||
| 0 | 14.44 | −2577.80 | 0.962 | 9.42 | −864.55 | 0.919 |
| 0.2 | 14.12 | −2590.05 | 0.995 | 10.45 | −1244.19 | 0.982 |
| 0.4 | 14.59 | −2871.97 | 0.992 | 11.62 | −1691.99 | 0.926 |
| 0.6 | 13.77 | −2787.06 | 0.995 | 9.81 | −1315.76 | 0.998 |
| 0.8 | 13.58 | −2944.81 | 0.986 | 8.28 | −1042.09 | 0.950 |
| 1 | 13.39 | −3145.99 | 0.962 | 7.87 | −1113.31 | 0.865 |
| Water/Isopropanol | ||||||
| 0 | 14.44 | −2577.80 | 0.962 | 9.42 | −864.55 | 0.919 |
| 0.2 | 13.92 | −2610.61 | 0.973 | 7.94 | −558.75 | 0.955 |
| 0.4 | 14.59 | −3009.05 | 0.984 | 10.23 | −1396.32 | 0.967 |
| 0.6 | 13.92 | −3012.34 | 0.995 | 8.65 | −1112.25 | 0.915 |
| 0.8 | 14.23 | −3384.24 | 0.977 | 7.68 | −4265.16 | 0.922 |
| 1 | 15.90 | −4265.16 | 0.952 | 6.77 | −1032.28 | 0.833 |
| Parameters | Water-MeOH | Water-EtOH | Water-i-PrOH |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.691 | 5.339 | 7.348 | |
| −2627 | −3164 | −4021 | |
| 0.342 | −0.338 | -2.850 | |
| 272.5 | 1578 | 2833 | |
| 433.4 | −1570 | −2027 | |
| −1215 | 1085 | 1229 | |
| 610.6 | −444.8 | −375.9 | |
| 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| MPD | 0.216 | 0.246 | 0.503 |
| RMSE | 0.0091 | 0.0128 | 0.0264 |
| (kJ mol | (J molK | (kJ mol | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 293 | 298 | 303 | 308 | 313 | 318 | 323 | 328 | 333 | |||
| Water/Methanol | |||||||||||
| 0 | 20.52 | 40.30 | 8.727 | 8.526 | 8.314 | 8.113 | 7.912 | 7.710 | 7.509 | 7.307 | 7.106 |
| 0.2 | 20.95 | 41.68 | 8.739 | 8.531 | 8.323 | 8.114 | 7.906 | 7.697 | 7.489 | 7.281 | 7.072 |
| 0.4 | 21.06 | 40.34 | 8.780 | 8.571 | 8.361 | 8.152 | 7.942 | 7.733 | 7.523 | 7.314 | 7.104 |
| 0.6 | 21.23 | 41.24 | 9.150 | 8.944 | 8.738 | 8.532 | 8.326 | 8.119 | 7.913 | 7.707 | 7.501 |
| 0.8 | 21.40 | 39.87 | 9.717 | 9.518 | 9.319 | 9.119 | 8.920 | 8.721 | 8.521 | 8.322 | 8.122 |
| 1 | 21.40 | 37.54 | 10.40 | 10.21 | 10.02 | 9.834 | 9.646 | 9.458 | 9.271 | 9.083 | 8.895 |
| Water/Ethanol | |||||||||||
| 0 | 20.52 | 40.30 | 8.717 | 8.516 | 8.314 | 8.113 | 7.912 | 7.710 | 7.509 | 7.307 | 7.106 |
| 0.2 | 20.61 | 40.68 | 8.692 | 8.489 | 8.285 | 8.082 | 7.879 | 7.675 | 7.472 | 7.268 | 7.065 |
| 0.4 | 23.01 | 47.06 | 9.217 | 8.981 | 8.749 | 8.511 | 8.276 | 8.040 | 7.805 | 7.570 | 7.334 |
| 0.6 | 22.56 | 42.94 | 9.980 | 9.765 | 9.550 | 9.336 | 9.121 | 8.906 | 8.692 | 8.477 | 8.262 |
| 0.8 | 24.09 | 43.67 | 11.30 | 11.08 | 10.86 | 10.64 | 10.43 | 10.21 | 9.990 | 9.771 | 9.553 |
| 1 | 25.96 | 43.26 | 13.29 | 13.07 | 12.85 | 12.64 | 12.42 | 12.21 | 11.99 | 11.77 | 11.56 |
| Water/Isopropanol | |||||||||||
| 0 | 20.52 | 40.30 | 8.717 | 8.516 | 8.314 | 8.113 | 7.912 | 7.710 | 7.509 | 7.307 | 7.106 |
| 0.2 | 20.89 | 40.46 | 9.039 | 8.837 | 8.635 | 8.433 | 8.230 | 8.028 | 7.826 | 7.624 | 7.421 |
| 0.4 | 24.30 | 49.21 | 9.217 | 8.981 | 8.746 | 8.511 | 8.276 | 8.040 | 7.805 | 7.570 | 7.334 |
| 0.6 | 24.57 | 46.61 | 10.92 | 10.68 | 10.45 | 10.22 | 9.984 | 9.751 | 9.518 | 9.285 | 9.052 |
| 0.8 | 27.87 | 51.58 | 12.75 | 12.49 | 12.24 | 11.98 | 11.72 | 11.46 | 11.21 | 10.95 | 10.69 |
| 1 | 35.33 | 67.32 | 15.61 | 15.27 | 14.94 | 14.60 | 14.26 | 13.93 | 13.59 | 13.25 | 12.92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yadav, J.; Dumitrescu, D.G.; Kendall, T.; Guguta, C.; Patel, S.A. Effect of Solvent Composition on Solubility, Thermodynamics, Metastable Zone Width (MSZW) and Crystal Habit of L-Ascorbic Acid. Crystals 2022, 12, 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121798
Yadav J, Dumitrescu DG, Kendall T, Guguta C, Patel SA. Effect of Solvent Composition on Solubility, Thermodynamics, Metastable Zone Width (MSZW) and Crystal Habit of L-Ascorbic Acid. Crystals. 2022; 12(12):1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121798
Chicago/Turabian StyleYadav, Jyoti, Dan G. Dumitrescu, Thomas Kendall, Carmen Guguta, and Swati A. Patel. 2022. "Effect of Solvent Composition on Solubility, Thermodynamics, Metastable Zone Width (MSZW) and Crystal Habit of L-Ascorbic Acid" Crystals 12, no. 12: 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121798
APA StyleYadav, J., Dumitrescu, D. G., Kendall, T., Guguta, C., & Patel, S. A. (2022). Effect of Solvent Composition on Solubility, Thermodynamics, Metastable Zone Width (MSZW) and Crystal Habit of L-Ascorbic Acid. Crystals, 12(12), 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121798






