4.1. Thermodynamics of AlN Formation
The thermodynamic analysis was carried out to evaluate the formation behavior of AlN inclusions. The analysis aimed at determining: the critical N content required for the formation of AlN in liquid steel, the effect of temperature on the formation of AlN, and the solid fraction (gs) values at which AlN forms during solidification.
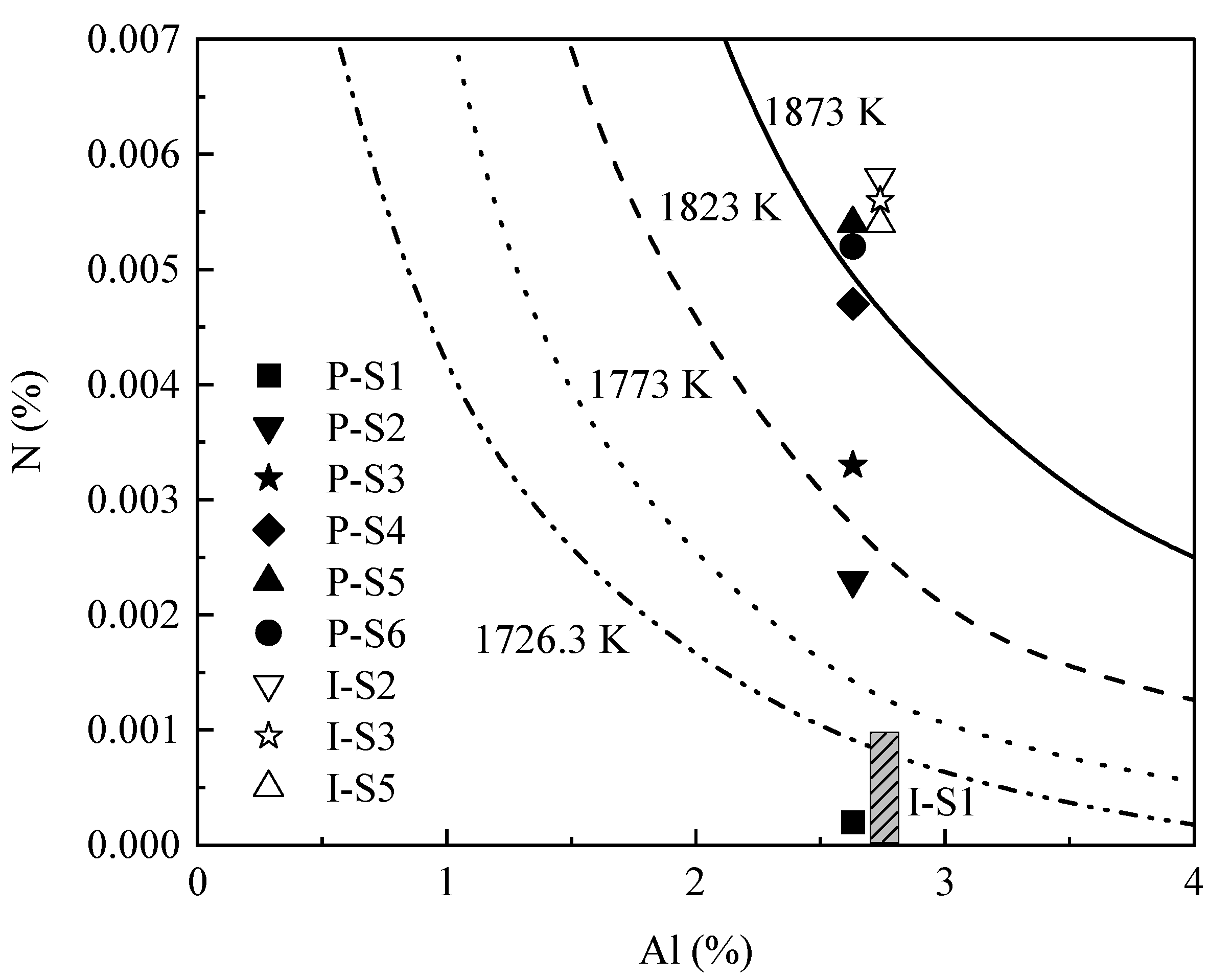
Figure 4 presents an AlN stability diagram for the experimental steel composition of 533N-P and 533N-I, obtained by using FactSage 7.3 (FSstel, FToxid, and FactPS databases). The figure also shows AlN stability lines for different temperatures, including liquidus temperature (
Tliq) of experimental steels.
Tliq was around 1726.3 K, while the critical N content for the formation of AlN at 1873 K was 50 ppm for the steel melt containing 2.67% Al (average value) in the current study. Whereas, at 1823 K and 1773 K it was 30 ppm and 15 ppm, respectively. The experimental compositions plotted in
Figure 4 indicate that AlN could form in liquid steel at 1873 K in sample S5 and S6 from 533N-P. The composition of S4 lay just below the 1873 K line, and those of S3 and S2 were above the 1773 K line. This indicates that AlN is not stable at 1873 K for S4, S3, and S2. However, AlN can form in liquid steel at temperatures above 1773 K during the cooling of these samples. Moreover, the composition of S1 was below the
Tliq line, suggesting that AlN can only form in the mushy zone during solidification of S1.
For the case of 533N-I steel, AlN can form at 1873 K in all the samples, except S1. The N content of S1 was not known. However, authors have observed in previous work [
15] that Fe5Mn3Si3Al steels (without N addition) contained < 10 ppm of N. Therefore, it was reasonable to assume that S1 in 533N-I steel had an N content of less than 10 ppm. This assumption would locate the S1 below the
Tliq line in
Figure 4. Thus, the AlN inclusions observed in S1 samples of both experiments were formed during solidification of the steel due to the enrichment of Al and N at the solidifying front. The enrichment led to a higher driving force for the formation of AlN. The solid fraction (
gs) values at which AlN would start to form for the S1 compositions were calculated by adopting the Scheil equation [
18,
29,
30]. The detailed procedure for this calculation was given elsewhere [
14,
18]. According to the estimates, the
gs values for S1 samples should be higher than 0.11 (based on 10 ppm N), and they could be as high as 0.71 assuming 2 ppm N content.
The current steel compositions could be divided into three groups following their N contents, i.e., low N (2–10 ppm), medium N (23–47 ppm), and high N (>50 ppm) containing steels. Based on the thermodynamic analysis, it could be inferred that for low N containing steel samples, AlN inclusions formed in the mushy zone due to the segregation of Al and N at the solidification front. For both medium and high N containing samples AlN formed in the liquid steel. However, AlN formation occurred during the cooling of medium N containing samples, whereas, AlN observed in high N containing samples formed at the experimental temperature.
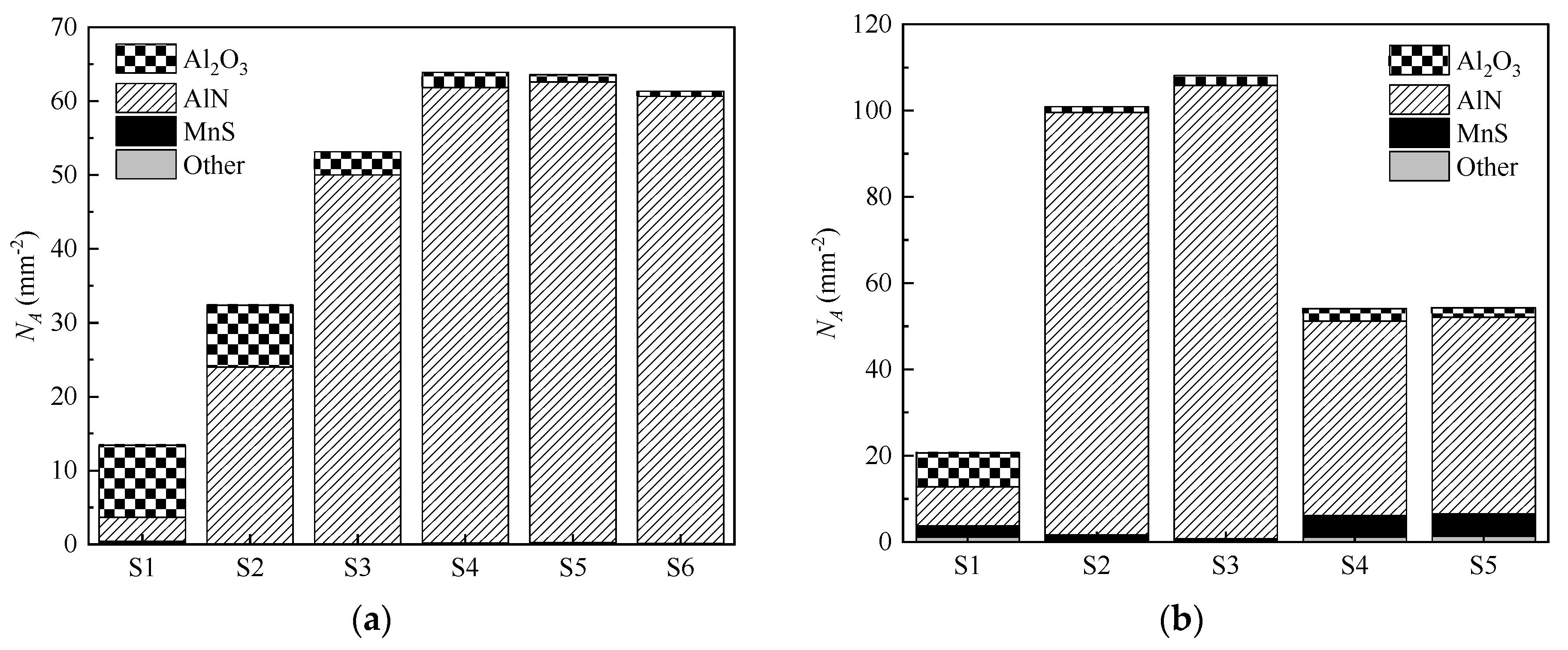
A variation in the characteristics of AlN inclusions in the above mentioned three groups could be expected due to the difference in the formation behavior of AlN inclusions in them. These characteristics included the number density of inclusions, their chemical composition, and their size distribution. The expected response was reflected in the results presented in
Figure 3a,b.
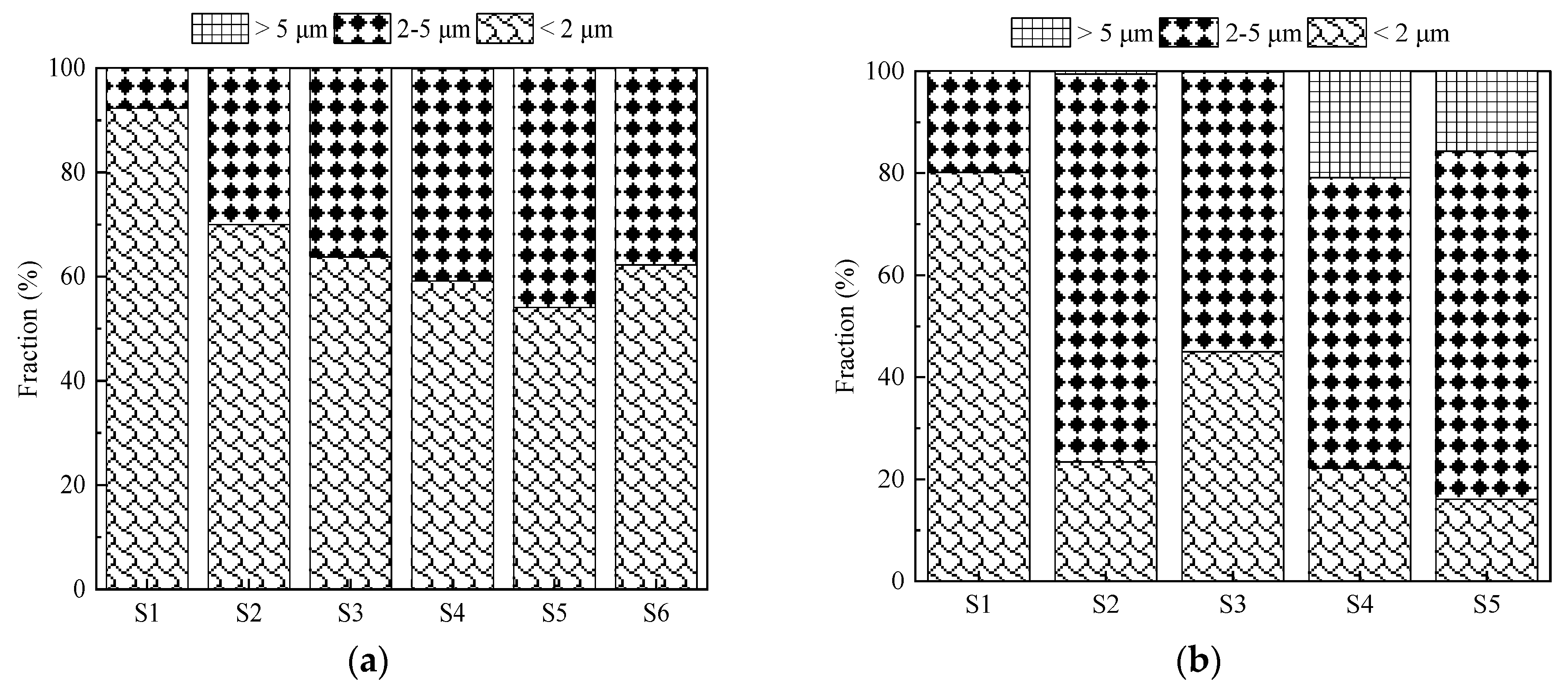
The influence of N content on the particle size distributions (PSD) of AlN inclusions can be seen in
Figure 5. In the case of low N containing samples (i.e., S1), most of the AlN inclusions lay in size range of 1–2 μm. Specifically, 92% and 80% of AlN inclusions in S1 from 533N-P and 533N-I steel melts had
Dave < 2 μm, respectively. It is evident from
Figure 5a that the percentage of AlN inclusions with
Dave < 2 μm decreased as the N content increased in samples of 533N-P steel. In high N containing samples (S5 and S6), ~40% of AlN inclusions were greater than 2 μm. Similarly, the samples with high N from the 533N-I melt (
Figure 5b) contained only ~20% of AlN (except S3, which contains ~45%) in the size range of
Dave < 2 μm in comparison to 80% in low
N sample. A higher fraction of small-sized inclusions (
Dave < 2 μm) in samples with low N levels supports the inference that AlN inclusions form during solidification in these samples. Interestingly, the fraction of large-sized inclusions in high N containing samples of 533N-I was considerably higher than in those of 533N-P. This can be attributed to a higher growth rate of AlN inclusions due to turbulence induced by injection of N
2 gas in the melt. The increased size of inclusions was also reflected as a decreased number of AlN inclusions in S4 and S5 of 533N-I (
Figure 2b) steel, which was probably due to the floatation of inclusions to the steel surface.
The thermodynamic analysis and characteristics of observed AlN inclusions also suggest that at low N levels, AlN-MnS inclusions are formed. Moreover, medium and high N levels resulted in AlN(pure) inclusions. It could be inferred that AlN formed at the solidification front ended up having a composition of AlN-MnS, while the ones formed in liquid steel did not promote AlN-MnS formation; instead, they became AlN(pure) inclusions. This phenomenon was investigated by considering the effect of the cooling rate and presented in the following section.
4.2. Formation of AlN Inclusions during Solidification
Samples from bulk steel had been analyzed to study the behavior of AlN at the solidification front. The bulk samples were cooled at a slow cooling rate, i.e., 0.167 K/s, as compared to 20–30 K/s [
31] of air-cooled pin samples. The obtained data were compared to the results of a previous study [
15]. The data of the prior research was for steel containing 5% Mn, 3% Si, 3% Al and < 10 ppm N. This steel was referred to as 533 steel in the current study.
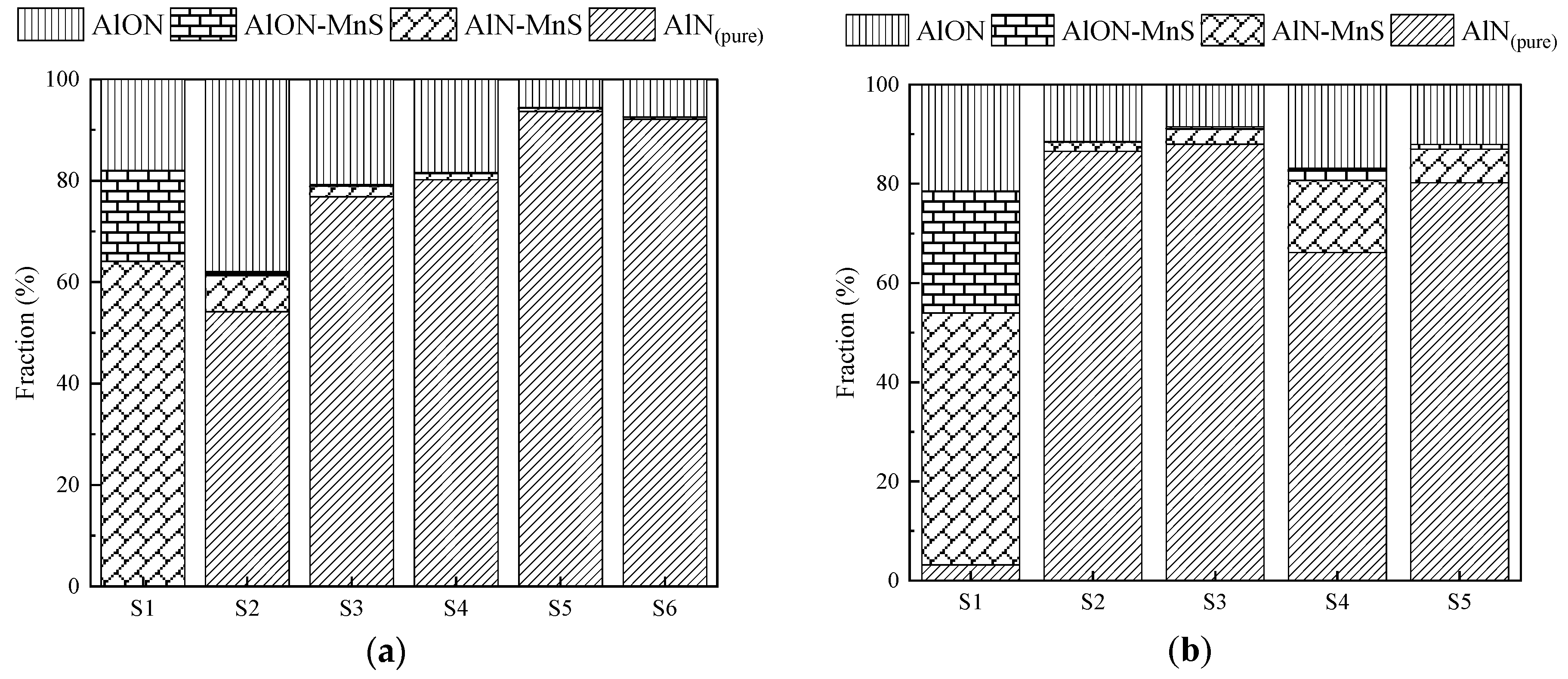
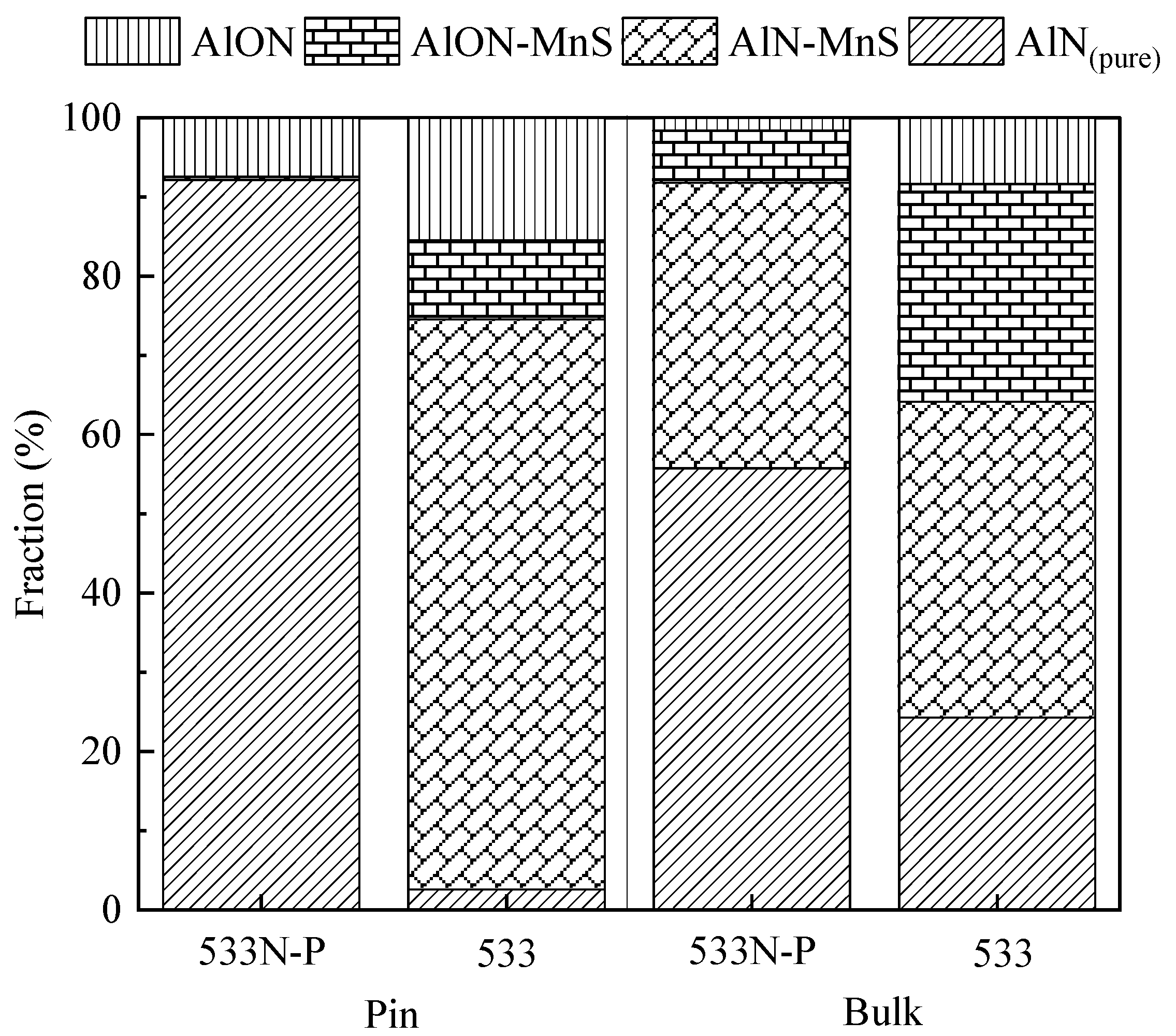
Figure 6 compares the fractions of different sub-classes of AlN inclusions observed in pin and bulk samples of 533N-P and 533 steel melts. For this comparison, the pin samples were taken before the cooling of bulk steel starts have been selected, i.e., the sample was taken at 300 min of holding time from 533N-P steel and at 41 min of holding time from 533 steel. The selection of these pin samples enabled a plausible comparison to their respective bulk samples, as in both experiments the bulk steel was exposed to similar holding time and cooling rates after these pin samples were taken.
As can be seen in
Figure 6, AlN
(pure) inclusions were the dominant sub-class (more than 90%) in the pin sample of 533N-P steel. Whereas, AlN-MnS made a significant portion (~80%) of AlN inclusions in 533 steel’s pin sample, and the remaining were AlON (15%), AlON-MnS (5%), and a negligible amount of AlN
(pure). The fraction of AlN
(pure) inclusions decreased to ~60% in the bulk sample of 533N-P as compared to its respective pin sample. Moreover, a significant fraction (~30%) of AlN-MnS inclusions appeared in the bulk sample, and these inclusions were not present in the pin sample. On the contrary, in 533 steel melt, the slow cooling resulted in an increase (~20%) and a decrease (~30%) in the percentage of AlN
(pure) and AlN-MnS inclusions, respectively. It was interesting to see that despite a high N level in both pin and bulk samples of 533N-P steel, a substantial quantity of AlN-MnS inclusions was found in the slowly cooled bulk sample. Similarly, although 533 steel contained a low N level, its bulk sample had a considerable amount of AlN
(pure) inclusions. To understand this and elucidate the formation behavior of AlN
(pure) and AlN-MnS inclusions, two things needed to be considered: formation temperature of AlN and MnS, and capability of AlN and MnS to heterogeneously nucleate on each other.
Firstly, the formation temperature of AlN (
TAlN) and that of MnS (
TMnS), along with liquidus and solidus temperature of both 533N-P and 533 steel samples are given in
Table 4. Secondly, it is known that AlN and MnS can co-precipitate together due to similarities in their crystal structures [
20]. For co-precipitation, AlN can act as the nucleation site for MnS or MnS can act as the nucleation site for AlN [
9].
For low N level samples (533 steel), TAlN was higher than TMnS and lay between liquidus and solidus temperature. AlN was formed at the solidification front, which was enriched in solute elements Al, N, Mn, and S. There was ~206 K difference between TAlN and TMnS. At a high cooling rate, the formation of AlN and MnS took place almost at the same time resulting in AlN-MnS inclusions. In the case of the bulk sample, the slow cooling rate facilitated the formation of AlN(pure) at an early stage of solidification (gs value in the range of 0.71–0.11 for N < 10 ppm). This occurred before the liquid steel at the solidification front became enriched in Mn and S at a level that enabled MnS formation. However, the AlN inclusions formed at the end of solidification, closer to Mn and S segregated region, became sites for heterogeneous nucleation of MnS and eventually had a composition of AlN-MnS inclusions.
In the case of a pin sample from 533N-P, a higher difference (~405 K) between TAlN and TMnS resulted in the formation of a higher fraction of AlN(pure) inclusions. When this high N containing steel solidified at a slow rate, AlN(pure) inclusions formed in liquid steel at 1873 K until the start of solidification and at the early stage of solidification, and AlN-MnS inclusions formed at the end of solidification.
According to the above discussion and in
Section 4.1, the AlN-MnS should always form due to segregation at the end of solidification. The fraction of AlN-MnS inclusions appeared to be very low in the pin sample of 533N-P (
Figure 6); however, as shown in
Table 3, there was a similar amount (
NA) of AlN-MnS present in all the pin samples of 533N-P. It is to mention that a scatter was observed in the
NA of AlN-MnS inclusions in the pin samples taken at different holding times during an experiment. This scatter could be caused by a difference in the mass of the sample, leading to some variation in the cooling rate of the individual pin sample. However, it appeared that the N content of steel did not influence the amount of AlN-MnS inclusions in samples taken during an experiment. For instance, the
NA value of AlN-MnS inclusions in low N sample (S1) of 533N-I was ~4.5 mm
−2, whereas S4 and S5 (high N samples) contained ~6.5 mm
−2 and ~3 mm
−2 of AlN-MnS inclusions. The
NA of AlN-MnS inclusions in low and high N samples (S1 and S4) of 533N-P was ~2 mm
−2 and ~0.8 mm
−2, respectively. Hence, there was no apparent influence of N content on the amount of AlN-MnS inclusions. This was in agreement with the explanation that AlN-MnS inclusions were formed at solidification front enriched with Mn and S and that their amount depended on the cooling rate.
As mentioned, AlN and AlN-MnS inclusions were the common types of inclusions present in the current experimental steels. Few studies [
32,
33] have focused on the influence of AlN and AlN-MnS inclusions on the mechanical properties of the steel. AlN inclusions could be found both inside the grain [
34] or at the grain boundaries [
32,
34]. However, the AlN inclusions were reported to be more detrimental when they were located at the grain boundaries. Kang et al. [
32] studied the hot ductility on the twinning-induced plasticity (TWIP) steels and observed that AlN inclusions precipitated at the austenite grain boundaries promoted the poor ductility of the steel. The AlN inclusions that precipitate at grain boundaries usually combine with MnS to form AlN-MnS due to the ease of co-precipitation of AlN and MnS to occur. Ushioda et al. [
33] observed that AlN-MnS inclusions formed in the austenite grain boundaries in low carbon steel and reported that the complex precipitation of AlN and MnS is harmful to the hot ductility of the steel. The current study suggests that the N content of steel did not influence the amount of AlN-MnS inclusions. However, this inference is based on fast cooled pin samples and inclusions having a D
ave > 2µm. In the case of slow-cooled samples, the N content of steel could influence the amount of AlN-MnS inclusions, i.e., a higher N content could result in a higher number of AlN-MnS inclusions especially considering that the AlN inclusions could be pushed to the solidification front during solidification of steel.
The formation of AlON and AlON-MnS took place as follows. First Al
2O
3 inclusions were formed in the liquid steel, as they were stable at 1873 K. It was followed by the formation of AlN inclusions when the N content in the steel was sufficient for AlN formation. AlON could be a result of AlN precipitation on Al
2O
3 or collision of AlN and Al
2O
3 particles. The precipitation of AlN on Al
2O
3 is possible, but on specific crystallographic orientations [
35], therefore, the number of observed AlON inclusions was small. Similar to AlN-MnS, the formation of AlON-MnS occurred during the solidification process, where either Al
2O
3 and/or AlN in AlON inclusion became the nucleation site for MnS inclusion.
4.3. Co-Precipitation of Inclusions
In the current study, the formation of complex inclusions (AlN-MnS, Al
2O
3-MnS, and AlON) mostly occurred due to co-precipitation. The co-precipitation behavior can be quantified by considering precipitation ratio (PR) of one phase on another. The PR of phase 1 on phase 2 to form co-precipitates is defined as the ratio of the number of co-precipitates to the sum of the number of phase 2 particles and co-precipitates. The PR value is related to the potency of a phase to act as a heterogeneous nucleation site for others. In a previous study [
15], the authors compared the PR values of MnS on AlN and Al
2O
3 for the formation of AlN-MnS and Al
2O
3-MnS co-precipitates, respectively. It was reported that the PR value of MnS on AlN was always higher than that on Al
2O
3 due to a low mismatch between MnS and AlN (~5%) [
36] as compared to that of MnS and Al
2O
3 (~12%) [
36]. However, that was based on low N containing steels. In the current study, it was observed that the PR values of AlN containing co-precipitates could be influenced by the N content of the steel.
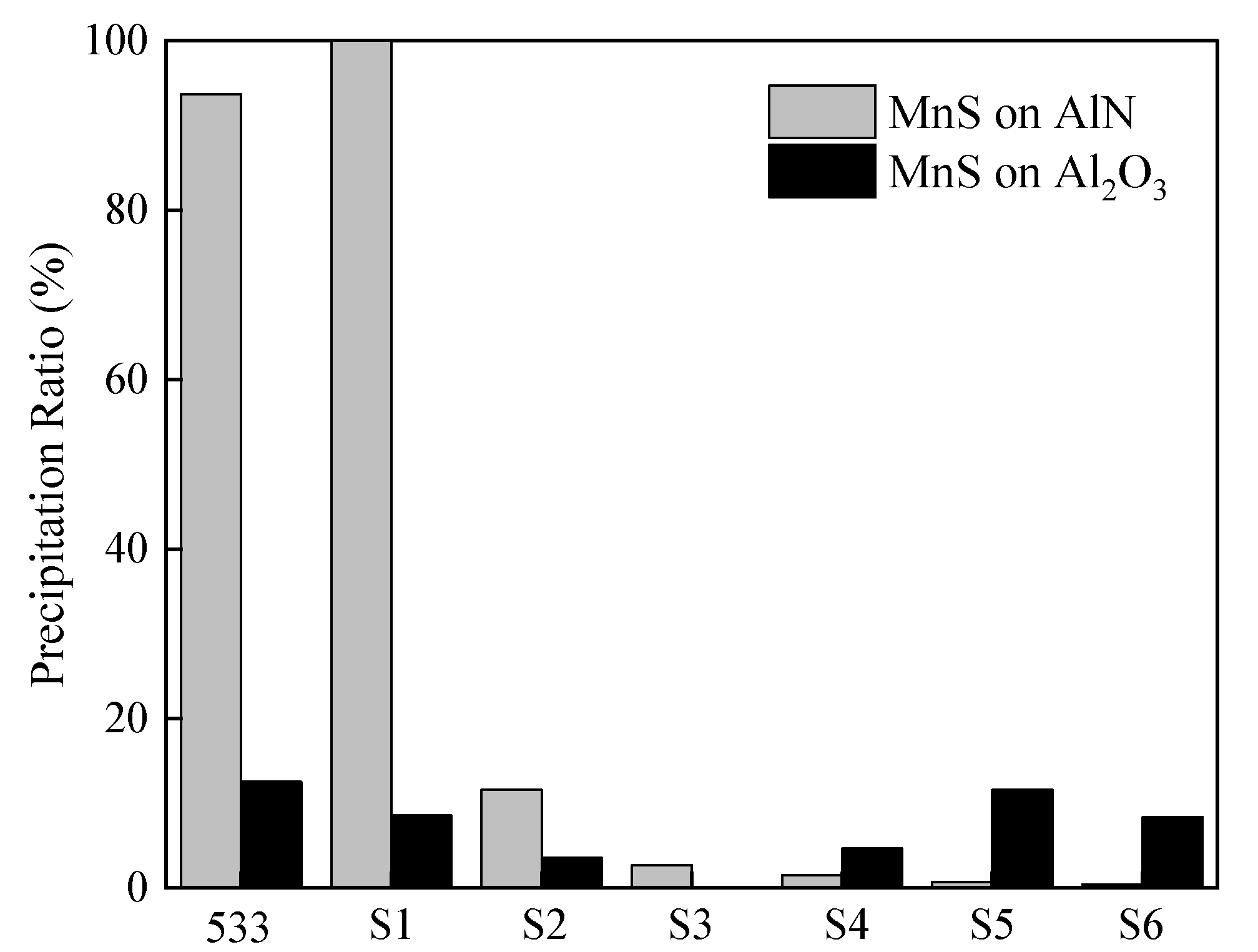
Figure 7 shows a comparison of the PR values of MnS on AlN and Al
2O
3 observed in the previous study [
15] (533 steel), which had low N content and the present study for 533N-P, which has low, medium, and high N containing samples. In the case of the PR value of MnS on AlN inclusions, in the low N content (533 and S1 of 533N-P), the PR value was more than 98%. However, in the medium (S2–S4) and high (S5 and S6) N containing samples, the PR values were significantly low, less than 15%. On the other hand, the PR values of MnS on Al
2O
3 were always less than 15% and were not influenced by the N content of the steel. It appeared that for samples having medium and high N content, the MnS PR values could be higher for Al
2O
3 as compared to for AlN. However, it should be noted that the lower PR values in medium and high N containing samples did not indicate that MnS prefers to nucleate on Al
2O
3. The lower MnS PR values on AlN were due to the formation of AlN
(pure) in liquid steel.
The N content also influenced the PR values of AlN on Al
2O
3 to form AlON.
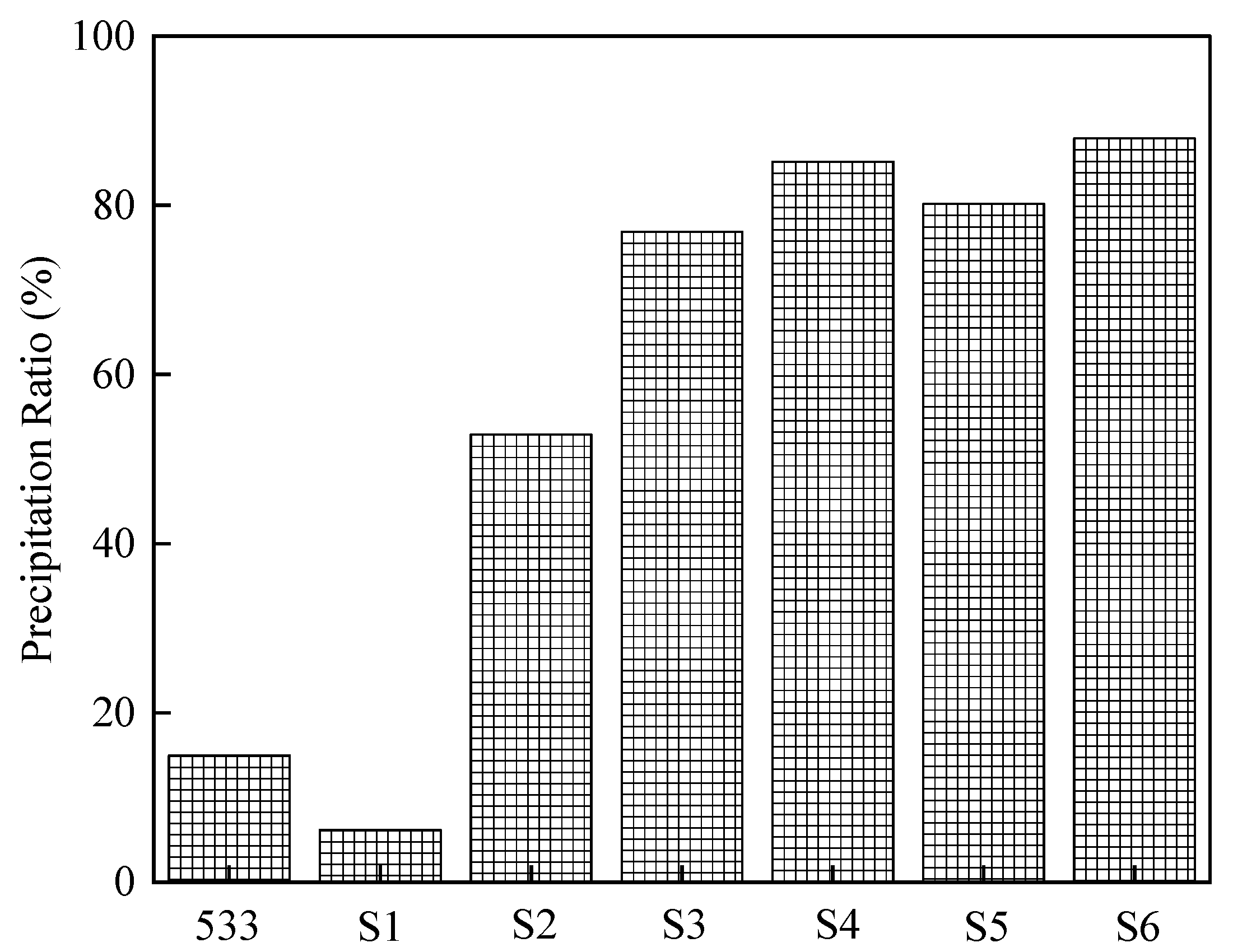
Figure 8 shows the AlN PR values observed in 533 [
15] and 533N-P. The low N containing samples (533 and S1 from 533N-P) had PR values of less than 20%. As the N content in the steel increased (S2–S6), the PR values increased dramatically to over 80%. This implied that more AlN inclusions were available to co-precipitate with Al
2O
3(pure) to form AlON inclusion.
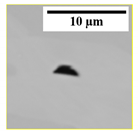
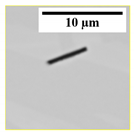
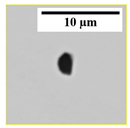
4.4. Effect of N Content on the Morphology of AlN(pure) Inclusions
In this study, the AlN
(pure) inclusions were classified into five types based on their morphology, as displayed in
Table 5. The inclusions having 5 or 6 sides were grouped as a plate-like type, and those with 3 or 4 sides were classified as angular. The inclusions exhibiting a long and thin morphology were grouped as a needle-like type. Agglomerates represented inclusions that consist of two or more particles. The remaining inclusions had irregular morphology.
The low N containing sample (S1) from 533N-P did not contain any AlN
(pure) inclusions, and that from 533N-I contained only 4 AlN
(pure) inclusions, which were all angular. The morphology of AlN
(pure) inclusions observed in the medium and high N containing samples of both steel melts was shown in
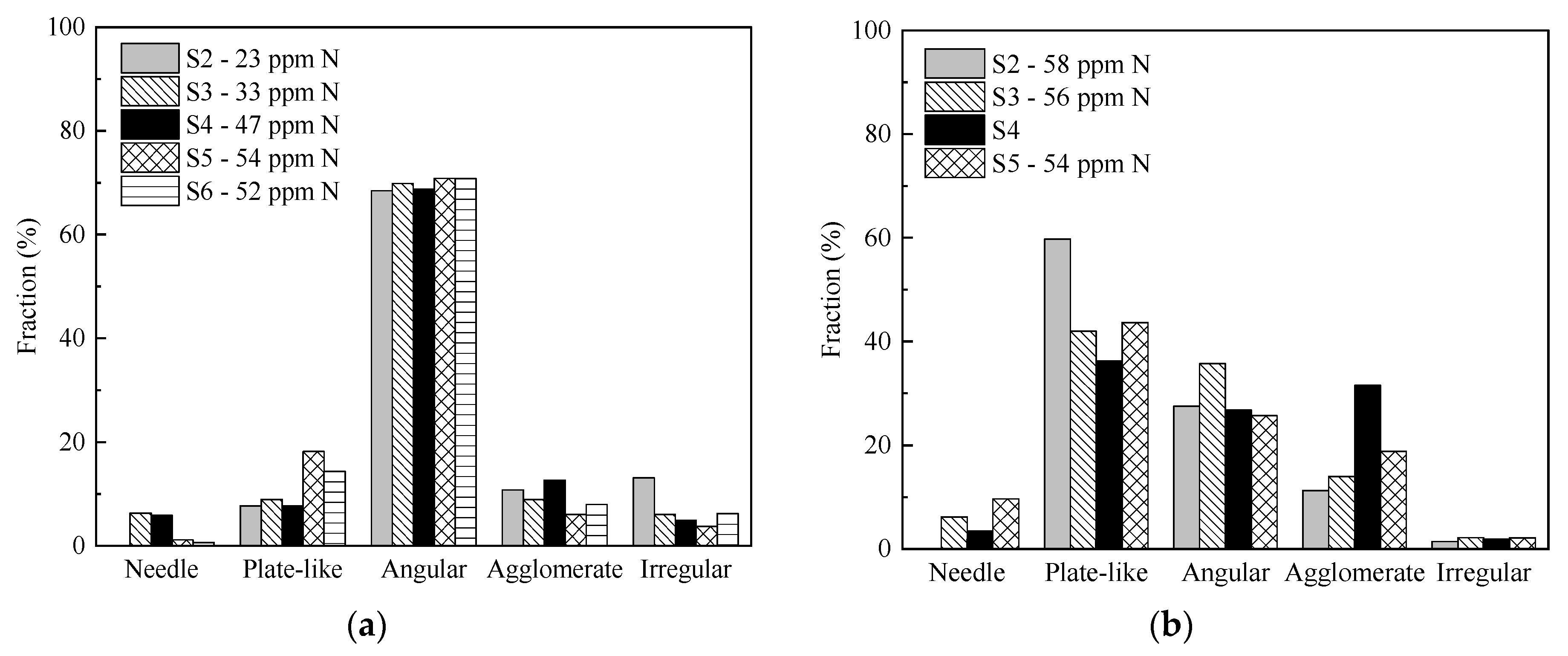
Figure 9a,b, respectively. In 533N-P samples, around 70% of AlN
(pure) inclusions have angular morphology. A small fraction (~6%) of inclusions with needle shape was found in samples containing medium N levels (S3 and S4). The number of plate-like inclusions was relatively higher in high N samples, i.e., around 14–18%, as compared to 8–9% in medium N samples. Approximately 6–13% inclusions were agglomerate, while irregular morphology makes 4–13%. In the case of 533N-I steel samples, plate-like morphology was a dominating type (36–60%). It was followed by an angular type that is around 26–36%. The fraction of agglomerate inclusions increased from 11 to 32% with increased holding time (S2 to S4) and then decreased to 19% in sample S5. The needle and irregular shaped inclusions were present in small amounts, i.e., 4–10% and ~2%, respectively.
It is of interest to observe a higher fraction of plate-like inclusions in samples with high N content. It could be related to the stability of AlN at 1873 K for high N containing samples. The effect of N content was observed in both experimental steel melts; moreover, the fraction of plate-like inclusions in 533N-I was significantly higher than that observed in S5 and S6 of 533N-P steel. This could be due to fast kinetics conditions in this steel. The turbulent conditions could lead to a faster growth rate of inclusions, enabling them to be detected under settings of current inclusion analysis (Dave > 2 µm).
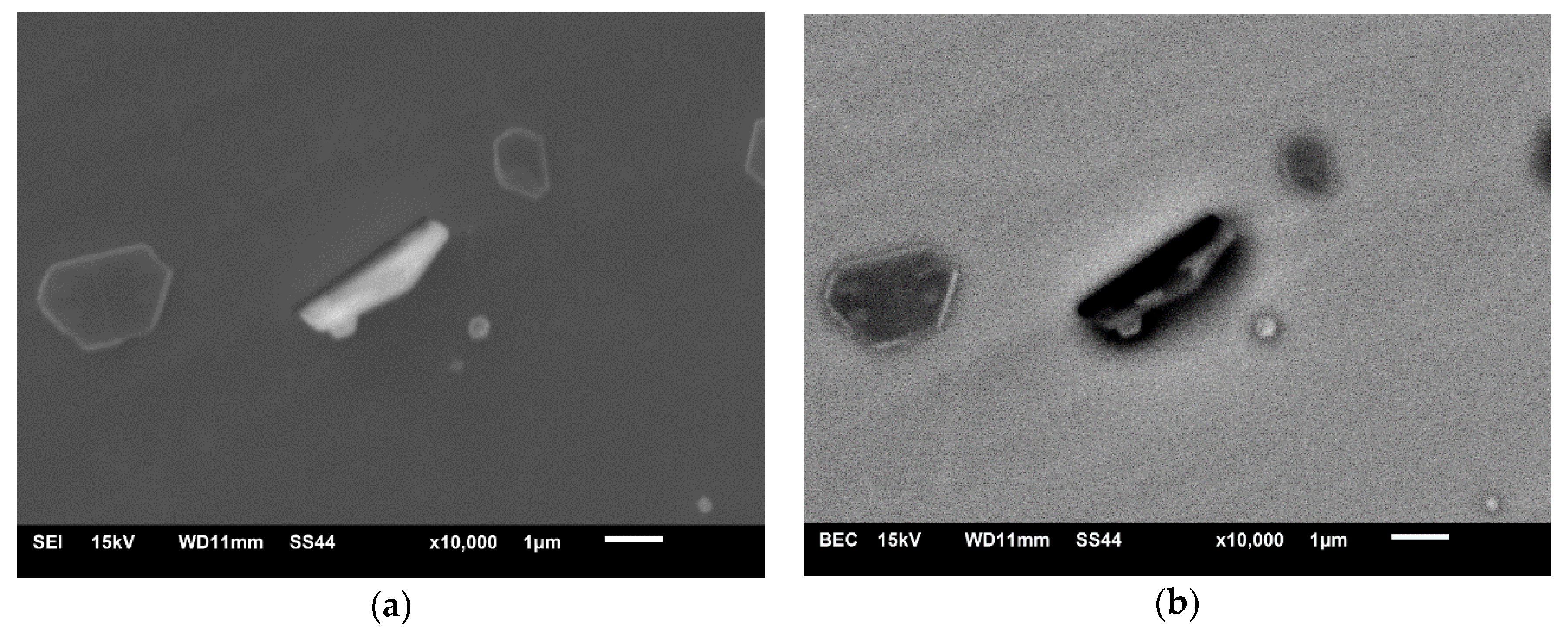
Moreover, a few samples were electrolytically etched in a 10% AA (10 v/v% acetylacetone – 1 w/v% tetramethylammonium chloride – methanol) electrolyte to expose three-dimensional morphology of inclusions. It was found that a considerable number of AlN inclusions were oriented at different angles to the analyzed surface. Such orientation of plate-like inclusions could make them appear as angular inclusions on a two-dimensional surface.
Figure 10 shows examples of such inclusions. It was clear from secondary electron images (SEI) (
Figure 10a) that the observed inclusions are, in fact, plate-like in shape. While from the back-scattered electron (BSE) images (
Figure 10b), they could be defined as angular inclusions, especially if the surface had been polished.
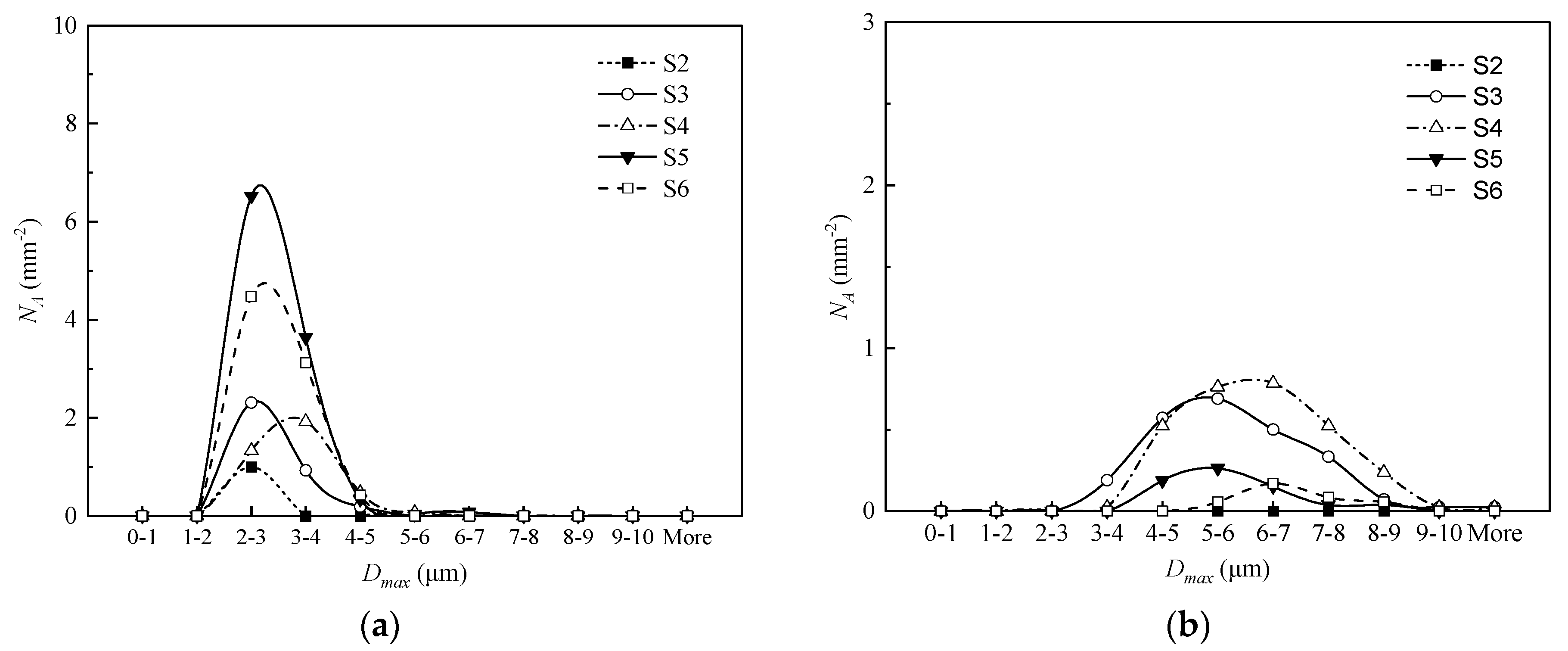
Applying the same reasoning, it could be argued that there is a possibility that inclusions with needle morphology could also be plate-like when observed in three-dimensions. To clarify this, the maximum diameter (
Dmax) of plate-like and needle inclusions observed in S4 and S5 of 533N-P steel was compared and shown in
Figure 11. It could be seen that the
Dmax values of plate-like inclusion varied from 1 to 5 μm (
Figure 11a). Whereas needle-shaped inclusions had
Dmax values in the range of 3 to 10 μm, and more than 90% of them were larger than 5 μm (
Figure 11b). It is evident from
Figure 11 that needle-shaped inclusions were not plate-like inclusions oriented at an angle as the
Dmax values of needle-shaped inclusions were significantly higher than those of plate-like inclusions.
Based on
Figure 9 through
Figure 11, AlN inclusions were detected in various morphologies. A similar observation was made by previous researchers [
3,
4,
9,
20]. Tuling and Mintz [
20] investigated the morphology of AlN inclusions in high Al transformation induced plasticity (TRIP) steels with 2.5% Mn, 60–70 ppm N, and 1–1.5% Al. According to the thermodynamics, AlN inclusions were formed during solidification for both 1% and 1.5% Al containing TRIP steels. Dendritic and hexagonal (plate-like) AlN inclusions were observed in steel with 1% Al and 1.5% Al, respectively. Liu et al. [
4] reported plate-like morphology of single AlN inclusions in the twin-induced plasticity (TWIP) steel (Fe-18Mn-1.5Al with 78 ppm N) and suggested that these AlN inclusions were formed above the
Tliq of the investigated steel. Wang et al. [
3] detected fine particles of AlN inclusions at the grain boundaries of TWIP steel (Fe-16Mn-0.54Al) with 63 ppm N content and coarse hexagonal (plate-like) AlN particles at the fracture site of TWIP steel (Fe-17Mn-2.1Al) with 43 ppm N content. For both these compositions of steel, thermodynamically AlN should form during solidification i.e., below the
Tliq. Moreover, Kang et al. [
9] suggested that the presence of MnS inclusions can affect the morphology of AlN inclusions. They observed AlN inclusions in high Al TWIP steel (Fe-18Mn-1.5Al and 80–93 ppm N) with different sulfur content. It was reported that in the absence of MnS inclusions i.e., when the steel had 32 ppm S, the AlN inclusions had hexagonal (plate-like) shape. In case of an abundance of MnS (S content up to 100–230 ppm), AlN inclusions exhibited dendritic and hexagonal (plate-like) morphologies. Based on thermodynamics, AlN inclusions would have formed during solidification for all the compositions investigated by Kang et al. [
9]. From the above mentioned literature it can be seen that AlN inclusions can exhibit various morphologies regardless of whether they are formed during solidification or above
Tliq. Similar behavior is observed in the current study. A three-dimensional inclusion analysis is recommended for further investigation.